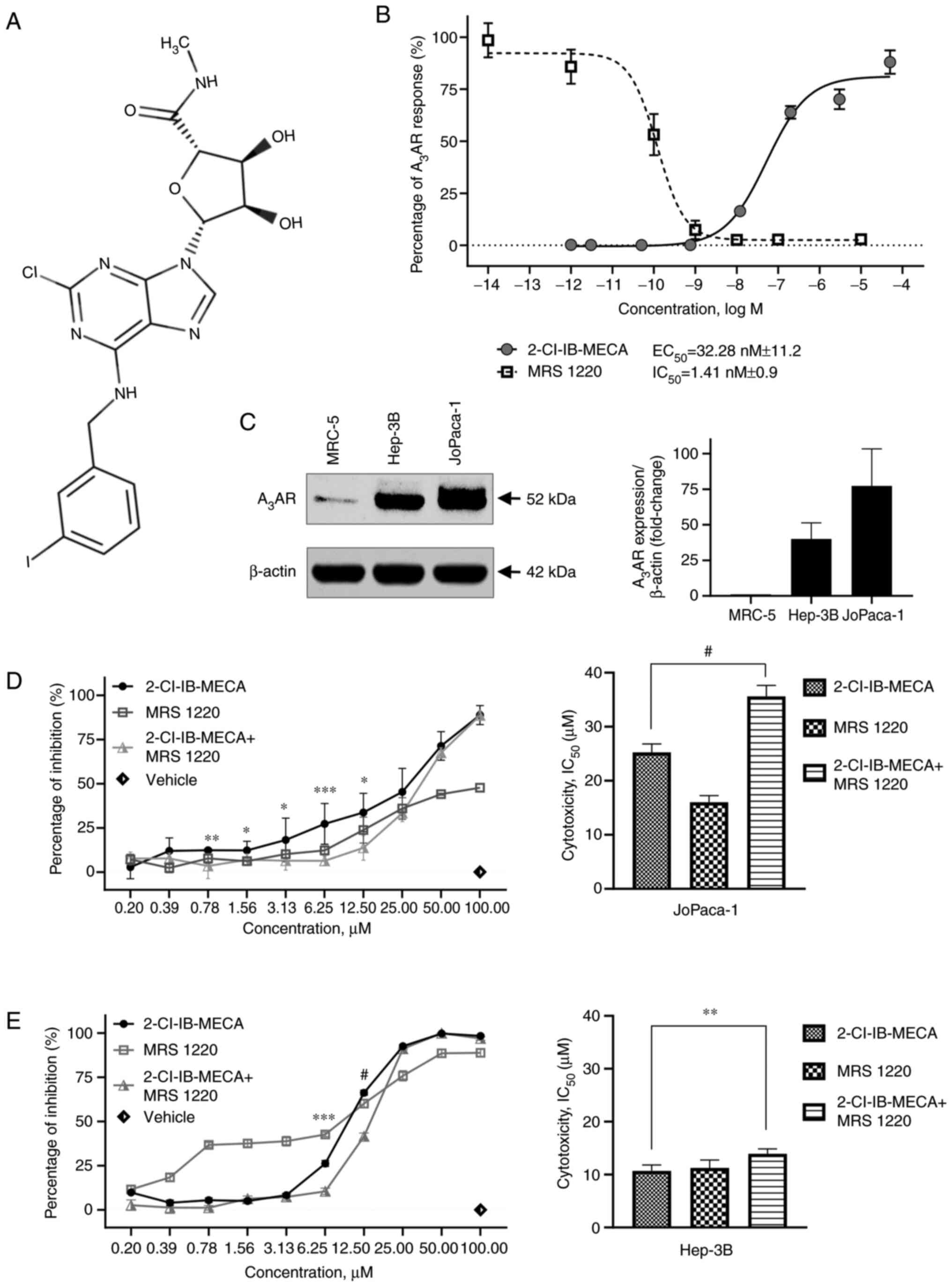
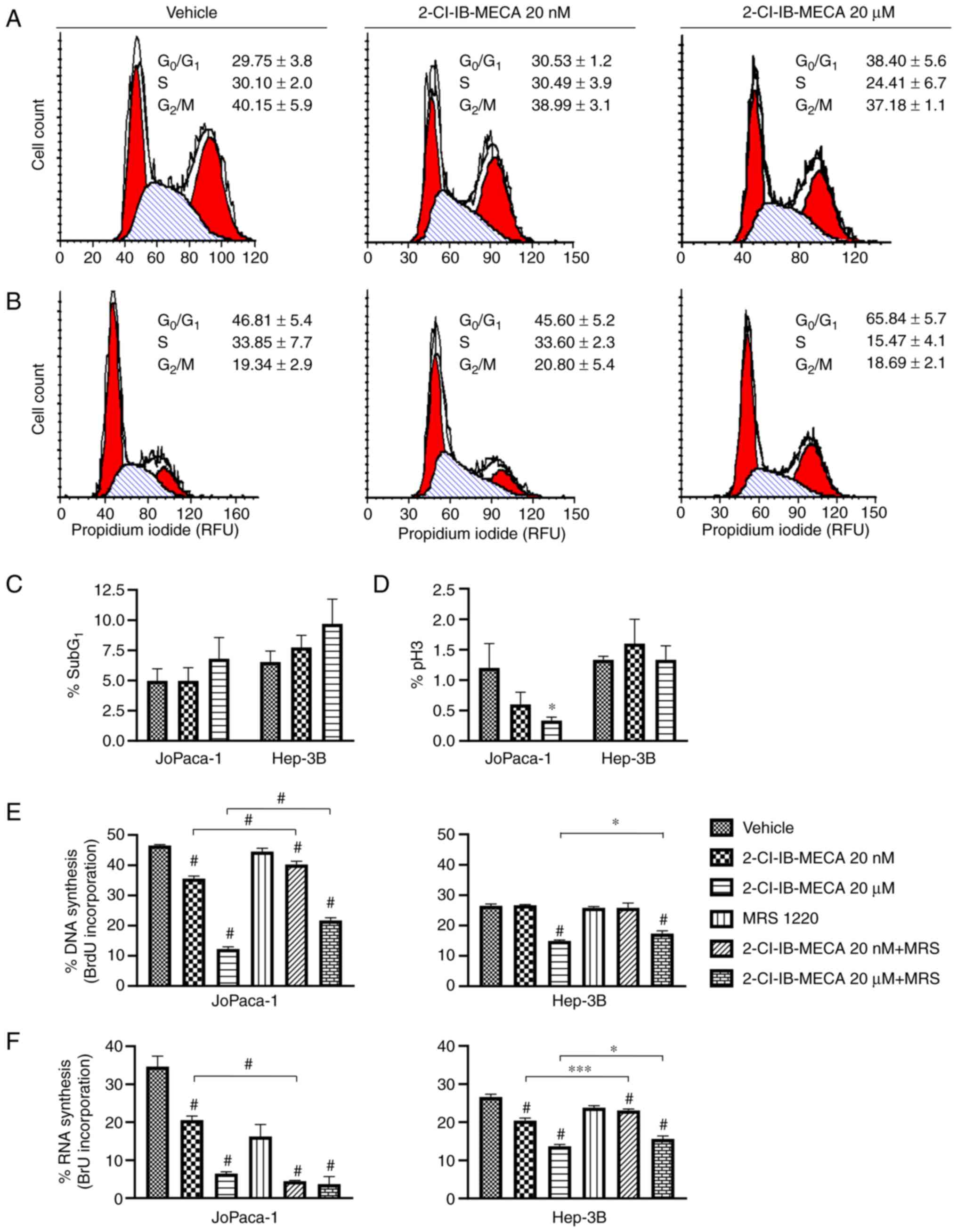
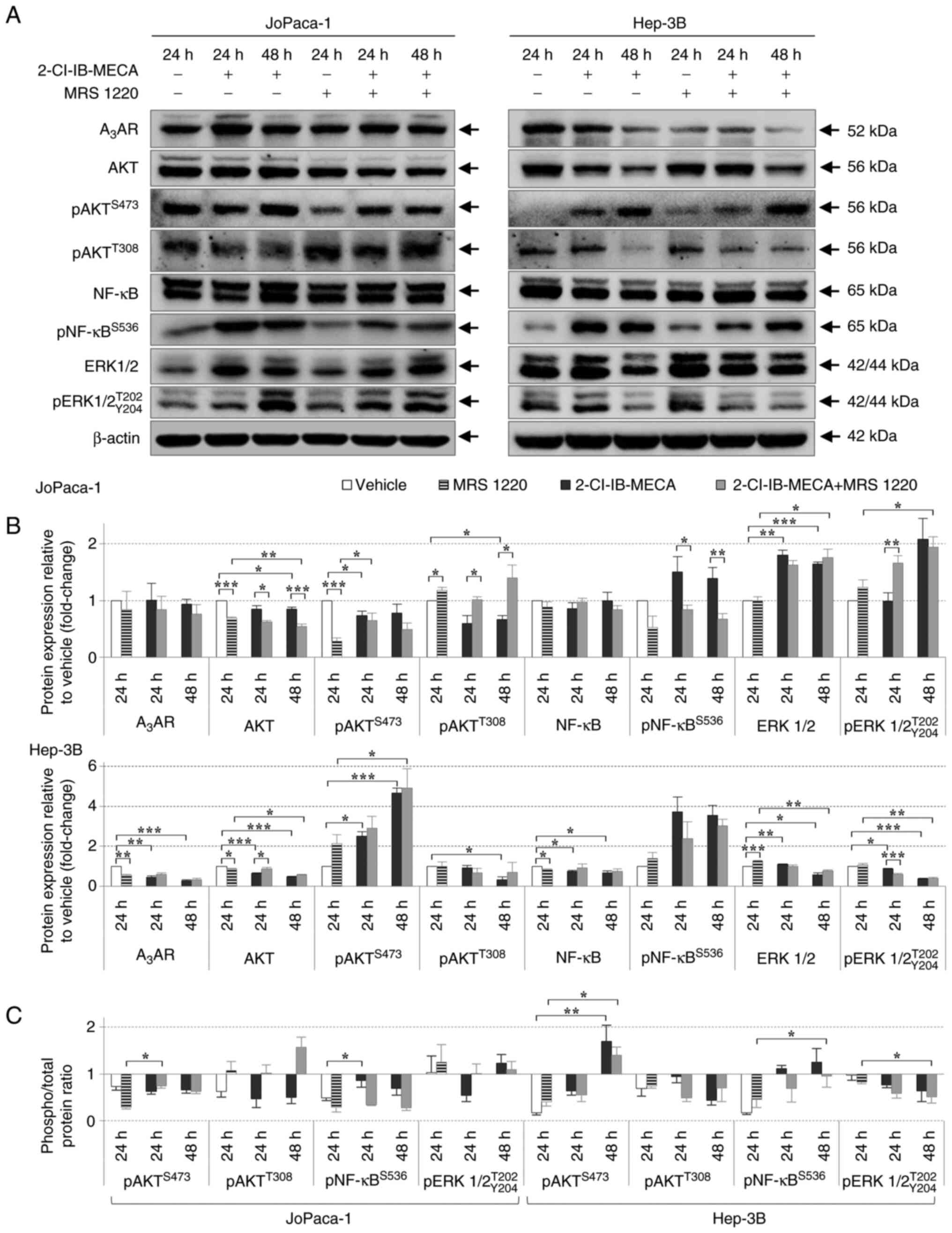
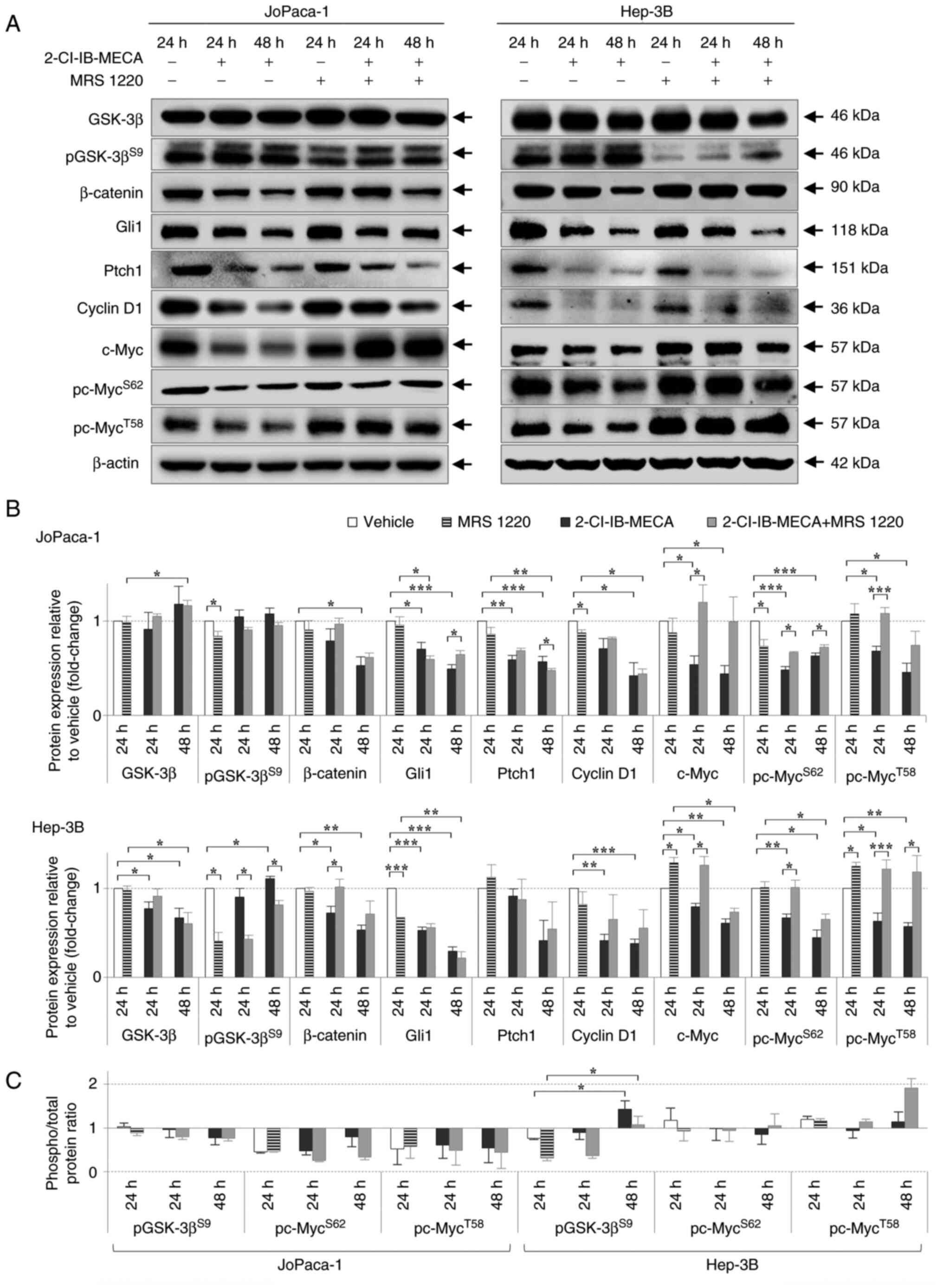
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery
L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Soerjomataram I and Bray F: Global cancer
observatory: Cancer today. Lyon, France: International Agency for
Research on Cancer; 2020, Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today. Accessed November 24,
2021.
|
|
2
|
Rawla P, Sunkara T and Gaduputi V:
Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Global trends, etiology and risk
factors. World J Oncol. 10:10–27. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marquardt JU, Gomez-Quiroz L, Arreguin
Camacho LO, Pinna F, Lee YH, Kitade M, Domínguez MP, Castven D,
Breuhahn K, Conner EA, et al: Curcumin effectively inhibits
oncogenic NF-κB signaling and restrains stemness features in liver
cancer. J Hepatol. 63:661–669. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Zeng SY, Pottler M, Lan B, Grutzmann R,
Pilarsky C and Yang H: Chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:45042019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Adamska A and Falasca M: ATP-binding
cassette transporters in progression and clinical outcome of
pancreatic cancer: What is the way forward? World J Gastroenterol.
24:3222–3238. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lohitesh K, Chowdhury R and Mukherjee S:
Resistance a major hindrance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma: An insight. Cancer Cell Int. 18:442018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu A, Wu Q, Peng D, Ares I, Anadón A,
Lopez-Torres B, Martínez-Larrañaga MR, Wang X and Martínez MA: A
novel strategy for the diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and
chemoresistance of hepatocellular carcinoma: DNA methylation. Med
Res Rev. 40:1973–2018. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Man S, Lu Y, Yin L, Cheng X and Ma L:
Potential and promising anticancer drugs from adenosine and its
analogs. Drug Discov Today. 26:1490–1500. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fredholm BB, IJzerman AP, Jacobson KA,
Linden J and Müller CE: International union of basic and clinical
pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine
receptors-an update. Pharmacol Rev. 63:1–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Madi L, Ochaion A, Rath-Wolfson L,
Bar-Yehuda S, Erlanger A, Ohana G, Harish A, Merimski O, Barer F
and Fishman P: The A3 adenosine receptor is highly expressed in
tumor versus normal cells: Potential target for tumor growth
inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4472–4479. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Morello S, Petrella A, Festa M, Popolo A,
Monaco M, Vuttariello E, Chiappetta G, Parente L and Pinto A:
Cl-IB-MECA inhibits human thyroid cancer cell proliferation
independently of A3 adenosine receptor activation. Cancer Biol
Ther. 7:278–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bar-Yehuda S, Stemmer SM, Madi L, Castel
D, Ochaion A, Cohen S, Barer F, Zabutti A, Perez-Liz G, Del Valle L
and Fishman P: The A3 adenosine receptor agonist CF102 induces
apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via de-regulation of the Wnt
and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathways. Int J Oncol.
33:287–295. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gessi S, Cattabriga E, Avitabile A, Gafa'
R, Lanza G, Cavazzini L, Bianchi N, Gambari R, Feo C, Liboni A, et
al: Elevated expression of A3 adenosine receptors in human
colorectal cancer is reflected in peripheral blood cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:5895–5901. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim HO, Ji XD, Siddiqi SM, Olah ME, Stiles
GL and Jacobson KA: 2-Substitution of
N6-benzyladenosine-5′-uronamides enhances selectivity for A3
adenosine receptors. J Med Chem. 37:3614–3621. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Van Schaick EA, Jacobson KA, Kim HO,
Ijzerman AP and Danhof M: Hemodynamic effects and histamine release
elicited by the selective adenosine A3 receptor agonist
2-Cl-IB-MECA in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 308:311–314. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wittendorp MC, Biber K and Boddeke HWGM:
CL-IB-MECA induced release of CCL2 by astrocytes: Possible role for
the adenosine A3 receptor? Naunyn-Schmiedeb Arch Pharmacol.
369:R1782004.
|
|
18
|
Ge ZD, Peart JN, Kreckler LM, Wan TC,
Jacobson MA, Gross GJ and Auchampach JA: Cl-IB-MECA
[2-chloro-N6-(3-iodobenzyl) adenosine-5′-N-methylcarboxamide]
reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by activating the A3
adenosine receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 319:1200–1210. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Coppi E, Cherchi F, Fusco I, Failli P,
Vona A, Dettori I, Gaviano L, Lucarini E, Jacobson KA, Tosh DK, et
al: Adenosine A3 receptor activation inhibits pronociceptive N-type
Ca2+ currents and cell excitability in dorsal root
ganglion neurons. Pain. 160:1103–1118. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cohen S, Stemmer SM, Zozulya G, Ochaion A,
Patoka R, Barer F, Bar-Yehuda S, Rath-Wolfson L, Jacobson KA and
Fishman P: CF102 an A3 adenosine receptor agonist mediates
anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory effects in the liver. J Cell
Physiol. 226:2438–2447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Morello S, Sorrentino R, Montinaro A,
Luciano A, Maiolino P, Ngkelo A, Arra C, Adcock IM and Pinto A:
NK1.1 cells and CD8 T cells mediate the antitumor activity of
Cl-IB-MECA in a mouse melanoma model. Neoplasia. 13:365–373. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bar Yehuda S, Stemmer SM, Madi L, Castel
D, Ochaion A, Cohen S, Barer F, Perez-Liz G, Del Valle L and
Fishman P: Effect of CF102 on growth suppression and apoptosis in
an orthotopic model of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
26(Suppl 15): S221132008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Safadi R, Braun M, Francis A, Milgrom Y,
Massarwa M, Hakimian D, Hazou W, Issachar A, Harpaz Z, Farbstein M,
et al: Randomised clinical trial: A phase 2 double-blind study of
namodenoson in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and
steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 54:1405–1415. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stemmer SM, Manojlovic NS, Marinca MV,
Petrov P, Cherciu N, Ganea D, Ciuleanu TE, Puscas IA, Beg MS,
Purcell WT, et al: A phase II, randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial evaluating efficacy and safety of
namodenoson (CF102), an A3 adenosine receptor agonist (A3AR), as a
second-line treatment in patients with Child-Pugh B (CPB) advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Clin Oncol. 37(Suppl 15):
S25032019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Stemmer SM, Manojlovic NS, Marinca MV,
Petrov P, Cherciu N, Ganea D, Ciuleanu TE, Pusca IA, Beg MS,
Purcell WT, et al: Namodenoson in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
and Child-Pugh B cirrhosis: Randomized placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Cancers (Basel). 13:1872021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ohana G, Cohen S, Rath-Wolfson L and
Fishman P: A3 adenosine receptor agonist, CF102, protects against
hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury following partial hepatectomy.
Mol Med Rep. 14:4335–4341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
David M, Gospodinov DK, Gheorghe N, Mateev
GS, Rusinova MV, Hristakieva E, Solovastru LG, Patel RV,
Giurcaneanu C, Hitova MC, et al: Treatment of plaque-type psoriasis
with oral CF101: Data from a phase II/III multicenter, randomized,
controlled trial. J Drugs Dermatol. 15:931–938. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Storme J, Tosh DK, Gao ZG, Jacobson KA and
Stove CP: Probing structure-activity relationship in β-arrestin2
recruitment of diversely substituted adenosine derivatives. Biochem
Pharmacol. 158:103–113. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suresh RR, Jain S, Chen Z, Tosh DK, Ma Y,
Podszun MC, Rotman Y, Salvemini D and Jacobson KA: Design and in
vivo activity of A3 adenosine receptor agonist prodrugs.
Purinergic Signal. 16:367–377. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Pottie E, Tosh DK, Gao ZG, Jacobson KA and
Stove CP: Assessment of biased agonism at the A3
adenosine receptor using β-arrestin and miniGαi
recruitment assays. Biochem Pharmacol. 177:1139342020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim SJ, Min HY, Chung HJ, Park EJ, Hong
JY, Kang YJ, Shin DH, Jeong LS and Lee SK: Inhibition of cell
proliferation through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by
thio-Cl-IB-MECA, a novel A3 adenosine receptor agonist, in human
lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 264:309–315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Baltos JA, Paoletta S, Nguyen AT, Gregory
KJ, Tosh DK, Christopoulos A, Jacobson KA and May LT:
Structure-activity analysis of biased agonism at the human
adenosine A3 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 90:12–22. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vecchio EA, Baltos JA, Nguyen ATN,
Christopoulos A, White PJ and May LT: New paradigms in adenosine
receptor pharmacology: Allostery, oligomerization and biased
agonism. Br J Pharmacol. 175:4036–4046. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Fredebohm J, Boettcher M, Eisen C, Gaidaμ
M, Heller A, Keleg S, Tost J, Greulich-Bode KM, Hotz-Wagenblatt A,
Lathrop M, et al: Establishment and characterization of a highly
tumourigenic and cancer stem cell enriched pancreatic cancer cell
line as a well defined model system. PLoS One. 7:e485032012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Novak I, Yu H, Magni L and Deshar G:
Purinergic signaling in pancreas-from physiology to therapeutic
strategies in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:87812020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Qiu GH, Xie X, Xu F, Shi XH, Wang Y and
Deng L: Distinctive pharmacological differences between liver
cancer cell lines HepG2 and Hep3B. Cytotechnology. 67:1–12. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Torres A, Vargas Y, Uribe D, Jaramillo C,
Gleisner A, Salazar-Onfray F, López MN, Melo R, Oyarzún C, San
Martín R and Quezada C: Adenosine A3 receptor elicits
chemoresistance mediated by multiple resistance-associated
protein-1 in human glioblastoma stem-like cells. Oncotarget.
7:67373–67386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Torres Á, Erices JI, Sanchez F, Ehrenfeld
P, Turchi L, Virolle T, Uribe D, Niechi I, Spichiger C, Rocha JD,
et al: Extracellular adenosine promotes cell migration/invasion of
glioblastoma stem-like cells through A3 Adenosine
Receptor activation under hypoxia. Cancer Lett. 446:112–122. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Montraveta A, Xargay-Torrent S,
López-Guerra M, Rosich L, Pérez-Galán P, Salaverria I, Beà S, Kalko
SG, de Frias M, Campàs C, et al: Synergistic anti-tumor activity of
acadesine (AICAR) in combination with the anti-CD20 monoclonal
antibody rituximab in in vivo and in vitro models of mantle cell
lymphoma. Oncotarget. 5:726–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Fishman P, Bar-Yehuda S, Barer F, Madi L,
Multani AS and Pathak S: The A3 adenosine receptor as a new target
for cancer therapy and chemoprotection. Exp Cell Res. 269:230–236.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Soares AS, Costa VM, Diniz C and Fresco P:
The combination of Cl-IB-MECA with paclitaxel: A new
anti-metastatic therapeutic strategy for melanoma. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 74:847–860. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Soares AS, Costa VM, Diniz C and Fresco P:
Potentiation of cytotoxicity of paclitaxel in combination with
Cl-IB-MECA in human C32 metastatic melanoma cells: A new possible
therapeutic strategy for melanoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:777–789.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mlejnek P, Dolezel P and Kosztyu P:
P-glycoprotein mediates resistance to A3 adenosine receptor agonist
2-chloro-N6-(3-io dobenzyl)-adenosine-5′-n-methyluronamide in human
leukemia cells. J Cell Physiol. 227:676–685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Abel B, Tosh DK, Durell SR, Murakami M,
Vahedi S, Jacobson KA and Ambudkar SV: Evidence for the interaction
of A3 adenosine receptor agonists at the drug-binding
site(s) of human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1). Mol Pharmacol. 96:180–192.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Noskova V, Dzubak P, Kuzmina G, Ludkova A,
Stehlik D, Trojanec R, Janostakova A, Korinkova G, Mihal V and
Hajduch M: In vitro chemoresistance profile and expression/function
of MDR associated proteins in resistant cell lines derived from
CCRF-CEM, K562, A549 and MDA MB 231 parental cells. Neoplasma.
49:418–425. 2002.
|
|
46
|
Le Poul E, Hisada S, Mizuguchi Y, Dupriez
VJ, Burgeon E and Detheux M: Adaptation of aequorin functional
assay to high throughput screening. J Biomol Screen. 7:57–65. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Borková L, Frydrych I, Jakubcová N, Adámek
R, Lišková B, Gurská S, Medvedíková M, Hajdúch M and Urban M:
Synthesis and biological evaluation of triterpenoid thiazoles
derived from betulonic acid, dihydrobetulonic acid, and ursonic
acid. Eur J Med Chem. 185:1118062020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chou TC: Theoretical basis, experimental
design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in
drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev. 58:621–681. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Bourderioux A, Naus P, Perlíková P, Pohl
R, Pichová I, Votruba I, Dzubák P, Konecný P, Hajdúch M, Stray KM,
et al: Synthesis and significant cytostatic activity of
7-hetaryl-7-deazaadenosines. J Med Chem. 54:5498–5507. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH image to imageJ: 25 Years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dzubák P, Hajdúch M, Gazák R, Svobodová A,
Psotová J, Walterová D, Sedmera P and Kren V: New derivatives of
silybin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin and their cytotoxic and
P-glycoprotein modulatory activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 14:3793–3810.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Borea PA, Varani K, Vincenzi F, Baraldi
PG, Tabrizi MA, Merighi S and Gessi S: The A3 adenosine receptor:
History and perspectives. Pharmacol Rev. 67:74–102. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Laudadio MA and Psarropoulou C: The A3
adenosine receptor agonist 2-Cl-IB-MECA facilitates epileptiform
discharges in the CA3 area of immature rat hippocampal slices.
Epilepsy Res. 59:83–94. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jafari SM, Panjehpour M, Aghaei M,
Joshaghani HR and Enderami SE: A3 adenosine receptor agonist
inhibited survival of breast cancer stem cells via GLI-1 and ERK1/2
pathway. J Cell Biochem. 118:2909–2920. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Merighi S, Benini A, Mirandola P, Gessi S,
Varani K, Leung E, Maclennan S and Borea PA: A3 adenosine receptor
activation inhibits cell proliferation via phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt-dependent inhibition of the extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation in A375 human melanoma
cells. J Biol Chem. 280:19516–19526. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Borea PA, Gessi S, Merighi S, Vincenzi F
and Varani K: Pharmacology of adenosine receptors: The state of the
art. Physiol Rev. 98:1591–1625. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Haines K, Sarabia SF, Alvarez KR,
Tomlinson G, Vasudevan SA, Heczey AA, Roy A, Finegold MJ, Parsons
DW, Plon SE, et al: Characterization of pediatric hepatocellular
carcinoma reveals genomic heterogeneity and diverse signaling
pathway activation. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 66:e277452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jones S, Zhang XS, Parsons DW, Lin JC,
Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Kamiyama H, Jimeno A, et
al: Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by
global genomic analyses. Science. 321:1801–1806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ,
Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, Madhu B, Goldgraben MA,
Caldwell ME, Allard D, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling
enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic
cancer. Science. 324:1457–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ding J, Zhou XT, Zou HY and Wu J: Hedgehog
signaling pathway affects the sensitivity of hepatoma cells to drug
therapy through the ABCC1 transporter. Lab Invest. 97:819–832.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Spoelstra EC, Westerhoff HV, Pinedo HM,
Dekker H and Lankelma J: The multidrug-resistance-reverser
verapamil interferes with cellular P-glycoprotein-mediated pumping
of daunorubicin as a non-competing substrate. Eur J Biochem.
221:363–373. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Queiroz KCS, Ruela-de-Sousa RR, Fuhler GM,
Aberson HL, Ferreira CV, Peppelenbosch MP and Spek CA: Hedgehog
signaling maintains chemoresistance in myeloid leukemic cells.
Oncogene. 29:6314–6322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Jacobson KA: Adenosine A3 receptors: Novel
ligands and paradoxical effects. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 19:184–191.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Aghaei M, Panjehpour M, Karami-Tehrani F
and Salami S: Molecular mechanisms of A3 adenosine receptor-induced
G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in androgen-dependent and
independent prostate cancer cell lines: Involvement of intrinsic
pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1511–1523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Gao ZG and Jacobson KA: Translocation of
arrestin induced by human A3 adenosine receptor ligands in an
engineered cell line: Comparison with G protein-dependent pathways.
Purinergic Signal. 4:S78–S79. 2008.
|
|
69
|
Mundell S and Kelly E: Adenosine receptor
desensitization and trafficking. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1808:1319–1328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Hu J, Nakano H, Sakurai H and Colburn NH:
Insufficient p65 phosphorylation at S536 specifically contributes
to the lack of NF-kappaB activation and transformation in resistant
JB6 cells. Carcinogenesis. 25:1991–2003. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
De Luca A, Maiello MR, D'Alessio A,
Pergameno M and Normanno N: The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT
signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications
for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16(Suppl 2):
S17–S27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hasnain SZ, Lourie R, Das I, Chen AC and
McGuckin MA: The interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and
inflammation. Immunol Cell Biol. 90:260–270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tam AB, Mercado EL, Hoffmann A and Niwa M:
ER stress activates NF-κB by integrating functions of basal IKK
activity, IRE1 and PERK. PLoS One. 7:e450782012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Makhov P, Naito S, Haifler M, Kutikov A,
Boumber Y, Uzzo RG and Kolenko VM: The convergent roles of NF-κB
and ER stress in sunitinib-mediated expression of pro-tumorigenic
cytokines and refractory phenotype in renal cell carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 9:3742018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, Cron
P, Morrice N, Cohen P and Hemmings BA: Mechanism of activation of
protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J. 15:6541–6551. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Vincent EE, Elder DJ, Thomas EC, Phillips
L, Morgan C, Pawade J, Sohail M, May MT, Hetzel MR and Tavaré JM:
Akt phosphorylation on Thr308 but not on Ser473 correlates with Akt
protein kinase activity in human non-small cell lung cancer. Br J
Cancer. 104:1755–1761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yung HW, Charnock-Jones DS and Burton GJ:
Regulation of AKT phosphorylation at Ser473 and Thr308 by
endoplasmic reticulum stress modulates substrate specificity in a
severity dependent manner. PLoS One. 6:e178942011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
78
|
Wu LF, Wei BL, Guo YT, Ye YQ, Li GP, Pu ZJ
and Feng JL: Apoptosis induced by adenosine involves endoplasmic
reticulum stress in EC109 cells. Int J Mol Med. 30:797–804. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Nie J, Liu A, Tan Q, Zhao K, Hu K, Li Y,
Yan B and Zhou L: AICAR activates ER stress-dependent apoptosis in
gallbladder cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 482:246–252.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Ding L and Billadeau DD: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3β: A novel therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 24:417–426. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fishman P, Bar Yehuda S, Stemmer SM and
Madi L: CF101 enhances the apoptotic effect of chemotherapy on
colon and pancreatic carcinoma cell lines: Molecular mechanisms
involved. J Clin Oncol. 22(Suppl 14): S31732004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Kwee SA and Tiirikainen M: Beta-catenin
activation and immunotherapy resistance in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Mechanisms and biomarkers. Hepatoma Res.
7:82021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A,
Scheidereit C and Strauss M: NF-kappaB function in growth control:
Regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:2690–2698. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Bar-Yehuda S, Madi L, Silberman D, Gery S,
Shkapenuk M and Fishman P: CF101, an agonist to the A3 adenosine
receptor, enhances the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in
a colon carcinoma murine model. Neoplasia. 7:85–90. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Varani K, Vincenzi F, Targa M, Paradiso B,
Parrilli A, Fini M, Lanza G and Borea PA: The stimulation of A(3)
adenosine receptors reduces bone-residing breast cancer in a rat
preclinical model. Eur J Cancer. 49:482–491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Frydrych I, Dolezel P and Mlejnek P:
P-glycoprotein overexpression confers resistance to A3 adenosine
receptor agonists
2-chloro-N6-(3-iodobenzyl)-adenosine-5′-N-methyluronamide
(Cl-IB-MECA) in human leukemia cells. Purinergic Signal. 4(Suppl
1): S1–S210. 2008.
|
|
87
|
Lim JC, Kania KD, Wijesuriya H, Chawla S,
Sethi JK, Pulaski L, Romero IA, Couraud PO, Weksler BB, Hladky SB
and Barrand MA: Activation of beta-catenin signalling by GSK-3
inhibition increases p-glycoprotein expression in brain endothelial
cells. J Neurochem. 106:1855–1865. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Buschauer S, Koch A, Wiggermann P, Müller
M and Hellerbrand C: Hepatocellular carcinoma cells surviving
doxorubicin treatment exhibit increased migratory potential and
resistance to doxorubicin re-treatment in vitro. Oncol Lett.
15:4635–4640. 2018.
|
|
89
|
Yin W, Xiang D, Wang T, Zhang Y, Pham CV,
Zhou S, Jiang G, Hou Y, Zhu Y, Han Y, et al: The inhibition of
ABCB1/MDR1 or ABCG2/BCRP enables doxorubicin to eliminate liver
cancer stem cells. Sci Rep. 11:107912021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Hoare SRJ: The problems of applying
classical pharmacology analysis to modern in vitro drug discovery
assays: Slow binding kinetics and high target concentration. SLAS
Discov. 26:835–850. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Fredholm BB: Adenosine receptors as drug
targets. Exp Cell Res. 316:1284–1288. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Kim SG, Ravi G, Hoffmann C, Jung YJ, Kim
M, Chen A and Jacobson KA: p53-Independent induction of Fas and
apoptosis in leukemic cells by an adenosine derivative, Cl-IB-MECA.
Biochem Pharmacol. 63:871–880. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Mlejnek P, Dolezel P and Frydrych I:
Effects of synthetic A3 adenosine receptor agonists on cell
proliferation and viability are receptor independent at micromolar
concentrations. J Physiol Biochem. 69:405–417. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Jajoo S, Mukherjea D, Watabe K and
Ramkumar V: Adenosine A(3) receptor suppresses prostate cancer
metastasis by inhibiting NADPH oxidase activity. Neoplasia.
11:1132–1145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|