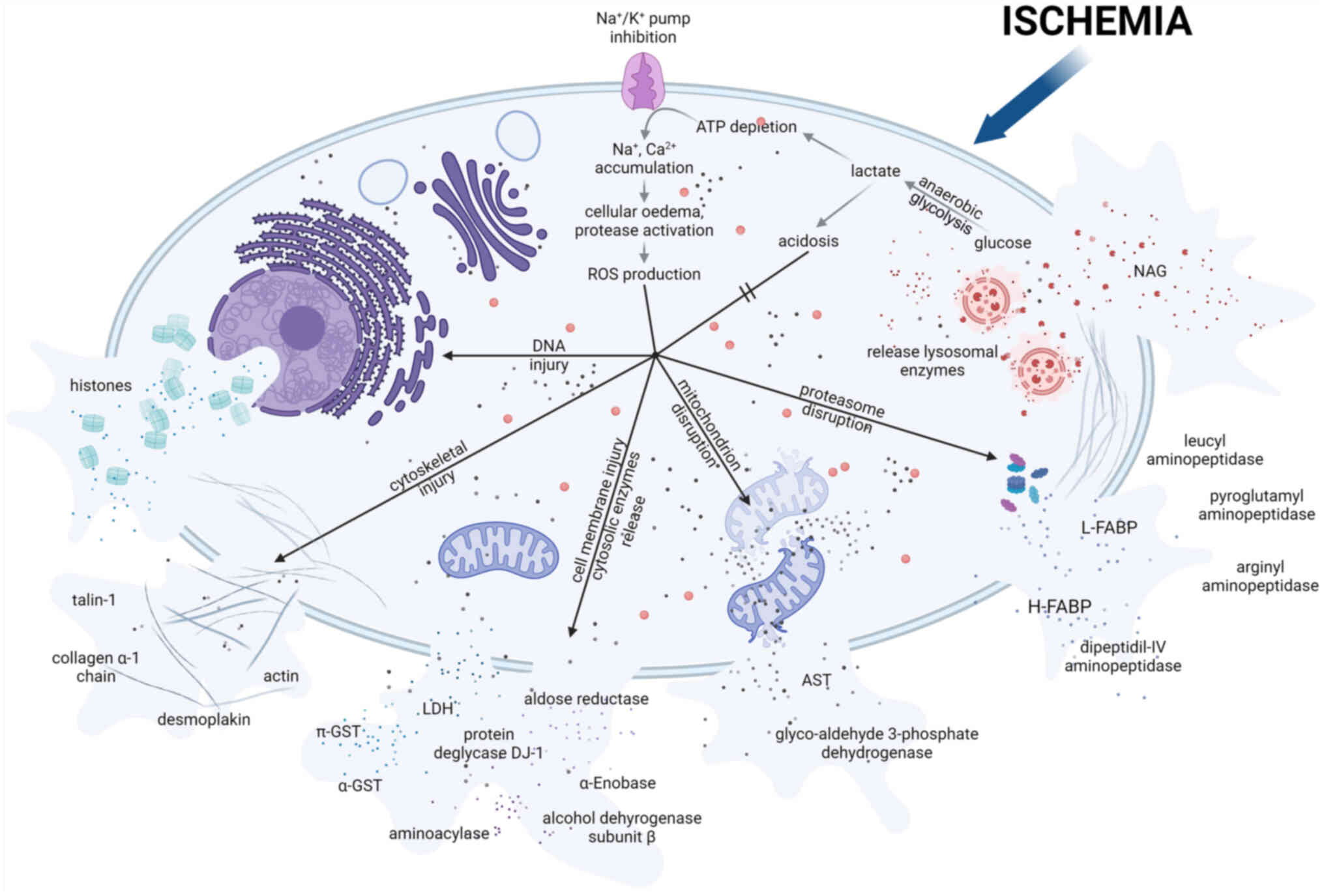
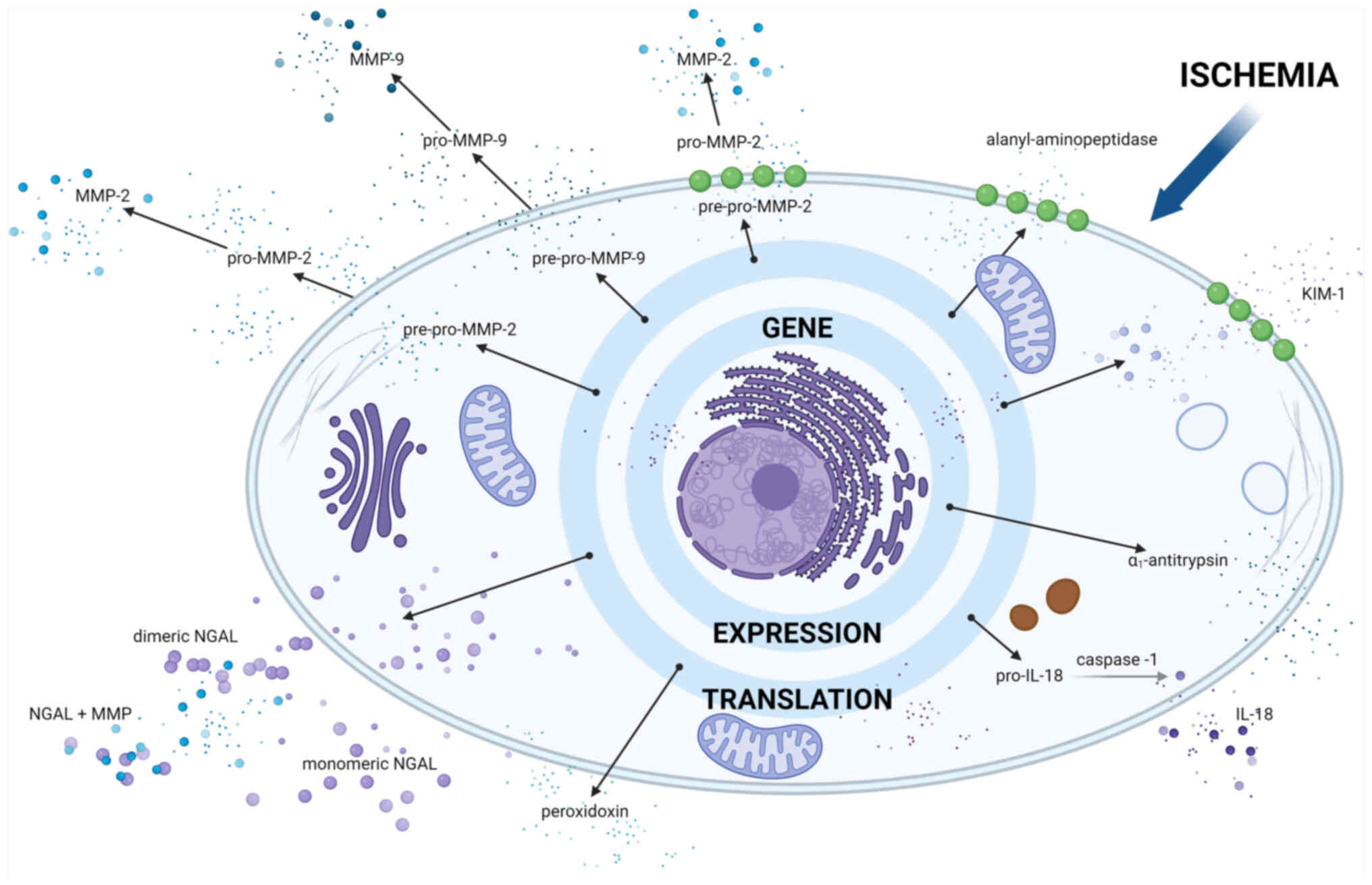
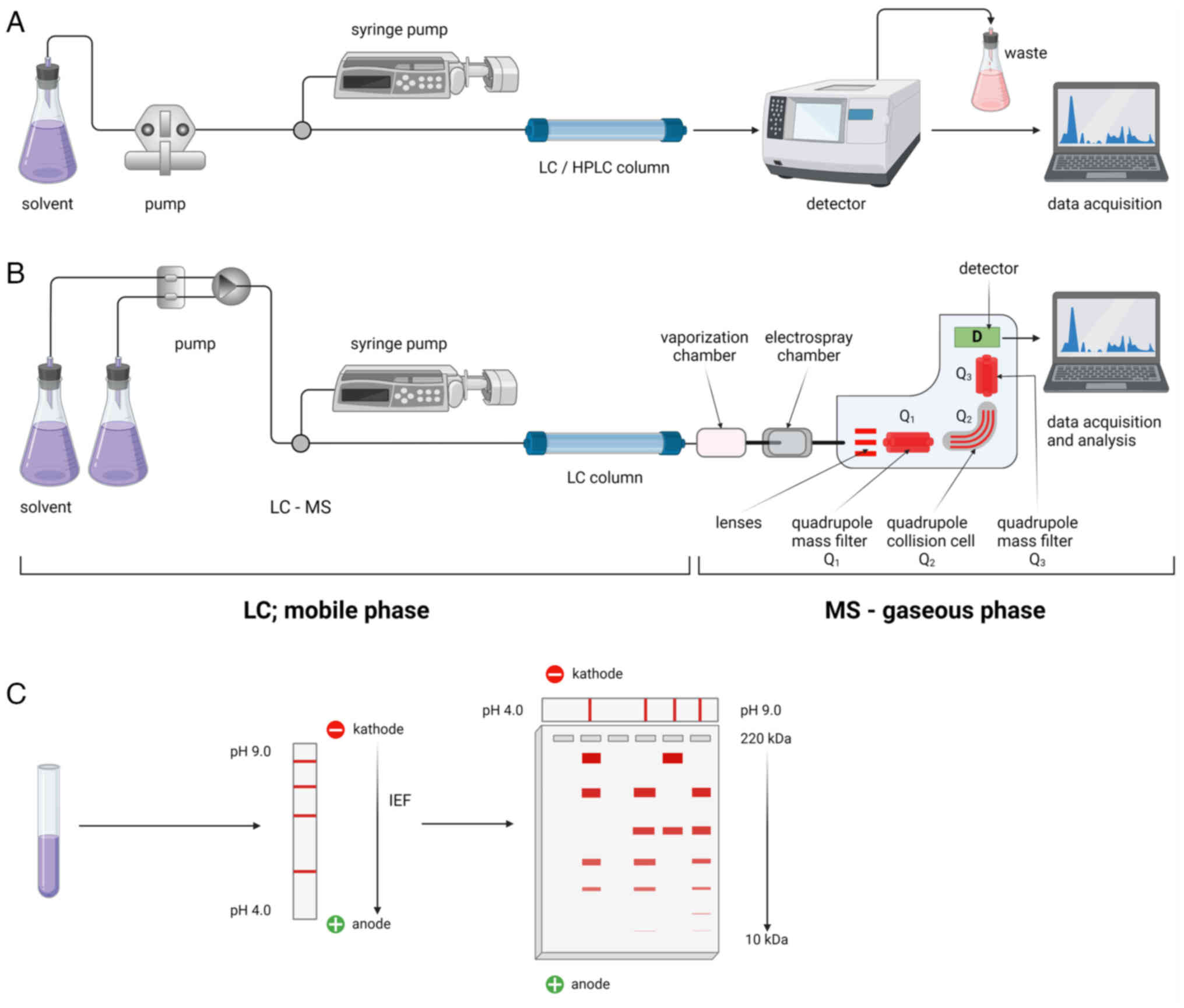
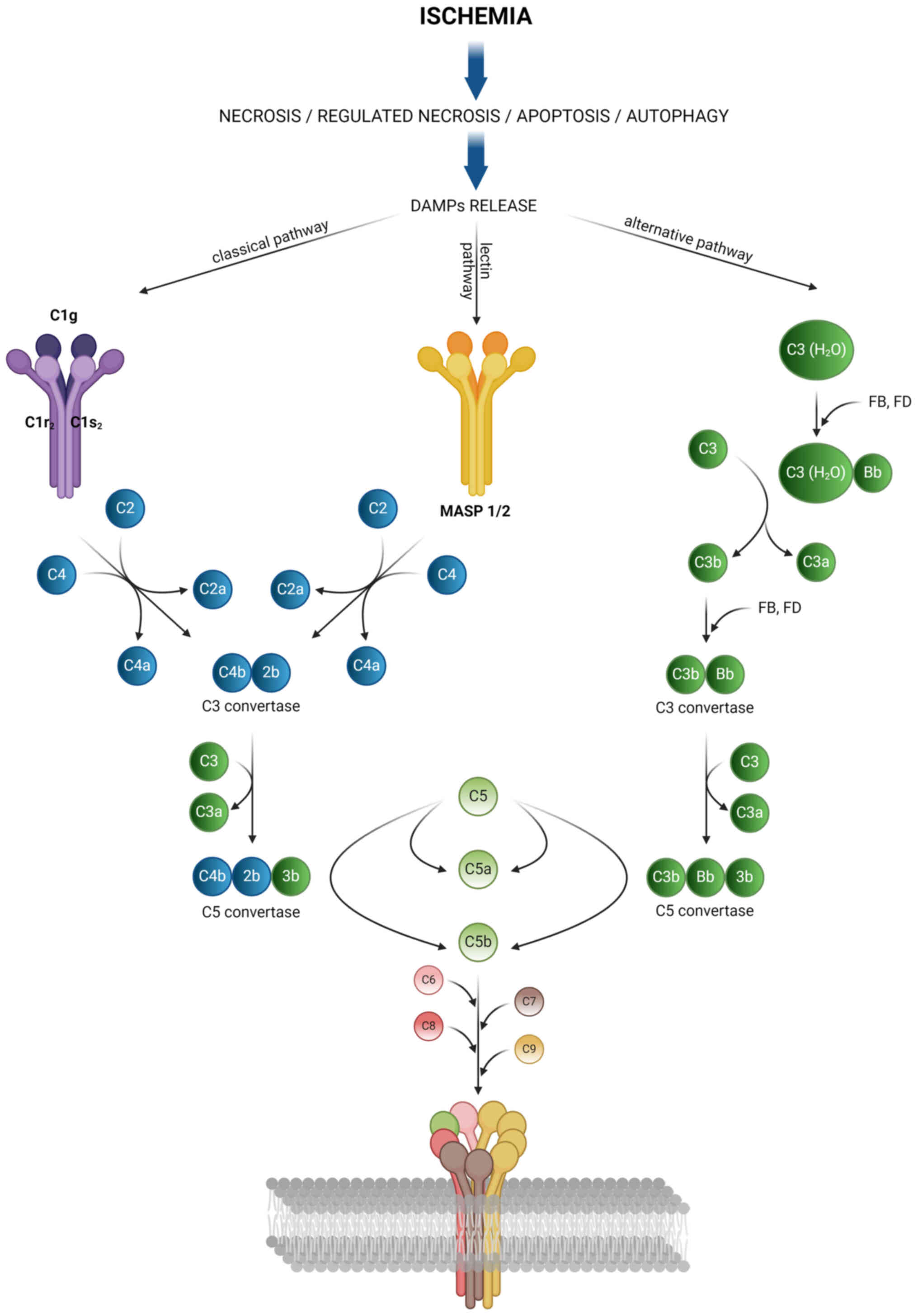
|
1
|
Querard AH, Le Borgne F, Dion A, Giral M,
Mourad G, Garrigue V, Rostaing L, Kamar N, Loupy A, Legendre C, et
al: Propensity score-based comparison of the graft failure risk
between kidney transplant recipients of standard and expanded
criteria donor grafts: Toward increasing the pool of marginal
donors. Am J Transplant. 18:1151–1157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Querard AH, Foucher Y, Combescure C,
Dantan E, Larmet D, Lorent M, Pouteau LM, Giral M and Gillaizeau F:
Comparison of survival outcomes between expanded criteria donor and
standard criteria donor kidney transplant recipients: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Transpl Int. 29:403–415. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barba J, Zudaire JJ, Robles JE, Rosell D,
Berian JM and Pascual I: Complications of kidney transplantation
with grafts from expanded criteria donors. World J Urol.
31:893–900. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Coupel S, Giral-Classe M, Karam G, Morcet
JF, Dantal J, Cantarovich D, Blancho G, Bignon JD, Daguin P,
Soulillou JP and Hourmant M: Ten-year survival of second kidney
transplants: Impact of immunologic factors and renal function at 12
months. Kidney Int. 64:674–680. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kousoulas L, Vondran FWR, Syryca P,
Klempnauer J, Schrem H and Lehner F: Risk-adjusted analysis of
relevant outcome drivers for patients after more than two kidney
transplants. J Transplant. 2015:7120492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zádori G, Kovács DÁ, Fedor R, Kanyári Z,
Zsom L, Asztalos L and Nemes B: Results of expanded-criteria donor
kidneys: A single-center experience in hungary. Transplant Proc.
47:2189–2191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hwang JK, Park SC, Kwon KH, Choi BS, Kim
JI, Yang CW, Kim YS and Moon IS: Long-term outcomes of kidney
transplantation from expanded criteria deceased donors at a single
center: Comparison with standard criteria deceased donors.
Transplant Proc. 46:431–436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
De Beule J and Jochmans I: Kidney
perfusion as an organ quality assessment tool-are we counting our
chickens before they have hatched? J Clin Med. 9:8792020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mourão TB, Mine KL, Campos EF,
Medina-Pestana JO, Tedesco-Silva H and Gerbase-DeLima M: Predicting
delayed kidney graft function with gene expression in
preimplantation biopsies and first-day posttransplant blood. Hum
Immunol. 77:353–357. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hall IE, Reese PP, Weng FL, Schröppel B,
Doshi MD, Hasz RD, Reitsma W, Goldstein MJ, Hong K and Parikh CR:
Preimplant histologic acute tubular necrosis and allograft
outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:573–582. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bachmann Q, Haberfellner F, Büttner-Herold
M, Torrez C, Haller B, Assfalg V, Renders L, Amann K, Heemann U,
Schmaderer C and Kemmner S: The kidney donor profile index (KDPI)
correlates with histopathologic findings in post-reperfusion
baseline biopsies and predicts kidney transplant outcome. Front Med
(Lausanne). 9:8752062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rege A, Irish B, Castleberry A, Vikraman
D, Sanoff S, Ravindra K, Collins B and Sudan D: Trends in usage and
outcomes for expanded criteria donor kidney transplantation in the
United States characterized by kidney donor profile index. Cureus.
8:e8872016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rao PS, Schaubel DE, Guidinger MK,
Andreoni KA, Wolfe RA, Merion RM, Port FK and Sung RS: A
comprehensive risk quantification score for deceased donor kidneys:
The kidney donor risk index. Transplantation. 88:231–236. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nyberg SL, Baskin-Bey ES, Kremers W,
Prieto M, Henry ML and Stegall MD: Improving the prediction of
donor kidney quality: Deceased donor score and resistive indices.
Transplantation. 80:925–929. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guzzi F, Knight SR, Ploeg RJ and Hunter
JP: A systematic review to identify whether perfusate biomarkers
produced during hypothermic machine perfusion can predict graft
outcomes in kidney transplantation. Transpl Int. 33:590–602. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bhangoo RS, Hall IE, Reese PP and Parikh
CR: Deceased-donor kidney perfusate and urine biomarkers for kidney
allograft outcomes: A systematic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
27:3305–3314. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Snoeijs MG, Pulinx B, van Dieijen-Visser
MP, Buurman WA, van Heurn LW and Wodzig WK: Characterization of the
perfusate proteome of human donor kidneys. Ann Clin Biochem.
50:140–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khan AA, Allemailem KS, Alhumaydhi FA,
Gowder SJT and Rahmani AH: The biochemical and clinical
perspectives of lactate dehydrogenase: An enzyme of active
metabolism. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 20:855–868.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mårtensson J and Bellomo R: The rise and
fall of NGAL in acute kidney injury. Blood Purif. 37:304–310. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Markert CL: Lactate dehydrogenase.
Biochemistry and function of lactate dehydrogenase. Cell Biochem
Funct. 2:131–134. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Holmes RS and Goldberg E: Computational
analyses of mammalian lactate dehydrogenases: Human, mouse, opossum
and platypus LDHs. Comput Biol Chem. 33:379–385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dubach UC: On the origin of lactic
dehydrogenase isoenzymes in urine. Helv Med Acta. 33:139–150.
1966.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Osis G, Traylor AM, Black LM, Spangler D,
George JF, Zarjou A, Verlander JW and Agarwal A: Expression of
lactate dehydrogenase A and B isoforms in the mouse kidney. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 320:F706–F718. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kootstra G and Daemen JH: The
non-heart-beating donor. Transplant Proc. 28:161996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Daemen JW, Oomen AP, Janssen MA, van de
Schoot L, van Kreel BK, Heineman E and Kootstra G: Glutathione
S-transferase as predictor of functional outcome in transplantation
of machine-preserved non-heart-beating donor kidneys.
Transplantation. 63:89–93. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Modgill VK, Wiggins PA, Rosenberg IL,
Humphrey CS and Giles GR: An evaluation of viability tests of human
cadaveric kidneys. Br J Surg. 64:548–553. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Skillen AW: Clinical biochemistry of
lactate dehydrogenase. Cell Biochem Funct. 2:140–144. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huijgen HJ, Sanders GT, Koster RW, Vreeken
J and Bossuyt PM: The clinical value of lactate dehydrogenase in
serum: A quantitative review. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem.
35:569–579. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moser MA, Arcand S, Lin HB, Wojnarowicz C,
Sawicka J, Banerjee T, Luo Y, Beck GR, Luke PP and Sawicki G:
Protection of the transplant kidney from preservation injury by
inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases. PLoS One. 11:e01575082016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nagelschmidt M, Minor T, Gallinat A, Moers
C, Jochmans I, Pirenne J, Ploeg RJ, Paul A and Treckmann J: Lipid
peroxidation products in machine perfusion of older donor kidneys.
J Surg Res. 180:337–342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
de Vries B, Snoeijs MGJ, von Bonsdorff L,
Ernest van Heurn LW, Parkkinen J and Buurman WA: Redox-active iron
released during machine perfusion predicts viability of
ischemically injured deceased donor kidneys. Am J Transplant.
6:2686–2693. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hoogland ER, de Vries EE, Christiaans MH,
Winkens B, Snoeijs MG and van Heurn LW: The value of machine
perfusion biomarker concentration in DCD kidney transplantations.
Transplantation. 95:603–610. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moers C, Varnav OC, van Heurn E, Jochmans
I, Kirste GR, Rahmel A, Leuvenink HG, Squifflet JP, Paul A, Pirenne
J, et al: The value of machine perfusion perfusate biomarkers for
predicting kidney transplant outcome. Transplantation. 90:966–973.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moser MAJ, Sawicka K, Arcand S, O'Brien P,
Luke P, Beck G, Sawicka J, Cohen A and Sawicki G: Proteomic
analysis of perfusate from machine cold perfusion of transplant
kidneys: Insights into protection from injury. Ann Transplant.
22:730–739. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Udomsinprasert R, Pongjaroenkit S,
Wongsantichon J, Oakley AJ, Prapanthadara LA, Wilce MC and
Ketterman AJ: Identification, characterization and structure of a
new Delta class glutathione transferase isoenzyme. Biochem J.
388:763–771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Di Ilio C, Aceto A, Bucciarelli T,
Angelucci S, Felaco M, Grilli A, Zezza A, Tenaglia R and Federici
G: Glutathione transferase isoenzymes in normal and neoplastic
human kidney tissue. Carcinogenesis. 12:1471–1475. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harrison DJ, Kharbanda R, Cunningham DS,
McLellan LI and Hayes JD: Distribution of glutathione S-transferase
isoenzymes in human kidney: Basis for possible markers of renal
injury. J Clin Pathol. 42:624–628. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Laborde E: Glutathione transferases as
mediators of signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation and
cell death. Cell Death Differ. 17:1373–1380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hall IE, Bhangoo RS, Reese PP, Doshi MD,
Weng FL, Hong K, Lin H, Han G, Hasz RD, Goldstein MJ, et al:
Glutathione S-transferase iso-enzymes in perfusate from pumped
kidneys are associated with delayed graft function. Am J
Transplant. 14:886–896. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qiao Y, Ding C, Li Y, Tian X, Tian P, Ding
X, Xiang H, Zheng J and Xue W: Predictive value of hypothermic
machine perfusion parameters combined perfusate biomarkers in
deceased donor kidney transplantation. Chin Med J (Engl).
135:181–186. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gok MA, Pelsers M, Glatz JFC, Bhatti AA,
Shenton BK, Peaston R, Cornell C, Mantle D and Talbot D: Comparison
of perfusate activities of glutathione S-transferase, alanine
aminopeptidase and fatty acid binding protein in the assessment of
non-heart-beating donor kidneys. Ann Clin Biochem. 40:252–258.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van Smaalen TC, Beurskens DMH, Hoogland
ERP, Winkens B, Christiaans MHL, Reutelingsperger CP, van Heurn LWE
and Nicolaes GAF: Presence of cytotoxic extracellular histones in
machine perfusate of donation after circulatory death kidneys.
Transplantation. 101:e93–e101. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Felsenfeld G and Groudine M: Controlling
the double helix. Nature. 421:448–453. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Silk E, Zhao H, Weng H and Ma D: The role
of extracellular histone in organ injury. Cell Death Dis.
8:e28122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wickman GR, Julian L, Mardilovich K,
Schumacher S, Munro J, Rath N, Zander SA, Mleczak A, Sumpton D,
Morrice N, et al: Blebs produced by actin-myosin contraction during
apoptosis release damage-associated molecular pattern proteins
before secondary necrosis occurs. Cell Death Differ. 20:1293–1305.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
van Smaalen TC, Beurskens DMH, Kox JJHFM,
Polonia R, Vos R, Duimel H, van de Wetering WJ, López-Iglesias C,
Reutelingsperger CP, Ernest van Heurn LW, et al: Extracellular
histone release by renal cells after warm and cold ischemic kidney
injury: Studies in an ex-vivo porcine kidney perfusion model. PLoS
One. 18:e02799442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Campos EI and Reinberg D: Histones:
Annotating chromatin. Annu Rev Genet. 43:559–599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Strahl BD and Allis CD: The language of
covalent histone modifications. Nature. 403:41–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kono H and Rock KL: How dying cells alert
the immune system to danger. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:279–289. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li B, Hao J, Zeng J and Sauter ER:
SnapShot: FABP functions. Cell. 182:1066–1066.e1. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zager RA, Johnson ACM and Hanson SY: Renal
tubular triglyercide accumulation following endotoxic, toxic, and
ischemic injury. Kidney Int. 67:111–121. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Bobulescu IA: Renal lipid metabolism and
lipotoxicity. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 19:393–402. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Storch J and Thumser AE: The fatty acid
transport function of fatty acid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1486:28–44. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Pelsers MMAL: Fatty acid-binding protein
as marker for renal injury. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl.
241:73–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yamamoto T, Noiri E, Ono Y, Doi K, Negishi
K, Kamijo A, Kimura K, Fujita T, Kinukawa T, Taniguchi H, et al:
Renal L-type fatty acid-binding protein in acute ischemic injury. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 18:2894–2902. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Parikh CR, Hall IE, Bhangoo RS, Ficek J,
Abt PL, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Lin H, Bimali M, Murray PT, Rao V, et
al: Associations of perfusate biomarkers and pump parameters with
delayed graft function and deceased donor kidney allograft
function. Am J Transplant. 16:1526–1539. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Sun Z, Gao Z, Li X, Zheng X, Wang W and
Qiao P: Perfusate neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin,
kidney injury molecular-1, liver-type fatty acid binding protein,
and interleukin-18 as potential biomarkers to predict delayed graft
function and long-term prognosis in kidney transplant recipients: A
single-center retrospective study. Med Sci Monit. 29:e9387582023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Borregaard N and Cowland JB: Granules of
the human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Blood.
89:3503–3521. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ,
Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S and Aderem A: Lipocalin 2 mediates an
innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating
iron. Nature. 432:917–921. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang J, Goetz D, Li JY, Wang W, Mori K,
Setlik D, Du T, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Strong R and Barasch
J: An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol Cell.
10:1045–1056. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cowland JB, Sørensen OE, Sehested M and
Borregaard N: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is
up-regulated in human epithelial cells by IL-1 beta, but not by
TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 171:6630–6639. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M,
Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J and Devarajan P: Identification of
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary
biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:2534–2543. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Barasch J
and Devarajan P: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: A
novel early urinary biomarker for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J
Nephrol. 24:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Weissenbacher A, Stone JP, Lo Faro ML,
Hunter JP, Ploeg RJ, Coussios CC, Fildes JE and Friend PJ:
Hemodynamics and metabolic parameters in normothermic kidney
preservation are linked with donor factors, perfusate cells, and
cytokines. Front Med (Lausanne). 8:8010982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cai L, Rubin J, Han W, Venge P and Xu S:
The origin of multiple molecular forms in urine of HNL/NGAL. Clin J
Am Soc Nephrol. 5:2229–2235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rosell A and Lo EH: Multiphasic roles for
matrix metalloproteinases after stroke. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
8:82–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Soccal PM, Gasche Y, Miniati DN, Hoyt G,
Berry GJ, Doyle RL, Theodore J and Robbins RC: Matrix
metalloproteinase inhibition decreases ischemia-reperfusion injury
after lung transplantation. Am J Transplant. 4:41–50. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Viappiani S, Sariahmetoglu M and Schulz R:
The role of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in
ischemia-reperfusion injury in the liver. Curr Pharm Des.
12:2923–2934. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nagase H, Visse R and Murphy G: Structure
and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc
Res. 69:562–573. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chow AK, Cena J and Schulz R: Acute
actions and novel targets of matrix metalloproteinases in the heart
and vasculature. Br J Pharmacol. 152:189–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Roach DM, Fitridge RA, Laws PE, Millard
SH, Varelias A and Cowled PA: Up-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9
leads to degradation of type IV collagen during skeletal muscle
reperfusion injury; protection by the MMP inhibitor, doxycycline.
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 23:260–269. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Mathalone N, Lahat N, Rahat MA,
Bahar-Shany K, Oron Y and Geyer O: The involvement of matrix
metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in rat retinal ischemia. Graefes Arch
Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 245:725–732. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Cavdar Z, Ural C, Celik A, Arslan S,
Terzioglu G, Ozbal S, Yildiz S, Ergur UB, Guneli E, Camsari T, et
al: Protective effects of taurine against renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibition of gelatinases,
MMP-2 and MMP-9, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling. Biotech Histochem. 92:524–535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhao H, Dong Y, Tian X, Tan TK, Liu Z,
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Harris DCh and Zheng G: Matrix metalloproteinases
contribute to kidney fibrosis in chronic kidney diseases. World J
Nephrol. 2:84–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cavdar Z, Ozbal S, Celik A, Ergur BU,
Guneli E, Ural C, Camsari T and Guner GA: The effects of
alpha-lipoic acid on MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities in a rat renal
ischemia and re-perfusion model. Biotech Histochem. 89:304–314.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Kunugi S, Shimizu A, Kuwahara N, Du X,
Takahashi M, Terasaki Y, Fujita E, Mii A, Nagasaka S, Akimoto T, et
al: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases reduces
ischemia-reperfusion acute kidney injury. Lab Invest. 91:170–180.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Han WK, Waikar SS, Johnson A, Betensky RA,
Dent CL, Devarajan P and Bonventre JV: Urinary biomarkers in the
early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 73:863–869.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Nagase H: Activation mechanisms of matrix
metalloproteinases. Biol Chem. 378:151–160. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Visse R and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases:
Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 92:827–839. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Nagase H and Woessner JF Jr: Matrix
metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 274:21491–21494. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Lijnen R, Baes M,
Lemaître V, Tipping P, Drew A, Eeckhout Y, Shapiro S, Lupu F and
Collen D: Urokinase-generated plasmin activates matrix
metalloproteinases during aneurysm formation. Nat Genet.
17:439–444. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Mazzieri R, Masiero L, Zanetta L, Monea S,
Onisto M, Garbisa S and Mignatti P: Control of type IV collagenase
activity by components of the urokinase-plasmin system: A
regulatory mechanism with cell-bound reactants. EMBO J.
16:2319–2332. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Emonard HP, Remacle AG, Noël AC, Grimaud
JA, Stetler-Stevenson WG and Foidart JM: Tumor cell
surface-associated binding site for the M(r) 72,000 type IV
collagenase. Cancer Res. 52:5845–5848. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Monsky WL, Kelly T, Lin CY, Yeh Y,
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Mueller SC and Chen WT: Binding and
localization of M(r) 72,000 matrix metalloproteinase at cell
surface invadopodia. Cancer Res. 53:3159–3164. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Aimes RT and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinase-2 is an interstitial collagenase. Inhibitor-free
enzyme catalyzes the cleavage of collagen fibrils and soluble
native type I collagen generating the specific 3/4- and 1/4-length
fragments. J Biol Chem. 270:5872–5876. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yabluchanskiy A, Ma Y, Iyer RP, Hall ME
and Lindsey ML: Matrix metalloproteinase-9: Many shades of function
in cardiovascular disease. Physiology (Bethesda). 28:391–403.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fu Z, Ye Q, Zhang Y, Zhong Z, Xiong Y,
Wang Y, Hu L, Wang W, Huang W and Ko DS: Hypothermic machine
perfusion reduced inflammatory reaction by downregulating the
expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in a reperfusion model of
donation after cardiac death. Artif Organs. 40:E102–E111. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Sulikowski T, Domanski L, Zietek Z, Adler
G, Pawlik A, Ciechanowicz A, Ciechanowski K and Ostrowski M: Effect
of preservation solutions UW and EC on the expression of matrix
metalloproteinase II and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase II
genes in rat kidney. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 66:45–50.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V, Wei H,
Hession CA, Cate RL and Sanicola M: Kidney injury molecule-1
(KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a
novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after
injury. J Biol Chem. 273:4135–4142. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Khan KNM, Hard GC and Alden CL: Chapter
47-Kidney. Haschek and Rousseaux's Handbook of Toxicologic
Pathology. 3rd. Haschek WM, Rousseaux CG and Wallig MA: Academic
Press; Boston: pp. 1667–1773. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
van Timmeren MM, van den Heuvel MC, Bailly
V, Bakker SJL, van Goor H and Stegeman CA: Tubular kidney injury
molecule-1 (KIM-1) in human renal disease. J Pathol. 212:209–217.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Amin RP, Vickers AE, Sistare F, Thompson
KL, Roman RJ, Lawton M, Kramer J, Hamadeh HK, Collins J, Grissom S,
et al: Identification of putative gene based markers of renal
toxicity. Environ Health Perspect. 112:465–479. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Griffin BR, You Z, Noureddine L, Gitomer
B, Perrenoud L, Wang W, Chonchol M and Jalal D; HALT Investigators:
KIM-1 and kidney disease progression in autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease: HALT-PKD results. Am J Nephrol.
51:473–479. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Han WK, Alinani A, Wu CL, Michaelson D,
Loda M, McGovern FJ, Thadhani R and Bonventre JV: Human kidney
injury molecule-1 is a tissue and urinary tumor marker of renal
cell carcinoma. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1126–1134. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Bonventre JV: Kidney injury molecule-1
(KIM-1): A urinary biomarker and much more. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 24:3265–3268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ichimura T, Asseldonk EJPV, Humphreys BD,
Gunaratnam L, Duffield JS and Bonventre JV: Kidney injury
molecule-1 is a phosphatidylserine receptor that confers a
phagocytic phenotype on epithelial cells. J Clin Invest.
118:1657–1668. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kaplanski G: Interleukin-18: Biological
properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol Rev.
281:138–153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Ghayur T, Banerjee S, Hugunin M, Butler D,
Herzog L, Carter A, Quintal L, Sekut L, Talanian R, Paskind M, et
al: Caspase-1 processes IFN-gamma-inducing factor and regulates
LPS-induced IFN-gamma production. Nature. 386:619–623. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Sugawara S, Uehara A, Nochi T, Yamaguchi
T, Ueda H, Sugiyama A, Hanzawa K, Kumagai K, Okamura H and Takada
H: Neutrophil proteinase 3-mediated induction of bioactive IL-18
secretion by human oral epithelial cells. J Immunol. 167:6568–6575.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ihim SA, Abubakar SD, Zian Z, Sasaki T,
Saffarioun M, Maleknia S and Azizi G: Interleukin-18 cytokine in
immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: Biological role in
induction, regulation, and treatment. Front Immunol. 13:9199732022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Banerjee S and Bond JS: Prointerleukin-18
is activated by meprin beta in vitro and in vivo in intestinal
inflammation. J Biol Chem. 283:31371–31377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Okamura H, Tsutsui H, Kashiwamura S,
Yoshimoto T and Nakanishi K: Interleukin-18: A novel cytokine that
augments both innate and acquired immunity. Adv Immunol.
70:281–312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Tsutsui H, Nakanishi K, Matsui K,
Higashino K, Okamura H, Miyazawa Y and Kaneda K: IFN-gamma-inducing
factor up-regulates Fas ligand-mediated cytotoxic activity of
murine natural killer cell clones. J Immunol. 157:3967–3973. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Li P, Li YL, Li ZY, Wu YN, Zhang CC, A X,
Wang CX, Shi HT, Hui MZ, Xie B, et al: Cross talk between vascular
smooth muscle cells and monocytes through
interleukin-1β/interleukin-18 signaling promotes vein graft
thickening. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:2001–2011. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Hoshino T, Wiltrout RH and Young HA: IL-18
is a potent coinducer of IL-13 in NK and T cells: A new potential
role for IL-18 in modulating the immune response. J Immunol.
162:5070–5077. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yoshimoto T, Mizutani H, Tsutsui H,
Noben-Trauth N, Yamanaka K, Tanaka M, Izumi S, Okamura H, Paul WE
and Nakanishi K: IL-18 induction of IgE: Dependence on CD4+ T
cells, IL-4 and STAT6. Nat Immunol. 1:132–137. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Yoshimoto T, Tsutsui H, Tominaga K,
Hoshino K, Okamura H, Akira S, Paul WE and Nakanishi K: IL-18,
although antiallergic when administered with IL-12, stimulates IL-4
and histamine release by basophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:13962–13966. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Doshi MD, Reese PP, Hall IE, Schröppel B,
Ficek J, Formica RN, Weng FL, Hasz RD, Thiessen-Philbrook H and
Parikh CR: Utility of applying quality assessment tools for kidneys
with KDPI ≥80. Transplantation. 101:1125–1133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Issaq H and Veenstra T: Two-dimensional
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE): Advances and
perspectives. Biotechniques. 44:697–698. 7002008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Smith BJ: SDS polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis of proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 32:23–34.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Kielkopf CL, Bauer W and Urbatsch IL:
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of
proteins. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 20212021.
|
|
112
|
Pitt JJ: Principles and applications of
liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in clinical biochemistry.
Clin Biochem Rev. 30:19–34. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Aslam B, Basit M, Nisar MA, Khurshid M and
Rasool MH: Proteomics: Technologies and their applications. J
Chromatogr Sci. 55:182–196. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Li C, Chu S, Tan S, Yin X, Jiang Y, Dai X,
Gong X, Fang X and Tian D: Towards higher sensitivity of mass
spectrometry: A perspective from the mass analyzers. Front Chem.
9:8133592021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Wieser A, Schneider L, Jung J and Schubert
S: MALDI-TOF MS in microbiological diagnostics-identification of
microorganisms and beyond (mini review). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
93:965–974. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
van Leeuwen LL, Spraakman NA, Brat A,
Huang H, Thorne AM, Bonham S, van Balkom BWM, Ploeg RJ, Kessler BM
and Leuvenink HGD: Proteomic analysis of machine perfusion solution
from brain dead donor kidneys reveals that elevated complement,
cytoskeleton and lipid metabolism proteins are associated with
1-year outcome. Transpl Int. 34:1618–1629. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Mulvey JF, Ul Shaheed S, Charles PD,
Snashall C, Lo Faro ML, Sutton CW, Jochmans I, Pirenne J, van
Kooten C, Leuvenink HGD, et al: Perfusate proteomes provide
biological insight into oxygenated versus standard hypothermic
machine perfusion in kidney transplantation. Ann Surg. 278:676–682.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Karpman D, Bekassy Z, Grunenwald A and
Roumenina LT: A role for complement blockade in kidney
transplantation. Cell Mol Immunol. 19:755–757. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Yamanaka K, Kakuta Y, Miyagawa S, Nakazawa
S, Kato T, Abe T, Imamura R, Okumi M, Maeda A, Okuyama H, et al:
Depression of complement regulatory factors in rat and human renal
grafts is associated with the progress of acute T-cell mediated
rejection. PLoS One. 11:e01488812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
De Vries B, Matthijsen RA, Wolfs TGAM, Van
Bijnen AAJHM, Heeringa P and Buurman WA: Inhibition of complement
factor C5 protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury:
Inhibition of late apoptosis and inflammation. Transplantation.
75:375–382. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Biglarnia AR, Huber-Lang M, Mohlin C,
Ekdahl KN and Nilsson B: The multifaceted role of complement in
kidney transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 14:767–781. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhang R: Donor-specific antibodies in
kidney transplant recipients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:182–192.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
123
|
Nauser CL, Farrar CA and Sacks SH:
Complement recognition pathways in renal transplantation. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 28:2571–2578. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Sato T, Van Dixhoorn MG, Prins FA, Mooney
A, Verhagen N, Muizert Y, Savill J, Van Es LA and Daha MR: The
terminal sequence of complement plays an essential role in
antibody-mediated renal cell apoptosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
10:1242–1252. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Shimizu A, Masuda Y, Kitamura H, Ishizaki
M, Ohashi R, Sugisaki Y and Yamanaka N: Complement-mediated killing
of mesangial cells in experimental glomerulonephritis: Cell death
by a combination of apoptosis and necrosis. Nephron. 86:152–160.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhou W, Farrar CA, Abe K, Pratt JR, Marsh
JE, Wang Y, Stahl GL and Sacks SH: Predominant role for C5b-9 in
renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest. 105:1363–1371.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Jane-wit D, Surovtseva YV, Qin L, Li G,
Liu R, Clark P, Manes TD, Wang C, Kashgarian M, Kirkiles-Smith NC,
et al: Complement membrane attack complexes activate noncanonical
NF-κB by forming an Akt+ NIK+ signalosome on Rab5+ endosomes. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:9686–9691. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Jager NM, Venema LH, Arykbaeva AS,
Meter-Arkema AH, Ottens PJ, van Kooten C, Mollnes TE, Alwayn IPJ,
Leuvenink HGD and Pischke SE; PROPER study consortium: Complement
is activated during normothermic machine perfusion of porcine and
human discarded kidneys. Front Immunol. 13:8313712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Coskun A, Baykal AT, Kazan D, Akgoz M,
Senal MO, Berber I, Titiz I, Bilsel G, Kilercik H, Karaosmanoglu K,
et al: Proteomic analysis of kidney preservation solutions prior to
renal transplantation. PLoS One. 11:e01687552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Nieuwenhuijs-Moeke GJ, Pischke SE, Berger
SP, Sanders JSF, Pol RA, Struys MMRF, Ploeg RJ and Leuvenink HGD:
Ischemia and reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: Relevant
mechanisms in injury and repair. J Clin Med. 9:2532020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kako K, Kato M, Matsuoka T and Mustapha A:
Depression of membrane-bound Na+-K+-ATPase activity induced by free
radicals and by ischemia of kidney. Am J Physiol. 254:C330–C337.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Salvadori M, Rosso G and Bertoni E: Update
on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation:
Pathogenesis and treatment. World J Transplant. 5:52–67. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Molitoris BA, Dahl R and Geerdes A:
Cytoskeleton disruption and apical redistribution of proximal
tubule Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase during ischemia. Am J Physiol.
263:F488–F495. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Caron A, Desrosiers RR and Béliveau R:
Kidney ischemia-reperfusion regulates expression and distribution
of tubulin subunits, beta-actin and rho GTPases in proximal
tubules. Arch Biochem Biophys. 431:31–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Genescà M, Sola A and Hotter G: Actin
cytoskeleton derangement induces apoptosis in renal
ischemia/reperfusion. Apoptosis. 11:563–571. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ramos AM and
Ortiz A: Regulated cell death pathways in kidney disease. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 19:281–299. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Garrod D and Chidgey M: Desmosome
structure, composition and function. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1778:572–587. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Chen CS and Zhu H: Protein microarrays.
Biotechniques. 40:423–425, 427 passim. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Uttamchandani M, Neo JL, Ong BNZ and
Moochhala S: Applications of microarrays in pathogen detection and
biodefence. Trends Biotechnol. 27:53–61. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Shome M and Labaer J: Protein microarrays
and their fabrication. Methods Mol Biol. 2597:131–142. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Baboudjian M, Gondran-Tellier B, Boissier
R, Ancel P, Marjollet J, Lyonnet L, François P, Sabatier F,
Lechevallier E, Dutour A and Paul P: An enhanced level of VCAM in
transplant preservation fluid is an independent predictor of early
kidney allograft dysfunction. Front Immunol. 13:9669512022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Gok MA, Pelzers M, Glatz JFC, Shenton BK,
Buckley PE, Peaston R, Cornell C, Mantle D, Soomro N, Jaques BC, et
al: Do tissue damage biomarkers used to assess machine-perfused
NHBD kidneys predict long-term renal function post-transplant? Clin
Chim Acta. 338:33–43. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Balupuri S, Talbot D, El-Sheikh M, Snowden
C, Manas DM, Kirby J and Mantle D: Comparison of proteolytic
enzymes and glutathione S-transferase levels in non-heart-beating
donors' (NHBD) kidney perfusates. Clin Chem Lab Med. 38:1099–1102.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Tejchman K, Sierocka A, Kotfis K, Kotowski
M, Dolegowska B, Ostrowski M and Sienko J: Assessment of oxidative
stress markers in hypothermic preservation of transplanted kidneys.
Antioxidants (Basel). 10:12632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Cohen J, Ratigan E, Shigeoka A, Steiner R,
Stocks L and McKay D: Inflammatory profiling of hypothermic machine
pumped kidney allografts. Am J Transplant. 15(Suppl 3):
C2732015.
|
|
146
|
Maritan E, Franchin M, Amico F, Ietto G,
Villa F, Tozzi M, Ferraro S, Negri S, Alberio MG and Carcano G:
Ischemia and reperfusion injury markers in kidney transplant:
Mechanical perfusion vs cold storage. Preliminary experience: 536.
Transplantation. 94(10S): S11592012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Boenink R, Astley ME, Huijben JA, Stel VS,
Kerschbaum J, Ots-Rosenberg M, Åsberg AA, Lopot F, Golan E, Castro
de la Nuez P, et al: The ERA registry annual report 2019: Summary
and age comparisons. Clin Kidney J. 15:452–472. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Aubert O, Kamar N, Vernerey D, Viglietti
D, Martinez F, Duong-Van-Huyen JP, Eladari D, Empana JP, Rabant M,
Verine J, et al: Long term outcomes of transplantation using
kidneys from expanded criteria donors: Prospective, population
based cohort study. BMJ. 351:h35572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Tomita Y, Tojimbara T, Iwadoh K, Nakajima
I and Fuchinoue S: Long-term outcomes in kidney transplantation
from expanded-criteria donors after circulatory death. Transplant
Proc. 49:45–48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Borda B, Németh T, Ottlakan A, Keresztes
C, Kemény É and Lázár G: Post-transplantation morphological and
functional changes in kidneys from expanded criteria donors.
Physiol Int. 104:329–333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Tingle SJ, Figueiredo RS, Moir JA,
Goodfellow M, Talbot D and Wilson CH: Machine perfusion
preservation versus static cold storage for deceased donor kidney
transplantation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
3:CD0116712019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Tingle SJ, Thompson ER, Figueiredo RS,
Moir JA, Goodfellow M, Talbot D and Wilson CH: Normothermic and
hypothermic machine perfusion preservation versus static cold
storage for deceased donor kidney transplantation. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 7:CD0116712024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Helanterä I, Ibrahim HN, Lempinen M and
Finne P: Donor age, cold ischemia time, and delayed graft function.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:813–821. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Heilman RL, Mathur A, Smith ML, Kaplan B
and Reddy KS: Increasing the use of kidneys from unconventional and
high-risk deceased donors. Am J Transplant. 16:3086–3092. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Tasaki M, Saito K, Nakagawa Y, Ikeda M,
Imai N, Narita I and Takahashi K: Effect of donor-recipient age
difference on long-term graft survival in living kidney
transplantation. Int Urol Nephrol. 46:1441–1446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Lim K, Lee YJ, Gwon JG, Jung CW, Yang J,
Oh SW, Jo SK, Cho WY and Kim MG: Impact of donor age on the
outcomes of kidney transplantation from deceased donors with
histologic acute kidney injury. Transplant Proc. 51:2593–2597.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Scurt FG, Ernst A, Hammoud B, Wassermann
T, Mertens PR, Schwarz A, Becker JU and Chatzikyrkou C: Effect of
creatinine metrics on outcome after transplantation of marginal
donor kidneys. Nephrology (Carlton). 27:973–982. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Irish GL, Coates PT and Clayton PA:
Association of admission, nadir, and terminal donor creatinine with
kidney transplantation outcomes. Kidney Int Rep. 6:2075–2083. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Perico N, Cattaneo D, Sayegh MH and
Remuzzi G: Delayed graft function in kidney transplantation.
Lancet. 364:1814–1827. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Lai C, Yee SY, Ying T and Chadban S:
Biomarkers as diagnostic tests for delayed graft function in kidney
transplantation. Transpl Int. 34:2431–2441. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Siedlecki A, Irish W and Brennan DC:
Delayed graft function in the kidney transplant. Am J Transplant.
11:2279–2296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Schrezenmeier E, Müller M, Friedersdorff
F, Khadzhynov D, Halleck F, Staeck O, Dürr M, Zhang K, Eckardt KU,
Budde K and Lehner LJ: Evaluation of severity of delayed graft
function in kidney transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
37:973–981. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Parsons FM: Haemodialysis; indications and
results. Postgrad Med J. 35:625–630, passim. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Clark JE and Soricelli RR: Indications for
dialysis. Med Clin North Am. 49:1213–1239. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Hosgood SA, Callaghan CJ, Wilson CH, Smith
L, Mullings J, Mehew J, Oniscu GC, Phillips BL, Bates L and
Nicholson ML: Normothermic machine perfusion versus static cold
storage in donation after circulatory death kidney transplantation:
A randomized controlled trial. Nat Med. 29:1511–1519. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Brat A, de Vries KM, van Heurn EWE,
Huurman VAL, de Jongh W, Leuvenink HGD, van Zuilen AD,
Haase-Kromwijk BJJM, de Jonge J, Berger SP and Hofker SH:
Hypothermic machine perfusion as a national standard preservation
method for deceased donor kidneys. Transplantation. 106:1043–1050.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
167
|
Rijkse E, Bouari S, Kimenai HJAN, de Jonge
J, de Bruin RWF, Slagter JS, van den Hoogen MWF, Ijzermans JNM,
Hoogduijn MJ and Minnee RC: Additional Normothermic machine
perfusion versus hypothermic machine perfusion in suboptimal donor
kidney transplantation: Protocol of a randomized, controlled,
open-label trial. Int J Surg Protoc. 25:227–237. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|