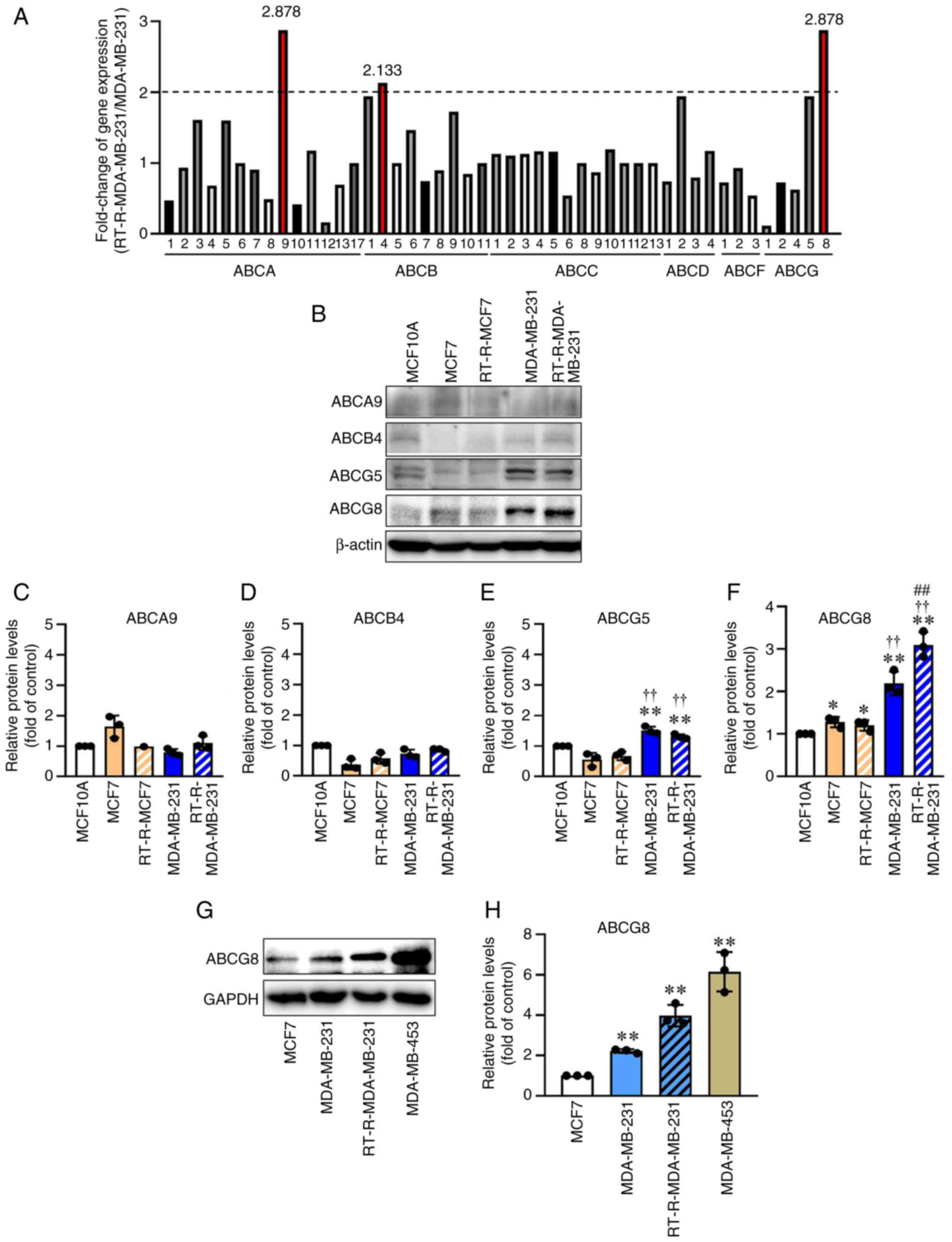
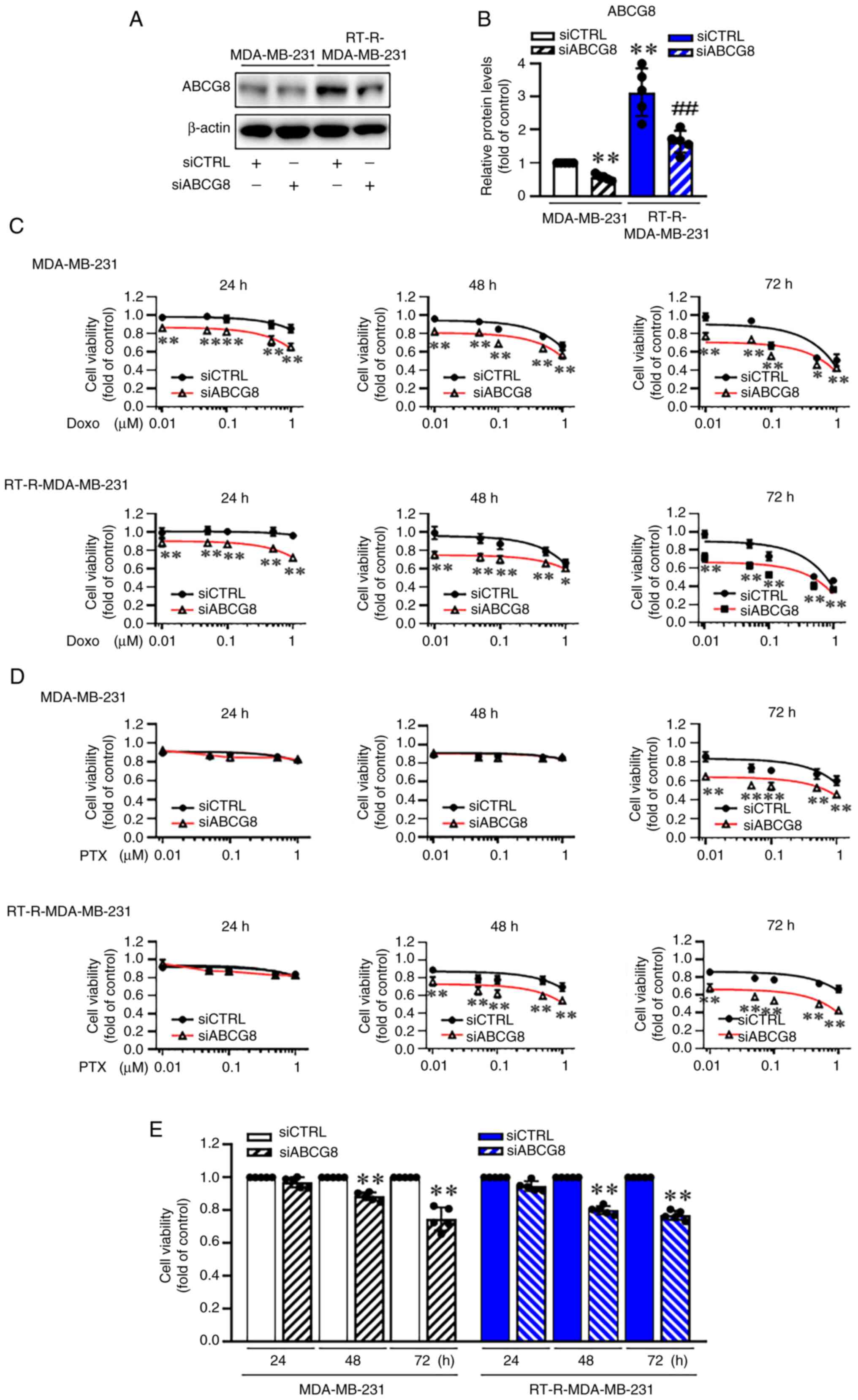
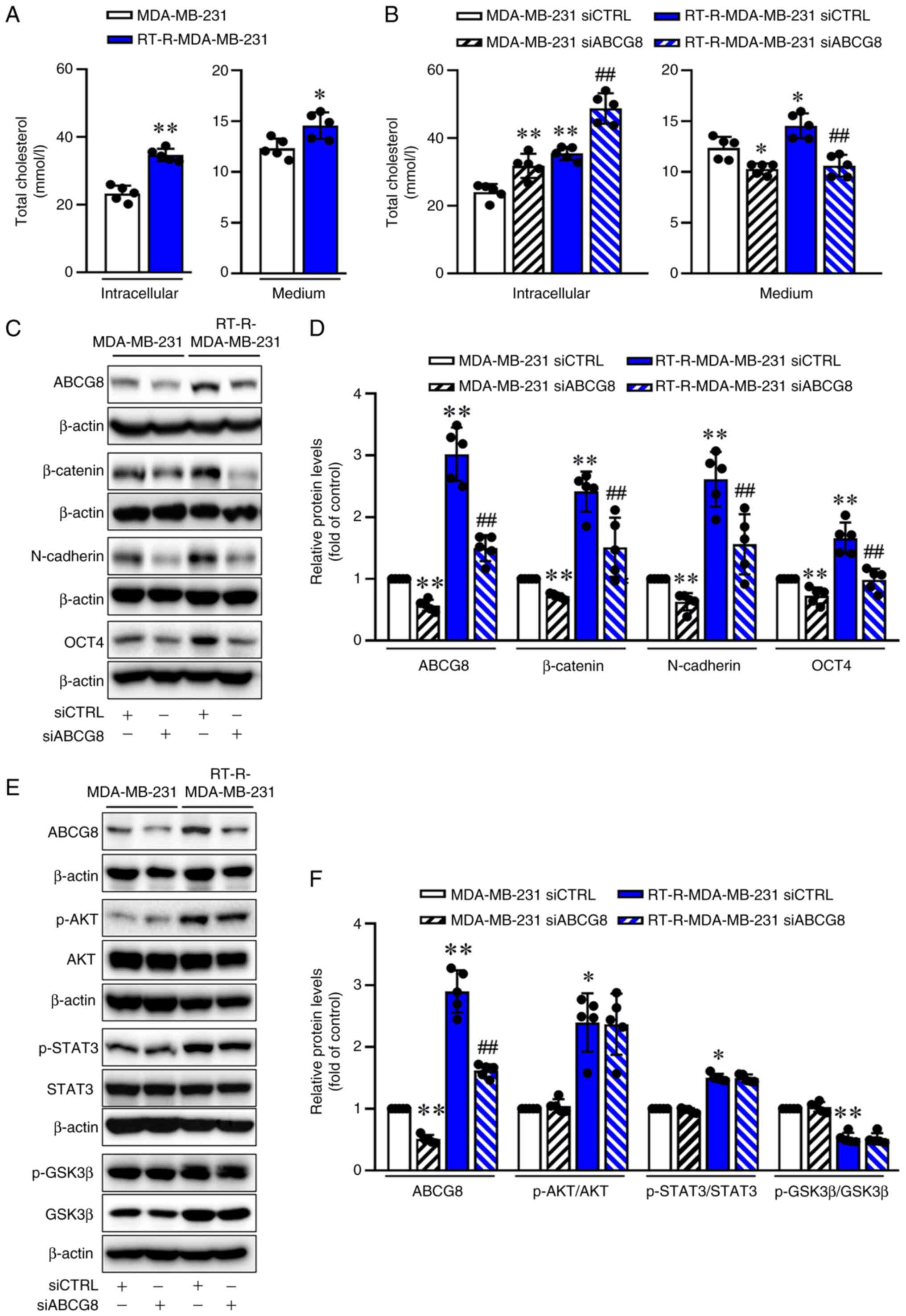
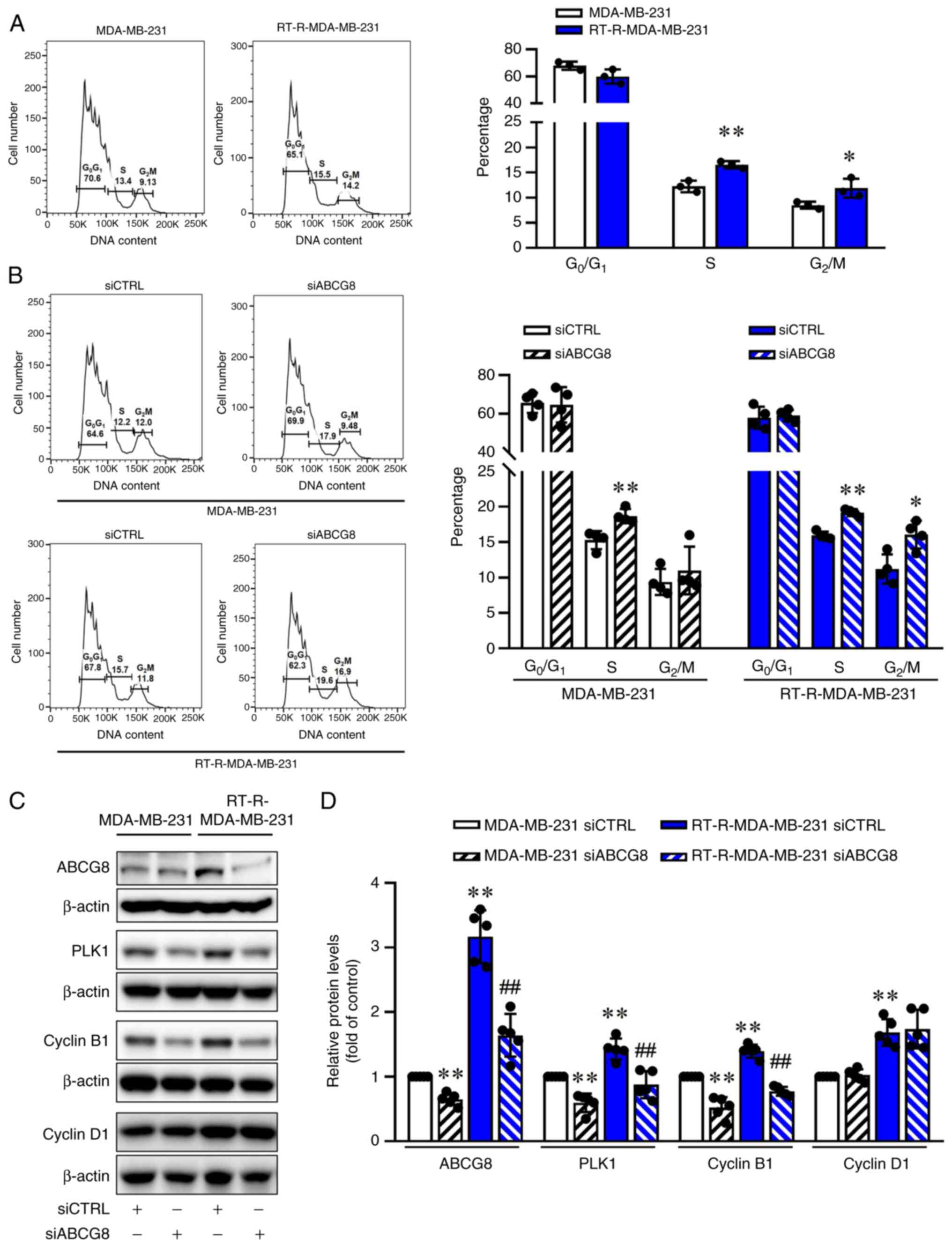
|
1
|
Xu Y, Gong M, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu S and
Zeng Q: Global trends and forecasts of breast cancer incidence and
deaths. Sci Data. 10:3342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Courtney D, Davey MG, Moloney BM, Barry
MK, Sweeney K, McLaughlin RP, Malone CM, Lowery AJ and Kerin MJL:
Breast cancer recurrence: Factors impacting occurrence and
survival. Ir J Med Sci. 191:2501–2510. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Ruijter TC, Veeck J, de Hoon JP, van
Engeland M and Tjan-Heijnen VC: Characteristics of triple-negative
breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1831922011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bai X, Ni J, Beretov J, Graham P and Li Y:
Triple-negative breast cancer therapeutic resistance: Where is the
Achilles' heel? Cancer Lett. 28(497): 100–111. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang C, Wang S, Israel HP, Yan SX,
Horowitz DP, Crockford S, Gidea-Addeo D, Chao KSC, Kalinsky K and
Connolly EP: Higher locoregional recurrence rate for
triple-negative breast cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy,
surgery and radiotherapy. Springer Plus. 4:3862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Wedad MP,
Harriet KH, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ko YS, Jin H, Lee JS, Park SW, Chang KC,
Kang KM, Jeong BK and Kim HJ: Radioresistant breast cancer cells
exhibit increased resistance to chemotherapy and enhanced invasive
properties due to cancer stem cells. Oncol Rep. 40:3752–3762.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ko YS, Rugira T, Jin H, Joo YN and Kim HJ:
Radiotherapy-resistant breast cancer cells enhance tumor
progression by enhancing premetastatic niche formation through the
HIF-1α-LOX axis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:80272020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Modi A, Roy D, Sharma S, Vishnoi JR,
Pareek P, Elhence P, Sharma P and Purohit P: ABC transporters in
breast cancer: Their roles in multidrug resistance and beyond. J
Drug Target. 9:927–947. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Beretta GL, Cassinelli G, Pennate M, Zuco
V and Gatti L: Overcoming ABC transporter-mediated multidrug
resistance: The dual role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors as
multitargeting agents. Eur J Med Chem. 142:271–289. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fletcher JI, Henderson MJ and Norris MD:
ABC transporters in cancer: More than just drug efflux pumps. Nat
Rev Cancer. 10:147–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Begicevic RR and Falasca M: ABC
transporters in cancer stem cells: Beyond chemoresistance. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:23622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen ZS and Tiwari AK: Multidrug
resistance proteins (MRPs/ABCCs) in cancer chemotherapy and genetic
diseases. FEBS J. 278:3266–3245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sun YL, Patel A, Kumar P and Chen ZS: Role
of ABC transporters in cancer chemotherapy. Chin J Cancer.
31:51–57. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sabeva NS, Liu J and Graf GA: The
ABCG5ABCG8 sterol transporter and phytosterols: Implications for
cardiometabolic disease. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes.
16:172–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Mitsche MA, Lütjohann D, Cohen JC,
Xie XS and Hobbs HH: Relative roles of ABCG5/ABCG8 in liver and
intestine. J Lipid Res. 56:319–330. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Xiao H, Zheng Y, Ma L, Tian L and Sun Q:
Clinically-relevant ABC transporter for anti-Cancer drug
resistance. Front Pharmacol. 19(12): 6484072021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cheng X, Li J and Guo D: SCAP/SREBPs are
central players in lipid metabolism and novel metabolic targets in
cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem. 18:484–493. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thu KL, Soria-Bretones I, Mak TW and
Cescona DW: Targeting the cell cycle in breast cancer: Towards the
next phase. Cell Cycle. 17:1871–1885. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lecarpentier Y, Schussler O, Hébert JL and
Vallée A: Multiple targets of the canonical WNT/β-Catenin signaling
in cancers. Front Oncol. 9:12482019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee SY, Jang C and Lee KA: Polo-like
kinases (plks), a key regulator of cell cycle and new potential
target for cancer therapy. Dev Reprod. 18:65–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kressin M, Fietz D, Becker S and
Strebhardt K: Modelling the functions of Polo-Like Kinases in mice
and their applications as cancer targets with a special focus on
ovarian cancer. Cells. 10:11762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Solc P, Kitajima TS, Yoshida S, Brzakova
A, Kaido M, Baran V, Mayer A, Samalova P, Motlik J and Ellenber J:
Multiple requirements of PLK1 during mouse oocyte maturation. PLoS
One. 10:e01167832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumar S, Sharma G, Chakraborty C, Sharma
AR and Kim JB: Regulatory functional territory of PLK-1 and their
substrates beyond mitosis. Oncotarget. 8:37942–37962. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shah K and Kazi J:
Phosphorylation-dependent regulation Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.
Front oncol. 12:8587822022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim DE, Shin SB, Kim CH, Kim YB, Oh HJ and
Yim HS: PLK1-mediated phosphrylatioh of β-catenin enhances its
stability and transcriptional activity for extracellular matrix
remodeling in metastaic NSCLC. Theranostics. 13:1198–1216. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: A
receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science.
232:34–47. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alrefaei AF and Abu-Elmagd M: LRP6
receptor plays essential functions in development and human
diseases. Genes (Basel). 13:1202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Raisch J, Côté-Biron A and Rivard N: A
role for the WNT Co-receptor LRP6 in pathogenesis and therapy of
epithelial cancers. Cancers (Basel). 11:11622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bengoechea-Alonso MT and Ericsson J: SREBP
in signal transduction: Cholesterol metabolism and beyond. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 19:215–222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horton JD, Goldstein JL and Brown MS:
SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty
acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 109:1125–1131. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eid W, Dauner K, Courtney KC, Gagnon A,
Parks RJ, Sorisky A and Zha X: mTORC1 activates SREBP-2 by
suppressing cholesterol trafficking to lysosomes in mammalian
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:7999–8004. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carroll RG, Zasłona Z, Galvan-Pena S,
Koppe EL, Sevin DC, Angiari S, Triantafilou M, Triantafilou K,
Modis LK and O'Neill LA: An unexpected link between fatty acid
synthase and cholesterol synthesis in proinflammatory macrophage
activation. J Biol Chem. 293:5509–5521. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jin Y, Chen Z, Dong J, Wang B, Fan S, Yang
X and Cui M: SEBP1/FASN/cholesterol axis facilitates
radioresistance in colorectal cancer. FEBS Open Bio. 11:1343–1352.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mylonis I, Simos G and Paraskeva E:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and the regulation of lipid metabolism.
Cells. 8:2142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dean M: The genetics of ATP-binding
cassette transporters. Methods Enzymol. 400:409–429. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fletcher JI, Williams RT, Henderson MJ,
Norris MD and Haber M: ABC transporters as mediators of drug
resistance and contributors to cancer cell biology. Drug Resist
Updat. 26:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Copsel S, Garcia C, Diez F, Vermeulem M,
Baldi A, Bianciotti LG, Russel FGM, Shayo C and Davio C: Multidrug
resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) regulates cAMP cellular levels
and controls human leukemia cell proliferation and differentiation.
J Biol Chem. 286:6979–6988. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Henderson MJ, Haber M, Porro A, Munoz MA,
Iraci N, Xue C, Murray J, Flemming CL, Smith J and Fletcher JI:
ABCC multidrug transporters in childhood neuroblastoma: Clinical
and biological effects independent of cytotoxic drug efflux. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 103:1236–1251. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Beloribi-Djefaflia S, Vasseur S and
Guillaumond F: Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells.
Oncogenesis. 5:e1892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yan A, Jia Z, Qiao C, Wang M and Ding X:
Cholesterol metabolism in drug-resistant cancer. Int J Oncol.
57:1103–1115. 2020.
|
|
42
|
Sheng R, Chen Y, Gee HY, Stec E, Melowic
HR, Blatner NR, Tun MP, Kim YJ, Källberg M and Fujiwara TK:
Cholesterol modulates cell signaling and protein networking by
specifically interacting with PDZ domain-containing scaffold
proteins. Nat Commun. 3:12492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Halimi H and Farjadian S: Cholesterol: An
important actor on the cancer immune scene. Front Immunol.
13:10575462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Song JW: Targeting Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol.
26:484–486. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Maharati A and Moghbeli M: PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway as a critical regulator of Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in colorectal tumor cells. Cell Commun Signal.
21:2012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Manore SG, Doheny DL, Wong GL and Lo HW:
IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling in breast cancer metastasis: Biology and
Treatment. Front Oncol. 12:8660142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang G, Hou S, Li S, Wang Y and Cui W:
Role of STAT3 in cancer cell Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int
J Oncol. 64:482024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sheng R, Kim HJ, Lee HY, Xin Y, Chen Y,
Tian Y, Cui Y, Choi JC, Doh JS, Han JK and Cho WH: Cholesterol
selectively activates canonical Wnt signalling over Non-canonical
Wnt signaling. Nat Commun. 5:43932014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu CC, Prior J, Piwnica-Worms D and Bu G:
LRP6 overexpression defines a class of breast cancer subtype and is
a target for therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:5136–5141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang L, Wu X, Wang Y, Zhang KW, Ju Y, Yuan
YC, Deng X, Chen L, Kim CCH and Lau S: FZD7 has a critical role in
cell proliferation in triple negative breast cancer. Oncogene.
30:4437–4446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ma J, Lu W, Chen D, Xu B and Li Y: Role of
Wnt Co-receptor LRP6 in triple negative breast cancer cell
migration and invasion. J Cell Biochem. 118:2968–2976. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang Y and Wang X: Targeting the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J Hematol Oncol.
13:1652020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Paskeh MDA, Mirzaei S, Ashrafizadeh M,
Zarrabi A and Sethi G: Wnt/β-Catenin signaling as a driver of
hepatocellular carcinoma progression: An emphasis on molecular
pathways. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 8:1415–1444. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders
ME and Gianni L: Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and
opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:674–690. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Weichert W: Polo-like kinase isoforms in
breast cancer: Expression patterns and prognostic implications.
Virchows Arch. 446:442–450. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Takahashi T: Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is
overexpressed in primary colorectal cancers. Cancer Sci.
94:148–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mann B, Gelos M, Siedow A, Hanski ML,
Gratchev A and Ilyas M: Target genes of beta-catenin-T
cell-factor/lymphoid-enhancer-factor signaling in human colorectal
carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:1603–1608. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Martin BT and Strebhardt K: Polo-like
kinase 1: Target and regulator of transcriptional control. Cell
Cycle. 5:2881–2085. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gao Y, Nan X, Shi X, Mu X, Liu B and Zhu
H: SREBP1 promotes the invasion of colorectal cancer accompanied
upregulation of MMP7 expression and NF-Kappa b pathway activation.
BMC Cancer. 19:6852019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Zhu Z, Zhao X, Zhao L, Yang H, Liu L and
Li J: P54(nrb)/NONO regulates lipid metabolism and breast cancer
growth through SREBP-1A. Oncogene. 35:1399–1410. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Li C, Yang W, Zhang J, Zheng X, Yao Y and
Tu K: SREBP-1 has a prognostic role and contributes to invasion and
metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
15:7124–7138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yong L, Tang S, Yu H, Zhang H, Zhang Y,
Wan Y and Cai F: The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in
multidrug-resistant breast cancer. Front Oncol. 12:9649342022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jun JC, Rathore A, Younas H, Gilkes D and
Polotsky YV: Hypoxia-inducible factors and cancer. Curr Sleep Med
Rep. 3:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M,
Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL and Simons
JW: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common
human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Generali D, Berruti A, Brizzi MP, Campo L,
Bonardi S and Wigfield S: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
expression predicts a poor response to primary chemoendocrine
therapy and disease-free survival in primary human breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:4562–4568. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ezzeddini R, Taghikhani M, Somi MH, Samadi
N and Rasaee MJ: Clinical importance of FASN in relation to HIF-1α
and SREBP-1c in gastric adenocarcinoma. Life Sci. 224:169–176.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Furuta E, Pai SK, Zhan R, Bandyopadhyay S,
Watabe M, Mo YY, Hirota S, Hosobe S, Tsukada T and Miura K: Fatty
Acid Synthase gene is up-regulated by hypoxia via activation of Akt
and Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein-1. Cancer Res.
68:1003–1011. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang L, Reue K, Fong LG, Young SG and
Tontonoz P: Feedback regulation of cholesterol uptake by the
LXR-IDOL-LDLR axis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:2541–2546.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yoon HJ, Jillian L, Shaw JL, Haigis MC and
Greka A: Lipid metabolism in sickness and in health: Emerging
regulators of lipotoxicity. Mol Cell. 81:3708–3730. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|