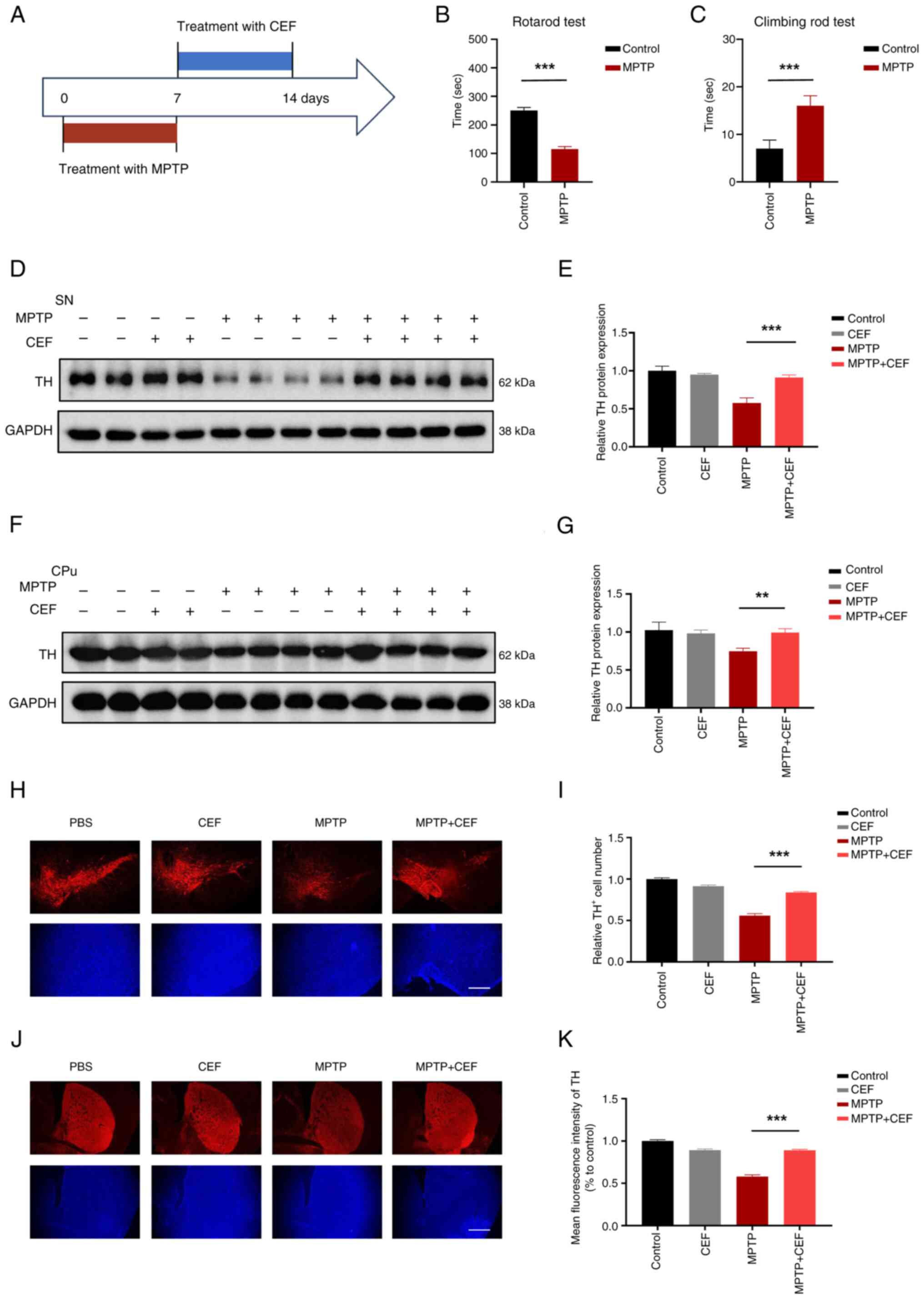
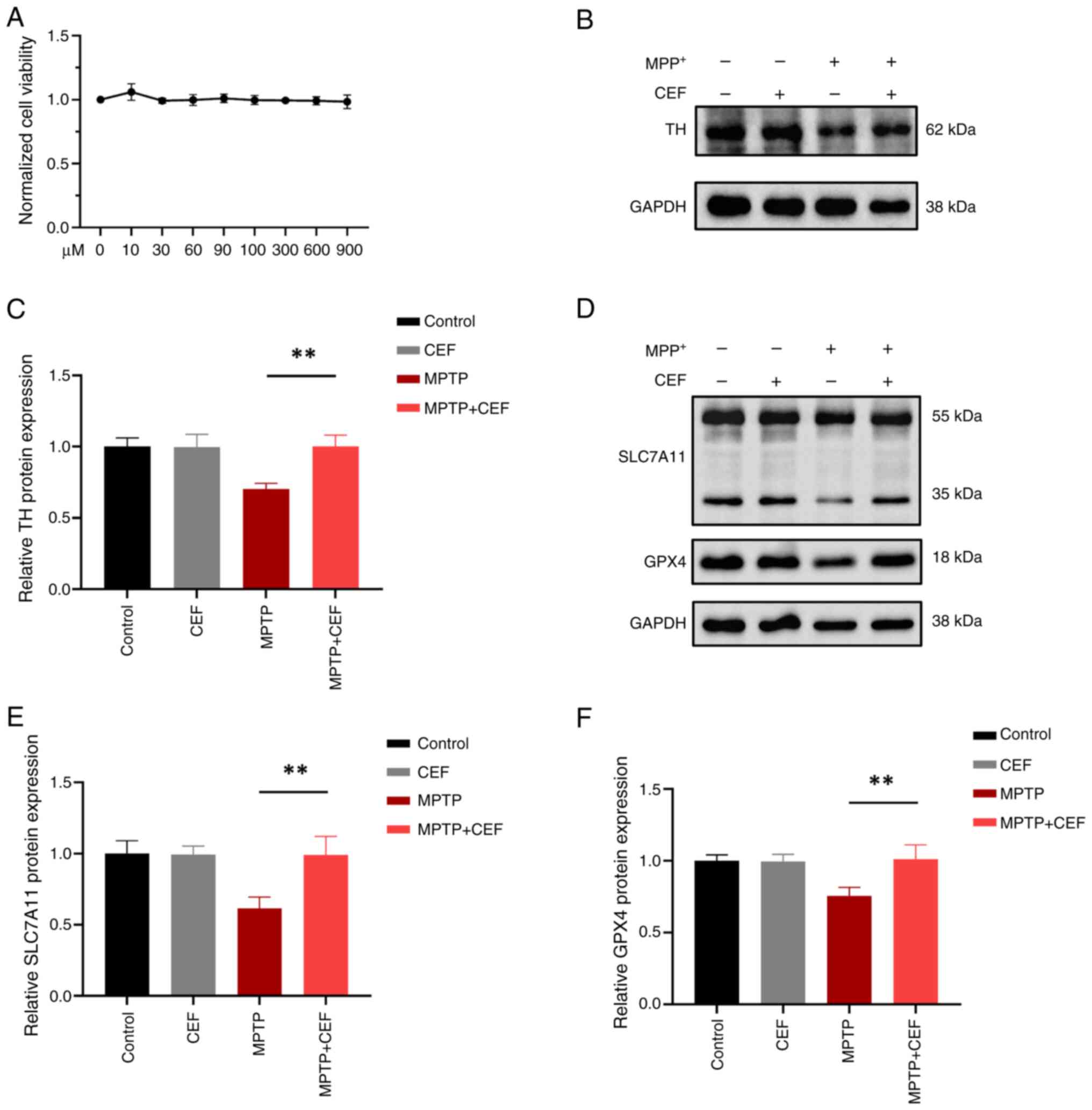
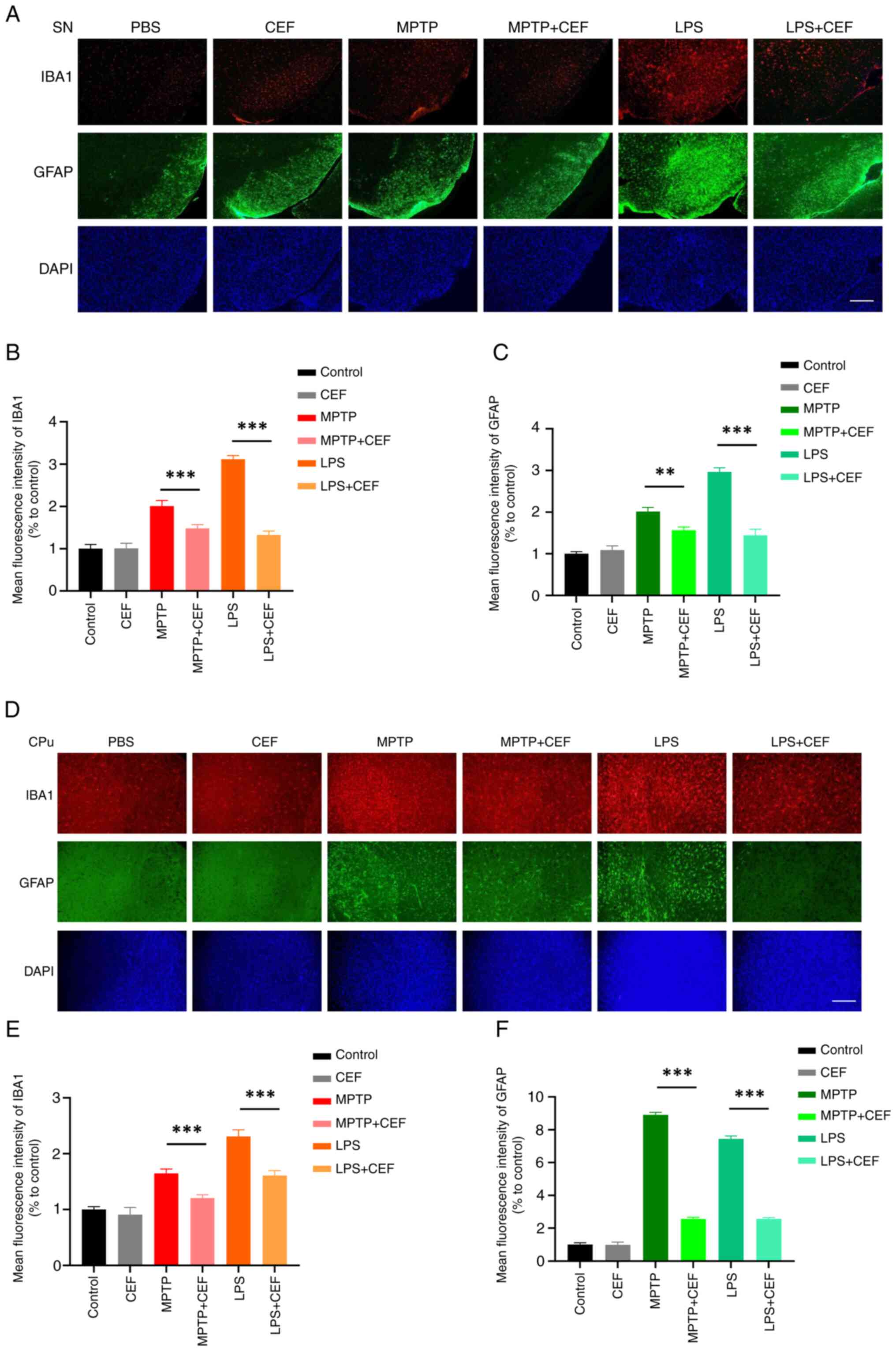
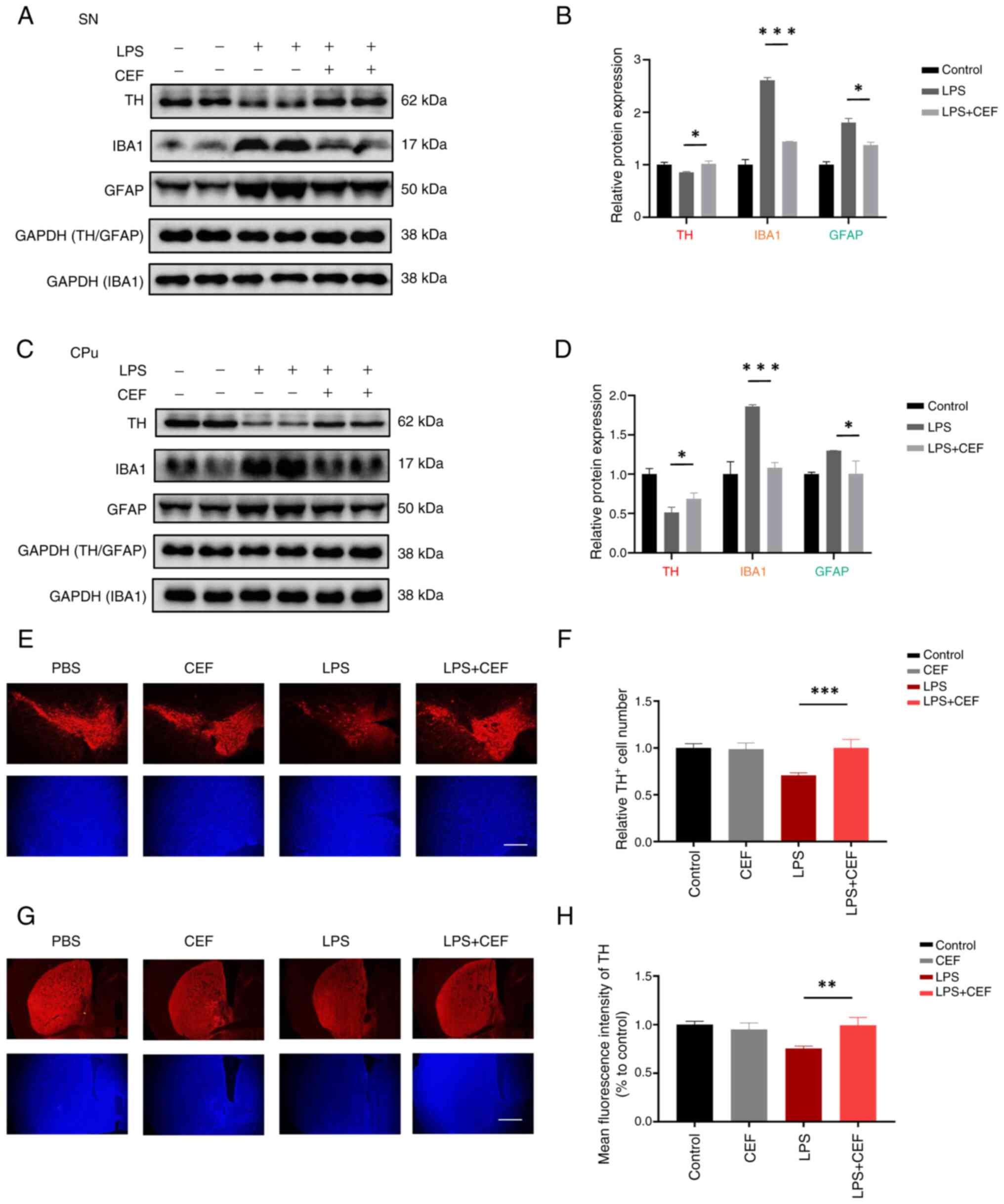
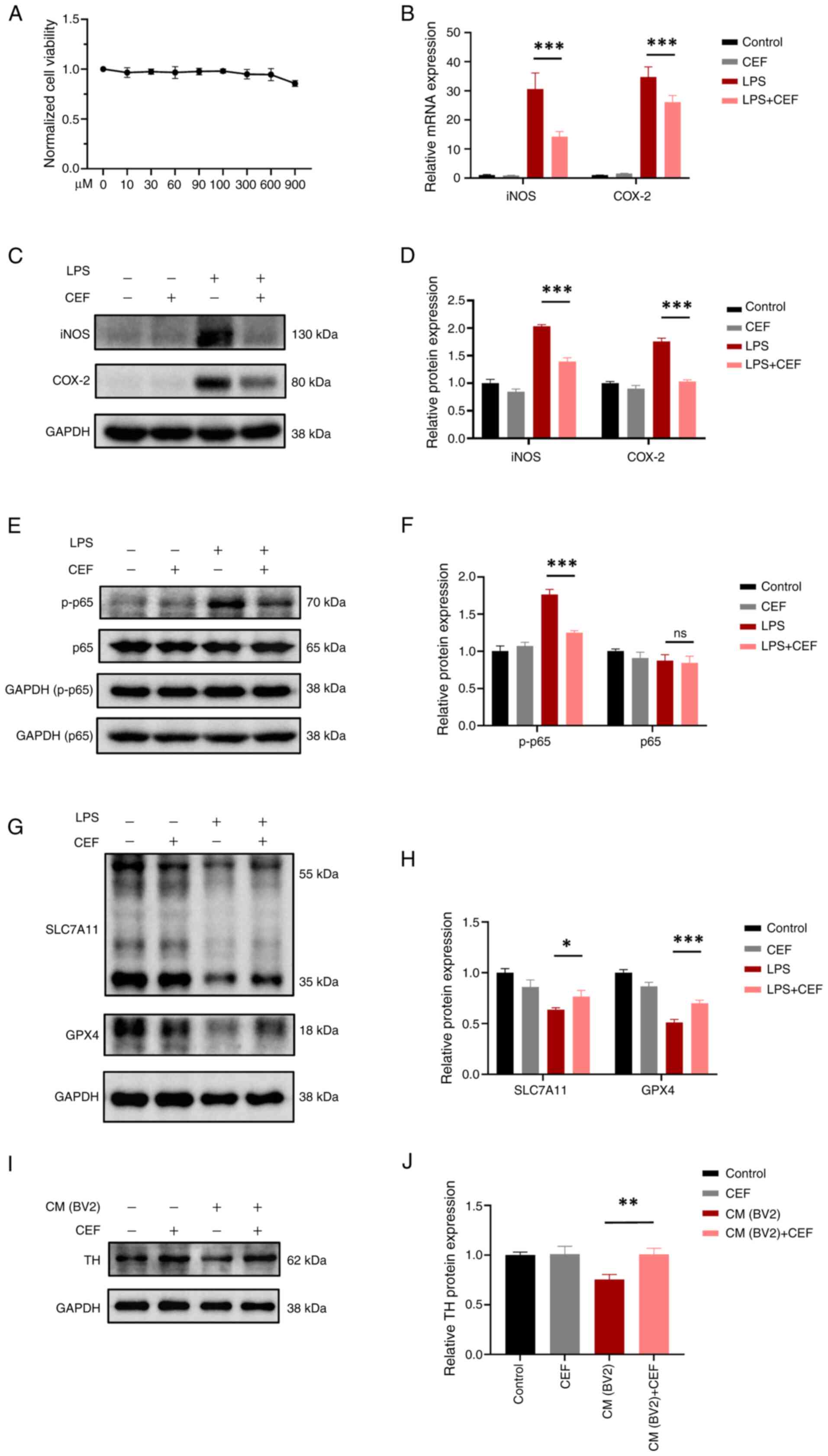
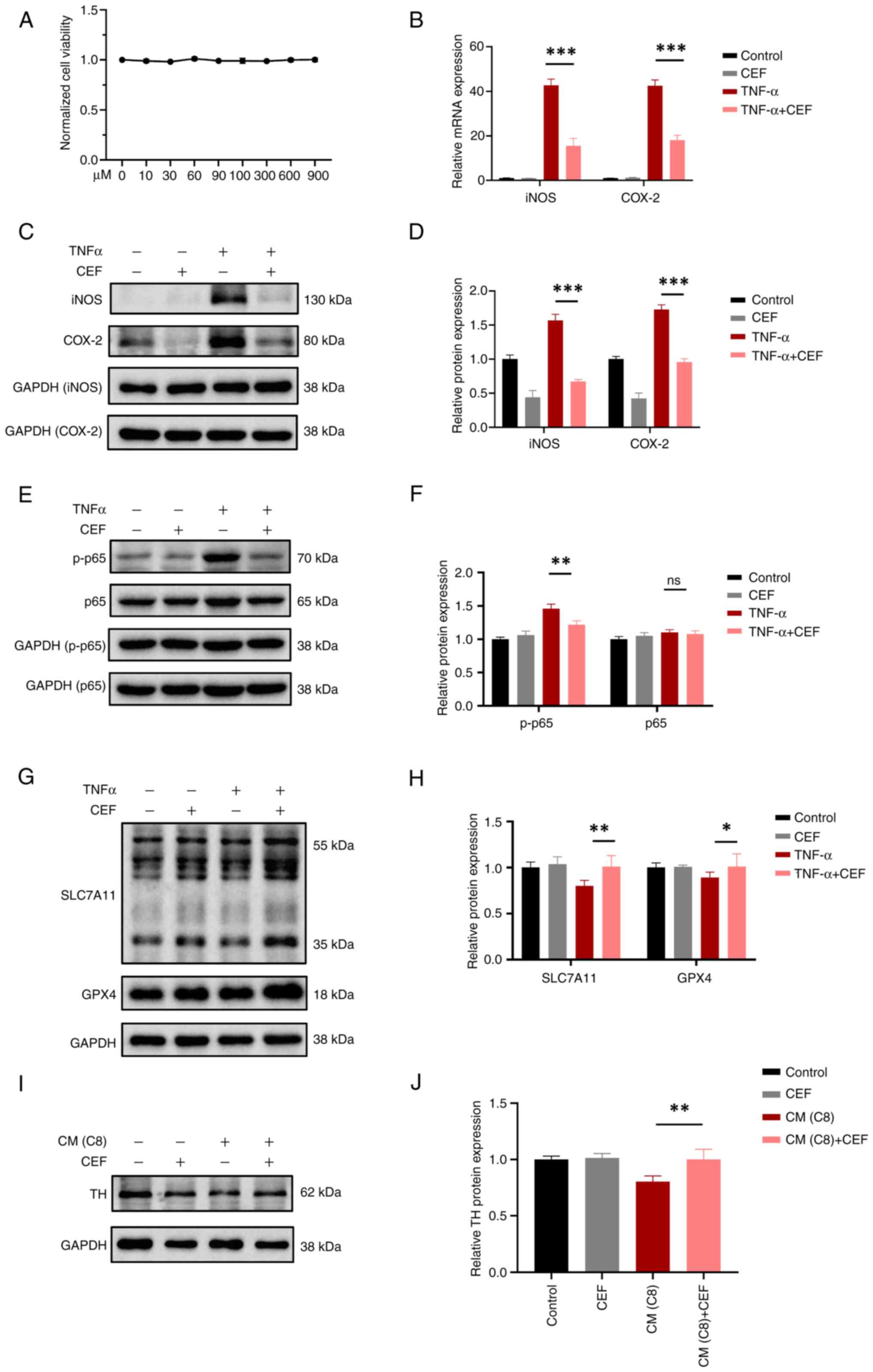
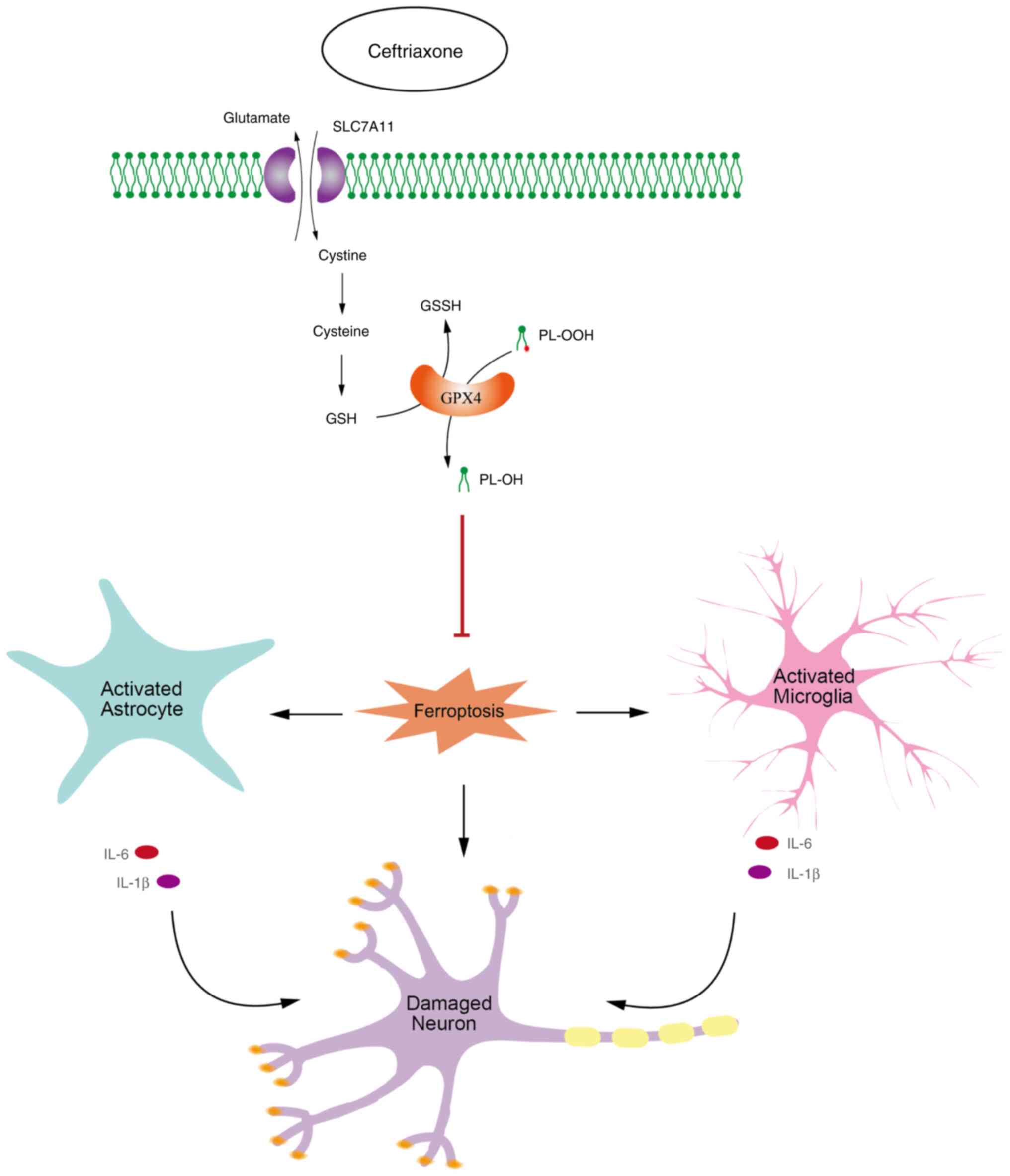
|
1
|
Weintraub D, Aarsland D, Chaudhuri KR,
Dobkin RD, Leentjens AF, Rodriguez-Violante M and Schrag A: The
neuropsychiatry of Parkinson's disease: Advances and challenges.
Lancet Neurol. 21:89–102. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Jankovic J and Tan EK: Parkinson's
disease: Etiopathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 91:795–808. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong-Chen X, Yong C, Yang X, Chen-Yu S and
Li-Hua P: Signaling pathways in Parkinson's disease: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 8:732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bloem BR, Okun MS and Klein C: Parkinson's
disease. Lancet. 397:2284–2303. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vijiaratnam N, Simuni T, Bandmann O,
Morris HR and Foltynie T: Progress towards therapies for disease
modification in Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 20:559–572.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hsieh MH, Meng WY, Liao WC, Weng JC, Li
HH, Su HL, Lin CL, Hung CS and Ho YJ: Ceftriaxone reverses deficits
of behavior and neurogenesis in an MPTP-induced rat model of
Parkinson's disease dementia. Brain Res Bull. 132:129–138. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsu CY, Hung CS, Chang HM, Liao WC, Ho SC
and Ho YJ: Ceftriaxone prevents and reverses behavioral and
neuronal deficits in an MPTP-induced animal model of Parkinson's
disease dementia. Neuropharmacology. 91:43–56. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bisht R, Kaur B, Gupta H and Prakash A:
Ceftriaxone mediated rescue of nigral oxidative damage and motor
deficits in MPTP model of Parkinson's disease in rats.
Neurotoxicology. 44:71–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaur B and Prakash A: Ceftriaxone
attenuates glutamate-mediated neuro-inflammation and restores BDNF
in MPTP model of Parkinson's disease in rats. Pathophysiology.
24:71–79. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ruzza P, Siligardi G, Hussain R, Marchiani
A, Islami M, Bubacco L, Delogu G, Fabbri D, Dettori MA, Sechi M, et
al: Ceftriaxone blocks the polymerization of α-synuclein and exerts
neuroprotective effects in vitro. ACS Chem Neurosci. 5:30–38. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang ZL, Yuan L, Li W and Li JY:
Ferroptosis in Parkinson's disease: Glia-neuron crosstalk. Trends
Mol Med. 28:258–269. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu LL, Han Y, Zhang ZJ, Wang YQ, Hu YW,
Kaznacheyeva E, Ding JQ, Guo DK, Wang GH, Li B and Ren HG: Loss of
DJ-1 function contributes to Parkinson's disease pathogenesis in
mice via RACK1-mediated PKC activation and MAO-B upregulation. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 44:1948–1961. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gu C, Zhang Y, Hu Q, Wu J, Ren H, Liu CF
and Wang G: P7C3 inhibits GSK3β activation to protect dopaminergic
neurons against neurotoxin-induced cell death in vitro and in vivo.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e28582017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nagatsu T and Nagatsu I: Tyrosine
hydroxylase (TH), its cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), other
catecholamine-related enzymes, and their human genes in relation to
the drug and gene therapies of Parkinson's disease (PD): Historical
overview and future prospects. J Neural Transm (Vienna).
123:1255–1278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kordower JH, Olanow CW, Dodiya HB, Chu Y,
Beach TG, Adler CH, Halliday GM and Bartus RT: Disease duration and
the integrity of the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson's disease.
Brain. 136:2419–2431. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng J and Conrad M: The metabolic
underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 32:920–937. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu H, Chang Q, Sun T, He X, Wen L, An J,
Feng J and Zhao Y: Metabolic reprogramming and polarization of
microglia in Parkinson's disease: Role of inflammasome and iron.
Ageing Res Rev. 90:1020322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Patani R, Hardingham GE and Liddelow SA:
Functional roles of reactive astrocytes in neuroinflammation and
neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 19:395–409. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kwon HS and Koh SH: Neuroinflammation in
neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes.
Transl Neurodegener. 9:422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mitchell JP and Carmody RJ: NF-κB and the
transcriptional control of inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
335:41–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lee J and Hyun DH: The interplay between
intracellular iron homeostasis and neuroinflammation in
neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:9182023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Wu S, Li Q, Sun H and Wang H:
Pharmacological inhibition of ferroptosis as a therapeutic target
for neurodegenerative diseases and strokes. Adv Sci (Weinh).
10:e23003252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tansey MG, Wallings RL, Houser MC, Herrick
MK, Keating CE and Joers V: Inflammation and immune dysfunction in
Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 22:657–673. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang W, Xiao D, Mao Q and Xia H: Role of
neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 8:2672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Isik S, Yeman Kiyak B, Akbayir R, Seyhali
R and Arpaci T: Microglia mediated neuroinflammation in Parkinson's
disease. Cells. 12:10122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Angelova PR, Choi ML, Berezhnov AV,
Horrocks MH, Hughes CD, De S, Rodrigues M, Yapom R, Little D, Dolt
KS, et al: Alpha synuclein aggregation drives ferroptosis: An
interplay of iron, calcium and lipid peroxidation. Cell Death
Differ. 27:2781–2796. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shibu MA, Bharath M and Velmurugan BK:
Regulating inflammation associated ferroptosis - A treatment
strategy for Parkinson disease. Curr Med Chem. 28:6895–6914. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grubbauer HM, Dornbusch HJ, Dittrich P,
Weippl G, Mutz I, Zobel G, Georgopoulos A and Fotter R: Ceftriaxone
monotherapy for bacterial meningitis in children. Chemotherapy.
36:441–447. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rothstein JD, Patel S, Regan MR, Haenggeli
C, Huang YH, Bergles DE, Jin L, Dykes Hoberg M, Vidensky S, Chung
DS, et al: Beta-lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by
increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature. 433:73–77.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pajarillo E, Rizor A, Lee J, Aschner M and
Lee E: The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and
GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for
neurotherapeutics. Neuropharmacology. 161:1075592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Malik AR and Willnow TE: Excitatory amino
acid transporters in physiology and disorders of the central
nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. 20:56712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abulseoud OA, Alasmari F, Hussein AM and
Sari Y: Ceftriaxone as a novel therapeutic agent for
hyperglutamatergic states: Bridging the gap between preclinical
results and clinical translation. Front Neurosci. 16:8410362022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gao J, Liu L, Liu C, Fan S, Liu L, Liu S,
Xian XH and Li WB: GLT-1 knockdown inhibits ceftriaxone-mediated
improvements on cognitive deficits, and GLT-1 and xCT expression
and activity in APP/PS1 AD mice. Front Aging Neurosci.
12:5807722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rao PSS, Saternos H, Goodwani S and Sari
Y: Effects of ceftriaxone on GLT1 isoforms, xCT and associated
signaling pathways in P rats exposed to ethanol. Psychopharmacology
(Berl). 232:2333–2342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lewerenz J, Albrecht P, Tien ML, Henke N,
Karumbayaram S, Kornblum HI, Wiedau-Pazos M, Schubert D, Maher P
and Methner A: Induction of Nrf2 and xCT are involved in the action
of the neuroprotective antibiotic ceftriaxone in vitro. J
Neurochem. 111:332–343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Patel SA, Warren BA, Rhoderick JF and
Bridges RJ: Differentiation of substrate and non-substrate
inhibitors of transport system xc(-): An obligate exchanger of
L-glutamate and L-cystine. Neuropharmacology. 46:273–284. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dar NJ, John U, Bano N, Khan S and Bhat
SA: Oxytosis/ferroptosis in neurodegeneration: The underlying role
of master regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Mol Neurobiol.
61:1507–1526. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Wan Y, Jiang Y, Zhang L and Cheng
W: GPX4: The hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and
treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1878:1888902023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sun S, Shen J, Jiang J, Wang F and Min J:
Targeting ferroptosis opens new avenues for the development of
novel therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3722023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Lv MN and Zhao WJ: Research on
ferroptosis as a therapeutic target for the treatment of
neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 91:1020352023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang X, Wu K, Ye XY, Xie T, Zhang P,
Blass BE and Bai R: Novel druggable mechanism of Parkinson's
disease: Potential therapeutics and underlying pathogenesis based
on ferroptosis. Med Res Rev. 43:872–896. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Smaga I, Fierro D, Mesa J, Filip M and
Knackstedt LA: Molecular changes evoked by the beta-lactam
antibiotic ceftriaxone across rodent models of substance use
disorder and neurological disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
115:116–130. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ritter K, Somnuke P, Hu L, Griemert EV and
Schäfer MKE: Current state of neuroprotective therapy using
antibiotics in human traumatic brain injury and animal models. BMC
Neurosci. 25:102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X and Qu S: Ceftriaxone
protects astrocytes from MPP(+) via suppression of NF-κB/JNK/c-Jun
signaling. Mol Neurobiol. 52:78–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhou X, Lu J, Wei K, Wei J, Tian P, Yue M,
Wang Y, Hong D, Li F, Wang B, et al: Neuroprotective effect of
ceftriaxone on MPTP-induced parkinson's disease mouse model by
regulating inflammation and intestinal microbiota. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2021:94245822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tieu K: A guide to neurotoxic animal
models of Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
1:a0093162011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mao Q, Qin WZ, Zhang A and Ye N: Recent
advances in dopaminergic strategies for the treatment of
Parkinson's disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 41:471–482. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jackson-Lewis V and Przedborski S:
Protocol for the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Nat
Protoc. 2:141–151. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Narmashiri A, Abbaszadeh M and Ghazizadeh
A: The effects of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
(MPTP) on the cognitive and motor functions in rodents: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
140:1047922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ge J, Lin H, Yang J, Li Q, Zhou J, Qin Z
and Wu F: TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR)
ameliorates lysosomal damage in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3,
6-tetrahydropyridine-mediated mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Toxicol Lett. 339:60–69. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Guo DK, Zhu Y, Sun HY, Xu XY, Zhang S, Hao
ZB, Wang GH, Mu CC and Ren HG: Pharmacological activation of
REV-ERBα represses LPS-induced microglial activation through the
NF-κB pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 40:26–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
He J, Zhu G, Wang G and Zhang F: Oxidative
stress and neuroinflammation potentiate each other to promote
progression of dopamine neurodegeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020:61375212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mohan S, Alhazmi HA, Hassani R, Khuwaja G,
Maheshkumar VP, Aldahish A and Chidambaram K: Role of ferroptosis
pathways in neuroinflammation and neurological disorders: From
pathogenesis to treatment. Heliyon. 10:e247862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|