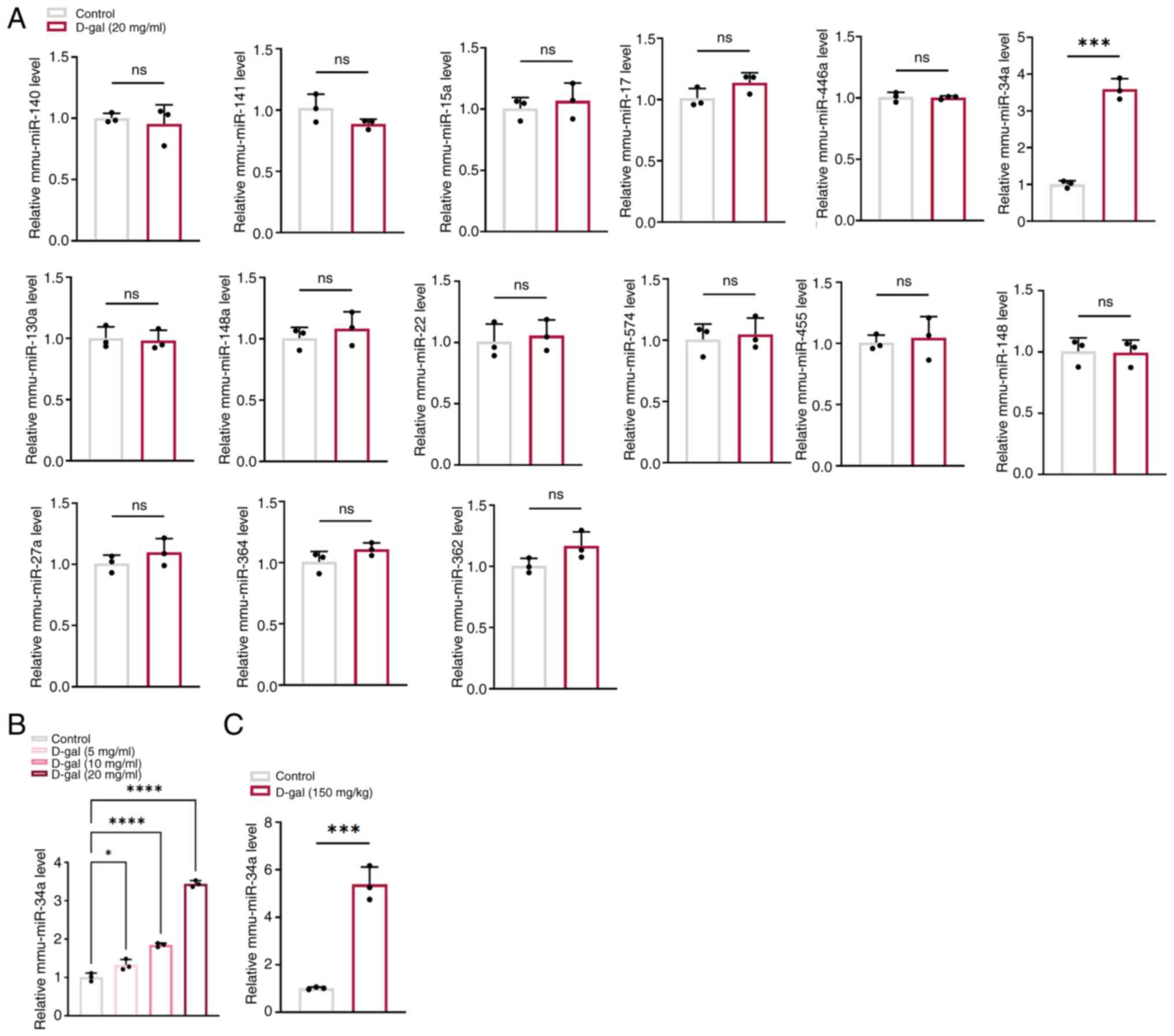
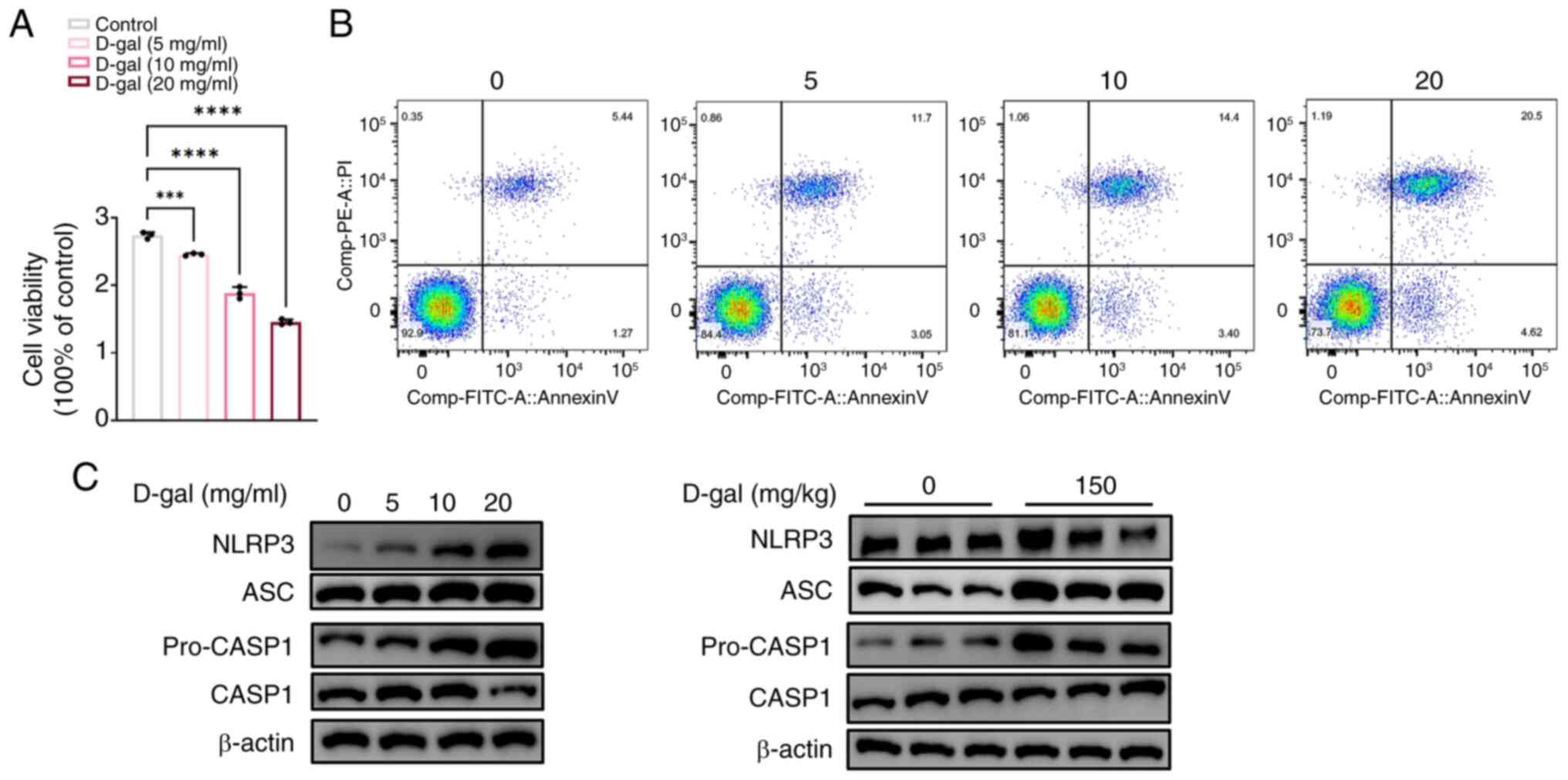
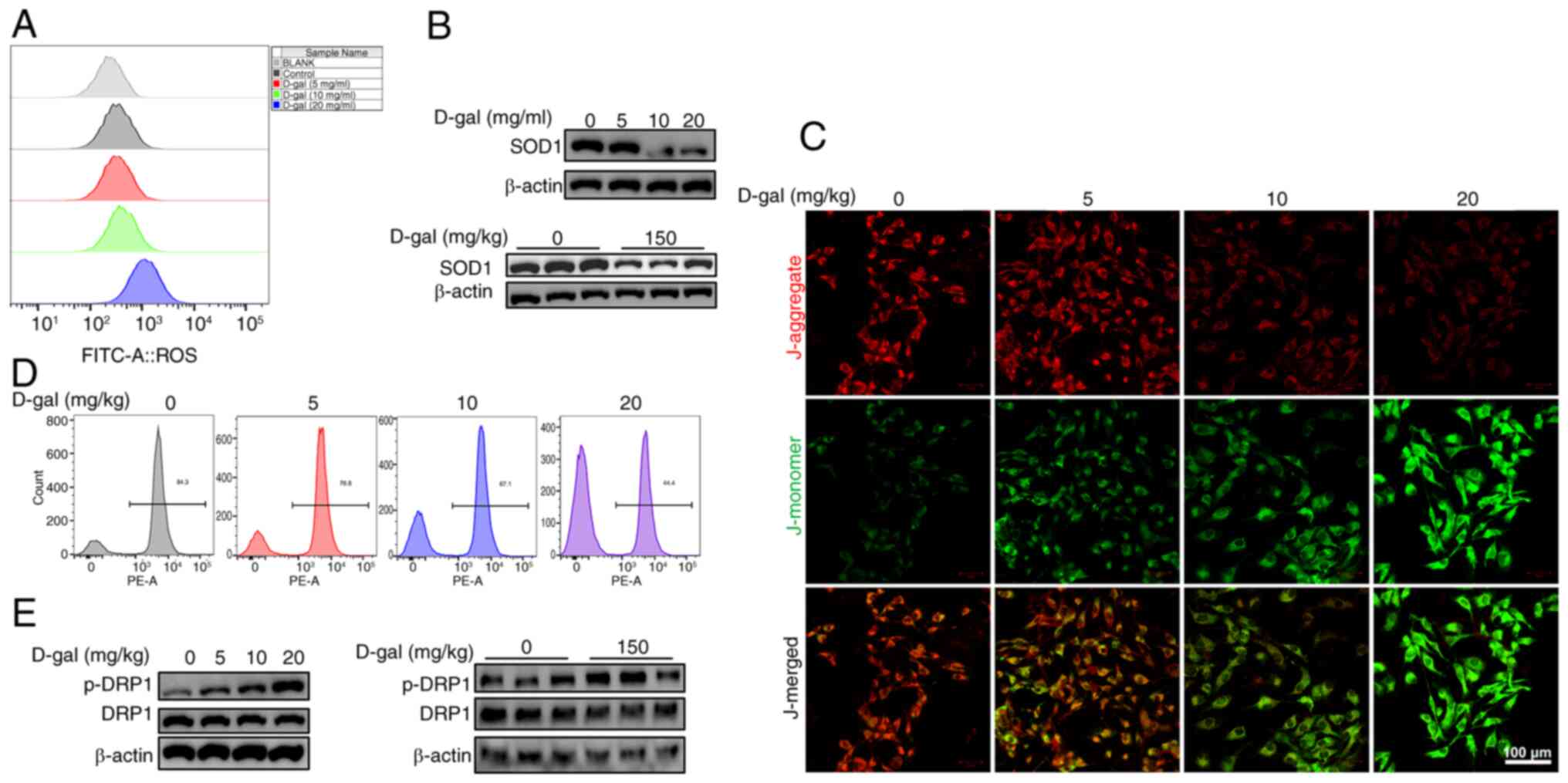
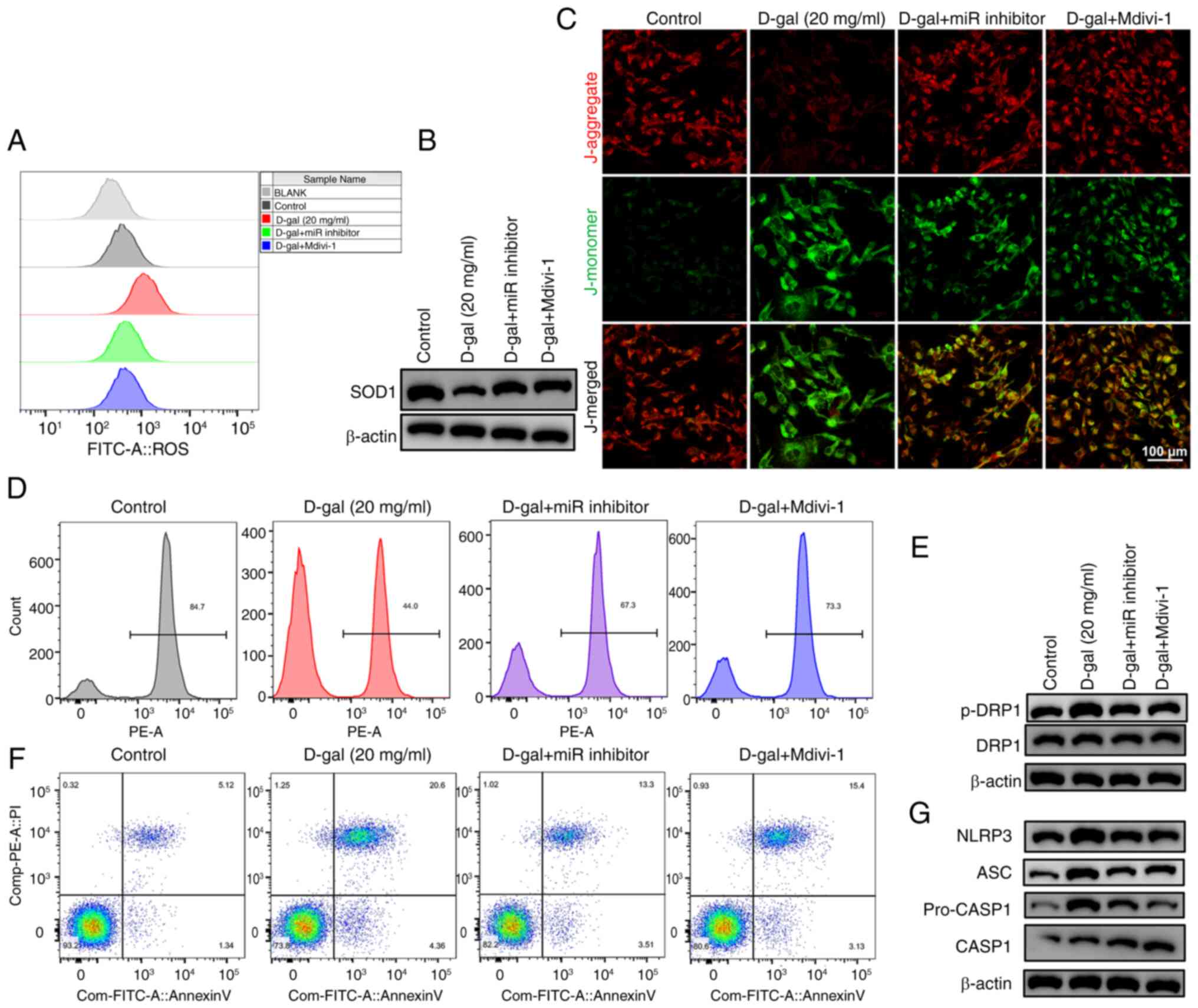
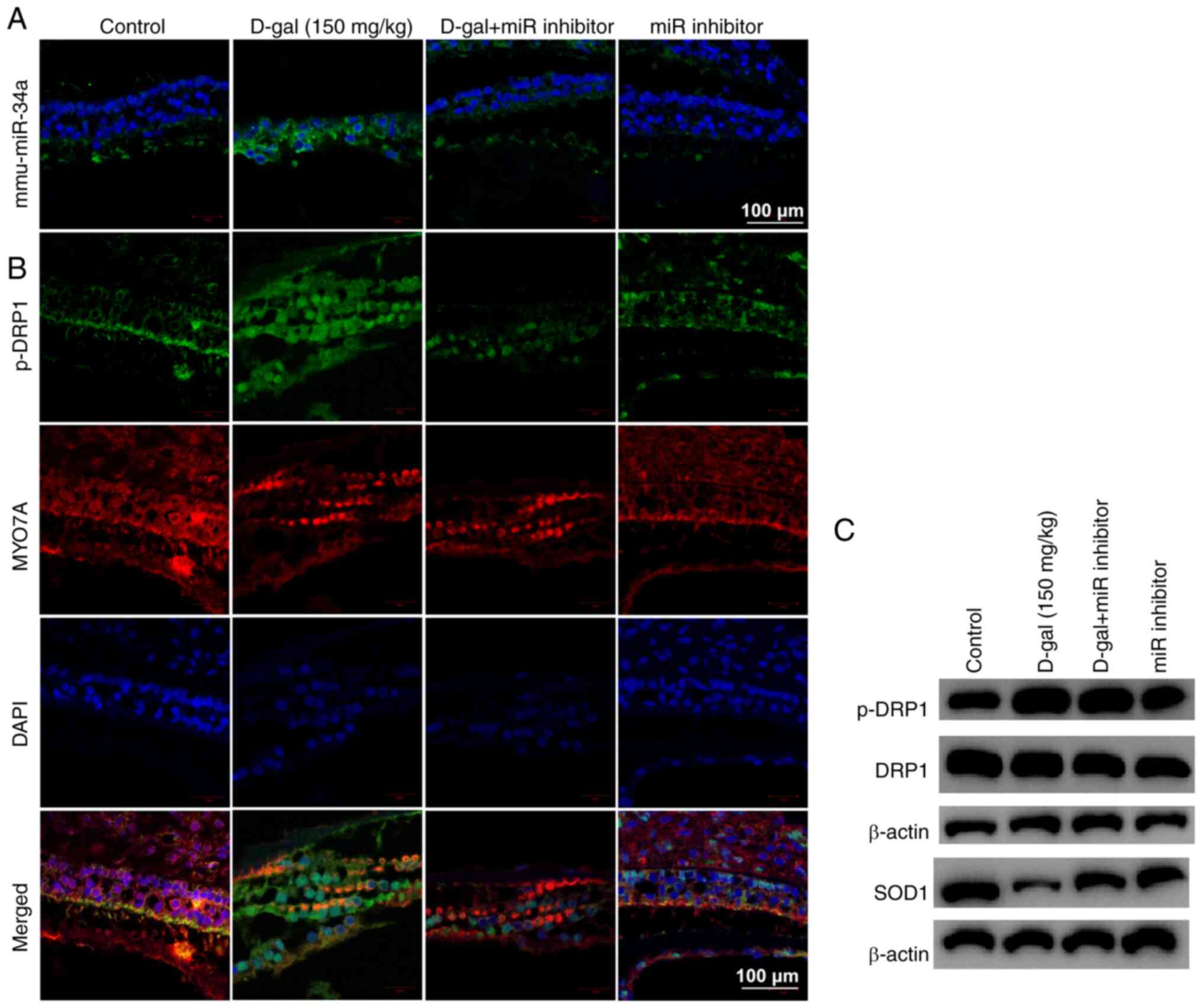
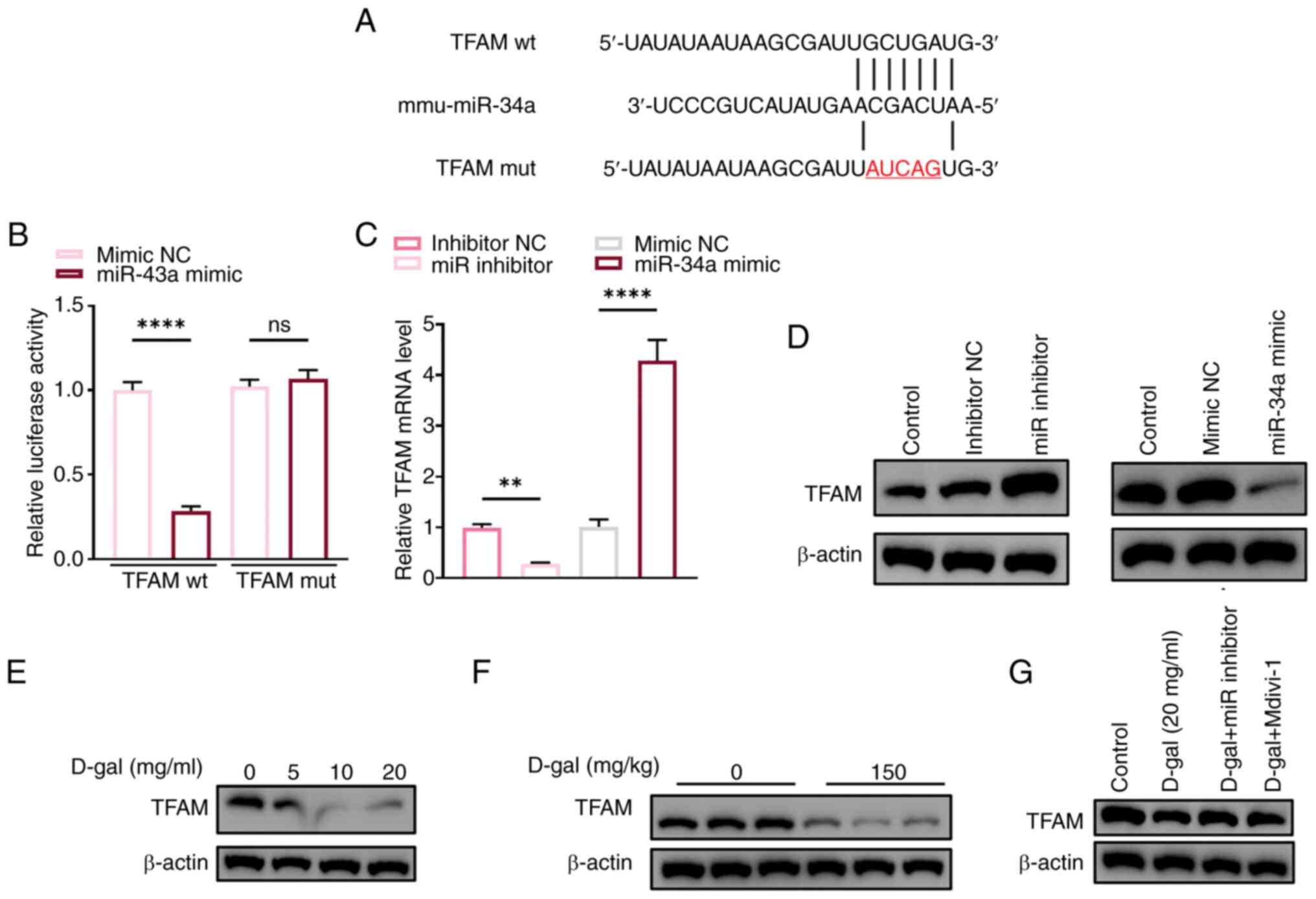
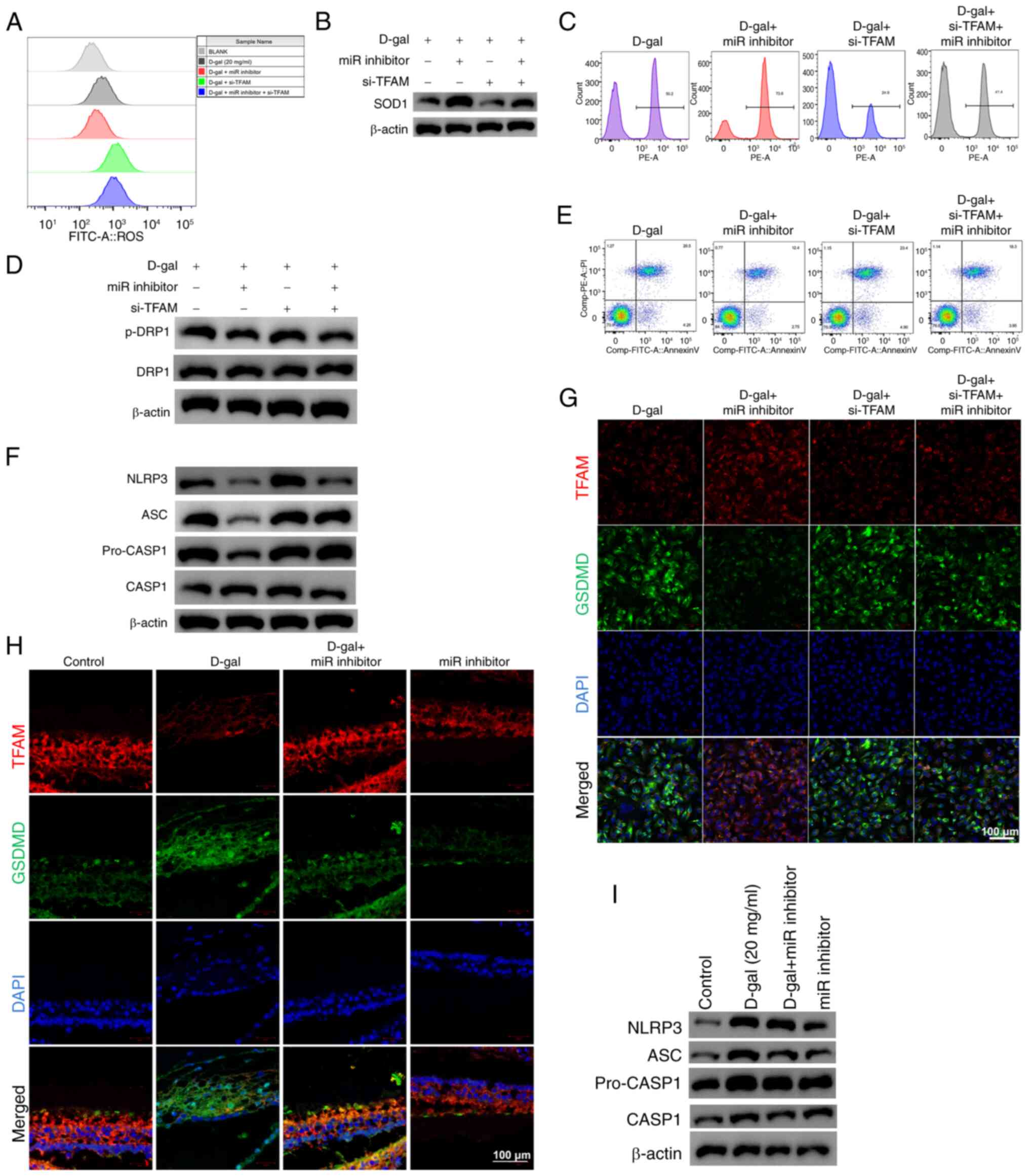
|
1
|
World Health Organization: World Report on
Hearing. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2021
|
|
2
|
Gates GA and Mills JH: Presbycusis.
Lancet. 366:1111–1120. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rutherford BR, Brewster K, Golub JS, Kim
AH and Roose SP: Sensation and psychiatry: Linking age-related
hearing loss to late-life depression and cognitive decline. Am J
Psychiatry. 175:215–224. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Bowl MR and Dawson SJ: Age-related hearing
loss. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 9:a0332172019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu PZ, O'Malley JT, de Gruttola V and
Liberman MC: Age-related hearing loss is dominated by damage to
inner ear sensory cells, not the cellular battery that powers them.
J Neurosci. 40:6357–6366. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhong Y, Hu Y, Peng W, Sun Y, Yang Y, Zhao
X, Huang X, Zhang H and Kong W: Age-related decline of the
cytochrome c oxidase subunit expression in the auditory cortex of
the mimetic aging rat model associated with the common deletion.
Hear Res. 294:40–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Du Z, Yang Y, Hu Y, Sun Y, Zhang S, Peng
W, Zhong Y, Huang X and Kong W: A long-term high-fat diet increases
oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in the inner
ear of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Hear Res. 287:15–24. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu J, Wang Y, Liu P, Li Q, Sun Y and Kong
W: Mitochondrial DNA common deletion increases susceptibility to
noise-induced hearing loss in a mimetic aging rat model. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 453:515–520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parameshwaran K, Irwin MH, Steliou K and
Pinkert CA: D-galactose effectiveness in modeling aging and
therapeutic antioxidant treatment in mice. Rejuvenation Res.
13:729–735. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen B, Zhong Y, Peng W, Sun Y and Kong
WJ: Age-related changes in the central auditory system: Comparison
of D-galactose-induced aging rats and naturally aging rats. Brain
Res. 1344:43–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He ZH, Li M, Fang QJ, Liao FL, Zou SY, Wu
X, Sun HY, Zhao XY, Hu YJ, Xu XX, et al: FOXG1 promotes aging inner
ear hair cell survival through activation of the autophagy pathway.
Autophagy. 17:4341–4362. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics biogenesis,
mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wienholds E, Kloosterman WP, Miska E,
Alvarez-Saavedra E, Berezikov E, de Bruijn E, Horvitz HR, Kauppinen
S and Plasterk RH: MicroRNA expression in zebrafish embryonic
development. Science. 309:310–311. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rudnicki A and Avraham KB: microRNAs: The
art of silencing in the ear. EMBO Mol Med. 4:849–859. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rudnicki A, Isakov O, Ushakov K, Shivatzki
S, Weiss I, Friedman LM, Shomron N and Avraham KB: Next-generation
sequencing of small RNAs from inner ear sensory epithelium
identifies microRNAs and defines regulatory pathways. BMC Genomics.
15:4842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition. The National
Academies Press; Washington, DC: pp. 2462011
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yang X, Wang G, Liu W, Zhang J, Deng B, Li
X and Wang L: Key genes and potential drugs in age-related hearing
loss: Transcriptome analysis of cochlear hair cells in old mice.
Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 69:67–74. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fujimoto C and Yamasoba T: Oxidative
stresses and mitochondrial dysfunction in age-related hearing loss.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:5828492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qiu Y, Liu Y and Tao J: Progress of
clinical evaluation for vascular aging in humans. J Transl Int Med.
9:17–23. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fridovich I: Superoxide anion radical
(O2-.), superoxide dismutases, and related matters. J Biol Chem.
272:18515–18517. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kowaltowski AJ, de Souza-Pinto NC,
Castilho RF and Vercesi AE: Mitochondria and reactive oxygen
species. Free Radic Biol Med. 47:333–343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kornfeld OS, Qvit N, Haileselassie B,
Shamloo M, Bernardi P and Mochly-Rosen D: Interaction of
mitochondrial fission factor with dynamin related protein 1 governs
physiological mitochondrial function in vivo. Sci Rep. 8:140342018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen KH, Dasgupta A, Lin J, Potus F,
Bonnet S, Iremonger J, Fu J, Mewburn J, Wu D, Dunham-Snary K, et
al: Epigenetic dysregulation of the dynamin-related protein 1
binding partners MiD49 and MiD51 increases mitotic mitochondrial
fission and promotes pulmonary arterial hypertension: Mechanistic
and therapeutic implications. Circulation. 138:287–304. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thounaojam MC, Jadeja RN, Warren M, Powell
FL, Raju R, Gutsaeva D, Khurana S, Martin PM and Bartoli M:
MicroRNA-34a (miR-34a) mediates retinal endothelial cell premature
senescence through mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of
antioxidant activities. Antioxidants (Basel). 8:3282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fan X, Zhou S, Zheng M, Deng X, Yi Y and
Huang T: MiR-199a-3p enhances breast cancer cell sensitivity to
cisplatin by downregulating TFAM (TFAM). Biomed Pharmacother.
88:507–514. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding L and Wang J: MiR-106a facilitates
the sensorineural hearing loss induced by oxidative stress by
targeting connexin-43. Bioengineered. 13:14080–14093. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nunez DA and Guo RC: Acquired
sensorineural hearing loss, oxidative stress, and microRNAs. Neural
Regen Res. 20:2513–2519. 2025.
|
|
29
|
Zhang J, Sun W, Kuang S, Gan Q, Li H, Ma
H, Yang G, Guo J, Tang Y and Yuan W: miR-130b-3p involved in the
pathogenesis of age-related hearing loss via targeting PPARγ and
autophagy. Hear Res. 449:1090292024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Verschuur CA, Dowell A, Syddall HE, Ntani
G, Simmonds SJ, Baylis D, Gale CR, Walsh B, Cooper C, Lord JM and
Sayer AA: Markers of inflammatory status are associated with
hearing threshold in older people: Findings from the hertfordshire
ageing study. Age Ageing. 41:92–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yang X, Wu Y, Zhang M, Zhang L, Zhao T,
Qian W, Zhu M, Wang X, Zhang Q, Sun J and Dong L: Piceatannol
protects against age-related hearing loss by inhibiting cellular
pyroptosis and inflammation through regulated Caspase11-GSDMD
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 163:1147042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang A, Pan Y, Wang H, Ding R, Zou T, Guo
D, Shen Y, Ji P, Huang W, Wen Q, et al: Excessive processing and
acetylation of OPA1 aggravate age-related hearing loss via the
dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Aging Cell. 23:e140912024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Safabakhsh S, Wijesinghe P, Nunez M and
Nunez DA: The role of hypoxia-associated miRNAs in acquired
sensorineural hearing loss. Front Cell Neurosci. 16:9166962022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiong H, Pang J, Min X, Ye Y, Lai L and
Zheng Y: miR-34a/ATG9A/TFEB signaling modulates autophagy in
cochlear hair cells and correlates with age-related hearing loss.
Neuroscience. 491:98–109. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pang J, Xiong H, Lin P, Lai L, Yang H, Liu
Y, Huang Q, Chen S, Ye Y, Sun Y and Zheng Y: Activation of miR-34a
impairs autophagic flux and promotes cochlear cell death via
repressing ATG9A: Implications for age-related hearing loss. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e30792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang H, Lin H, Kang W, Huang L, Gong S,
Zhang T, Huang X, He F, Ye Y, Tang Y, et al: miR-34a/DRP-1-mediated
mitophagy participated in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity via
increasing oxidative stress. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 24:162023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Boon RA, Iekushi K, Lechner S, Seeger T,
Fischer A, Heydt S, Kaluza D, Tréguer K, Carmona G, Bonauer A, et
al: MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature.
495:107–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ito T, Yagi S and Yamakuchi M:
MicroRNA-34a regulation of endothelial senescence. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 398:735–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang J, Chen D, He Y, Meléndez A, Feng Z,
Hong Q, Bai X, Li Q, Cai G, Wang J and Chen X: MiR-34 modulates
Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan via repressing the autophagy gene
atg9. Age (Dordr). 35:11–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bai XY, Ma Y, Ding R, Fu B, Shi S and Chen
XM: miR-335 and miR-34a Promote renal senescence by suppressing
mitochondrial antioxidative enzymes. J Am Soc Nephrol.
22:1252–1261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhong Z, Gao Y, Zhou J, Wang F, Zhang P,
Hu S, Wu H, Lou H, Chi J, Lin H and Guo H: Inhibiting mir-34a-5p
regulates doxorubicin-induced autophagy disorder and alleviates
myocardial pyroptosis by targeting Sirt3-AMPK pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 168:1156v2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen S, Ding R, Hu Z, Yin X, Xiao F, Zhang
W, Yan S and Lv C: MicroRNA-34a inhibition alleviates lung injury
in cecal ligation and puncture induced septic mice. Front Immunol.
11:18292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li C, Qu L, Farragher C, Vella A and Zhou
B: MicroRNA regulated macrophage activation in obesity. J Transl
Int Med. 7:46–52. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bao H and Peng A: The green tea
polyphenol(-)-epigallocate-chin-3-gallate and its beneficial roles
in chronic kidney disease. J Transl Int Med. 4:99–103. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Li Q, Shi N, Cai C, Zhang M, He J, Tan Y
and Fu W: The role of mitochondria in pyroptosis. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 8:6307712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Campbell CT, Kolesar JE and Kaufman BA:
Mitochondrial transcription factor A regulates mitochondrial
transcription initiation, DNA packaging, and genome copy number.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1819:921–929. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhu M, Ding Q, Lin Z, Chen X, Chen S and
Zhu Y: New insights of epigenetics in vascular and cellular
senescence. J Transl Int Med. 9:239–248. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wang P, Zhang N, Wu B, Wu S, Zhang Y and
Sun Y: The role of mitochondria in vascular calcification. J Transl
Int Med. 8:80–90. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Desdín-Micó G, Soto-Heredero G, Aranda JF,
Oller J, Carrasco E, Gabandé-Rodríguez E, Blanco EM, Alfranca A,
Cussó L, Desco M, et al: T cells with dysfunctional mitochondria
induce multimorbidity and premature senescence. Science.
368:1371–1376. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao M, Liu S, Wang C, Wang Y, Wan M, Liu
F, Gong M, Yuan Y, Chen Y, Cheng J, et al: Mesenchymal stem
cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate mitochondrial damage
and inflammation by stabilizing mitochondrial DNA. ACS Nano.
15:1519–1538. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chen JW, Ma PW, Yuan H, Wang WL, Lu PH,
Ding XR, Lun YQ, Yang Q and Lu LJ: mito-TEMPO attenuates oxidative
stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in noise-induced hearing loss
via maintaining TFAM-mtDNA interaction and mitochondrial
biogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci. 16:8037182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nong H, Song X, Li Y, Xu Y, Wang F, Wang
Y, Zhang J, Chen C and Li J: AdipoRon reduces cisplatin-induced
ototoxicity in hair cells:possible relation to the regulation of
mitochondrial biogenesis. Neurosci Lett. 819:1375772024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhong Y, Hu YJ, Chen B, Peng W, Sun Y,
Yang Y, Zhao XY, Fan GR, Huang X and Kong WJ: Mitochondrial
transcription factor A overexpression and base excision repair
deficiency in the inner ear of rats with D-galactose-induced aging.
FEBS J. 278:2500–2510. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|