|
1
|
Wiese O, Zemlin AE and Pillay TS:
Molecules in pathogenesis: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).
J Clin Pathol. 74:285–290. 2021.
|
|
2
|
Santos RAS, Sampaio WO, Alzamora AC,
Motta-Santos D, Alenina N, Bader M and Campagnole-Santos MJ: The
ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS axis of the renin-angiotensin system:
Focus on angiotensin-(1-7). Physiol Rev. 98:505–553. 2018.
|
|
3
|
Verano-Braga T, Mar tins A LV,
Motta-Santos D, Campagnole-Santos MJ and Santos RAS: ACE2 in the
renin-angiotensin system. Clin Sci (Lond). 134:3063–3078. 2020.
|
|
4
|
Abdel-Fattah MM, Elgendy A and Mohamed WR:
Xanthenone, ACE2 activator, counteracted gentamicin-induced
nephrotoxicity in rats: Impact on oxidative stress and
ACE2/Ang-(1-7) signaling. Life Sci. 275:1193872021.
|
|
5
|
Xue QQ, Liu CH, Zhang DY, Li MX and Li Y:
α-Mangostin attenuates blood pressure and reverses vascular
remodeling by balancing ACE/AT1R and ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR axes in
ang II-infused hypertensive mice. Phytother Res. 38:5918–5929.
2024.
|
|
6
|
Nardo AD, Schneeweiss-Gleixner M, Bakail
M, Dixon ED, Lax SF and Trauner M: Pathophysiological mechanisms of
liver injury in COVID-19. Liver Int. 41:20–32. 2021.
|
|
7
|
Prestes TR, Rocha NP, Miranda AS, Teixeira
AL and Simoes ESAC: The anti-inf lammatory potential of
ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis: Evidence from basic and
clinical research. Curr Drug Targets. 18:1301–1313. 2017.
|
|
8
|
Pan H, Huang W, Wang Z, Ren F, Luo L, Zhou
J, Tian M and Tang L: The ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-mas axis modulates M1/M2
macrophage polarization to relieve CLP-induced inflammation via
TLR4-mediated NF-кb and MAPK pathways. J Inflamm Res. 14:2045–2060.
2021.
|
|
9
|
Guo J, Zhao S, Chu X, Wang C, Meng J, Wei
S, Wang J, Guo Y, Kong W, Sun W, et al: Angiotensin-converting
enzyme 2 modulation of pyroptosis pathway in traumatic brain
injury: A potential therapeutic target. Clin Transl Med.
15:e701672025.
|
|
10
|
Mehrabadi ME, Hemmati R, Tashakor A,
Homaei A, Yousefzadeh M, Hemati K and Hosseinkhani S: Induced
dysregulation of ACE2 by SARS-CoV-2 plays a key role in COVID-19
severity. Biomed Pharmacother. 137:1113632021.
|
|
11
|
Lennol MP, García-Ayllón MS,
Avilés-Granados C, Trasciatti C, Tolassi C, Quaresima V, Arici D,
Cristillo V, Volonghi I, Caprioli F, et al: Increased cerebrospinal
fluid ACE2 fragments as a read-out of brain infection in COVID-19
encephalopathy patients. J Infect Dis. 231:e929–e940. 2025.
|
|
12
|
Gao Y, Lin J, Ye C, Guo S and Jiang C:
Microbial transformations of bile acids and their receptors in the
regulation of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver
disease. Liver Res. 7:165–176. 2023.
|
|
13
|
Badmus OO, Hillhouse SA, Anderson CD,
Hinds TD and Stec DE: Molecular mechanisms of metabolic associated
fatty liver disease (MAFLD): Functional analysis of lipid
metabolism pathways. Clin Sci (Lond). 136:1347–1366. 2022.
|
|
14
|
Sundekilde UK, Kristensen CM, Olsen MA,
Pilegaard H and Rasmussen MK: Time-dependent regulation of hepatic
cytochrome P450 mRNA in male liver-specific PGC-1α knockout mice.
Toxicology. 469:1531212022.
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Yang P, Ye J, Xu Q, Wu J and Wang Y:
Updated mechanisms of MASLD pathogenesis. Lipids Health Dis.
23:1172024.
|
|
16
|
Zou X, Chen K, Zou J, Han P, Hao J and Han
Z: Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2
expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs
vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front Med. 14:185–192. 2020.
|
|
17
|
Baig AM, Khaleeq A, Ali U and Syeda H:
Evidence of the COVID-19 virus targeting the CNS: Tissue
distribution, host-virus interaction, and proposed neurotropic
mechanisms. ACS Chem Neurosci. 11:995–998. 2020.
|
|
18
|
Barone M: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
and AMPK/mTOR pathway in the treatment of liver fibrosis: Should we
consider further implications? World J Gastroenterol. 30:2391–2396.
2024.
|
|
19
|
Rajapaksha IG, Gunarathne LS, Asadi K,
Cunningham SC, Sharland A, Alexander IE, Angus PW and Herath CB:
Liver-Targeted angiotensin converting enzyme 2 therapy inhibits
chronic biliary fibrosis in multiple drug-resistant gene 2-knockout
mice. Hepatol Commun. 3:1656–1673. 2019.
|
|
20
|
Liu L, Li Y, Li JX, Xiao X, Wan TT, Li HH
and Guo SB: ACE2 expressed on myeloid cells alleviates
sepsis-induced acute liver injury via the Ang-(1-7)-Mas receptor
axis. Inflammation. 47:891–908. 2024.
|
|
21
|
Cao X, Yang F, Shi T, Yuan M, Xin Z, Xie
R, Li S, Li H and Yang J: Angiotensin-converting enzyme
2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas axis activates Akt signaling to ameliorate
hepatic steatosis. Sci Rep. 6:215922016.
|
|
22
|
Warner FJ, Rajapaksha H, Shackel N and
Herath CB: ACE2: From protection of liver disease to propagation of
COVID-19. Clin Sci (Lond). 134:3137–3158. 2020.
|
|
23
|
Gao Y, Chen Q, Yang S, Cao J, Li F, Li R,
Wu Z, Wang Y and Yuan L: Indole alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease in an ACE2-dependent manner. FASEB J. 38:e700612024.
|
|
24
|
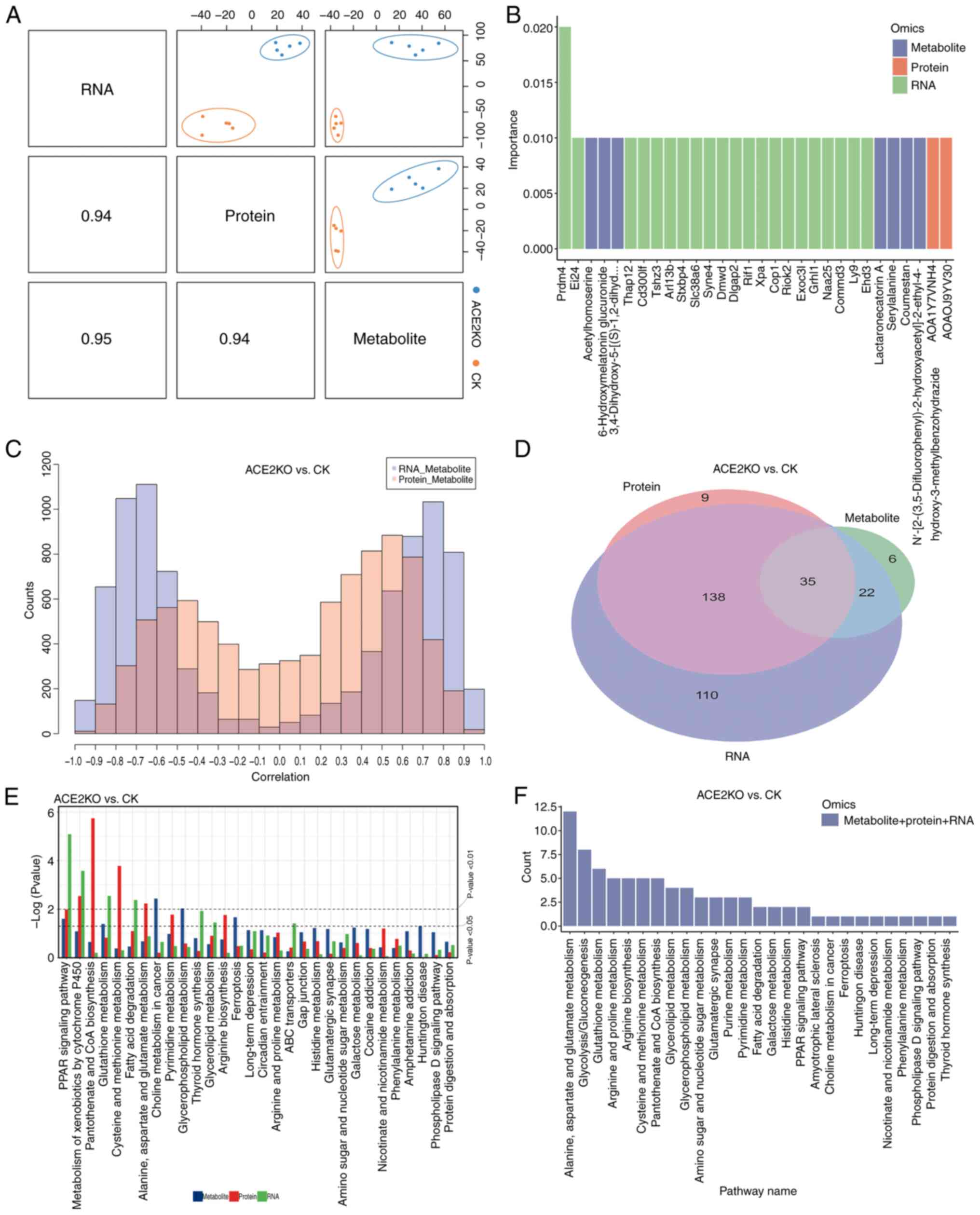
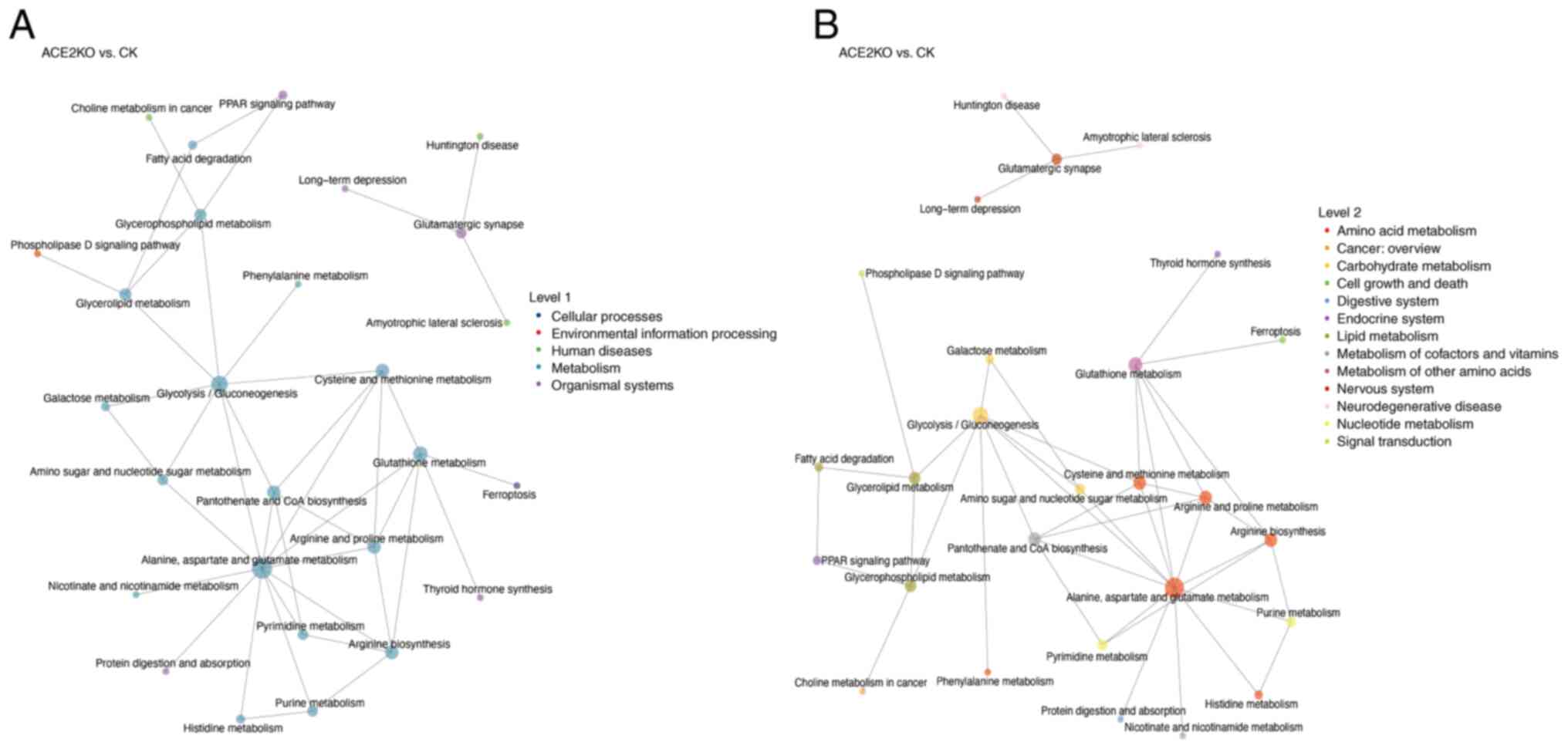
Sanches PHG, de Melo NC, Porcari AM and de
Carvalho LM: Integrating molecular perspectives: Strategies for
comprehensive multi-omics integrative data analysis and machine
learning applications in transcriptomics, proteomics, and
metabolomics. Biology (Basel). 13:8482024.
|
|
25
|
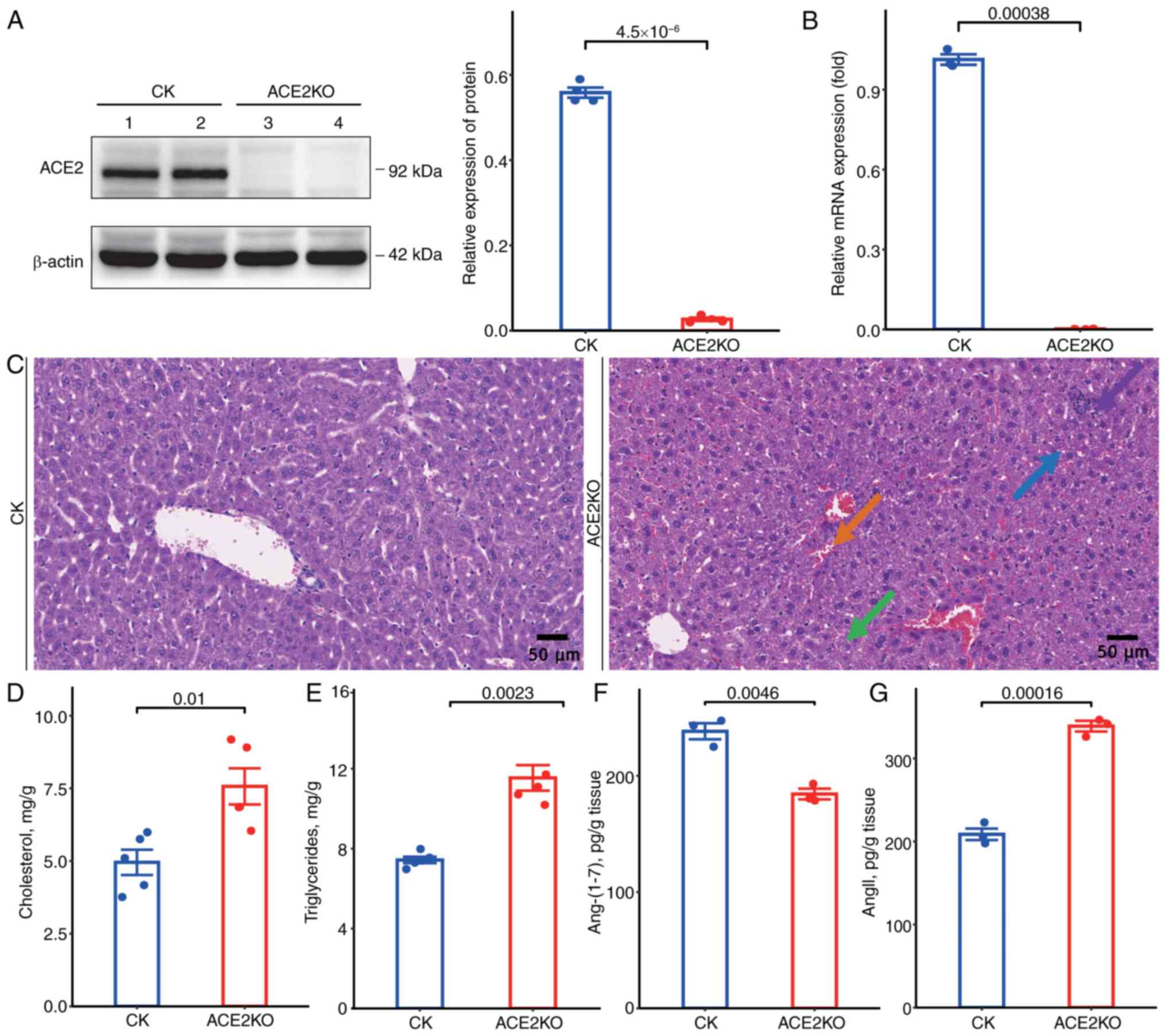
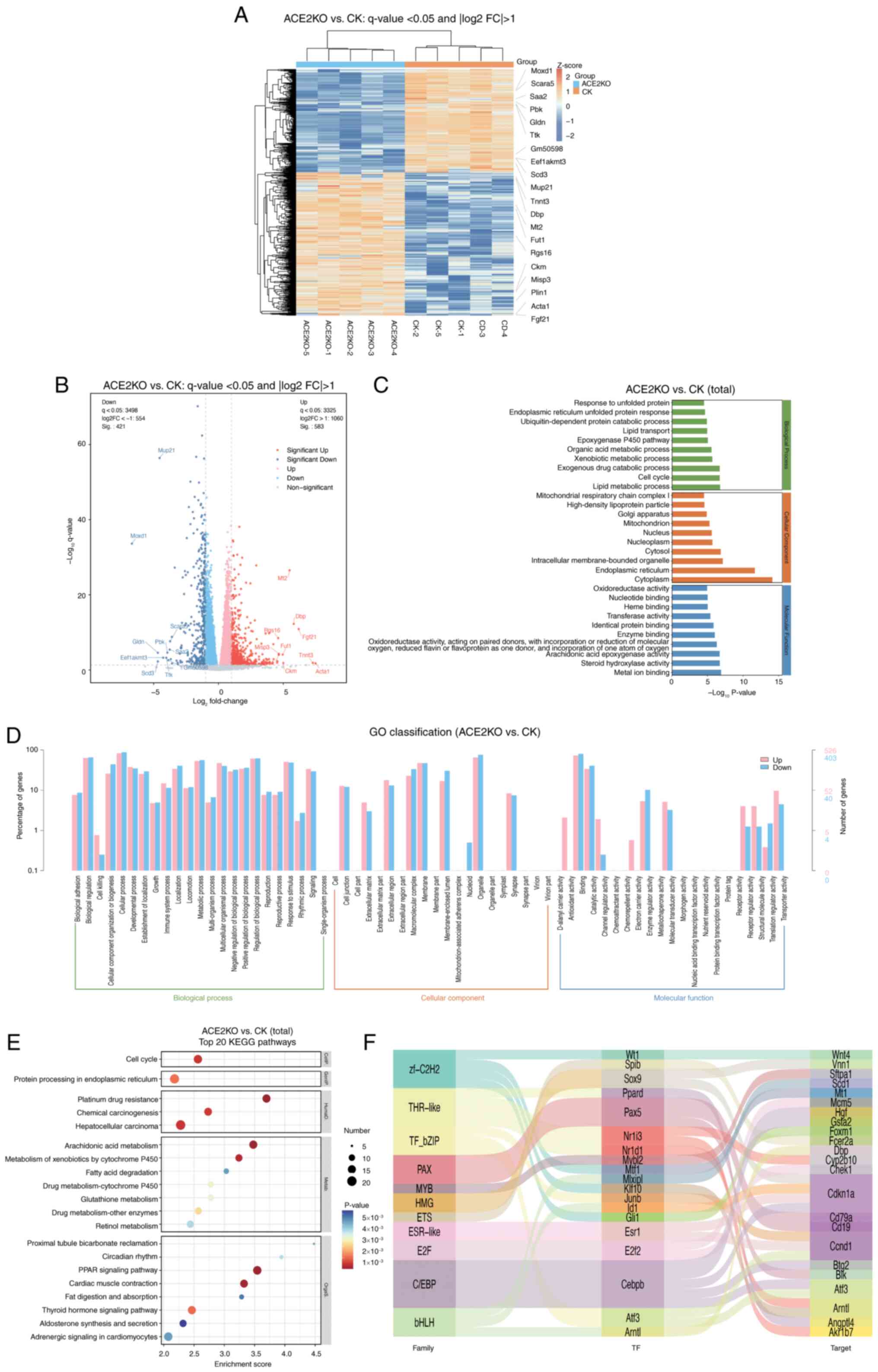
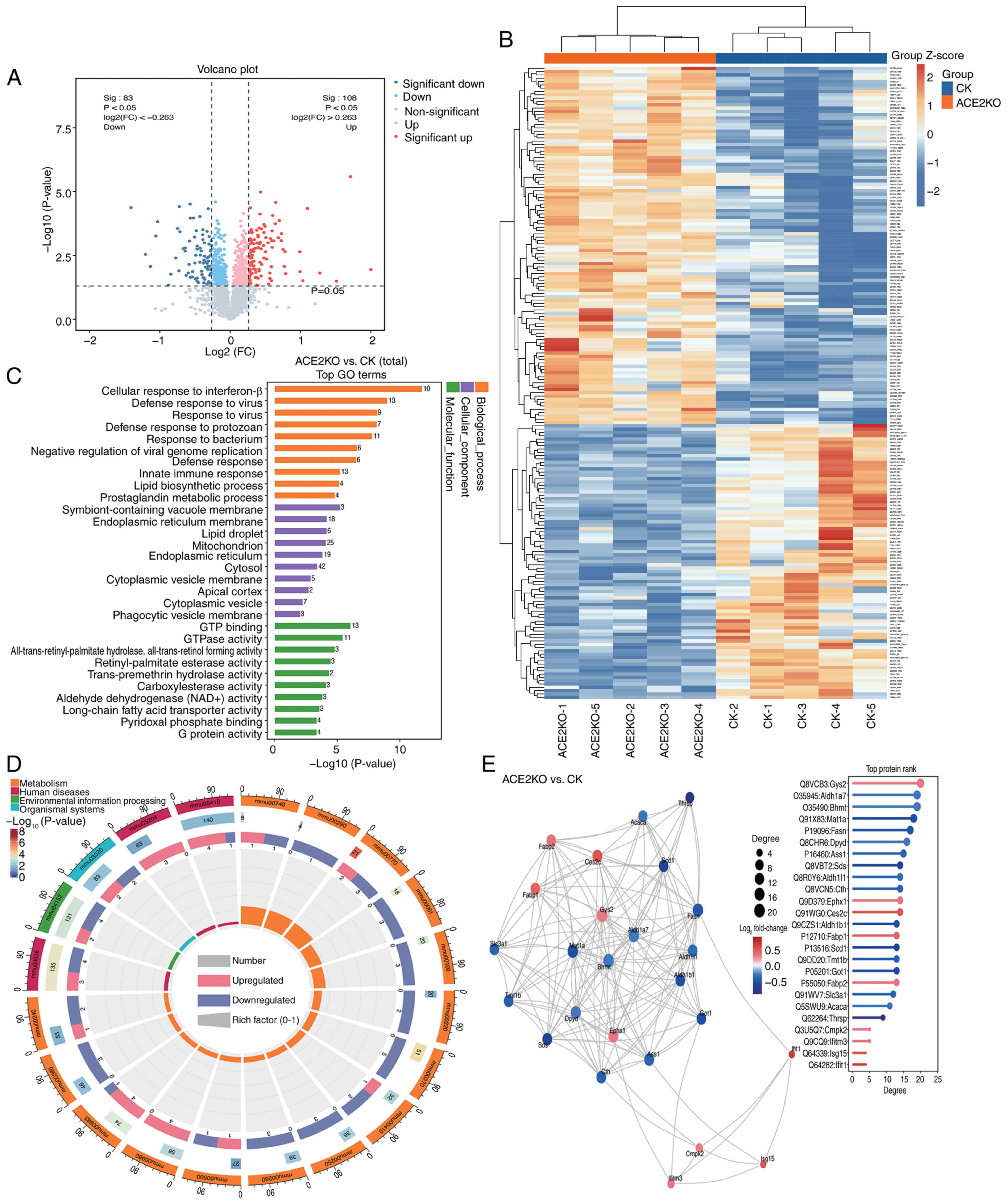
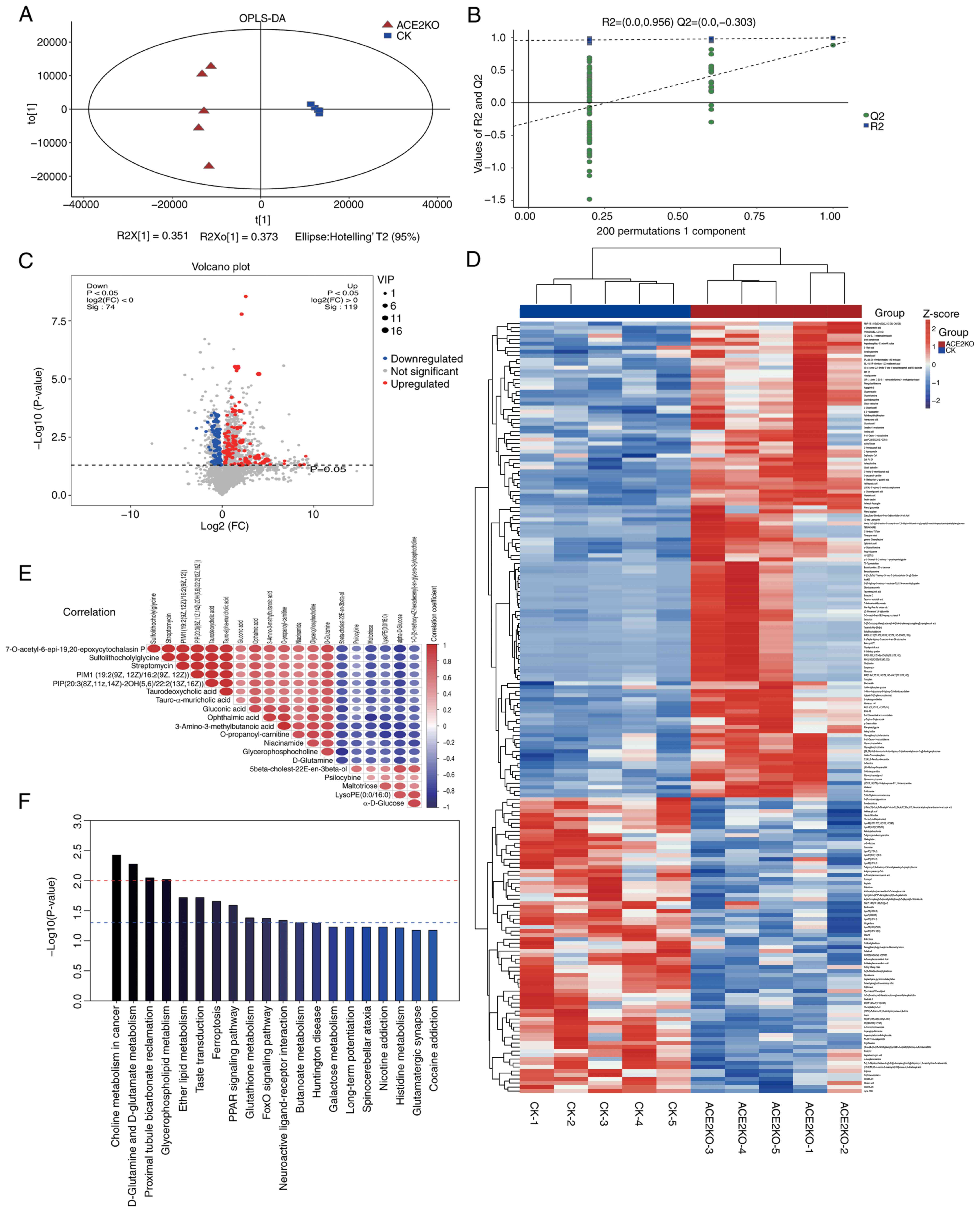
Zhao L, Yang W, Ji W, Pan Q, Yang J and
Cao X: Untargeted metabolomics uncovers metabolic dysregulation and
tissue sensitivity in ACE2 knockout mice. Heliyon.
10:e274722024.
|
|
26
|
Reel PS, Reel S, Pearson E, Trucco E and
Jefferson E: Using machine learning approaches for multi-omics data
analysis: A review. Biotechnol Adv. 49:1077392021.
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
28
|
Bolger AM, Lohse M and Usadel B:
Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data.
Bioinformatics. 30:2114–2120. 2014.
|
|
29
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015.
|
|
30
|
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G,
Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ and Pachter
L: Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals
unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell
differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 28:511–515. 2010.
|
|
31
|
Chu X, Hou Y, Peng C, Li W, Liang M, Mei
J, Qian M, Wang J, Xu S, Jiang Y, et al: Exosome-derived miR-548ag
drives hepatic lipid accumulation via upregulating FASN through
inhibition of DNMT3B. J Lipid Res. 66:1008182025.
|
|
32
|
Luque-Urbano MR, Fernández-Ramos D,
Lopitz-Otsoa F, Gutiérrez de Juan V, Bizkarguenaga M,
Castro-Espadas L, Hermoso-Martínez U, Barbier-Torres L, Lu SC,
Millet O and Mato JM: S-adenosylmethionine deficit disrupts very
low-density lipoprotein metabolism promoting liver lipid
accumulation in mice. J Lipid Res. 66:1007942025.
|
|
33
|
Tsochantaridis I, Brisimis D, Tsifintaris
M, Anastasiadou A, Lazos E, Ermogenous A, Christou S, Antonopoulou
N, Panayiotidis MI, Koukourakis MI, et al: Exploring the role and
pathophysiological significance of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1B1
(ALDH1B1) in human lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
25:103012024.
|
|
34
|
Song L, Guo X, Zhao F, Wang W, Zhao Z, Jin
L, Wu C, Yao J and Ma Z: TTC36 inactivation induce malignant
properties via Wnt-β-catenin pathway in gastric carcinoma. J
Cancer. 12:2598–2609. 2021.
|
|
35
|
Tian B, Yuan Y, Yang Y, Luo Z, Sui B, Zhou
M, Fu ZF and Zhao L: Interferon-Inducible GTPase 1 impedes the
dimerization of rabies virus phosphoprotein and restricts viral
replication. J Virol. 94:e01203–e01220. 2020.
|
|
36
|
Prakash P, Erdjument-Bromage H, O'Dea MR,
Munson CN, Labib D, Fossati V, Neubert TA and Liddelow SA:
Proteomic profiling of interferon-responsive reactive astrocytes in
rodent and human. Glia. 72:625–642. 2024.
|
|
37
|
Thibaut MM, Roumain M, Piron E, Gillard J,
Loriot A, Neyrinck AM, Rodriguez J, Massart I, Thissen JP, Huot JR,
et al: The microbiota-derived bile acid taurodeoxycholic acid
improves hepatic cholesterol levels in mice with cancer cachexia.
Gut Microbes. 17:24495862025.
|
|
38
|
Ye X, Shen S, Xu Z, Zhuang Q, Xu J, Wang
J, Dong Z and Wan X: Sodium butyrate alleviates cholesterol
gallstones by regulating bile acid metabolism. Eur J Pharmacol.
908:1743412021.
|
|
39
|
Yan T, Luo Y, Yan N, Hamada K, Zhao N, Xia
Y, Wang P, Zhao C, Qi D, Yang S, et al: Intestinal peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor α-fatty acid-binding protein 1 axis
modulates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 77:239–255.
2023.
|
|
40
|
Xiao W, Wang RS, Handy DE and Loscalzo J:
NAD(H) and NADP(H) redox couples and cellular energy metabolism.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 28:251–272. 2018.
|
|
41
|
Rui L: Energy metabolism in the liver.
Compr Physiol. 4:177–197. 2014.
|
|
42
|
Glatz JF, Luiken JJ and Bonen A: Membrane
fatty acid transporters as regulators of lipid metabolism:
Implications for metabolic disease. Physiol Rev. 90:367–417.
2010.
|
|
43
|
Casas-Grajales S and Muriel P:
Antioxidants in liver health. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther.
6:59–72. 2015.
|
|
44
|
Bigot A, Tchan MC, Thoreau B, Blasco H and
Maillot F: Liver involvement in urea cycle disorders: A review of
the literature. J Inherit Metab Dis. 40:757–769. 2017.
|
|
45
|
Ding HR, Wang JL, Ren HZ and Shi XL:
Lipometabolism and glycometabolism in liver diseases. Biomed Res
Int. 2018:12871272018.
|
|
46
|
Holeček M: Role of impaired glycolysis in
perturbations of amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Int J
Mol Sci. 24:17242023.
|
|
47
|
Zhang M, Zhao Y, Li Z and Wang C: Pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinase 4 mediates lipogenesis and contributes to the
pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 495:582–586. 2018.
|
|
48
|
Chen Q, Liu J, Wang W, Liu S, Yang X, Chen
M, Cheng L, Lu J, Guo T and Huang F: Sini decoction ameliorates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury via regulating ACE2-Ang (1-7)-Mas
axis and inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 115:1089712019.
|
|
49
|
Liu P, Liang WL, Huang RT, Chen XX, Zou
DH, Kurihara H, Li YF, Xu YH, Ouyang SH and He RR: Hepatic
microcirculatory disturbance in liver diseases: Intervention with
traditional Chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. 15:13995982024.
|
|
50
|
Shim KY, Eom YW, Kim MY, Kang SH and Baik
SK: Role of the renin-angiotensin system in hepatic fibrosis and
portal hypertension. Korean J Intern Med. 33:453–461. 2018.
|
|
51
|
Rajapaksha IG, Gunarathne LS, Angus PW and
Herath CB: Update on new aspects of the renin-angiotensin system in
hepatic fibrosis and portal hypertension: Implications for novel
therapeutic options. J Clin Med. 10:7022021.
|
|
52
|
Ahn YM, Kim HY, Yoon JJ, Kim HJ, Lee YJ,
Yun YG, Shin HK, Cho KW, Kang DG and Lee HS: Amelioration of
hypertension by oryeongsan through improvements of body fluid and
sodium balance: Roles of the renin-angiotensin system and atrial
natriuretic peptide system. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2022:91592922022.
|
|
53
|
Babaeenezhad E, Farahmandian N,
Sotoudeheian M, Dezfoulian O, Askari E, Taghipour N and Yarahmadi
S: Resveratrol relieves hepatic steatosis and enhances the effects
of atorvastatin in a mouse model of NAFLD by regulating the
renin-angiotensin system, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Food
Sci Nutr. 13:e700732025.
|
|
54
|
Delli Bovi AP, Marciano F, Mandato C,
Siano MA, Savoia M and Vajro P: Oxidative stress in non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. An updated mini review. Front Med (Lausanne).
8:5953712021.
|
|
55
|
Besse-Patin A and Estall JL: An intimate
relationship between ROS and insulin signalling: Implications for
antioxidant treatment of fatty liver disease. Int J Cell Biol.
2014:5191532014.
|
|
56
|
Mercado-Gómez M, Prieto-Fernández E,
Goikoetxea-Usandizaga N, Vila-Vecilla L, Azkargorta M, Bravo M,
Serrano-Maciá M, Egia-Mendikute L, Rodríguez-Agudo R,
Lachiondo-Ortega S, et al: The spike of SARS-CoV-2 promotes
metabolic rewiring in hepatocytes. Commun Biol. 5:8272022.
|
|
57
|
Wang L, Sun Y, Du L, Wang Q, Zhan M, Li S
and Xiao X: Daily koumiss has positive regulatory effects on blood
lipids and immune system: A metabolomics study. Heliyon.
10:e364292024.
|
|
58
|
Liu T, Li R, Sun L, Xu Z, Wang S, Zhou J,
Wu X and Shi K: Menin orchestrates hepatic glucose and fatty acid
uptake via deploying the cellular translocation of SIRT1 and PPARγ.
Cell Biosci. 13:1752023.
|
|
59
|
Santacroce G, Gentile A, Soriano S,
Novelli A, Lenti MV and Di Sabatino A: Glutathione: Pharmacological
aspects and implications for clinical use in non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease. Front Med (Lausanne). 10:11242752023.
|
|
60
|
Rabelo LA, Todiras M, Nunes-Souza V, Qadri
F, Szijártó IA, Gollasch M, Penninger JM, Bader M, Santos RA and
Alenina N: Genetic deletion of ACE2 induces vascular dysfunction in
C57BL/6 mice: Role of nitric oxide imbalance and oxidative stress.
PLoS One. 11:e01502552016.
|
|
61
|
Mundi MS, Velapati S, Patel J, Kellogg TA,
Dayyeh BK and Hurt RT: Evolution of NAFLD and its management. Nutr
Clin Pract. 35:72–84. 2020.
|
|
62
|
Akkız H, Gieseler RK and Canbay A: Liver
fibrosis: From basic science towards clinical progress, focusing on
the central role of hepatic stellate cells. Int J Mol Sci.
25:78732024.
|
|
63
|
Wagner N and Wagner KD: The role of PPARs
in disease. Cells. 9:23672020.
|
|
64
|
Dong J, Li M, Peng R, Zhang Y, Qiao Z and
Sun N: ACACA reduces lipid accumulation through dual regulation of
lipid metabolism and mitochondrial function via AMPK-PPARα-CPT1A
axis. J Transl Med. 22:1962024.
|
|
65
|
Kudo T, Zhao ML, Jeknić S, Kovary KM,
LaGory EL, Covert MW and Teruel MN: Context-dependent regulation of
lipid accumulation in adipocytes by a HIF1α-PPARγ feedback network.
Cell Syst. 14:1074–1086.e7. 2023.
|
|
66
|
Feldstein AE, Lopez R, Tamimi TA, Yerian
L, Chung YM, Berk M, Zhang R, McIntyre TM and Hazen SL: Mass
spectrometric profiling of oxidized lipid products in human
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
J Lipid Res. 51:3046–3054. 2010.
|
|
67
|
Xu Y, Han J, Dong J, Fan X, Cai Y, Li J,
Wang T, Zhou J and Shang J: Metabolomics characterizes the effects
and mechanisms of quercetin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
development. Int J Mol Sci. 20:12202019.
|
|
68
|
Afonso MB, Islam T, Magusto J, Amorim R,
Lenoir V, Simões RF, Teixeira J, Silva LC, Wendum D, Jéru I, et al:
RIPK3 dampens mitochondrial bioenergetics and lipid droplet
dynamics in metabolic liver disease. Hepatology. 77:1319–1334.
2023.
|
|
69
|
Choi J, Smith DM, Scafidi S, Riddle RC and
Wolfgang MJ: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 facilitates fatty
acid oxidation in a non-cell-autonomous manner. Cell Rep.
43:1150062024.
|
|
70
|
Chan JKW, Bittner S, Bittner A, Atwal S,
Shen WJ, Inayathullah M, Rajada J, Nicolls MR, Kraemer FB and Azhar
S: Nordihydroguaiaretic acid, a lignan from larrea tridentata
(Creosote Bush), protects against american lifestyle-induced
obesity syndrome diet-induced metabolic dysfunction in mice. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 365:281–290. 2018.
|
|
71
|
Hu Y, Lang Z, Li X, Lin L, Li Y, Zhang R,
Zheng J and Yu Z: Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes hepatic stellate cell
ferroptosis by epigenetically regulating ACSL4 to suppress liver
fibrosis progression. Phytomedicine. 124:1552892024.
|
|
72
|
Wang G, Bonkovsky HL, de Lemos A and
Burczynski FJ: Recent insights into the biological functions of
liver fatty acid binding protein 1. J Lipid Res. 56:2238–2247.
2015.
|
|
73
|
Nunes-Souza V, Alenina N, Qadri F,
Penninger JM, Santos RA, Bader M and Rabelo LA: CD36/Sirtuin 1 axis
impairment contributes to hepatic steatosis in ACE2-deficient mice.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:64875092016.
|
|
74
|
Hardwick JP, Osei-Hyiaman D, Wiland H,
Abdelmegeed MA and Song BJ: PPAR/RXR regulation of fatty acid
metabolism and fatty acid omega-hydroxylase (CYP4) isozymes:
Implications for prevention of lipotoxicity in fatty liver disease.
PPAR Res. 2009:9527342009.
|
|
75
|
Ogunsuyi OM, Fasakin PT, Ajibiye OP,
Ogunsuyi OI and Adekoya KO: Perfluoroundecanoic acid induces DNA
damage, reproductive and pathophysiological dysfunctions via
oxidative stress in male Swiss mice. Chemosphere.
338:1394912023.
|
|
76
|
Cebula M and Morgenstern R: Enzymology of
reactive intermediate protection: Kinetic analysis and temperature
dependence of the mesophilic membrane protein catalyst MGST1. FEBS
J. 290:3448–3460. 2023.
|
|
77
|
Raza H: Dual localization of glutathione
S-transferase in the cytosol and mitochondria: Implications in
oxidative stress, toxicity and disease. FEBS J. 278:4243–4251.
2011.
|
|
78
|
Hayashi K and Anzai N: L-type amino acid
transporter 1 as a target for inflammatory disease and cancer
immunotherapy. J Pharmacol Sci. 148:31–40. 2022.
|
|
79
|
Soria LR, Nitzahn M, De Angelis A, Khoja
S, Attanasio S, Annunziata P, Palmer DJ, Ng P, Lipshutz GS and
Brunetti-Pierri N: Hepatic glutamine synthetase augmentation
enhances ammonia detoxification. J Inherit Metab Dis. 42:1128–1135.
2019.
|
|
80
|
Frieg B, Görg B, Gohlke H and Häussinger
D: Glutamine synthetase as a central element in hepatic glutamine
and ammonia metabolism: Novel aspects. Biol Chem. 402:1063–1072.
2021.
|
|
81
|
Voss CM, Arildsen L, Nissen JD,
Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A, Maechler P, Ott P, Vilstrup H and
Walls AB: Glutamate dehydrogenase is important for ammonia fixation
and amino acid homeostasis in brain during hyperammonemia. Front
Neurosci. 15:6462912021.
|
|
82
|
Liao Y, Chen Q, Liu L, Huang H, Sun J, Bai
X, Jin C, Li H, Sun F, Xiao X, et al: Amino acid is a major carbon
source for hepatic lipogenesis. Cell Metab. 36:2437–2448.e8.
2024.
|
|
83
|
Jiménez-Torres C, El-Kehdy H,
Hernández-Kelly LC, Sokal E, Ortega A and Najimi M: Acute liver
toxicity modifies protein expression of glutamate transporters in
liver and cerebellar tissue. Front Neurosci. 14:6132252020.
|
|
84
|
Silberman A, Goldman O, Assayag O, Jacob
A, Rabinovich S, Adler L, Lee JS, Keshet R, Sarver A, Frug J, et
al: Acid-Induced downregulation of ASS1 contributes to the
maintenance of intracellular pH in cancer. Cancer Res. 79:518–533.
2019.
|
|
85
|
Xu HY, Jiao YH, Li SY, Zhu X, Wang S,
Zhang YY, Wei YJ, Shen YJ, Wang W, Shen YX and Shao JT:
Hepatocyte-derived MANF mitigates ethanol-induced liver steatosis
in mice via enhancing ASS1 activity and activating AMPK pathway.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 44:157–168. 2023.
|