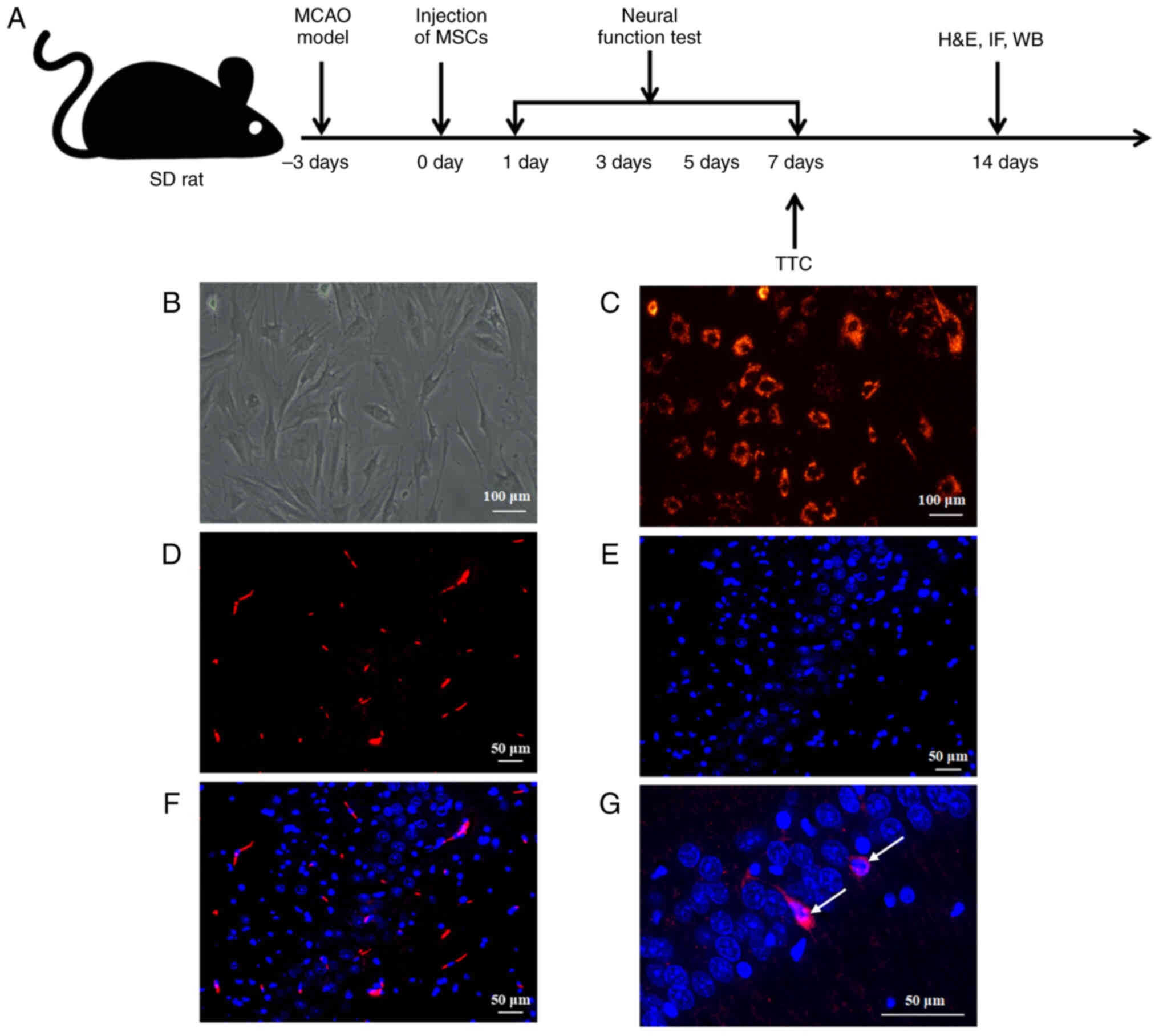
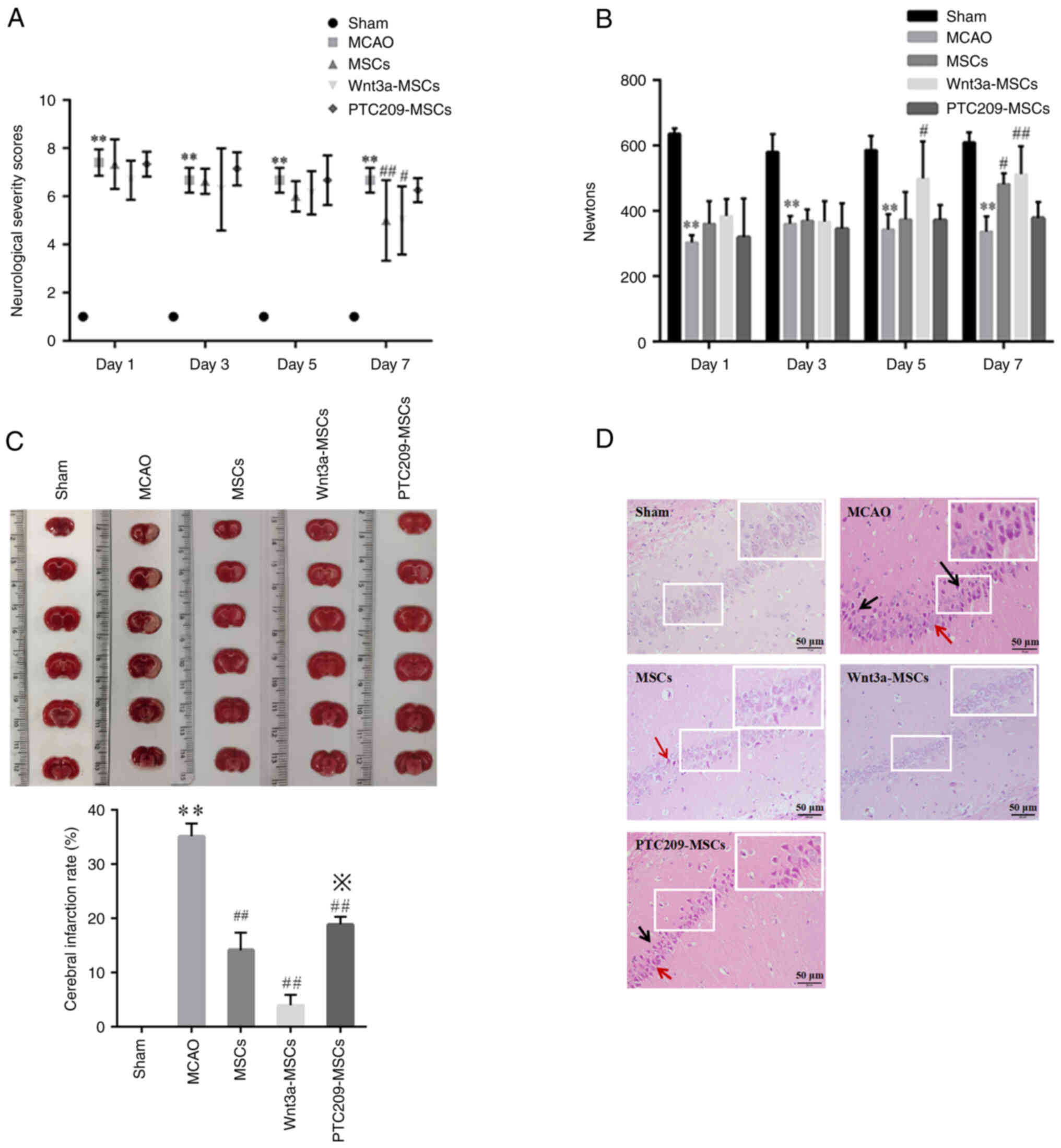
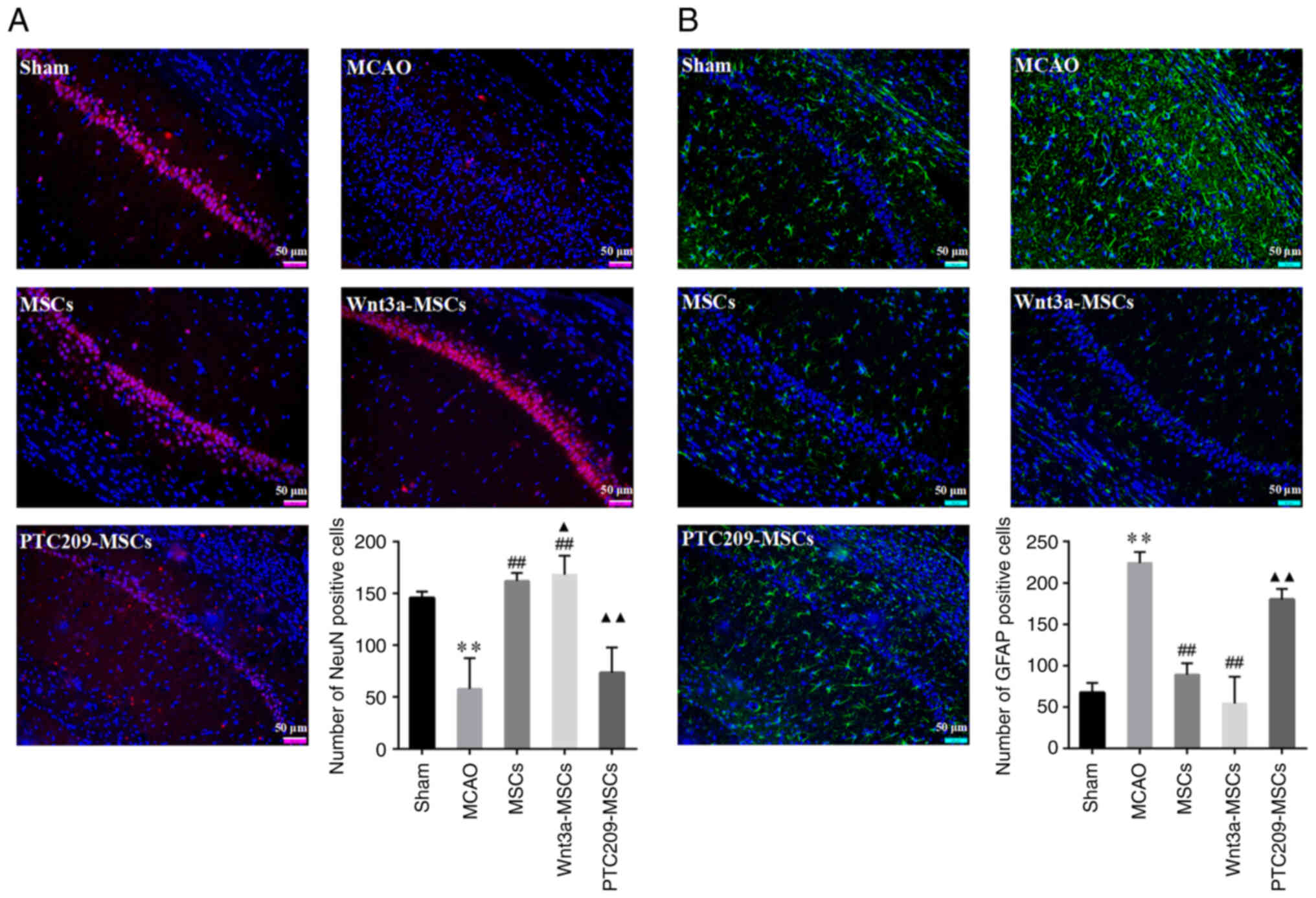
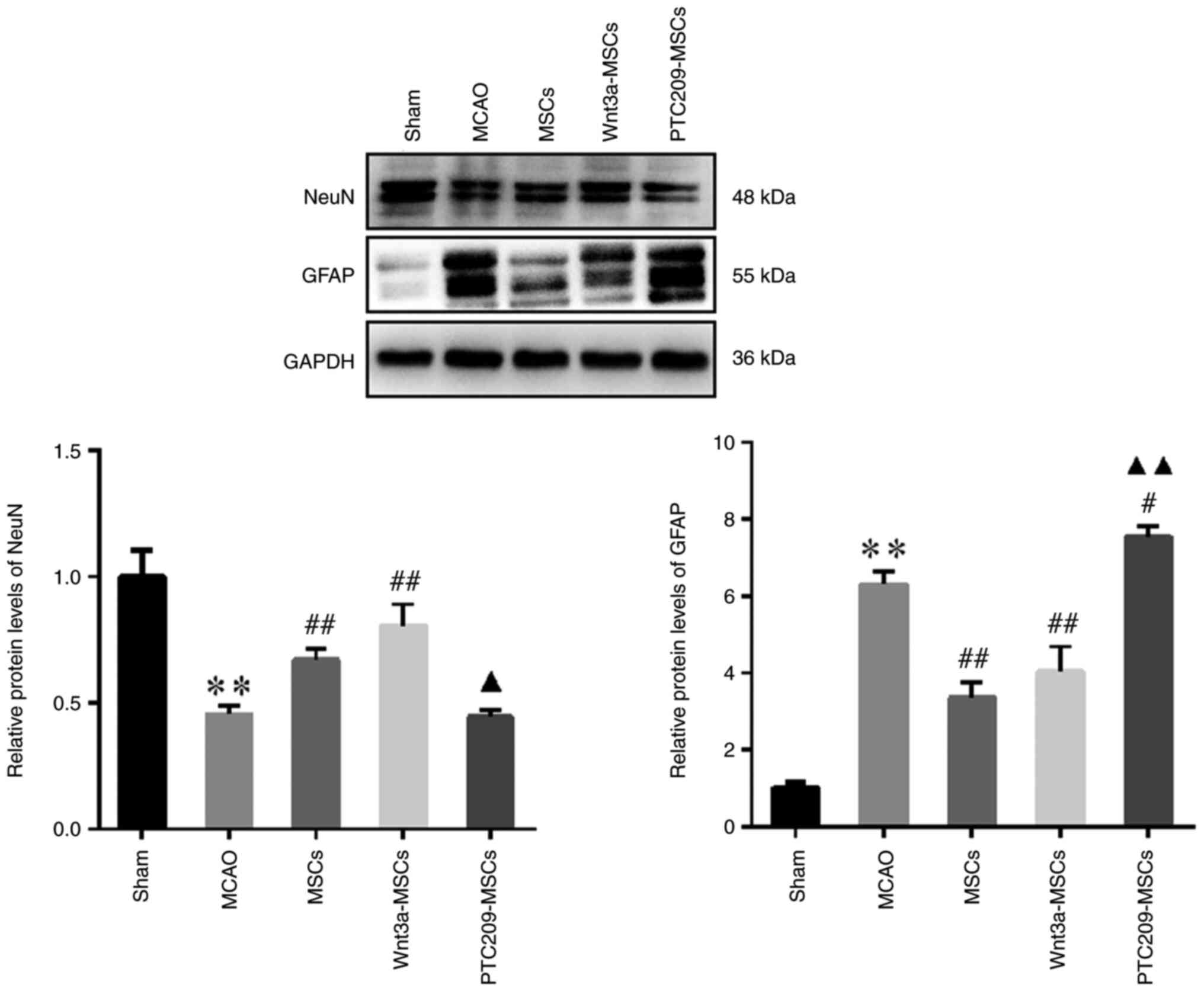
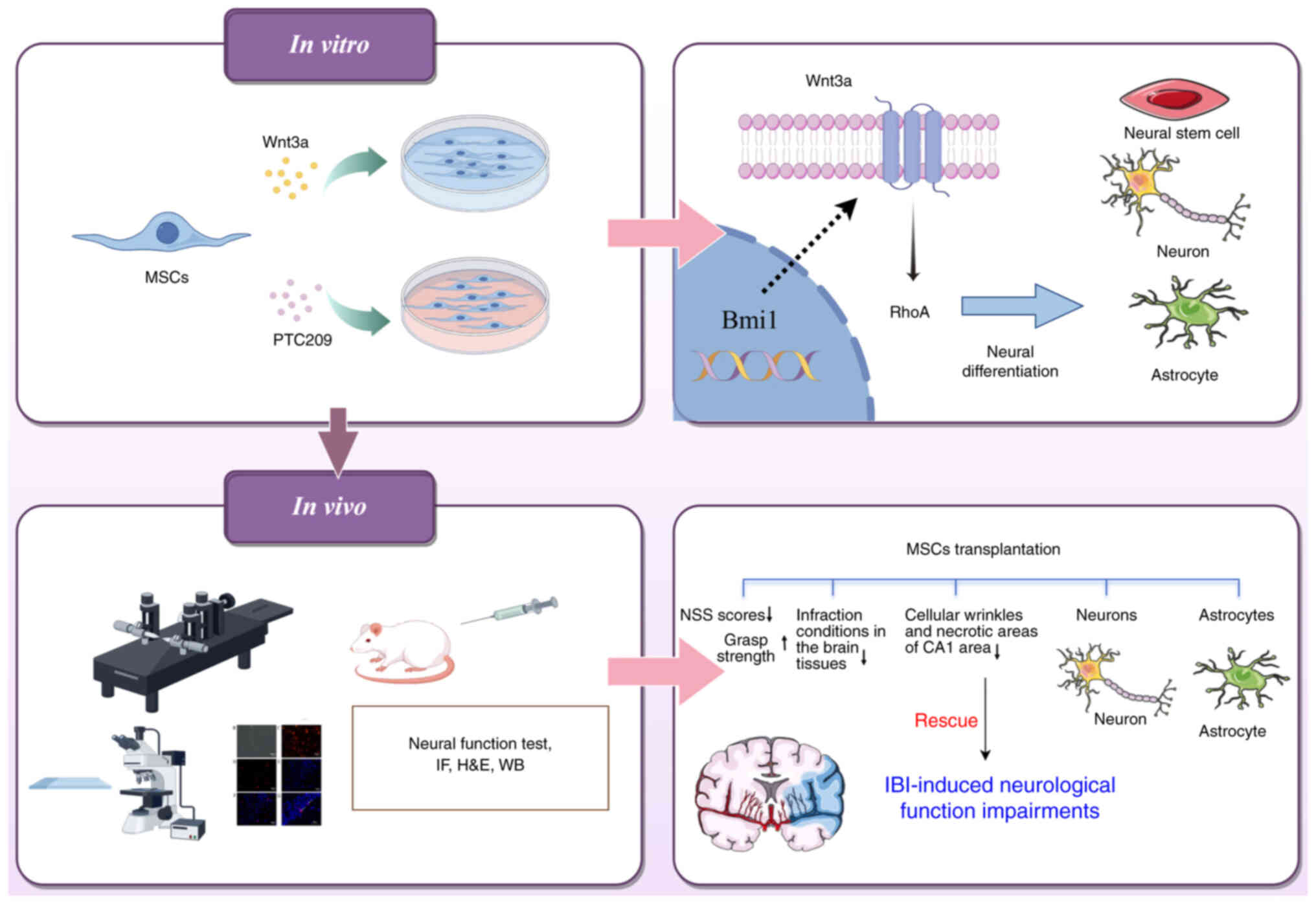
|
1
|
Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries
in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis
for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 396:1204–1222.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McIntyre CW and Goldsmith DJ: Ischemic
brain injury in hemodialysis patients: Which is more dangerous,
hypertension or intradialytic hypotension? Kidney Int.
87:1109–1115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu X and Jia X: Neuroprotection of stem
cells against ischemic brain injury: From bench to clinic. Transl
Stroke Res. 15:691–713. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Sakai S and Shichita T: Inflammation and
neural repair after ischemic brain injury. Neurochem Int.
130:1043162019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nie X, Leng X, Miao Z, Fisher M and Liu L:
Clinically ineffective reperfusion after endovascular therapy in
acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 54:873–881. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Guo Y, Peng Y, Zeng H and Chen G: Progress
in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke. Stem Cells
Int. 2021:99235662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chrostek MR, Fellows EG, Crane AT, Grande
AW and Low WC: Efficacy of stem Cell-based therapies for stroke.
Brain Res. 1722:1463622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li C, Sun T and Jiang C: Recent advances
in nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Acta Pharm
Sin B. 11:1767–1788. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leveque X, Hochane M, Geraldo F, Dumont S,
Gratas C, Oliver L, Gaignier C, Trichet V, Layrolle P, Heymann D,
et al: Low-dose pesticide mixture induces accelerated mesenchymal
stem cell aging in vitro. Stem Cells. 37:1083–1094. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cao Z, Xie Y, Yu L, Li Y and Wang Y:
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and stem cell factor (SCF)
maintained the stemness of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
(hBMSCs) during long-term expansion by preserving mitochondrial
function via the PI3K/AKT, ERK1/2, and STAT3 signaling pathways.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:3292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Xiong N, Liu Y and Gan L:
Biomimetic cell-adhesive ligand-functionalized peptide composite
hydrogels maintain stemness of human amniotic mesenchymal stem
cells. Regen Biomater. 8:rbaa0572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou T, Yang Y, Chen Q and Xie L:
Glutamine metabolism is essential for stemness of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells and bone homeostasis. Stem Cells Int.
2019:89289342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Morree A and Rando TA: Regulation of
adult stem cell quiescence and its functions in the maintenance of
tissue integrity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24:334–354. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sahasrabuddhe AA: BMI1: A biomarker of
hematologic malignancies. Biomark Cancer. 8:65–75. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang J, Xue J, Hu W, Zhang L, Xu R, Wu S,
Wang J, Ma J, Wei J, Wang Y, et al: Human embryonic stem
cell-derived mesenchymal stem cell secretome reverts silica-induced
airway epithelial cell injury by regulating Bmi1 signaling. Environ
Toxicol. 38:2084–2099. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng X, Wang Q, Xie Z and Li J: The
elevated level of IL-1α in the bone marrow of aged mice leads to
MSC senescence partly by down-regulating Bmi-1. Exp Gerontol.
148:1113132021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mich JK, Signer RA, Nakada D, Pineda A,
Burgess RJ, Vue TY, Johnson JE and Morrison SJ: Prospective
identification of functionally distinct stem cells and
neurosphere-initiating cells in adult mouse forebrain. Elife.
3:e026692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kraus L, Bryan C, Wagner M, Kino T,
Gunchenko M, Jalal W, Khan M and Mohsin S: Bmi1 augments
proliferation and survival of cortical Bone-derived stem cells
after injury through novel epigenetic signaling via histone 3
Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 22:78132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang D, Huang J, Wang F, Ding H, Cui Y,
Yang Y, Xu J, Luo H, Gao Y, Pan L, et al: BMI1 regulates multiple
myeloma-associated macrophage's pro-myeloma functions. Cell Death
Dis. 12:4952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Russell JO and Monga SP: Wnt/β-Catenin
signaling in liver development, homeostasis, and pathobiology. Annu
Rev Pathol. 13:351–378. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yu Q, Liu L, Duan Y, Wang Y, Xuan X, Zhou
L and Liu W: Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates neuronal
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 439:297–302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schunk SJ, Floege J, Fliser D and Speer T:
WNT-β-catenin signalling-a versatile player in kidney injury and
repair. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:172–184. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Torban E and Sokol SY: Planar cell
polarity pathway in kidney development, function and disease. Nat
Rev Nephrol. 17:369–385. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bengoa-Vergniory N, Gorroño-Etxebarria I,
González-Salazar I and Kypta RM: A switch from canonical to
noncanonical Wnt signaling mediates early differentiation of human
neural stem cells. Stem Cells. 32:3196–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Govek EE, Newey SE and Van Aelst L: The
role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev.
19:1–49. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Li HQ, Lu L, Fu DL, Liu AJ, Li JH
and Zheng GQ: Ginsenoside Rg1 provides neuroprotection against
blood brain barrier disruption and neurological injury in a rat
model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion through downregulation of
aquaporin 4 expression. Phytomedicine. 21:998–1003. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao P, Yu Q, Zhu L, Li J, Zhou X, Wu L,
Cai Y, Shen H and Zhou L: Wnt/PCP pathway regulates the migration
and neural differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 60:44–54. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zaghloul RA, Elsherbiny NM, Kenawy HI,
El-Karef A, Eissa LA and El-Shishtawy MM: Hepatoprotective effect
of hesperidin in hepatocellular carcinoma: Involvement of Wnt
signaling pathways. Life Sci. 185:114–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu D, Ye Y, Xu L, Yuan W and Zhang Q:
Icariin and mesenchymal stem cells synergistically promote
angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia via PI3K and
ERK1/2 pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:663–669. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goldman SA: Stem and Progenitor Cell-based
therapy of the central nervous system: Hopes, hype, and wishful
thinking. Cell Stem Cell. 18:174–188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Q, Guo Y, Chen F, Liu J and Jin P:
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes human adipose tissue-derived
stem cell survival and chronic wound healing. Exp Ther Med.
12:45–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meng Z, Feng G, Hu X, Yang L, Yang X and
Jin Q: SDF Factor-1α promotes the migration, proliferation, and
osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Dev.
30:106–117. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Marquez-Curtis LA and Janowska-Wieczorek
A: Enhancing the migration ability of mesenchymal stromal cells by
targeting the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Biomed Res Int. 2013:5610982013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu P, Xu J, Chen Y, Xu Q, Zhang W, Hu B,
Li A and Zhu Q: Electrophysiological signatures in global cerebral
ischemia: Neuroprotection via chemogenetic inhibition of CA1
pyramidal neurons in rats. J Am Heart Assoc. 13:e0361462024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fu HY, Cui Y, Li Q, Wang D, Li H, Yang L,
Wang DJ and Zhou JW: LAMP-2A ablation in hippocampal CA1 astrocytes
confers cerebroprotection and ameliorates neuronal injury after
global brain ischemia. Brain Pathol. 33:e131142023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lalkovičová M, Bonová P, Burda J and
Danielisová V: Effect of bradykinin postconditioning on ischemic
and toxic brain damage. Neurochem Res. 40:1728–1738. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mao M, Xu Y, Zhang XY, Yang L, An XB, Qu
Y, Chai YN, Wang YR, Li TT and Ai J: MicroRNA-195 prevents
hippocampal microglial/macrophage polarization towards the M1
phenotype induced by chronic brain hypoperfusion through regulating
CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling. J Neuroinflammation. 17:2442020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chang CY, Liang MZ, Wu CC, Huang PY, Chen
HI, Yet SF, Tsai JW, Kao CF and Chen L: WNT3A promotes neuronal
regeneration upon traumatic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci.
21:14632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He M, Shi X, Yang M, Yang T, Li T and Chen
J: Mesenchymal stem cells-derived IL-6 activates AMPK/mTOR
signaling to inhibit the proliferation of reactive astrocytes
induced by hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Exp Neurol. 311:15–32.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pourheydar B, Soleimani Asl S, Azimzadeh
M, Rezaei Moghadam A, Marzban A and Mehdizadeh M: Neuroprotective
effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on bilateral common
carotid arteries occlusion model of cerebral ischemia in rat. Behav
Neurol. 2016:29647122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xin H, Katakowski M, Wang F, Qian JY, Liu
XS, Ali MM, Buller B, Zhang ZG and Chopp M: MicroRNA cluster
miR-17-92 cluster in exosomes enhance neuroplasticity and
functional recovery after stroke in rats. Stroke. 48:747–753. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park IK, Qian D, Kiel M, Becker MW,
Pihalja M, Weissman IL, Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Bmi-1 is
required for maintenance of adult self-renewing haematopoietic stem
cells. Nature. 423:635–642. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wen T, Zhang X, Gao Y, Tian H, Fan L and
Yang P: SOX4-BMI1 axis promotes non-small cell lung cancer
progression and facilitates angiogenesis by suppressing ZNF24. Cell
Death Dis. 15:6982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao Y, Yang W, Zheng K, Chen J and Jin X:
The role of BMI1 in endometrial cancer and other cancers. Gene.
856:1471292023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kreso A, van Galen P, Pedley NM,
Lima-Fernandes E, Frelin C, Davis T, Cao L, Baiazitov R, Du W,
Sydorenko N, et al: Self-renewal as a therapeutic target in human
colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 20:29–36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Shan W, Zhou L, Liu L, Lin D and Yu Q:
Polycomb group protein Bmi1 is required for the neuronal
differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Exp Ther
Med. 21:6192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Okoh OS, Akintunde JK, Akamo AJ and Akpan
U: Thymoquinone inhibits Neuroinflammatory mediators and
vasoconstriction injury via NF-κB dependent NeuN/GFAP/Ki-67 in
hypertensive Dams and F1 male pups on exposure to a mixture of
Bisphenol-A analogues. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 494:1171622025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li M, Li Z, Yao Y, Jin WN, Wood K, Liu Q,
Shi FD and Hao J: Astrocyte-derived interleukin-15 exacerbates
ischemic brain injury via propagation of cellular immunity. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E396–E405. 2017.
|
|
49
|
Duan CL, Liu CW, Shen SW, Yu Z, Mo JL,
Chen XH and Sun FY: Striatal astrocytes transdifferentiate into
functional mature neurons following ischemic brain injury. Glia.
63:1660–1670. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sullivan SM, Sullivan RK, Miller SM,
Ireland Z, Björkman ST, Pow DV and Colditz PB: Phosphorylation of
GFAP is associated with injury in the neonatal pig hypoxic-ischemic
brain. Neurochem Res. 282:29414–29423. 2012.
|
|
51
|
Hosoya A, Takebe H, Seki-Kishimoto Y,
Noguchi Y, Ninomiya T, Yukita A, Yoshiba N, Washio A, Iijima M,
Morotomi T, et al: Polycomb protein Bmi1 promotes odontoblast
differentiation by accelerating Wnt and BMP signaling pathways.
Histochem Cell Biol. 163:112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yu J, Shen C, Lin M, Chen X, Dai X, Li Z,
Wu Y, Fu Y, Lv J, Huang X, et al: BMI1 promotes spermatogonial stem
cell maintenance by epigenetically repressing Wnt10b/β-catenin
signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 18:2807–2820. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
53
|
Chen MH, Fu LS, Zhang F, Yang Y and Wu XZ:
LncAY controls BMI1 expression and activates BMI1/Wnt/β-catenin
signaling axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci.
280:1197482021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yu H, Gao R, Chen S, Liu X, Wang Q, Cai W,
Vemula S, Fahey AC, Henley D, Kobayashi M, et al: Bmi1 regulates
wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Stem Cell
Rev Rep. 17:2304–2313. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bartucci M, Hussein MS, Huselid E,
Flaherty K, Patrizii M, Laddha SV, Kui C, Bigos RA, Gilleran JA, El
Ansary MMS, et al: Synthesis and characterization of novel BMI1
Inhibitors Targeting Cellular Self-renewal in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Target Oncol. 12:449–462. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhu D, Wan X, Huang H, Chen X, Liang W,
Zhao F, Lin T, Han J and Xie W: Knockdown of Bmi1 inhibits the
stemness properties and tumorigenicity of human bladder cancer stem
cell-like side population cells. Oncol Rep. 31:727–736. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|