|
1
|
Ferreira MJ, Rodrigues TA, Pedrosa AG,
Gales L, Salvador A, Francisco T and Azevedo JE: The mammalian
peroxisomal membrane is permeable to both GSH and GSSG-Implications
for intraperoxisomal redox homeostasis. Redox Biol. 63:1027642023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fujiki Y, Abe Y, Imoto Y, Tanaka AJ,
Okumoto K, Honsho M, Tamura S, Miyata N, Yamashita T, Chung WK and
Kuroiwa T: Recent insights into peroxisome biogenesis and
associated diseases. J Cell Sci. 133:jcs2369432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Agmon E, Solon J, Bassereau P and
Stockwell BR: Modeling the effects of lipid peroxidation during
ferroptosis on membrane properties. Sci Rep. 8:51552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jambunathan N: Determination and detection
of reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipid peroxidation, and
electrolyte leakage in plants. Methods Mol Biol. 639:292–298.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M,
Shchepinov MS and Stockwell BR: Peroxidation of polyunsaturated
fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:E4966–E4975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grishanova AY and Perepechaeva ML: Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in oxidative stress as a double agent and its
biological and therapeutic significance. Int J Mol Sci.
23:67192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sondermann NC, Faßbender S, Hartung F,
Hätälä AM, Rolfes KM, Vogel CFA and Haarmann-Stemmann T: Functions
of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) beyond the canonical
AHR/ARNT signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 208:1153712023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Hu DG, Marri S, McKinnon RA, Mackenzie PI
and Meech R: Deregulation of the genes that are involved in drug
absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 368:363–381. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Martins M, Santos JM, Diniz MS, Ferreira
AM, Costa MH and Costa PM: Effects of carcinogenic versus
non-carcinogenic AHR-active PAHs and their mixtures: Lessons from
ecological relevance. Environ Res. 138:101–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brantley E, Callero MA, Berardi DE,
Campbell P, Rowland L, Zylstra D, Amis L, Yee M, Simian M, Todaro
L, et al: AhR ligand Aminoflavone inhibits α6-integrin expression
and breast cancer sphere-initiating capacity. Cancer Lett.
376:53–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McLean L, Soto U, Agama K, Francis J,
Jimenez R, Sowers L and Brantley E: Aminoflavone induces oxidative
DNA damage and reactive oxidative species-mediated apoptosis in
breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 122:1665–1674. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Elson DJ, Nguyen BD, Korjeff NA, Wilferd
SF, Sanvicens VP, Jang HS, Bernales S, Chakravarty S, Belmar S,
Ureta G, et al: Suppression of Ah Receptor (AhR) increases the
aggressiveness of TNBC cells and 11-Cl-BBQ-activated AhR inhibits
their growth. Biochem Pharmacol. 215:1157062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kober C, Roewe J, Schmees N, Roese L,
Roehn U, Bader B, Stoeckigt D, Prinz F, Gorjánácz M, Roider HG, et
al: Targeting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) with BAY 2416964:
A selective small molecule inhibitor for cancer immunotherapy. J
Immunother Cancer. 11:e0074952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X, He B, Chen E, Lu J, Wang J, Cao H
and Li L: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand ITE inhibits cell
proliferation and migration and enhances sensitivity to
drug-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Physiol.
236:178–192. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang L, Liu Y, Du T, Yang H, Lei L, Guo M,
Ding HF, Zhang J, Wang H, Chen X and Yan C: ATF3 promotes
erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc. Cell Death
Differ. 27:662–675. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kwon OS, Kwon EJ, Kong HJ, Choi JY, Kim
YJ, Lee EW, Kim W, Lee H and Cha HJ: Systematic identification of a
nuclear receptor-enriched predictive signature for erastin-induced
ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 37:1017192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Yao Y, Gong G, He T, Ma C and Yu
J: The potential role of AhR/NR4A1 in androgen-dependent prostate
cancer: Focus on TCDD-induced ferroptosis. Biochem Cell Biol.
103:1–11. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kou Z, Tran F, Colon T, Shteynfeld Y, Noh
S, Chen F, Choi BH and Dai W: AhR signaling modulates ferroptosis
by regulating SLC7A11 expression. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
486:1169362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng Y, Ouyang L, Zhou Y, Lai W, Chen Y,
Wang Z, Yan B, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Peng X, et al: AhR promotes the
development of non-small cell lung cancer by inducing
SLC7A11-dependent antioxidant function. J Cancer. 14:821–834. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Filippidis G,
Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Reoxygenation induces reactive
oxygen species production and ferroptosis in renal tubular
epithelial ; cells by activating aryl hydrocarbon
receptor. Mol Med Rep. 23:412021.
|
|
22
|
Kwon JI, Heo H, Chae YJ, Min J, Lee DW,
Kim ST, Choi MY, Sung YS, Kim KW, Choi Y, et al: Is aryl
hydrocarbon receptor antagonism after ischemia effective in
alleviating acute hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats?
Heliyon. 9:e155962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Wang B, Yuan S, Xue K, Zhang J and
Xu A: Blocking the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor alleviates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Curr Med Sci. 42:966–973.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma C, Han L, Zhao W, Chen F, Huang R, Pang
CH, Zhu Z and Pan G: Targeting AhR suppresses hepatocyte
ferroptosis in MASH by regulating the Pten/Akt/β catenin axis.
Biochem Pharmacol. 232:1167112025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Qian C, Yang C, Lu M, Bao J, Shen H, Deng
B, Li S, Li W, Zhang M and Cao C: Activating AhR alleviates
cognitive deficits of Alzheimer's disease model mice by
upregulating endogenous Aβ catabolic enzyme Neprilysin.
Theranostics. 11:8797–8812. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Panda SK, Peng V, Sudan R, Ulezko Antonova
A, Di Luccia B, Ohara TE, Fachi JL, Grajales-Reyes GE, Jaeger N,
Trsan T, et al: Repression of the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor
prevents oxidative stress and ferroptosis of intestinal
intraepithelial lymphocytes. Immunity. 56:797–812.e4. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu H, Zhang C, Pan H, Gao X, Wang X, Xiao
W, Yan S, Gao Y, Fu J and Zhou Y: Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene enhances
the sensitivity of airway epithelial cells to ferroptosis and
aggravates asthma. Chemosphere. 363:1428852024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Avilla MN, Malecki KMC, Hahn ME, Wilson RH
and Bradfield CA: The Ah receptor: Adaptive metabolism, ligand
diversity, and the xenokine model. Chem Res Toxicol. 33:860–879.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan HF, Zou T, Tuo QZ, Xu S, Li H, Belaidi
AA and Lei P: Ferroptosis: Mechanisms and links with diseases.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rochette L, Dogon G, Rigal E, Zeller M,
Cottin Y and Vergely C: Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: Two
corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int J Mol
Sci. 24:4492022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ramana KV, Srivastava S and Singhal SS:
Lipid peroxidation products in human health and disease 2016. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2017:21632852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu Y, Ran L, Yang Y, Gao X, Peng M, Liu S,
Sun L, Wan J, Wang Y, Yang K, et al: Deferasirox alleviates
DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by inhibiting ferroptosis
and improving intestinal microbiota. Life Sci. 314:1213122023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Kang R and Tang D: Signaling
pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. FEBS J.
289:7038–7050. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nakamura T, Hipp C, Santos Dias Mourão A,
Borggräfe J, Aldrovandi M, Henkelmann B, Wanninger J, Mishima E,
Lytton E, Emler D, et al: Phase separation of FSP1 promotes
ferroptosis. Nature. 619:371–377. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Tan H, Daniels JD, Zandkarimi F,
Liu H, Brown LM, Uchida K, O'Connor OA and Stockwell BR: Imidazole
ketone erastin induces ferroptosis and slows tumor growth in a
mouse lymphoma model. Cell Chem Biol. 26:623–633.e9. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xuan Y, Wang H, Yung MM, Chen F, Chan WS,
Chan YS, Tsui SK, Ngan HY, Chan KK and Chan DW: SCD1/FADS2 fatty
acid desaturases equipoise lipid metabolic activity and
redox-driven ferroptosis in ascites-derived ovarian cancer cells.
Theranostics. 12:3534–3552. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu D, Hu Q, Wang Y, Jin M, Tao Z and Wan
J: Identification of HMOX1 as a critical ferroptosis-related gene
in atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9:8336422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adham AN, Abdelfatah S, Naqishbandi AM,
Mahmoud N and Efferth T: Cytotoxicity of apigenin toward multiple
myeloma cell lines and suppression of iNOS and COX-2 expression in
STAT1-transfected HEK293 cells. Phytomedicine. 80:1533712021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
He F, Zhang P, Liu J, Wang R, Kaufman RJ,
Yaden BC and Karin M: ATF4 suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis by
inducing SLC7A11 (xCT) to block stress-related ferroptosis. J
Hepatol. 79:362–377. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dodson M, Castro-Portuguez R and Zhang DD:
NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and
ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 23:1011072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu C, Zhang C, Wu H, Zhao Z, Wang Z,
Zhang X, Yang J, Yu W, Lian Z, Gao M and Zhou L: The
AKR1C1-CYP1B1-cAMP signaling axis controls tumorigenicity and
ferroptosis susceptibility of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cell
Death Differ. 32:506–520. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Apetoh L, Quintana FJ, Pot C, Joller N,
Xiao S, Kumar D, Burns EJ, Sherr DH and Weiner HL: The aryl
hydrocarbon receptor interacts with c-Maf to promote the
differentiation of type 1 regulatory T cells induced by IL-27. Nat
Immunol. 11:854–861. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Adachi J, Mori Y, Matsui S and Matsuda T:
Comparison of gene expression patterns between
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and a natural arylhydrocarbon
receptor ligand, indirubin. Toxicol Sci. 80:161–169. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Murray IA, Morales JL, Flaveny CA,
DiNatale BC, Chiaro C, Gowdahalli K, Amin S and Perdew GH: Evidence
for ligand-mediated selective modulation of Aryl hydrocarbon
receptor activity. Mol Pharmacol. 77:247–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Lo R and Matthews J: High-resolution
genome-wide mapping of AHR and ARNT binding sites by ChIP-Seq.
Toxicol Sci. 130:349–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hao N, Lee KL, Furness SGB, Bosdotter C,
Poellinger L and Whitelaw ML: Xenobiotics and loss of cell adhesion
drive distinct transcriptional outcomes by aryl hydrocarbon
receptor signaling. Mol Pharmacol. 82:1082–1093. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen G and Shin JA: AhR/Arnt:XRE
interaction: Turning false negatives into true positives in the
modified yeast one-hybrid assay. Anal Biochem. 382:101–106. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vogel CFA, Van Winkle LS, Esser C and
Haarmann-Stemmann T: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a target of
environmental stressors-implications for pollution mediated stress
and inflammatory responses. Redox Biol. 34:1015302020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lim HJ, Jang WB, Rethineswaran VK, Choi J,
Lee EJ, Park S, Jeong Y, Ha JS, Yun J, Choi YJ, et al:
StemRegenin-1 attenuates endothelial progenitor cell senescence by
regulating the AhR pathway-mediated CYP1A1 and ROS generation.
Cells. 12:20052023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Shertzer HG, Clay CD, Genter MB, Chames
MC, Schneider SN, Oakley GG, Nebert DW and Dalton TP:
Uncoupling-mediated generation of reactive oxygen by halogenated
aromatic hydrocarbons in mouse liver microsomes. Free Radic Biol
Med. 36:618–631. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mi P, Li N, Ai K, Li L and Yuan D:
AhR-mediated lipid peroxidation contributes to TCDD-induced cardiac
defects in zebrafish. Chemosphere. 317:1379422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yuan J, Sun X, Che S, Zhang L, Ruan Z, Li
X and Yang J: AhR-mediated CYP1A1 and ROS overexpression are
involved in hepatotoxicity of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209).
Toxicol Lett. 352:26–33. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yan L, Gu L, Lv X, Ni Z, Qian W, Chen Z,
Yang S, Zhuge Q, Yuan L and Ni H: Butylphthalide mitigates
traumatic brain injury by activating anti-ferroptotic AHR-CYP1B1
pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 337:1187582025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Nakahara T, Mitoma C, Hashimoto-Hachiya A,
Takahara M, Tsuji G, Uchi H, Yan X, Hachisuka J, Chiba T, Esaki H,
et al: Antioxidant opuntia ficus-indica extract activates AHR-NRF2
signaling and upregulates filaggrin and loricrin expression in
human keratinocytes. J Med Food. 18:1143–1149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Takei K, Mitoma C, Hashimoto-Hachiya A,
Uchi H, Takahara M, Tsuji G, Kido-Nakahara M, Nakahara T and Furue
M: Antioxidant soybean tar Glyteer rescues T-helper-mediated
downregulation of filaggrin expression via aryl hydrocarbon
receptor. J Dermatol. 42:171–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Takei K, Hashimoto-Hachiya A, Takahara M,
Tsuji G, Nakahara T and Furue M: Cynaropicrin attenuates
UVB-induced oxidative stress via the AhR-Nrf2-Nqo1 pathway. Toxicol
Lett. 234:74–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Miao W, Hu L, Scrivens PJ and Batist G:
Transcriptional regulation of NF-E2 p45-related factor (NRF2)
expression by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-xenobiotic response
element signaling pathway: Direct cross-talk between phase I and II
drug-metabolizing enzymes. J Biol Chem. 280:20340–20348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jiang L, Yin X, Chen YH, Chen Y, Jiang W,
Zheng H, Huang FQ, Liu B, Zhou W, Qi LW and Li J: Proteomic
analysis reveals ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting ROS production from
mitochondrial complex I. Theranostics. 11:1703–1720. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kou Z, Tran F and Dai W: Heavy metals,
oxidative stress, and the role of AhR signaling. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 482:1167692024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Li X, Ma N, Xu J, Zhang Y, Yang P, Su X,
Xing Y, An N, Yang F, Zhang G, et al: Targeting ferroptosis:
pathological mechanism and treatment of ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:15879222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang X, Shen T, Lian J, Deng K, Qu C, Li
E, Li G, Ren Y, Wang Z, Jiang Z, et al: Resveratrol reduces
ROS-induced ferroptosis by activating SIRT3 and compensating the
GSH/GPX4 pathway. Mol Med. 29:1372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yan HF, Tuo QZ, Yin QZ and Lei P: The
pathological role of ferroptosis in ischemia/reperfusion-related
injury. Zool Res. 41:220–230. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Paraskevaidis IA, Iliodromitis EK,
Vlahakos D, Tsiapras DP, Nikolaidis A, Marathias A, Michalis A and
Kremastinos DT: Deferoxamine infusion during coronary artery bypass
grafting ameliorates lipid peroxidation and protects the myocardium
against reperfusion injury: Immediate and long-term significance.
Eur Heart J. 26:263–270. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wang B and Xu A: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
pathway participates in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by
regulating mitochondrial apoptosis. Med Hypotheses. 123:2–5. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kou Z, Yang R, Lee E, Cuddapah S, Choi BH
and Dai W: Oxidative stress modulates expression of immune
checkpoint genes via activation of AhR signaling. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 457:1163142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Golfinopoulos
S, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Role of indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase in ischemia-reperfusion injury of renal tubular
epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 23:4722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Han L, Ma C, Wu Z, Xu H, Li H and Pan G:
AhR-STAT3-HO-1/COX-2 signalling pathway may restrict ferroptosis
and improve hMSC accumulation and efficacy in mouse liver. Br J
Pharmacol. 181:125–141. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zheng C, Zhang B, Li Y, Liu K, Wei W,
Liang S, Guo H, Ma K, Liu Y, Wang J and Liu L: Donafenib and GSK-J4
synergistically induce ferroptosis in liver cancer by upregulating
HMOX1 expression. Adv Sci (Weinh). 10:e22067982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wong PS, Li W, Vogel CF and Matsumura F:
Characterization of MCF mammary epithelial cells overexpressing the
Arylhydrocarbon receptor (AhR). BMC Cancer. 9:2342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhu P, Zhou K, Lu S, Bai Y, Qi R and Zhang
S: Modulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor inhibits esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma progression by repressing COX2/PGE2/STAT3
axis. J Cell Commun Signal. 14:175–192. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lo R and Matthews J: The aryl hydrocarbon
receptor and estrogen receptor alpha differentially modulate
nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 transactivation in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 270:139–148.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Fader KA, Nault R, Kirby MP, Markous G,
Matthews J and Zacharewski TR: Convergence of hepcidin deficiency,
systemic iron overloading, heme accumulation, and REV-ERBα/β
activation in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-elicited hepatotoxicity.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 321:1–17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Davies R, Clothier B, Robinson SW, Edwards
RE, Greaves P, Luo J, Gant TW, Chernova T and Smith AG: Essential
role of the AH receptor in the dysfunction of heme metabolism
induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Chem Res Toxicol.
21:330–340. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhao Z, Wu J, Xu H, Zhou C, Han B, Zhu H,
Hu Z, Ma Z, Ming Z, Yao Y, et al: XJB-5-131 inhibited ferroptosis
in tubular epithelial cells after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell
Death Dis. 11:6292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cai W, Liu L, Shi X, Liu Y, Wang J, Fang
X, Chen Z, Ai D, Zhu Y and Zhang X: Alox15/15-HpETE aggravates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting cardiomyocyte
ferroptosis. Circulation. 147:1444–1460. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhan J, Chen Y, Liu Y, Chen Y, Li Z, Li X,
He Z, Meng F, Qian X, Yang L and Yang Q: IDO1-mediated AhR
activation up-regulates pentose phosphate pathway via NRF2 to
inhibit ferroptosis in lung cancer. Biochem Pharmacol.
236:1169132025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Xu J, Sun X, Qin F, Wang X, Chen Q and Yan
R: Protective effects of salvianolic acid B on intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by regulating the
AhR/IL-22/STAT6 axis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 43:73–82.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shen L, Zhang J, Zheng Z, Yang F, Liu S,
Wu Y, Chen Y, Xu T, Mao S, Yan Y, et al: PHGDH inhibits ferroptosis
and promotes malignant progression by upregulating SLC7A11 in
bladder cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 18:5459–5474. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Conrad M and Pratt DA: The chemical basis
of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 15:1137–1147. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lin CJ, Liu HL, Pan CF, Chuang CK,
Jayakumar T, Wang TJ, Chen HH and Wu CJ: Indoxyl sulfate predicts
cardiovascular disease and renal function deterioration in advanced
chronic kidney disease. Arch Med Res. 43:451–456. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chen H, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Zhou W, Xu L, Shang
D, Ni J and Song Z: Indoxyl sulfate exacerbates alveolar bone loss
in chronic kidney disease through ferroptosis. Oral Dis.
31:264–277. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Curran CS and Kopp JB: The complexity of
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), hypoxic, and aryl
hydrocarbon receptor cell signaling in chronic kidney disease. J
Transl Med. 21:7062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Yuan S, Wei C, Liu G, Zhang L, Li J, Li L,
Cai S and Fang L: Sorafenib attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering
hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11 pathway. Cell
Prolif. 55:e131582022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Fan Y, Ma L, Fang X, Du S, Mauck J, Loor
JJ, Sun X, Jia H, Xu C and Xu Q: Role of
hypoxia-inducible-factor-1α (HIF-1α) in ferroptosis of adipose
tissue during ketosis. J Dairy Sci. 107:10611–10627. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Jin HO, Hong SE, Kim JY, Jang SK and Park
IC: Amino acid deprivation induces AKT activation by inducing
GCN2/ATF4/REDD1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 12:11272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Swanda RV, Ji Q, Wu X, Yan J, Dong L, Mao
Y, Uematsu S, Dong Y and Qian SB: Lysosomal cystine governs
ferroptosis sensitivity in cancer via cysteine stress response. Mol
Cell. 83:3347–3359.e9. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhao C, Bao L, Qiu M, Feng L, Chen L, Liu
Z, Duan S, Zhao Y, Wu K, Zhang N, et al: Dietary
tryptophan-mediated Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by the gut
microbiota alleviates escherichia coli-induced endometritis in
mice. Microbiol Spectr. 10:e00811222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang J, Zhu N, Su X, Gao Y and Yang R:
Gut-microbiota-derived metabolites maintain gut and systemic immune
homeostasis. Cells. 12:7932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Fiore A, Zeitler L, Russier M, Groß A,
Hiller MK, Parker JL, Stier L, Köcher T, Newstead S and Murray PJ:
Kynurenine importation by SLC7A11 propagates anti-ferroptotic
signaling. Mol Cell. 82:920–932.e7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Cui Y, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Zhao Z, Zhao R, Xu
X, Kong X, Ren J, Yao X, Wen Q, et al: Microglia and macrophage
exhibit attenuated inflammatory response and ferroptosis resistance
after RSL3 stimulation via increasing Nrf2 expression. J
Neuroinflammation. 18:2492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Cui W, Guo M, Liu D, Xiao P, Yang C, Huang
H, Liang C, Yang Y, Fu X, Zhang Y, et al: Gut microbial metabolite
facilitates colorectal cancer development via ferroptosis
inhibition. Nat Cell Biol. 26:124–137. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Marcato P, Dean CA, Liu RZ, Coyle KM,
Bydoun M, Wallace M, Clements D, Turner C, Mathenge EG, Gujar SA,
et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3 influences breast cancer
progression via differential retinoic acid signaling. Mol Oncol.
9:17–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Schwab A, Rao Z, Zhang J, Gollowitzer A,
Siebenkäs K, Bindel N, D'Avanzo E, Van Roey R, Hajjaj Y, Özel E, et
al: Zeb1 mediates EMT/plasticity-associated ferroptosis sensitivity
in cancer cells by regulating lipogenic enzyme expression and
phospholipid composition. Nat Cell Biol. 26:1470–1481. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Tang LJ, Luo XJ, Tu H, Chen H, Xiong XM,
Li NS and Peng J: Ferroptosis occurs in phase of reperfusion but
not ischemia in rat heart following ischemia or
ischemia/reperfusion. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
394:401–410. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Scindia Y, Leeds J and Swaminathan S: Iron
homeostasis in healthy kidney and its role in acute kidney injury.
Semin Nephrol. 39:76–84. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Doskey CM, Fader KA, Nault R, Lydic T,
Matthews J, Potter D, Sharratt B, Williams K and Zacharewski T:
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) alters hepatic
polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism and eicosanoid biosynthesis
in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
398:1150342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Aboutabl ME, Zordoky BNM and El-Kadi AOS:
3-Methylcholanthrene and benzo(a)pyrene modulate cardiac cytochrome
P450 gene expression and arachidonic acid metabolism in male
Sprague Dawley rats. Br J Pharmacol. 158:1808–1819. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Sroczyńska K, Totoń-Żurańska J, Czepiel J,
Zając-Grabiec A, Jurczyszyn A, Wołkow P, Librowski T and
Gdula-Argasińska J: Therapeutic role of eicosapentaenoic and
arachidonic acid in benzo(a) pyrene-induced toxicity in HUVEC
endothelial cells. Life Sci. 293:1203452022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Zhang C, He M, Ni L, He K, Su K, Deng Y,
Li Y and Xia H: The role of arachidonic acid metabolism in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Biochem Biophys.
78:255–265. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Bock KW and Köhle C: Contributions of the
Ah receptor to bilirubin homeostasis and its antioxidative and
atheroprotective functions. Biol Chem. 391:645–653. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Kim R, Hashimoto A, Markosyan N, Tyurin
VA, Tyurina YY, Kar G, Fu S, Sehgal M, Garcia-Gerique L, Kossenkov
A, et al: Ferroptosis of tumor neutrophils causes immune
suppression in cancer. Nature. 612:338–346. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Paris A, Tardif N, Galibert MD and Corre
S: AhR and cancer: From gene profiling to targeted therapy. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:7522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hezaveh K, Shinde RS, Klötgen A, Halaby
MJ, Lamorte S, Ciudad MT, Quevedo R, Neufeld L, Liu ZQ, Jin R, et
al: Tryptophan-derived microbial metabolites activate the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in tumor-associated macrophages to suppress
anti-tumor immunity. Immunity. 55:324–340.e8. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Duan Z, Li Y and Li L: Promoting
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by D-kynurenine via activating
aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Mol Cell Biochem. 448:165–173. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Li HM, Li X, Xia R, Zhang X, Jin TZ and
Zhang HS: PHGDH knockdown increases sensitivity to SR1, an aryl
hydrocarbon receptor antagonist, in colorectal cancer by activating
the autophagy pathway. FEBS J. 291:1780–1794. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zeitler L, Fiore A, Meyer C, Russier M,
Zanella G, Suppmann S, Gargaro M, Sidhu SS, Seshagiri S, Ohnmacht
C, et al: Anti-ferroptotic mechanism of IL4i1-mediated amino acid
metabolism. Elife. 10:e648062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Lian J, Lin H, Zhong Z, Song Y, Shao X,
Zhou J, Xu L, Sun Z, Yang Y, Chi J, et al: Indole-3-lactic acid
inhibits doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis through activating Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor/Nrf2 signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
29:e703582025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Tian Q, Dan G, Wang X, Zhu J, Chen C, Tang
D, Wang Z, Chen D, Lei S, Yang C, et al: IDO1 inhibits ferroptosis
by regulating FTO-mediated m6A methylation and SLC7A11 mRNA
stability during glioblastoma progression. Cell Death Discov.
11:222025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cui JX, Xu XH, He T, Liu JJ, Xie TY, Tian
W and Liu JY: L-kynurenine induces NK cell loss in gastric cancer
microenvironment via promoting ferroptosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
42:522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yu L, Shang D, Lang L, Liu Y, Yu M, Song
D, Jia S, Han S, Li C, Liu J, et al: TMF, a natural
dihydroflavonoid isolated from Scutellaria javanica Jungh,
stimulates anticancer activity of s180 cancer-bearing mice, induces
apoptosis, inhibits invasion and migration on HepG-2 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 263:1130722020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Liu S: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inducing hepatic stellate cell
ferroptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e702782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Guo L, Zhang J and Li Y, Gao Y, Huang J,
Liu M, Li J, Chai W and Li Y: 3,3′-Diindolylmethane induces
ferroptosis and inhibits proliferation in non-small-cell lung
cancer through the AHR/NRF2/GPX4 axis. Discov Oncol. 16:3442025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Prasanth MI, Malar DS, Verma K,
Prasansuklab A and Tencomnao T: Hibiscus sabdariffa calyx extract
protects human keratinocyte cells from fluoranthene-induced
ferroptosis via the repression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 291:1178712025. View Article : Google Scholar
|















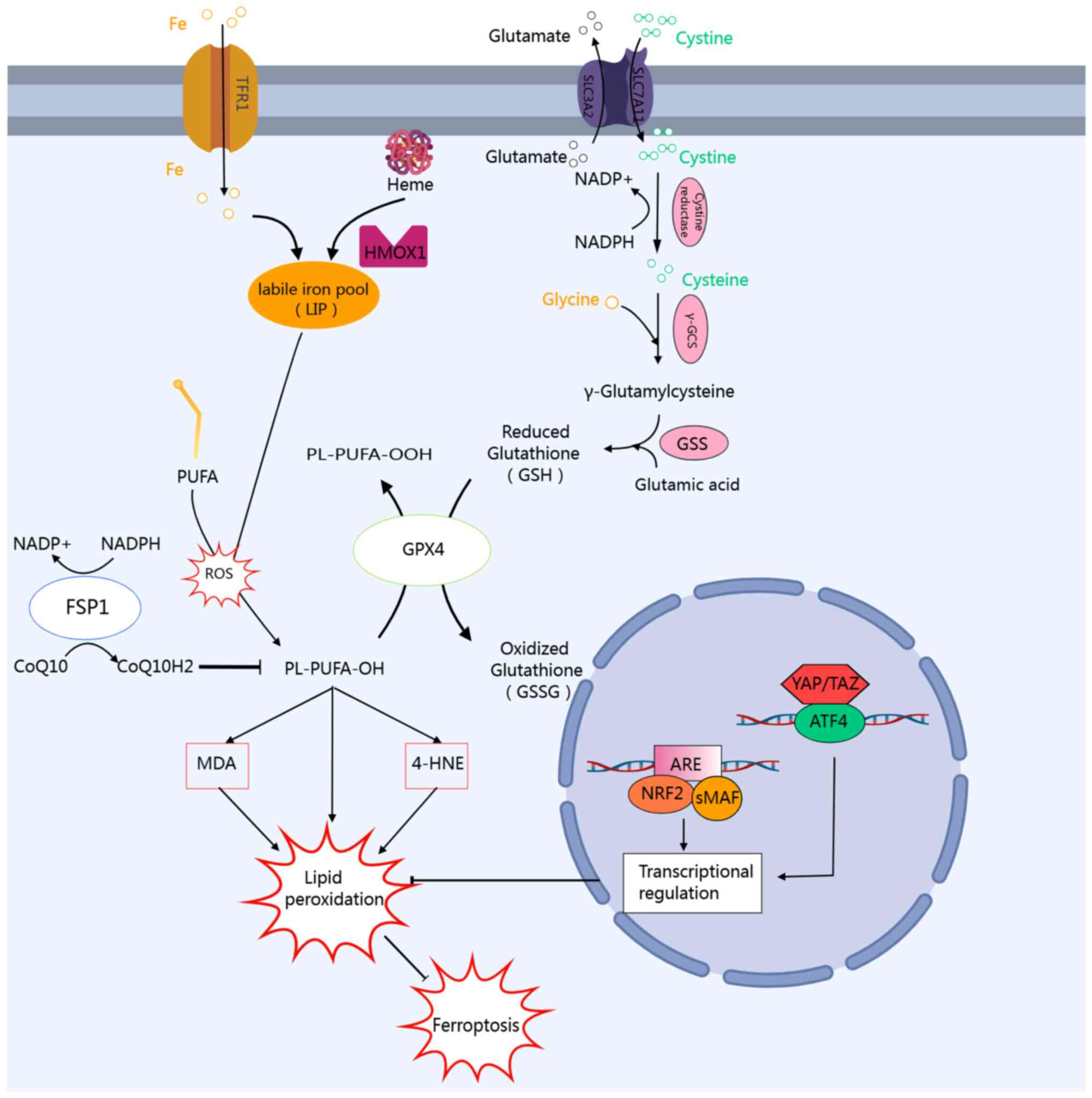
![Oxidative and antioxidant AhR ligands
regulate lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis via an
oxidative-antioxidant bidirectional regulatory network. Exogenous
pro-oxidative AhR ligands, such as the toxins TCDD and
benzo[a]pyrene, bind to AhR, forming the AhR-ARNT complex that
translocates into the nucleus. This complex subsequently binds to
the XRE, initiating the transcription of various progenitor
enzymes, including CYP1A1, CYP1B1, CYP1A2, COX-2 and NOX, then
mediating ROS production, which in turn induces lipid peroxidation
and ferroptosis. Conversely, natural AhR ligands derived from plant
sources, such as snake tail grass, soybean, fig tree, and fish tail
grass, activate the transcription of antioxidant enzymes (e.g.,
NQO1, GST and UGT1A1) through AhR signaling. This activation
suppresses ROS production, thereby mitigating lipid peroxidation
and inhibiting ferroptosis. AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; TCDD,
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; ARNT, AhR nuclear
translocator; NOX, nitrogen oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species;
NQO1, NAD(P) H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1; GST, glutathione
S-transferase; UGT1A1, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-1; HMOX1, heme
oxygenase 1; IDO1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; SLC7A11, solute
carrier family 7 member 11; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; ALDH1A3,
aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A3.](/article_images/ijmm/56/4/ijmm-56-04-05597-g01.jpg)
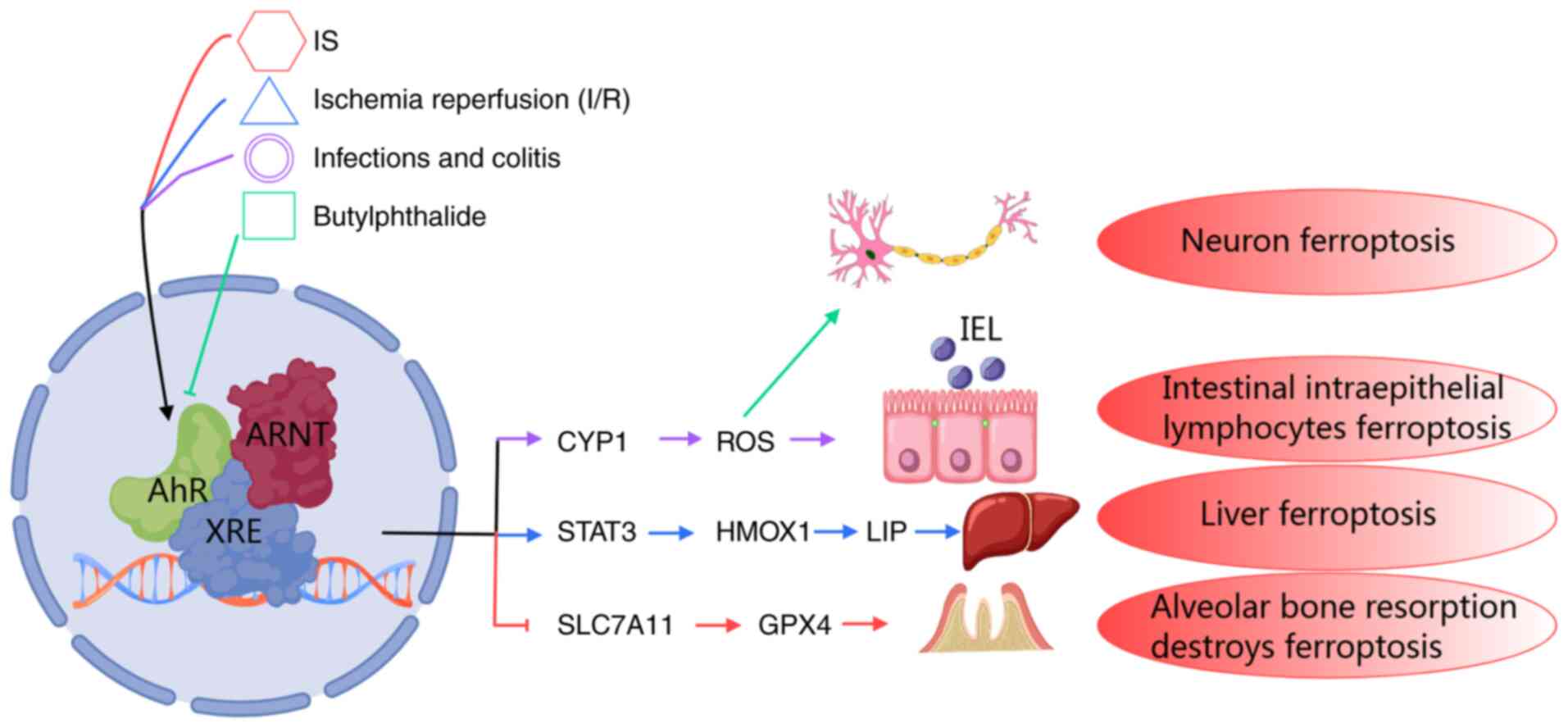
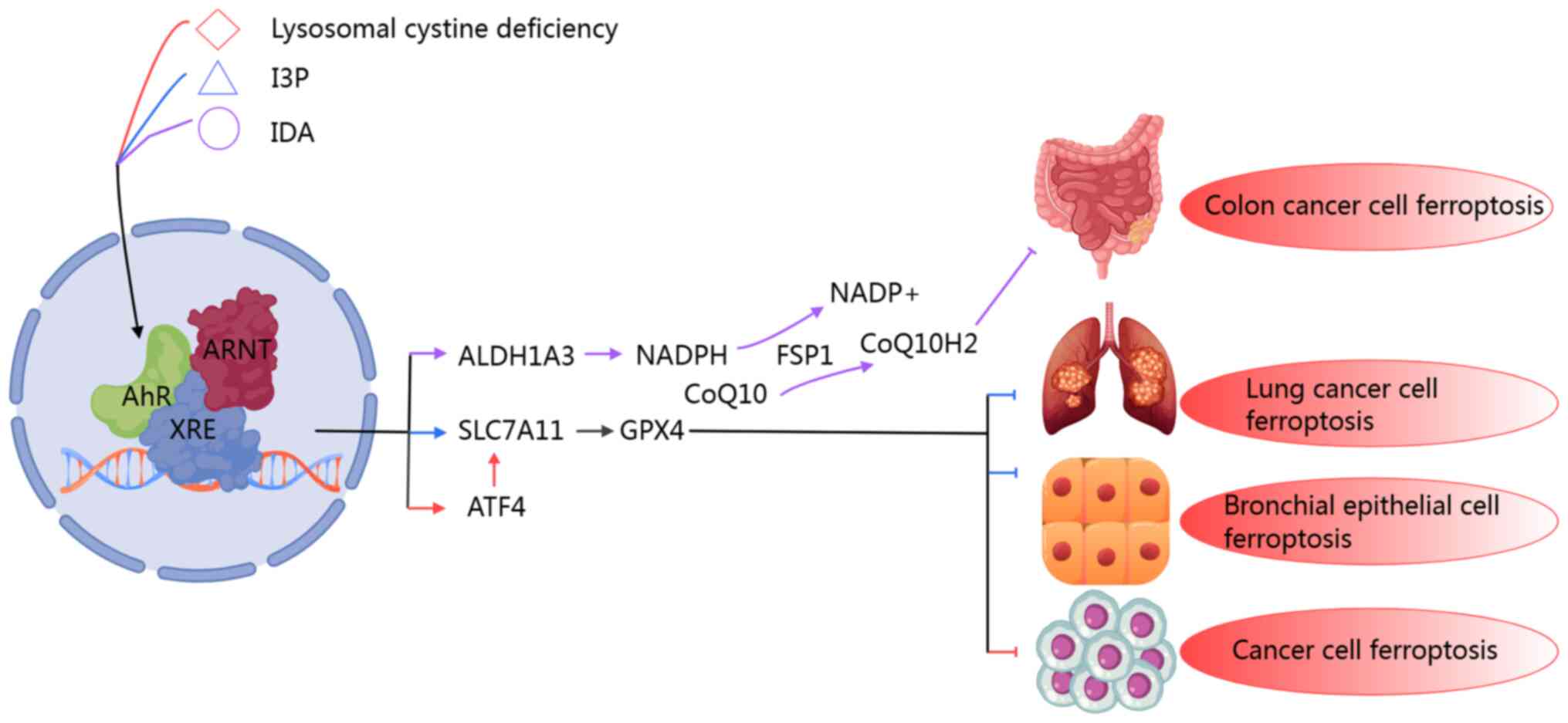
![Pharmacological targeting of AhR to
modulate ferroptosis in cancer and I/R injury. AhR ligands regulate
lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis through different molecular
axes, demonstrating environment-dependent therapeutic potential. In
parenchymal organs, such as the heart, liver and kidneys, AhR
antagonists CH223191 and SR1 alleviate I/R injury by inhibiting the
iron-stimulating pathway: CH223191 downregulates CYP1A-driven ROS
amplification and COX-2-mediated inflammatory signals, while SR1
inhibits HMOX1-dependent iron release and IDO1-induced oxidative
stress, jointly maintaining the redox balance of cells. In tumors,
AhR is pharmacologically regulated through AhR ligands, such as
aminoflavone, ITE, SR1 and CH223191, thereby influencing key
molecules in various lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis processes,
and further inducing ferroptosis in tumor cells or enhancing their
sensitivity to erastin. This is expected to eliminate tumor cells,
alleviate tumor progression and enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of
iron deposition inducers. AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; HMOX1,
heme oxygenase 1; IDO1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; ROS,
reactive oxygen species; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; TCDD,
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; NQO1, NAD(P)H dehydrogenase
[quinone] 1; GST, glutathione S-transferase; UGT1A1,
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-1.](/article_images/ijmm/56/4/ijmm-56-04-05597-g04.jpg)