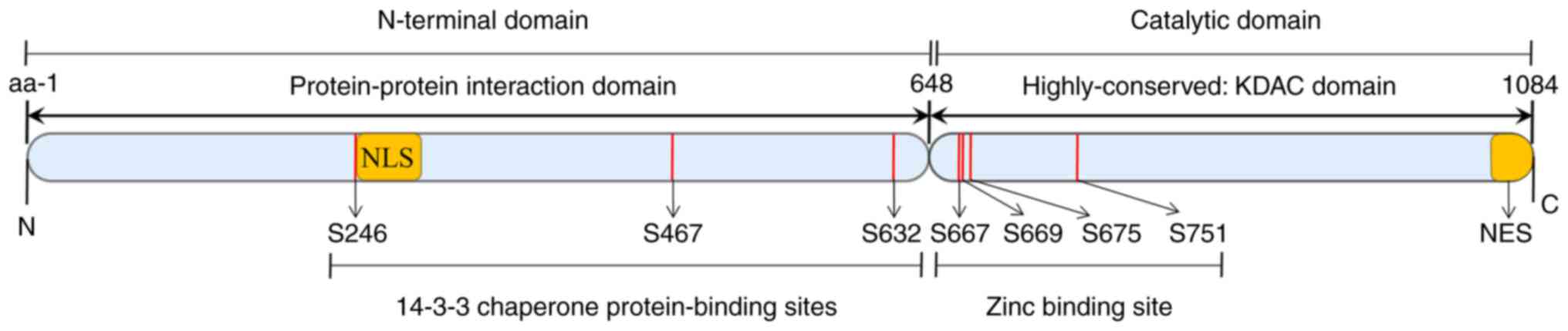
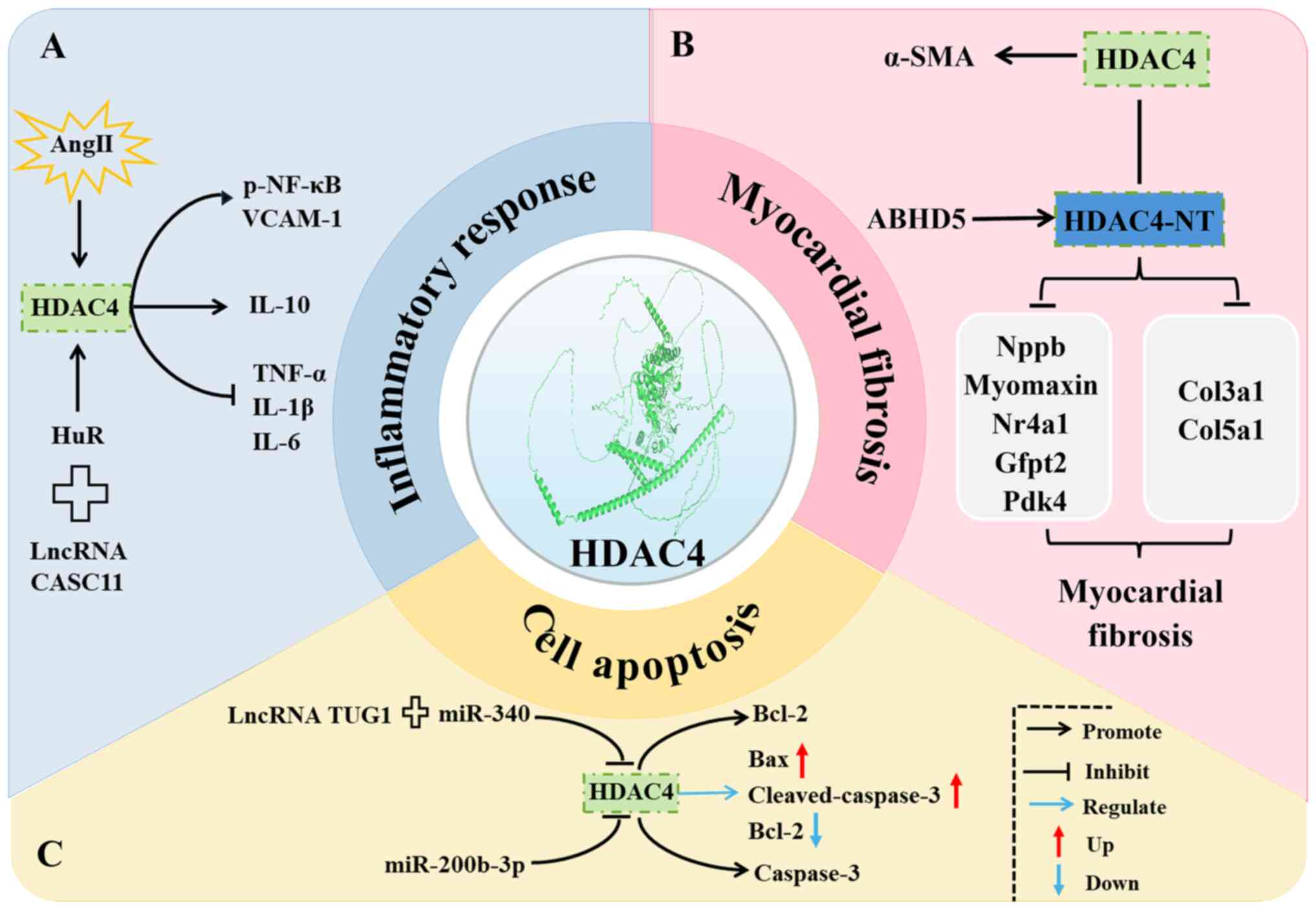
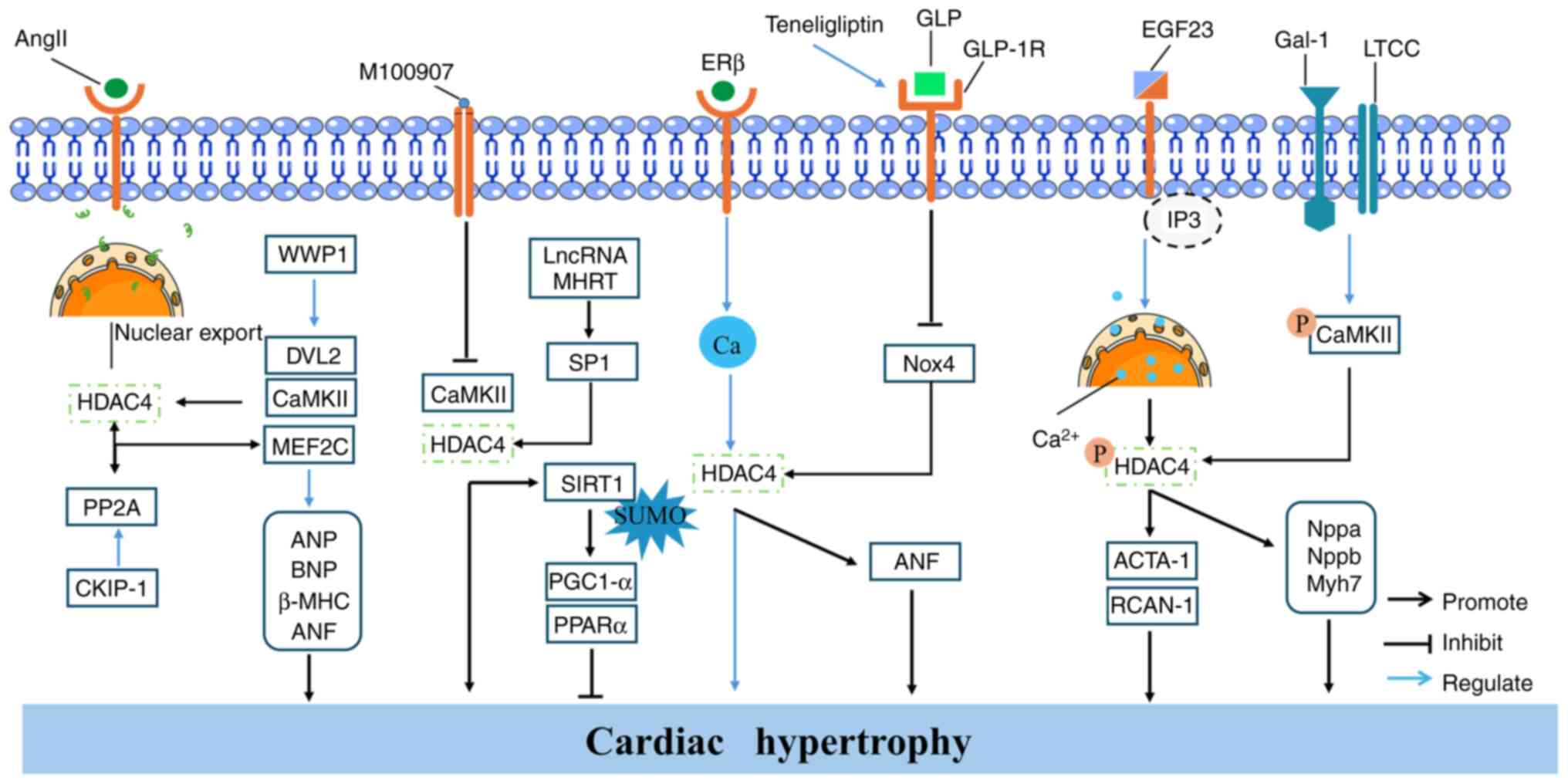
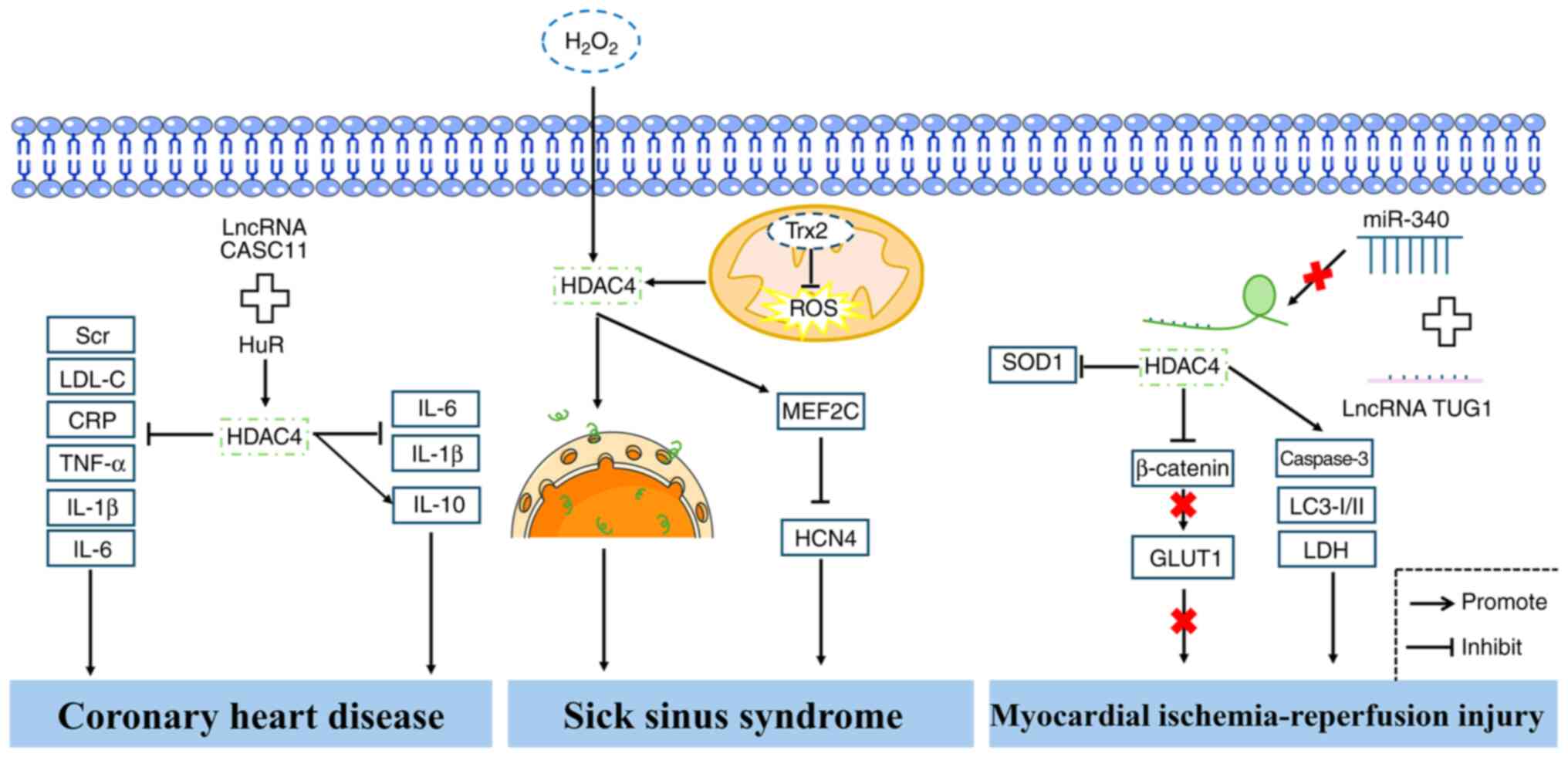
|
1
|
Li P, Ge J and Li H: Lysine
acetyltransferases and lysine deacetylases as targets for
cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 17:96–115. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Haberland M, Montgomery RL and Olson EN:
The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and
physiology: Implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet.
10:32–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang D, Hu X, Henning RH and Brundel BJ:
Keeping up the balance: Role of HDACs in cardiac proteostasis and
therapeutic implications for atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res.
109:519–526. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Backs J and Olson EN: Control of cardiac
growth by histone acetylation/deacetylation. Circ Res. 98:15–24.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hohl M, Wagner M, Reil JC, Müller SA,
Tauchnitz M, Zimmer AM, Lehmann LH, Thiel G, Böhm M, Backs J and
Maack C: HDAC4 controls histone methylation in response to elevated
cardiac load. J Clin Invest. 123:1359–1370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, Qin G and Zhao TC: HDAC4:
Mechanism of regulation and biological functions. Epigenomics.
6:139–150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ouyang J, Wang H and Huang J: The role of
lactate in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Commun Signal. 21:3172023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alves PKN, Schauer A, Augstein A, Männel
A, Barthel P, Joachim D, Friedrich J, Prieto ME, Moriscot AS, Linke
A and Adams V: Leucine Supplementation improves diastolic function
in HFpEF by HDAC4 inhibition. Cells. 12:25612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ling S, Sun Q, Li Y, Zhang L, Zhang P,
Wang X, Tian C, Li Q, Song J, Liu H, et al: CKIP-1 inhibits cardiac
hypertrophy by regulating class II histone deacetylase
phosphorylation through recruiting PP2A. Circulation.
126:3028–3040. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Gao Q, Wang S, Kang Z, Li Z, Lei S,
Sun X, Zhao M, Chen X, Jiao G, et al: Sustained increased CaMKII
phosphorylation is involved in the impaired regression of
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats. J Pharmacol Sci.
144:30–42. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ginnan R, Sun LY, Schwarz JJ and Singer
HA: MEF2 is regulated by CaMKIIdelta2 and a HDAC4-HDAC5 heterodimer
in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem J. 444:105–114. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Berthouze-Duquesnes M, Lucas A, Sauliere
A, Sin YY, Laurent AC, Galés C, Baillie G and Lezoualc'h F:
Specific interactions between Epac1, β-arrestin2 and PDE4D5
regulate β-adrenergic receptor subtype differential effects on
cardiac hypertrophic signaling. Cell Signal. 25:970–980. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Guo Z, Wu Y, Feng Q, Wang C, Wang Z, Zhu
Y, Lu X, Chen W, Yang Q and Huo Y: Circulating HDAC4 reflects lipid
profile, coronary stenosis and inflammation in coronary heart
disease patients. Biomark Med. 17:41–49. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kong Q, Hao Y, Li X, Wang X, Ji B and Wu
Y: HDAC4 in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential.
Clin Epigenetics. 10:1172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Z, Zhang Z, Guo L, Wei X, Zhang Y,
Wang X and Wei L: The role of histone deacetylase 4 during
chondrocyte hypertrophy and endochondral bone development. Bone
Joint Res. 9:82–89. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mathias RA, Guise AJ and Cristea IM:
Post-translational modifications regulate class IIa histone
deacetylase (HDAC) function in health and disease. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 14:456–470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cuttini E, Goi C, Pellarin E, Vida R and
Brancolini C: HDAC4 in cancer: A multitasking platform to drive not
only epigenetic modifications. Front Mol Biosci. 10:11166602023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Duarte LRF, Pinho V, Rezende BM and
Teixeira MM: Resolution of inflammation in acute
graft-versus-host-disease: Advances and perspectives. Biomolecules.
12:752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liberale L, Badimon L, Montecucco F,
Luscher TF, Libby P and Camici GG: Inflammation, aging, and
cardiovascular disease: JACC review topic of the week. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 79:837–847. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui C, Liu L, Qi Y, Han N, Xu H, Wang Z,
Shang X, Han T, Zha Y, Wei X and Wu Z: Joint association of TyG
index and high sensitivity C-reactive protein with cardiovascular
disease: A national cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 23:1562024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fredman G and Serhan CN: Specialized
pro-resolving mediators in vascular inflammation and
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol.
21:808–823. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang D, Xiao C, Long F, Su Z, Jia W, Qin
M, Huang M, Wu W, Suguro R, Liu X and Zhu Y: HDAC4 regulates
vascular inflammation via activation of autophagy. Cardiovasc Res.
114:1016–1028. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y and Yamawaki H:
Exploring calmodulin-related proteins, which mediate development of
hypertension, in vascular tissues of spontaneous hypertensive rats.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 405:47–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu K, Huang MJ, Ling S, Li YX, Cao XY,
Chen YF, Lei JM, Fu WZ and Tan BF: LncRNA CASC11 upregulation
promotes HDAC4 to alleviate oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-induced injury of cardiac microvascular endothelial
cells. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 39:758–768. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ravassa S, Lopez B, Treibel TA, José GS,
Losada-Fuentenebro B, Tapia L, Bayés-Genís A, Díez J and González
A: Cardiac Fibrosis in heart failure: Focus on non-invasive
diagnosis and emerging therapeutic strategies. Mol Aspects Med.
93:1011942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Gao F, Tang Y, Xiao J, Li C,
Ouyang Y and Hou Y: Valproic acid regulates Ang II-induced
pericyte-myofibroblast trans-differentiation via MAPK/ERK pathway.
Am J Transl Res. 10:1976–1989. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang LX, DeNicola M, Qin X, Du J, Ma J,
Zhao YT, Zhuang S, Liu PY, Wei L, Qin G, et al: Specific inhibition
of HDAC4 in cardiac progenitor cells enhances myocardial repairs.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 307:C358–C372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang LX, Du J, Zhao YT, Wang J, Zhang S,
Dubielecka PM, Wei L, Zhuang S, Qin G, Chin YE and Zhao TC:
Transgenic overexpression of active HDAC4 in the heart attenuates
cardiac function and exacerbates remodeling in infarcted
myocardium. J Appl Physiol (1985). 125:1968–1978. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jebessa ZH, Shanmukha KD, Dewenter M,
Lehmann LH, Xu C, Schreiter F, Siede D, Gong XM, Worst BC, Federico
G, et al: The lipid droplet-associated protein ABHD5 protects the
heart through proteolysis of HDAC4. Nat Metab. 1:1157–1167. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lehmann LH, Jebessa ZH, Kreusser MM,
Horsch A, He T, Kronlage M, Dewenter M, Sramek V, Oehl U,
Krebs-Haupenthal J, et al: A proteolytic fragment of histone
deacetylase 4 protects the heart from failure by regulating the
hexosamine biosynthetic pathway. Nat Med. 24:62–72. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhan J, Wang J, Liang Y, Wang L, Huang L,
Liu S, Zeng X, Zeng E and Wang H: Apoptosis dysfunction:
Unravelling the interplay between ZBP1 activation and viral
invasion in innate immune responses. Cell Commun Signal.
22:1492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Emdad L, Bhoopathi P, Talukdar S, Pradhan
AK, Sarkar D, Wang XY, Das SK and Fisher PB: Recent insights into
apoptosis and toxic autophagy: The roles of MDA-7/IL-24, a
multidimensional anti-cancer therapeutic. Semin Cancer Biol.
66:140–154. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Zou G, Zhong W, Wu F, Wang X and Liu L:
Catalpol attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy via Neat1/miR-140-5p/HDAC4 axis. Biochimie.
165:90–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang L, Wang H, Zhao Y, Wang J,
Dubielecka PM, Zhuang S, Qin G, Chin YE, Kao RL and Zhao TC:
Myocyte-specific overexpressing HDAC4 promotes myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med. 24:372018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu X, Liu Y, Mo S, Wei W, Ye Z and Su Q:
LncRNA TUG1 competitively binds to miR-340 to accelerate myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 35:e211632021.
|
|
36
|
Zhang F, Cheng N, Du J, Zhang H and Zhang
C: MicroRNA-200b-3p promotes endothelial cell apoptosis by
targeting HDAC4 in atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
21:1722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bazgir F, Nau J, Nakhaei-Rad S, Amin E,
Wolf MJ, Saucerman JJ, Lorenz K and Ahmadian MR: The
microenvironment of the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy. Cells.
12:17802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ago T, Liu T, Zhai P, Chen W, Li H,
Molkentin JD, Vatner SF and Sadoshima J: A redox-dependent pathway
for regulating class II HDACs and cardiac hypertrophy. Cell.
133:978–993. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Backs J, Song K, Bezprozvannaya S, Chang S
and Olson EN: CaM kinase II selectively signals to histone
deacetylase 4 during cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Clin Invest.
116:1853–1864. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fujioka R, Yamamoto T, Maruta A, Nakamura
Y, Tominaga N, Inamitsu M, Oda T, Kobayashi S and Yano M: Herpud1
modulates hypertrophic signals independently of calmodulin nuclear
translocation in rat myocardium-derived H9C2 cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 652:61–67. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zheng L, Wang J, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Geng J,
Cao L, Zhao X, Geng J, Du X, Hu Y and Cong H: Angiotensin II
mediates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in atrial cardiomyopathy via
epigenetic transcriptional regulation. Comput Math Methods Med.
2022:63121002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao D, Zhong G, Li J, Pan J, Zhao Y, Song
H, Sun W, Jin X, Li Y, Du R, et al: Targeting E3 ubiquitin ligase
WWP1 prevents cardiac hypertrophy through destabilizing DVL2 via
inhibition of K27-linked ubiquitination. Circulation. 144:694–711.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li C, Cai X, Sun H, Bai T, Zheng X, Zhou
XW, Chen X, Gill DL, Li J and Tang XD: The deltaA isoform of
calmodulin kinase II mediates pathological cardiac hypertrophy by
interfering with the HDAC4-MEF2 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 409:125–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lairez O, Cognet T, Schaak S, Calise D,
Guilbeau-Frugier C, Parini A and Mialet-Perez J: Role of serotonin
5-HT2A receptors in the development of cardiac hypertrophy in
response to aortic constriction in mice. J Neural Transm (Vienna).
120:927–935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu MY, Yue LJ, Luo YC, Lu J, Wu GD, Sheng
SQ, Shi YQ and Dong ZX: SUMOylation of SIRT1 activating
PGC-1alpha/PPARalpha pathway mediates the protective effect of
LncRNA-MHRT in cardiac hypertrophy. Eur J Pharmacol.
930:1751552022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pedram A, Razandi M, Narayanan R, Dalton
JT, McKinsey TA and Levin ER: Estrogen regulates histone
deacetylases to prevent cardiac hypertrophy. Mol Biol Cell.
24:3805–3818. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Okabe K, Matsushima S, Ikeda S, Ikeda M,
Ishikita A, Tadokoro T, Enzan N, Yamamoto T, Sada M, Deguchi H, et
al: DPP (Dipeptidyl Peptidase)-4 inhibitor attenuates Ang II
(Angiotensin II)-induced cardiac hypertrophy via GLP (Glucagon-Like
Peptide)-1-dependent suppression of Nox (Nicotinamide Adenine
Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase) 4-HDAC (Histone Deacetylase) 4
pathway. Hypertension. 75:991–1001. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mhatre KN, Wakula P, Klein O, Bisping E,
Völkl J, Pieske B and Heinzel FR: Crosstalk between FGF23- and
angiotensin II-mediated Ca(2+) signaling in pathological cardiac
hypertrophy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 75:4403–4416. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fan J, Fan W, Lei J, Zhou Y, Xu H, Kapoor
I, Zhu G and Wang J: Galectin-1 attenuates cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy through splice-variant specific modulation of
CaV1.2 calcium channel. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1865:218–229. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Matsushima S, Kuroda J, Ago T, Zhai P,
Park JY, Xie LH, Tian B and Sadoshima J: Increased oxidative stress
in the nucleus caused by Nox4 mediates oxidation of HDAC4 and
cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 112:651–663. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Zhou P, Zhao XN, Ma YY, Tang TJ, Wang SS,
Wang L and Huang J: Virtual screening analysis of natural
flavonoids as trimethylamine (TMA)-lyase inhibitors for coronary
heart disease. J Food Biochem. 46:e143762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shaya GE, Leucker TM, Jones SR, Martin SS
and Toth PP: Coronary heart disease risk: Low-density lipoprotein
and beyond. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 32:181–194. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang Y, Zhang J, Wang Z, Wang C and Ma D:
Endothelial-cell-mediated mechanism of coronary microvascular
dysfunction leading to heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction. Heart Fail Rev. 28:169–178. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Yan P, Sun C, Ma J, Jin Z, Guo R and Yang
B: MicroRNA-128 confers protection against cardiac microvascular
endothelial cell injury in coronary heart disease via negative
regulation of IRS1. J Cell Physiol. 234:13452–13463. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang X, Zhou H and Chang X: Involvement
of mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy in diabetic endothelial
dysfunction and cardiac microvascular injury. Arch Toxicol.
97:3023–3035. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Haqqani HM and Kalman JM: Aging and
sinoatrial node dysfunction: Musings on the not-so-funny side.
Circulation. 115:1178–1179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mesquita T, Miguel-Dos-Santos R and
Cingolani E: Aging and sinus node dysfunction: Mechanisms and
future directions. Clin Sci (Lond). 139:577–593. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang H, Li L, Hao M, Chen K, Lu Y, Qi J,
Chen W, Ren L, Cai X, Chen C, et al: Yixin-Fumai granules improve
sick sinus syndrome in aging mice through Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway: A new
target for sick sinus syndrome. J Ethnopharmacol. 277:1142542021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chang X, Zhou S, Liu J, Wang Y, Guan X, Wu
Q, Zhang Q, Liu Z and Liu R: Zishen Tongyang Huoxue decoction
(TYHX) alleviates sinoatrial node cell ischemia/reperfusion injury
by directing mitochondrial quality control via the VDAC1-β-tubulin
signaling axis. J Ethnopharmacol. 320:1173712024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Chang X, Li Y, Liu J, Wang Y, Guan X, Wu
Q, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Chen Y, Huang Y and Liu R: β-tubulin
contributes to Tongyang Huoxue decoction-induced protection against
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury of sinoatrial node cells
through SIRT1-mediated regulation of mitochondrial quality
surveillance. Phytomedicine. 108:1545022023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yang B, Huang Y, Zhang H, Huang Y, Zhou
HJ, Young L, Xiao H and Min W: Mitochondrial thioredoxin-2
maintains HCN4 expression and prevents oxidative stress-mediated
sick sinus syndrome. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 138:291–303. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Chen L, Mao LS, Xue JY, Jian YH, Deng ZW,
Mazhar M, Zou Y, Liu P, Chen MT, Luo G and Liu MN: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: The balance mechanism between
mitophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome. Life Sci. 355:1229982024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chang X, Zhou S, Liu J, Wang Y, Guan X, Wu
Q, Liu Z and Liu R: Zishenhuoxue decoction-induced myocardial
protection against ischemic injury through TMBIM6-VDAC1-mediated
regulation of calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial quality
surveillance. Phytomedicine. 132:1553312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chang X, Liu R, Li R, Peng Y, Zhu P and
Zhou H: Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial quality control in
ischemic cardiomyopathy. Int J Biol Sci. 19:426–448. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang J, Zhuang H, Jia L, He X, Zheng S, Ji
K, Xie K, Ying T, Zhang Y, Li C and Chang X: Nuclear receptor
subfamily 4 group A member 1 promotes myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury through inducing mitochondrial fission
factor-mediated mitochondrial fragmentation and inhibiting FUN14
domain containing 1-depedent mitophagy. Int J Biol Sci.
20:4458–4475. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Pu X, Zhang Q, Liu J, Wang Y, Guan X, Wu
Q, Liu Z, Liu R and Chang X: Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates heart
failure through DUSP-1-TMBIM-6-mediated mitochondrial quality
control and gut flora interactions. Phytomedicine. 132:1558802024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhao YT, Wang H, Zhang S, Du J, Zhuang S
and Zhao TC: Irisin ameliorates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced
injury through modulation of histone deacetylase 4. PLoS One.
11:e01661822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lee SY and Pearce EN: Hyperthyroidism: A
review. JAMA. 330:1472–1483. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kim HJ and McLeod DSA: Subclinical
hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular disease. Thyroid. 34:1335–1345.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Nie D, Xia C, Wang Z, Ding P, Meng Y, Liu
J, Li T, Gan T, Xuan B, Huang Y, et al: CaMKII inhibition protects
against hyperthyroid arrhythmias and adverse myocardial remodeling.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 615:136–142. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Diniz GP, Lino CA, Moreno CR, Senger N and
Barreto-Chaves MLM: MicroRNA-1 overexpression blunts cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy elicited by thyroid hormone. J Cell Physiol.
232:3360–3368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Huang ZP, Chen J, Seok HY, Zhang Z,
Kataoka M, Hu X and Wang DZ: MicroRNA-22 regulates cardiac
hypertrophy and remodeling in response to stress. Circ Res.
112:1234–1243. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang W, Lin J, Zhou J, Zheng Y, Jiang S,
He S and Li D: Innate lymphoid cells and myocardial infarction.
Front Immunol. 12:7582722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Turkieh A, El Masri Y, Pinet F and
Dubois-Deruy E: Mitophagy regulation following myocardial
infarction. Cells. 11:1992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Asensio-Lopez MC, Lax A, Del Palacio MJ,
Sassi Y, Hajjar RJ, Januzzi JL, Bayes-Genis A and Pascual-Figal DA:
Yin-Yang 1 transcription factor modulates ST2 expression during
adverse cardiac remodeling post-myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 130:216–233. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Lv F, Xie L, Li L and Lin J: LMK235
ameliorates inflammation and fibrosis after myocardial infarction
by inhibiting LSD1-related pathway. Sci Rep. 14:234502024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li L, Fu W, Gong X, Chen Z, Tang L, Yang
D, Liao Q, Xia X, Wu H, Liu C, et al: The role of G protein-coupled
receptor kinase 4 in cardiomyocyte injury after myocardial
infarction. Eur Heart J. 42:1415–1430. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
78
|
Zhao J, Li L, Wang X and Shen J: KN-93
promotes HDAC4 nucleus translocation to promote fatty acid
oxidation in myocardial infarction. Exp Cell Res. 438:1140502024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hermann DM, Xin W, Bahr M, Giebel B and
Doeppner TR: Emerging roles of extracellular vesicle-associated
non-coding RNAs in hypoxia: Insights from cancer, myocardial
infarction and ischemic stroke. Theranostics. 12:5776–5802. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Li Y, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Li R, Cheng Y,
Shang B, Han Y, Liu B and Xie X: Histone deacetylase 1 inhibition
protects against hypoxia-induced swelling in H9c2 cardiomyocytes
through regulating cell stiffness. Circ J. 82:192–202. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Savarese G, Becher PM, Lund LH, Seferovic
P, Rosano GMC and Coats AJS: Global burden of heart failure: A
comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res.
118:3272–3287. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Ljubojevic-Holzer S, Herren AW, Djalinac
N, Voglhuber J, Morotti S, Holzer M, Wood BM, Abdellatif M, Matzer
I, Sacherer M, et al: CaMKIIdeltaC drives early adaptive
Ca2+ change and late eccentric cardiac hypertrophy. Circ
Res. 127:1159–1178. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lkhagva B, Lin YK, Kao YH, Chazo TF, Chung
CC, Chen SA and Chen YJ: Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor
modulates cardiac peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and
inflammatory cytokines in heart failure. Pharmacology. 96:184–191.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Calalb MB, McKinsey TA, Newkirk S, Huynh
K, Sucharov CC and Bristow MR: Increased phosphorylation-dependent
nuclear export of class II histone deacetylases in failing human
heart. Clin Transl Sci. 2:325–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Jiang H, Jia D, Zhang B, Yang W, Dong Z,
Sun X, Cui X, Ma L, Wu J, Hu K, et al: Exercise improves cardiac
function and glucose metabolism in mice with experimental
myocardial infarction through inhibiting HDAC4 and upregulating
GLUT1 expression. Basic Res Cardiol. 115:282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Dzau VJ and Hodgkinson CP: Precision
hypertension. Hypertension. 81:702–708. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Kanbay M, Copur S, Tanriover C, Ucku D and
Laffin L: Future treatments in hypertension: Can we meet the unmet
needs of patients? Eur J Intern Med. 115:18–28. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Laurent S, Alivon M, Beaussier H and
Boutouyrie P: Aortic stiffness as a tissue biomarker for predicting
future cardiovascular events in asymptomatic hypertensive subjects.
Ann Med. 44(Suppl 1): S93–S97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Usui T, Okada M, Mizuno W, Oda M, Ide N,
Morita T, Hara Y and Yamawaki H: HDAC4 mediates development of
hypertension via vascular inflammation in spontaneous hypertensive
rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302:H1894–H1904. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kim GR, Cho SN, Kim HS, Yu SY, Choi SY,
Ryu Y, Lin MQ, Jin L, Kee HJ and Jeong MH: Histone deacetylase and
GATA-binding factor 6 regulate arterial remodeling in angiotensin
II-induced hypertension. J Hypertens. 34:2206–2219. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Saigusa R, Winkels H and Ley K: T cell
subsets and functions in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol.
17:387–401. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chen F, Li J, Zheng T, Chen T and Yuan Z:
KLF7 alleviates atherosclerotic lesions and inhibits glucose
metabolic reprogramming in macrophages by regulating
HDAC4/miR-148b-3p/NCOR1. Gerontology. 68:1291–1310. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhu XX, Meng XY, Chen G, Sru JB, Fu X, Xu
AJ, Liu Y, Hou XH, Qiu HB, Sun QY, et al: Nesfatin-1 enhances
vascular smooth muscle calcification through facilitating BMP-2
osteogenic signaling. Cell Commun Signal. 22:4882024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhao X, Liu S, Wang X, Chen Y, Pang P,
Yang Q, Lin J, Deng S, Wu S, Fan G and Wang B: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: Clinical phenotype and practice. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13:10322682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ma X, Mei S, Wuyun Q, Zhou L, Sun D and
Yan J: Epigenetics in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Clin Epigenetics.
16:522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Kronlage M, Dewenter M, Grosso J, Fleming
T, Oehl U, Lehmann LH, Falcão-Pires I, Leite-Moreira AF, Volk N,
Gröne HJ, et al: O-GlcNAcylation of histone deacetylase 4 protects
the diabetic heart from failure. Circulation. 140:580–594. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Heymans S, Lakdawala NK, Tschope C and
Klingel K: Dilated cardiomyopathy: Causes, mechanisms, and current
and future treatment approaches. Lancet. 402:998–1011. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Castillero E, Ali ZA, Akashi H, Giangreco
N, Wang C, Stöhr EJ, Ji R, Zhang X, Kheysin N, Park JS, et al:
Structural and functional cardiac profile after prolonged duration
of mechanical unloading: Potential implications for myocardial
recovery. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 315:H1463–H1476. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lu D, Bao D, Dong W, Liu N, Zhang X, Gao
S, Ge W, Gao X and Zhang L: Dkk3 prevents familial dilated
cardiomyopathy development through Wnt pathway. Lab Invest.
96:239–248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Li T, Mu N, Yin Y, Yu L and Ma H:
Targeting AMP-activated protein kinase in aging-related
cardiovascular diseases. Aging Dis. 11:967–977. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Tyrrell DJ and Goldstein DR: Ageing and
atherosclerosis: Vascular intrinsic and extrinsic factors and
potential role of IL-6. Nat Rev Cardiol. 18:58–68. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Saravi SS and Feinberg MW: Can removal of
zombie cells revitalize the aging cardiovascular system? Eur Heart
J. 45:867–869. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Shabanian K, Shabanian T, Karsai G,
Pontiggia L, Paneni F, Ruschitzka F, Beer JH and Saravi SS: AQP1
differentially orchestrates endothelial cell senescence. Redox
Biol. 76:1033172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Bhatt DL, Lopes RD and Harrington RA:
Diagnosis and treatment of acute coronary syndromes: A review.
JAMA. 327:662–675. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Xu H, Zhang J, Jia H, Xing F and Cong H:
Serum histone deacetylase 4 longitudinal change for estimating
major adverse cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome
patients receiving percutaneous coronary intervention. Ir J Med
Sci. 192:2689–2696. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Kang Y, Kim J, Anderson JP, Wu J, Gleim
SR, Kundu RK, McLean DL, Kim JD, Park H, Jin S, et al: Apelin-APJ
signaling is a critical regulator of endothelial MEF2 activation in
cardiovascular development. Circ Res. 113:22–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Helmstadter KG, Ljubojevic-Holzer S, Wood
BM, Taheri KD, Sedej S, Erickson JR, Bossuyt J and Bers DM: CaMKII
and PKA-dependent phosphorylation co-regulate nuclear localization
of HDAC4 in adult cardiomyocytes. Basic Res Cardiol. 116:112021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Li Y, Yu J, Li R, Zhou H and Chang X: New
insights into the role of mitochondrial metabolic dysregulation and
immune infiltration in septic cardiomyopathy by integrated
bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 29:212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Chang X, Zhang Q, Huang Y, Liu J, Wang Y,
Guan X, Wu Q, Liu Z and Liu R: Quercetin inhibits necroptosis in
cardiomyocytes after ischemia-reperfusion via
DNA-PKcs-SIRT5-orchestrated mitochondrial quality control.
Phytother Res. 38:2496–2517. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang J, Zhuang H, Yang X, Guo Z, Zhou K,
Liu N, An Y, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Wang M, et al: Exploring the
mechanism of ferroptosis induction by sappanone A in cancer:
Insights into the mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by
NRF2/xCT/GPX4 axis. Int J Biol Sci. 20:5145–5161. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Pang B, Dong G, Pang T, Sun X, Liu X, Nie
Y and Chang X: Emerging insights into the pathogenesis and
therapeutic strategies for vascular endothelial injury-associated
diseases: Focus on mitochondrial dysfunction. Angiogenesis.
27:623–639. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Du J, Zhang L, Zhuang S, Qin GJ and Zhao
TC: HDAC4 degradation mediates HDAC inhibition-induced protective
effects against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. J Cell Physiol.
230:1321–1331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
113
|
Marek L, Hamacher A, Hansen FK, Kuna K,
Gohlke H, Kassack MU and Kurz T: Histone deacetylase (HDAC)
inhibitors with a novel connecting unit linker region reveal a
selectivity profile for HDAC4 and HDAC5 with improved activity
against chemoresistant cancer cells. J Med Chem. 56:427–436. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Chen M, Cheng H, Chen X, Gu J, Su W, Cai
G, Yan Y, Wang C, Xia X, Zhang K, et al: The activation of histone
deacetylases 4 prevented endothelial dysfunction: A crucial
mechanism of HuangqiGuizhiWuwu decoction in improving
microcirculation dysfunction in diabetes. J Ethnopharmacol.
307:1162402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Choi SY, Kee HJ, Sun S, Seok YM, Ryu Y,
Kim GR, Kee SJ, Pflieger M, Kurz T, Kassack MU and Jeong MH:
Histone deacetylase inhibitor LMK235 attenuates vascular
constriction and aortic remodelling in hypertension. J Cell Mol
Med. 23:2801–2812. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Lkhagva B, Chang SL, Chen YC, Kao YH, Lin
YK, Chiu CT, Chen SA and Chen YJ: Histone deacetylase inhibition
reduces pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis through calcium regulation.
Int J Cardiol. 177:982–989. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Chen Y, Yuan J, Jiang G, Zhu J, Zou Y and
Lv Q: Lercanidipine attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy by blocking calcineurin-NFAT3 and CaMKII-HDAC4
signaling. Mol Med Rep. 16:4545–4552. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wang S, Li J, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zheng X, Sun
X, Lei S, Kang Z, Chen X, Lei M, et al: Distinct roles of
calmodulin and Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in
isopreterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 526:960–966. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Sun H, Ling S, Zhao D, Li Y, Zhong G, Guo
M, Li Y, Yang L, Du J, Zhou Y, et al: Panax quinquefolium saponin
attenuates cardiac remodeling induced by simulated microgravity.
Phytomedicine. 56:83–93. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Liu F, Su H, Liu B, Mei Y, Ke Q, Sun X and
Tan W: STVNa attenuates isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy
response through the HDAC4 and Prdx2/ROS/Trx1 pathways. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:6822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Akbay B, Omarova Z, Trofimov A, Sailike B,
Karapina O, Molnár F and Tokay T: Double-Edge effects of leucine on
cancer cells. Biomolecules. 14:14012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Dulf PL, Coada CA, Florea A, Moldovan R,
Baldea I, Dulf DV, Blendea D and Filip AG: Mitigating
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through quercetin intervention:
An experimental study in rats. Antioxidants (Basel). 13:10682024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhang W, Zheng Y, Yan F, Dong M and Ren Y:
Research progress of quercetin in cardiovascular disease. Front
Cardiovasc Med. 10:12037132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Lin CY, Shibu MA, Wen R, Day CH, Chen RJ,
Kuo CH, Ho TJ, Viswanadha VP, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Leu(27)
IGF-II-induced hypertrophy in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts is ameliorated
by saffron by regulation of calcineurin/NFAT and CaMKIIδ signaling.
Environ Toxicol. 36:2475–2483. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Sehgel NL, Zhu Y, Sun Z, Trzeciakowski JP,
Hong Z, Hunter WC, Vatner DE, Meininger GA and Vatner SF: Increased
vascular smooth muscle cell stiffness: A novel mechanism for aortic
stiffness in hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
305:H1281–H1287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Choi SY, Kee HJ, Jin L, Ryu Y, Sun S, Kim
GR and Jeong MH: Inhibition of class IIa histone deacetylase
activity by gallic acid, sulforaphane, TMP269, and panobinostat.
Biomed Pharmacother. 101:145–154. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Xiang Z, Guan H, Zhao X, Xie Q, Xie Z, Cai
F, Dang R, Li M and Wang C: Dietary gallic acid as an antioxidant:
A review of its food industry applications, health benefits,
bioavailability, nano-delivery systems, and drug interactions. Food
Res Int. 180:1140682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Hadidi M, Linan-Atero R, Tarahi M,
Christodoulou MC and Aghababaei F: The potential health benefits of
gallic acid: Therapeutic and food applications. Antioxidants
(Basel). 13:10012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Ago T, Yang Y, Zhai P and Sadoshima J:
Nifedipine inhibits cardiac hypertrophy and left ventricular
dysfunction in response to pressure overload. J Cardiovasc Transl
Res. 3:304–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Guo YJ, Yao JJ, Guo ZZ, Ding M, Zhang KL,
Shen QH, Li Y, Yu SF, Wan T, Xu FP, et al: HBB contributes to
individualized aconitine-induced cardiotoxicity in mice via
interfering with ABHD5/AMPK/HDAC4 axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
45:1224–1236. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Tucker WJ, Fegers-Wustrow I, Halle M,
Haykowsky MJ, Chung EH and Kovacic JC: Exercise for primary and
secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: JACC focus seminar
1/4. J Am Coll Cardiol. 80:1091–1106. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Wang Y, Yuan J, Liu H, Chen J, Zou J, Zeng
X, Du L, Sun X, Xia Z, Geng Q, et al: Elevated meteorin-like
protein from high-intensity interval training improves heart
function via AMPK/HDAC4 pathway. Genes Dis. 11:1011002024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Chen Y, Liu J, Zhang Q, Chai L, Chen H, Li
D, Wang Y, Qiu Y, Shen N, Zhang J, et al: Activation of
CaMKII/HDAC4 by SDF1 contributes to pulmonary arterial hypertension
via stabilization Runx2. Eur J Pharmacol. 970:1764832024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Xiong C and Yang B: Revising the
hemodynamic criteria for pulmonary hypertension: A perspective from
China. J Transl Int Med. 11:1–3. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|