|
1
|
Saberi M, Zhang X and Mobasheri A:
Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction with small molecules in
intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Geroscience.
43:517–537. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang F, Cai F, Shi R, Wang XH and Wu XT:
Aging and age related stresses: A senescence mechanism of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
24:398–408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang Y, Cheng H, Wang T, Zhang K, Zhang Y
and Kang X: Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration:
Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif.
56:e134482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiang Q, Zhao Y and Li W: Identification
and validation of ferroptosis-related gene signature in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
14:10897962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yi J, Zhou Q, Huang J, Niu S, Ji G and
Zheng T: Lipid metabolism disorder promotes the development of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother.
166:1154012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koroth J, Buko EO, Abbott R, Johnson CP,
Ogle BM, Stone LS, Ellingson AM and Bradley EW: Macrophages and
intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 24:13672023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Samanta A, Lufkin T and Kraus P:
Intervertebral disc degeneration: Current therapeutic options and
challenges. Front Public Health. 11:11567492023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Silwal P, Nguyen-Thai AM, Mohammad HA,
Wang Y, Robbins PD, Lee JY and Vo NV: Cellular senescence in
intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: Molecular mechanisms
and potential therapeutic opportunities. Biomolecules. 13:6862023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang HS, Lin S and Yu HM: Exosome-mediated
repair of intervertebral disc degeneration: The potential role of
miRNAs. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 19:798–808. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sharma Y, Saini AK, Kashyap S, Chandan G,
Kaur N, Gupta VK, Thakur VK, Saini V and Saini RV: Host miRNA and
immune cell interactions: Relevance in nano-therapeutics for human
health. Immunol Res. 70:1–18. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schell SL and Rahman ZSM: miRNA-mediated
control of B cell responses in immunity and SLE. Front Immunol.
12:6837102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bronevetsky Y and Ansel KM: Regulation of
miRNA biogenesis and turnover in the immune system. Immunol Rev.
253:304–316. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wythe SE, Nicolaidou V and Horwood NJ:
Cells of the immune system orchestrate changes in bone cell
function. Calcif Tissue Int. 94:98–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sun K, Jiang J, Wang Y, Sun X, Zhu J, Xu
X, Sun J and Shi J: The role of nerve fibers and their
neurotransmitters in regulating intervertebral disc degeneration.
Ageing Res Rev. 81:1017332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu H, Li J, Fei Q and Jiang L:
Contribution of immune cells to intervertebral disc degeneration
and the potential of immunotherapy. Connect Tissue Res. 64:413–427.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song C, Zhou Y, Cheng K, Liu F, Cai W,
Zhou D, Chen R, Shi H, Fu Z, Chen J and Liu Z: Cellular
senescence-molecular mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration
from an immune perspective. Biomed Pharmacother. 162:1147112023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Role of
cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc
content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun Z, Liu ZH, Chen YF, Zhang YZ, Wan ZY,
Zhang WL, Che L, Liu X, Wang HQ and Luo ZJ: Molecular immunotherapy
might shed a light on the treatment strategies for disc
degeneration and herniation. Med Hypotheses. 81:477–480. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang T, He Z, Zhu Z, Wang F, Chen H, Zhang
F, Zhou J, Wang J, Li B, Liu X, et al: Identification of novel gene
signatures and immune cell infiltration in intervertebral disc
degeneration using bioinformatics analysis. Front Mol Biosci.
10:11697182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Sun Z, Wang H, Ning R,
Xu L, Zhao Y, Yang K, Xi X and Tian J: MAPK8 and CAPN1 as potential
biomarkers of intervertebral disc degeneration overlapping immune
infiltration, autophagy, and ceRNA. Front Immunol. 14:11887742023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen LG, Tubbs JD, Liu Z, Thach TQ and
Sham PC: Mendelian randomization: Causal inference leveraging
genetic data. Psychol Med. 54:1461–1474. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fang A, Zhao Y, Yang P, Zhang X and
Giovannucci EL: Vitamin D and human health: Evidence from Mendelian
randomization studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 39:467–490. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Swanson SA, Labrecque J and Hernán MA:
Causal null hypotheses of sustained treatment strategies: What can
be tested with an instrumental variable? Eur J Epidemiol.
33:723–728. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Evans DM and Davey Smith G: Mendelian
randomization: New applications in the coming age of
hypothesis-free causality. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 16:327–350.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang P, Li Z and Ye D: Single-cell RNA-seq
analysis reveals the Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway with
inflammation, apoptosis in nucleus pulposus degeneration. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 25:3212024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huan T, Rong J, Liu C, Zhang X, Tanriverdi
K, Joehanes R, Chen BH, Murabito JM, Yao C, Courchesne P, et al:
Genome-wide identification of microRNA expression quantitative
trait loci. Nat Commun. 6:66012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Orrù V, Steri M, Sidore C, Marongiu M,
Serra V, Olla S, Sole G, Lai S, Dei M, Mulas A, et al: Complex
genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform
therapy. Nat Genet. 52:1036–1045. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Burgess S and Thompson SG; CRP CHD
Genetics Collaboration: Avoiding bias from weak instruments in
Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol. 40:755–764. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bowden J, Del Greco MF, Minelli C, Zhao Q,
Lawlor DA, Sheehan NA, Thompson J and Davey Smith G: Improving the
accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: Moving
beyond the NOME assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 48:728–742. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Glickman ME, Rao SR and Schultz MR: False
discovery rate control is a recommended alternative to
Bonferroni-type adjustments in health studies. J Clin Epidemiol.
67:850–857. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dudbridge F: Polygenic Mendelian
randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 11:a0395862021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Greco MFD, Minelli C, Sheehan NA and
Thompson JR: Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation
studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat Med.
34:2926–2940. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fan C, Wang W, Yu Z, Wang J, Xu W, Ji Z,
He W, Hua D, Wang W, Yao L, et al: M1 macrophage-derived exosomes
promote intervertebral disc degeneration by enhancing nucleus
pulposus cell senescence through LCN2/NF-κB signaling axis. J
Nanobiotechnology. 22:3012024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lin Z, Xu G, Lu X, Liu S, Zou F, Ma X,
Jiang J, Wang H and Song J: Chondrocyte-targeted exosome-mediated
delivery of Nrf2 alleviates cartilaginous endplate degeneration by
modulating mitochondrial fission. J Nanobiotechnology. 22:2812024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dai J, Liu J, Shen Y, Zhang B, Li C and
Liu Z: Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress on autophagy and
apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral disc
degeneration and its related mechanisms. PeerJ. 12:e172122024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao W, Bao J, Zhang Y, He D, Zhang L,
Zhang J, Pan H and Wang D: Injectable kaempferol-loaded fibrin glue
regulates the metabolic balance and inhibits inflammation in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Sci Rep. 13:200012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen X, Zhang A, Zhao K, Gao H, Shi P,
Chen Y, Cheng Z, Zhou W and Zhang Y: The role of oxidative stress
in intervertebral disc degeneration: Mechanisms and therapeutic
implications. Ageing Res Rev. 98:1023232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guo W, Mu K, Geng JC, Xing HY, Dong Y, Liu
WD, Wang SC, Shi JX, Xing BR, Zhao JY and Li XM: ATF1 and
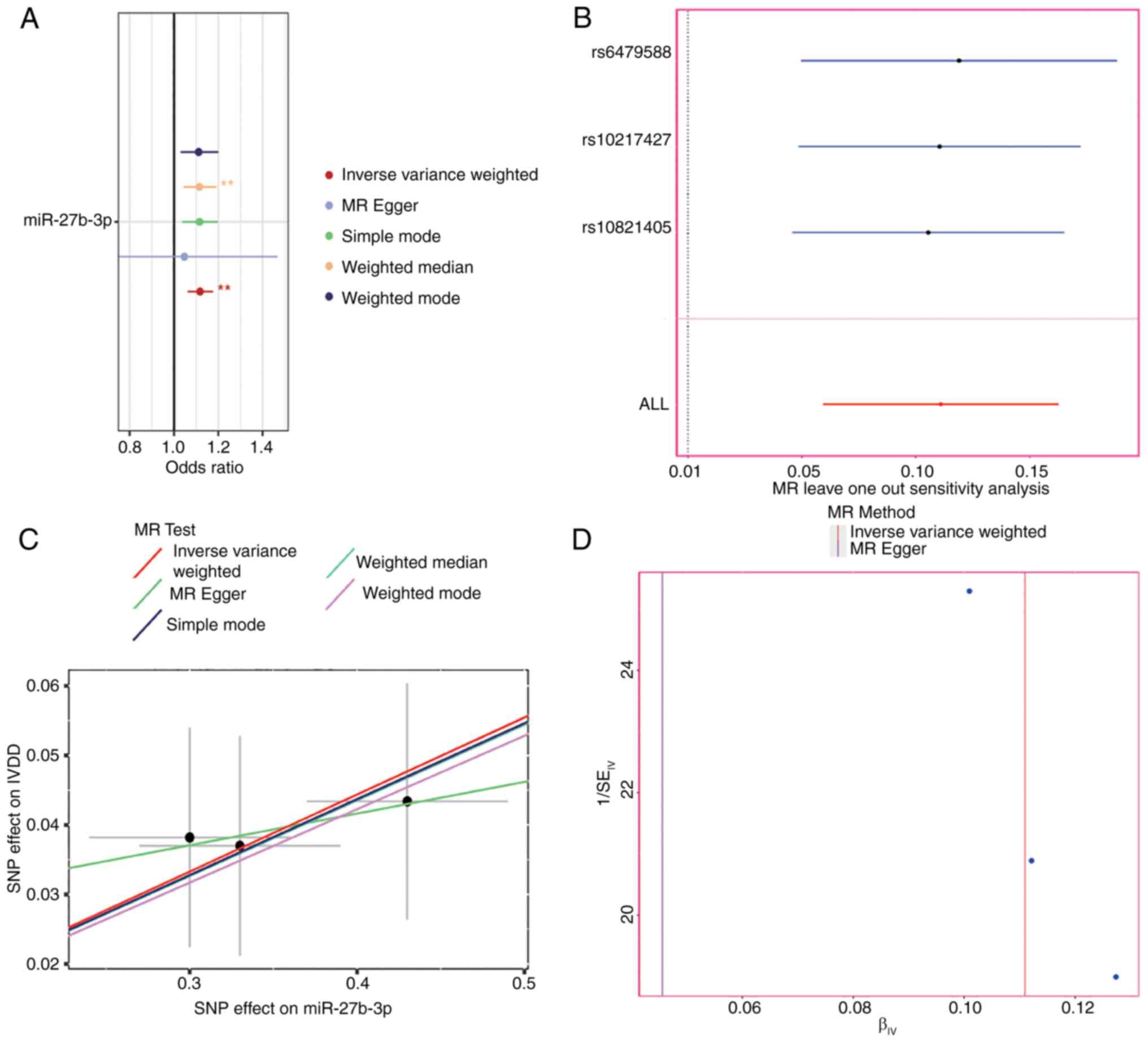
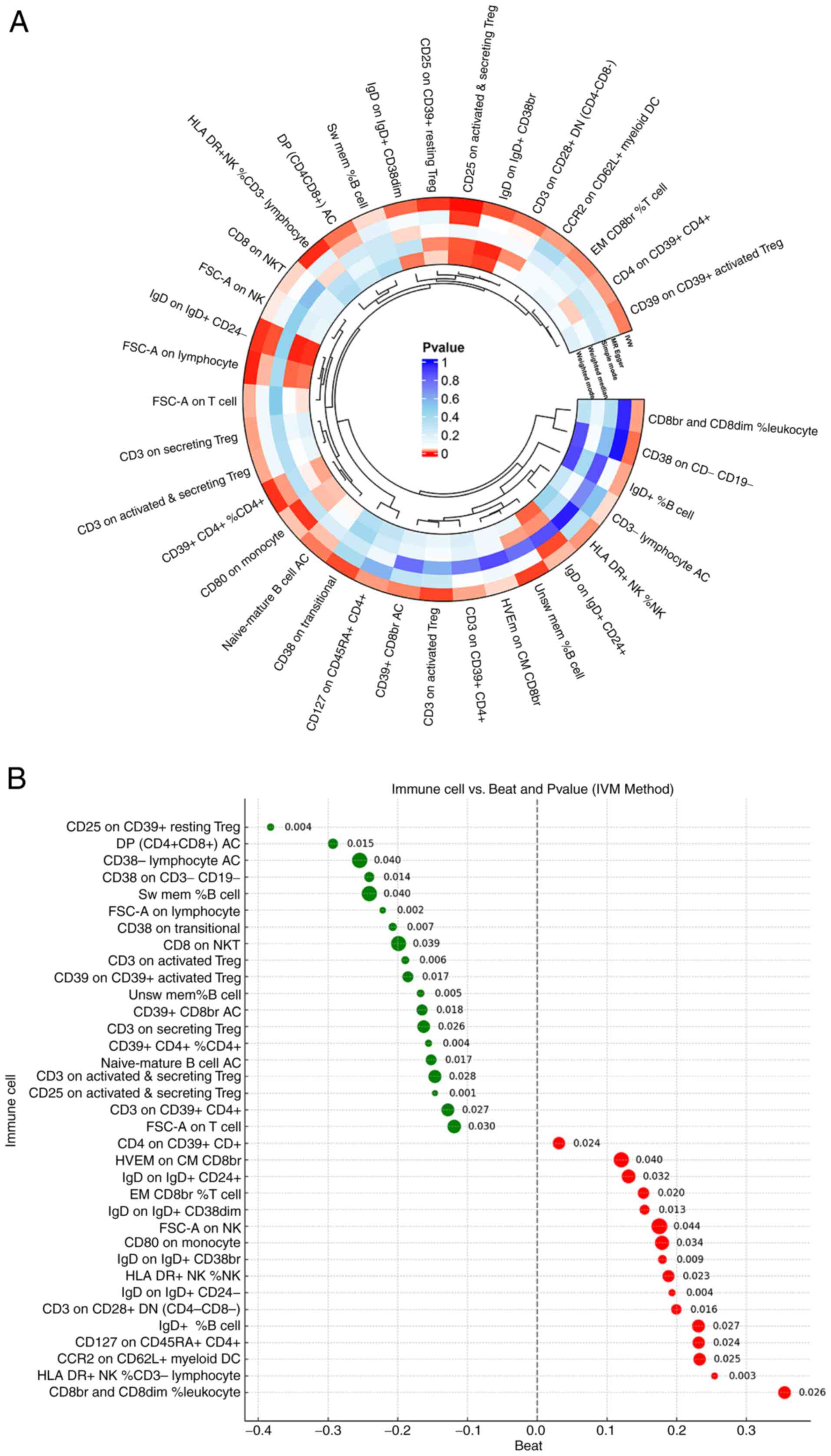
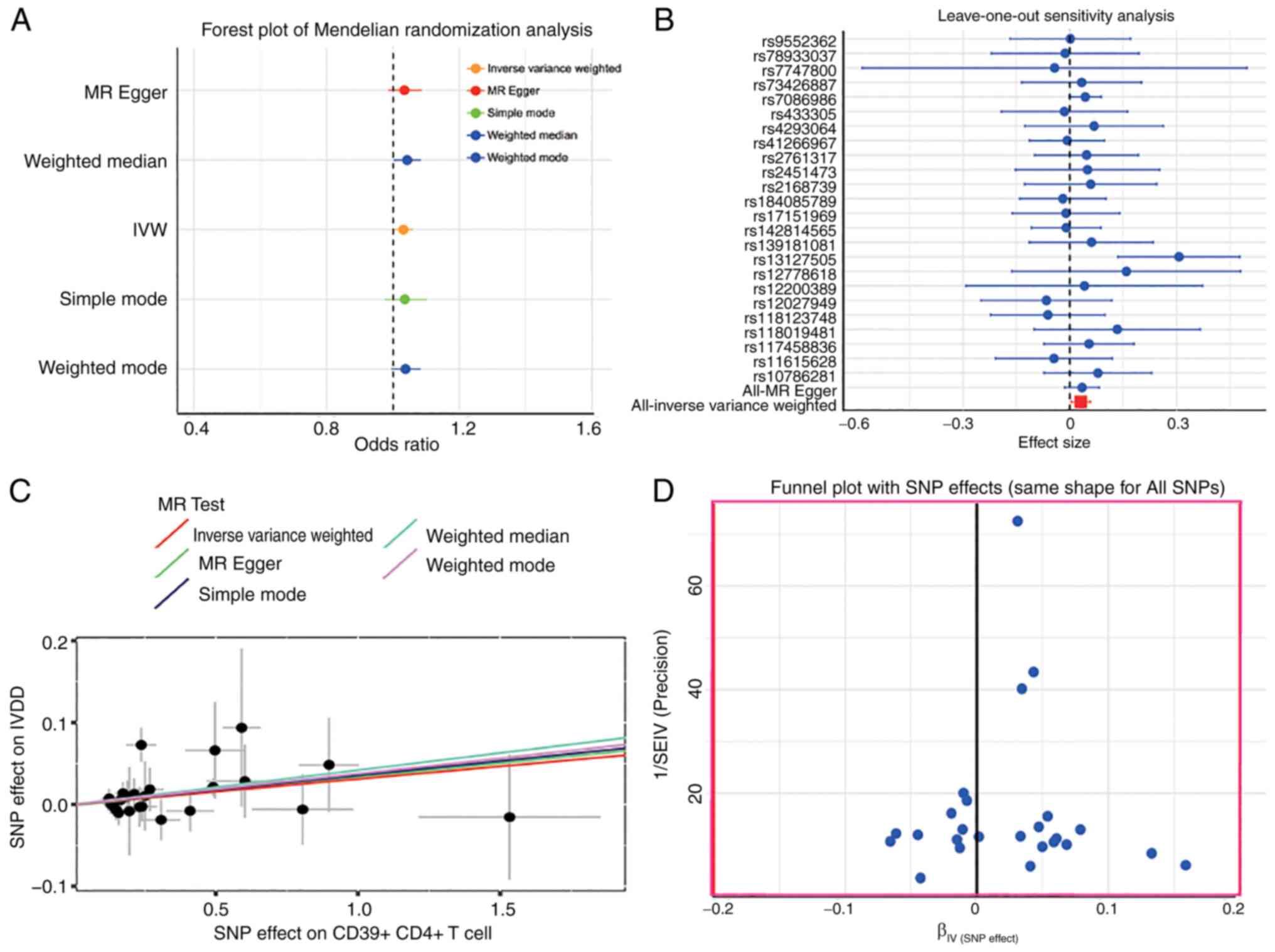
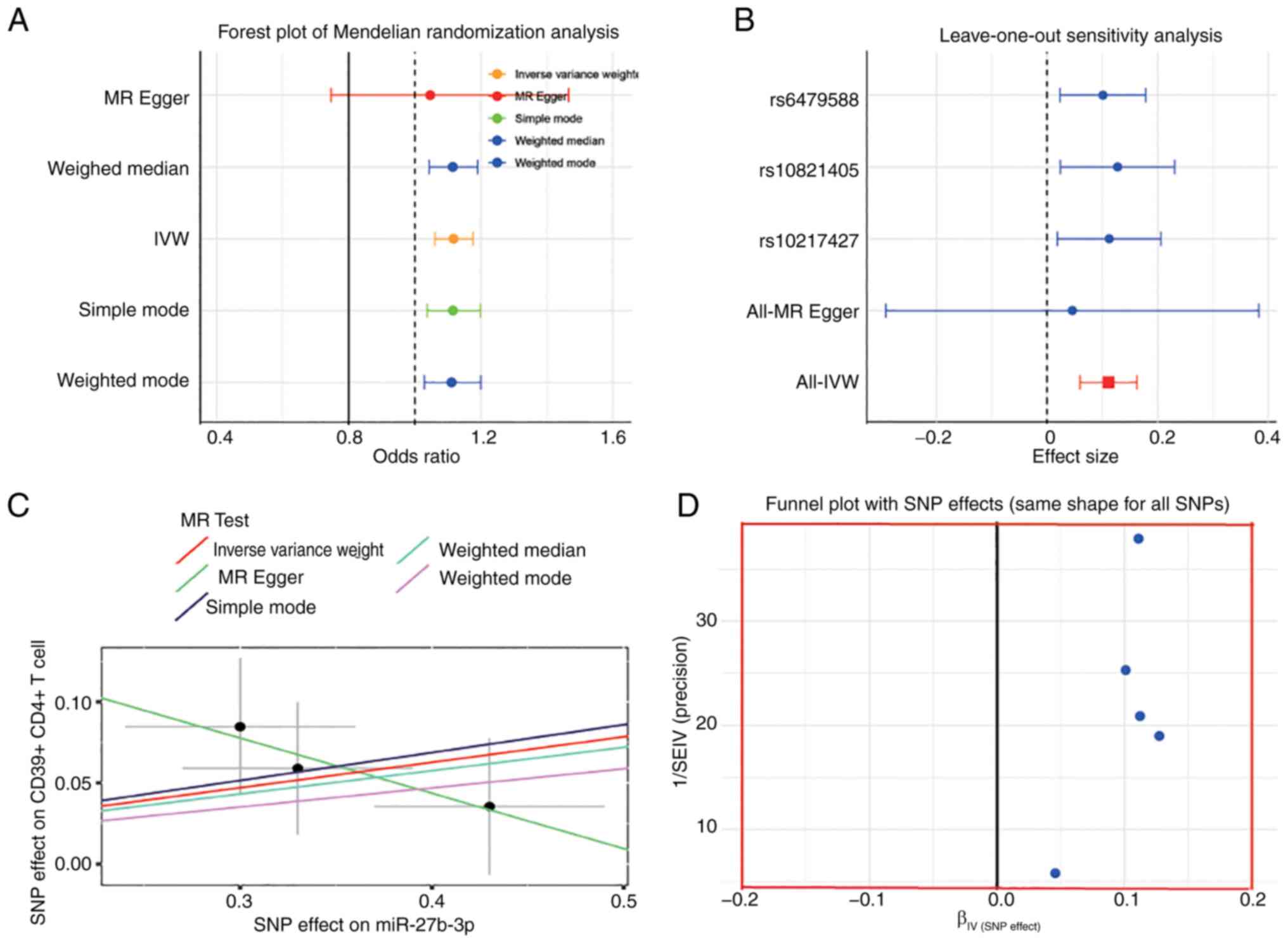
miR-27b-3p drive intervertebral disc degeneration through the
PPARG/NF-κB signaling axis. Commun Biol. 8:7512025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Rouas R, Merimi M, Najar M, El Zein N,
Fayyad-Kazan M, Berehab M, Agha D, Bron D, Burny A, Rachidi W, et
al: Human CD8+ CD25+ CD127low
regulatory T cells: microRNA signature and impact on TGF-β and
IL-10 expression. J Cell Physiol. 234:17459–17472. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Diener C, Keller A and Meese E: Emerging
concepts of miRNA therapeutics: From cells to clinic. Trends Genet.
38:613–626. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ferragut Cardoso AP, Banerjee M, Nail AN,
Lykoudi A and States JC: miRNA dysregulation is an emerging
modulator of genomic instability. Semin Cancer Biol. 76:120–131.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vafadar A, Shirazi-Tehrani E, Vosough P,
Khalili Alashti S, Kargar Jahromi H, Bagheri Lankarani K,
Savardashtaki A and Ehtiati S: Non-coding RNAs in celiac disease.
Clin Chim Acta. 576:1204172025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang Y, Kang J, Guo X, Zhu D, Liu M, Yang
L, Zhang G and Kang X: Intervertebral disc degeneration models for
pathophysiology and regenerative therapy-benefits and limitations.
J Invest Surg. 35:935–952. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hu A, Xing R, Jiang L, Li Z, Liu P, Wang
H, Li X and Dong J: Thermosensitive hydrogels loaded with
human-induced pluripotent stem cells overexpressing growth
differentiation factor-5 ameliorate intervertebral disc
degeneration in rats. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.
108:2005–2016. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol.
8:e10004122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Griffith JF, Wang YXJ, Antonio GE, Choi
KC, Yu A, Ahuja AT and Leung PC: Modified Pfirrmann grading system
for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
32:E708–E712. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Genedy HH, Humbert P, Laoulaou B, Le Moal
B, Fusellier M, Passirani C, Le Visage C, Guicheux J, Lepeltier É
and Clouet J: MicroRNA-targeting nanomedicines for the treatment of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
207:1152142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang Y, Deng M, Wu Y, Zheng C, Zhang F,
Guo C, Zhang B, Hu C, Kong Q and Wang Y: A multifunctional
mitochondria-protective gene delivery platform promote
intervertebral disc regeneration. Biomaterials. 317:1230672025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu YQ, Zhang ZH, Zheng YF and Feng SQ:
Dysregulated miR-133a mediates loss of type II collagen by directly
targeting matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) in human intervertebral
disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:E717–E724. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Li X, Xu M, Ding L and Tang J: MiR-27a: A
novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target in tumors. J
Cancer. 10:2836–2848. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang J, Cao Z, Yang G, You L, Zhang T and
Zhao Y: MicroRNA-27a (miR-27a) in solid tumors: A review based on
mechanisms and clinical observations. Front Oncol. 9:8932019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Su L, Li R, Zhang Z, Liu J, Du J and Wei
H: Identification of altered exosomal microRNAs and mRNAs in
Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Res Rev. 73:1014972022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Speiser DE, Chijioke O, Schaeuble K and
Münz C: CD4+ T cells in cancer. Nat Cancer. 4:317–329.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sun L, Su Y, Jiao A, Wang X and Zhang B: T
cells in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:2352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhu J, Yamane H and Paul WE:
Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*). Annu Rev
Immunol. 28:445–489. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Borst J, Ahrends T, Bąbała N, Melief CJM
and Kastenmüller W: CD4+ T cell help in cancer
immunology and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 18:635–647. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Thomas R, Qiao S and Yang X: Th17/Treg
imbalance: Implications in lung inflammatory diseases. Int J Mol
Sci. 24:48652023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sakaguchi S, Mikami N, Wing JB, Tanaka A,
Ichiyama K and Ohkura N: Regulatory T cells and human disease. Annu
Rev Immunol. 38:541–566. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Churov AV, Mamashov KY and Novitskaia AV:
Homeostasis and the functional roles of CD4+ Treg cells
in aging. Immunol Lett. 226:83–89. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wei B, Zhao Y, Li W, Zhang S, Yan M, Hu Z
and Gao B: Innovative immune mechanisms and antioxidative therapies
of intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
10:10238772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dou Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Sun X, Liu X, Li B
and Yang Q: Role of macrophage in intervertebral disc degeneration.
Bone Res. 13:152025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lee S and Lee W: A review of Mendelian
randomization: Assumptions, methods, and application to
obesity-related diseases. J Obes Metab Syndr. 34:14–26. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen B, Yan Y, Wang H and Xu J:
Association between genetically determined telomere length and
health-related outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
Mendelian randomization studies. Aging Cell. 22:e138742023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Ni F, Liu X and Wang S: Impact of negative
emotions and insomnia on sepsis: A mediation Mendelian
randomization study. Comput Biol Med. 180:1088582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|