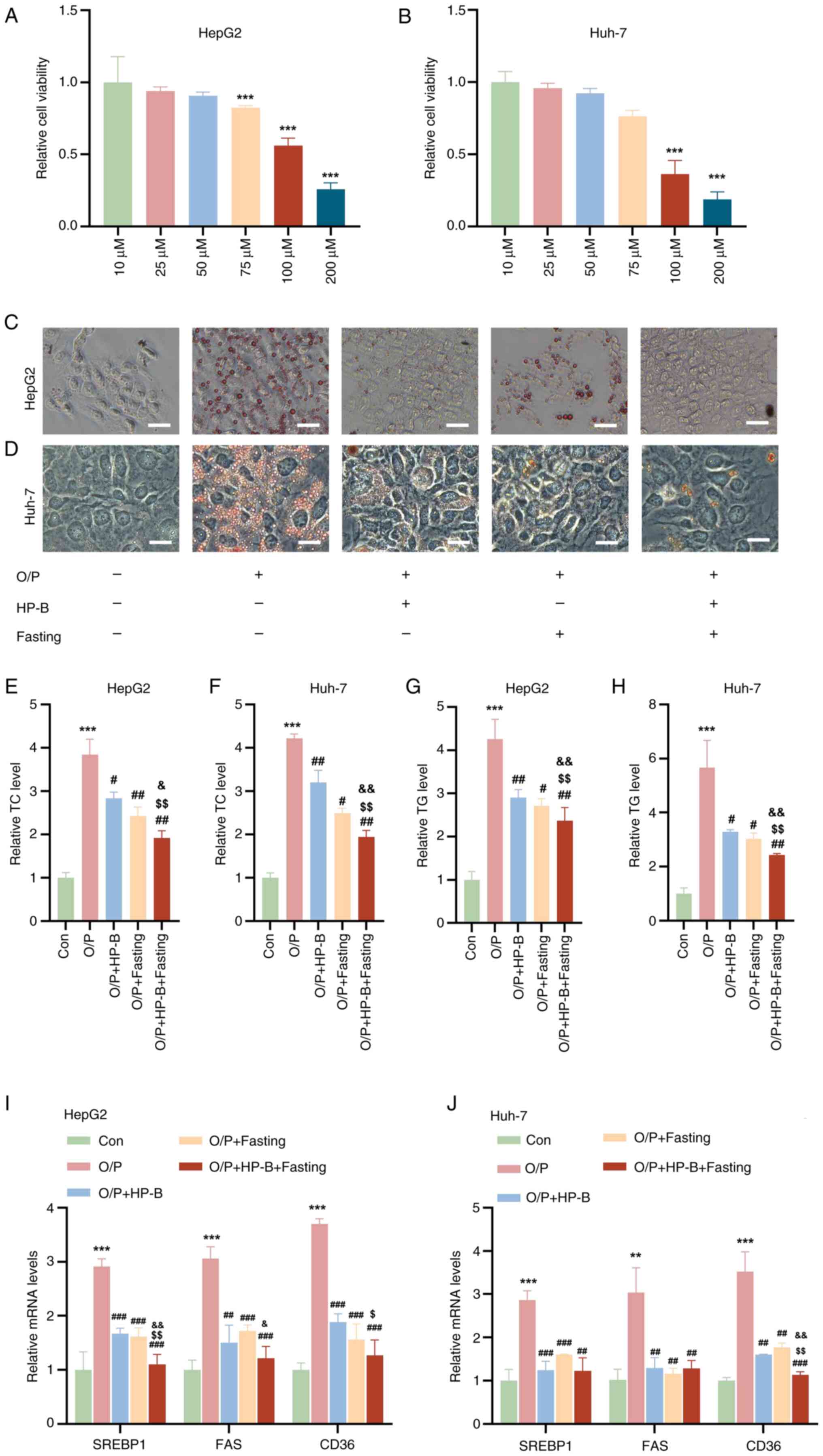
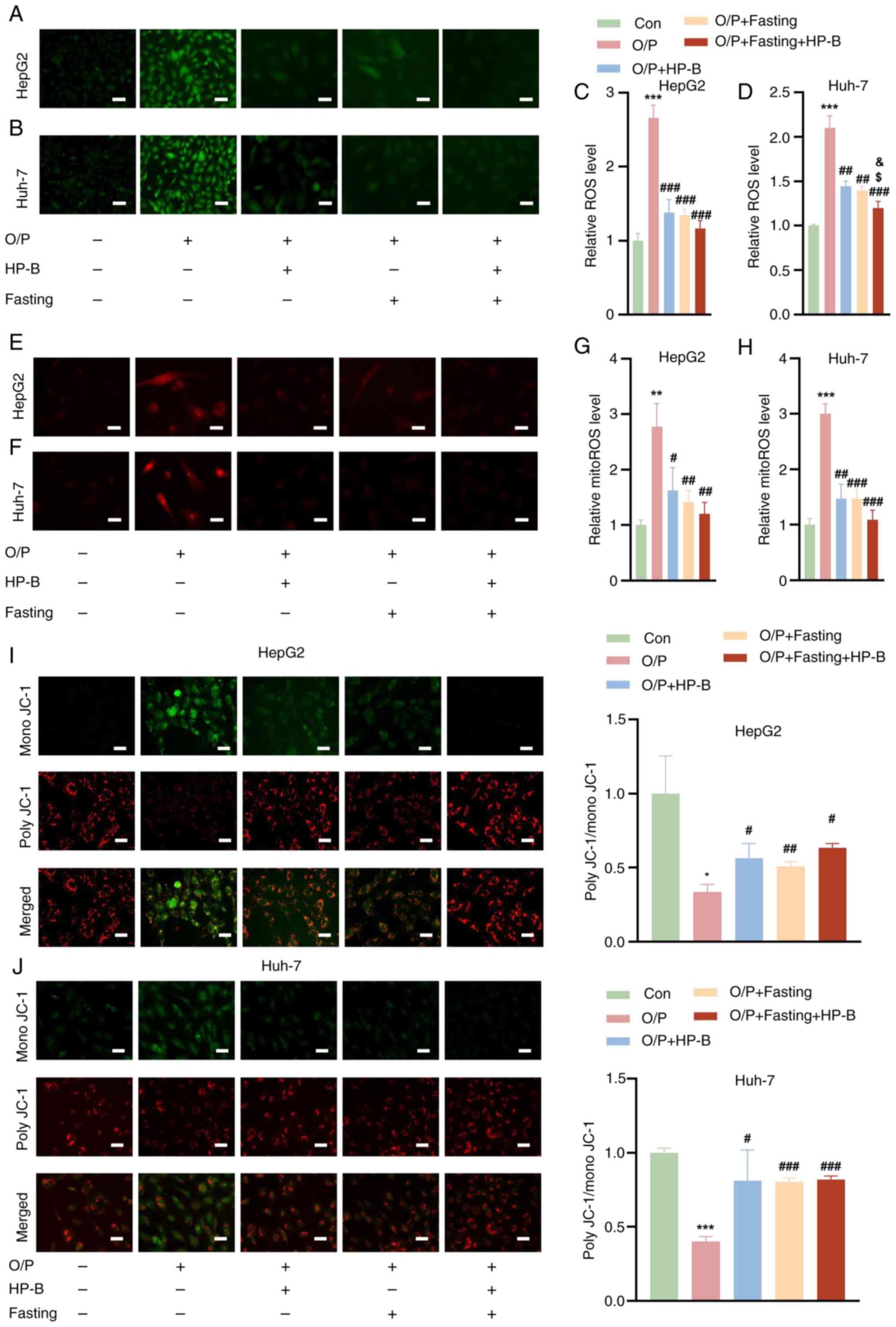
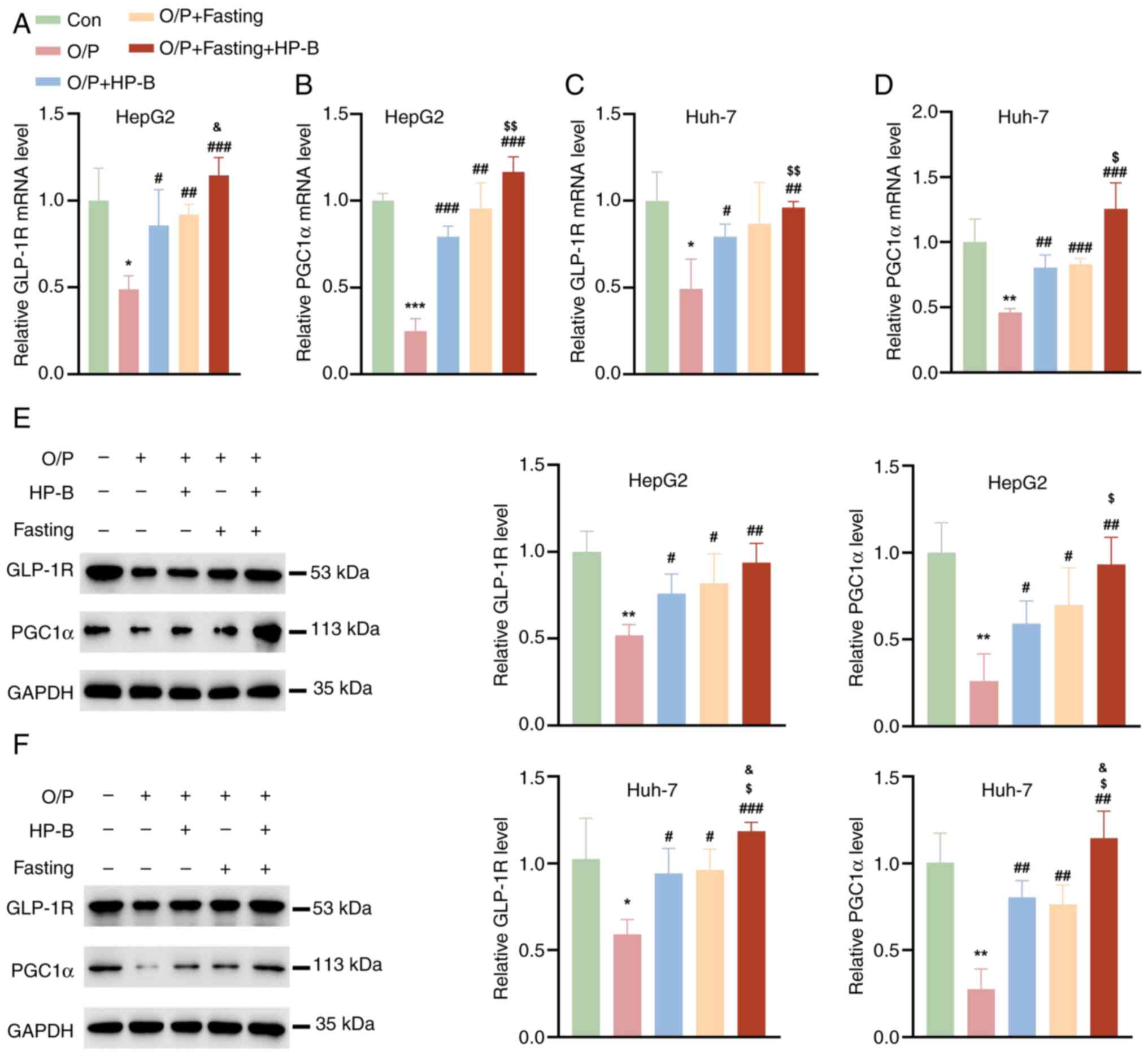
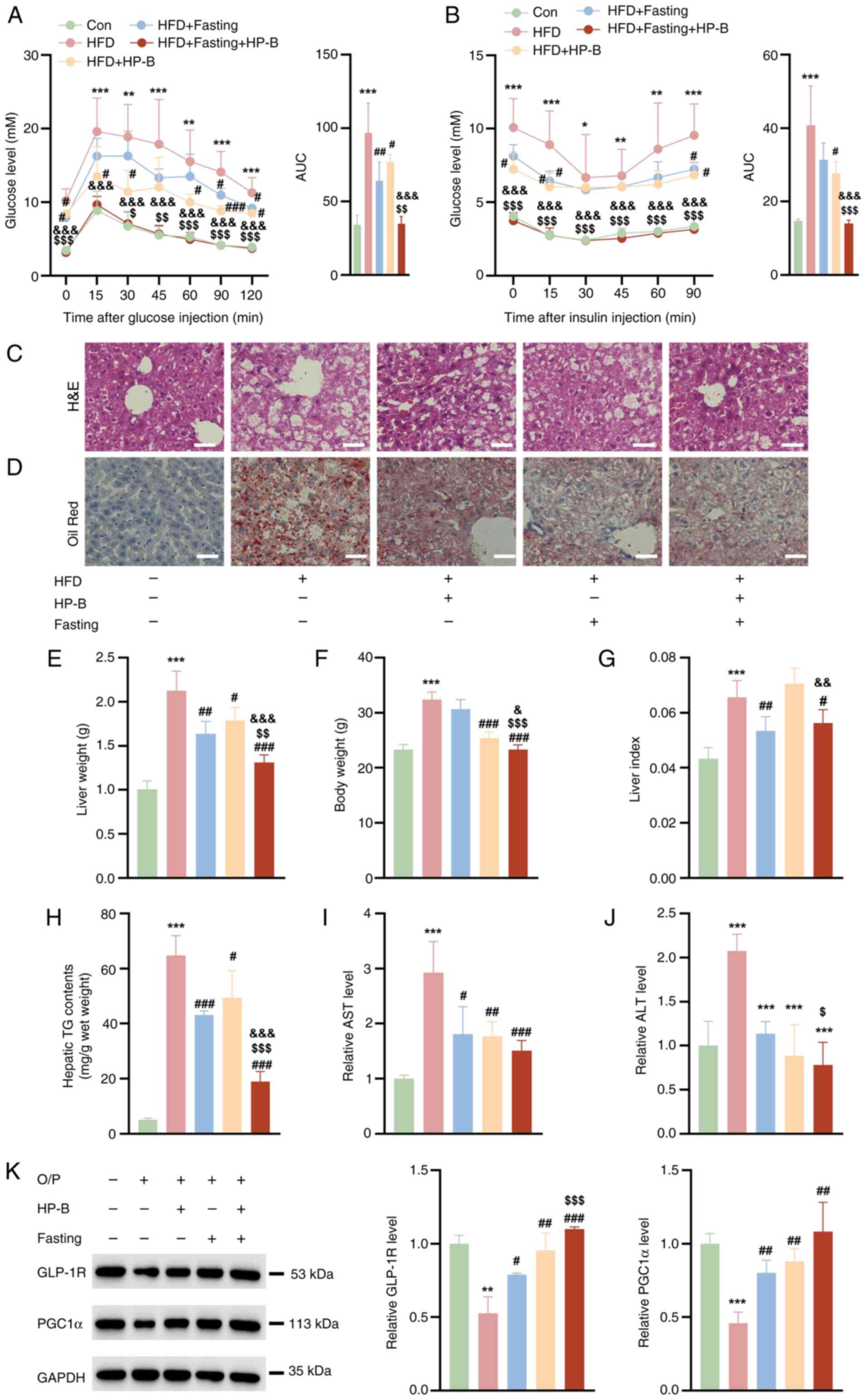
|
1
|
Marjot T, Tomlinson JW, Hodson L and Ray
DW: Timing of energy intake and the therapeutic potential of
intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating in NAFLD. Gut.
72:1607–1619. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vasim I, Majeed CN and DeBoer MD:
Intermittent fasting and metabolic health. Nutrients. 14:6312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patikorn C, Roubal K, Veettil SK, Chandran
V, Pham T, Lee YY, Giovannucci EL, Varady KA and Chaiyakunapruk N:
Intermittent fasting and obesity-related health outcomes: An
umbrella review of meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials.
JAMA Netw Open. 4:e21395582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gallage S, Ali A, Barragan Avila JE,
Seymen N, Ramadori P, Joerke V, Zizmare L, Aicher D, Gopalsamy IK,
Fong W, et al: A 5:2 intermittent fasting regimen ameliorates NASH
and fibrosis and blunts HCC development via hepatic PPARα and PCK1.
Cell Metab. 36:1371–1393.e7. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ezpeleta M, Gabel K, Cienfuegos S, Kalam
F, Lin S, Pavlou V, Song Z, Haus JM, Koppe S, Alexandria SJ, et al:
Effect of alternate day fasting combined with aerobic exercise on
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial.
Cell Metab. 35:56–70.e3. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Wang X, Wang J, Ying C, Xing Y, Su X and
Men K: Fenofibrate alleviates NAFLD by enhancing the PPARα/PGC-1α
signaling pathway coupling mitochondrial function. BMC Pharmacol
Toxicol. 25:72024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu L, Mo W, Feng J, Li J, Yu Q, Li S,
Zhang J, Chen K, Ji J, Dai W, et al: Astaxanthin attenuates hepatic
damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease by up-regulating the FGF21/PGC-1α pathway. Br J Pharmacol.
177:3760–3777. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Quan Y, Shou D, Yang S, Cheng J, Li Y,
Huang C, Chen H and Zhou Y: Mdivi1 ameliorates mitochondrial
dysfunction in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting JNK/MFF
signaling. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 38:2215–2227. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng D, Zhang M, Zheng Y, Wang M, Gao Y,
Wang X, Liu X, Lv W, Zeng X, Belosludtsev KN, et al:
α-Ketoglutarate prevents hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver
mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress by activating the
AMPK-pgc-1α/Nrf2 pathway. Redox Biol. 74:1032302024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhao Q, Liu J, Deng H, Ma R, Liao JY,
Liang H, Hu J, Li J, Guo Z, Cai J, et al: Targeting
mitochondria-located circRNA SCAR alleviates NASH via reducing mROS
output. Cell. 183:76–93.e22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang T, Xu Q, Cao Y, Zhang C, Chen S,
Zhang Y and Liang T: Luteolin ameliorates hepatic steatosis and
enhances mitochondrial biogenesis via AMPK/PGC-1α pathway in
western diet-fed mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 69:259–267.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang Y, Qiu W, Xiao J, Sun J, Ren X and
Jiang L: Dihydromyricetin ameliorates hepatic steatosis and insulin
resistance via AMPK/PGC-1α and PPARα-mediated autophagy pathway. J
Transl Med. 22:3092024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Meng D, Yin G, Chen S, Zhang X, Yu W, Wang
L, Liu H, Jiang W, Sun Y and Zhang F: Diosgenin attenuates
nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis through the hepatic SIRT1/PGC-1α
pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 977:1767372024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liao HJ and Tzen JTC: Investigating
potential GLP-1 receptor agonists in cyclopeptides from
Pseudostellaria heterophylla, Linum usitatissimum, and Drymaria
diandra, and peptides derived from heterophyllin B for the
treatment of type 2 diabetes: An in silico study. Metabolites.
12:5492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Z, Zhang C, Li X, Ma Z, Ge Y, Qian Z
and Song C: Heterophyllin B, a cyclopeptide from Pseudostellaria
heterophylla, enhances cognitive function via neurite outgrowth and
synaptic plasticity. Phytother Res. 35:5318–5329. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deng J, Feng X, Zhou L, He C, Li H, Xia J,
Ge Y, Zhao Y, Song C, Chen L and Yang Z: Heterophyllin B, a
cyclopeptide from Pseudostellaria heterophylla, improves memory via
immunomodulation and neurite regeneration in i.c.v.Aβ-induced mice.
Food Res Int. 158:1115762022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hutchison AL, Tavaglione F, Romeo S and
Charlton M: Endocrine aspects of metabolic dysfunction-associated
steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Beyond insulin resistance. J
Hepatol. 79:1524–1541. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xia M, Wu Z, Wang J, Buist-Homan M and
Moshage H: The coumarin-derivative esculetin protects against
lipotoxicity in primary rat hepatocytes via attenuating
JNK-mediated oxidative stress and attenuates free fatty
acid-induced lipid accumulation. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:19222023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang H, Wang W, Hu X, Wang Z, Lou J, Cui
P, Zhao X, Wang Y, Chen X and Lu S: Heterophyllin B enhances
transcription factor EB-mediated autophagy and alleviates
pyroptosis and oxidative stress after spinal cord injury. Int J
Biol Sci. 20:5415–5435. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Holmer M, Lindqvist C, Petersson S,
Moshtaghi-Svensson J, Tillander V, Brismar TB, Hagström H and Stål
P: Treatment of NAFLD with intermittent calorie restriction or
low-carb high-fat diet-a randomised controlled trial. JHEP Rep.
3:1002562021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mao T, Sun Y, Xu X and He K: Overview and
prospect of NAFLD: Significant roles of nutrients and dietary
patterns in its progression or prevention. Hepatol Commun.
7:e02342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Baggio LL and Drucker DJ: Glucagon-like
peptide-1 receptor co-agonists for treating metabolic disease. Mol
Metab. 46:1010902021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Boland ML, Laker RC, Mather K, Nawrocki A,
Oldham S, Boland BB, Lewis H, Conway J, Naylor J, Guionaud S, et
al: Resolution of NASH and hepatic fibrosis by the GLP-1R/GcgR
dual-agonist Cotadutide via modulating mitochondrial function and
lipogenesis. Nat Metab. 2:413–431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei Y, Yin L, Zhang J, Tang J, Yu X, Wu Z
and Gao Y: Heterophyllin B inhibits the malignant phenotypes of
gastric cancer cells via CXCR4. Hum Cell. 36:676–688. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Han W, Li Y, Cheng J, Zhang J, Chen D,
Fang M, Xiang G, Wu Y, Zhang H, Xu K, et al: Sitagliptin improves
functional recovery via GLP-1R-induced anti-apoptosis and
facilitation of axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury. J
Cell Mol Med. 24:8687–8702. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amorim M, Martins B and Fernandes R:
Immune fingerprint in diabetes: Ocular surface and retinal
inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 24:98212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roberts LD, Hornsby AK, Thomas A, Sassi M,
Kinzett A, Hsiao N, David BR, Good M, Wells T and Davies JS: The
5:2 diet does not increase adult hippocampal neurogenesis or
enhance spatial memory in mice. EMBO Rep. 24:e572692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|