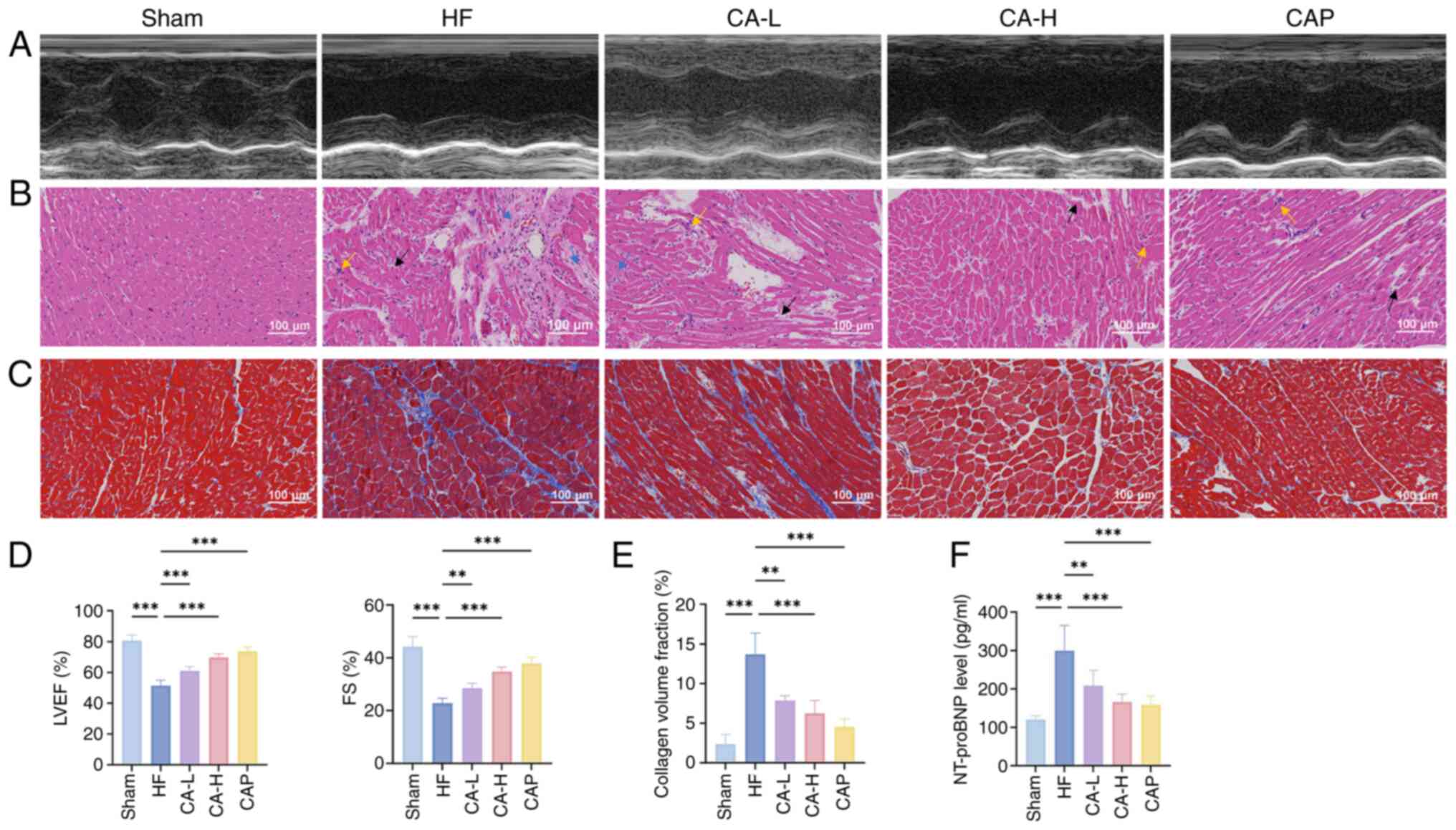
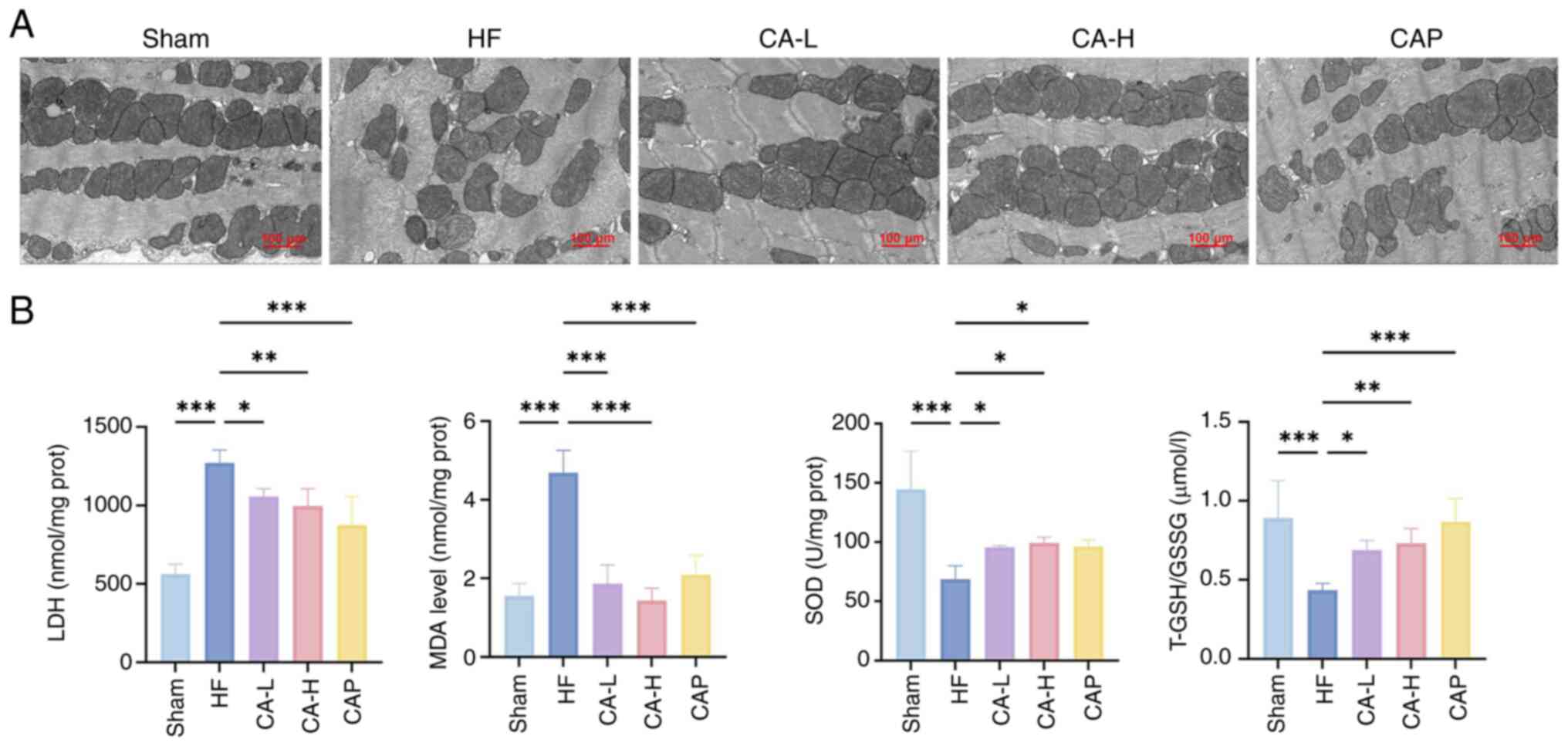
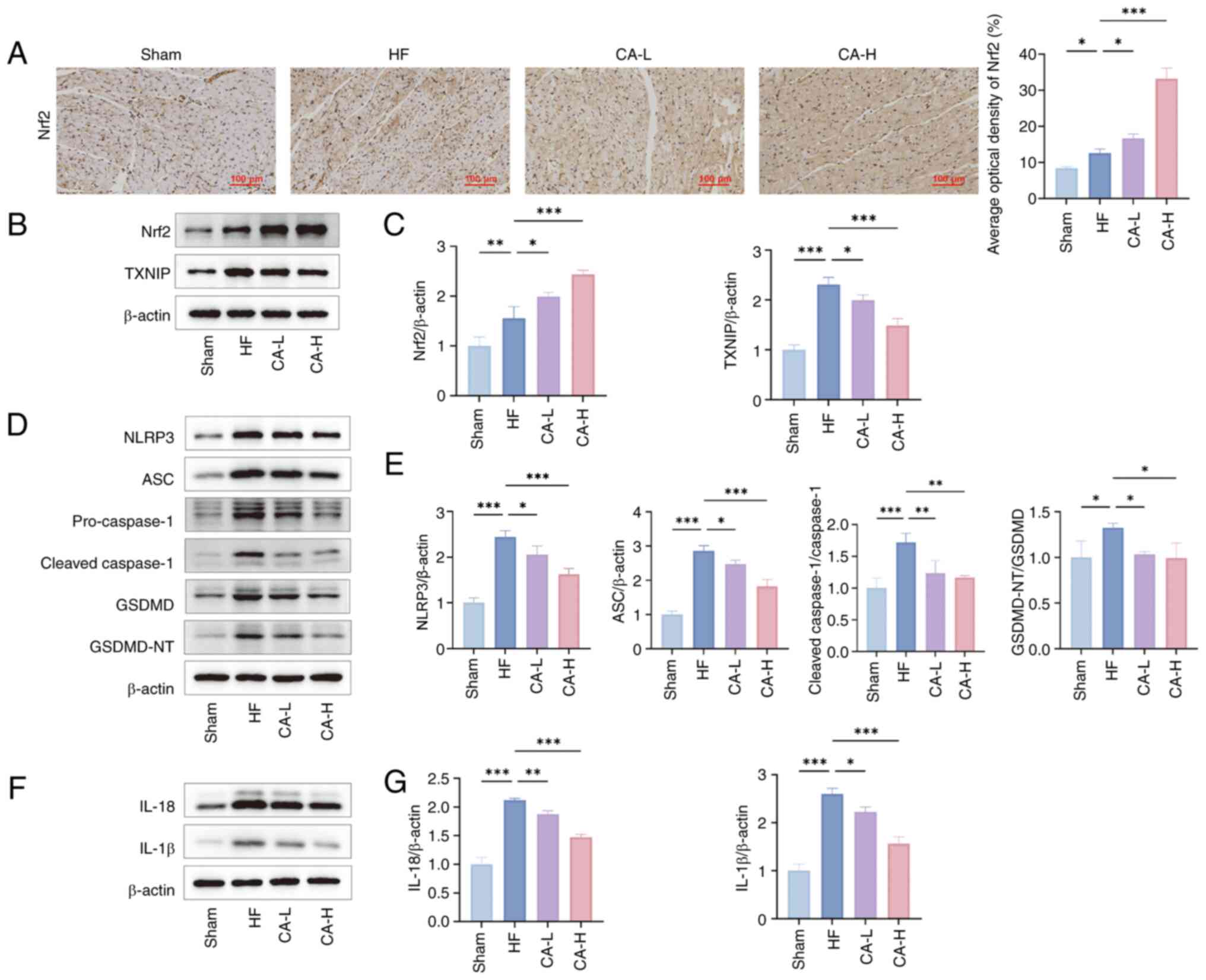
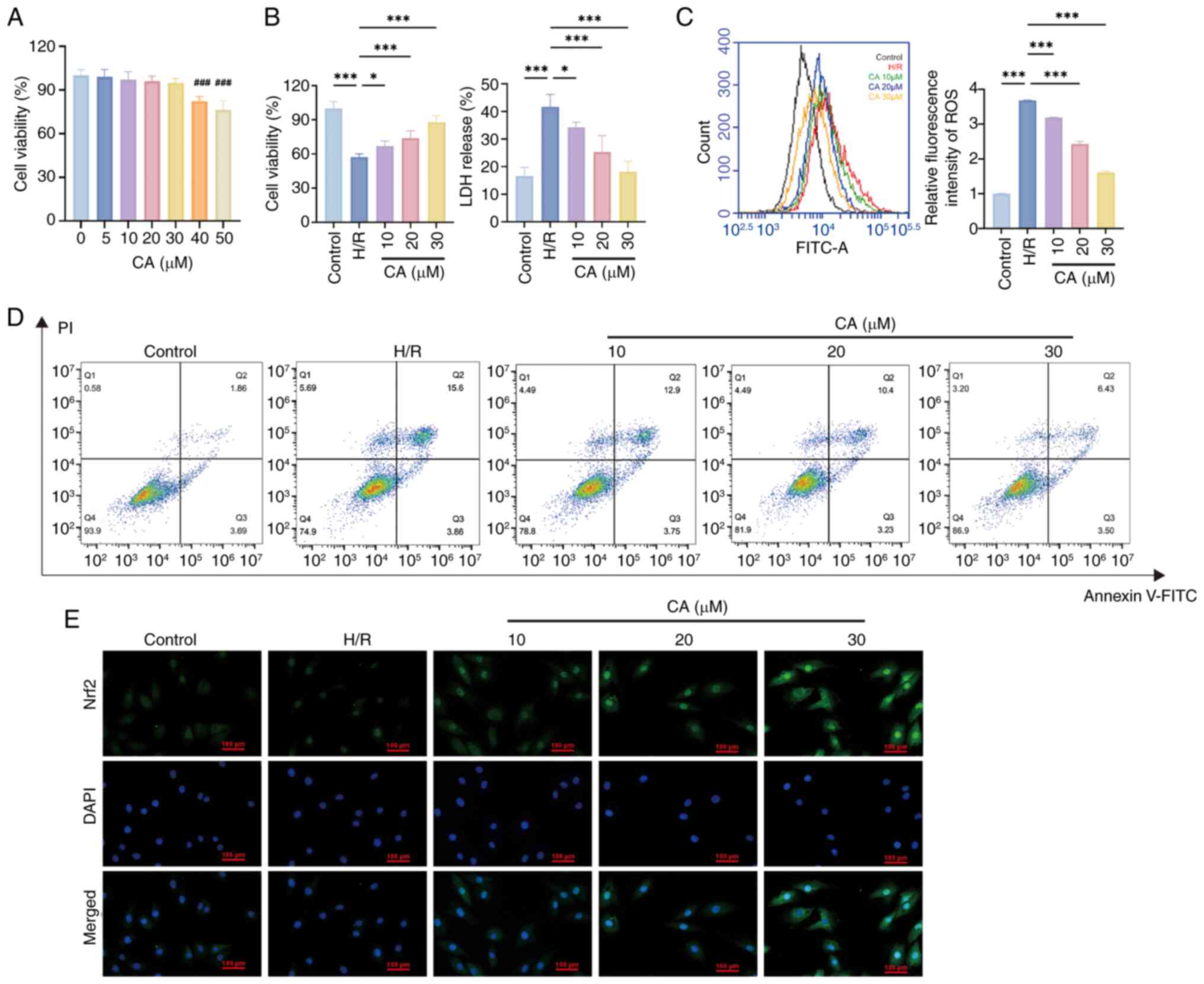
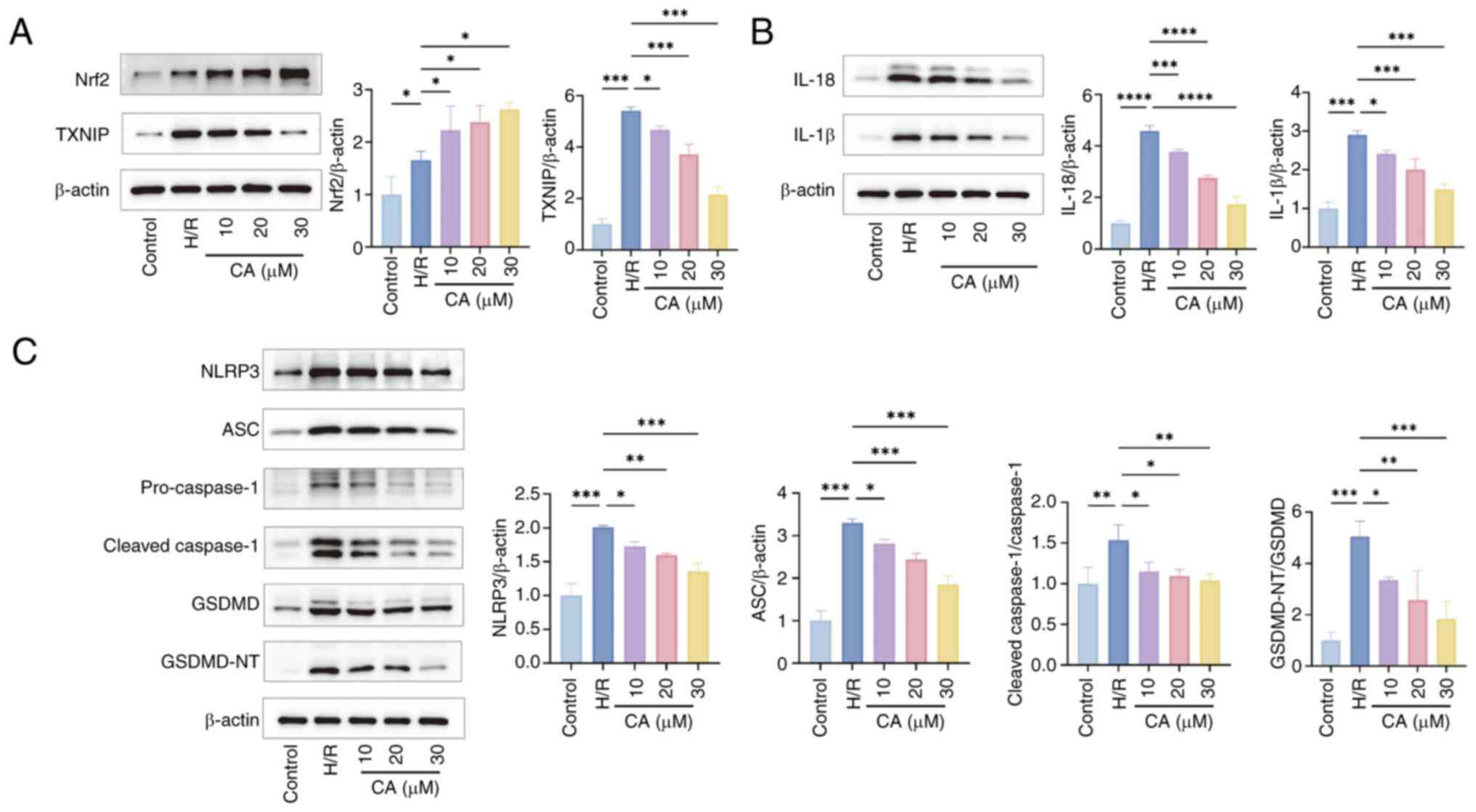
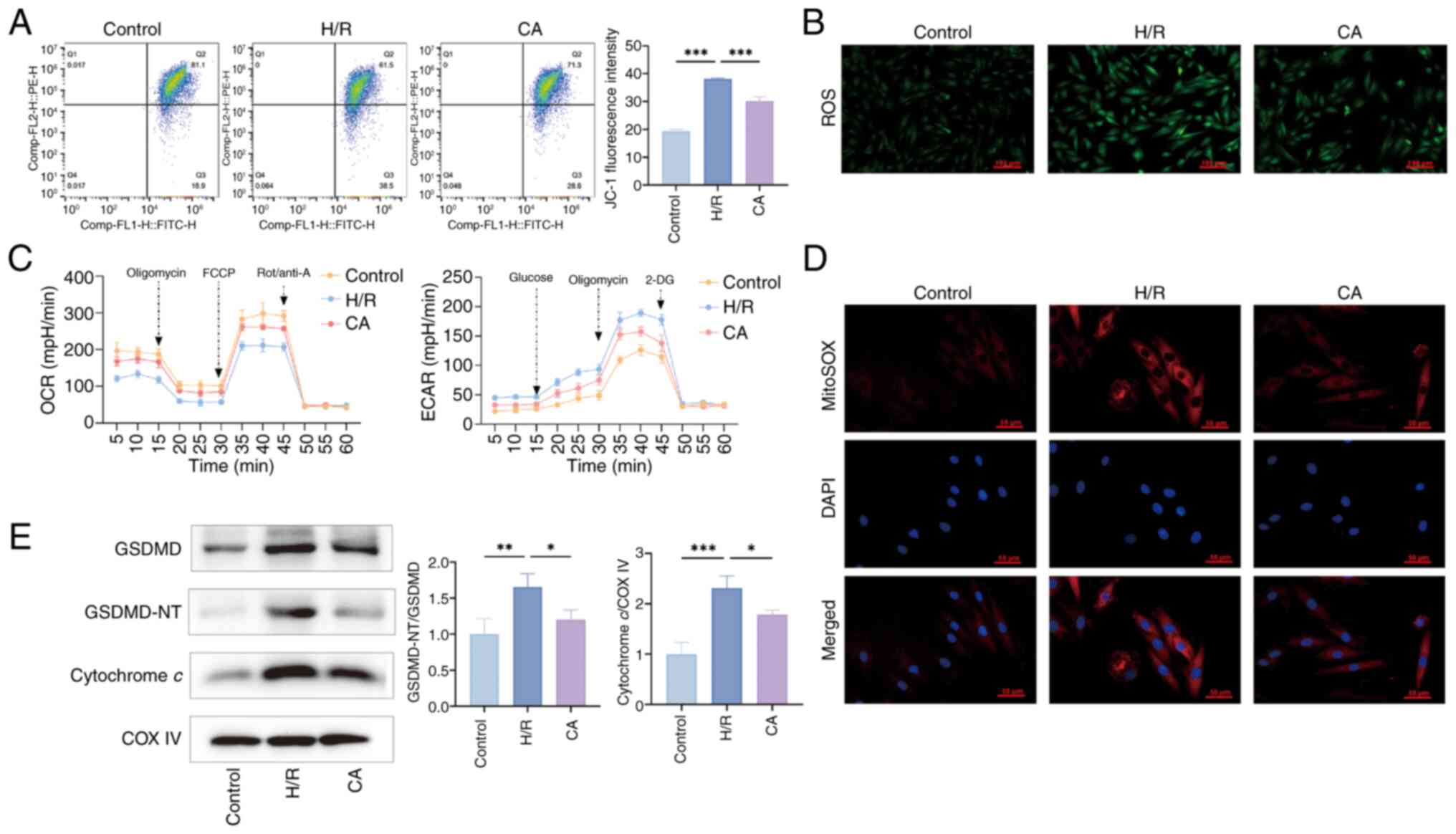
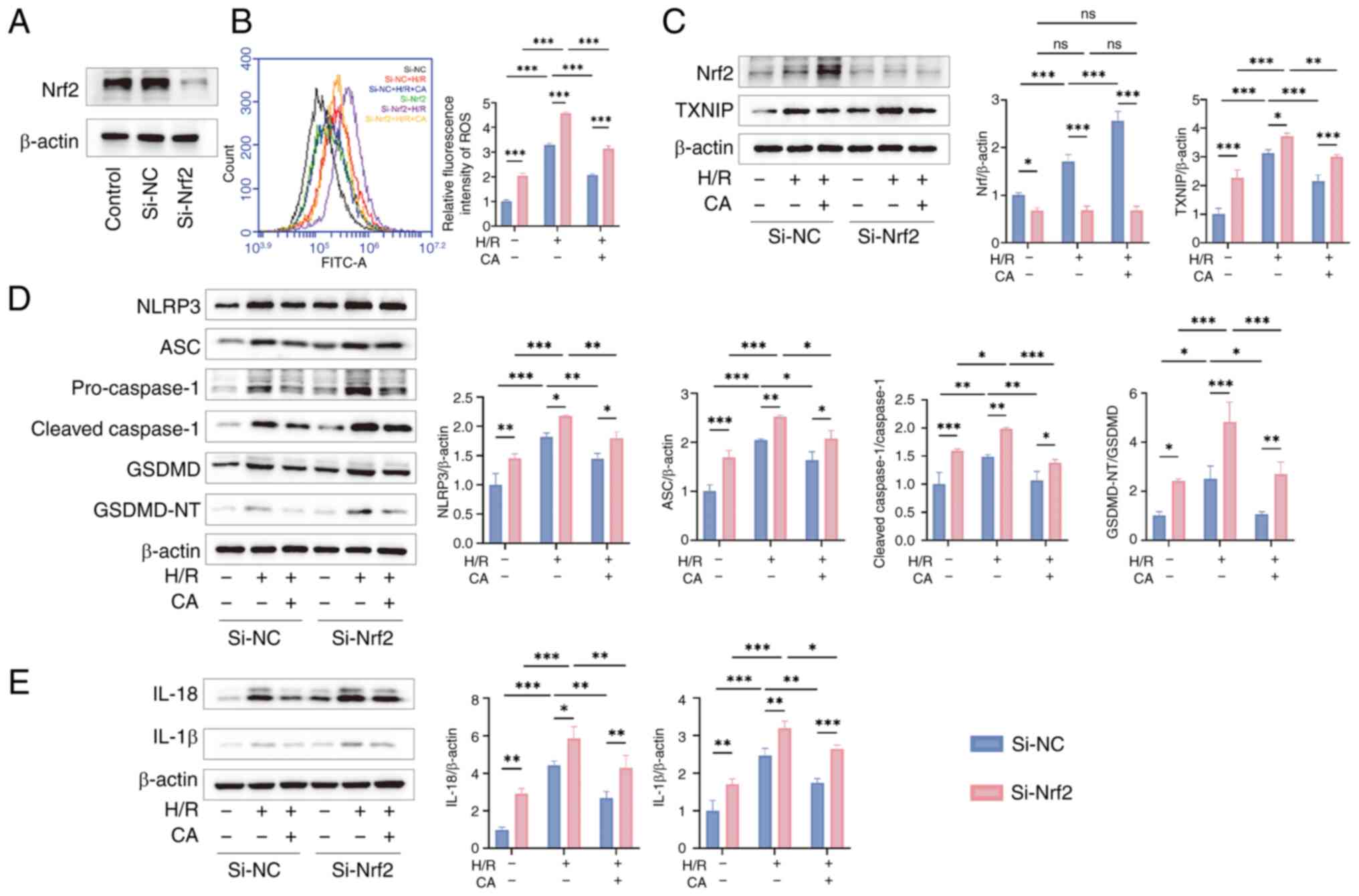
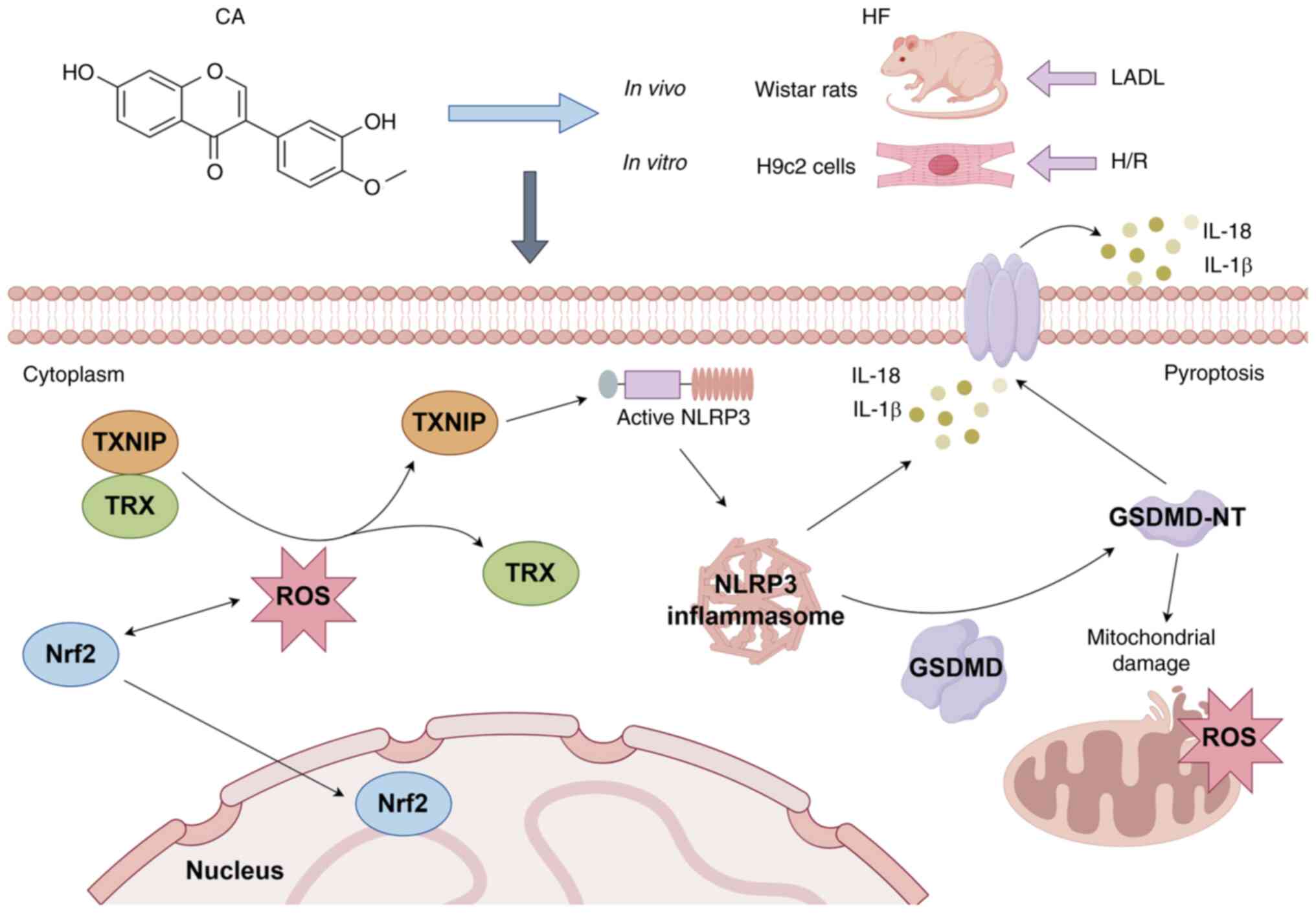
|
1
|
Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson
CAM, Arora P, Avery CL, Baker-Smith CM, Beaton AZ, Boehme AK,
Buxton AE, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update:
A report from the American heart association. Circulation.
147:e93–e621. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khan MS, Shahid I, Bennis A, Rakisheva A,
Metra M and Butler J: Global epidemiology of heart failure. Nat Rev
Cardiol. 21:717–734. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bozkurt B, Fonarow GC, Goldberg LR, Guglin
M, Josephson RA, Forman DE, Lin G, Lindenfeld J, O'Connor C,
Panjrath G, et al: Cardiac rehabilitation for patients with heart
failure: JACC expert panel. J Am Coll Cardiol. 77:1454–1469. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zannad F, O'Connor CM, Butler J, McMullan
CJ, Anstrom KJ, Barash I, Bonaca MP, Borentain M, Corda S, Gates D,
et al: Vericiguat for patients with heart failure and reduced
ejection fraction across the risk spectrum: An individual
participant data analysis of the VICTORIA and VICTOR trials.
Lancet. August 30–2025.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cools JMT, Goovaerts BK, Feyen E, Van den
Bogaert S, Fu Y, Civati C, Van Fraeyenhove J, Tubeeckx MRL, Ott J,
Nguyen L, et al: Small-molecule-induced ERBB4 activation to treat
heart failure. Nat Commun. 16:5762025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rossignol P, Hernandez AF, Solomon SD and
Zannad F: Heart failure drug treatment. Lancet. 393:1034–1044.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brown DA, Perry JB, Allen ME, Sabbah HN,
Stauffer BL, Shaikh SR, Cleland JG, Colucci WS, Butler J, Voors AA,
et al: Expert consensus document: Mitochondrial function as a
therapeutic target in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 14:238–250.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
van der Pol A, van Gilst WH, Voors AA and
van der Meer P: Treating oxidative stress in heart failure: Past,
present and future. Eur J Heart Fail. 21:425–435. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dridi H, Kushnir A, Zalk R, Yuan Q,
Melville Z and Marks AR: Intracellular calcium leak in heart
failure and atrial fibrillation: A unifying mechanism and
therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cardiol. 17:732–747. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiang Q, Yi X, Zhu XH, Wei X and Jiang DS:
Regulated cell death in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 35:219–234. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang Z, Yang Z, Wang S, Wang X and Mao J:
Overview of pyroptosis mechanism and in-depth analysis of
cardiomyocyte pyroptosis mediated by NF-κB pathway in heart
failure. Biomed Pharmacother. 179:1173672024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miao R, Jiang C, Chang WY, Zhang H, An J,
Ho F, Chen P, Zhang H, Junqueira C, Amgalan D, et al: Gasdermin D
permeabilization of mitochondrial inner and outer membranes
accelerates and enhances pyroptosis. Immunity. 56:2523–2541.e8.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I and
Tschopp J: Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress
to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. 11:136–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Morgenstern C, Lastres-Becker I,
Demirdöğen BC, Costa VM, Daiber A, Foresti R, Motterlini R,
Kalyoncu S, Arioz BI, Genc S, et al: Biomarkers of NRF2 signalling:
Current status and future challenges. Redox Biol. 72:1031342024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sies H and Jones DP: Reactive oxygen
species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:363–383. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng M, Chen H, Long J, Song J, Xie L and
Li X: Calycosin: A review of its pharmacological effects and
application prospects. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 19:911–925.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ding WJ, Chen GH, Deng SH, Zeng KF, Lin
KL, Deng B, Zhang SW, Tan ZB, Xu YC, Chen S, et al: Calycosin
protects against oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis
by activating aldehyde dehydrogenase 2. Phytother Res. 37:35–49.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang X, Li W, Zhang Y, Sun Q, Cao J, Tan
N, Yang S, Lu L, Zhang Q, Wei P, et al: Calycosin as a Novel PI3K
activator reduces inflammation and fibrosis in heart failure
through AKT-IKK/STAT3 axis. Front Pharmacol. 13:8280612022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen G, Xu H, Xu T, Ding W, Zhang G, Hua
Y, Wu Y, Han X, Xie L, Liu B and Zhou Y: Calycosin reduces
myocardial fibrosis and improves cardiac function in
post-myocardial infarction mice by suppressing TGFBR1 signaling
pathways. Phytomedicine. 104:1542772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Fan C, Jiao HC, Zhang Q, Jiang
YH, Cui J, Liu Y, Jiang YH, Zhang J, Yang MQ, et al: Calycosin
alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and pyroptosis by
inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022:17338342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan HJ, Han QC, Yu H, Yu YD, Liu XJ, Xue
YT and Li Y: Calycosin treats acute myocardial infarction via NLRP3
inflammasome: Bioinformatics, network pharmacology and experimental
validation. Eur J Pharmacol. 997:1776212025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han Q, Shi J, Yu Y, Yuan H, Guo Y, Liu X,
Xue Y and Li Y: Calycosin alleviates ferroptosis and attenuates
doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury via the Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4
signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 15:14977332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu S, Huang P, Yang J, Du H, Wan H and He
Y: Calycosin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by
repressing autophagy via STAT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway.
Phytomedicine. 115:1548452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang Q, Chen X, Gong K, Xu Z, Chen L and
Zhang F: M6a demethylase FTO regulates the oxidative stress,
mitochondrial biogenesis of cardiomyocytes and PGC-1a stability in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Redox Rep. 30:24548922025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Del Re DP, Amgalan D, Linkermann A, Liu Q
and Kitsis RN: Fundamental mechanisms of regulated cell death and
implications for heart disease. Physiol Rev. 99:1765–1817. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Evavold CL, Hafner-Bratkovič I, Devant P,
D'Andrea JM, Ngwa EM, Boršić E, Doench JG, LaFleur MW, Sharpe AH,
Thiagarajah JR and Kagan JC: Control of gasdermin D oligomerization
and pyroptosis by the ragulator-Rag-mTORC1 pathway. Cell.
184:4495–4511.e19. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qi XM, Zhang WZ, Zuo YQ, Qiao YB, Zhang
YL, Ren JH and Li QS: Nrf2/NRF1 signaling activation and crosstalk
amplify mitochondrial biogenesis in the treatment of
triptolide-induced cardiotoxicity using calycosin. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 41:22024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu CY, Day CH, Kuo CH, Wang TF, Ho TJ, Lai
PF, Chen RJ, Yao CH, Viswanadha VP, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Calycosin
alleviates H2 O2-induced astrocyte injury by
restricting oxidative stress through the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
pathway. Environ Toxicol. 37:858–867. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kobayashi EH, Suzuki T, Funayama R,
Nagashima T, Hayashi M, Sekine H, Tanaka N, Moriguchi T, Motohashi
H, Nakayama K and Yamamoto M: Nrf2 suppresses macrophage
inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine
transcription. Nat Commun. 7:116242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Li X, Han X, Liu R and Fang J:
Targeting the thioredoxin system for cancer therapy. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 38:794–808. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Y, Cao X, Pan B, Du H, Li B, Yang X,
Chen X, Wang X, Zhou T, Qin A, et al: Verapamil attenuates
intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing ROS overproduction
and pyroptosis via targeting the Nrf2/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis in four-week
puncture-induced rat models both in vivo and in vitro. Int
Immunopharmacol. 123:1107892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choi EH and Park SJ: TXNIP: A key protein
in the cellular stress response pathway and a potential therapeutic
target. Exp Mol Med. 55:1348–1356. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abderrazak A, Syrovets T, Couchie D, El
Hadri K, Friguet B, Simmet T and Rouis M: NLRP3 inflammasome: From
a danger signal sensor to a regulatory node of oxidative stress and
inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 4:296–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu Y, An L, Taylor MRG and Chen QM: Nrf2
signaling in heart failure: Expression of Nrf2, Keap1, antioxidant,
and detoxification genes in dilated or ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Physiol Genomics. 54:115–127. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang B, Jin Y, Liu J, Liu Q, Shen Y, Zuo S
and Yu Y: EP1 activation inhibits doxorubicin-cardiomyocyte
ferroptosis via Nrf2. Redox Biol. 65:1028252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou P, Yang L, Li R, Yin Y, Xie G, Liu X,
Shi L, Tao K and Zhang P: IRG1/itaconate alleviates acute liver
injury in septic mice by suppressing NLRP3 expression and its
mediated macrophage pyroptosis via regulation of the Nrf2 pathway.
Int Immunopharmacol. 135:1122772024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhan Y, Xu D, Tian Y, Qu X, Sheng M, Lin
Y, Ke M, Jiang L, Xia Q, Kaldas FM, et al: Novel role of macrophage
TXNIP-mediated CYLD-NRF2-OASL1 axis in stress-induced liver
inflammation and cell death. JHEP Rep. 4:1005322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Devant P and Kagan JC: Molecular
mechanisms of gasdermin D pore-forming activity. Nat Immunol.
24:1064–1075. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu C, Zhang Z, Zhang W and Liu X:
Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial therapies in heart
failure. Pharmacol Res. 175:1060382022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sunagawa Y, Iwashimizu S, Ono M, Mochizuki
S, Iwashita K, Sato R, Shimizu S, Funamoto M, Shimizu K,
Hamabe-Horiike T, et al: The citrus flavonoid nobiletin prevents
the development of doxorubicin-induced heart failure by inhibiting
apoptosis. J Pharmacol Sci. 158:84–94. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu Y, Huang X, He Y, Chang J, Fang X, Kang
P, Feng N, Liu R, Xiao P, Shi D, et al: Mechanism of puerarin
alleviating myocardial remodeling through NSUN2-mediated m5C
methylation modification. Phytomedicine. 143:1568492025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun SN, Liu X, Chen XL, Liang SL, Li J,
Liao HL, Fang HC, Ni SH, Li Y, Lu L, et al: Calycosin alleviates
myocardial fibrosis after myocardial infarction by restoring fatty
acid metabolism homeostasis through inhibiting FAP. Phytomedicine.
145:1570452025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bai Y, Chen Q, Sun YP, Wang X, Lv L, Zhang
LP, Liu JS, Zhao S and Wang XL: Sulforaphane protection against the
development of doxorubicin-induced chronic heart failure is
associated with Nrf2 upregulation. Cardiovasc Ther. 35:2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang S, Han J, Li T, Xin Z, Ma Z, Di W,
Hu W, Gong B, Di S, Wang D and Yang Y: Curcumin as a potential
protective compound against cardiac diseases. Pharmacol Res.
119:373–383. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Saeidinia A, Keihanian F, Butler AE,
Bagheri RK, Atkin SL and Sahebkar A: Curcumin in heart failure: A
choice for complementary therapy? Pharmacol Res. 131:112–119. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pan Y, Zhu G, Wang Y, Cai L, Cai Y, Hu J,
Li Y, Yan Y, Wang Z, Li X, et al: Attenuation of
high-glucose-induced inflammatory response by a novel curcumin
derivative B06 contributes to its protection from diabetic
pathogenic changes in rat kidney and heart. J Nutr Biochem.
24:146–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Grilo GA, Munoz J Jr, Lee DH, Hossain S,
Ma Y, Kain V, Lindsey ML and Halade GV: Macro- and microinjury
define the heart failure progression after permanent coronary
ligation or ischemia-reperfusion in young healthy mice. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 329:H521–H533. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Heusch G: Molecular basis of
cardioprotection: Signal transduction in ischemic pre-, post-, and
remote conditioning. Circ Res. 116:674–699. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Laudette M, Lindbom M, Cinato M, Bergh PO,
Skålén K, Arif M, Miljanovic A, Czuba T, Perkins R, Smith JG, et
al: PCSK9 regulates cardiac mitochondrial cholesterol by promoting
TSPO degradation. Circ Res. 136:924–942. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Khodade VS, Liu Q, Zhang C, Keceli G,
Paolocci N and Toscano JP: Arylsulfonothioates: Thiol-activated
donors of hydropersulfides which are excreted to maintain cellular
redox homeostasis or retained to counter oxidative stress. J Am
Chem Soc. 147:7765–7776. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao ST, Qiu ZC, Xu ZQ, Tao ED, Qiu RB,
Peng HZ, Zhou LF, Zeng RY, Lai SQ and Wan L: Curcumin attenuates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy-dependent
ferroptosis via Sirt1/AKT/FoxO3a signaling. Int J Mol Med.
55:512025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|