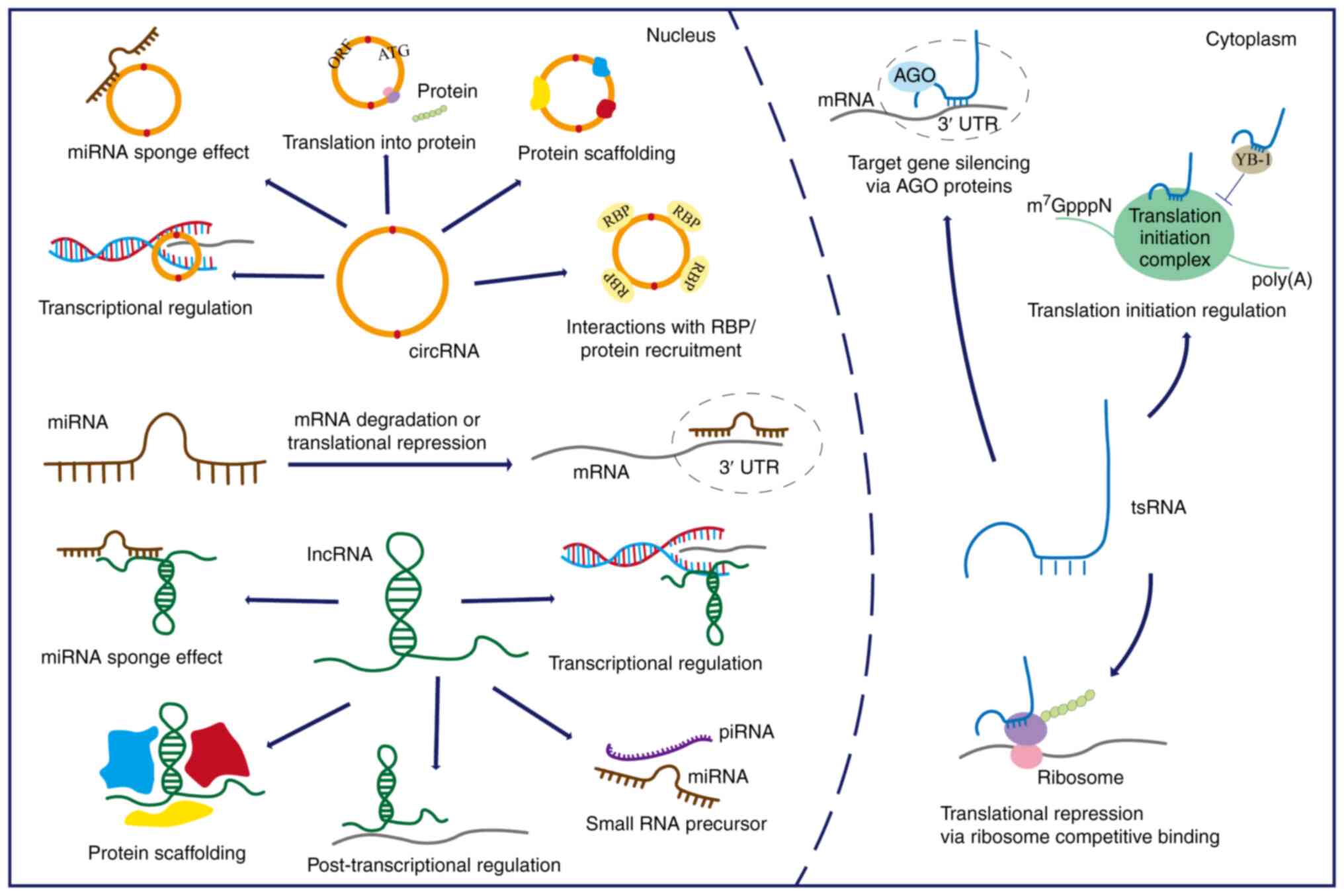
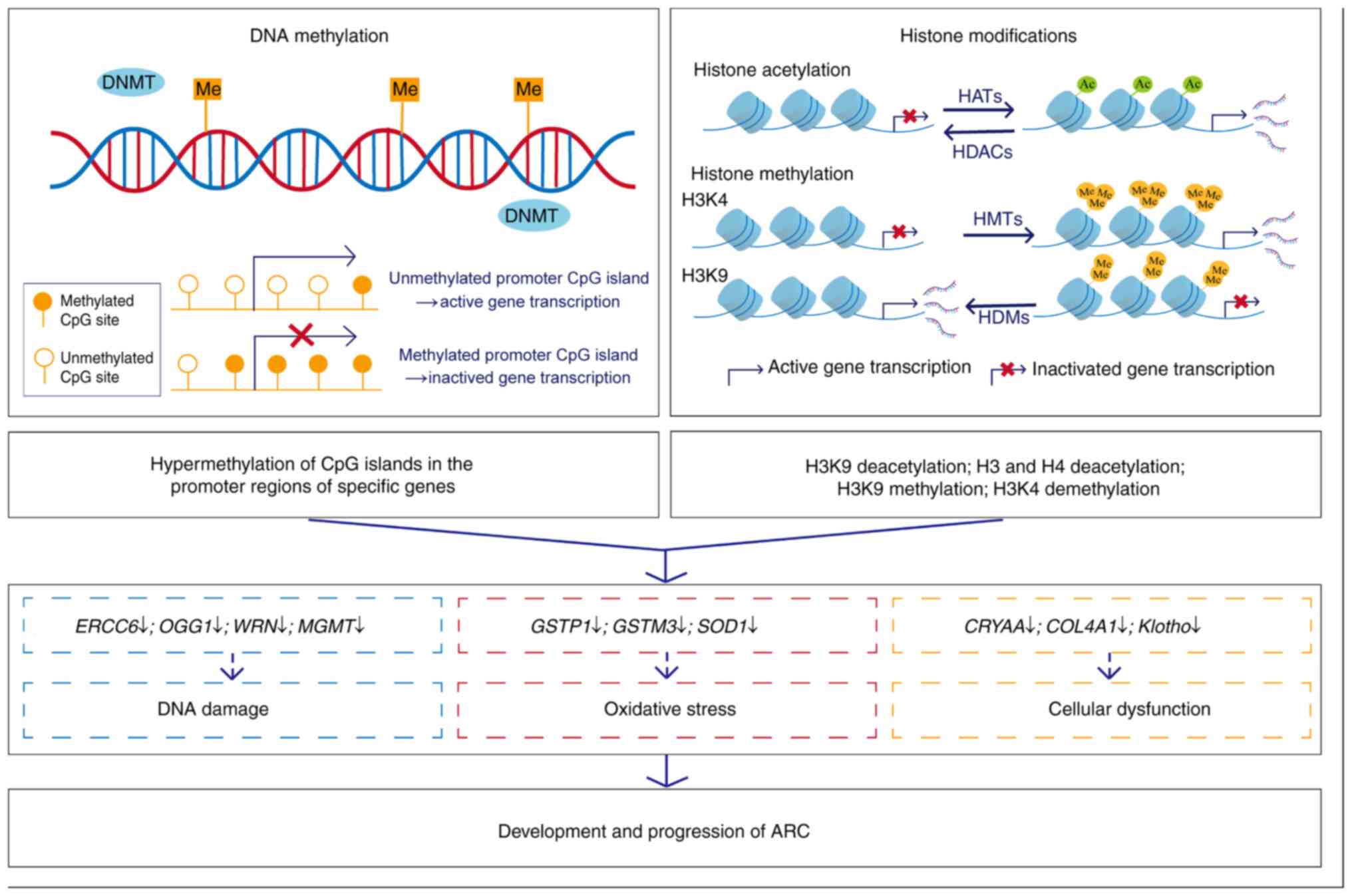
|
1
|
Cicinelli MV, Buchan JC, Nicholson M,
Varadaraj V and Khanna RC: Cataracts. Lancet. 401:377–389. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shiels A and Hejtmancik JF: Mutations and
mechanisms in congenital and age-related cataracts. Exp Eye Res.
156:95–102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Asbell PA, Dualan I, Mindel J, Brocks D,
Ahmad M and Epstein S: Age-related cataract. Lancet. 365:599–609.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abdelkader H, Alany RG and Pierscionek B:
Age-related cataract and drug therapy: Opportunities and challenges
for topical antioxidant delivery to the lens. J Pharm Pharmacol.
67:537–550. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meacock WR, Spalton DJ, Boyce J and
Marshall J: The effect of posterior capsule opacification on visual
function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:4665–4669. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang C, An Q, Zhou H and Ge H: Research
progress on the impact of cataract surgery on corneal endothelial
cells. Adv Ophthalmol Pract Res. 4:194–201. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Beebe DC, Holekamp NM and Shui YB:
Oxidative damage and the prevention of age-related cataracts.
Ophthalmic Res. 44:155–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kulbay M, Wu KY, Nirwal GK, Bélanger P and
Tran SD: Oxidative stress and cataract formation: Evaluating the
efficacy of antioxidant therapies. Biomolecules. 14:10552024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lou MF: Redox regulation in the lens. Prog
Retin Eye Res. 22:657–682. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rahman K: Studies on free radicals,
antioxidants, and co-factors. Clin Interv Aging. 2:219–236.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Berthoud VM and Beyer EC: Oxidative
stress, lens gap junctions, and cataracts. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:339–353. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Petrash JM: Aging and age-related diseases
of the ocular lens and vitreous body. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
54:ORSF54–ORSF59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Babizhayev MA and Costa EB: Lipid peroxide
and reactive oxygen species generating systems of the crystalline
lens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1225:326–337. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dische Z and Zil H: Studies on the
oxidation of cysteine to cystine in lens proteins during cataract
formation. Am J Ophthalmol. 34:104–113. 1951. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kleiman NJ and Spector A: DNA single
strand breaks in human lens epithelial cells from patients with
cataract. Curr Eye Res. 12:423–431. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kruk J, Kubasik-Kladna K and Aboul-Enein
HY: The role oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of eye diseases:
Current status and a dual role of physical activity. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 16:241–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kubota M, Shui YB, Liu M, Bai F, Huang AJ,
Ma N, Beebe DC and Siegfried CJ: Mitochondrial oxygen metabolism in
primary human lens epithelial cells: Association with age, diabetes
and glaucoma. Free Radic Biol Med. 97:513–519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brennan LA, McGreal RS and Kantorow M:
Oxidative stress defense and repair systems of the ocular lens.
Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:141–155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cekić S, Zlatanović G, Cvetković T and
Petrović B: Oxidative stress in cataractogenesis. Bosn J Basic Med
Sci. 10:265–269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li G, Song H, Chen L, Yang W, Nan K and Lu
P: TUG1 promotes lens epithelial cell apoptosis by regulating
miR-421/caspase-3 axis in age-related cataract. Exp Cell Res.
356:20–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li WC, Kuszak JR, Dunn K, Wang RR, Ma W,
Wang GM, Spector A, Leib M, Cotliar AM, Weiss M, et al: Lens
epithelial cell apoptosis appears to be a common cellular basis for
non-congenital cataract development in humans and animals. J Cell
Biol. 130:169–181. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Xu H, Shu X and Song CX: Mapping
epigenetic modifications by sequencing technologies. Cell Death
Differ. 32:56–65. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Hong T, Wang S, Mo J, Tian T and
Zhou X: Epigenetic modification of nucleic acids: From basic
studies to medical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 46:2844–2872. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mazzio EA and Soliman KF: Basic concepts
of epigenetics: Impact of environmental signals on gene expression.
Epigenetics. 7:119–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dawson MA and Kouzarides T: Cancer
epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell. 150:12–27. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peixoto P, Cartron PF, Serandour AA and
Hervouet E: From 1957 to nowadays: A brief history of epigenetics.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:75712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gangisetty O, Cabrera MA and Murugan S:
Impact of epigenetics in aging and age related neurodegenerative
diseases. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 23:1445–1464. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nikolac Perkovic M, Videtic Paska A,
Konjevod M, Kouter K, Svob Strac D, Nedic Erjavec G and Pivac N:
Epigenetics of Alzheimer's disease. Biomolecules. 11:1952021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suárez R, Chapela SP, Álvarez-Córdova L,
Bautista-Valarezo E, Sarmiento-Andrade Y, Verde L, Frias-Toral E
and Sarno G: Epigenetics in obesity and diabetes mellitus: New
insights. Nutrients. 15:8112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun L, Zhang H and Gao P: Metabolic
reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer.
Protein Cell. 13:877–919. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Okugawa Y, Grady WM and Goel A: Epigenetic
alterations in colorectal cancer: Emerging biomarkers.
Gastroenterology. 149:1204–1225.e12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Trnkova L, Buocikova V, Mego M, Cumova A,
Burikova M, Bohac M, Miklikova S, Cihova M and Smolkova B:
Epigenetic deregulation in breast cancer microenvironment:
Implications for tumor progression and therapeutic strategies.
Biomed Pharmacother. 174:1165592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Henikoff S and Greally JM: Epigenetics,
cellular memory and gene regulation. Curr Biol. 26:R644–R648. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meng H, Cao Y, Qin J, Song X, Zhang Q, Shi
Y and Cao L: DNA methylation, its mediators and genome integrity.
Int J Biol Sci. 11:604–617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Z, Zhang W, Qu J and Liu GH: Emerging
epigenetic insights into aging mechanisms and interventions. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 45:157–172. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Desmettre TJ: Epigenetics in age-related
macular degeneration (AMD). J Fr Ophtalmol. 41:e407–e415. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kapuganti RS and Alone DP: Current
understanding of genetics and epigenetics in pseudoexfoliation
syndrome and glaucoma. Mol Aspects Med. 94:1012142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kowluru RA, Kowluru A, Mishra M and Kumar
B: Oxidative stress and epigenetic modifications in the
pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 48:40–61.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Y and Guan H: The role of DNA
methylation in lens development and cataract formation. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 37:979–984. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ling C and Rönn T: Epigenetics in human
obesity and type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 29:1028–1044. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li P, Yu H, Zhang G, Kang L, Qin B, Cao Y,
Luo J, Chen X, Wang Y, Qin M, et al: Identification and
characterization of N6-methyladenosine CircRNAs and
methyltransferases in the lens epithelium cells from age-related
cataract. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 61:132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei YL and Sun H: Identification of
hsa-mir-34a, hsa-mir-124, and hsa-mir-204 as signatures for
cataract. J Cell Physiol. 234:10709–10717. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhu X, Zhang G, Kang L and Guan H:
Epigenetic regulation of Werner syndrome gene in age-related
cataract. J Ophthalmol. 2015:5796952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Crick F: Central dogma of molecular
biology. Nature. 227:561–563. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Crick FH: On protein synthesis. Symp Soc
Exp Biol. 12:138–163. 1958.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kim SS and Lee SJV: Non-coding RNAs in
caenorhabditis elegans aging. Mol Cells. 42:379–385.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yao ZT, Yang YM, Sun MM, He Y, Liao L,
Chen KS and Li B: New insights into the interplay between long
non-coding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in cancer. Cancer Commun
(Lond). 42:117–140. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dykes IM and Emanueli C: Transcriptional
and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA.
Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 15:177–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Smillie CL, Sirey T and Ponting CP:
Complexities of post-transcriptional regulation and the modeling of
ceRNA crosstalk. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 53:231–245. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Luo S, He F, Luo J, Dou S, Wang Y, Guo A
and Lu J: Drosophila tsRNAs preferentially suppress general
translation machinery via antisense pairing and participate in
cellular starvation response. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:5250–5268.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kim HK, Xu J, Chu K, Park H, Jang H, Li P,
Valdmanis PN, Zhang QC and Kay MA: A tRNA-derived small RNA
regulates ribosomal protein S28 protein levels after translation
initiation in humans and mice. Cell Rep. 29:3816–3824.e4. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ardekani AM and Naeini MM: The role of
MicroRNAs in human diseases. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2:161–179.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Condrat CE, Thompson DC, Barbu MG, Bugnar
OL, Boboc A, Cretoiu D, Suciu N, Cretoiu SM and Voinea SC: miRNAs
as biomarkers in disease: Latest findings regarding their role in
diagnosis and prognosis. Cells. 9:2762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wawrzyniak O, Zarębska Ż, Rolle K and
Gotz-Więckowska A: Circular and long non-coding RNAs and their role
in ophthalmologic diseases. Acta Biochim Pol. 65:497–508.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen S, Zhang C, Shen L, Hu J, Chen X and
Yu Y: Noncoding RNAs in cataract formation: Star molecules emerge
in an endless stream. Pharmacol Res. 184:1064172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang C, Hu J and Yu Y: CircRNA is a
rising star in researches of ocular diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:8502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zheng JL, Sun J, Zhang H and Zhang Y: Role
of microRNA and lncRNA in lens development and cataract formation.
Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 54:390–395. 2018.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Michlewski G and Cáceres JF:
Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA. 25:1–16.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
59
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Broughton JP, Lovci MT, Huang JL, Yeo GW
and Pasquinelli AE: Pairing beyond the seed supports MicroRNA
targeting specificity. Mol Cell. 64:320–333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Yamamura S,
Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Deng G and Dahiya R: MicroRNA-205-directed
transcriptional activation of tumor suppressor genes in prostate
cancer. Cancer. 116:5637–5649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ and
Dahiya R: MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with
complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:1608–1613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Vasudevan S: Posttranscriptional
upregulation by microRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 3:311–330.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N,
Fang Z, Khanin R and Rajewsky N: Widespread changes in protein
synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 455:58–63. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kang L, Luo J, Li P, Zhang G, Wei M, Ji M
and Guan H: miR-125a-3p regulates apoptosis by suppressing TMBIM4
in lens epithelial cells. Int Ophthalmol. 43:1261–1274. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Cao Y, Li P, Zhang G, Kang L, Zhou T, Wu
J, Wang Y, Wang Y, Chen X and Guan H: MicroRNA Let-7c-5p-mediated
regulation of ERCC6 disrupts autophagic flux in age-related
cataract via the binding to VCP. Curr Eye Res. 46:1353–1362. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li ZN, Ge MX and Yuan ZF: MicroRNA-182-5p
protects human lens epithelial cells against oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis by inhibiting NOX4 and p38 MAPK
signalling. BMC Ophthalmol. 20:2332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang C, Chen M, Zhou N and Qi Y:
Metformin prevents H2O2-induced senescence in
human lens epithelial B3 cells. Med Sci Monit Basic Res.
26:e9233912020.
|
|
70
|
Zou X, Kang L, Yang M, Wu J and Guan H:
MicroRNA binding mediated Functional sequence variant in 3'-UTR of
DNA repair gene XPC in age-related cataract. Sci Rep. 8:151982018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wu C, Lin H, Wang Q, Chen W, Luo H, Chen W
and Zhang H: Discrepant expression of microRNAs in transparent and
cataractous human lenses. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:3906–3912.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kim YJ, Lee WJ, Ko BW, Lim HW, Yeon Y, Ahn
SJ and Lee BR: Investigation of MicroRNA expression in anterior
lens capsules of senile cataract patients and MicroRNA differences
according to the cataract type. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 10:142021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Peng CH, Liu JH, Woung LC, Lin TJ, Chiou
SH, Tseng PC, Du WY, Cheng CK, Hu CC, Chien KH and Chen SJ:
MicroRNAs and cataracts: Correlation among let-7 expression, age
and the severity of lens opacity. Br J Ophthalmol. 96:747–751.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chylack LT Jr, Wolfe JK, Singer DM, Leske
MC, Bullimore MA, Bailey IL, Friend J, McCarthy D and Wu SY: The
lens opacities classification system III. The longitudinal study of
cataract study group. Arch Ophthalmol. 111:831–836. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chien KH, Chen SJ, Liu JH, Chang HM, Woung
LC, Liang CM, Chen JT, Lin TJ, Chiou SH and Peng CH: Correlation
between microRNA-34a levels and lens opacity severity in
age-related cataracts. Eye (Lond). 27:883–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Xu C, Xu J, Zhang W, Zheng F and Lou X:
Expression of miR-210-3p in the aqueous humor of patients with
age-related cataracts and its effect on human lens epithelial cell
injury induced by hydrogen peroxide. Arq Bras Oftalmol.
87:e202202742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li Y, Liu S, Zhang F, Jiang P, Wu X and
Liang Y: Expression of the microRNAs hsa-miR-15a and hsa-miR-16-1
in lens epithelial cells of patients with age-related cataract. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:2405–2410. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhou W, Xu J, Wang C, Shi D and Yan Q:
miR-23b-3p regulates apoptosis and autophagy via suppressing SIRT1
in lens epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 120:19635–19646. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lu B, Christensen IT, Ma LW, Wang XL,
Jiang LF, Wang CX, Feng L, Zhang JS and Yan QC: miR-211 promotes
lens epithelial cells apoptosis by targeting silent mating-type
information regulation 2 homolog 1 in age-related cataracts. Int J
Ophthalmol. 11:201–207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Maiti B, Li J, de Bruin A, Gordon F,
Timmers C, Opavsky R, Patil K, Tuttle J, Cleghorn W and Leone G:
Cloning and characterization of mouse E2F8, a novel mammalian E2F
family member capable of blocking cellular proliferation. J Biol
Chem. 280:18211–18220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shen ZG, Liu XZ, Chen CX and Lu JM:
Knockdown of E2F3 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion
and increases apoptosis in glioma cells. Oncol Res. 25:1555–1566.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chen Q, Liang D, Yang T, Leone G and
Overbeek PA: Distinct capacities of individual E2Fs to induce cell
cycle re-entry in postmitotic lens fiber cells of transgenic mice.
Dev Neurosci. 26:435–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Chong JL, Tsai SY, Sharma N, Opavsky R,
Price R, Wu L, Fernandez SA and Leone G: E2f3a and E2f3b contribute
to the control of cell proliferation and mouse development. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:414–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
84
|
Wenzel PL, Chong JL, Sáenz-Robles MT,
Ferrey A, Hagan JP, Gomez YM, Rajmohan R, Sharma N, Chen HZ, Pipas
JM, et al: Cell proliferation in the absence of E2F1-3. Dev Biol.
351:35–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Yan Q, Liu JP and Li DWC: Apoptosis in
lens development and pathology. Differentiation. 74:195–211. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xiang W, Lin H, Wang Q and Chen W, Liu Z,
Chen H, Zhang H and Chen W: miR-34a suppresses proliferation and
induces apoptosis of human lens epithelial cells by targeting E2F3.
Mol Med Rep. 14:5049–5056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Li Q, Pan H and Liu Q: MicroRNA-15a
modulates lens epithelial cells apoptosis and proliferation through
targeting B-cell lymphoma-2 and E2F transcription factor 3 in
age-related cataracts. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201917732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gong W, Li J, Wang Y, Meng J and Zheng G:
miR-221 promotes lens epithelial cells apoptosis through
interacting with SIRT1 and E2F3. Chem Biol Interact. 306:39–46.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Gao W, Zhou X and Lin R: miR-378a-5p and
miR-630 induce lens epithelial cell apoptosis in cataract via
suppression of E2F3. Braz J Med Biol Res. 53:e96082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Fan F, Zhuang J, Zhou P, Liu X and Luo Y:
MicroRNA-34a promotes mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis
in human lens epithelial cells by targeting Notch2. Oncotarget.
8:110209–110220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Feng L, Wei Y, Sun Y, Zhou L, Bi S, Chen W
and Xiang W: MIR34A modulates lens epithelial cell apoptosis and
cataract development via the HK1/caspase 3 signaling pathway. Aging
(Albany NY). 15:6331–6345. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Liu Y, Li H and Liu Y: microRNA-378a
regulates the reactive oxygen species (ROS)/phosphatidylinositol
3-kinases (PI3K)/AKT signaling pathway in human lens epithelial
cells and cataract. Med Sci Monit. 25:4314–4321. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang F, Meng W and Tong B:
Down-regulation of MicroRNA-133b suppresses apoptosis of lens
epithelial cell by up-regulating BCL2L2 in age-related cataracts.
Med Sci Monit. 22:4139–4145. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Qin Y, Zhao J, Min X, Wang M, Luo W, Wu D,
Yan Q, Li J, Wu X and Zhang J: MicroRNA-125b inhibits lens
epithelial cell apoptosis by targeting p53 in age-related cataract.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1842:2439–2447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Gao M, Huang Y, Wang L, Huang M, Liu F,
Liao S, Yu S, Lu Z, Han S, Hu X, et al: HSF4 regulates lens fiber
cell differentiation by activating p53 and its downstream
regulators. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Li L, Fan DB, Zhao YT, Li Y, Kong DQ, Cai
FF and Zheng GY: Two novel mutations identified in ADCC families
impair crystallin protein distribution and induce apoptosis in
human lens epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 7:178482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Peng J, Zheng TT, Liang Y, Duan LF, Zhang
YD, Wang LJ, He GM and Xiao HT: p-Coumaric acid protects human lens
epithelial cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by MAPK
signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:85490522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Zhang DJ, Du FF, Jing XY, Wang L, Liu D
and Yang XQ: Sequence and expression regulation of the BCL2L2 gene
in pigs. Gene. 851:1469922023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
İçme G, Yilmaz A, Dinç E, Görür A, Fidanci
ŞB and Tamer L: Assessment of miR-182, miR-183, miR-184, and
miR-221 expressions in primary pterygium and comparison with the
normal conjunctiva. Eye Contact Lens. 45:208–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liu Y, Bailey JC, Helwa I, Dismuke WM, Cai
J, Drewry M, Brilliant MH, Budenz DL, Christen WG, Chasman DI, et
al: A common variant in MIR182 is associated with primary
open-angle glaucoma in the NEIGHBORHOOD consortium. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:4528–4535. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Szemraj M, Oszajca K, Szemraj J and
Jurowski P: MicroRNA expression analysis in serum of patients with
congenital hemochromatosis and age-related macular degeneration
(AMD). Med Sci Monit. 23:4050–4060. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Ren H, Tao H, Gao Q, Shen W, Niu Z, Zhang
J, Mao H, Du A and Li W: MiR-326 antagomir delays the progression
of age-related cataract by upregulating FGF1-mediated expression of
betaB2-crystallin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 505:505–510. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Fang R, Li HL, Lv NX, Yue PL, Jia YX, Liu
ZC, Zhou HG and Song XD: Inhibition of miR-29a-3p alleviates
apoptosis of lens epithelial cells via upregulation of CAND1. Curr
Eye Res. 49:391–400. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Wang F and Ren Y: Nanofluorescence probe
in detection of miR-187 and its correlation with oxidative stress
response in cataracts. Altern Ther Health Med. 29:73–79. 2023.
|
|
106
|
Vymetalkova V, Pardini B, Rosa F,
Jiraskova K, Di Gaetano C, Bendova P, Levy M, Veskrnova V, Buchler
T, Vodickova L, et al: Polymorphisms in microRNA binding sites of
mucin genes as predictors of clinical outcome in colorectal cancer
patients. Carcinogenesis. 38:28–39. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Liu XC, Liu XF, Hu ZD and Li ZH:
Polymorphisms of DNA repair genes XPD (Lys751Gln) and XRCC1
(Arg399Gln), and the risk of age-related cataract: A meta-analysis.
Curr Eye Res. 40:676–682. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Wang Y, Li F, Zhang G, Kang L and Guan H:
Ultraviolet-B induces ERCC6 repression in lens epithelium cells of
age-related nuclear cataract through coordinated DNA
hypermethylation and histone deacetylation. Clin Epigenetics.
8:622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kang L, Zou X, Zhang G, Xiang J, Wang Y,
Yang M, Chen X, Wu J and Guan H: A variant in a microRNA binding
site in NEIL2 3'UTR confers susceptibility to age-related
cataracts. FASEB J. 33:10469–10476. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhao Y, Li X and Zhu S: rs78378222
polymorphism in the 3'-untranslated region of TP53 contributes to
development of age-associated cataracts by modifying
microRNA-125b-induced apoptosis of lens epithelial cells. Mol Med
Rep. 14:2305–2310. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Luo J, Li P, Kang L, Ji M, Zhou T, Qin B,
Zhang J and Guan H: Exosomal microRNA-222-3p increases UVB
sensitivity of lens epithelium cells by suppressing MGMT. Int
Ophthalmol. 43:1611–1628. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Denzer K, Kleijmeer MJ, Heijnen HF,
Stoorvogel W and Geuze HJ: Exosome: From internal vesicle of the
multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J Cell Sci.
113:3365–3374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Meldolesi J: Exosomes and ectosomes in
intercellular communication. Curr Biol. 28:R435–R444. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Perez-Hernandez J, Olivares D, Forner MJ,
Ortega A, Solaz E, Martinez F, Chaves FJ, Redon J and Cortes R:
Urinary exosome miR-146a is a potential marker of albuminuria in
essential hypertension. J Transl Med. 16:2282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Creemers EE, Tijsen AJ and Pinto YM:
Circulating microRNAs: Novel biomarkers and extracellular
communicators in cardiovascular disease? Circ Res. 110:483–495.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Turchinovich A, Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG
and Burwinkel B: Circulating miRNAs: Cell-cell communication
function? Front Genet. 4:1192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Fan Q, Yang L, Zhang X, Peng X, Wei S, Su
D, Zhai Z, Hua X and Li H: The emerging role of exosome-derived
non-coding RNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Lett. 414:107–115. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Machida T, Tomofuji T, Ekuni D, Maruyama
T, Yoneda T, Kawabata Y, Mizuno H, Miyai H, Kunitomo M and Morita
M: MicroRNAs in salivary exosome as potential biomarkers of aging.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:21294–21309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zamani P, Fereydouni N, Butler AE,
Navashenaq JG and Sahebkar A: The therapeutic and diagnostic role
of exosomes in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc Med.
29:313–323. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Li J, Wang J and Chen Z: Emerging role of
exosomes in cancer therapy: Progress and challenges. Mol Cancer.
24:132025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Moreno JA, Hamza E, Guerrero-Hue M,
Rayego-Mateos S, García-Caballero C, Vallejo-Mudarra M, Metzinger L
and Metzinger-Le Meuth V: Non-coding RNAs in kidney diseases: The
long and short of them. Int J Mol Sci. 22:60772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Goodall GJ and Wickramasinghe VO: RNA in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 21:22–36. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Javed Z, Khan K, Sadia H, Raza S, Salehi
B, Sharifi-Rad J and Cho WC: LncRNA & Wnt signaling in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 20:3262020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I,
Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A and Bozzoni I: A
long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning
as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell. 147:358–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Gong C and Maquat LE: lncRNAs
transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3' UTRs
via Alu elements. Nature. 470:284–288. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Hong Y, Wu J, Sun Y, Zhang S, Lu Y and Ji
Y: ceRNA network construction and identification of hub genes as
novel therapeutic targets for age-related cataracts using
bioinformatics. PeerJ. 11:e150542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Zhou T, Yang M, Zhang G, Kang L, Yang L
and Guan H: Long non-coding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly
transcript 1 protects human lens epithelial cells against
H2O2 stimuli through the nuclear factor kappa
b/p65 and p38/mitogen-activated protein kinase axis. Ann Transl
Med. 8:16532020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Zhou T, Zhang J, Qin B, Xu H, Zhang S and
Guan H: Long non-coding RNA NONHSAT143692.2 is involved in
oxidative DNA damage repair in the lens by regulating the
miR-4728-5p/OGG1 axis. Int J Mol Med. 46:1838–1848. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhang N, Zhang C, Wang X and Qi Y:
High-throughput sequencing reveals novel lincRNA in age-related
cataract. Int J Mol Med. 40:1829–1839. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Li H, Gao L, Du J, Ma T, Ye Z and Li Z:
Differentially expressed gene profiles and associated ceRNA network
in ATG7-deficient lens epithelial cells under oxidative stress.
Front Genet. 13:10889432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Jin X, Jin H, Shi Y, Guo Y and Zhang H:
Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes cataractogenesis via miR-214
and activation of the caspase-1 pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
42:295–305. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Zhang M and Cheng K: Long non-coding RNA
KCNQ1OT1 promotes hydrogen peroxide-induced lens epithelial cell
apoptosis and oxidative stress by regulating miR-223-3p/BCL2L2
axis. Exp Eye Res. 206:1085432021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Xu Y, Zheng Y, Shen P and Zhou L: Role of
long noncoding RNA KCNQ1 overlapping transcript
1/microRNA-124-3p/BCL-2-like 11 axis in hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2)-stimulated human lens epithelial
cells. Bioengineered. 13:5035–5045. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Shen Q and Zhou T: Knockdown of lncRNA
TUG1 protects lens epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced
injury by regulating miR-196a-5p expression in age-related
cataracts. Exp Ther Med. 22:12862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Sun M, Li K, Li X, Wang H, Li L and Zheng
G: lncRNA TUG1 regulates Smac/DIABLO expression by competitively
inhibiting miR-29b and modulates the apoptosis of lens epithelial
cells in age-related cataracts. Chin Med J (Engl). 136:2340–2350.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Guo X, Li C, Wang Y, Jiang C and Yang L:
Long non-coding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1
downregulation protects lens epithelial cells from oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis by regulating the
microRNA-124-3p/death-associated protein kinase 1 axis in
age-related cataract. Int Ophthalmol. 43:3413–3424. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Tu Y, Xie L, Chen L, Yuan Y, Qin B, Wang
K, Zhu Q, Ji N, Zhu M and Guan H: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes
cataractogenesis by upregulating TP53INP1 expression in age-related
cataract. Exp Eye Res. 199:1081852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Zhang X, Zheng C, Zhao J, Xu X and Yao J:
LncRNA MEG3 regulates ferroptosis of lens epithelial cells via
PTBP1/GPX4 axis to participate in age-related cataract. J Cell
Physiol. 239:e313302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Jing R, Ma B, Qi T, Hu C, Liao C, Wen C,
Shao Y and Pei C: Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 promotes cell
apoptosis and cataract formation by blocking POLG expression under
oxidative stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 61:32020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Xiang J, Chen Q, Kang L, Zhang G, Wang Y,
Qin B, Wu J, Zhou T, Han Y and Guan H: LncRNA PLCD3-OT1 functions
as a CeRNA to prevent age-related cataract by sponging miR-224-5p
and regulating PLCD3 expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
60:4670–4680. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Cheng T, Xu M, Qin B, Wu J, Tu Y, Kang L,
Wang Y and Guan H: lncRNA H19 contributes to oxidative damage
repair in the early age-related cataract by regulating miR-29a/TDG
axis. J Cell Mol Med. 23:6131–6139. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Alkan AH and Akgül B: Endogenous miRNA
sponges. Methods Mol Biol. 2257:91–104. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Alshahrani SH, Al-Hadeithi ZSM, Almalki
SG, Malviya J, Hjazi A, Mustafa YF, Alawady AHR, Alsaalamy AH,
Joshi SK and Alkhafaji AT: LncRNA-miRNA interaction is involved in
colorectal cancer pathogenesis by modulating diverse signaling
pathways. Pathol Res Pract. 251:1548982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Karagkouni D, Karavangeli A,
Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG: Characterizing
miRNA-lncRNA Interplay. Methods Mol Biol. 2372:243–262. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Zhang Y, Cai S, Jia Y, Qi C, Sun J, Zhang
H, Wang F, Cao Y and Li X: Decoding noncoding RNAs: Role of
MicroRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in ocular neovascularization.
Theranostics. 7:3155–3167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Magistri M, Faghihi MA, St Laurent G III
and Wahlestedt C: Regulation of chromatin structure by long
noncoding RNAs: Focus on natural antisense transcripts. Trends
Genet. 28:389–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Xue Y, Ma G, Zhang Z, Hua Q, Chu H, Tong
N, Yuan L, Qin C, Yin C, Zhang Z and Wang M: A novel antisense long
noncoding RNA regulates the expression of MDC1 in bladder cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:484–493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
150
|
Zhang CL, Zhu KP and Ma XL: Antisense
lncRNA FOXC2-AS1 promotes doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma by
increasing the expression of FOXC2. Cancer Lett. 396:66–75. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
He A, He S, Li X and Zhou L: ZFAS1: A
novel vital oncogenic lncRNA in multiple human cancers. Cell
Prolif. 52:e125132019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Zong X, Nakagawa S, Freier SM, Fei J, Ha
T, Prasanth SG and Prasanth KV: Natural antisense RNA promotes 3'
end processing and maturation of MALAT1 lncRNA. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:2898–2908. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Tu Y, Li L, Qin B, Wu J, Cheng T, Kang L
and Guan H: Long noncoding RNA glutathione peroxidase 3-antisense
inhibits lens epithelial cell apoptosis by upregulating glutathione
peroxidase 3 expression in age-related cataract. Mol Vis.
25:734–744. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Zhu M, Dong Q, Bing J, Songbuerbatu, Zheng
L, Dorjee T, Liu Q, Zhou Y and Gao F: Combined lncRNA and mRNA
expression profiles identified the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA modules
regulating the cold stress response in Ammopiptanthus nanus. Int J
Mol Sci. 24:65022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Liu X, Liu C, Shan K, Zhang S, Lu Y, Yan B
and Luo Y: Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates human lens epithelial
cells function. Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:246–260. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Harland R and Misher L: Stability of RNA
in developing Xenopus embryos and identification of a destabilizing
sequence in TFIIIA messenger RNA. Development. 102:837–852. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Zhang XO, Dong R, Zhang Y, Zhang JL, Luo
Z, Zhang J, Chen LL and Yang L: Diverse alternative back-splicing
and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res.
26:1277–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK,
Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF and Sharpless NE: Circular RNAs are
abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA.
19:141–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
159
|
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW,
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB and Kjems J: The biogenesis, biology and
characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 20:675–691. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Panda AC: Circular RNAs Act as miRNA
sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1087:67–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Tong KL, Tan KE, Lim YY, Tien XY and Wong
PF: CircRNA-miRNA interactions in atherogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem.
477:2703–2733. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM,
Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, Roslan S, Schreiber AW, Gregory PA and
Goodall GJ: The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of
circRNAs. Cell. 160:1125–1134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR,
Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N and
Kadener S: circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol
Cell. 56:55–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang
X, Zhong G, Yu B, Hu W, Dai L, et al: Exon-intron circular RNAs
regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
22:256–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M,
Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, Hanan M, Wyler E,
Perez-Hernandez D, Ramberger E, et al: Translation of CircRNAs. Mol
Cell. 66:9–21.e7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang
Y, Jin Y, Yang Y, Chen LL, Wang Y, et al: Extensive translation of
circular RNAs driven by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res.
27:626–641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Liu J, Liu T, Wang X and He A: Circles
reshaping the RNA world: From waste to treasure. Mol Cancer.
16:582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Qiu JN, Shan K, Xiang J, Gu JY, Zhou RM,
Zhang XL, Zhang CR and Xu JJ: Comprehensive analysis of
circRNA-associated-ceRNA networks in human corneal endothelial
dysfunction. Cornea. 41:1545–1552. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Qu B, Wang J, Li Y, Wu X and Zhang M:
Hsa_circ_0023826 protects against glaucoma by regulating
miR-188-3p/MDM4 axis. Acta Biochim Pol. 70:253–260. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Tian H, Zhao L, Li H, Huang Y and Wang Y:
Circular RNA in retina: A potential biomarker and therapeutic
target. Ophthalmic Res. 66:516–528. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Li D, Che X, Gao N and Li J: CircSTRBP
contributes to H2O2-induced lens epithelium
cell dysfunction through increasing NOX4 mRNA stability by
recruiting IGF2BP1. Exp Eye Res. 241:1098172024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Wang Y, Zhang G, Li P, Kang L, Qin B, Cao
Y, Luo J, Chen X, Qin M and Guan H: Profiling and integrated
analysis of the ERCC6-regulated circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in lens
epithelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 46:1341–1352. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Xu X, Gao R, Li S, Jiang K, Sun X and
Zhang J: Circular RNA circZNF292 regulates H2
O2-induced injury in human lens epithelial HLE-B3 cells
depending on the regulation of the miR-222-3p/E2F3 axis. Cell Biol
Int. 45:1757–1767. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Mao W and Zhang Z: The
Hsa_circ_0105558/miR-182-5p/ATF6 cascade affects
H2O2-triggered oxidative damage and apoptosis
of human lens epithelial cells. Biochem Genet. 63:1241–1257. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Li R, Zhu H, Li Q, Tang J, Jin Y and Cui
H: METTL3-mediated m6A modification of has_circ_0007905 promotes
age-related cataract progression through miR-6749-3p/EIF4EBP1.
PeerJ. 11:e148632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Liu J, Zhang J, Zhang G, Zhou T, Zou X,
Guan H and Wang Y: CircMRE11A_013 binds to UBXN1 and integrates ATM
activation enhancing lens epithelial cells senescence in
age-related cataract. Aging (Albany NY). 13:5383–5402. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Cui G, Wang L and Huang W: Circular RNA
HIPK3 regulates human lens epithelial cell dysfunction by targeting
the miR-221-3p/PI3K/AKT pathway in age-related cataract. Exp Eye
Res. 198:1081282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Liu X, Liu B, Zhou M, Fan F, Yu M, Gao C,
Lu Y and Luo Y: Circular RNA HIPK3 regulates human lens epithelial
cells proliferation and apoptosis by targeting the miR-193a/CRYAA
axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:2277–2285. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Chen S, Wang M, Jian R, Li H, Liu G, Zhou
C, Xiong Y and Wang W: Circ_HIPK3 Inhibits
H2O2-induced lens epithelial cell injury in
age-related cataract depending on the regulation of
miR-495-3p/HDAC4 pathway. Biochem Genet. 61:565–577. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Liu T, Zhao L, Yan D and Wang N:
Circ_0060,144 inhibits the occurrence and development of
age-related cataract via the miR-23b-3p/HIPK3 axis. Exp Eye Res.
222:1091792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Zhou C, Huang X, Li X and Xiong Y:
Circular RNA erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 assuages
ultraviolet irradiation-induced apoptosis of lens epithelial cells
by stimulating 5'-bisphosphate nucleotidase 1 in a
miR-24-3p-dependent manner. Bioengineered. 12:8953–8964. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Fang R, Li JH, Li HL, Yue PL, Ding XF, Jia
YX, Liu ZC, Zhou HG, Yang C and Song XD: CircRNA 06209 inhibits
cataract development by sponging miR-6848-5p and regulating ALOX15
expression. Exp Eye Res. 235:1096402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Li R, Jiang J, Shi H, Qian H, Zhang X and
Xu W: CircRNA: A rising star in gastric cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
77:1661–1680. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Cui F, Sun Z, Zhang X and Liu C:
CircMAP3K4 suppresses H2O2-induced human lens
epithelial cell injury by miR-630/ERCC6 axis in age-related
cataract. Curr Eye Res. 49:487–495. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Sun L, Li F, Bai S and Bi C: CircRNA HLCS
regulates lens epithelial cell apoptosis via miR-338-3p/BPNT1 axis.
Int Ophthalmol. 44:1422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Wu Q, Liu H, Ma B and Wang C: Circular RNA
Circ_0122396 regulates human lens epithelial cell progression by
regulating miR-23a-3p and MMP16 in age-related cataract. Curr Eye
Res. 49:1161–1170. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Liu B, Cao J, Wang X, Guo C, Liu Y and
Wang T: Deciphering the tRNA-derived small RNAs: Origin,
development, and future. Cell Death Dis. 13:242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Xie Y, Yao L, Yu X, Ruan Y, Li Z and Guo
J: Action mechanisms and research methods of tRNA-derived small
RNAs. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:1092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Pan J, Liu Z, Shen B, Xu J, Dai G, Xu W,
Wang J, Li L and Cheng L: tsRNA-04002 alleviates intervertebral
disk degeneration by targeting PRKCA to inhibit apoptosis of
nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 18:4132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Zeng T, Hua Y, Sun C, Zhang Y, Yang F,
Yang M, Yang Y, Li J, Huang X, Wu H, et al: Relationship between
tRNA-derived fragments and human cancers. Int J Cancer.
147:3007–3018. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Zhang L, Liu J and Hou Y: Classification,
function, and advances in tsRNA in non-neoplastic diseases. Cell
Death Dis. 14:7482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Wang S, Luo Z, Yuan L, Lin X, Tang Y, Yin
L, Liang P and Jiang B: tRNA-derived small RNAs: Novel insights
into the pathogenesis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 16:300–309. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Zhang X, Trebak F, Souza LAC, Shi J, Zhou
T, Kehoe PG, Chen Q and Feng Earley Y: Small RNA modifications in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 145:1050582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Zhou M, He X, Zhang J, Mei C, Zhong B and
Ou C: tRNA-derived small RNAs in human cancers: Roles, mechanisms,
and clinical application. Mol Cancer. 23:762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Han X, Cai L, Lu Y, Li D and Yang J:
Identification of tRNA-derived fragments and their potential roles
in diabetic cataract rats. Epigenomics. 12:1405–1418. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Ma Y, Zhang Y, Zhang HY, Zhao Y, Li XM,
Jiang YF, Yao MD, Jiang Q and Yan B: Dual anti-angiogenic and
anti-inflammatory action of tRNA-Cys-5-0007 in ocular vascular
disease. J Transl Med. 22:5622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Peng Y, Zou J, Wang JH, Zeng H, Tan W,
Yoshida S, Zhang L, Li Y and Zhou Y: Small RNA sequencing reveals
transfer RNA-derived small RNA expression profiles in retinal
neovascularization. Int J Med Sci. 17:1713–1722. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Zhang G, Kang L, Li P, Ran Q, Chen X, Ji M
and Guan H: Genome-wide repertoire of transfer RNA-derived
fragments in a mouse model of age-related cataract. Curr Eye Res.
47:1397–1404. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS and Slack FJ:
Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:5–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Ma Y, Liu Y, Shu B, Yang J, Lv L, Zhou L,
Wang L and Shi Z: CircMAP3K4 protects human lens epithelial cells
from H2O2-induced dysfunction by targeting
miR-193a-3p/PLCD3 axis in age-related cataract. Cell Cycle.
22:303–315. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Xu J, Shao T, Ding N, Li Y and Li X:
miRNA-miRNA crosstalk: From genomics to phenomics. Brief Bioinform.
18:1002–1011. 2017.
|
|
202
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Shao T, Wang G, Chen H, Xie Y, Jin X, Bai
J, Xu J, Li X, Huang J, Jin Y and Li Y: Survey of miRNA-miRNA
cooperative regulation principles across cancer types. Brief
Bioinform. 20:1621–1638. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Chiu HS, Somvanshi S, Patel E, Chen TW,
Singh VP, Zorman B, Patil SL, Pan Y, Chatterjee SS; Cancer Genome
Atlas Research Network; et al: Pan-cancer analysis of lncRNA
regulation supports their targeting of cancer genes in each tumor
context. Cell Rep. 23:297–312.e12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Zhang K, Chen L, Qu L and Yan H: A
comprehensive investigation of identifying miRNA biomarkers and
their potential role in age-related cataract by meta-analysis and
bioinformatics analysis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
263:1307–1325. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Michalak EM, Burr ML, Bannister AJ and
Dawson MA: The roles of DNA, RNA and histone methylation in ageing
and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:573–589. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Dossin F, Pinheiro I, Żylicz JJ, Roensch
J, Collombet S, Le Saux A, Chelmicki T, Attia M, Kapoor V, Zhan Y,
et al: SPEN integrates transcriptional and epigenetic control of
X-inactivation. Nature. 578:455–460. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Grigoryan A, Pospiech J, Krämer S, Lipka
D, Liehr T, Geiger H, Kimura H, Mulaw MA and Florian MC: Attrition
of X chromosome inactivation in aged hematopoietic stem cells. Stem
Cell Reports. 16:708–716. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Kulis M, Queirós AC, Beekman R and
Martín-Subero JI: Intragenic DNA methylation in transcriptional
regulation, normal differentiation and cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1829:1161–1174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Nishiyama A and Nakanishi M: Navigating
the DNA methylation landscape of cancer. Trends Genet.
37:1012–1027. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
May MS and Hattaman S: Deoxyribonucleic
acid-cytosine methylation by host- and plasmid-controlled enzymes.
J Bacteriol. 122:129–138. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Kohli RM and Zhang Y: TET enzymes, TDG and
the dynamics of DNA demethylation. Nature. 502:472–479. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Harris AJ and Goldman AD: The complex
phylogenetic relationships of a 4mC/6mA DNA methyltransferase in
prokaryotes. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 149:1068372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Thomas B, Matson S, Chopra V, Sun L,
Sharma S, Hersch S, Rosas HD, Scherzer C, Ferrante R and Matson W:
A novel method for detecting 7-methyl guanine reveals aberrant
methylation levels in Huntington disease. Anal Biochem.
436:112–120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Hashimoto H, Pais JE, Zhang X, Saleh L, Fu
ZQ, Dai N, Corrêa IR Jr, Zheng Y and Cheng X: Structure of a
Naegleria Tet-like dioxygenase in complex with 5-methylcytosine
DNA. Nature. 506:391–395. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Angeloni A and Bogdanovic O: Enhancer DNA
methylation: Implications for gene regulation. Essays Biochem.
63:707–715. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Zeng Y and Chen T: DNA methylation
reprogramming during mammalian development. Genes (Basel).
10:2572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Zong FF, Jia DD, Huang GK, Pan M, Hu H,
Song SY, Xiao L, Wang RW and Liang L: New perspectives on DNA
methylation modifications in ocular diseases. Int J Ophthalmol.
18:340–350. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Li Y, Chen X and Lu C: The interplay
between DNA and histone methylation: Molecular mechanisms and
disease implications. EMBO Rep. 22:e518032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and
epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 16:6–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Boyes J and Bird A: DNA methylation
inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein.
Cell. 64:1123–1134. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Cvekl A and Mitton KP: Epigenetic
regulatory mechanisms in vertebrate eye development and disease.
Heredity (Edinb). 105:135–151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Gao Y, Yan Y and Huang T: Human
age-related cataracts: epigenetic suppression of the nuclear factor
erythroid 2-related factor 2-mediated antioxidant system. Mol Med
Rep. 11:1442–1447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
224
|
Jin B and Robertson KD: DNA
methyltransferases, DNA damage repair, and cancer. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 754:3–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Kim DJ: The role of the DNA
methyltransferase family and the therapeutic potential of DNMT
inhibitors in tumor treatment. Curr Oncol. 32:882025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Asada M, Hayashi H and Takagi N: Possible
involvement of DNA methylation and protective effect of zebularine
on neuronal cell death after glutamate excitotoxity. Biol Pharm
Bull. 45:770–779. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Liu S, Hu C, Luo Y and Yao K: Genome-wide
DNA methylation profiles may reveal new possible epigenetic
pathogenesis of sporadic congenital cataract. Epigenomics.
12:771–788. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Song J, VanBuskirk JA and Merbs SL:
Regulation of opsin gene expression by DNA methylation and histone
acetylation. Int J Mol Sci. 23:14082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Johnson WM, Finnegan LK, Hauser MA and
Stamer WD: lncRNAs, DNA methylation, and the pathobiology of
exfoliation glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 27:202–209. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
230
|
Zhou P, Luo Y, Liu X, Fan L and Lu Y:
Down-regulation and CpG island hypermethylation of CRYAA in
age-related nuclear cataract. FASEB J. 26:4897–4902. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Baird PN and Wei L: Age-related macular
degeneration and DNA methylation. Epigenomics. 5:239–241. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Chai P, Jia R, Li Y, Zhou C, Gu X, Yang L,
Shi H, Tian H, Lin H, Yu J, et al: Regulation of epigenetic
homeostasis in uveal melanoma and retinoblastoma. Prog Retin Eye
Res. 89:1010302022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Wolff SP: Cataract and UV radiation. Doc
Ophthalmol. 88:201–204. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Li X, Xie J, Xu J, Deng L, Cao G, Huang S,
Zeng C, Liu C, Zhu S, He G, et al: Long-term exposure to ambient
PM2.5 and age-related cataracts among chinese
middle-aged and older adults: Evidence from two national cohort
studies. Environ Sci Technol. 57:11792–11802. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Chen J, Zhou J, Wu J, Zhang G, Kang L, Ben
J, Wang Y, Qin B and Guan H: Aberrant epigenetic alterations of
glutathione-S-transferase P1 in age-related nuclear cataract. Curr
Eye Res. 42:402–410. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
236
|
Liu X, Zhou P, Fan F, Li D, Wu J, Lu Y and
Luo Y: CpG site methylation in CRYAA promoter affect transcription
factor Sp1 binding in human lens epithelial cells. BMC Ophthalmol.
16:1412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Jin SL, Zhang Y, Chen ZH, Qian DW, Qine
YJ, Yongjie Q, He SK and Guo HK: Epigenetic changes of the Klotho
gene in age-related cataracts. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:2544–2553. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Wang Y, Zhang G, Kang L and Guan H:
Expression profiling of DNA methylation and transcriptional
repression associated genes in lens epithelium cells of age-related
cataract. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 37:537–543. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
239
|
Chen X, Su D, Sun Z, Fu Y, Hu Y, Zhang Y,
Zhang X, Wei Q, Zhu W, Ma X and Hu S: Preliminary study on whole
genome methylation and transcriptomics in age-related cataracts.
Gene. 898:1480962024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
240
|
Wang L, Li P and Guo X: Screening of
methylation genes in age-related cataract. Int J Ophthalmol.
11:1102–1107. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Pendergrass W, Penn P, Possin D and Wolf
N: Accumulation of DNA, nuclear and mitochondrial debris, and ROS
at sites of age-related cortical cataract in mice. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:4661–4670. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhang L, Bai J, Ge H and
Liu P: Expression changes in DNA repair enzymes and mitochondrial
DNA damage in aging rat lens. Mol Vis. 16:1754–1763.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Li B, Zhou J, Zhang G, Wang Y, Kang L, Wu
J, Chen J and Guan H: Relationship between the altered expression
and epigenetics of GSTM3 and age-related cataract. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:4721–4732. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Rushmore TH, Morton MR and Pickett CB: The
antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and
identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for
functional activity. J Biol Chem. 266:11632–11639. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Ling X, Zhu L, Yan Y, Qian H, Kang Z, Ye
W, Xie Z and Xue C: Ferulic acid protects human lens epithelial
cells against UVA-induced oxidative damage by downregulating the
DNA demethylation of the keap1 promoter. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
38:e700312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Palsamy P, Bidasee KR and Shinohara T:
Selenite cataracts: Activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and
loss of Nrf2/Keap1-dependent stress protection. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:1794–1805. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Rabbani PS, Soares MA, Hameedi SG, Qian H,
Kang Z, Ye W, Xie Z and Xue C: Dysregulation of Nrf2/Keap1 redox
pathway in diabetes affects multipotency of stromal cells.
Diabetes. 68:141–155. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
248
|
Raghunath A, Sundarraj K, Nagarajan R,
Arfuso F, Bian J, Kumar AP, Sethi G and Perumal E: Antioxidant
response elements: Discovery, classes, regulation and potential
applications. Redox Biol. 17:297–314. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Li J, Wang T, Liu P, Yang F, Wang X, Zheng
W and Sun W: Hesperetin ameliorates hepatic oxidative stress and
inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE pathway in oleic
acid-induced HepG2 cells and a rat model of high-fat diet-induced
NAFLD. Food Funct. 12:3898–3918. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Osama A, Zhang J, Yao J, Yao X and Fang J:
Nrf2: A dark horse in Alzheimer's disease treatment. Ageing Res
Rev. 64:1012062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Palsamy P, Bidasee KR and Shinohara T:
Valproic acid suppresses Nrf2/Keap1 dependent antioxidant
protection through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and
Keap1 promoter DNA demethylation in human lens epithelial cells.
Exp Eye Res. 121:26–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Palsamy P, Bidasee KR, Ayaki M, Augusteyn
RC, Chan JY and Shinohara T: Methylglyoxal induces endoplasmic
reticulum stress and DNA demethylation in the Keap1 promoter of
human lens epithelial cells and age-related cataracts. Free Radic
Biol Med. 72:134–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Zduńska K, Dana A, Kolodziejczak A and
Rotsztejn H: Antioxidant properties of ferulic acid and its
possible application. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 31:332–336. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
254
|
Rampelotto CR, Pereira VG, da Silva
Silveira L, Rossato A, Machado AK, Sagrillo MR, Gündel A, Burger
ME, Schaffazick SR and de Bona da Silva C: Ferulic acid-loaded
nanocapsules: Evaluation of mucosal interaction, safety and
antioxidant activity in human mononucleated cells. Toxicol In
Vitro. 78:1052592022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
255
|
Mathew S and Abraham TE: Ferulic acid: an
antioxidant found naturally in plant cell walls and feruloyl
esterases involved in its release and their applications. Crit Rev
Biotechnol. 24:59–83. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Yang SP, Yang XZ and Cao GP:
Acetyl-l-carnitine prevents homocysteine-induced suppression of
Nrf2/Keap1 mediated antioxidation in human lens epithelial cells.
Mol Med Rep. 12:1145–1150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Giblin FJ: Glutathione: A vital lens
antioxidant. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 16:121–135. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Sheehan D, Meade G, Foley VM and Dowd CA:
Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases:
Implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an
ancient enzyme superfamily. Biochem J. 360:1–16. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
259
|
Whalen R and Boyer TD: Human glutathione
S-transferases. Semin Liver Dis. 18:345–358. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
260
|
Hayes JD and Pulford DJ: The glutathione
S-transferase super-gene family: Regulation of GST and the
contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug
resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 30:445–600. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
261
|
Choi YJ, Yeo HJ, Shin MJ, Youn GS, Park
JH, Yeo EJ, Kwon HJ, Lee LR, Kim NY, Kwon SY, et al: Tat-GSTpi
inhibits dopaminergic cells against MPP+-induced
cellular damage via the reduction of oxidative stress and MAPK
activation. Biomedicines. 11:8362023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
262
|
Laborde E: Glutathione transferases as
mediators of signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation and
cell death. Cell Death Differ. 17:1373–1380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Hayes JD and McLellan LI: Glutathione and
glutathione-dependent enzymes represent a co-ordinately regulated
defence against oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 31:273–300. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Babizhayev MA: Generation of reactive
oxygen species in the anterior eye segment. Synergistic codrugs of
N-acetylcarnosine lubricant eye drops and mitochondria-targeted
antioxidant act as a powerful therapeutic platform for the
treatment of cataracts and primary open-angle glaucoma. BBA Clin.
6:49–68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Sorte K, Sune P, Bhake A, Shivkumar VB,
Gangane N and Basak A: Quantitative assessment of DNA damage
directly in lens epithelial cells from senile cataract patients.
Mol Vis. 17:1–6. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Xu B, Kang L, Zhang G, Wu J, Zhu R, Yang M
and Guan H: The changes of 8-OHdG, hOGG1, APE1 and Pol β in lenses
of patients with age-related cataract. Curr Eye Res. 40:378–385.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
267
|
Chatterjee N and Walker GC: Mechanisms of
DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ Mol Mutagen.
58:235–263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Maugeri-Saccà M, Bartucci M and De Maria
R: DNA damage repair pathways in cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 11:1627–1636. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Kong M, Liu L, Chen X, Driscoll KI, Mao P,
Böhm S, Kad NM, Watkins SC, Bernstein KA, Wyrick JJ, et al:
Single-molecule imaging reveals that Rad4 employs a dynamic DNA
damage recognition process. Mol Cell. 64:376–387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Licht CL, Stevnsner T and Bohr VA:
Cockayne syndrome group B cellular and biochemical functions. Am J
Hum Genet. 73:1217–1239. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Fleming AM and Burrows CJ:
8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine, friend and foe: Epigenetic-like regulator
versus initiator of mutagenesis. DNA Repair (Amst). 56:75–83. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Dinçer Y, Akkaya Ç, Mutlu T, Yavuzer S,
Erkol G, Bozluolcay M and Guven M: DNA repair gene OGG1
polymorphism and its relation with oxidative DNA damage in patients
with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 709:1343622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Synowiec E, Blasiak J, Zaras M, Szaflik J
and Szaflik JP: Association between polymorphisms of the DNA base
excision repair genes MUTYH and hOGG1 and age-related macular
degeneration. Exp Eye Res. 98:58–66. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Wu X, Lai W, Lin H and Liu Y: Association
of OGG1 and MTHFR polymorphisms with age-related cataract: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 12:e01720922017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
275
|
Wang Y, Li F, Zhang G, Kang L, Qin B and
Guan H: Altered DNA methylation and expression profiles of
8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 in lens tissue from age-related
cataract patients. Curr Eye Res. 40:815–821. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
276
|
Yan H, McCane J, Toczylowski T and Chen C:
Analysis of the Xenopus Werner syndrome protein in DNA
double-strand break repair. J Cell Biol. 171:217–227. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
277
|
Tranah GJ, Bugni J, Giovannucci E, Ma J,
Fuchs C, Hines L, Samson L and Hunter DJ: O6-methylguanine-DNA
methyltransferase Leu84Phe and Ile143Val polymorphisms and risk of
colorectal cancer in the nurses' health study and physicians'
health study (United States). Cancer Causes Control. 17:721–731.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Li F, Wang Y, Zhang G, Zhou J, Yang L and
Guan H: Expression and methylation of DNA repair genes in lens
epithelium cells of age-related cataract. Mutat Res. 766-767:31–36.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
279
|
Andley UP: Effects of alpha-crystallin on
lens cell function and cataract pathology. Curr Mol Med. 9:887–892.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
280
|
Horwitz J: Alpha-crystallin can function
as a molecular chaperone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:10449–10453.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
281
|
Thampi P, Hassan A, Smith JB and Abraham
EC: Enhanced C-terminal truncation of alphaA- and
alphaB-crystallins in diabetic lenses. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
43:3265–3272. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
282
|
Horwitz J: Alpha-crystallin. Exp Eye Res.
76:145–153. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
283
|
Christopher KL, Pedler MG, Shieh B, Ammar
DA, Petrash JM and Mueller NH: Alpha-crystallin-mediated protection
of lens cells against heat and oxidative stress-induced cell death.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:309–315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
284
|
Wang Z, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang R,
Li C, Liu X, Pan F, Qiao D, Shi X, et al: Identification of seven
variants in the col4a1 gene that alter RNA splicing by minigene
assay. Clin Genet. 106:336–341. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
285
|
Wang L, Zhu D, Yang Y, He Y, Sun J, Li YM,
Wang ZJ and Li P: DNA hypermethylation of COL4A1 in
ultraviolet-B-induced age-related cataract models in vitro and in
vivo. Int J Ophthalmol. 17:1791–1799. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
286
|
Fujisawa T and Filippakopoulos P:
Functions of bromodomain-containing proteins and their roles in
homeostasis and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 18:246–262. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
287
|
Bhaumik SR, Smith E and Shilatifard A:
Covalent modifications of histones during development and disease
pathogenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 14:1008–1016. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
288
|
Zhang Z, Fu J, Rack JGM, Li C, Voorneveld
J, Filippov DV, Ahel I, Luo ZQ and Das C: Legionella metaeffector
MavL reverses ubiquitin ADP-ribosylation via a conserved
arginine-specific macrodomain. Nat Commun. 15:24522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
289
|
Zhu D, Zhang Y and Wang S: Histone
citrullination: A new target for tumors. Mol Cancer. 20:902021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
290
|
Rong X, Qiu X, Jiang Y, Li D, Xu J, Zhang
Y and Lu Y: Effects of histone acetylation on superoxide dismutase
1 gene expression in the pathogenesis of senile cataract. Sci Rep.
6:347042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
291
|
Kouzarides T: Chromatin modifications and
their function. Cell. 128:693–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
292
|
de Lera AR and Ganesan A: Epigenetic
polypharmacology: From combination therapy to multitargeted drugs.
Clin Epigenetics. 8:1052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
293
|
Scarano N, Brullo C, Musumeci F, Millo E,
Bruzzone S, Schenone S and Cichero E: Recent advances in the
discovery of SIRT1/2 inhibitors via computational methods: A
perspective. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 17:6012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
294
|
Li G, Jiang H, Chang M, Xie H and Hu L:
HDAC6 α-tubulin deacetylase: A potential therapeutic target in
neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurol Sci. 304:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
295
|
Mimura T, Kaji Y, Noma H, Funatsu H and
Okamoto S: The role of SIRT1 in ocular aging. Exp Eye Res.
116:17–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
296
|
Ağaoğlu NB, Varol N, Yıldız SH,
Karaosmanoğlu C, Duman R, Özdemir Erdoğan M and Solak M:
Relationship between SIRT1 gene expression level and disease in
age-related cataract cases. Turk J Med Sci. 49:1068–1072. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
297
|
Zheng T and Lu Y: Changes in SIRT1
expression and its downstream pathways in age-related cataract in
humans. Curr Eye Res. 36:449–455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
298
|
Zentner GE and Henikoff S: Regulation of
nucleosome dynamics by histone modifications. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
20:259–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
299
|
Bannister AJ and Kouzarides T: Regulation
of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 21:381–395. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
300
|
Black JC, Van Rechem C and Whetstine JR:
Histone lysine methylation dynamics: Establishment, regulation, and
biological impact. Mol Cell. 48:491–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
301
|
Cheng X: Structural and functional
coordination of DNA and histone methylation. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 6:a0187472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
302
|
Bachman KE, Rountree MR and Baylin SB:
Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are transcriptional repressors that exhibit
unique localization properties to heterochromatin. J Biol Chem.
276:32282–32287. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
303
|
Shi H, Chai P, Jia R and Fan X: Novel
insight into the regulatory roles of diverse RNA modifications:
Re-defining the bridge between transcription and translation. Mol
Cancer. 19:782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
304
|
Tang J, Zhou C, Ye F, Zuo S, Zhou M, Lu L,
Chai P and Fan X: RNA methylation homeostasis in ocular diseases:
All eyes on Me. Prog Retin Eye Res. 105:1013352025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
305
|
Jia G, Fu Y and He C: Reversible RNA
adenosine methylation in biological regulation. Trends Genet.
29:108–115. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
306
|
Kumari R, Ranjan P, Suleiman ZG, Goswami
SK, Li J, Prasad R and Verma SK: mRNA modifications in
cardiovascular biology and disease: With a focus on m6A
modification. Cardiovasc Res. 118:1680–1692. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
307
|
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S,
Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K,
Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, et al: Topology of the human
and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature.
485:201–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
308
|
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O,
Mason CE and Jaffrey SR: Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation
reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons. Cell.
149:1635–1646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
309
|
Zaccara S, Ries RJ and Jaffrey SR:
Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 20:608–624. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
310
|
Chen X, Wang Y, Wang JN, Cao QC, Sun RX,
Zhu HJ, Zhang YR, Ji JD and Liu QH: m6A modification of
circSPECC1 suppresses RPE oxidative damage and maintains retinal
homeostasis. Cell Rep. 41:1116712022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
311
|
Sheng Z, Pan Y, Shao L and Bao Y: METTL3
mediates CPB1 expression by regulating transcription factor BACH2
to promote apoptosis and oxidative stress of lens epithelial cells.
J Bioenerg Biomembr. 57:161–171. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
312
|
Wang T, Kong S, Tao M and Ju S: The
potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in cancer progression. Mol
Cancer. 19:882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
313
|
Kang L, Bao S, Li P, Zhang G, Zhu X, Ji M
and Guan H: METTL14-mediated depression of NEIL1 aggravates
oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction of lens epithelial
cells through regulating KEAP1/NRF2 pathways. Cell Signal.
127:1116232025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
314
|
Ye HF, Zhang X, Zhao ZN, Zheng C, Fei P,
Xu Y, Lyu J, Chen JL, Guo XX, Zhu H and Zhao PQ: Characterization
of N6-methyladenosine long non-coding RNAs in sporadic
congenital cataract and age-related cataract. Int J Ophthalmol.
17:1973–1986. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
315
|
Wang Y, Li P, Wang C, Bao S, Wang S, Zhang
G, Zou X, Wu J, Guan Y, Ji M and Guan H: Lens epithelium cell
ferroptosis mediated by m6A-lncRNA and GPX4 expression
in lens tissue of age-related cataract. BMC Ophthalmol. 23:5142023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
316
|
Luo G, Xu W, Chen X, Wang S, Wang J, Dong
F, Hu DN, Reinach PS and Yan D: NSUN2-mediated RNA m5C
modification modulates uveal melanoma cell proliferation and
migration. Epigenetics. 17:922–933. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
317
|
Zhao Y, Kong L, Pei Z, Li F, Li C, Sun X,
Shi B and Ge J: m7G methyltransferase METTL1 promotes
post-ischemic angiogenesis via promoting VEGFA mRNA translation.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6420802021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
318
|
Wu C, Liu Z, Ma L, Pei C, Qin L, Gao N, Li
J and Yin Y: MiRNAs regulate oxidative stress related genes via
binding to the 3' UTR and TATA-box regions: A new hypothesis for
cataract pathogenesis. BMC Ophthalmol. 17:1422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
319
|
Gu X, Sun J, Li S, Wu X and Li L:
Oxidative stress induces DNA demethylation and histone acetylation
in SH-SY5Y cells: Potential epigenetic mechanisms in gene
transcription in Aβ production. Neurobiol Aging. 34:1069–1079.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
320
|
Niu Y, DesMarais TL, Tong Z, Yao Y and
Costa M: Oxidative stress alters global histone modification and
DNA methylation. Free Radic Biol Med. 82:22–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
321
|
Li Q, Li X, Tang H, Jiang B, Dou Y,
Gorospe M and Wang W: NSUN2-mediated m5C methylation and
METTL3/METTL14-mediated m6A methylation cooperatively enhance p21
translation. J Cell Biochem. 118:2587–2598. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
322
|
Wu Q and Ni X: ROS-mediated DNA
methylation pattern alterations in carcinogenesis. Curr Drug
Targets. 16:13–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
323
|
Chouliaras L, Mastroeni D, Delvaux E,
Grover A, Kenis G, Hof PR, Steinbusch HW, Coleman PD, Rutten BP and
van den Hove DL: Consistent decrease in global DNA methylation and
hydroxymethylation in the hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease
patients. Neurobiol Aging. 34:2091–2099. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
324
|
Sjöström M, Zhao SG, Levy S, Zhang M, Ning
Y, Shrestha R, Lundberg A, Herberts C, Foye A, Aggarwal R, et al:
The 5-hydroxymethylcytosine landscape of prostate cancer. Cancer
Res. 82:3888–3902. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
325
|
Vatapalli R, Rossi AP, Chan HM and Zhang
J: Cancer epigenetic therapy: Recent advances, challenges, and
emerging opportunities. Epigenomics. 17:59–74. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
326
|
Gomez S, Tabernacki T, Kobyra J, Roberts P
and Chiappinelli KB: Combining epigenetic and immune therapy to
overcome cancer resistance. Semin Cancer Biol. 65:99–113. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
327
|
Zhang P and Zhang M: Epigenetic
alterations and advancement of treatment in peripheral T-cell
lymphoma. Clin Epigenetics. 12:1692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
328
|
Raj K and Mufti GJ: Azacytidine
(Vidaza(R)) in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes. Ther
Clin Risk Manag. 2:377–388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
329
|
Welch JS, Petti AA, Miller CA, Fronick CC,
O'Laughlin M, Fulton RS, Wilson RK, Baty JD, Duncavage EJ, Tandon
B, et al: TP53 and decitabine in acute myeloid leukemia and
myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 375:2023–2036. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
330
|
Duvic M and Vu J: Vorinostat in cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma. Drugs Today (Barc). 43:585–599. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
331
|
McDermott J and Jimeno A: Belinostat for
the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Drugs Today (Barc).
50:337–345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
332
|
Smolewski P and Robak T: The discovery and
development of romidepsin for the treatment of T-cell lymphoma.
Expert Opin Drug Discov. 12:859–873. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
333
|
Kim YH, Bagot M, Pinter-Brown L, Rook AH,
Porcu P, Horwitz SM, Whittaker S, Tokura Y, Vermeer M, Zinzani PL,
et al: Mogamulizumab versus vorinostat in previously treated
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (MAVORIC): An international, open-label,
randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:1192–1204.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
334
|
Geissler K, Koristek Z, Del Castillo TB,
Novák J, Rodríguez-Macías G, Metzelder SK, Illes A, Mayer J, Arnan
M, Keating MM, et al: Oral decitabine/cedazuridine versus
intravenous decitabine for acute myeloid leukaemia: A randomised,
crossover, registration, pharmacokinetics study. Br J Haematol.
205:1734–1745. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
335
|
Fu S, Hu W, Iyer R, Kavanagh JJ, Coleman
RL, Levenback CF, Sood AK, Wolf JK, Gershenson DM, Markman M, et
al: Phase 1b-2a study to reverse platinum resistance through use of
a hypomethylating agent, azacitidine, in patients with
platinum-resistant or platinum-refractory epithelial ovarian
cancer. Cancer. 117:1661–1669. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
336
|
Mathew OP, Ranganna K and Milton SG:
Involvement of the antioxidant effect and anti-inflammatory
response in butyrate-inhibited vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 7:1008–1027. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
337
|
Ziemka-Nalecz M and Zalewska T:
Neuroprotective effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors in brain
ischemia. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 74:383–395. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
338
|
Qiu X, Rong X, Yang J and Lu Y: Evaluation
of the antioxidant effects of different histone deacetylase
inhibitors (HDACis) on human lens epithelial cells (HLECs) after
UVB exposure. BMC Ophthalmol. 19:422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
339
|
Hong DS, Kang YK, Borad M, Sachdev J,
Ejadi S, Lim HY, Brenner AJ, Park K, Lee JL, Kim TY, et al: Phase 1
study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with
advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 122:1630–1637. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
340
|
Ottosen S, Parsley TB, Yang L, Zeh K, van
Doorn LJ, van der Veer E, Raney AK, Hodges MR and Patick AK: In
vitro antiviral activity and preclinical and clinical resistance
profile of miravirsen, a novel anti-hepatitis C virus therapeutic
targeting the human factor miR-122. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
59:599–608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
341
|
Vermeire S, Sands BE, Tilg H, Tulassay Z,
Kempinski R, Danese S, Bunganič I, Nitcheu J, Santo J, Scherrer D,
et al: ABX464 (obefazimod) for moderate-to-severe, active
ulcerative colitis: a phase 2b, double-blind, randomised,
placebo-controlled induction trial and 48 week, open-label
extension. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:1024–1035. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
342
|
Winkle M, El-Daly SM, Fabbri M and Calin
GA: Noncoding RNA therapeutics-challenges and potential solutions.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:629–651. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
343
|
Zhang X, Qiu H, Zhang F and Ding S:
Advances in single-cell multi-omics and application in
cardiovascular research. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8838612022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
344
|
Armand EJ, Li J, Xie F, Luo C and Mukamel
EA: Single-cell sequencing of brain cell transcriptomes and
epigenomes. Neuron. 109:11–26. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
345
|
Nam AS, Chaligne R and Landau DA:
Integrating genetic and non-genetic determinants of cancer
evolution by single-cell multi-omics. Nat Rev Genet. 22:3–18. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
346
|
Liu X, Zhang L, Li X, Chen L, Lu L, Yang
Y, Wu Y, Zheng L, Tang J, Wang F, et al: Single-cell multi-omics
profiling uncovers the immune heterogeneity in HIV-infected
immunological non-responders. EBioMedicine. 115:1056672025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
347
|
Tangeman JA, Rebull SM, Grajales-Esquivel
E, Bendezu-Sayas S, Robinson ML, Lachke SA and Del Rio-Tsonis K:
Integrated single-cell multiomics uncovers foundational regulatory
mechanisms of lens development and pathology. Development.
151:dev2022492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
348
|
Vickovic S, Eraslan G, Salmén F,
Klughammer J, Stenbeck L, Schapiro D, Äijö T, Bonneau R,
Bergenstråhle L, Navarro JF, et al: High-definition spatial
transcriptomics for in situ tissue profiling. Nat Methods.
16:987–990. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
349
|
Robles-Remacho A, Sanchez-Martin RM and
Diaz-Mochon JJ: Spatial transcriptomics: emerging technologies in
tissue gene expression profiling. Anal Chem. 95:15450–15460. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
350
|
Cilento MA, Sweeney CJ and Butler LM:
Spatial transcriptomics in cancer research and potential clinical
impact: A narrative review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 150:2962024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
351
|
Duan R, Fu Q, Sun Y and Li Q: Epigenetic
clock: A promising biomarker and practical tool in aging. Ageing
Res Rev. 81:1017432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
352
|
Horvath S, Lu AT, Haghani A, Zoller JA, Li
CZ, Lim AR, Brooke RT, Raj K, Serres-Armero A, Dreger DL, et al:
DNA methylation clocks for dogs and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
119:e21208871192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
353
|
Margiotti K, Monaco F, Fabiani M, Mesoraca
A and Giorlandino C: Epigenetic clocks: In aging-related and
complex diseases. Cytogenet Genome Res. 163:247–256. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
354
|
Chen J, Yuan XL, Zhou X, Xu J, Zhang X and
Duan X: Mendelian randomization implicates causal association
between epigenetic age acceleration and age-related eye diseases or
glaucoma endophenotypes. Clin Epigenetics. 16:1062024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|