|
1
|
Ma J, Yiu WH and Tang SCW: Complement
anaphylatoxins: Potential therapeutic target for diabetic kidney
disease. Diabet Med. 42:e154272025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Li X, Zhao S, Xie J, Li M, Tong S, Ma J,
Yang R, Zhao Q, Zhang J and Xu A: Targeting the NF-κB p65-MMP28
axis: Wogonoside as a novel therapeutic agent for attenuating
podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. Phytomedicine.
138:1564062025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang T, Chen Y, Liu Z, Zhou J, Li N, Shan
Y and He Y: Long noncoding RNA Glis2 regulates podocyte
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy via
sponging miR-328-5p. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e182042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Woroniecka KI, Park ASD, Mohtat D, Thomas
DB, Pullman JM and Susztak K: Transcriptome analysis of human
diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes. 60:2354–2369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wehner H, Höhn D, Faix-Schade U, Huber H
and Walzer P: Glomerular changes in mice with spontaneous
hereditary diabetes. Lab Invest. 27:331–340. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li L, Chen L, Zang J, Tang X, Liu Y, Zhang
J, Bai L, Yin Q, Lu Y, Cheng J, et al: C3a and C5a receptor
antagonists ameliorate endothelial-myofibroblast transition via the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic kidney disease.
Metabolism. 64:597–610. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li L, Yin Q, Tang X, Bai L, Zhang J, Gou
S, Zhu H, Cheng J, Fu P and Liu F: C3a receptor antagonist
ameliorates inflammatory and fibrotic signals in type 2 diabetic
nephropathy by suppressing the activation of TGF-β/smad3 and IKBα
pathway. PLoS One. 9:e1136392014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Morigi M, Perico L, Corna D, Locatelli M,
Cassis P, Carminati CE, Bolognini S, Zoja C, Remuzzi G, Benigni A
and Buelli S: C3a receptor blockade protects podocytes from injury
in diabetic nephropathy. JCI Insight. 5:e1318492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma K, Chen G, Li W, Kepp O, Zhu Y and Chen
Q: Mitophagy, mitochondrial homeostasis, and cell fate. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 8:4672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stanigut AM, Tuta L, Pana C, Alexandrescu
L, Suceveanu A, Blebea NM and Vacaroiu IA: Autophagy and mitophagy
in diabetic kidney disease-a literature review. Int J Mol Sci.
26:8062025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tagawa A, Yasuda M, Kume S, Yamahara K,
Nakazawa J, Chin-Kanasaki M, Araki H, Araki S, Koya D, Asanuma K,
et al: Impaired podocyte autophagy exacerbates proteinuria in
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 65:755–767. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhou D, Zhou M, Wang Z, Fu Y, Jia M, Wang
X, Liu M, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Zhou Y, et al: Progranulin alleviates
podocyte injury via regulating CAMKK/AMPK-mediated autophagy under
diabetic conditions. J Mol Med (Berl). 97:1507–1520. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou D, Zhou M, Wang Z, Fu Y, Jia M, Wang
X, Liu M, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Lu Y, et al: PGRN acts as a novel
regulator of mitochondrial homeostasis by facilitating mitophagy
and mitochondrial biogenesis to prevent podocyte injury in diabetic
nephropathy. Cell Death Dis. 10:5242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martini S, Nair V, Keller BJ, Eichinger F,
Hawkins JJ, Randolph A, Böger CA, Gadegbeku CA, Fox CS, Cohen CD,
et al: Integrative biology identifies shared transcriptional
networks in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:2559–2572. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ju W, Greene CS, Eichinger F, Nair V,
Hodgin JB, Bitzer M, Lee YS, Zhu Q, Kehata M, Li M, et al: Defining
cell-type specificity at the transcriptional level in human
disease. Genome Res. 23:1862–1873. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
National Research Council Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the C. and A. Use of Laboratory. The
National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health, in Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. National Academies Press. Copyright© 2011. National
Academy of Sciences; Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
17
|
Ames RS, Lee D, Foley JJ, Jurewicz AJ,
Tornetta MA, Bautsch W, Settmacher B, Klos A, Erhard KF, Cousins
RD, et al: Identification of a selective nonpeptide antagonist of
the anaphylatoxin C3a receptor that demonstrates antiinflammatory
activity in animal models. J Immunol. 166:6341–6348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yasuda-Yamahara M, Kume S, Tagawa A,
Maegawa H and Uzu T: Emerging role of podocyte autophagy in the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. Autophagy. 11:2385–2386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Flyvbjerg A: The role of the complement
system in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:311–318. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tesch GH: Diabetic nephropathy-is this an
immune disorder? Clin Sci (Lond). 131:2183–2199. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sahu A and Lambris JD: Structure and
biology of complement protein C3, a connecting link between innate
and acquired immunity. Immunol Rev. 180:35–48. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kelly KJ, Liu Y, Zhang J and Dominguez JH:
Renal C3 complement component: Feed forward to diabetic kidney
disease. Am J Nephrol. 41:48–56. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Racine KC, Iglesias-Carres L, Herring JA,
Wieland KL, Ellsworth PN, Tessem JS, Ferruzzi MG, Kay CD and
Neilson AP: The high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin type-2
diabetes model induces hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in
male but not female C57BL/6J mice. Nutr Res. 131:135–146. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Zhou R, Li G, Zhang X, Li Y, Shen
Y and Fang J: Multi-omics characterization of diabetic nephropathy
in the db/db mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Comput Struct
Biotechnol J. 27:3399–3409. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin J, Shi Y, Gong J, Zhao L, Li Y, He Q
and Huang H: Exosome secreted from adipose-derived stem cells
attenuates diabetic nephropathy by promoting autophagy flux and
inhibiting apoptosis in podocyte. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:952019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yuen DA, Stead BE, Zhang Y, White KE,
Kabir MG, Thai K, Advani SL, Connelly KA, Takano T, Zhu L, et al:
eNOS deficiency predisposes podocytes to injury in diabetes. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 23:1810–1823. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Angeletti A, Cantarelli C, Petrosyan A,
Andrighetto S, Budge K, D'Agati VD, Hartzell S, Malvi D, Donadei C,
Thurman JM, et al: Loss of decay-accelerating factor triggers
podocyte injury and glomerulosclerosis. J Exp Med.
217:e201916992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Galvan DL, Green NH and Danesh FR: The
hallmarks of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease.
Kidney Int. 92:1051–1057. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen K, Dai H, Yuan J, Chen J, Lin L,
Zhang W, Wang L, Zhang J, Li K and He Y: Optineurin-mediated
mitophagy protects renal tubular epithelial cells against
accelerated senescence in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Death Dis.
9:1052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen TN, Padman BS and Lazarou M:
Deciphering the molecular signals of PINK1/parkin mitophagy. Trends
Cell Biol. 26:733–744. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li W, Du M, Wang Q, Ma X, Wu L, Guo F, Ji
H, Huang F and Qin G: FoxO1 promotes mitophagy in the podocytes of
diabetic male mice via the PINK1/parkin pathway. Endocrinology.
158:2155–2167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao Y and Sun M: Metformin rescues Parkin
protein expression and mitophagy in high glucose-challenged human
renal epithelial cells by inhibiting NF-κB via PP2A activation.
Life Sci. 246:1173822020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yi X, Yan W, Guo T, Liu N, Wang Z, Shang
J, Wei X, Cui X, Sun Y, Ren S and Chen L: Erythropoietin mitigates
diabetic nephropathy by restoring PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy.
Front Pharmacol. 13:8830572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun J, Zhu H, Wang X, Gao Q, Li Z and
Huang H: CoQ10 ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic
nephropathy through mitophagy. J Endocrinol. 240:445–465. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu X, Wang W, Song G, Wei X, Zeng Y, Han
P, Wang D, Shao M, Wu J, Sun H, et al: Astragaloside IV ameliorates
diabetic nephropathy by modulating the mitochondrial quality
control network. PLoS One. 12:e01825582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu X, Lu J, Liu S, Huang D, Chen M, Xiong
G and Li S: Huangqi-Danshen decoction alleviates diabetic
nephropathy in db/db mice by inhibiting PINK1/Parkin-mediated
mitophagy. Am J Transl Res. 12:989–998. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang M, Li C, Yang S, Xiao Y, Chen W, Gao
P, Jiang N, Xiong S, Wei L, Zhang Q, et al: Mitophagy: A novel
therapeutic target for treating DN. Curr Med Chem. 28:2717–2728.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang L, Li W, Gong M, Zhang Z, Xue X, Mao
J, Zhang H, Li S, Liu X, Wu F, et al: C-reactive protein inhibits
C3a/C3aR-dependent podocyte autophagy in favor of diabetic kidney
disease. FASEB J. 36:e223322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang C, Wang Z, Xu J, Ma H, Jin K, Xu T,
Pan X, Feng X and Zhang W: C3aR antagonist alleviates C3a induced
tubular profibrotic phenotype transition via restoring PPARα/CPT-1α
mediated mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in renin-dependent
hypertension. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 28:2382023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen Y, Zheng YF, Lin XH, Zhang JP, Lin F
and Shi H: Dendrobium mixture attenuates renal damage in rats with
diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol
Med Rep. 24:5902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ma Z, Liu Y, Li C, Zhang Y and Lin N:
Repurposing a clinically approved prescription Colquhounia root
tablet to treat diabetic kidney disease via suppressing
PI3K/AKT/NF-kB activation. Chin Med. 17:22022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dong R, Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhao T, Sun Z, Liu
P, Xiang Q, Xiong J, Du X, Yang X, et al: Rutin alleviates EndMT by
restoring autophagy through inhibiting HDAC1 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway in diabetic kidney disease. Phytomedicine. 112:1547002023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y, Yang S, Cui X, Yang J, Zheng M,
Jia J, Han F, Yang X, Wang J, Guo Z, et al: Hyperinsulinemia can
cause kidney disease in the IGT stage of OLETF rats via the
INS/IRS-1/PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway. J Diabetes Res.
2019:47097152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zheng D, Tao M, Liang X, Li Y, Jin J and
He Q: p66Shc regulates podocyte autophagy in high glucose
environment through the Notch-PTEN-PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Histol
Histopathol. 35:405–415. 2020.
|
|
45
|
Wang X, Jiang L, Liu XQ, Huang YB, Wang
AL, Zeng HX, Gao L, Zhu QJ, Xia LL and Wu YG: Paeoniflorin binds to
VEGFR2 to restore autophagy and inhibit apoptosis for podocyte
protection in diabetic kidney disease through PI3K-AKT signaling
pathway. Phytomedicine. 106:1544002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen Y, Li Z, Li H, Su W, Xie Y, Pan Y,
Chen X and Liang D: Apremilast regulates the Teff/Treg balance to
ameliorate uveitis via PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 signaling pathway. Front
Immunol. 11:5816732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miao Z, Liu Y, Xu Y, Bu J and Yang Q:
Oxaloacetate promotes the transition from glycolysis to
gluconeogenesis through the Akt-FoxO1 and JNK/c-Jun-FoxO1 axes and
inhibits the survival of liver cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
161:1150512025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu Z, Liu K, Zhang G, Yang F, He Y, Nan W,
Li Y and Lin J: Transcriptome analysis reveals that the injection
of mesenchymal stem cells remodels extracellular matrix and
complement components of the brain through PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling
pathway in a neuroinflammation mouse model. Genomics.
117:1110332025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Deng A, Wang Y, Huang K, Xie P, Mo P, Liu
F, Chen J, Chen K, Wang Y and Xiao B: Artichoke (Cynara scolymus
L.) water extract alleviates palmitate-induced insulin resistance
in HepG2 hepatocytes via the activation of IRS1/PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 and
GSK-3β signaling pathway. BMC Complement Med Ther. 23:4602023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Cosenso-Martin LN, Takaoka LY and
Vilela-Martin JF: Randomized study comparing vildagliptin vs
glibenclamide on glucose variability and endothelial function in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Diabetes
Metab Syndr Obes. 13:3221–3229. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|















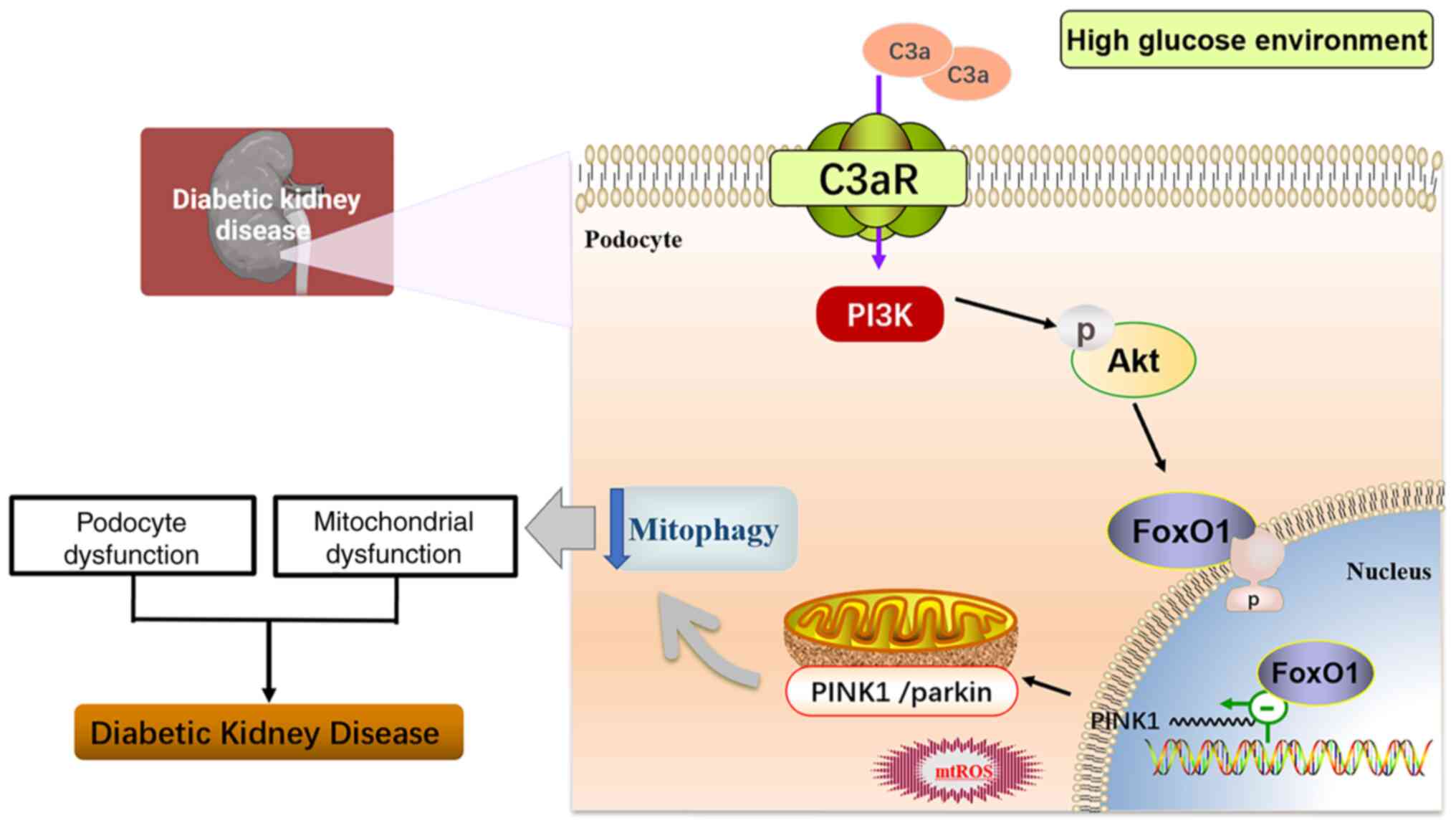
![Expression levels of mitophagy and
related pathway proteins in mouse renal tissues. (A)
Immunohistochemical analysis of the mitophagy-specific protein
PINK1. Magnification, x100. (B) Protein levels of LC3B I/II, parkin
and PINK1 in kidney tissues (n=6). Corresponding histograms are
shown on the right panel of representative protein bands. (C)
Protein levels of PI3K [PI3-kinase p85α (54 + 85 kDa)],
phosphorylated-AKT and FoxO1 in kidney tissues (n=6). Corresponding
histograms are shown on the right panel of representative protein
bands. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and
***P<0.001. p-, phosphorylated.](/article_images/ijmm/56/6/ijmm-56-06-05664-g03.jpg)