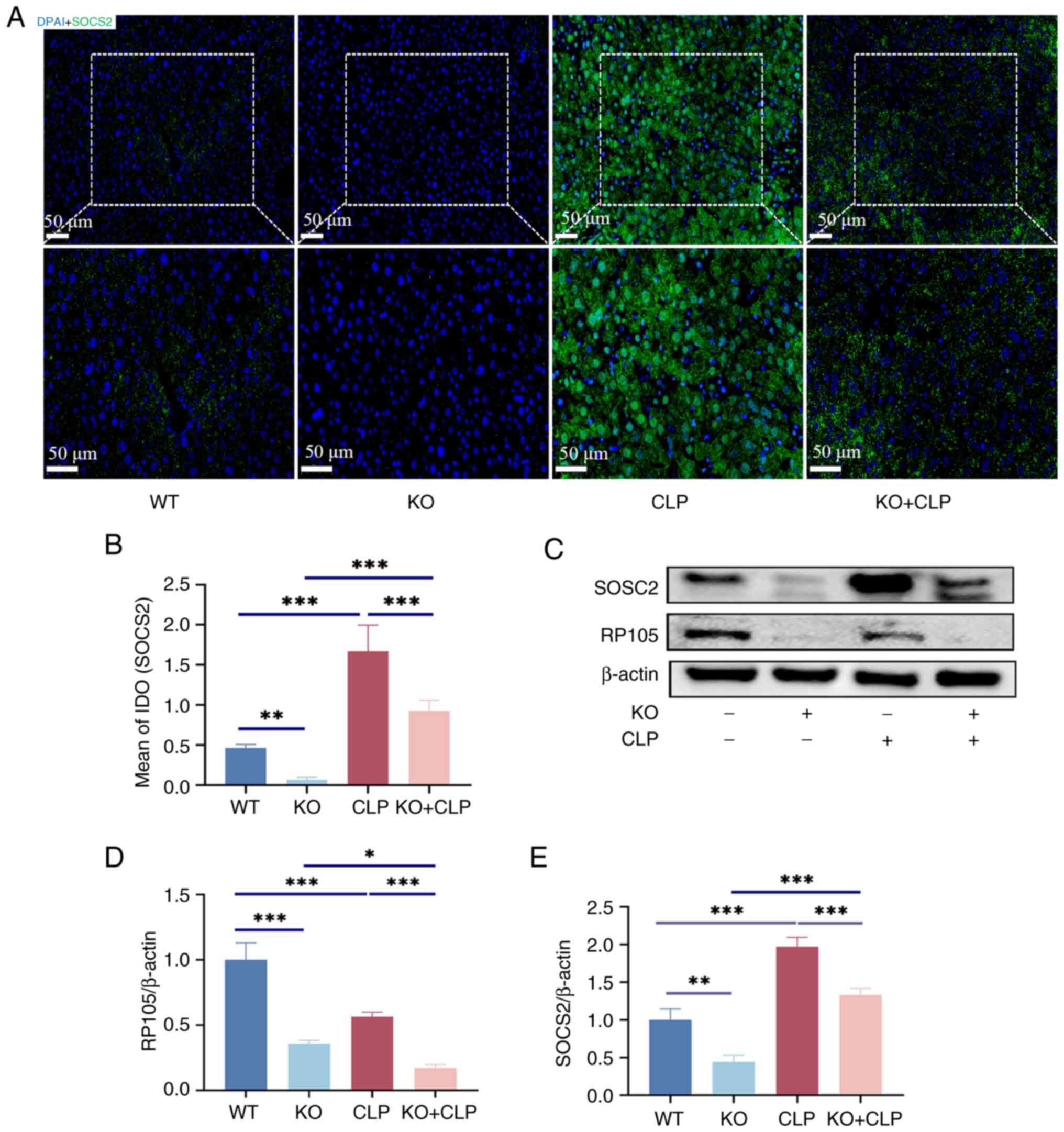
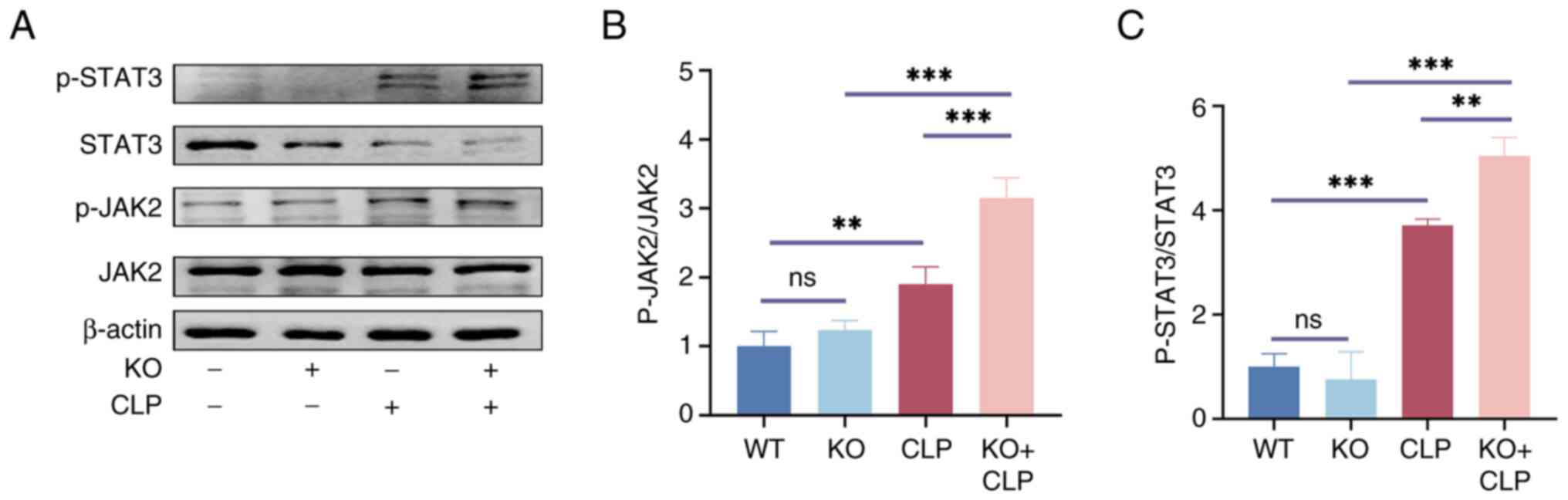
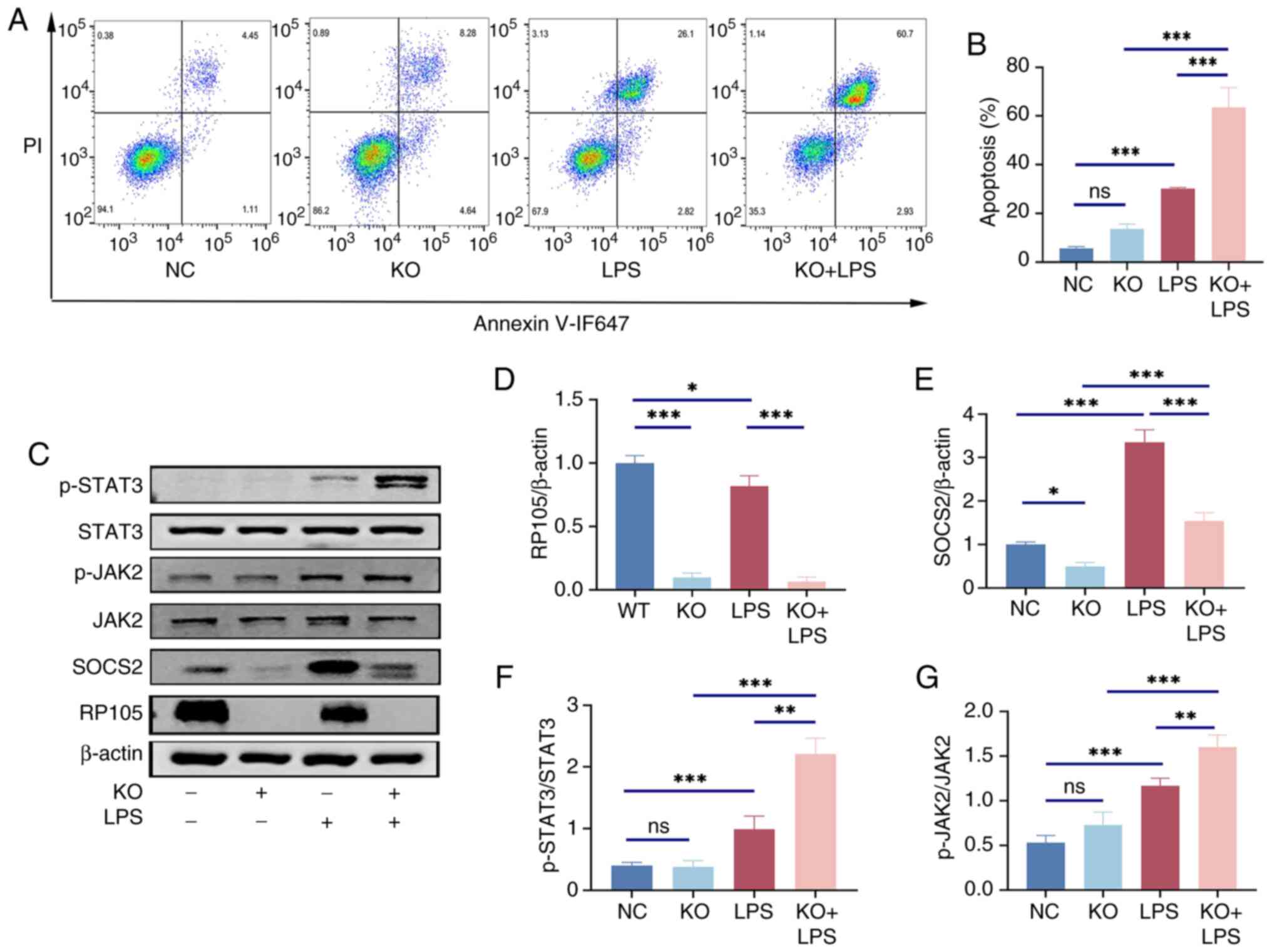
|
1
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease
study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takeuchi O and Akira S: Pattern
recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 140:805–820. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raymond SL, Holden DC, Mira JC, Stortz JA,
Loftus TJ, Mohr AM, Moldawer LL, Moore FA, Larson SD and Efron PA:
Microbial recognition and danger signals in sepsis and trauma.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:2564–2573. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fajgenbaum DC and June CH: Cytokine storm.
N Engl J Med. 383:2255–2273. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chousterman BG, Swirski FK and Weber GF:
Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Semin Immunopathol.
39:517–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Protzer U, Maini MK and Knolle PA: Living
in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat Rev Immunol. 12:201–213.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heymann F and Tacke F: Immunology in the
liver-from homeostasis to disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
13:88–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan J and Li S and Li S: The role of the
liver in sepsis. Int Rev Immunol. 33:498–510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Elmi AN and Kwo PY: The liver in sepsis.
Clin Liver Dis. 29:453–467. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Miyake K, Yamashita Y, Ogata M, Sudo T and
Kimoto M: RP105, a novel B cell surface molecule implicated in B
cell activation, is a member of the leucine-rich repeat protein
family. J Immunol. 154:3333–3340. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Divanovic S, Trompette A, Atabani SF,
Madan R, Golenbock DT, Visintin A, Finberg RW, Tarakhovsky A, Vogel
SN, Belkaid Y, et al: Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor 4
signaling by the Toll-like receptor homolog RP105. Nat Immunol.
6:571–578. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schultz TE and Blumenthal A: The
RP105/MD-1 complex: Molecular signaling mechanisms and
pathophysiological implications. J Leukoc Biol. 101:183–192. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang J, Yang C, Yang J, Ding J, Li X, Yu
Q, Guo X, Fan Z and Wang H: RP105 alleviates myocardial ischemia
reperfusion injury via inhibiting TLR4/TRIF signaling pathways. Int
J Mol Med. 41:3287–3295. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan Z, Pathak JL and Ge L: The potential
role of RP105 in regulation of inflammation and osteoclastogenesis
during inflammatory diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7132542021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu J, Zhang Y, Shi L, Xia Y, Zha H, Li H
and Song Z: RP105 protects against ischemic and septic acute kidney
injury via suppressing TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 109:1089042022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wezel A, de Vries MR, Maassen JM, Kip P,
Peters EA, Karper JC, Kuiper J, Bot I and Quax PHA: Deficiency of
the TLR4 analogue RP105 aggravates vein graft disease by inducing a
pro-inflammatory response. Sci Rep. 6:242482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen F, Xu W, Tang M, Tian Y, Shu Y, He X,
Zhou L, Liu Q, Zhu Q, Lu X, et al: hnRNPA2B1 deacetylation by SIRT6
restrains local transcription and safeguards genome stability. Cell
Death Differ. 32:382–396. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li T, Sun H, Li Y, Su L, Jiang J, Liu Y,
Jiang N, Huang R, Zhang J and Peng Z: Downregulation of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome mediated
pyroptosis in sepsis-induced AKI. Cell Death Discov. 8:612022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Duo H, Yang Y, Luo J, Cao Y, Liu Q, Zhang
J, Du S, You J, Zhang G, Ye Q and Pan H: Modulatory role of
radioprotective 105 in mitigating oxidative stress and ferroptosis
via the HO-1/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis in sepsis-mediated renal injury.
Cell Death Discov. 11:2902025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kollias NS, Hess WJ, Johnson CL, Murphy M
and Golab G: A literature review on current practices, knowledge,
and viewpoints on pentobarbital euthanasia performed by
veterinarians and animal remains disposal in the United States. J
Am Vet Med Assoc. 261:733–738. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gong S, Yan Z, Liu Z, Niu M, Fang H, Li N,
Huang C, Li L, Chen G, Luo H, et al: Intestinal microbiota mediates
the susceptibility to polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver injury by
granisetron generation in mice. Hepatology. 69:1751–1767. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liang H, Song H, Zhang X, Song G, Wang Y,
Ding X, Duan X, Li L, Sun T and Kan Q: Metformin attenuated
sepsis-related liver injury by modulating gut microbiota. Emerg
Microbes Infect. 11:815–828. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhong X, Xiao Q, Liu Z, Wang W, Lai CH,
Yang W, Yue P, Ye Q and Xiao J: TAK242 suppresses the TLR4
signaling pathway and ameliorates DCD liver IRI in rats. Mol Med
Rep. 20:2101–2110. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li S, Han S, Jin K, Yu T, Chen H, Zhou X,
Tan Z and Zhang G: SOCS2 suppresses inflammation and apoptosis
during NASH progression through limiting NF-κB activation in
macrophages. Int J Biol Sci. 17:4165–4175. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Posselt G, Schwarz H, Duschl A and
Horejs-Hoeck J: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 is a feedback
inhibitor of TLR-induced activation in human monocyte-derived
dendritic cells. J Immunol. 187:2875–2884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baetz A, Frey M, Heeg K and Dalpke AH:
Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins indirectly
regulate toll-like receptor signaling in innate immune cells. J
Biol Chem. 279:54708–54715. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang J, Zeng P, Yang J and Fan ZX: The
role of RP105 in cardiovascular disease through regulating TLR4 and
PI3K signaling pathways. Curr Med Sci. 39:185–189. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Divanovic S, Trompette A, Petiniot LK,
Allen JL, Flick LM, Belkaid Y, Madan R, Haky JJ and Karp CL:
Regulation of TLR4 signaling and the host interface with pathogens
and danger: The role of RP105. J Leukoc Biol. 82:265–271. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M and Rhodes A:
Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 392:75–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Recknagel P, Gonnert FA, Westermann M,
Lambeck S, Lupp A, Rudiger A, Dyson A, Carré JE, Kortgen A, Krafft
C, et al: Liver dysfunction and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
signalling in early sepsis: Experimental studies in rodent models
of peritonitis. PLoS Med. 9:e10013382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bastarache JA and Matthay MA: Cecal
ligation model of sepsis in mice: New insights. Crit Care Med.
41:356–357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Dejager L, Pinheiro I, Dejonckheere E and
Libert C: Cecal ligation and puncture: The gold standard model for
polymicrobial sepsis? Trends Microbiol. 19:198–208. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miyake K, Yamashita Y, Hitoshi Y, Takatsu
K and Kimoto M: Murine B cell proliferation and protection from
apoptosis with an antibody against a 105-kD molecule:
Unresponsiveness of X-linked immunodeficient B cells. J Exp Med.
180:1217–1224. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Miura Y, Shimazu R, Miyake K, Akashi S,
Ogata H, Yamashita Y, Narisawa Y and Kimoto M: RP105 is associated
with MD-1 and transmits an activation signal in human B cells.
Blood. 92:2815–2822. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ishii A, Matsuo A, Sawa H, Tsujita T,
Shida K, Matsumoto M and Seya T: Lamprey TLRs with properties
distinct from those of the variable lymphocyte receptors. J
Immunol. 178:397–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yang J, Zhai Y, Huang C, Xiang Z, Liu H,
Wu J, Huang Y, Liu L, Li W, Wang W, et al: RP105 attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in the myocardium via
activation of the Lyn/Syk/STAT3 signaling pathway. Inflammation.
47:1371–1385. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo X, Hu S, Liu JJ, Huang L, Zhong P, Fan
ZX, Ye P and Chen MH: Piperine protects against pyroptosis in
myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by regulating the
miR-383/RP105/AKT signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 25:244–258.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Guo X, Jiang H and Chen J: RP105-PI3K-Akt
axis: A potential therapeutic approach for ameliorating myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 206:95–96. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu B, Zhang N, Liu Z, Fu Y, Feng S, Wang
S, Cao Y, Li D, Liang D, Li F, et al: RP105 involved in activation
of mouse macrophages via TLR2 and TLR4 signaling. Mol Cell Biochem.
378:183–193. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang W and Yang J, He C and Yang J: RP105
plays a cardioprotective role in myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury by regulating the Toll-like receptor 2/4 signaling pathways.
Mol Med Rep. 22:1373–1381. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun Y, Liu L, Yuan J, Sun Q, Wang N and
Wang Y: RP105 protects PC12 cells from oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reoxygenation injury via activation of the PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 41:3081–3089. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sarajlic M, Neuper T, Föhrenbach Quiroz
KT, Michelini S, Vetter J, Schaller S and Horejs-Hoeck J: IL-1β
induces SOCS2 expression in human dendritic cells. Int J Mol Sci.
20:59312019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Krebs DL and Hilton DJ: SOCS proteins:
Negative regulators of cytokine signaling. Stem Cells. 19:378–387.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Elliott J and Johnston JA: SOCS: Role in
inflammation, allergy and homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 25:434–440.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Keating N and Nicholson SE: SOCS-mediated
immunomodulation of natural killer cells. Cytokine. 118:64–70.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hu J, Winqvist O, Flores-Morales A,
Wikström AC and Norstedt G: SOCS2 influences LPS induced human
monocyte-derived dendritic cell maturation. PLoS One. 4:e71782009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang D, Pan A, Gu J, Liao R, Chen X and
Xu Z: Upregulation of miR-144-3p alleviates Doxorubicin-induced
heart failure and cardiomyocytes apoptosis via SOCS2/PI3K/AKT axis.
Chem Biol Drug Des. 101:24–39. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Monti-Rocha R, Cramer A, Gaio Leite P,
Antunes MM, Pereira RVS, Barroso A, Queiroz-Junior CM, David BA,
Teixeira MM, Menezes GB and Machado FS: SOCS2 is critical for the
balancing of immune response and oxidate stress protecting against
acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury. Front Immunol.
9:31342018. View Article : Google Scholar
|