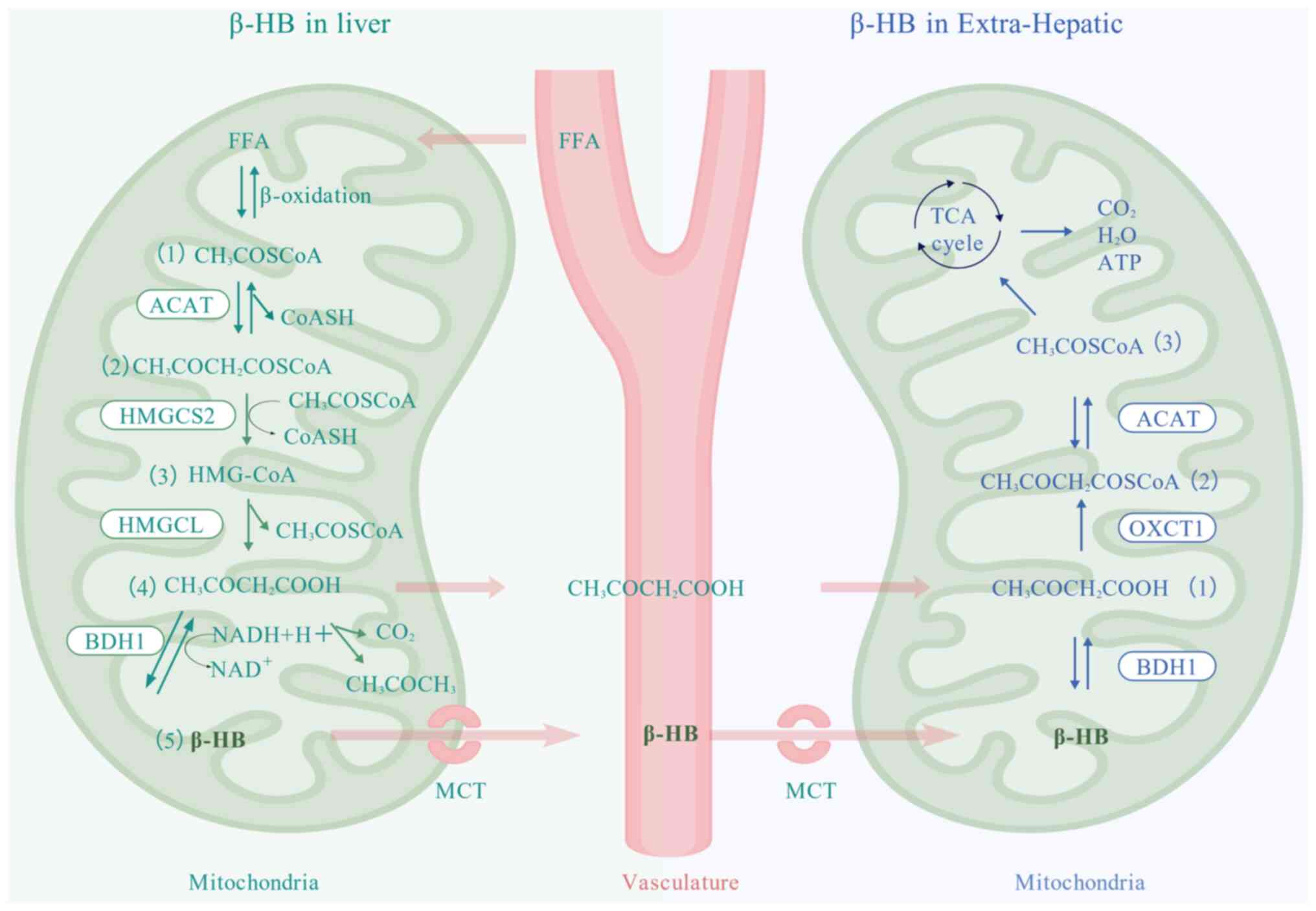
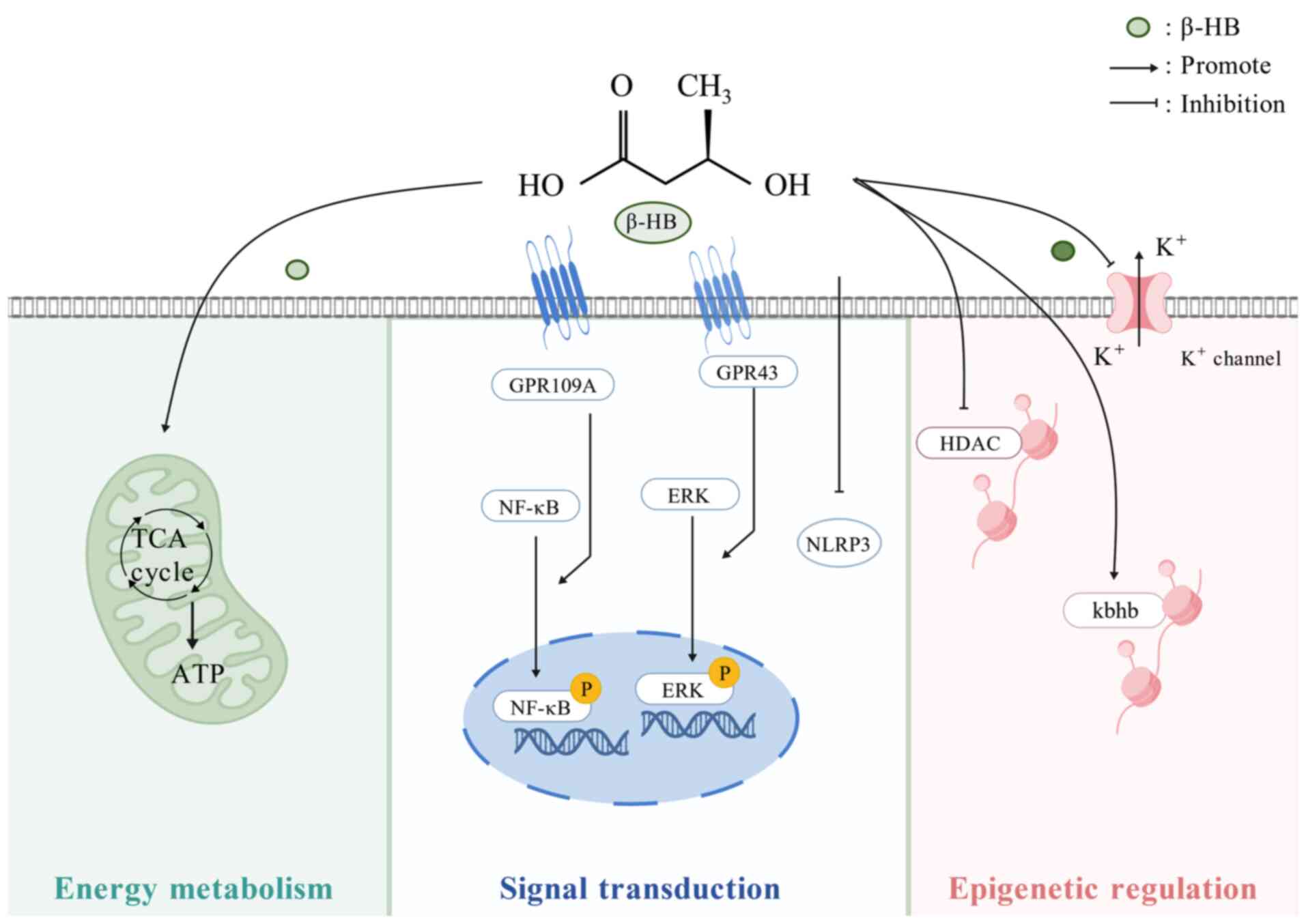
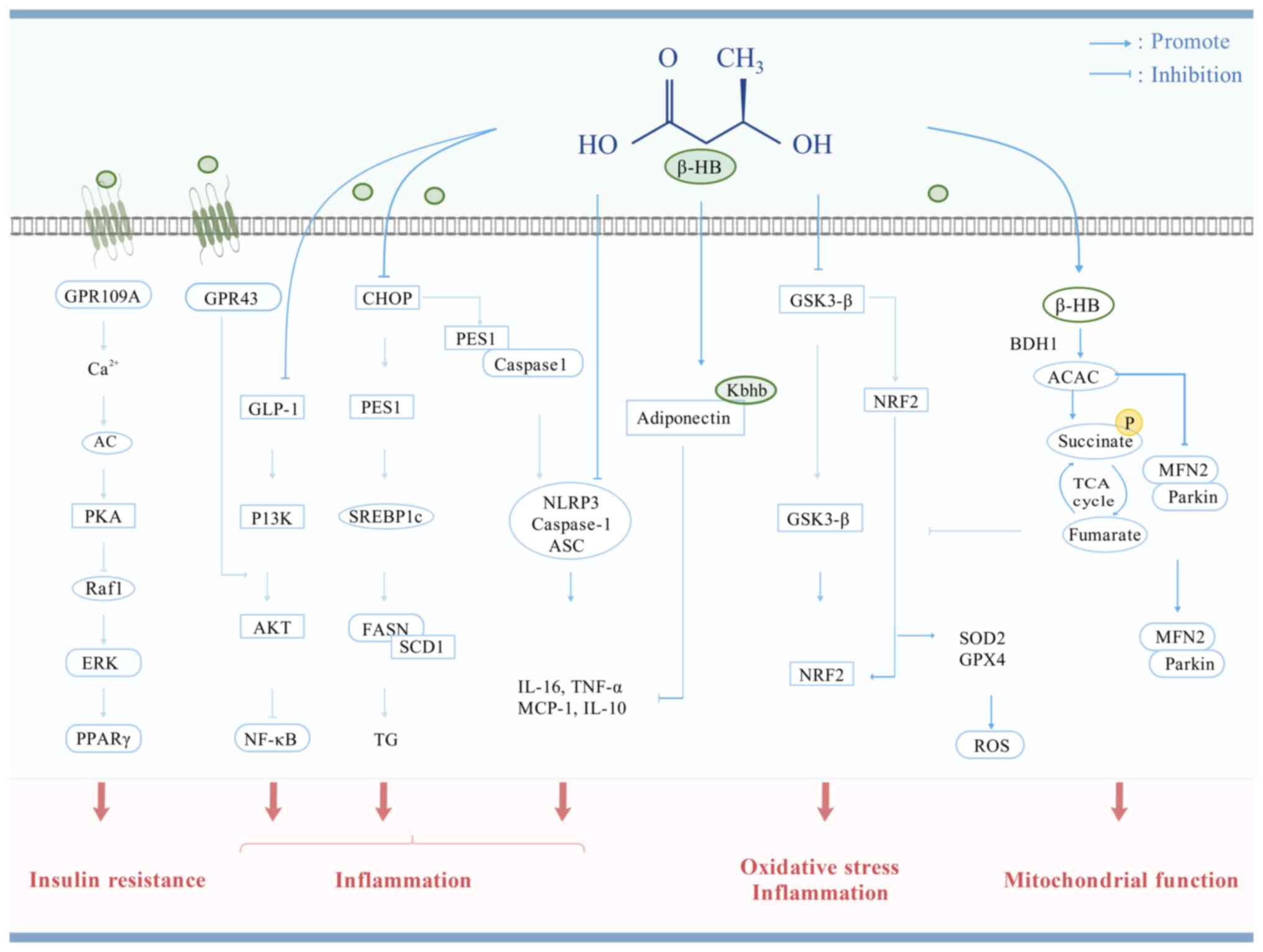
|
1
|
IDF Diabetes Atlas 11th Edition 2025. The
International Diabetes Federation; 2025
|
|
2
|
Karamanou M, Protogerou A, Tsoucalas G,
Androutsos G and Poulakou-Rebelakou E: Milestones in the history of
diabetes mellitus: The main contributors. World J Diabetes. 7:1–7.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zheng Y, Ley SH and Hu FB: Global
aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:88–98. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Roden M and Shulman GI: The integrative
biology of type 2 diabetes. Nature. 576:51–60. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Holst JJ and Orskov C: Incretin
hormones-an update. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 234:75–85.
2001.
|
|
6
|
Kwak SH and Park KS: Recent progress in
genetic and epigenetic research on type 2 diabetes. Exp Mol Med.
48:e2202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y, Ding Y, Tanaka Y and Zhang W: Risk
factors contributing to type 2 diabetes and recent advances in the
treatment and prevention. Int J Med Sci. 11:1185–1200. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan MH: α-Glucosidase inhibitors in the
treatment of diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obesity.
4:48–55. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chaudhury A, Duvoor C, Reddy Dendi VS,
Kraleti S, Chada A, Ravilla R, Marco A, Shekhawat NS, Montales MT,
Kuriakose K, et al: Clinical review of antidiabetic drugs:
Implications for type 2 diabetes mellitus management. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 8:62017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nauck MA, Wefers J and Meier JJ: Treatment
of type 2 diabetes: Challenges, hopes, and anticipated successes.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 9:525–544. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rosenstock J, Bajaj HS, Lingvay I and
Heller SR: Clinical perspectives on the frequency of hypoglycemia
in treat-to-target randomized controlled trials comparing basal
insulin analogs in type 2 diabetes: A narrative review. BMJ Open
Diabetes Res Care. 12:e0039302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Malakar S, Singh SK and Usman K:
Optimizing blood pressure management in type 2 Diabetes: A
comparative investigation of One-time versus periodic lifestyle
modification counseling. Cureus. 16:e616072024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pitak P, Tasai S, Kumpat N, Na Songkla P,
Fuangchan A, Krass I and Dhippayom T: The prevalence of glycemic
control in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health. 225:218–228.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei S, Binbin L, Yuan W, Zhong Z, Donghai
L and Caihua H: β-Hydroxybutyrate in Cardiovascular diseases: A
minor metabolite of great expectations. Front Mol Biosci.
9:8236022022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Holmes E, Wilson ID and Nicholson JK:
Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell. 134:714–717.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wishart DS: Metabolomics for investigating
physiological and pathophysiological processes. Physiol Rev.
99:1819–1875. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu D, Wang L, Gao H, Wang Z, Li K, Ma X,
Zhao L and Xiao W: Aerobic exercise delays Age-related sarcopenia
in mice via alleviating imbalance in mitochondrial quality control.
Metabolites. 15:4722025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ge Z, Chen C, Chen J, Jiang Z, Chen L, Wei
Y, Chen H, He L, Zou Y, Long X, et al: Gut Microbiota-derived
3-Hydroxybutyrate blocks GPR43-mediated IL6 signaling to ameliorate
radiation proctopathy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23062172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li K, Wang WH, Wu JB and Xiao WH:
β-hydroxybutyrate: A crucial therapeutic target for diverse liver
diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 165:1151912023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang M, Yu Y, Tang X, Dong R, Li X, Li F,
Jin Y, Gong S, Wang X, Zeng Z, et al: 3-Hydroxybutyrate ameliorates
sepsis-associated acute lung injury by promoting autophagy through
the activation of GPR109α in macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol.
213:1156322023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mishima M, Takeda S, Nagane M, Suzuki T,
Ogata M, Shima A, Aihara N, Kamiie J, Suzuki R, Mizugaki H, et al:
Prebiotic effect of poly-D-3-hydroxybutyrate prevents dyslipidemia
in obese mice. FASEB J. 37:e231212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Li Z, Liu X, Chen X, Zhang S,
Chen Y, Chen J, Chen J, Wu F and Chen GQ: 3-Hydroxybutyrate
ameliorates insulin resistance by inhibiting PPARγ Ser273
phosphorylation in type 2 diabetic mice. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 8:1902023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhou J, Lu Y, Jia Y, Lu J, Jiang Z and
Chen K: Ketogenic diet ameliorates lipid dysregulation in type 2
diabetic mice by downregulating hepatic pescadillo 1. Mol Med.
28:12022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo Z, Zhong F, Hou M, Xie J, Zhang AZ, Li
X, Li Y, Chang B and Yang J: Key enzyme in charge of ketone
reabsorption of renal tubular SMCT1 may be a new target in diabetic
kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 38:2754–2766. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nishitani S, Fukuhara A, Shin J, Okuno Y,
Otsuki M and Shimomura I: Metabolomic and microarray analyses of
adipose tissue of dapagliflozin-treated mice, and effects of
3-hydroxybutyrate on induction of adiponectin in adipocytes. Sci
Rep. 8:88052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Puchalska P, Nelson AB, Stagg DB and
Crawford PA: Determination of ketone bodies in biological samples
via rapid UPLC-MS/MS. Talanta. 225:1220482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Newman JC and Verdin E: β-Hydroxybutyrate:
A signaling metabolite. Annu Rev Nutr. 37:51–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McGarry JD and Foster DW: Ketogenesis and
its regulation. Am J Med. 61:9–13. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guzmán M and Blázquez C: Is there an
astrocyte-neuron ketone body shuttle? Trends Endocrinol Metab.
12:169–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Silva B, Mantha OL, Schor J, Pascual A,
Plaçais PY, Pavlowsky A and Preat T: Glia fuel neurons with locally
synthesized ketone bodies to sustain memory under starvation. Nat
Metab. 4:213–224. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang D, Yang H, Kong X, Wang K, Mao X,
Yan X, Wang Y, Liu S, Zhang X, Li J, et al: Proteomics analysis
reveals diabetic kidney as a ketogenic organ in type 2 diabetes. Am
J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 300:E287–E295. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
El Azzouny M, Longacre MJ, Ansari IH,
Kennedy RT, Burant CF and MacDonald MJ: Knockdown of ATP citrate
lyase in pancreatic beta cells does not inhibit insulin secretion
or glucose flux and implicates the acetoacetate pathway in insulin
secretion. Mol Metab. 5:980–987. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Adijanto J, Du J, Moffat C, Seifert EL,
Hurle JB and Philp NJ: The retinal pigment epithelium utilizes
fatty acids for ketogenesis. J Biol Chem. 289:20570–20582. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Reyes-Reveles J, Dhingra A, Alexander D,
Bragin A, Philp NJ and Boesze-Battaglia K: Phagocytosis-dependent
ketogenesis in retinal pigment epithelium. J Biol Chem.
292:8038–8047. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Grabacka MM, Wilk A, Antonczyk A, Banks P,
Walczyk-Tytko E, Dean M, Pierzchalska M and Reiss K: Fenofibrate
induces ketone body production in melanoma and glioblastoma cells.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 7:52016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Venable AH, Lee LE, Feola K, Santoyo J,
Broomfield T and Huen SC: Fasting-induced HMGCS2 expression in the
kidney does not contribute to circulating ketones. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 322:F460–F467. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Puchalska P and Crawford PA:
Multi-dimensional roles of ketone bodies in fuel metabolism,
signaling, and therapeutics. Cell Metab. 25:262–284. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mudaliar S, Alloju S and Henry RR: Can a
shift in fuel energetics explain the beneficial cardiorenal
outcomes in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME study? A unifying hypothesis.
Diabetes Care. 39:1115–1122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Orii KE, Fukao T, Song XQ, Mitchell GA and
Kondo N: Liver-specific silencing of the human gene encoding
succinyl-CoA: 3-ketoacid CoA transferase. Tohoku J Exp Med.
215:227–236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Halestrap AP: The monocarboxylate
transporter family-Structure and functional characterization. IUBMB
Life. 64:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bricker DK, Taylor EB, Schell JC, Orsak T,
Boutron A, Chen YC, Cox JE, Cardon CM, Van Vranken JG, Dephoure N,
et al: A mitochondrial pyruvate carrier required for pyruvate
uptake in yeast, Drosophila, and humans. Science. 337:96–100. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Halestrap AP: The SLC16 gene
family-structure, role and regulation in health and disease. Mol
Aspects Med. 34:337–349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Halestrap AP and Meredith D: The SLC16
gene family-from monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) to aromatic
amino acid transporters and beyond. Pflugers Arch. 447:619–628.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Carneiro L and Pellerin L: Monocarboxylate
transporters: New players in body weight regulation. Obes Rev.
16(Suppl 1): S55–S66. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Vijay N and Morris ME: Role of
monocarboxylate transporters in drug delivery to the brain. Curr
Pharm Des. 20:1487–1498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Martin PM, Gopal E, Ananth S, Zhuang L,
Itagaki S, Prasad BM, Smith SB, Prasad PD and Ganapathy V: Identity
of SMCT1 (SLC5A8) as a neuron-specific Na+-coupled transporter for
active uptake of L-lactate and ketone bodies in the brain. J
Neurochem. 98:279–288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bröer S, Schneider HP, Bröer A, Rahman B,
Hamprecht B and Deitmer JW: Characterization of the monocarboxylate
transporter 1 expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes by changes in
cytosolic pH. Biochem J. 333:167–174. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hugo SE, Cruz-Garcia L, Karanth S,
Anderson RM, Stainier DY and Schlegel A: A monocarboxylate
transporter required for hepatocyte secretion of ketone bodies
during fasting. Genes Dev. 26:282–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Koehler-Stec EM, Simpson IA, Vannucci SJ,
Landschulz KT and Landschulz WH: Monocarboxylate transporter
expression in mouse brain. Am J Physiol. 275:E516–E524.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bonen A: The expression of lactate
transporters (MCT1 and MCT4) in heart and muscle. Eur J Appl
Physiol. 86:6–11. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Enerson BE and Drewes LR: Molecular
features, regulation, and function of monocarboxylate transporters:
Implications for drug delivery. J Pharm Sci. 92:1531–1544. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Felmlee MA, Morse BL and Morris ME:
γ-Hydroxybutyric acid: Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and
toxicology. AAPS J. 23:222021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Costa TJ, Linder BA, Hester S, Fontes M,
Pernomian L, Wenceslau CF, Robinson AT and McCarthy CG: The janus
face of ketone bodies in hypertension. J Hypertens. 40:2111–2119.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yao A, Li Z, Lyu J, Yu L, Wei S, Xue L,
Wang H and Chen GQ: On the nutritional and therapeutic effects of
ketone body D-β-hydroxybutyrate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
105:6229–6243. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang L, Chen P and Xiao W:
β-hydroxybutyrate as an Anti-aging metabolite. Nutrients.
13:34202021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Balasse EO and Féry F: Ketone body
production and disposal: Effects of fasting, diabetes, and
exercise. Diabetes Metab Rev. 5:247–270. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Veech RL, Chance B, Kashiwaya Y, Lardy HA
and Cahill GF Jr: Ketone bodies, potential therapeutic uses. IUBMB
Life. 51:241–247. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Veech RL: The therapeutic implications of
ketone bodies: The effects of ketone bodies in pathological
conditions: Ketosis, ketogenic diet, redox states, insulin
resistance, and mitochondrial metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 70:309–319. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hawkins RA and Biebuyck JF: Ketone bodies
are selectively used by individual brain regions. Science.
205:325–327. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Taggart AK, Kero J, Gan X, Cai TQ, Cheng
K, Ippolito M, Ren N, Kaplan R, Wu K, Wu TJ, et al:
(D)-beta-Hydroxybutyrate inhibits adipocyte lipolysis via the
nicotinic acid receptor PUMA-G. J Biol Chem. 280:26649–26652. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kimura I, Inoue D, Maeda T, Hara T,
Ichimura A, Miyauchi S, Kobayashi M, Hirasawa A and Tsujimoto G:
Short-chain fatty acids and ketones directly regulate sympathetic
nervous system via G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41). Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:8030–8035. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Won YJ, Lu VB, Puhl HL III and Ikeda SR:
β-Hydroxybutyrate modulates N-type calcium channels in rat
sympathetic neurons by acting as an agonist for the
G-protein-coupled receptor FFA3. J Neuroscience. 33:19314–19325.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J, He W,
Shirakawa K, Le Moan N, Grueter CA, Lim H, Saunders LR, Stevens RD,
et al: Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an
endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science. 339:211–214.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Xie Z, Zhang D, Chung D, Tang Z, Huang H,
Dai L, Qi S, Li J, Colak G, Chen Y, et al: Metabolic regulation of
gene expression by histone lysine β-hydroxybutyrylation. Mol Cell.
62:194–206. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Newman JC and Verdin E: Ketone bodies as
signaling metabolites. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:42–52. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Lund TM, Ploug KB, Iversen A, Jensen AA
and Jansen-Olesen I: The metabolic impact of β-hydroxybutyrate on
neurotransmission: Reduced glycolysis mediates changes in calcium
responses and KATP channel receptor sensitivity. J Neurochem.
132:520–531. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, Goldberg EL,
Bodogai M, Kim D, D'Agostino D, Planavsky N, Lupfer C, Kanneganti
TD, et al: The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 21:263–269.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Robinson AM and Williamson DH:
Physiological roles of ketone bodies as substrates and signals in
mammalian tissues. Physiological Rev. 60:143–187. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Pięta A, Frączek B, Wiecek M and
Mazur-Kurach P: Impact of paleo diet on body composition,
carbohydrate and fat metabolism of professional handball players.
Nutrients. 15:41552023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Evans M, Cogan KE and Egan B: Metabolism
of ketone bodies during exercise and training: Physiological basis
for exogenous supplementation. J Physiol. 595:2857–2871. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
71
|
Keller U, Lustenberger M, Müller-Brand J,
Gerber PP and Stauffacher W: Human ketone body production and
utilization studied using tracer techniques: Regulation by free
fatty acids, insulin, catecholamines, and thyroid hormones.
Diabetes Metab Rev. 5:285–298. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Poff AM, Koutnik AP and Egan B:
Nutritional ketosis with ketogenic diets or exogenous ketones:
Features, convergence, and divergence. Curr Sports Med Rep.
19:251–259. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Crabtree CD, Kackley ML, Buga A, Fell B,
LaFountain RA, Hyde PN, Sapper TN, Kraemer WJ, Scandling D,
Simonetti OP and Volek JS: Comparison of ketogenic diets with and
without ketone salts versus a Low-fat diet: Liver fat responses in
overweight adults. Nutrients. 13:9662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Di Lorenzo C, Pinto A, Ienca R, Coppola G,
Sirianni G, Di Lorenzo G, Parisi V, Serrao M, Spagnoli A, Vestri A,
et al: A Randomized Double-blind, Cross-over trial of very
Low-calorie diet in overweight migraine patients: A possible role
for ketones? Nutrients. 11:17422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Joo NS, Lee DJ, Kim KM, Kim BT, Kim CW,
Kim KN and Kim SM: Ketonuria after fasting may be related to the
metabolic superiority. J Korean Med Sci. 25:1771–1776. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kim G, Lee SG, Lee BW, Kang ES, Cha BS,
Ferrannini E, Lee YH and Cho NH: Spontaneous ketonuria and risk of
incident diabetes: A 12 year prospective study. Diabetologia.
62:779–788. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Firman CH, Mellor DD, Unwin D and Brown A:
Does a ketogenic diet have a place within diabetes clinical
practice? review of current evidence and controversies. Diabetes
Ther. 15:77–97. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
78
|
Dhillon KK and Gupta S: Biochemistry,
Ketogenesis. StatPearls StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2025.
StatPearls Publishing LLC., Treasure Island (FL) ineligible
companies. Disclosure: Sonu Gupta declares no relevant financial
relationships with ineligible companies. 2025
|
|
79
|
Dhatariya KK, Glaser NS, Codner E and
Umpierrez GE: Diabetic ketoacidosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:402020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Umpierrez GE, Davis GM, ElSayed NA, Fadini
GP, Galindo RJ, Hirsch IB, Klonoff DC, McCoy RG, Misra S, Gabbay
RA, et al: Hyperglycemic crises in adults with diabetes: A
consensus report. Diabetes Care. 47:1257–1275. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Cahill GF Jr and Veech RL: Ketoacids? Good
medicine? Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 114:149–163.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ and van Haeften
TW: Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy.
Lancet. 365:1333–1346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari
S, Larrea-Sebal A, Siddiqi H, Uribe KB, Ostolaza H and Martín C:
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci.
21:62752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Christensen AA and Gannon M: The beta cell
in type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 19:812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yurista SR, Chong CR, Badimon JJ, Kelly
DP, de Boer RA and Westenbrink BD: Therapeutic potential of ketone
bodies for patients with cardiovascular disease: JACC
State-of-the-Art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 77:1660–1669. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang L, Wang H, Wu J, Ji C, Wang Y, Gu M,
Li M and Yang H: Gut microbiota and metabolomics in metabolic
dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Interaction, mechanism,
and therapeutic value. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 15:16356382025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Song K, Kong X, Xian Y, Yu Z, He M, Xiao
D, Liang D, Zhang Z, Liu T, Huang Z, et al: Roux-en-Y gastric
bypass improves liver and glucose homeostasis in Zucker diabetic
fatty rats by upregulating hepatic trefoil factor family 3 and
activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B
pathway. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 21:792–805. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Xiang H, Lyu Q, Chen S, Ouyang J, Xiao D,
Liu Q, Long H, Zheng X, Yang X and Lu H: PACS2/CPT1A/DHODH
signaling promotes cardiomyocyte ferroptosis in diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 23:4322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xu BT, Teng FY, Wu Q, Wan SR, Li XY, Tan
XZ, Xu Y and Jiang ZZ: Bdh1 overexpression ameliorates hepatic
injury by activation of Nrf2 in a MAFLD mouse model. Cell Death
Discov. 8:492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Jager KJ, Kovesdy C, Langham R, Rosenberg
M, Jha V and Zoccali C: A single number for advocacy and
communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have
kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 96:1048–1050. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Tuttle KR, Agarwal R, Alpers CE, Bakris
GL, Brosius FC, Kolkhof P and Uribarri J: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int.
102:248–260. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Sagoo MK and Gnudi L: Diabetic
Nephropathy: An Overview. Diabetic Nephropathy: Methods and
Protocols. Gnudi L and Long DA: Springer US; New York, NY: pp. 3–7.
2020, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Gopal E, Fei YJ, Sugawara M, Miyauchi S,
Zhuang L, Martin P, Smith SB, Prasad PD and Ganapathy V: Expression
of slc5a8 in kidney and its role in Na(+)-coupled transport of
lactate. J Biol Chem. 279:44522–44532. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xie J, Zhong F, Guo Z, Li X, Wang J, Gao
Z, Chang B and Yang J: Hyperinsulinemia impairs the metabolic
switch to ketone body utilization in proximal renal tubular
epithelial cells under energy crisis via the inhibition of the
SIRT3/SMCT1 pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:9608352022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wan SR, Teng FY, Fan W, Xu BT, Li XY, Tan
XZ, Guo M, Gao CL, Zhang CX, Jiang ZZ and Xu Y: BDH1-mediated βOHB
metabolism ameliorates diabetic kidney disease by activation of
NRF2-mediated antioxidative pathway. Aging. 15:13384–13410. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Fang Y, Chen B, Gong AY, Malhotra DK,
Gupta R, Dworkin LD and Gong R: The ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate
mitigates the senescence response of glomerular podocytes to
diabetic insults. Kidney Int. 100:1037–1053. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lean ME: Obesity: Burdens of illness and
strategies for prevention or management. Drugs Today. 36:773–784.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Biondi G, Marrano N, Borrelli A, Rella M,
Palma G, Calderoni I, Siciliano E, Lops P, Giorgino F and
Natalicchio A: Adipose tissue secretion pattern influences β-cell
wellness in the transition from obesity to type 2 diabetes. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:55222022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Schaffer JE: Lipotoxicity: When tissues
overeat. Curr Opin Lipidol. 14:281–287. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Meex RCR, Blaak EE and van Loon LJC:
Lipotoxicity plays a key role in the development of both insulin
resistance and muscle atrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Obesity Rev. 20:1205–1217. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Kim JE, Kim JS, Jo MJ, Cho E, Ahn SY, Kwon
YJ and Ko GJ: The roles and associated mechanisms of adipokines in
development of metabolic syndrome. Molecules. 27:3342022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Booth A, Magnuson A, Fouts J and Foster
MT: Adipose tissue: An endocrine organ playing a role in metabolic
regulation. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 26:25–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Kim AY, Park YJ, Pan X, Shin KC, Kwak SH,
Bassas AF, Sallam RM, Park KS, Alfadda AA, Xu A and Kim JB:
Obesity-induced DNA hypermethylation of the adiponectin gene
mediates insulin resistance. Nat Commun. 6:75852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Sakurai N, Mochizuki K and Goda T:
Modifications of histone H3 at lysine 9 on the adiponectin gene in
3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 55:131–138. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Iwaki M, Matsuda M, Maeda N, Funahashi T,
Matsuzawa Y, Makishima M and Shimomura I: Induction of adiponectin,
a fat-derived antidiabetic and antiatherogenic factor, by nuclear
receptors. Diabetes. 52:1655–1663. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Segawa K, Matsuda M, Fukuhara A, Morita K,
Okuno Y, Komuro R and Shimomura I: Identification of a novel distal
enhancer in human adiponectin gene. J Endocrinol. 200:107–116.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Park S, Kim DS, Kang S and Daily JW III: A
ketogenic diet impairs energy and glucose homeostasis by the
attenuation of hypothalamic leptin signaling and hepatic insulin
signaling in a rat model of non-obese type 2 diabetes. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 236:194–204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Biesiekierska M, Strigini M, Śliwińska A,
Pirola L and Balcerczyk A: The impact of ketogenic nutrition on
obesity and metabolic health: Mechanisms and clinical implications.
Nutr Rev. 83:1957–1972. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Carrière A, Jeanson Y, Berger-Müller S,
André M, Chenouard V, Arnaud E, Barreau C, Walther R, Galinier A,
Wdziekonski B, et al: Browning of white adipose cells by
intermediate metabolites: An adaptive mechanism to alleviate redox
pressure. Diabetes. 63:3253–3265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
de Oliveira Caminhotto R, Andreotti S,
Komino ACM, de Fatima Silva F, Antônio Laurato Sertié R, Augusto
Christoffolete M, Boltes Reis G and Lima FB: Physiological
concentrations of β-hydroxybutyrate do not promote adipocyte
browning. Life Sci. 232:1166832019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Gast KB, Tjeerdema N, Stijnen T, Smit JW
and Dekkers OM: Insulin resistance and risk of incident
cardiovascular events in adults without diabetes: Meta-analysis.
PLoS One. 7:e520362012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Nesto RW: Correlation between
cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus: Current concepts. Am
J Med. 116(Suppl 5A): 11S–22S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Dillmann WH: Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Circ
Res. 124:1160–1162. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ritchie RH and Abel ED: Basic mechanisms
of diabetic heart disease. Circ Res. 126:1501–1525. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Song K, Liang D, Xiao D, Kang A and Ren Y:
Role of bariatric surgery in improving diabetic cardiomyopathy:
Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives (Review). Mol Med
Rep. 30:1992024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wang S, Zhou J, Lu J, Lin Y, Liu S and
Chen K: A ketogenic diet improves vascular hyperpermeability in
type 2 diabetic mice by downregulating vascular pescadillo1
expression. J Cell Mol Med. 27:1410–1422. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Thai PN, Miller CV, King MT, Schaefer S,
Veech RL, Chiamvimonvat N, Bers DM and Dedkova EN: Ketone Ester
D-β-Hydroxybutyrate-(R)-1,3 butanediol prevents decline in cardiac
function in type 2 diabetic mice. J Am Heart Assoc. 10:e0207292021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Lin J, Ren Q, Zhang F, Gui J, Xiang X and
Wan Q: D-β-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase mitigates Diabetes-induced
atherosclerosis through the activation of Nrf2. Thromb Haemost.
123:1003–1015. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Uchihashi M, Hoshino A, Okawa Y, Ariyoshi
M, Kaimoto S, Tateishi S, Ono K, Yamanaka R, Hato D, Fushimura Y,
et al: Cardiac-Specific Bdh1 overexpression ameliorates oxidative
stress and cardiac remodeling in pressure overload-induced heart
failure. Circ Heart Fail. 10:e0044172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
van Knegsel AT, van den Brand H, Dijkstra
J, Tamminga S and Kemp B: Effect of dietary energy source on energy
balance, production, metabolic disorders and reproduction in
lactating dairy cattle. Reprod Nutr Dev. 45:665–688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Liepinsh E, Vilskersts R, Zvejniece L,
Svalbe B, Skapare E, Kuka J, Cirule H, Grinberga S, Kalvinsh I and
Dambrova M: Protective effects of mildronate in an experimental
model of type 2 diabetes in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Br J Pharmacol.
157:1549–1556. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Antal B, McMahon LP, Sultan SF, Lithen A,
Wexler DJ, Dickerson B, Ratai EM and Mujica-Parodi LR: Type 2
diabetes mellitus accelerates brain aging and cognitive decline:
Complementary findings from UK Biobank and meta-analyses. eLife.
11:e731382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Reske-Nielsen E, Lundbaek K, Gregersen G
and Harmsen A: Pathological changes in the central and peripheral
nervous system of young long-term diabetics. The terminal
neuro-muscular apparatus. Diabetologia. 6:98–103. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Lionetti N, Di Lago MG, Brescia T,
Bevilacqua F and Gnoni A: Diabetes and brain: Omics approaches to
study diabetic encephalopathy. Front Endocrinol. 16:15705852025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Xu Y, Huang C, Zhang Y, Li H, Yang H, Liu
M, Zhu L, Li C, Zhong Y, Tang L, et al: Diabetic encephalopathy
models: A systematic review from cells to animals. Exp Neurol.
395:1154772025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Hein ZM, Arbain MFF, Kumar S, Mehat MZ,
Hamid HA, Che Ramli MD and Che Mohd Nassir CMN: Intermittent
fasting as a neuroprotective strategy: Gut-brain axis modulation
and metabolic reprogramming in neurodegenerative disorders.
Nutrients. 17:22662025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Andersen JV, Christensen SK, Nissen JD and
Waagepetersen HS: Improved cerebral energetics and ketone body
metabolism in db/db mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 37:1137–1147.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Pierre K, Parent A, Jayet PY, Halestrap
AP, Scherrer U and Pellerin L: Enhanced expression of three
monocarboxylate transporter isoforms in the brain of obese mice. J
Physiol. 583:469–486. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Pellerin L, Bergersen LH, Halestrap AP and
Pierre K: Cellular and subcellular distribution of monocarboxylate
transporters in cultured brain cells and in the adult brain. J
Neurosci Res. 79:55–64. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Park S, Kim DS and Daily JW: Central
infusion of ketone bodies modulates body weight and hepatic insulin
sensitivity by modifying hypothalamic leptin and insulin signaling
pathways in type 2 diabetic rats. Brain Res. 1401:95–103. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Majrashi M, Altukri M, Ramesh S,
Govindarajulu M, Schwartz J, Almaghrabi M, Smith F, Thomas T,
Suppiramaniam V, Moore T, et al: β-hydroxybutyric acid attenuates
oxidative stress and improves markers of mitochondrial function in
the HT-22 hippocampal cell line. J Integr Neurosci. 20:321–329.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Dabke P, Brogden G, Naim HY and Das AM:
Ketogenic diet: Impact on cellular lipids in hippocampal murine
neurons. Nutrients. 12:38702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Sayin N, Kara N and Pekel G: Ocular
complications of diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes. 6:92–108.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Jian Q, Wu Y and Zhang F: Metabolomics in
diabetic retinopathy: From potential biomarkers to molecular basis
of oxidative stress. Cells. 11:30052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Herat LY, Matthews VB, Rakoczy PE,
Carnagarin R and Schlaich M: Focusing on sodium glucose
cotransporter-2 and the sympathetic nervous system: Potential
impact in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Endocrinol. 2018:92541262018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Heng LZ, Comyn O, Peto T, Tadros C, Ng E,
Sivaprasad S and Hykin PG: Diabetic retinopathy: Pathogenesis,
clinical grading, management and future developments. Diabet Med.
30:640–650. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Wong TY, Cheung CM, Larsen M, Sharma S and
Simó R: Diabetic retinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160122016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Saika S, Yamanaka O, Okada Y, Tanaka S,
Miyamoto T, Sumioka T, Kitano A, Shirai K and Ikeda K: TGF beta in
fibroproliferative diseases in the eye. Front Biosci (Schol Ed).
1:376–390. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Yadav H, Quijano C, Kamaraju AK, Gavrilova
O, Malek R, Chen W, Zerfas P, Zhigang D, Wright EC, Stuelten C, et
al: Protection from obesity and diabetes by blockade of TGF-β/Smad3
signaling. Cell Metab. 14:67–79. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Chen HY, Ho YJ, Chou HC, Liao EC, Tsai YT,
Wei YS, Lin LH, Lin MW, Wang YS, Ko ML and Chan HL: The role of
transforming growth factor-beta in retinal ganglion cells with
hyperglycemia and oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci. 21:64822020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Trotta MC, Maisto R, Guida F, Boccella S,
Luongo L, Balta C, D'Amico G, Herman H, Hermenean A, Bucolo C and
D'Amico M: The activation of retinal HCA2 receptors by systemic
beta-hydroxybutyrate inhibits diabetic retinal damage through
reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the NLRP3
inflammasome. PLoS One. 14:e02110052019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Szili-Torok T, de Borst MH, Garcia E,
Gansevoort RT, Dullaart RPF, Connelly MA, Bakker SJL and Tietge
UJF: Fasting ketone bodies and incident type 2 diabetes in the
general population. Diabetes. 72:1187–1192. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Bae J, Kim YE, Jung KJ, Jee SH and Lee BW:
Association between serum beta-hydroxybutyrate levels and risk of
type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with impaired fasting glucose.
Nutr Diabetes. 15:162025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Mahendran Y, Vangipurapu J, Cederberg H,
Stancáková A, Pihlajamäki J, Soininen P, Kangas AJ, Paananen J,
Civelek M, Saleem NK, et al: Association of ketone body levels with
hyperglycemia and type 2 diabetes in 9,398 Finnish men. Diabetes.
62:3618–3626. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Lucidi P, Perriello G, Porcellati F,
Pampanelli S, De Fano M, Tura A, Bolli GB and Fanelli CG: Diurnal
cycling of insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes: Evidence for
deviation from physiology at an early stage. Diabetes.
72:1364–1373. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Garcia E, Shalaurova I, Matyus SP,
Oskardmay DN, Otvos JD, Dullaart RPF and Connelly MA: Ketone bodies
are mildly elevated in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus and
are inversely associated with insulin resistance as measured by the
lipoprotein insulin resistance index. J Clin Med. 9:3212020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Gogna N, Krishna M, Oommen AM and Dorai K:
Investigating correlations in the altered metabolic profiles of
obese and diabetic subjects in a South Indian Asian population
using an NMR-based metabolomic approach. Mol Biosyst. 11:595–606.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Fikri AM, Smyth R, Kumar V, Al-Abadla Z,
Abusnana S and Munday MR: Pre-diagnostic biomarkers of type 2
diabetes identified in the UAE's obese national population using
targeted metabolomics. Sci Rep. 10:176162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Lee S, Bae J, Jo DR, Lee M, Lee YH, Kang
ES, Cha BS and Lee BW: Impaired ketogenesis is associated with
metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in subjects with type 2
diabetes. Front Endocrinol. 14:11245762023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Lim K, Kang M and Park J: Association
between fasting ketonuria and advanced liver fibrosis in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients without prediabetes and
diabetes mellitus. Nutrients. 13:34002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Liu Y, Wang J, Xu F, Zhang S, Cui S, Li Y,
Wang X, Zheng H, Li J, Kong Y, et al: A J-shaped relationship
between ketones and the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients
with type 2 diabetes: New insights from a cross-sectional study.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 25:3317–3326. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Lee M, Cho Y, Lee YH, Kang ES, Cha BS and
Lee BW: β-hydroxybutyrate as a biomarker of β-cell function in
new-onset type 2 diabetes and its association with treatment
response at 6 months. Diabetes Metab. 49:1014272023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Park SB and Yang SJ: Ketogenic diet
preserves muscle mass and strength in a mouse model of type 2
diabetes. PLoS One. 19:e02966512024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Miller VJ, Villamena FA and Volek JS:
Nutritional Ketosis and Mitohormesis: Potential Implications for
Mitochondrial Function and Human Health. J Nutr Metab.
2018:51576452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Arnason TG, Bowen MW and Mansell KD:
Effects of intermittent fasting on health markers in those with
type 2 diabetes: A pilot study. World J Diabetes. 8:154–164. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Nuttall FQ, Almokayyad RM and Gannon MC:
Circulating lipids in men with type 2 diabetes following 3 days on
a carbohydrate-free diet versus 3 days of fasting. Physiological
Rep. 8:e145692020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Steven S, Hollingsworth KG, Al-Mrabeh A,
Avery L, Aribisala B, Caslake M and Taylor R: Very low-calorie diet
and 6 months of weight stability in type 2 diabetes:
Pathophysiological changes in responders and nonresponders.
Diabetes Care. 39:808–815. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Vigili de Kreutzenberg S and Avogaro A:
The role of point-of-care 3-hydroxybutyrate testing in patients
with type 2 diabetes undergoing coronary angiography. J Endocrinol
Invest. 40:627–634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Goldberg IJ, Ibrahim N, Bredefeld C, Foo
S, Lim V, Gutman D, Huggins LA and Hegele RA: Ketogenic diets, not
for everyone. J Clin Lipidol. 15:61–67. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
160
|
Goday A, Bellido D, Sajoux I, Crujeiras
AB, Burguera B, García-Luna PP, Oleaga A, Moreno B and Casanueva
FF: Short-term safety, tolerability and efficacy of a very
low-calorie-ketogenic diet interventional weight loss program
versus hypocaloric diet in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Nutr Diabetes. 6:e2302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Merovci A, Finley B, Hansis-Diarte A,
Neppala S, Abdul-Ghani MA, Cersosimo E, Triplitt C and DeFronzo RA:
Effect of weight-maintaining ketogenic diet on glycemic control and
insulin sensitivity in obese T2D subjects. BMJ Open Diabetes Res
Care. 12:e0041992024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Durrer C, Lewis N, Wan Z, Ainslie PN,
Jenkins NT and Little JP: Short-term Low-carbohydrate high-fat diet
in healthy young males renders the endothelium susceptible to
hyperglycemia-induced damage, an exploratory analysis. Nutrients.
11:4892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Harvey C, Schofield GM and Williden M: The
use of nutritional supplements to induce ketosis and reduce
symptoms associated with keto-induction: A narrative review. PeerJ.
6:e44882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Holland AM, Qazi AS, Beasley KN and
Bennett HR: Blood and cardiovascular health parameters after
supplementing with ketone salts for six weeks. J Insul Resist.
4:e472019.
|
|
165
|
Falkenhain K, Islam H and Little JP:
Exogenous ketone supplementation: An emerging tool for
physiologists with potential as a metabolic therapy. Exp Physiol.
108:177–187. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Suissa L, Kotchetkov P, Guigonis JM, Doche
E, Osman O, Pourcher T and Lindenthal S: Ingested ketone ester
leads to a rapid rise of Acetyl-CoA and competes with glucose
metabolism in the brain of Non-fasted mice. Int J Mol Sci.
22:5242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Stubbs BJ, Cox PJ, Evans RD, Santer P,
Miller JJ, Faull OK, Magor-Elliott S, Hiyama S, Stirling M and
Clarke K: On the metabolism of exogenous ketones in humans. Front
Physiol. 8:8482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Soto-Mota A, Norwitz NG, Evans R, Clarke K
and Barber TM: Exogenous ketosis in patients with type 2 diabetes:
Safety, tolerability and effect on glycaemic control. Endocrinol
Diabetes Metab. 4:e002642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Monteyne AJ, Falkenhain K, Whelehan G,
Neudorf H, Abdelrahman DR, Murton AJ, Wall BT, Stephens FB and
Little JP: A ketone monoester drink reduces postprandial blood
glucose concentrations in adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomised
controlled trial. Diabetologia. 67:1107–1113. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Falkenhain K, Oliveira BF, Islam H,
Neudorf H, Cen HH, Johnson JD, Madden K, Singer J, Walsh JJ and
Little JP: The effect of acute and 14-day exogenous ketone
supplementation on glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes:
Two randomized controlled trials. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
326:E61–E72. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Jensen NJ, Nilsson M, Ingerslev JS, Olsen
DA, Fenger M, Svart M, Møller N, Zander M, Miskowiak KW and Rungby
J: Effects of β-hydroxybutyrate on cognition in patients with type
2 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol. 182:233–242. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Baranowski BJ, Oliveira BF, Falkenhain K,
Little JP, Mohammad A, Beaudette SM, Finch MS, Caldwell HG, Neudorf
H, MacPherson REK and Walsh JJ: Effect of exogenous
β-hydroxybutyrate on BDNF signaling, cognition, and amyloid
precursor protein processing in humans with T2D and
insulin-resistant rodents. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
328:C541–C556. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Solis-Herrera C, Qin Y, Honka H, Cersosimo
E, Triplitt C, Neppala S, Rajan J, Acosta FM, Moody AJ, Iozzo P, et
al: Effect of hyperketonemia on myocardial function in patients
with heart failure and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 74:43–52. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Gopalasingam N, Berg-Hansen K, Christensen
KH, Ladefoged BT, Poulsen SH, Andersen MJ, Borlaug BA, Nielsen R,
Møller N and Wiggers H: Randomized crossover trial of 2-week ketone
ester treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and heart failure
with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation. 150:1570–1583. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Clarke K, Tchabanenko K, Pawlosky R,
Carter E, Knight NS, Murray AJ, Cochlin LE, King MT, Wong AW,
Roberts A, et al: Oral 28-day and developmental toxicity studies of
(R)-3-hydroxybutyl (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.
63:196–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Clarke K, Tchabanenko K, Pawlosky R,
Carter E, Todd King M, Musa-Veloso K, Ho M, Roberts A, Robertson J,
Vanitallie TB and Veech RL: Kinetics, safety and tolerability of
(R)-3-hydroxybutyl (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate in healthy adult subjects.
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 63:401–408. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Engel MH and Macko SA: Isotopic evidence
for extraterrestrial non-racemic amino acids in the Murchison
meteorite. Nature. 389:265–268. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Fischer T, Och U, Klawon I, Och T,
Grüneberg M, Fobker M, Bordewick-Dell U and Marquardt T: Effect of
a Sodium and Calcium DL-β-Hydroxybutyrate salt in healthy adults. J
Nutr Metab. 2018:98128062018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Soto-Mota A, Vansant H, Evans RD and
Clarke K: Safety and tolerability of sustained exogenous ketosis
using ketone monoester drinks for 28 days in healthy adults. Regul
Toxicol Pharmacol. 109:1045062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Elebring E, Casselbrant A, Persson SMT,
Fändriks L and Wallenius V: βHB inhibits glucose-induced GLP-1
secretion in GLUTag and human jejunal enteroids. J Mol Endocrinol.
70:e2201152023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Wallenius V, Elias E, Elebring E, Haisma
B, Casselbrant A, Larraufie P, Spak E, Reimann F, le Roux CW,
Docherty NG, et al: Suppression of enteroendocrine cell
glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 release by fat-induced small
intestinal ketogenesis: A mechanism targeted by Roux-en-Y gastric
bypass surgery but not by preoperative very-low-calorie diet. Gut.
69:1423–1431. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Wang N, Yang A, Tian X, Liao J, Yang Z,
Pan Y, Guo Y and He S: Label-free analysis of the
β-hydroxybutyricacid drug on mitochondrial redox states repairment
in type 2 diabetic mice by resonance raman scattering. Biomed
Pharmacother. 172:1163202024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Féry F and Balasse EO: Response of ketone
body metabolism to exercise during transition from postabsorptive
to fasted state. Am J Physiol. 250:E495–E501. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Féry F and Balasse EO: Effect of exercise
on the disposal of infused ketone bodies in humans. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 67:245–250. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Wang T, Ning M, Mo Y, Tian X, Fu Y, Laher
I and Li S: Metabolomic profiling reveals that exercise lowers
biomarkers of cardiac dysfunction in rats with type 2 diabetes.
Antioxidants (Basel). 13:11672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Kramer CK, Zinman B, Feig DS and
Retnakaran R: Effect of time-restricted eating on β-cell function
in adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized cross-over trial. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 110:e2045–e2053. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|