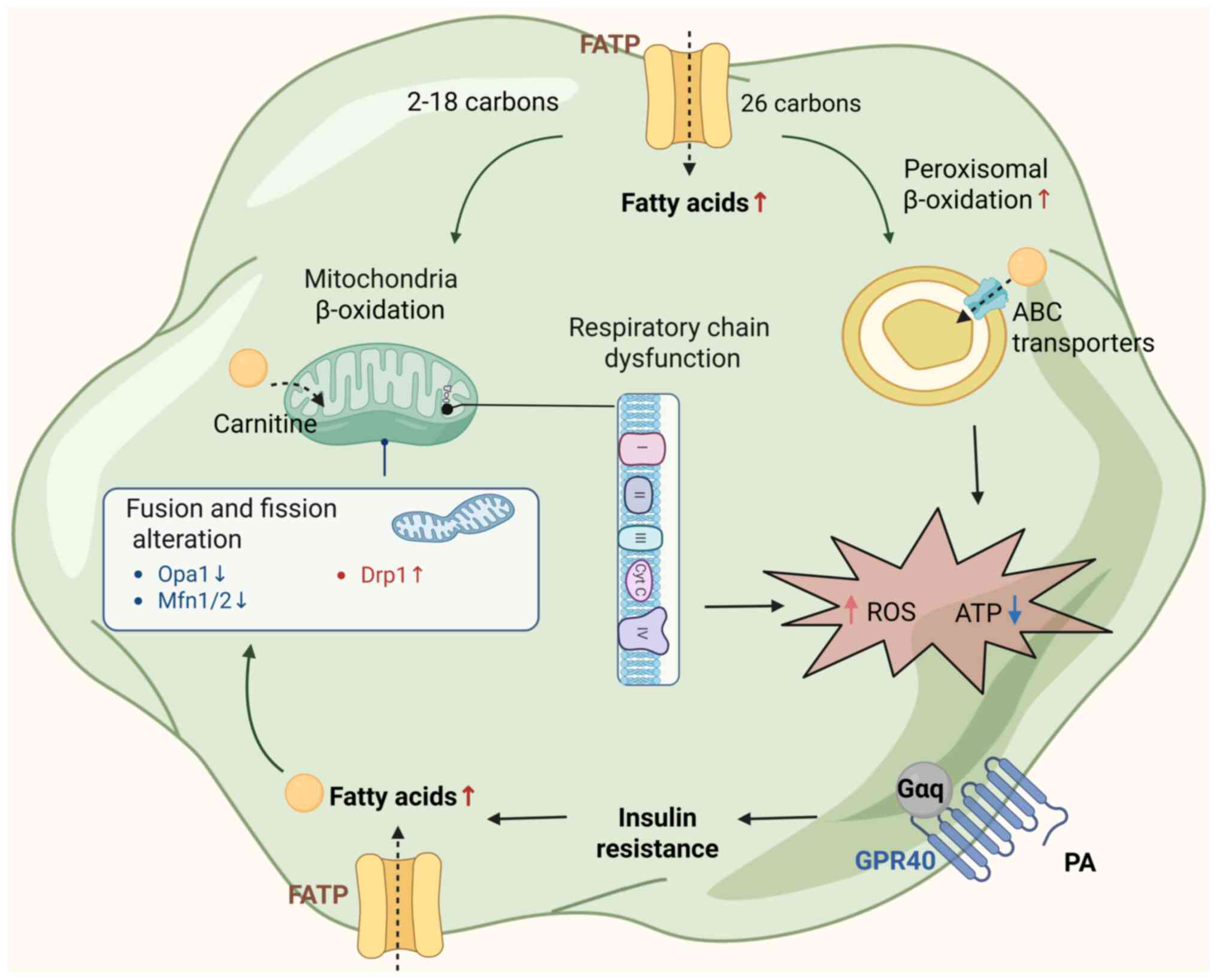
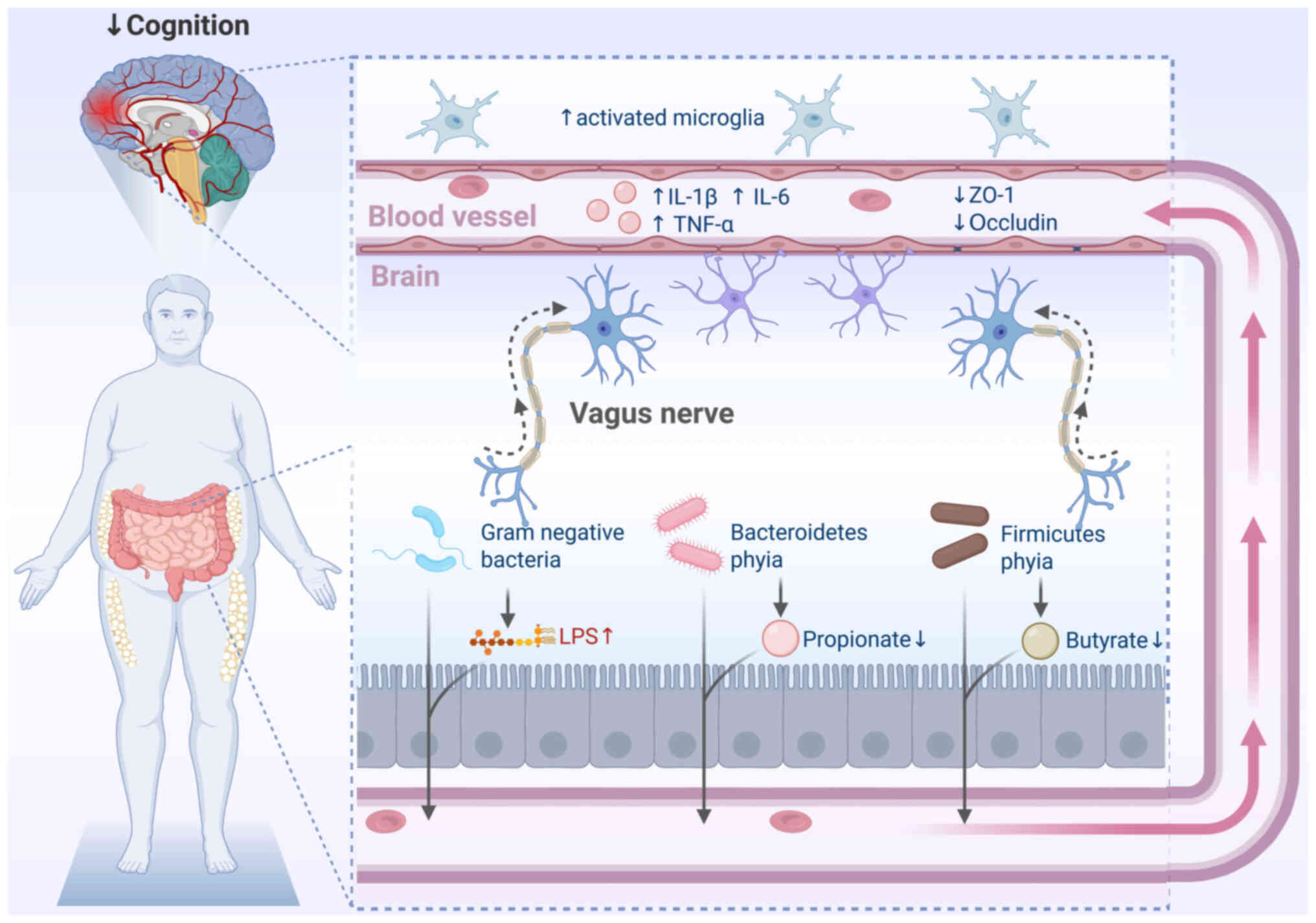
|
1
|
Roberts R and Knopman DS: Classification
and epidemiology of MCI. Clin Geriatr Med. 29:753–772. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wimo A, Guerchet M, Ali GC, Wu YT, Prina
AM, Winblad B, Jönsson L, Liu Z and Prince M: The worldwide costs
of dementia 2015 and comparisons with 2010. Alzheimers Dement.
13:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yi W, Chen F, Yuan M, Wang C, Wang S, Wen
J, Zou Q, Pu Y and Cai Z: High-fat diet induces cognitive
impairment through repression of SIRT1/AMPK-mediated autophagy. Exp
Neurol. 371:1145912024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
GBD 2019 Dementia Forecasting
Collaborators: Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in
2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Public Health. 7:e105–e125.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frazier K, Kambal A, Zale EA, Pierre JF,
Hubert N, Miyoshi S, Miyoshi J, Ringus DL, Harris D, Yang K, et al:
High-fat diet disrupts REG3γ and gut microbial rhythms promoting
metabolic dysfunction. Cell Host Microbe. 30:809–823. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang X, Song R, Clinchamps M and Dutheil
F: New insights into high-fat diet with chronic diseases.
Nutrients. 15:40312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones-Muhammad M and Warrington JP: When
high-fat diet plus hypertension does not equal vascular
dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 321:H128–H130. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cao GY, Li M, Han L, Tayie F, Yao SS,
Huang Z, Ai P, Liu YZ, Hu YH and Xu B: Dietary fat intake and
cognitive function among older populations: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 6:204–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Song M, Bai Y and Song F: High-fat diet
and neuroinflammation: The role of mitochondria. Pharmacol Res.
212:1076152025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Roberts RO, Roberts LA, Geda YE, Cha RH,
Pankratz VS, O'Connor HM, Knopman DS and Petersen RC: Relative
intake of macronutrients impacts risk of mild cognitive impairment
or dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 32:329–339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Valentin-Escalera J, Leclerc M and Calon
F: High-Fat diets in animal models of Alzheimer's disease: How can
eating too much fat increase Alzheimer's disease Risk? J Alzheimers
Dis. 97:977–1005. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoscheidt S, Sanderlin AH, Baker LD, Jung
Y, Lockhart S, Kellar D, Whitlow CT, Hanson AJ, Friedman S,
Register T, et al: Mediterranean and western diet effects on
Alzheimer's disease biomarkers, cerebral perfusion, and cognition
in mid-life: A randomized trial. Alzheimers Dement. 18:457–468.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yanai H: Effects of N-3 polyunsaturated
fatty acids on dementia. J Clin Med Res. 9:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Román GC, Jackson RE, Gadhia R, Román AN
and Reis J: Mediterranean diet: The role of long-chain ω-3 fatty
acids in fish; polyphenols in fruits, vegetables, cereals, coffee,
tea, cacao and wine; probiotics and vitamins in prevention of
stroke, age-related cognitive decline, and Alzheimer disease. Rev
Neurol (Paris). 175:724–741. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Di Meco A and Praticò D: Early-life
exposure to high-fat diet influences brain health in aging mice.
Aging Cell. 18:e130402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
de Paula GC, Brunetta HS, Engel DF, Gaspar
JM, Velloso LA, Engblom D, de Oliveira J and de Bem AF: Hippocampal
function is impaired by a short-term high-fat diet in mice:
Increased blood-brain barrier permeability and neuroinflammation as
triggering events. Front Neurosci. 15:7341582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiong J, Deng I, Kelliny S, Lin L,
Bobrovskaya L and Zhou X: Long term high fat diet induces metabolic
disorders and aggravates behavioral disorders and cognitive
deficits in MAPT P301L transgenic mice. Metab Brain Dis.
37:1941–1957. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boitard C, Cavaroc A, Sauvant J, Aubert A,
Castanon N, Layé S and Ferreira G: Impairment of
hippocampal-dependent memory induced by juvenile high-fat diet
intake is associated with enhanced hippocampal inflammation in
rats. Brain Behav Immun. 40:9–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sanguinetti E, Guzzardi MA, Panetta D,
Tripodi M, De Sena V, Quaglierini M, Burchielli S, Salvadori PA and
Iozzo P: Combined effect of fatty diet and cognitive decline on
brain metabolism, food intake, body weight, and counteraction by
intranasal insulin therapy in 3xTg mice. Front Cell Neurosci.
13:1882019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Attuquayefio T, Stevenson RJ, Boakes RA,
Oaten MJ, Yeomans MR, Mahmut M and Francis HM: A high-fat
high-sugar diet predicts poorer hippocampal-related memory and a
reduced ability to suppress wanting under satiety. J Exp Psychol
Anim Learn Cogn. 42:415–428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Holloway CJ, Cochlin LE, Emmanuel Y,
Murray A, Codreanu I, Edwards LM, Szmigielski C, Tyler DJ, Knight
NS, Saxby BK, et al: A high-fat diet impairs cardiac high-energy
phosphate metabolism and cognitive function in healthy human
subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 93:748–755. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morris MC, Tangney CC, Wang Y, Sacks FM,
Barnes LL, Bennett DA and Aggarwal NT: MIND diet slows cognitive
decline with aging. Alzheimers Dement. 11:1015–1022. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, Tangney
CC, Bennett DA, Aggarwal N, Schneider J and Wilson RS: Dietary fats
and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol.
60:194–200. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, Tangney
CC and Wilson RS: Dietary fat intake and 6-year cognitive change in
an older biracial community population. Neurology. 62:1573–1579.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Galloway S, Takechi R, Nesbit M,
Pallebage-Gamarallage MM, Lam V and Mamo JCL: The differential
effects of fatty acids on enterocytic abundance of amyloid-beta.
Lipids Health Dis. 18:2092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Evans AK, Saw NL, Woods CE, Vidano LM,
Blumenfeld SE, Lam RK, Chu EK, Reading C and Shamloo M: Impact of
high-fat diet on cognitive behavior and central and systemic
inflammation with aging and sex differences in mice. Brain Behav
Immun. 118:334–354. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boraxbekk CJ, Stomby A, Ryberg M, Lindahl
B, Larsson C, Nyberg L and Olsson T: diet-induced weight loss
alters functional brain responses during an episodic memory task.
Obes Facts. 8:261–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yao X, Yang C, Jia X, Yu Z, Wang C, Zhao
J, Chen Y, Xie B, Zhuang H, Sun C, et al: High-fat diet consumption
promotes adolescent neurobehavioral abnormalities and hippocampal
structural alterations via microglial overactivation accompanied by
an elevated serum free fatty acid concentration. Brain Behav Immun.
119:236–250. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ruan Y, Tang J, Guo X, Li K and Li D:
Dietary fat intake and risk of Alzheimer's disease and dementia: A
meta-analysis of cohort studies. Curr Alzheimer Res. 15:869–876.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
You SC, Geschwind MD, Sha SJ, Apple A,
Satris G, Wood KA, Johnson ET, Gooblar J, Feuerstein JS, Finkbeiner
S, et al: Executive functions in premanifest Huntington's disease.
Mov Disord. 29:405–409. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Klaus K, Vaht M, Pennington K and Harro J:
Interactive effects of DRD2 rs6277 polymorphism, environment and
sex on impulsivity in a population-representative study. Behav
Brain Res. 403:1131312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nieto-Estévez V, Defterali Ç and Vicario
C: Distinct effects of BDNF and NT-3 on the dendrites and
presynaptic boutons of developing olfactory bulb GABAergic
interneurons in vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 42:1399–1417. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
McLean FH, Grant C, Morris AC, Horgan GW,
Polanski AJ, Allan K, Campbell FM, Langston RF and Williams LM:
Rapid and reversible impairment of episodic memory by a high-fat
diet in mice. Sci Rep. 8:119762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Peng Y, Deng W, Xiang Q, Zhang W
and Liu M: Association between dietary inflammatory index and
cognitive impairment among American elderly: A cross-sectional
study. Front Aging Neurosci. 16:13718732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Valcarcel-Ares MN, Tucsek Z, Kiss T, Giles
CB, Tarantini S, Yabluchanskiy A, Balasubramanian P, Gautam T,
Galvan V, Ballabh P, et al: Obesity in aging exacerbates
neuroinflammation, dysregulating synaptic function-related genes
and altering eicosanoid synthesis in the mouse hippocampus:
Potential role in impaired synaptic plasticity and cognitive
decline. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 74:290–298. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Kothari V, Luo Y, Tornabene T, O'Neill AM,
Greene MW, Geetha T and Babu JR: High fat diet induces brain
insulin resistance and cognitive impairment in mice. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:499–508. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Julien C, Tremblay C, Phivilay A,
Berthiaume L, Emond V, Julien P and Calon F: High-fat diet
aggravates amyloid-beta and tau pathologies in the 3xTg-AD mouse
model. Neurobiol Aging. 31:1516–1531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Henn RE, Elzinga SE, Glass E, Parent R,
Guo K, Allouch AM, Mendelson FE, Hayes J, Webber-Davis I, Murphy
GG, et al: Obesity-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive
impairment in young adult versus middle-aged mice. Immun Ageing.
19:672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morris MC, Evans DA, Tangney CC, Bienias
JL, Schneider JA, Wilson RS and Scherr PA: Dietary copper and high
saturated and trans fat intakes associated with cognitive decline.
Arch Neurol. 63:1085–1088. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chatterjee S, Peters SA, Woodward M,
Arango SM, Batty GD, Beckett N, Beiser A, Borenstein AR, Crane PK,
Haan M, et al: Type 2 diabetes as a risk factor for dementia in
women compared with men: A pooled analysis of 2.3 million people
comprising more than 100,000 cases of dementia. Diabetes Care.
39:300–307. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Sanz-Martos AB, Roca M, Plaza A, Merino B,
Ruiz-Gayo M and Olmo ND: Long-term saturated fat-enriched diets
impair hippocampal learning and memory processes in a sex-dependent
manner. Neuropharmacology. 259:1101082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Muscat SM, Butler MJ, Mackey-Alfonso SE
and Barrientos RM: Young adult and aged female rats are vulnerable
to amygdala-dependent, but not hippocampus-dependent, memory
impairment following short-term high-fat diet. Brain Res Bull.
195:145–156. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Armstrong NM, An Y, Beason-Held L, Doshi
J, Erus G, Ferrucci L, Davatzikos C and Resnick SM: Predictors of
neurodegeneration differ between cognitively normal and
subsequently impaired older adults. Neurobiol Aging. 75:178–186.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Laitinen MH, Ngandu T, Rovio S, Helkala
EL, Uusitalo U, Viitanen M, Nissinen A, Tuomilehto J, Soininen H
and Kivipelto M: Fat intake at midlife and risk of dementia and
Alzheimer's disease: A population-based study. Dement Geriatr Cogn
Disord. 22:2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kleinridders A, Ferris HA, Cai W and Kahn
CR: Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain
function. Diabetes. 63:2232–2243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Martiskainen H, Helisalmi S, Viswanathan
J, Kurki M, Hall A, Herukka SK, Sarajärvi T, Natunen T, Kurkinen
KM, Huovinen J, et al: Effects of Alzheimer's disease-associated
risk loci on cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and disease
progression: A polygenic risk score approach. J Alzheimers Dis.
43:565–573. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Fan L, Borenstein AR, Wang S, Nho K, Zhu
X, Wen W, Huang X, Mortimer JA, Shrubsole MJ and Dai Q; Alzheimer's
Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: Associations of circulating
saturated long-chain fatty acids with risk of mild cognitive
impairment and Alzheimer's disease in the Alzheimer's disease
neuroimaging initiative (ADNI) cohort. EBioMedicine. 97:1048182023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Arnold SE, Lucki I, Brookshire BR, Carlson
GC, Browne CA, Kazi H, Bang S, Choi BR, Chen Y, McMullen MF and Kim
SF: High fat diet produces brain insulin resistance,
synaptodendritic abnormalities and altered behavior in mice.
Neurobiol Dis. 67:79–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li C, Shi L, Wang Y, Peng C, Wu L, Zhang Y
and Du Z: High-fat diet exacerbates lead-induced blood-brain
barrier disruption by disrupting tight junction integrity. Environ
Toxicol. 36:1412–1421. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Meza-Miranda ER, Camargo A, Rangel-Zuñiga
OA, Delgado-Lista J, Garcia-Rios A, Perez-Martinez P, Tasset-Cuevas
I, Tunez I, Tinahones FJ, Perez-Jimenez F and Lopez-Miranda J:
Postprandial oxidative stress is modulated by dietary fat in
adipose tissue from elderly people. Age (Dordr). 36:507–517. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Valdearcos M, Douglass JD, Robblee MM,
Dorfman MD, Stifler DR, Bennett ML, Gerritse I, Fasnacht R, Barres
BA, Thaler JP and Koliwad SK: Microglial inflammatory signaling
orchestrates the hypothalamic immune response to dietary excess and
mediates obesity susceptibility. Cell Metab. 26:185–197. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yanguas-Casás N, Crespo-Castrillo A, de
Ceballos ML, Chowen JA, Azcoitia I, Arevalo MA and Garcia-Segura
LM: Sex differences in the phagocytic and migratory activity of
microglia and their impairment by palmitic acid. Glia. 66:522–537.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Block ML, Zecca L and Hong JS:
Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular
mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:57–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Ransohoff RM: How neuroinflammation
contributes to neurodegeneration. Science. 353:777–783. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liang Z, Gong X, Ye R, Zhao Y, Yu J, Zhao
Y and Bao J: Long-Term high-fat diet consumption induces cognitive
decline accompanied by tau hyper-phosphorylation and microglial
activation in aging. Nutrients. 15:2502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kipnis J, Cohen H, Cardon M, Ziv Y and
Schwartz M: T cell deficiency leads to cognitive dysfunction:
Implications for therapeutic vaccination for schizophrenia and
other psychiatric conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:8180–8185. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yirmiya R and Goshen I: Immune modulation
of learning, memory, neural plasticity and neurogenesis. Brain
Behav Immun. 25:181–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Toyama K, Koibuchi N, Hasegawa Y, Uekawa
K, Yasuda O, Sueta D, Nakagawa T, Ma M, Kusaka H, Lin B, et al:
ASK1 is involved in cognitive impairment caused by long-term
high-fat diet feeding in mice. Sci Rep. 5:108442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sobesky JL, Barrientos RM, De May HS,
Thompson BM, Weber MD, Watkins LR and Maier SF: High-fat diet
consumption disrupts memory and primes elevations in hippocampal
IL-1β, an effect that can be prevented with dietary reversal or
IL-1 receptor antagonism. Brain Behav Immun. 42:22–32. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Spencer SJ, Korosi A, Layé S, Shukitt-Hale
B and Barrientos RM: Food for thought: how nutrition impacts
cognition and emotion. NPJ Sci Food. 1:72017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Crupi R, Marino A and Cuzzocrea S: n-3
fatty acids: Role in neurogenesis and neuroplasticity. Curr Med
Chem. 20:2953–2963. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Butler MJ, Mackey-Alfonso SE, Massa N,
Baskin KK and Barrientos RM: Dietary fatty acids differentially
impact phagocytosis, inflammatory gene expression, and
mitochondrial respiration in microglial and neuronal cell models.
Front Cell Neurosci. 17:12272412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Alkan I, Altunkaynak BZ, Gültekin Gİ and
Bayçu C: Hippocampal neural cell loss in high-fat diet-induced
obese rats-exploring the protein networks, ultrastructure,
biochemical and bioinformatical markers. J Chem Neuroanat.
114:1019472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lin MT and Beal MF: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.
Nature. 443:787–795. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kelty TJ, Taylor CL, Wieschhaus NE, Thorne
PK, Amin AR, Mueller CM, Olver TD, Tharp DL, Emter CA, Caulk AW and
Rector RS: Western diet-induced obesity results in brain
mitochondrial dysfunction in female Ossabaw swine. Front Mol
Neurosci. 16:13208792023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Grel H, Woznica D, Ratajczak K, Kalwarczyk
E, Anchimowicz J, Switlik W, Olejnik P, Zielonka P, Stobiecka M and
Jakiela S: Mitochondrial dynamics in neurodegenerative diseases:
Unraveling the role of fusion and fission processes. Int J Mol Sci.
24:130332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Madreiter-Sokolowski CT, Hiden U, Krstic
J, Panzitt K, Wagner M, Enzinger C, Khalil M, Abdellatif M, Malle
E, Madl T, et al: Targeting organ-specific mitochondrial
dysfunction to improve biological aging. Pharmacol Ther.
262:1087102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Haack F, Lemcke H, Ewald R, Rharass T and
Uhrmacher AM: Spatio-temporal model of endogenous ROS and
raft-dependent WNT/beta-catenin signaling driving cell fate
commitment in human neural progenitor cells. PLoS Comput Biol.
11:e10041062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ghosh P, Fontanella RA, Scisciola L,
Pesapane A, Taktaz F, Franzese M, Puocci A, Ceriello A,
Prattichizzo F, Rizzo MR, et al: Targeting redox imbalance in
neurodegeneration: Characterizing the role of GLP-1 receptor
agonists. Theranostics. 13:4872–4884. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Bórquez DA, Urrutia PJ, Wilson C, van
Zundert B, Núñez MT and González-Billault C: Dissecting the role of
redox signaling in neuronal development. J Neurochem. 137:506–517.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Morrison CD, Pistell PJ, Ingram DK,
Johnson WD, Liu Y, Fernandez-Kim SO, White CL and Purpera MN: High
fat diet increases hippocampal oxidative stress and cognitive
impairment in aged mice: Implications for decreased Nrf2 signaling.
J Neurochem. 114:1581–1589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Iqbal G and Ahmed T: Co-exposure of metals
and high fat diet causes aging like neuropathological changes in
non-aged mice brain. Brain Res Bull. 147:148–158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu Y, Fu X, Lan N, Li S, Zhang J, Wang S,
Li C, Shang Y, Huang T and Zhang L: Luteolin protects against high
fat diet-induced cognitive deficits in obesity mice. Behav Brain
Res. 267:178–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Könner AC, Janoschek R, Plum L, Jordan SD,
Rother E, Ma X, Xu C, Enriori P, Hampel B, Barsh GS, et al: Insulin
action in AgRP-expressing neurons is required for suppression of
hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab. 5:438–449. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Huang CC, Lee CC and Hsu KS: An
investigation into signal transduction mechanisms involved in
insulin-induced long-term depression in the CA1 region of the
hippocampus. J Neurochem. 89:217–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Pearson-Leary J and McNay EC: Novel roles
for the insulin-regulated glucose transporter-4 in hippocampally
dependent memory. J Neurosci. 36:11851–11864. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL,
Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR and de la Monte SM: Impaired
insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling
mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease-is this type 3 diabetes? J
Alzheimers Dis. 7:63–80. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Denver P, Gault VA and McClean PL:
Sustained high-fat diet modulates inflammation, insulin signalling
and cognition in mice and a modified xenin peptide ameliorates
neuropathology in a chronic high-fat model. Diabetes Obes Metab.
20:1166–1175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Arnold SE, Arvanitakis Z, Macauley-Rambach
SL, Koenig AM, Wang HY, Ahima RS, Craft S, Gandy S, Buettner C,
Stoeckel LE, et al: Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and
Alzheimer disease: Concepts and conundrums. Nat Rev Neurol.
14:168–181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ehtewish H, Arredouani A and El-Agnaf O:
Diagnostic, prognostic, and mechanistic biomarkers of diabetes
mellitus-associated cognitive decline. Int J Mol Sci. 23:61442022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang H, Liang JL, Wu QY, Li JX, Liu Y, Wu
LW, Huang JL, Wu XW, Wang MH and Chen N: Swimming suppresses
cognitive decline of HFD-induced obese mice through reversing
hippocampal inflammation, insulin resistance, and BDNF level.
Nutrients. 14:24322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Bomfim TR, Forny-Germano L, Sathler LB,
Brito-Moreira J, Houzel JC, Decker H, Silverman MA, Kazi H, Melo
HM, McClean P, et al: An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse
brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer's
disease-associated Aβ oligomers. J Clin Invest. 122:1339–1353.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Socała K, Doboszewska U, Szopa A, Serefko
A, Włodarczyk M, Zielińska A, Poleszak E, Fichna J and Wlaź P: The
role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and
neurological disorders. Pharmacol Res. 172:1058402021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH and
Mazmanian SK: The central nervous system and the gut microbiome.
Cell. 167:915–932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Carabotti M, Scirocco A, Maselli MA and
Severi C: The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric
microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann Gastroenterol.
28:203–209. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Fasina OB, Wang J, Mo J, Osada H, Ohno H,
Pan W, Xiang L and Qi J: Gastrodin from gastrodia elata enhances
cognitive function and neuroprotection of AD mice via the
regulation of gut microbiota composition and inhibition of neuron
inflammation. Front Pharmacol. 13:8142712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Schneeberger M, Everard A, Gómez-Valadés
AG, Matamoros S, Ramírez S, Delzenne NM, Gomis R, Claret M and Cani
PD: Akkermansia muciniphila inversely correlates with the onset of
inflammation, altered adipose tissue metabolism and metabolic
disorders during obesity in mice. Sci Rep. 5:166432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhang B, Qiu J, Qu Z, Xiao R, Wang L, Tian
P, Zhang H, Chen W and Wang G: Bifidobacterium adolescentis
FJSSZ23M10 modulates gut microbiota and metabolism to alleviate
obesity through strain-specific genomic features. Food Funct.
16:2415–2431. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Turnbaugh PJ, Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey
FE, Knight R and Gordon JI: The effect of diet on the human gut
microbiome: A metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice.
Sci Transl Med. 1:6ra142009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Wan Y, Wang F, Yuan J, Li J, Jiang D,
Zhang J, Li H, Wang R, Tang J, Huang T, et al: Effects of dietary
fat on gut microbiota and faecal metabolites, and their
relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: A 6-month
randomised controlled-feeding trial. Gut. 68:1417–1429. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Bruce-Keller AJ, Salbaum JM, Luo M,
Blanchard E IV, Taylor CM, Welsh DA and Berthoud HR: Obese-type gut
microbiota induce neurobehavioral changes in the absence of
obesity. Biol Psychiatry. 77:607–615. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
92
|
Zheng M, Ye H, Yang X, Shen L, Dang X, Liu
X, Gong Y, Wu Q, Wang L, Ge X, et al: Probiotic Clostridium
butyricum ameliorates cognitive impairment in obesity via the
microbiota-gut-brain axis. Brain Behav Immun. 115:565–587. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Krüger JF, Hillesheim E, Pereira ACSN,
Camargo CQ and Rabito EI: Probiotics for dementia: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev.
79:160–170. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Fung TC, Olson CA and Hsiao EY:
Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in
health and disease. Nat Neurosci. 20:145–155. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Visekruna A and Luu M: The role of
short-chain fatty acids and bile acids in intestinal and liver
function, inflammation, and carcinogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:7032182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Lin H, An Y, Hao F, Wang Y and Tang H:
Correlations of fecal metabonomic and microbiomic changes induced
by high-fat diet in the pre-obesity state. Sci Rep. 6:216182016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P
and Bäckhed F: From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain
fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell. 165:1332–1345.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Stilling RM, van de Wouw M, Clarke G,
Stanton C, Dinan TG and Cryan JF: The neuropharmacology of
butyrate: The bread and butter of the microbiota-gut-brain axis?
Neurochem Int. 99:110–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Stephenson J, Nutma E, van der Valk P and
Amor S: Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology.
154:204–219. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hargrave SL, Davidson TL, Zheng W and
Kinzig KP: Western diets induce blood-brain barrier leakage and
alter spatial strategies in rats. Behav Neurosci. 130:123–135.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
101
|
Takechi R, Galloway S,
Pallebage-Gamarallage MM, Lam V, Dhaliwal SS and Mamo JC: Probucol
prevents blood-brain barrier dysfunction in wild-type mice induced
by saturated fat or cholesterol feeding. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 40:45–52. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Tan BL and Norhaizan ME: Effect of
high-fat diets on oxidative stress, cellular inflammatory response
and cognitive function. Nutrients. 11:25792019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Heyward FD, Walton RG, Carle MS, Coleman
MA, Garvey WT and Sweatt JD: Adult mice maintained on a high-fat
diet exhibit object location memory deficits and reduced
hippocampal SIRT1 gene expression. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 98:25–32.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Finnerup NB, Kuner R and Jensen TS:
Neuropathic pain: From mechanisms to treatment. Physiol Rev.
101:259–301. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Hardingham GE and Bading H: Synaptic
versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: Implications for
neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 11:682–696. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Martinelli I, Tayebati SK, Roy P, Di
Bonaventura MV, Moruzzi M, Cifani C, Amenta F and Tomassoni D:
Obesity-Related brain cholinergic system impairment in
high-fat-diet-fed rats. Nutrients. 14:12432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Morris MC, Tangney CC, Wang Y, Sacks FM,
Bennett DA and Aggarwal NT: MIND diet associated with reduced
incidence of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 11:1007–1014.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Barnes LL, Dhana K, Liu X, Carey VJ,
Ventrelle J, Johnson K, Hollings CS, Bishop L, Laranjo N, Stubbs
BJ, et al: Trial of the MIND diet for prevention of cognitive
decline in older persons. N Engl J Med. 389:602–611. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Franco GA, Interdonato L, Cordaro M,
Cuzzocrea S and Di Paola R: Bioactive compounds of the
mediterranean diet as nutritional support to fight
neurodegenerative disease. Int J Mol Sci. 24:73182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Martínez-Lapiscina EH, Clavero P, Toledo
E, Estruch R, Salas-Salvadó J, San Julián B, Sanchez-Tainta A, Ros
E, Valls-Pedret C and Martinez-Gonzalez MÁ: Mediterranean diet
improves cognition: The PREDIMED-NAVARRA randomised trial. J Neurol
Neurosurg Psychiatry. 84:1318–1325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Ng TP, Feng L, Yap KB, Lee TS, Tan CH and
Winblad B: Long-term metformin usage and cognitive function among
older adults with diabetes. J Alzheimers Dis. 41:61–68. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Zhu X, Shen J, Feng S, Huang C, Wang H,
Huo F and Liu H: Akkermansia muciniphila, which is enriched in the
gut microbiota by metformin, improves cognitive function in aged
mice by reducing the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6.
Microbiome. 11:1202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Lochhead JJ, Kellohen KL, Ronaldson PT and
Davis TP: Distribution of insulin in trigeminal nerve and brain
after intranasal administration. Sci Rep. 9:26212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Stranahan AM, Norman ED, Lee K, Cutler RG,
Telljohann RS, Egan JM and Mattson MP: Diet-induced insulin
resistance impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognition in
middle-aged rats. Hippocampus. 18:1085–1088. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Kaelber S, Pantcheva P and Borlongan CV:
Drug- and cell-based therapies for targeting neuroinflammation in
traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 11:1575–1576. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Fielder E, Tweedy C, Wilson C, Oakley F,
LeBeau FEN, Passos JF, Mann DA, von Zglinicki T and Jurk D:
Anti-inflammatory treatment rescues memory deficits during aging in
nfkb1−/− mice. Aging Cell. 19:e131882020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Wang QJ, Shen YE, Wang X, Fu S, Zhang X,
Zhang YN and Wang RT: Concomitant memantine and Lactobacillus
plantarum treatment attenuates cognitive impairments in APP/PS1
mice. Aging (Albany NY). 12:628–649. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Li X, Zheng P, Cao W, Cao Y, She X, Yang
H, Ma K, Wu F, Gao X, Fu Y, et al: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG
ameliorates noise-induced cognitive deficits and systemic
inflammation in rats by modulating the gut-brain axis. Front Cell
Infect Microbiol. 13:10673672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Dong J, Ping L, Cao T, Sun L, Liu D, Wang
S, Huo G and Li B: Immunomodulatory effects of the Bifidobacterium
longum BL-10 on lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal mucosal
immune injury. Front Immunol. 13:9477552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Mandelbaum N, Zhang L, Carasso S, Ziv T,
Lifshiz-Simon S, Davidovich I, Luz I, Berinstein E, Gefen T, Cooks
T, et al: Extracellular vesicles of the Gram-positive gut symbiont
Bifidobacterium longum induce immune-modulatory, anti-inflammatory
effects. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 9:302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Smith PJ and Blumenthal JA: Dietary
factors and cognitive decline. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 3:53–64.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Petersson SD and Philippou E:
Mediterranean diet, cognitive function, and dementia: A systematic
review of the evidence. Adv Nutr. 7:889–904. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Valls-Pedret C, Sala-Vila A, Serra-Mir M,
Corella D, de la Torre R, Martínez-González MÁ, Martínez-Lapiscina
EH, Fitó M, Pérez-Heras A, Salas-Salvadó J, et al: Mediterranean
diet and age-related cognitive decline: A randomized clinical
trial. JAMA Intern Med. 175:1094–1103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Liu X, Morris MC, Dhana K, Ventrelle J,
Johnson K, Bishop L, Hollings CS, Boulin A, Laranjo N, Stubbs BJ,
et al: Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay
(MIND) study: Rationale, design and baseline characteristics of a
randomized control trial of the MIND diet on cognitive decline.
Contemp Clin Trials. 102:1062702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Jiwani R, Robbins R, Neri A, Renero J,
Lopez E and Serra MC: Effect of dietary intake through whole foods
on cognitive function: Review of randomized controlled trials. Curr
Nutr Rep. 11:146–160. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Bazinet RP and Layé S: Polyunsaturated
fatty acids and their metabolites in brain function and disease.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 15:771–785. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Dyall SC: Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids
and the brain: A review of the independent and shared effects of
EPA, DPA and DHA. Front Aging Neurosci. 7:522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Calon F and Cole G: Neuroprotective action
of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids against neurodegenerative
diseases: Evidence from animal studies. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 77:287–293. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Külzow N, Witte AV, Kerti L, Grittner U,
Schuchardt JP, Hahn A and Flöel A: Impact of omega-3 fatty acid
supplementation on memory functions in healthy older adults. J
Alzheimers Dis. 51:713–725. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Danthiir V, Hosking DE, Nettelbeck T,
Vincent AD, Wilson C, O'Callaghan N, Calvaresi E, Clifton P and
Wittert GA: An 18-mo randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
trial of DHA-rich fish oil to prevent age-related cognitive decline
in cognitively normal older adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 107:754–762.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Power R, Nolan JM, Prado-Cabrero A, Roche
W, Coen R, Power T and Mulcahy R: Omega-3 fatty acid, carotenoid
and vitamin E supplementation improves working memory in older
adults: A randomised clinical trial. Clin Nutr. 41:405–414. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Engin A: Misalignment of circadian rhythms
in diet-induced obesity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1460:27–71. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Altaha B, Heddes M, Pilorz V, Niu Y,
Gorbunova E, Gigl M, Kleigrewe K, Oster H, Haller D and Kiessling
S: Genetic and environmental circadian disruption induce weight
gain through changes in the gut microbiome. Mol Metab.
66:1016282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Su X, Li Q, Yang M, Zhang W, Liu X, Ba Y,
Deng Q, Zhang Y, Han L and Huang H: Resveratrol protects against a
high-fat diet-induced neuroinflammation by suppressing
mitochondrial fission via targeting SIRT1/PGC-1α. Exp Neurol.
380:1148992024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Pivari F, Mingione A, Piazzini G,
Ceccarani C, Ottaviano E, Brasacchio C, Dei Cas M, Vischi M,
Cozzolino MG, Fogagnolo P, et al: Curcumin supplementation
(Meriva®) modulates inflammation, lipid peroxidation and
gut microbiota composition in chronic kidney disease. Nutrients.
14:2312022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Alghadir A, Gabr SA and Iqbal A: Enhancing
cognitive performance and mitigating dyslipidemia: The impact of
moderate aerobic training on sedentary older adults. BMC Geriatr.
24:6782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Blumenthal JA, Smith PJ, Mabe S,
Hinderliter A, Lin PH, Liao L, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Browndyke JN, Kraus
WE, Doraiswamy PM, et al: Lifestyle and neurocognition in older
adults with cognitive impairments: A randomized trial. Neurology.
92:e212–e223. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
138
|
Saslow LR, Jones LM, Sen A, Wolfson JA,
Diez HL, O'Brien A, Leung CW, Bayandorian H, Daubenmier J, Missel
AL and Richardson C: Comparing very low-carbohydrate vs DASH diets
for overweight or obese adults with hypertension and prediabetes or
type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann Fam Med. 21:256–263. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Erickson KI, Voss MW, Prakash RS, Basak C,
Szabo A, Chaddock L, Kim JS, Heo S, Alves H, White SM, et al:
Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves
memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:3017–3022. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Sabouri M, Kordi M, Shabkhiz F,
Taghibeikzadehbadr P and Geramian ZS: Moderate treadmill exercise
improves spatial learning and memory deficits possibly via changing
PDE-5, IL-1 β and pCREB expression. Exp Gerontol. 139:1110562020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Noble EE, Mavanji V, Little MR, Billington
CJ, Kotz CM and Wang C: Exercise reduces diet-induced cognitive
decline and increases hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor
in CA3 neurons. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 114:40–50. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
De la Rosa A, Olaso-Gonzalez G,
Arc-Chagnaud C, Millan F, Salvador-Pascual A, García-Lucerga C,
Blasco-Lafarga C, Garcia-Dominguez E, Carretero A, Correas A, et
al: Physical exercise in the prevention and treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. J Sport Health Sci. 9:394–404. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Chang YS, Lin CL, Lee CW, Lin HC, Wu YT
and Shih YH: Exercise normalized the hippocampal renin-angiotensin
system and restored spatial memory function, neurogenesis, and
blood-brain barrier permeability in the 2K1C-hypertensive mouse.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:55312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Smith PJ, Blumenthal JA, Babyak MA,
Craighead L, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Browndyke JN, Strauman TA and
Sherwood A: Effects of the dietary approaches to stop hypertension
diet, exercise, and caloric restriction on neurocognition in
overweight adults with high blood pressure. Hypertension.
55:1331–1338. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Cartee GD, Hepple RT, Bamman MM and
Zierath JR: Exercise promotes healthy aging of skeletal muscle.
Cell Metab. 23:1034–1047. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Kang EB and Cho JY: Effects of treadmill
exercise on brain insulin signaling and β-amyloid in
intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced-memory impairment in
rats. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 18:89–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Gleeson M, Bishop NC, Stensel DJ, Lindley
MR, Mastana SS and Nimmo MA: The anti-inflammatory effects of
exercise: Mechanisms and implications for the prevention and
treatment of disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:607–615. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Spencer SJ, D'Angelo H, Soch A, Watkins
LR, Maier SF and Barrientos RM: High-fat diet and aging interact to
produce neuroinflammation and impair hippocampal- and
amygdalar-dependent memory. Neurobiol Aging. 58:88–100. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Ionescu-Tucker A and Cotman CW: Emerging
roles of oxidative stress in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 107:86–95. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Hadizadeh M, Hamidi GA and Salami M:
Probiotic supplementation improves the cognitive function and the
anxiety-like behaviors in the stressed rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci.
22:506–514. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Akbari E, Asemi Z, Kakhaki RD, Bahmani F,
Kouchaki E, Tamtaji OR, Hamidi GA and Salami M: Effect of probiotic
supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in
alzheimer's disease: A randomized, double-blind and controlled
trial. Front Aging Neurosci. 8:2562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Small GW, Siddarth P, Silverman DH, Ercoli
LM, Miller KJ, Lavretsky H, Bookheimer SY, Huang SC, Barrio JR and
Phelps ME: Cognitive and cerebral metabolic effects of celecoxib
versus placebo in people with age-related memory loss: Randomized
controlled study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 16:999–1009. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Kohman RA, Bhattacharya TK, Kilby C, Bucko
P and Rhodes JS: Effects of minocycline on spatial learning,
hippocampal neurogenesis and microglia in aged and adult mice.
Behav Brain Res. 242:17–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Leigh SJ, Kaakoush NO, Westbrook RF and
Morris MJ: Minocycline-induced microbiome alterations predict
cafeteria diet-induced spatial recognition memory impairments in
rats. Transl Psychiatry. 10:922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Craft S and Watson GS: Insulin and
neurodegenerative disease: Shared and specific mechanisms. Lancet
Neurol. 3:169–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Ismail TR, Yap CG, Naidu R and Pamidi N:
Environmental enrichment and metformin improve metabolic functions,
hippocampal neuron survival, and hippocampal-dependent memory in
high-fat/high-sucrose diet-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Biology
(Basel). 12:169–178. 2023.
|
|
157
|
Ameen O, Samaka RM and Abo-Elsoud RAA:
Metformin alleviates neurocognitive impairment in aging via
activation of AMPK/BDNF/PI3K pathway. Sci Rep. 12:170842022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
d'Angelo M, Castelli V, Catanesi M,
Antonosante A, Dominguez-Benot R, Ippoliti R, Benedetti E and
Cimini A: PPARγ and cognitive performance. Int J Mol Sci.
20:50682019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Chen Z, Deng X, Shi C, Jing H, Tian Y,
Zhong J, Chen G, Xu Y, Luo Y and Zhu Y: GLP-1R-positive neurons in
the lateral septum mediate the anorectic and weight-lowering
effects of liraglutide in mice. J Clin Invest. 134:e1782392024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Delanogare E, Bullich S, Barbosa LADS,
Barros WM, Braga SP, Kraus SI, Kasprowicz JN, Dos Santos GJ, Guiard
BP and Moreira ELG: Metformin improves neurobehavioral impairments
of streptozotocin-treated and western diet-fed mice: Beyond
glucose-lowering effects. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 37:94–106. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Lennox R, Porter DW, Flatt PR, Holscher C,
Irwin N and Gault VA: Comparison of the independent and combined
effects of sub-chronic therapy with metformin and a stable GLP-1
receptor agonist on cognitive function, hippocampal synaptic
plasticity and metabolic control in high-fat fed mice.
Neuropharmacology. 86:22–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Leal G, Comprido D and Duarte CB:
BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity.
Neuropharmacology. 76:639–656. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Zuo X, Zhu Z, Liu M, Zhao Q, Li X, Zhao X
and Feng X: Fluoxetine ameliorates cognitive deficits in high-fat
diet mice by regulating BDNF expression. ACS Chem Neurosci.
15:4229–4240. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Davidson TL, Jones S, Roy M and Stevenson
RJ: the cognitive control of eating and body weight: It's more than
what you 'Think'. Front Psychol. 10:622019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Maki KC, Slavin JL, Rains TM and
Kris-Etherton PM: Limitations of observational evidence:
Implications for evidence-based dietary recommendations. Adv Nutr.
5:7–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Wu M, Liao M, Huang R, Chen C, Tian T,
Wang H, Li J, Li J, Sun Y, Wu C, et al: Hippocampal overexpression
of TREM2 ameliorates high fat diet induced cognitive impairment and
modulates phenotypic polarization of the microglia. Genes Dis.
9:401–414. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
167
|
Song T, Song X, Zhu C, Patrick R, Skurla
M, Santangelo I, Green M, Harper D, Ren B, Forester BP, et al:
Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and
metabolic alterations in the progression of Alzheimer's disease: A
meta-analysis of in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies.
Ageing Res Rev. 72:1015032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Mozhui K, Lu AT, Li CZ, Haghani A,
Sandoval-Sierra JV, Wu Y, Williams RW and Horvath S: Genetic loci
and metabolic states associated with murine epigenetic aging.
Elife. 11:e752442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Kamoga R, Rukundo GZ, Kalungi S,
Obungoloch J, Obua C and Ihunwo A: Vagus nerve stimulation in
dementia: A scoping review of clinical and pre-clinical studies.
AIMS Neurosci. 11:398–420. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Amelianchik A, Sweetland-Martin L and
Norris EH: The effect of dietary fat consumption on Alzheimer's
disease pathogenesis in mouse models. Transl Psychiatry.
12:2932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Elzinga SE, Guo K, Turfah A, Henn RE,
Webber-Davis IF, Hayes JM, Pacut CM, Teener SJ, Carter AD, Rigan
DM, et al: Metabolic stress and age drive inflammation and
cognitive decline in mice and humans. Alzheimers Dement.
21:e700602025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Townsend RF, Logan D, O'Neill RF, Prinelli
F, Woodside JV and McEvoy CT: Whole dietary patterns, cognitive
decline and cognitive disorders: A systematic review of prospective
and intervention studies. Nutrients. 15:3332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Yako H, Niimi N, Takaku S and Sango K:
Advantages of omics approaches for elucidating metabolic changes in
diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Front Endocrinol. 14:12084412023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Zhang R, Zhang M and Wang P: The intricate
interplay between dietary habits and cognitive function: Insights
from the gut-brain axis. Front Nutr. 12:15393552025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|