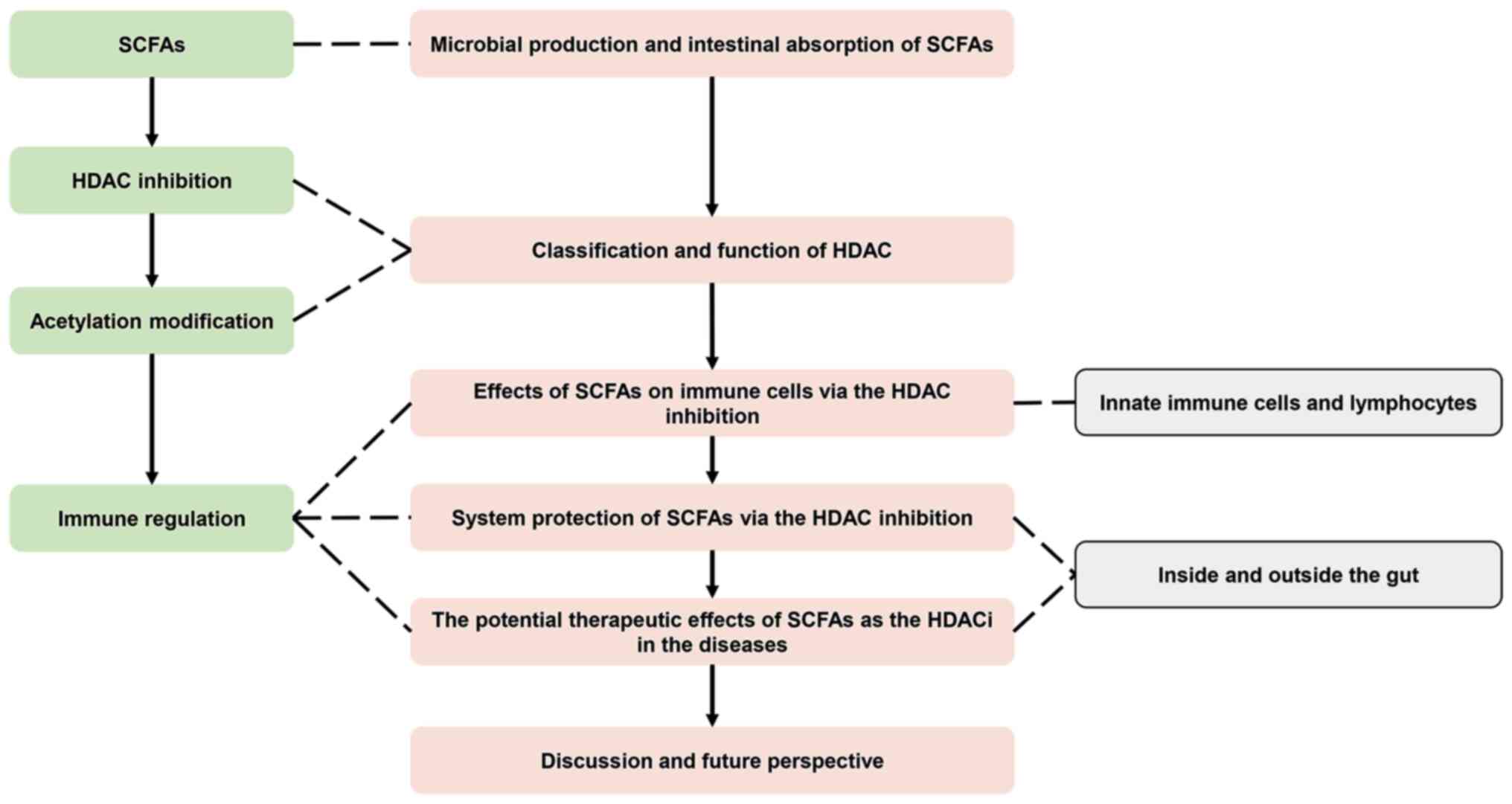
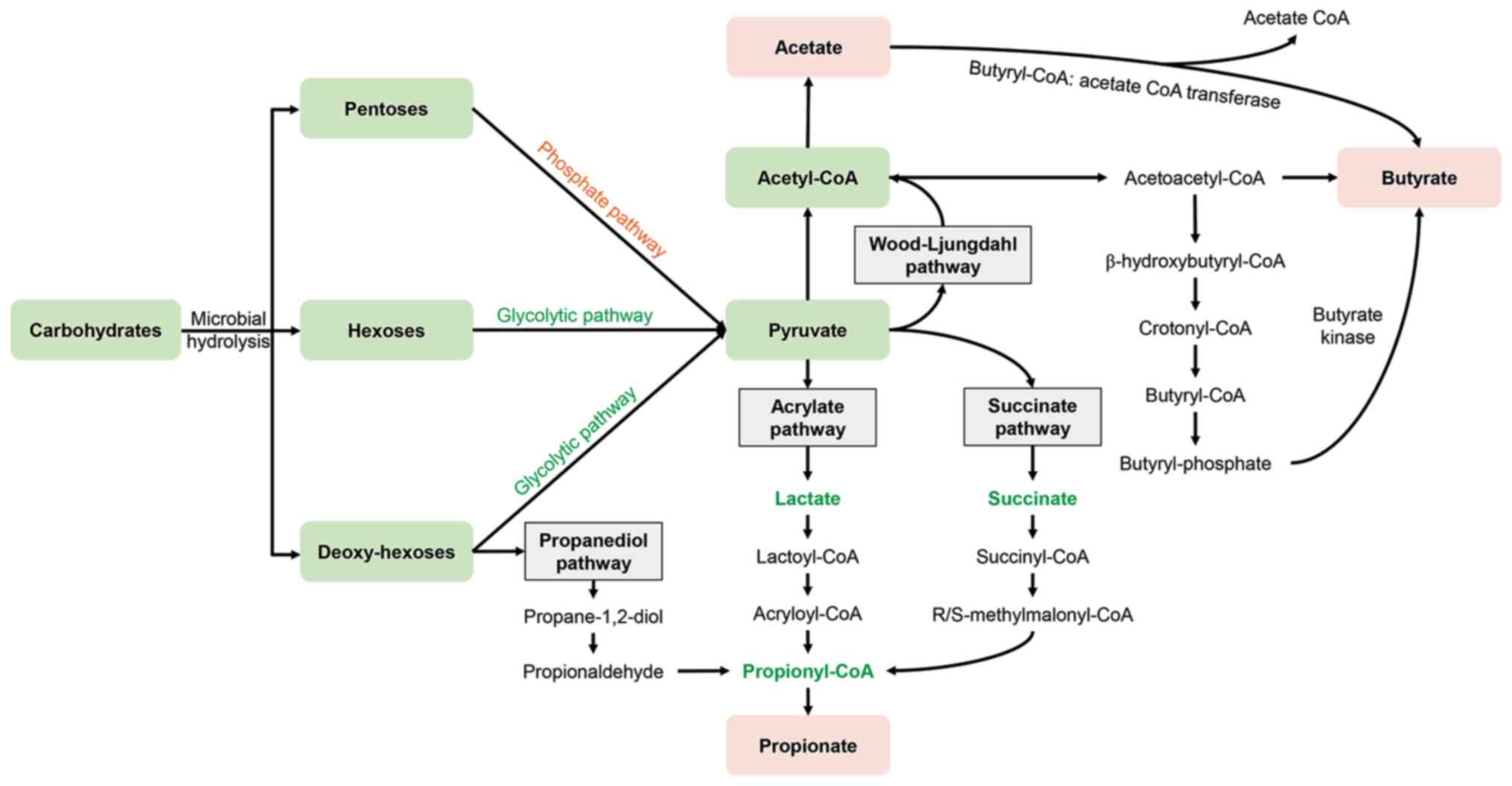
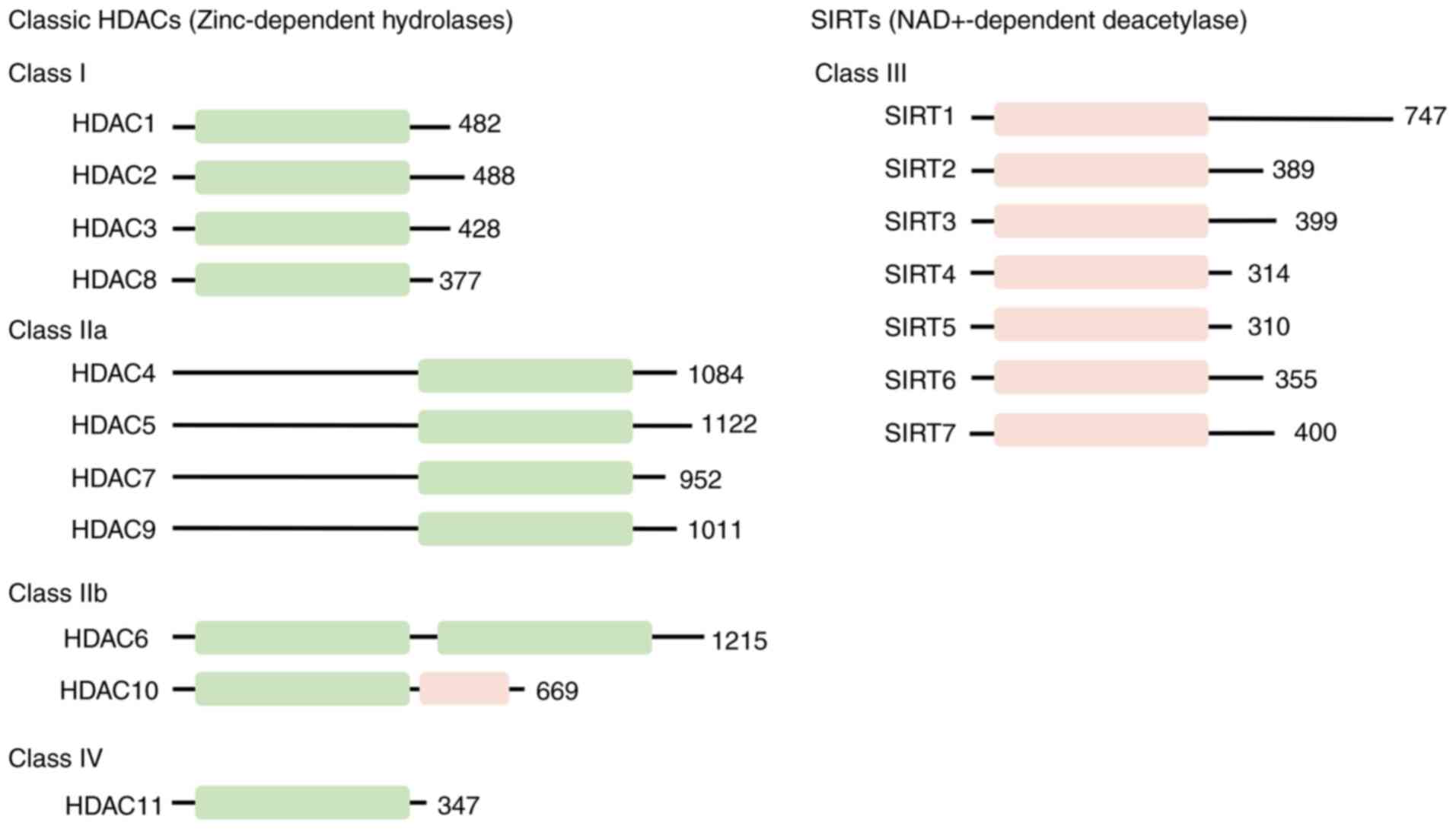
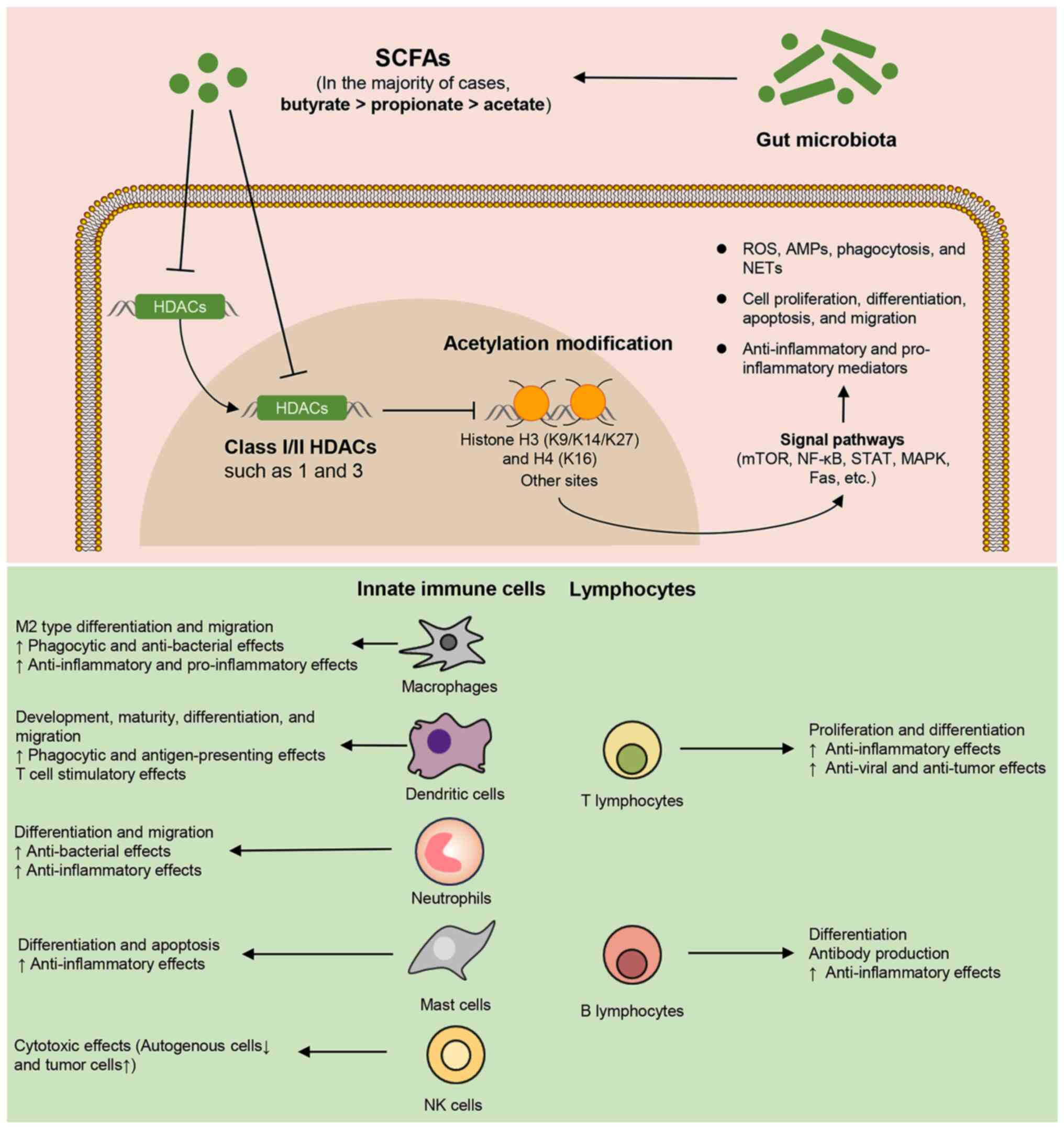
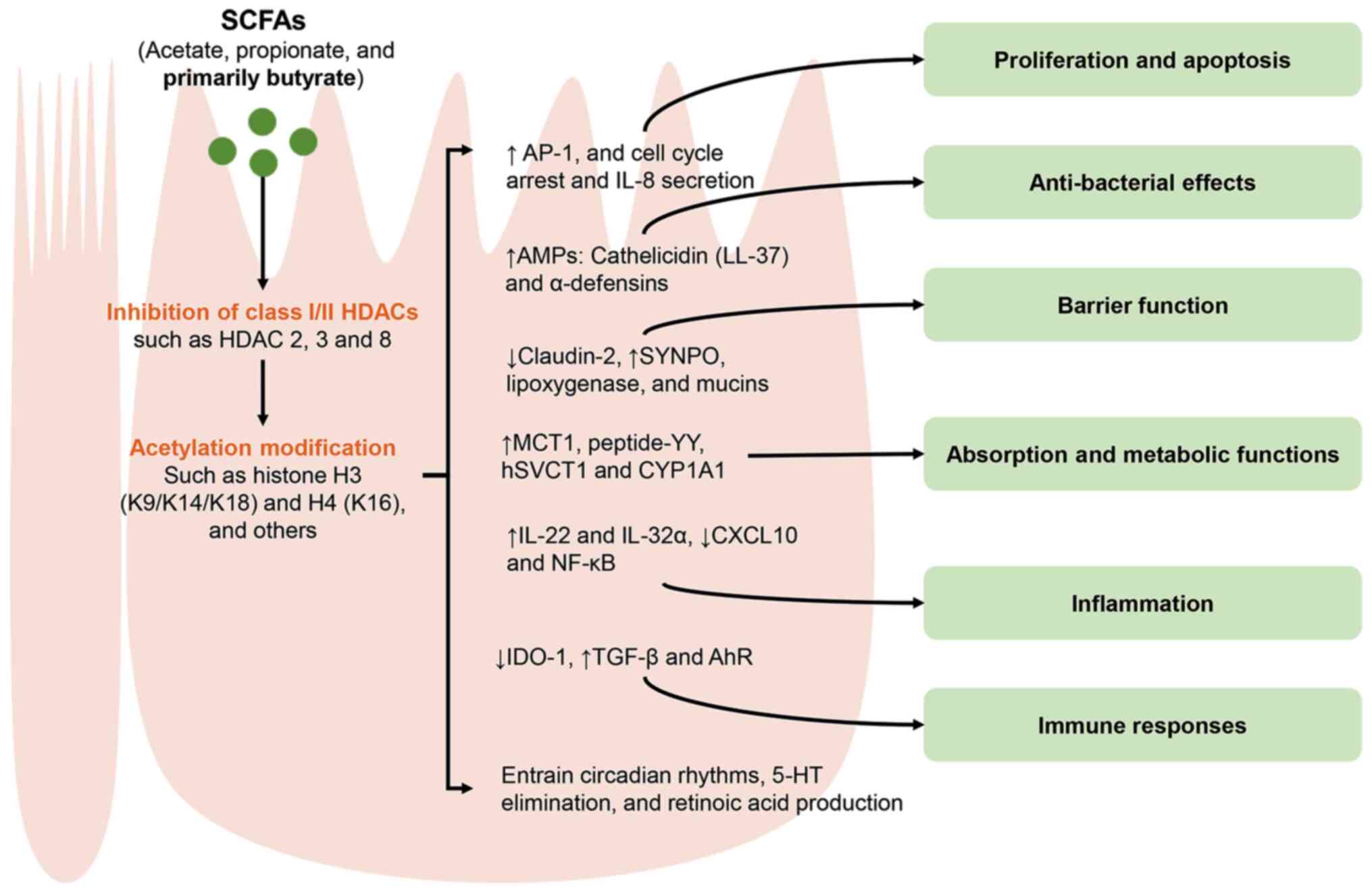
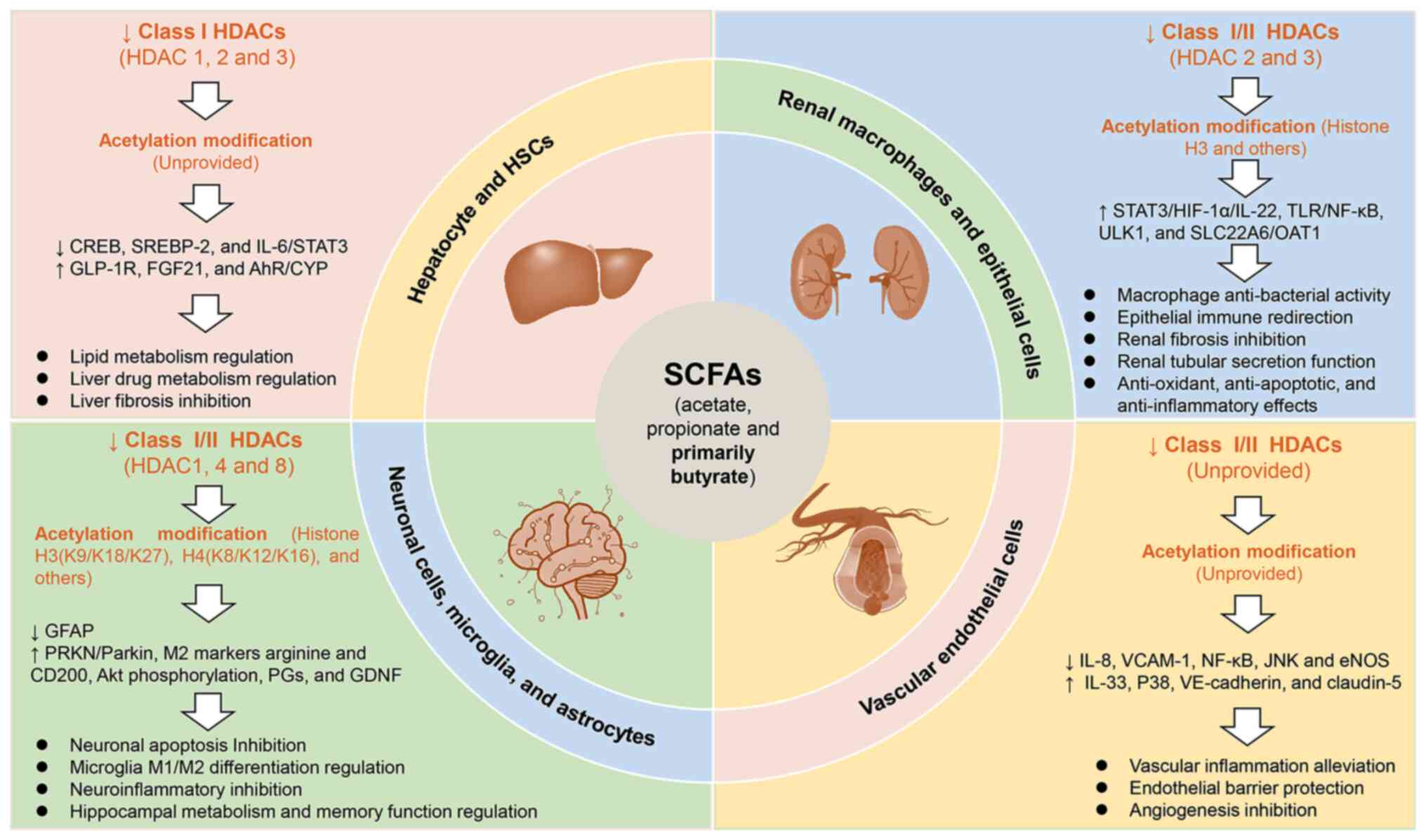
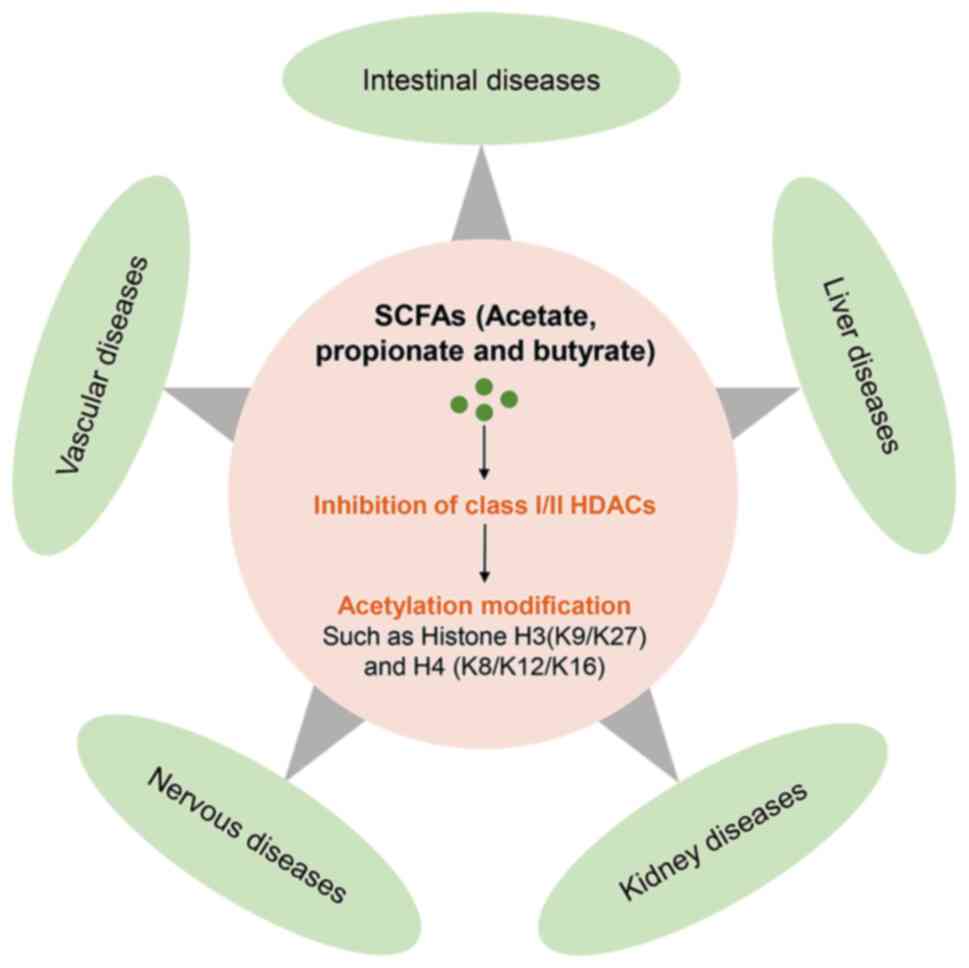
|
1
|
Millán-Zambrano G, Burton A, Bannister AJ
and Schneider R: Histone post-translational modifications-cause and
consequence of genome function. Nat Rev Genet. 23:563–580. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhao S, Zhang X and Li H: Beyond histone
acetylation-writing and erasing histone acylations. Curr Opin
Struct Biol. 53:169–177. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shvedunova M and Akhtar A: Modulation of
cellular processes by histone and Non-histone protein acetylation.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:329–349. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shakespear MR, Halili MA, Irvine KM,
Fairlie DP and Sweet MJ: Histone deacetylases as regulators of
inflammation and immunity. Trends Immunol. 32:335–343. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bondarev AD, Attwood MM, Jonsson J,
Chubarev VN, Tarasov VV and Schiöth HB: Recent developments of HDAC
inhibitors: Emerging indications and novel molecules. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 87:4577–4597. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rooks MG and Garrett WS: Gut microbiota,
metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 16:341–352. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, He M, Yang M and Ai X: Gut
microbiota as a key regulator of intestinal mucosal immunity. Life
Sci. 345:1226122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Woo V and Alenghat T: Epigenetic
regulation by gut microbiota. Gut Microbes. 14:20224072022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mann ER, Lam YK and Uhlig HH: Short-chain
fatty acids: Linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat Rev
Immunol. 24:577–595. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin MY, de Zoete MR, van Putten JP and
Strijbis K: Redirection of epithelial immune responses by
Short-Chain fatty acids through inhibition of histone deacetylases.
Front Immunol. 6:5542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Licciardi PV, Ververis K and Karagiannis
TC: Histone deacetylase inhibition and dietary Short-chain Fatty
acids. ISRN Allergy. 2011:8696472011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372:n712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wardman JF, Bains RK, Rahfeld P and
Withers SG: Carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) in the gut
microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 20:542–556. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sasaki M, Suaini NHA, Afghani J, Heye KN,
O'Mahony L, Venter C, Lauener R, Frei R and Roduit C: Systematic
review of the association between Short-chain fatty acids and
allergic diseases. Allergy. 79:1789–1811. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deleu S, Machiels K, Raes J, Verbeke K and
Vermeire S: Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An
overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine. 66:1032932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Portincasa P, Bonfrate L, Vacca M, De
Angelis M, Farella I, Lanza E, Khalil M, Wang DQ, Sperandio M and
Di Ciaula A: Gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids:
Implications in glucose homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 23:11052022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reichardt N, Duncan SH, Young P, Belenguer
A, McWilliam Leitch C, Scott KP, Flint HJ and Louis P: Phylogenetic
distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the
human gut microbiota. ISME J. 8:1323–1335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Louis P and Flint HJ: Formation of
propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ
Microbiol. 19:29–41. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mahdi T, Desmons A, Krasniqi P, Lacorte
JM, Kapel N, Lamazière A, Fourati S and Eguether T: Effect of stool
sampling on a routine clinical method for the quantification of six
short chain fatty acids in stool using gas Chromatography-mass
spectrometry. Microorganisms. 12:8282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sivaprakasam S, Bhutia YD, Yang S and
Ganapathy V: Short-chain fatty acid transporters: Role in colonic
homeostasis. Compr Physiol. 8:299–314. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang LY, He LH, Xu LJ and Li SB:
Short-chain fatty acids: Bridges between diet, gut microbiota, and
health. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 39:1728–1736. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morrison DJ and Preston T: Formation of
short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on
human metabolism. Gut Microbes. 7:189–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yao Y, Cai X, Fei W, Ye Y, Zhao M and
Zheng C: The role of Short-chain fatty acids in immunity,
inflammation and metabolism. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 62:1–12. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li M, van Esch B, Wagenaar GTM, Garssen J,
Folkerts G and Henricks PAJ: Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of
short chain fatty acids on immune and endothelial cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 831:52–59. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seto E and Yoshida M: Erasers of histone
acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 6:a0187132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bassett SA and Barnett MP: The role of
dietary histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors in health and
disease. Nutrients. 6:4273–4301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kutil Z, Novakova Z, Meleshin M, Mikesova
J, Schutkowski M and Barinka C: Histone deacetylase 11 is a
Fatty-acid deacylase. ACS Chem Biol. 13:685–693. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schiedel M, Robaa D, Rumpf T, Sippl W and
Jung M: The current state of NAD+ -Dependent histone deacetylases
(Sirtuins) as novel therapeutic targets. Med Res Rev. 38:147–200.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Reichert N, Choukrallah MA and Matthias P:
Multiple roles of class I HDACs in proliferation, differentiation,
and development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:2173–2187. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Parra M: Class IIa HDACs-new insights into
their functions in physiology and pathology. FEBS J. 282:1736–1744.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T and Oehme I:
HDAC family: What are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett.
277:8–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hull EE, Montgomery MR and Leyva KJ: HDAC
Inhibitors as epigenetic regulators of the immune system: Impacts
on cancer therapy and inflammatory diseases. Biomed Res Int.
2016:87972062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grabiec AM and Potempa J: Epigenetic
regulation in bacterial infections: Targeting histone deacetylases.
Crit Rev Microbiol. 44:336–350. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Schulthess J, Pandey S, Capitani M,
Rue-Albrecht KC, Arnold I, Franchini F, Chomka A, Ilott NE,
Johnston DGW, Pires E, et al: The short Chain fatty acid butyrate
imprints an antimicrobial program in macrophages. Immunity.
50:432–445.e437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen X, Xie X, Sun N, Liu X, Liu J, Zhang
W and Cao Y: Gut microbiota-derived butyrate improved acute
leptospirosis in hamster via promoting macrophage ROS mediated by
HDAC3 inhibition. mBio. 15:e01906242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fernando MR, Saxena A, Reyes JL and McKay
DM: Butyrate enhances antibacterial effects while suppressing other
features of alternative activation in IL-4-induced macrophages. Am
J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 310:G822–G831. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pineda Molina C, Hussey GS, Eriksson J,
Shulock MA, Cárdenas Bonilla LL, Giglio RM, Gandhi RM, Sicari BM,
Wang D, Londono R, et al: 4-Hydroxybutyrate promotes endogenous
antimicrobial peptide expression in macrophages. Tissue Eng Part A.
25:693–706. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Strizova Z, Benesova I, Bartolini R,
Novysedlak R, Cecrdlova E, Foley LK and Striz I: M1/M2 macrophages
and their overlaps-myth or reality? Clin Sci (Lond). 137:1067–1093.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chang PV, Hao L, Offermanns S and
Medzhitov R: The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal
macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:2247–2252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park JW, Kim HY, Kim MG, Jeong S, Yun CH
and Han SH: Short-chain fatty acids inhibit staphylococcal
Lipoprotein-induced nitric oxide production in murine macrophages.
Immune Netw. 19:e92019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Maa MC, Chang MY, Hsieh MY, Chen YJ, Yang
CJ, Chen ZC, Li YK, Yen CK, Wu RR and Leu TH: Butyrate reduced
lipopolysaccharide-mediated macrophage migration by suppression of
Src enhancement and focal adhesion kinase activity. J Nutr Biochem.
21:1186–1192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ji J, Shu D, Zheng M, Wang J, Luo C, Wang
Y, Guo F, Zou X, Lv X, Li Y, et al: Microbial metabolite butyrate
facilitates M2 macrophage polarization and function. Sci Rep.
6:248382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang W, Dernst A, Martin B, Lorenzi L,
Cadefau-Fabregat M, Phulphagar K, Wagener A, Budden C, Stair N,
Wagner T, et al: Butyrate and propionate are microbial danger
signals that activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages
upon TLR stimulation. Cell Rep. 43:1147362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Park GY, Joo M, Pedchenko T, Blackwell TS
and Christman JW: Regulation of macrophage cyclooxygenase-2 gene
expression by modifications of histone H3. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 286:L956–L962. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cougoule C, Lastrucci C, Guiet R, Mascarau
R, Meunier E, Lugo-Villarino G, Neyrolles O, Poincloux R and
Maridonneau-Parini I: Podosomes, but not the maturation status,
determine the protease-Dependent 3D migration in human dendritic
cells. Front Immunol. 9:8462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Singh N, Thangaraju M, Prasad PD, Martin
PM, Lambert NA, Boettger T, Offermanns S and Ganapathy V: Blockade
of dendritic cell development by bacterial fermentation products
butyrate and propionate through a transporter (Slc5a8)-dependent
inhibition of histone deacetylases. J Biol Chem. 285:27601–27608.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu L, Li L, Min J, Wang J, Wu H, Zeng Y,
Chen S and Chu Z: Butyrate interferes with the differentiation and
function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Cell Immunol.
277:66–73. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nascimento CR, Freire-de-Lima CG, da Silva
de Oliveira A, Rumjanek FD and Rumjanek VM: The short chain fatty
acid sodium butyrate regulates the induction of CD1a in developing
dendritic cells. Immunobiology. 216:275–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kim YH and Lee JK: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors suppress immature dendritic cell's migration by
regulating CC chemokine receptor 1 expression. Cell Immunol.
316:11–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim YH, Han SB and Lee JK: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors suppress CXCR4-mediated dendritic cell
migration by regulation of maturation process. Cell Immunol.
284:139–145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Inamoto T, Furuta K, Han C, Uneme M, Kano
T, Ishikawa K and Kaito C: Short-chain fatty acids stimulate
dendrite elongation in dendritic cells by inhibiting histone
deacetylase. FEBS J. 290:5794–5810. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Andrusaite A, Lewis J, Frede A, Farthing
A, Kästele V, Montgomery J, Mowat A, Mann E and Milling S:
Microbiota-derived butyrate inhibits cDC development via HDAC
inhibition, diminishing their ability to prime T cells. Mucosal
Immunol. 17:1199–1211. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kaisar MMM, Pelgrom LR, van der Ham AJ,
Yazdanbakhsh M and Everts B: Butyrate conditions human dendritic
cells to prime type 1 Regulatory T cells via both histone
deacetylase inhibition and G Protein-coupled receptor 109A
signaling. Front Immunol. 8:14292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Berndt BE, Zhang M, Owyang SY, Cole TS,
Wang TW, Luther J, Veniaminova NA, Merchant JL, Chen CC, Huffnagle
GB, et al: Butyrate increases IL-23 production by stimulated
dendritic cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
303:G1384–G1392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Íñiguez-Gutiérrez L, Godínez-Méndez LA,
Fafutis-Morris M, Padilla-Arellano JR, Corona-Rivera A,
Bueno-Topete MR, Rojas-Rejón ÓA and Delgado-Rizo V: Physiological
concentrations of short-chain fatty acids induce the formation of
neutrophil extracellular traps in vitro. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 34:20587384209589492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yasuda H, Takishita Y, Morita A, Tsutsumi
T, Nakagawa N and Sato EF: Sodium acetate enhances neutrophil
extracellular trap formation via histone acetylation pathway in
Neutrophil-like HL-60 Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 25:87572024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Vinolo MA, Rodrigues HG, Hatanaka E, Sato
FT, Sampaio SC and Curi R: Suppressive effect of short-chain fatty
acids on production of proinflammatory mediators by neutrophils. J
Nutr Biochem. 22:849–855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Li G, Lin J, Zhang C, Gao H, Lu H, Gao X,
Zhu R, Li Z, Li M and Liu Z: Microbiota metabolite butyrate
constrains neutrophil functions and ameliorates mucosal
inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes.
13:19682572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Aoyama M, Kotani J and Usami M: Butyrate
and propionate induced activated or non-activated neutrophil
apoptosis via HDAC inhibitor activity but without activating
GPR-41/GPR-43 pathways. Nutrition. 26:653–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Bartels M, Geest CR, Bierings M,
Buitenhuis M and Coffer PJ: Histone deacetylase inhibition
modulates cell fate decisions during myeloid differentiation.
Haematologica. 95:1052–1060. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Folkerts J, Redegeld F, Folkerts G,
Blokhuis B, van den Berg MPM, de Bruijn MJW, van IWFJ, Junt T, Tam
SY, Galli SJ, et al: Butyrate inhibits human mast cell activation
via epigenetic regulation of FcεRI-mediated signaling. Allergy.
75:1966–1978. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang H, Du M, Yang Q and Zhu MJ: Butyrate
suppresses murine mast cell proliferation and cytokine production
through inhibiting histone deacetylase. J Nutr Biochem. 27:299–306.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Gudneppanavar R, Sabu Kattuman EE, Teegala
LR, Southard E, Tummala R, Joe B, Thodeti CK and Paruchuri S:
Epigenetic histone modification by butyrate downregulates KIT and
attenuates mast cell function. J Cell Mol Med. 27:2983–2994. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
MacDonald CA, Qian H, Pundir P and Kulka
M: Sodium butyrate supresses malignant human mast cell
proliferation, downregulates expression of KIT and promotes
differentiation. Front Allergy. 4:11097172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Carlini F, Squillario M, Casella V, Capaia
M, Lusi V, Bagnara D, Colombo M, Palmeri S, Ivaldi F, Loiacono F,
et al: Butyrate enhances CD56bright NK cell-driven killing of
activated T cells and modulates NK cell chromatin accessibility.
Genes Immun. 26:342–351. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Schmudde M, Braun A, Pende D, Sonnemann J,
Klier U, Beck JF, Moretta L and Bröker BM: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors sensitize tumour cells for cytotoxic effects of natural
killer cells. Cancer Lett. 272:110–121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dong C: Cytokine regulation and function
in T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 39:51–76. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kibbie JJ, Dillon SM, Thompson TA, Purba
CM, McCarter MD and Wilson CC: Butyrate directly decreases human
gut lamina propria CD4 T cell function through histone deacetylase
(HDAC) inhibition and GPR43 signaling. Immunobiology.
226:1521262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang W, Yu T, Huang X, Bilotta AJ, Xu L,
Lu Y, Sun J, Pan F, Zhou J, Zhang W, et al: Intestinal
microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulation of immune
cell IL-22 production and gut immunity. Nat Commun. 11:44572020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Dagtas AS, Edens RE and Gilbert KM:
Histone deacetylase inhibitor uses p21(Cip1) to maintain anergy in
CD4+ T cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:1289–1297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zimmerman MA, Singh N, Martin PM,
Thangaraju M, Ganapathy V, Waller JL, Shi H, Robertson KD, Munn DH
and Liu K: Butyrate suppresses colonic inflammation through
HDAC1-dependent Fas upregulation and Fas-mediated apoptosis of T
cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302:G1405–G415.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Moore TV, Scurti GM, DeJong M, Wang SY,
Dalheim AV, Wagner CR, Hutchens KA, Speiser JJ, Godellas CV,
Fountain C, et al: HDAC inhibition prevents transgene expression
downregulation and loss-of-function in T-cell-receptor-transduced T
cells. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 20:352–363. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Luu M, Riester Z, Baldrich A, Reichardt N,
Yuille S, Busetti A, Klein M, Wempe A, Leister H, Raifer H, et al:
Microbial short-chain fatty acids modulate CD8+ T cell responses
and improve adoptive immunotherapy for cancer. Nat Commun.
12:40772021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Luu M, Weigand K, Wedi F, Breidenbend C,
Leister H, Pautz S, Adhikary T and Visekruna A: Regulation of the
effector function of CD8+ T cells by gut microbiota-derived
metabolite butyrate. Sci Rep. 8:144302018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Bolduc JF, Hany L, Barat C, Ouellet M and
Tremblay MJ: Epigenetic metabolite acetate inhibits class I/II
histone deacetylases, promotes histone acetylation, and increases
HIV-1 integration in CD4+ T cells. J Virol. 91:e01943–e01916. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Park J, Kim M, Kang SG, Jannasch AH,
Cooper B, Patterson J and Kim CH: Short-chain fatty acids induce
both effector and regulatory T cells by suppression of histone
deacetylases and regulation of the mTOR-S6K pathway. Mucosal
Immunol. 8:80–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Chen L, Sun M, Wu W, Yang W, Huang X, Xiao
Y, Ma C, Xu L, Yao S, Liu Z and Cong Y: Microbiota metabolite
butyrate differentially regulates Th1 and Th17 cells'
Differentiation and function in induction of colitis. Inflamm Bowel
Dis. 25:1450–1461. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kespohl M, Vachharajani N, Luu M, Harb H,
Pautz S, Wolff S, Sillner N, Walker A, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Boettger
T, et al: The microbial metabolite butyrate induces expression of
Th1-associated factors in CD4+ T cells. Front Immunol. 8:10362017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
79
|
Wang J, Hou Y, Mu L, Yang M and Ai X: Gut
microbiota contributes to the intestinal and extraintestinal immune
homeostasis by balancing Th17/Treg cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
143:1135702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhang M, Zhou L, Wang Y, Dorfman RG, Tang
D, Xu L, Pan Y, Zhou Q, Li Y, Yin Y, et al: Faecalibacterium
prausnitzii produces butyrate to decrease c-Myc-related metabolism
and Th17 differentiation by inhibiting histone deacetylase 3. Int
Immunol. 31:499–514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhou L, Zhang M, Wang Y, Dorfman RG, Liu
H, Yu T, Chen X, Tang D, Xu L, Yin Y, et al: Faecalibacterium
prausnitzii produces butyrate to maintain Th17/treg balance and to
ameliorate colorectal colitis by inhibiting histone deacetylase 1.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 24:1926–1940. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sałkowska A, Karaś K, Walczak-Drzewiecka
A, Dastych J and Ratajewski M: Differentiation stage-specific
effect of histone deacetylase inhibitors on the expression of RORγT
in human lymphocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 102:1487–1495. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, Dikiy S, van
der Veeken J, deRoos P, Liu H, Cross JR, Pfeffer K, Coffer PJ and
Rudensky AY: Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote
peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 504:451–455. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sanchez HN, Moroney JB, Gan H, Shen T, Im
JL, Li T, Taylor JR, Zan H and Casali P: B cell-intrinsic
epigenetic modulation of antibody responses by dietary
fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids. Nat Commun. 11:602020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zou F, Qiu Y, Huang Y, Zou H, Cheng X, Niu
Q, Luo A and Sun J: Effects of short-chain fatty acids in
inhibiting HDAC and activating p38 MAPK are critical for promoting
B10 cell generation and function. Cell Death Dis. 12:5822021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Föh B, Buhre JS, Lunding HB,
Moreno-Fernandez ME, König P, Sina C, Divanovic S and Ehlers M:
Microbial metabolite butyrate promotes induction of IL-10+IgM+
plasma cells. PLoS One. 17:e02660712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xiao P, Cai X, Zhang Z, Guo K, Ke Y, Hu Z,
Song Z, Zhao Y, Yao L, Shen M, et al: Butyrate prevents the
pathogenic Anemia-inflammation circuit by facilitating macrophage
iron export. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23065712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Dupraz L, Magniez A, Rolhion N, Richard
ML, Da Costa G, Touch S, Mayeur C, Planchais J, Agus A, Danne C, et
al: Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulate IL-17
production by mouse and human intestinal γδ T cells. Cell Rep.
36:1093322021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Nepelska M, Cultrone A, Béguet-Crespel F,
Le Roux K, Doré J, Arulampalam V and Blottière HM: Butyrate
produced by commensal bacteria potentiates phorbol esters induced
AP-1 response in human intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS One.
7:e528692012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Eshleman EM, Rice T, Potter C, Waddell A,
Hashimoto-Hill S, Woo V, Field S, Engleman L, Lim HW, Schumacher
MA, et al: Microbiota-derived butyrate restricts tuft cell
differentiation via histone deacetylase 3 to modulate intestinal
type 2 immunity. Immunity. 57:319–332.e316. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Bilotta AJ, Ma C, Yang W, Yu Y, Yu Y, Zhao
X, Zhou Z, Yao S, Dann SM and Cong Y: Propionate enhances cell
speed and persistence to promote intestinal epithelial turnover and
repair. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:1023–1044. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
92
|
Mariadason JM, Velcich A, Wilson AJ,
Augenlicht LH and Gibson PR: Resistance to butyrate-induced cell
differentiation and apoptosis during spontaneous Caco-2 cell
differentiation. Gastroenterology. 120:889–899. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Gibson PR, Rosella O, Wilson AJ,
Mariadason JM, Rickard K, Byron K and Barkla DH: Colonic epithelial
cell activation and the paradoxical effects of butyrate.
Carcinogenesis. 20:539–544. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Siavoshian S, Segain JP, Kornprobst M,
Bonnet C, Cherbut C, Galmiche JP and Blottière HM: Butyrate and
trichostatin A effects on the proliferation/differentiation of
human intestinal epithelial cells: Induction of cyclin D3 and p21
expression. Gut. 46:507–514. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Fischer N, Sechet E, Friedman R, Amiot A,
Sobhani I, Nigro G, Sansonetti PJ and Sperandio B: Histone
deacetylase inhibition enhances antimicrobial peptide but not
inflammatory cytokine expression upon bacterial challenge. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E2993–E3001. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Schauber J, Iffland K, Frisch S, Kudlich
T, Schmausser B, Eck M, Menzel T, Gostner A, Lührs H and Scheppach
W: Histone-deacetylase inhibitors induce the cathelicidin LL-37 in
gastrointestinal cells. Mol Immunol. 41:847–854. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Beisner J, Filipe Rosa L, Kaden-Volynets
V, Stolzer I, Günther C and Bischoff SC: Prebiotic inulin and
sodium butyrate attenuate Obesity-induced intestinal barrier
dysfunction by induction of antimicrobial peptides. Front Immunol.
12:6783602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Dou X, Gao N, Lan J, Han J, Yang Y and
Shan A: TLR2/EGFR are two sensors for pBD3 and pEP2C induction by
sodium butyrate independent of HDAC inhibition. J Agric Food Chem.
68:512–522. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Korsten S, Vromans H, Garssen J and
Willemsen LEM: Butyrate protects barrier integrity and suppresses
immune activation in a Caco-2/PBMC Co-Culture model while HDAC
inhibition mimics butyrate in restoring Cytokine-induced barrier
disruption. Nutrients. 15:27602023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zheng L, Kelly CJ, Battista KD, Schaefer
R, Lanis JM, Alexeev EE, Wang RX, Onyiah JC, Kominsky DJ and Colgan
SP: Microbial-derived butyrate promotes epithelial barrier function
through IL-10 Receptor-dependent repression of Claudin-2. J
Immunol. 199:2976–2984. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang RX, Lee JS, Campbell EL and Colgan
SP: Microbiota-derived butyrate dynamically regulates intestinal
homeostasis through regulation of actin-associated protein
synaptopodin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:11648–11657. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ohata A, Usami M and Miyoshi M:
Short-chain fatty acids alter tight junction permeability in
intestinal monolayer cells via lipoxygenase activation. Nutrition.
21:838–847. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Gaudier E, Jarry A, Blottière HM, de
Coppet P, Buisine MP, Aubert JP, Laboisse C, Cherbut C and Hoebler
C: Butyrate specifically modulates MUC gene expression in
intestinal epithelial goblet cells deprived of glucose. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G1168–G1174. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Borthakur A, Saksena S, Gill RK, Alrefai
WA, Ramaswamy K and Dudeja PK: Regulation of monocarboxylate
transporter 1 (MCT1) promoter by butyrate in human intestinal
epithelial cells: Involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. J Cell Biochem.
103:1452–1463. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Larraufie P, Martin-Gallausiaux C, Lapaque
N, Dore J, Gribble FM, Reimann F and Blottiere HM: SCFAs strongly
stimulate PYY production in human enteroendocrine cells. Sci Rep.
8:742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Subramanian VS, Teafatiller T, Moradi H
and Marchant JS: Histone deacetylase inhibitors regulate vitamin C
transporter functional expression in intestinal epithelial cells. J
Nutr Biochem. 98:1088382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zapletal O, Tylichová Z, Neča J, Kohoutek
J, Machala M, Milcová A, Pokorná M, Topinka J, Moyer MP, Hofmanová
J, et al: Butyrate alters expression of cytochrome P450 1A1 and
metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene via its histone deacetylase activity
in colon epithelial cell models. Arch Toxicol. 91:2135–2150. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Bachmann M, Meissner C, Pfeilschifter J
and Mühl H: Cooperation between the bacterial-derived short-chain
fatty acid butyrate and interleukin-22 detected in human Caco2
colon epithelial/carcinoma cells. Biofactors. 43:283–292. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Kobori A, Bamba S, Imaeda H, Ban H,
Tsujikawa T, Saito Y, Fujiyama Y and Andoh A: Butyrate stimulates
IL-32alpha expression in human intestinal epithelial cell lines.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:2355–2361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Korsten S, Peracic L, van Groeningen LMB,
Diks MAP, Vromans H, Garssen J and Willemsen LEM: Butyrate prevents
induction of CXCL10 and Non-canonical IRF9 expression by activated
human intestinal epithelial cells via HDAC inhibition. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:39802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Inan MS, Rasoulpour RJ, Yin L, Hubbard AK,
Rosenberg DW and Giardina C: The luminal short-chain fatty acid
butyrate modulates NF-kappaB activity in a human colonic epithelial
cell line. Gastroenterology. 118:724–734. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Martin-Gallausiaux C, Larraufie P, Jarry
A, Béguet-Crespel F, Marinelli L, Ledue F, Reimann F, Blottière HM
and Lapaque N: Butyrate produced by commensal bacteria
Down-regulates indolamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1) expression via
a dual mechanism in human intestinal epithelial cells. Front
Immunol. 9:28382018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Martin-Gallausiaux C, Béguet-Crespel F,
Marinelli L, Jamet A, Ledue F, Blottière HM and Lapaque N: Butyrate
produced by gut commensal bacteria activates TGF-beta1 expression
through the transcription factor SP1 in human intestinal epithelial
cells. Sci Rep. 8:97422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Xu L, Ma C, Huang X, Yang W, Chen L,
Bilotta AJ, Yao S and Cong Y: Microbiota metabolites short-chain
fatty acid butyrate conditions intestinal epithelial cells to
promote development of Treg cells and T cell IL-10 production. J
Immunol. 200:53.162018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Jin UH, Cheng Y, Park H, Davidson LA,
Callaway ES, Chapkin RS, Jayaraman A, Asante A, Allred C, Weaver EA
and Safe S: Short chain fatty acids enhance aryl hydrocarbon (Ah)
responsiveness in mouse colonocytes and Caco-2 human colon cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 7:101632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Modoux M, Rolhion N, Lefevre JH, Oeuvray
C, Nádvorník P, Illes P, Emond P, Parc Y, Mani S, Dvorak Z and
Sokol H: Butyrate acts through HDAC inhibition to enhance aryl
hydrocarbon receptor activation by gut microbiota-derived ligands.
Gut Microbes. 14:21056372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Fawad JA, Luzader DH, Hanson GF, Moutinho
TJ Jr, McKinney CA, Mitchell PG, Brown-Steinke K, Kumar A, Park M,
Lee S, et al: Histone deacetylase inhibition by gut
microbe-Generated Short-Chain fatty acids entrains intestinal
epithelial circadian rhythms. Gastroenterology. 163:1377–1390.e11.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Gill RK, Kumar A, Malhotra P, Maher D,
Singh V, Dudeja PK, Alrefai W and Saksena S: Regulation of
intestinal serotonin transporter expression via epigenetic
mechanisms: Role of HDAC2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
304:C334–C341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
119
|
Schilderink R, Verseijden C, Seppen J,
Muncan V, van den Brink GR, Lambers TT, van Tol EA and de Jonge WJ:
The SCFA butyrate stimulates the epithelial production of retinoic
acid via inhibition of epithelial HDAC. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 310:G1138–G1146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zheng M, Yang X, Wu Q, Gong Y, Pang N, Ge
X, Nagaratnam N, Jiang P, Zhou M, Hu T, et al: Butyrate attenuates
hepatic steatosis induced by a High-fat and Fiber-deficient diet
via the hepatic GPR41/43-CaMKII/HDAC1-CREB pathway. Mol Nutr Food
Res. 67:e22005972023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Zhou D, Chen YW, Zhao ZH, Yang RX, Xin FZ,
Liu XL, Pan Q, Zhou H and Fan JG: Sodium butyrate reduces high-fat
diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through upregulation of
hepatic GLP-1R expression. Exp Mol Med. 50:1–12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Li H, Gao Z, Zhang J, Ye X, Xu A, Ye J and
Jia W: Sodium butyrate stimulates expression of fibroblast growth
factor 21 in liver by inhibition of histone deacetylase 3.
Diabetes. 61:797–806. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Bridgeman S, Woo HC, Newsholme P and
Mamotte C: Butyrate lowers cellular cholesterol through HDAC
Inhibition and Impaired SREBP-2 Signalling. Int J Mol Sci.
23:155062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Jourova L, Anzenbacherova E, Dostal Z,
Anzenbacher P, Briolotti P, Rigal E, Daujat-Chavanieu M and
Gerbal-Chaloin S: Butyrate, a typical product of gut microbiome,
affects function of the AhR gene, being a possible agent of
crosstalk between gut microbiome, and hepatic drug metabolism. J
Nutr Biochem. 107:1090422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Zhao Y, Xu X, Liu S, Wang X, Musha J, Li
T, Ge L, Sun Y, Zhang S, Zhao L and Zhan J: Butyrate inhibits
histone deacetylase 2 expression to alleviate liver fibrosis in
biliary atresia. BMC Pediatr. 25:2862025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhang J, Wang W, Liang S, Zhou X, Rekha
RS, Gudmundsson GH, Bergman P, Ai Q, Mai K and Wan M: Butyrate
induces STAT3/HIF-1α/IL-22 signaling via GPCR and HDAC3 inhibition
to activate autophagy in head kidney macrophages from turbot
(Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 143:1092142023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Ma X and Wang Q: Short-Chain fatty acids
attenuate renal fibrosis and enhance autophagy of renal tubular
cells in diabetic mice through the HDAC2/ULK1 axis. Endocrinol
Metab (Seoul). 37:432–443. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Giordano L, Ahmed S, van der Made TK,
Masereeuw R and Mihăilă SM: Gut microbial-derived short chain fatty
acids enhance kidney proximal tubule cell secretory function.
Biomed Pharmacother. 188:1182142025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Du Y, Tang G and Yuan W: Suppression of
HDAC2 by sodium butyrate alleviates apoptosis of kidney cells in
db/db mice and HG-induced NRK-52E cells. Int J Mol Med. 45:210–222.
2020.
|
|
130
|
Felizardo RJF, de Almeida DC, Pereira RL,
Watanabe IKM, Doimo NTS, Ribeiro WR, Cenedeze MA, Hiyane MI, Amano
MT, Braga TT, et al: Gut microbial metabolite butyrate protects
against proteinuric kidney disease through epigenetic- and
GPR109a-mediated mechanisms. FASEB J. 33:11894–11908. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Xu Y, Wei S, Zhu L, Huang C, Yang T, Wang
S, Zhang Y, Duan Y, Li X, Wang Z, et al: Low expression of the
intestinal metabolite butyric acid and the corresponding memory
pattern regulate HDAC4 to promote apoptosis in rat hippocampal
neurons. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 253:1146602023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Cho JH, Chae CW, Lim JR, Jung YH, Han SJ,
Yoon JH, Park JY and Han HJ: Sodium butyrate ameliorates high
glucose-suppressed neuronal mitophagy by restoring PRKN expression
via inhibiting the RELA-HDAC8 complex. Autophagy. 20:1505–1522.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Song L, Sun Q, Zheng H, Zhang Y, Wang Y,
Liu S and Duan L: Roseburia hominis alleviates neuroinflammation
via Short-Chain fatty acids through histone deacetylase inhibition.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 66:e22001642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Ziabska K, Gargas J, Sypecka J and
Ziemka-Nalecz M: The impact of the histone deacetylase inhibitor
sodium butyrate on microglial polarization after oxygen and glucose
deprivation. Pharmacol Rep. 74:909–919. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Chen PS, Wang CC, Bortner CD, Peng GS, Wu
X, Pang H, Lu RB, Gean PW, Chuang DM and Hong JS: Valproic acid and
other histone deacetylase inhibitors induce microglial apoptosis
and attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced dopaminergic
neurotoxicity. Neuroscience. 149:203–212. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Wang P, Zhang Y, Gong Y, Yang R, Chen Z,
Hu W, Wu Y, Gao M, Xu X, Qin Y and Huang C: Sodium butyrate
triggers a functional elongation of microglial process via
Akt-small RhoGTPase activation and HDACs inhibition. Neurobiol Dis.
111:12–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Singh V, Bhatia HS, Kumar A, de Oliveira
AC and Fiebich BL: Histone deacetylase inhibitors valproic acid and
sodium butyrate enhance prostaglandins release in
lipopolysaccharide-activated primary microglia. Neuroscience.
265:147–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Wu X, Chen PS, Dallas S, Wilson B, Block
ML, Wang CC, Kinyamu H, Lu N, Gao X, Leng Y, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors up-regulate astrocyte GDNF and BDNF gene
transcription and protect dopaminergic neurons. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 11:1123–1134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Wu KLH, Liu WC, Wu CW, Fu MH, Huang HM,
Tain YL, Liang CK, Hung CY, Chen IC, Hung PL, et al: Butyrate
reduction and HDAC4 increase underlie maternal high
fructose-induced metabolic dysfunction in hippocampal astrocytes in
female rats. J Nutr Biochem. 126:1095712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Kanski R, Sneeboer MA, van Bodegraven EJ,
Sluijs JA, Kropff W, Vermunt MW, Creyghton MP, De Filippis L,
Vescovi A, Aronica E, et al: Histone acetylation in astrocytes
suppresses GFAP and stimulates a reorganization of the intermediate
filament network. J Cell Sci. 127:4368–4380. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Li M, van Esch B, Henricks PAJ, Folkerts G
and Garssen J: The Anti-inflammatory effects of short Chain fatty
acids on Lipopolysaccharide- or tumor necrosis factor α-Stimulated
endothelial cells via activation of GPR41/43 and inhibition of
HDACs. Front Pharmacol. 9:5332018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Li M, van Esch B, Henricks PAJ, Garssen J
and Folkerts G: IL-33 is involved in the Anti-inflammatory effects
of butyrate and propionate on TNFα-activated endothelial cells. Int
J Mol Sci. 22:24472021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Miyoshi M, Usami M and Ohata A:
Short-chain fatty acids and trichostatin A alter tight junction
permeability in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Nutrition.
24:1189–1198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Nicese MN, Bijkerk R, Van Zonneveld AJ,
Van den Berg BM and Rotmans JI: Sodium butyrate as key regulator of
mitochondrial function and barrier integrity of human glomerular
endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 24:130902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Rössig L, Li H, Fisslthaler B, Urbich C,
Fleming I, Förstermann U, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S: Inhibitors of
histone deacetylation downregulate the expression of endothelial
nitric oxide synthase and compromise endothelial cell function in
vasorelaxation and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 91:837–844. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Farsetti A, Illi B and Gaetano C: How
epigenetics impacts on human diseases. Eur J Intern Med. 114:15–22.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Surace AEA and Hedrich CM: The role of
epigenetics in Autoimmune/inflammatory disease. Front Immunol.
10:15252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Tang J, Yan H and Zhuang S: Histone
deacetylases as targets for treatment of multiple diseases. Clin
Sci (Lond). 124:651–662. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Zhang SY, Zhang LY, Wen R, Yang N and
Zhang TN: Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in inflammatory
diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 179:1172952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Zhang LY, Zhang SY, Wen R, Zhang TN and
Yang N: Role of histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in
neurological diseases. Pharmacol Res. 208:1074102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Peng K, Xiao S, Xia S, Li C, Yu H and Yu
Q: Butyrate inhibits the HDAC8/NF-κB Pathway to Enhance Slc26a3
expression and improve the intestinal epithelial barrier to relieve
colitis. J Agric Food Chem. 72:24400–24416. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Lee C, Kim BG, Kim JH, Chun J, Im JP and
Kim JS: Sodium butyrate inhibits the NF-kappa B signaling pathway
and histone deacetylation, and attenuates experimental colitis in
an IL-10 independent manner. Int Immunopharmacol. 51:47–56. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Simeoli R, Mattace Raso G, Pirozzi C, Lama
A, Santoro A, Russo R, Montero-Melendez T, Berni Canani R,
Calignano A, Perretti M and Meli R: An orally administered
butyrate-releasing derivative reduces neutrophil recruitment and
inflammation in dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine colitis. Br
J Pharmacol. 174:1484–1496. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Feng Z, Wang X, Kang G, Zhao J, Ye Y, Liu
L, Huang H and Cao X: P006 Engineered propionate-producing bacteria
attenuates murine colitis by modulating the immune function of
resident macrophages via histone deacetylase. J Crohn's Colitis.
17:i174–i177. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Kang G, Wang X, Gao M, Wang L, Feng Z,
Meng S, Wu J, Zhu Z, Gao X, Cao X and Huang H: Propionate-producing
engineered probiotics ameliorated murine ulcerative colitis by
restoring anti-inflammatory macrophage via the GPR43/HDAC1/IL-10
axis. Bioeng Transl Med. 9:e106822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Zhang L, Ma Z, Zhang X, Wang J, Tian W,
Ren Y, Liu Y, Wang T, Li Y, Liu Y, et al: Butyrate alleviates
alcoholic liver disease-associated inflammation through macrophage
regulation and polarization via the HDAC1/miR-155 axis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 131:1118522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Sun J, Wu Q, Sun H and Qiao Y: Inhibition
of histone deacetylase by butyrate protects rat liver from ischemic
reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Sci. 15:21069–21079. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Olaniyi KS and Amusa OA: Sodium
acetate-mediated inhibition of histone deacetylase alleviates
hepatic lipid dysregulation and its accompanied injury in
streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 128:1102262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Liu Y, Li YJ, Loh YW, Singer J, Zhu W,
Macia L, Mackay CR, Wang W, Chadban SJ and Wu H: Fiber derived
microbial metabolites prevent acute kidney injury through G-Protein
coupled receptors and HDAC inhibition. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6486392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Khan S and Jena G: Sodium butyrate, a HDAC
inhibitor ameliorates eNOS, iNOS and TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis,
apoptosis and DNA damage in the kidney of juvenile diabetic rats.
Food Chem Toxicol. 73:127–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Al-Harbi NO, Nadeem A, Ahmad SF, Alotaibi
MR, AlAsmari AF, Alanazi WA, Al-Harbi MM, El-Sherbeeny AM and
Ibrahim KE: Short chain fatty acid, acetate ameliorates
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by inhibition of NADPH oxidase
signaling in T cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 58:24–31. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Li Z, Sun T, He Z, Li Z, Zhang W, Wang J
and Xiang H: SCFAs ameliorate chronic postsurgical Pain-related
cognition dysfunction via the ACSS2-HDAC2 axis in rats. Mol
Neurobiol. 59:6211–6227. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Patnala R, Arumugam TV, Gupta N and Dheen
ST: HDAC inhibitor sodium Butyrate-mediated epigenetic regulation
enhances neuroprotective function of microglia during ischemic
stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 54:6391–6411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Sharma S, Taliyan R and Singh S:
Beneficial effects of sodium butyrate in 6-OHDA induced
neurotoxicity and behavioral abnormalities: Modulation of histone
deacetylase activity. Behav Brain Res. 291:306–314. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Soliman ML, Smith MD, Houdek HM and
Rosenberger TA: Acetate supplementation modulates brain histone
acetylation and decreases interleukin-1β expression in a rat model
of neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 9:512012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Moleón J, González-Correa C, Miñano S,
Robles-Vera I, de la Visitación N, Barranco AM, Gómez-Guzmán M,
Sánchez M, Riesco P, Guerra-Hernández E, et al: Protective effect
of microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids on vascular
dysfunction in mice with systemic lupus erythematosus induced by
toll like receptor 7 activation. Pharmacol Res. 198:1069972023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Ma H, Yang L, Liu Y, Yan R, Wang R, Zhang
P, Bai Z, Liu Y, Ren Y, Li Y, et al: Butyrate suppresses
atherosclerotic inflammation by regulating macrophages and
polarization via GPR43/HDAC-miRNAs axis in ApoE-/-mice. PLoS One.
18:e02826852023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Karoor V, Strassheim D, Sullivan T, Verin
A, Umapathy NS, Dempsey EC, Frank DN, Stenmark KR and
Gerasimovskaya E: The Short-Chain fatty acid butyrate attenuates
pulmonary vascular remodeling and inflammation in Hypoxia-induced
pulmonary hypertension. Int J Mol Sci. 22:99162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Chen H, Wang SH, Li HL, Zhou XB, Zhou LW,
Chen C, Mansell T, Novakovic B, Saffery R, Baker PN, et al: The
attenuation of gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids
elevates lipid transportation through suppression of the intestinal
HDAC3-H3K27ac-PPAR-γ axis in gestational diabetes mellitus. J Nutr
Biochem. 133:1097082024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Jiang M, Wang J, Li Z, Xu D, Jing J, Li F,
Ding J and Li Q: Dietary Fiber-derived microbial butyrate
suppresses ILC2-dependent airway inflammation in COPD. Mediators
Inflamm. 2024:62634472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Whitt J, Woo V, Lee P, Moncivaiz J,
Haberman Y, Denson L, Tso P and Alenghat T: Disruption of
epithelial HDAC3 in intestine prevents Diet-induced obesity in
mice. Gastroenterology. 155:501–513. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Islam R, Dash D and Singh R: Intranasal
curcumin and sodium butyrate modulates airway inflammation and
fibrosis via HDAC inhibition in allergic asthma. Cytokine.
149:1557202022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Olaniyi KS, Areloegbe SE and Fiemotongha
FE: Cardiac energy depletion in a rat model of polycystic ovarian
syndrome is reversed by acetate and associated with inhibitory
effect of HDAC2/mTOR. Eur J Pharmacol. 962:1762432024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Olaniyi KS, Amusa OA, Areola ED and
Olatunji LA: Suppression of HDAC by sodium acetate rectifies
cardiac metabolic disturbance in
streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 245:667–676. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Du HX, Yue SY, Niu D, Liu C, Zhang LG,
Chen J, Chen Y, Guan Y, Hua XL, Li C, et al: Gut microflora
modulates Th17/Treg cell differentiation in experimental autoimmune
prostatitis via the Short-Chain fatty acid propionate. Front
Immunol. 13:9152182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Cavalli G and Heard E: Advances in
epigenetics link genetics to the environment and disease. Nature.
571:489–499. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Narita T, Weinert BT and Choudhary C:
Functions and mechanisms of non-histone protein acetylation. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:156–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Lang C, Campbell KR, Ryan BJ, Carling P,
Attar M, Vowles J, Perestenko OV, Bowden R, Baig F, Kasten M, et
al: Single-cell sequencing of iPSC-dopamine neurons reconstructs
disease progression and identifies HDAC4 as a regulator of
parkinson cell phenotypes. Cell Stem Cell. 24:93–106.e6. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
179
|
Sussman JH, Xu J, Amankulor N and Tan K:
Dissecting the tumor microenvironment of epigenetically driven
gliomas: Opportunities for single-cell and spatial multiomics.
Neurooncol Adv. 5:vdad1012023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Camargo Tavares L and Marques FZ: Clinical
trial evidence of the gut microbial metabolite butyrate in
hypertension. Hypertension. 81:2137–2139. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Gong X, Geng H, Yang Y, Zhang S, He Z, Fan
Y, Yin F, Zhang Z and Chen GQ: Metabolic engineering of commensal
bacteria for gut butyrate delivery and dissection of host-microbe
interaction. Metab Eng. 80:94–106. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Dalile B, Van Oudenhove L, Vervliet B and
Verbeke K: The role of short-chain fatty acids in
microbiota-gut-brain communication. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
16:461–478. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
van der Beek CM, Bloemen JG, van den Broek
MA, Lenaerts K, Venema K, Buurman WA and Dejong CH: Hepatic uptake
of rectally administered butyrate prevents an increase in systemic
butyrate concentrations in humans. J Nutr. 145:2019–2024. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|