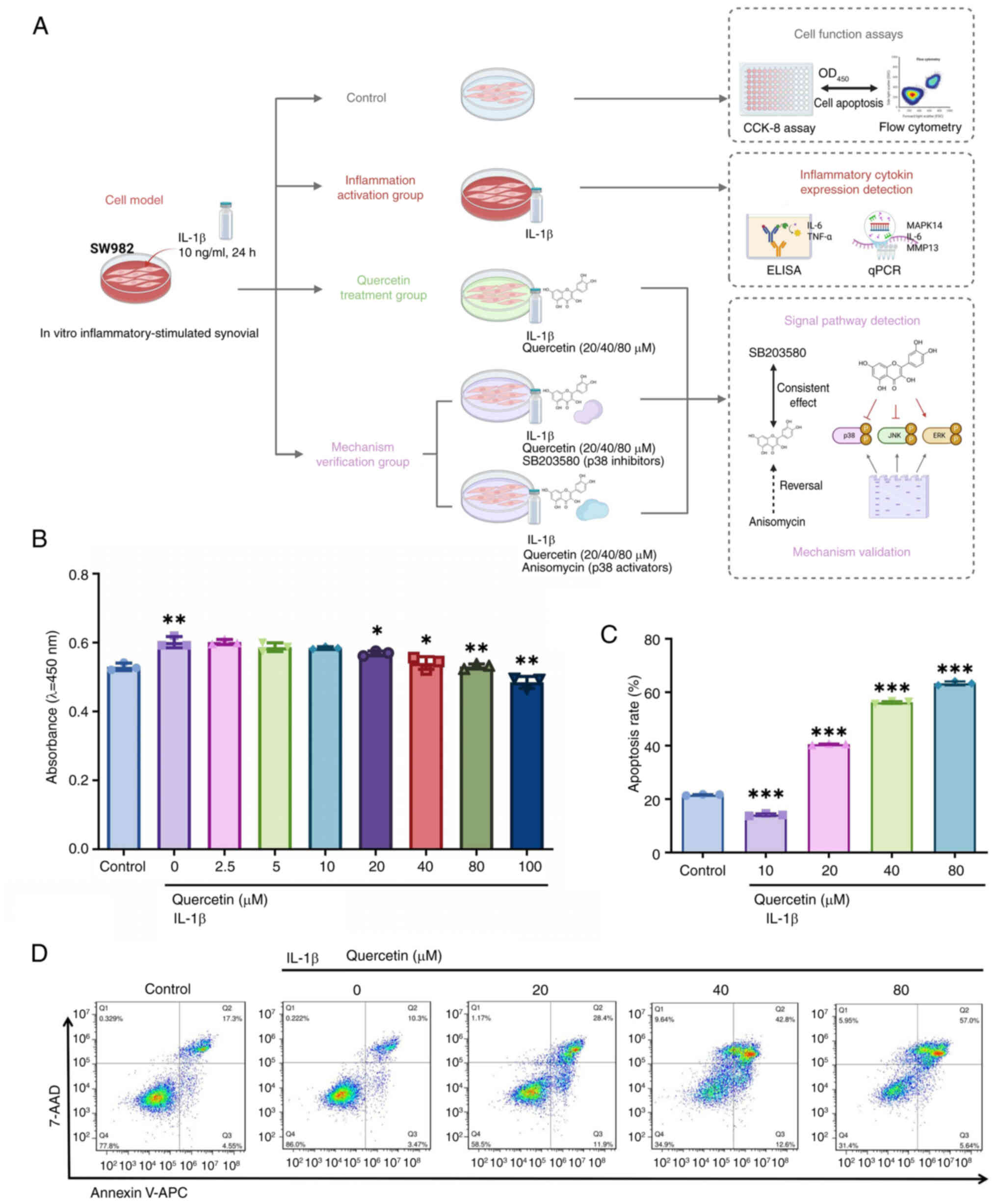
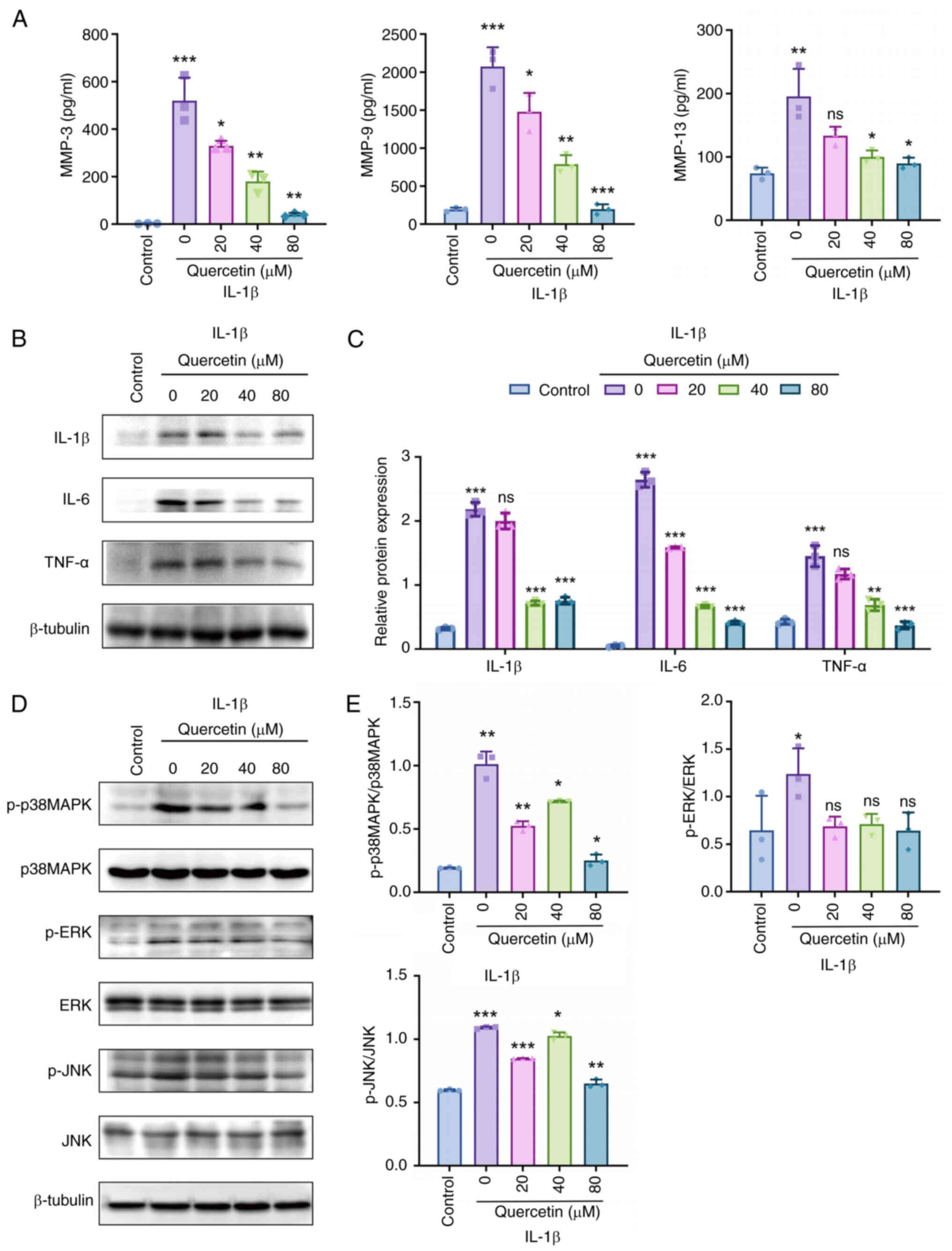
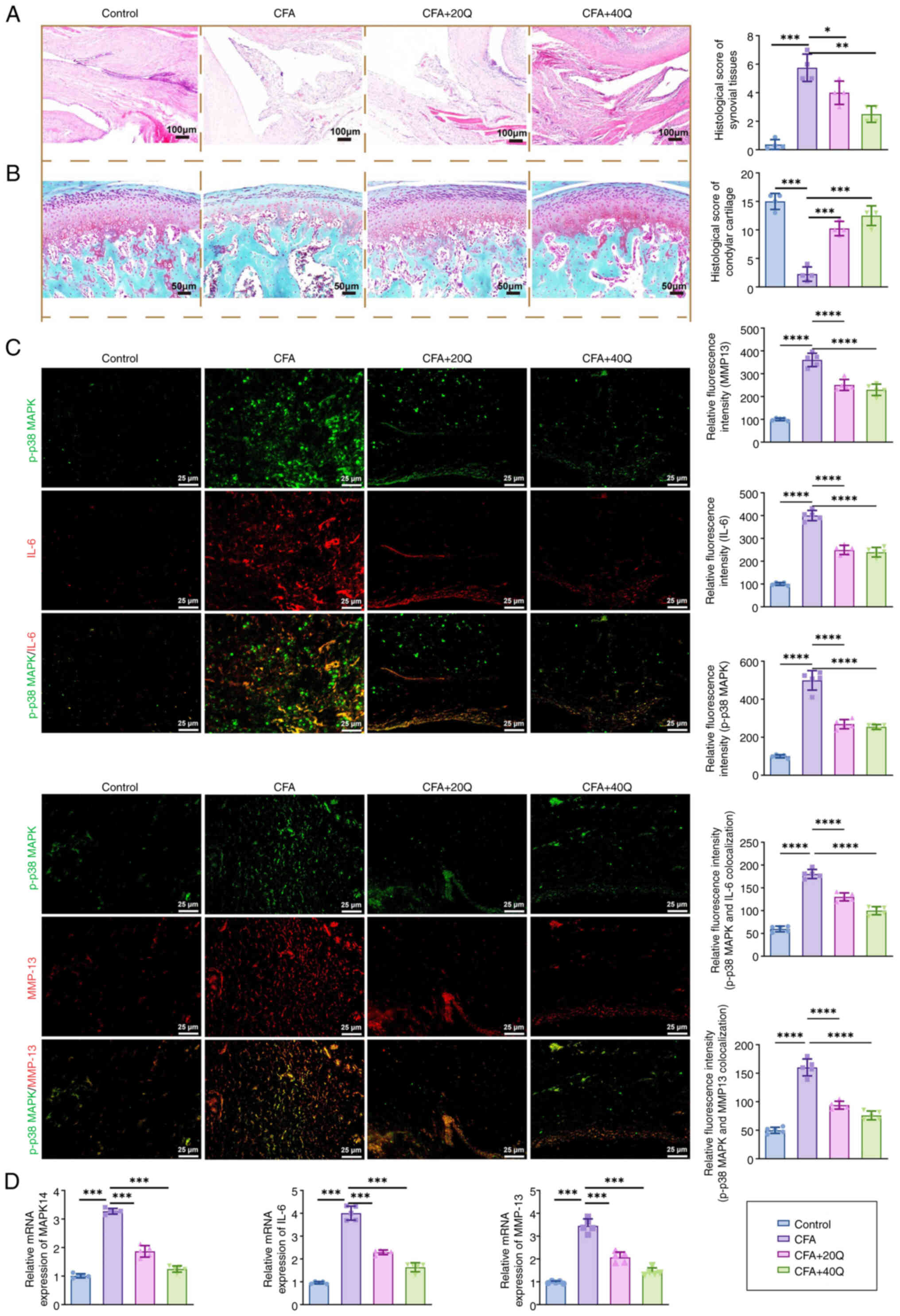
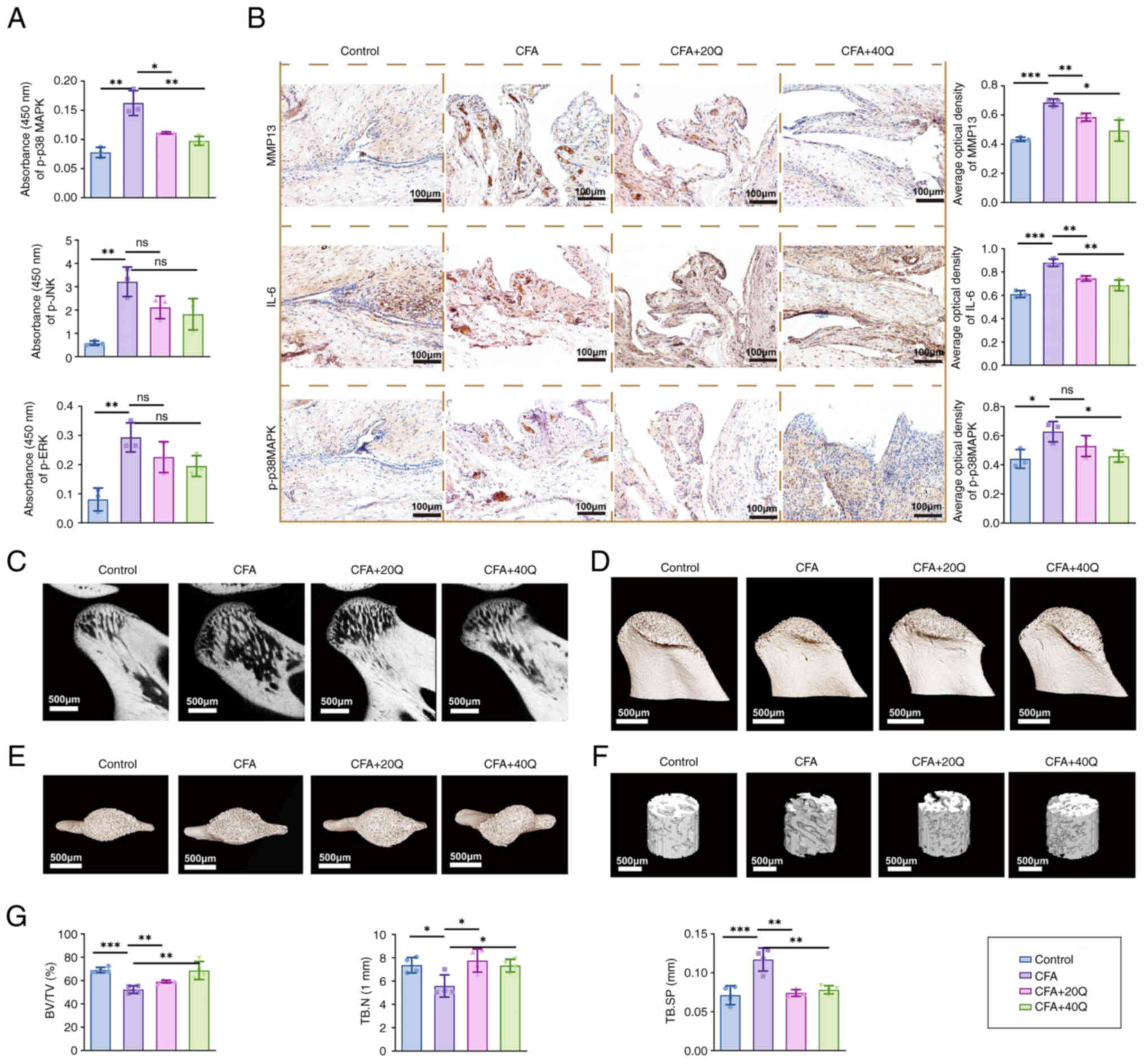
|
1
|
Kapos FP, Exposto FG, Oyarzo JF and Durham
J: Temporomandibular disorders: A review of current concepts in
aetiology, diagnosis and management. Oral Surg. 13:321–334. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zieliński G, Pająk-Zielińska B and Ginszt
M: A meta-analysis of the global prevalence of temporomandibular
disorders. J Clin Med. 13:13652024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zieliński G: Quo vadis temporomandibular
disorders? By 2050, the global prevalence of TMD may approach 44%.
J Clin Med. 14:44142025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li DTS and Leung YY: Temporomandibular
disorders: Current concepts and controversies in diagnosis and
management. Diagnostics (Basel). 11:4592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang XD, Zhang JN, Gan YH and Zhou YH:
Current understanding of pathogenesis and treatment of TMJ
osteoarthritis. J Dent Res. 94:666–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gil-Martinez A, Paris-Alemany A,
López-de-Uralde-Villanueva I and La Touche R: Management of pain in
patients with temporomandibular disorder (TMD): challenges and
solutions. J Pain Res. 11:571–587. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andre A, Kang J and Dym H: Pharmacologic
treatment for temporomandibular and temporomandibular joint
disorders. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 34:49–59. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tamer TM: Hyaluronan and synovial joint:
Function, distribution and healing. Interdiscip Toxicol. 6:111–125.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jerosch J: Effects of glucosamine and
chondroitin sulfate on cartilage metabolism in OA: Outlook on other
nutrient partners especially omega-3 fatty acids. Int J Rheumatol.
2011:1–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wujec M and Feldo M: Can we improve
diosmetin activity? The state-of-the-art and promising research
directions. Molecules. 28:79102023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun Z, Liu K, Liang C, Wen L, Wu J, Liu X
and Li X: Diosmetin as a promising natural therapeutic agent: In
vivo, in vitro mechanisms, and clinical studies. Phytother Res.
38:3660–3694. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aghababaei F and Hadidi M: Recent advances
in potential health benefits of quercetin. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
16:10202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang G, Wang Y, Yao L, Gu W, Zhao S, Shen
Z, Lin Z, Liu W and Yan T: Pharmacological activity of quercetin:
An updated review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022:1–12.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Silva-Pinto PA, de Pontes JTC,
Aguilar-Morón B, Canales CSC, Pavan FR and Roque-Borda CA:
Phytochemical insights into flavonoids in cancer: Mechanisms,
therapeutic potential, and the case of quercetin. Heliyon.
11:e426822025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shabir I, Kumar Pandey V, Shams R, Dar AH,
Dash KK, Khan SA, Bashir I, Jeevarathinam G, Rusu AV, Esatbeyoglu T
and Pandiselvam R: Promising bioactive properties of quercetin for
potential food applications and health benefits: A review. Front
Nutr. 9:9997522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding H, Ding H, Mu P, Lu X and Xu Z:
Diosmetin inhibits subchondral bone loss and indirectly protects
cartilage in a surgically-induced osteoarthritis mouse model. Chem
Biol Interact. 370:1103112023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao L, Zhang H, Li N, Chen J, Xu H, Wang
Y and Liang Q: Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal
the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula. J
Ethnopharmacol. 309:1163062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang P, Zhang D, Zhou W, Wang L, Wang B,
Zhang T and Li S: Network pharmacology: Towards the artificial
intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine. Brief
Bioinform. 25:bbad5182023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bhoi A, Dwivedi SD, Singh D, Keshavkant S
and Singh MR: Mechanistic prospective and pharmacological
attributes of quercetin in attenuation of different types of
arthritis. 3 Biotech. 13:3622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang Y, Kim SC, Yu T, Yi YS, Rhee MH, Sung
GH, Yoo BC and Cho JY: Functional roles of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses.
Mediator Inflamm. 2014:1–13. 2014.
|
|
21
|
Kim AL, Labasi JM, Zhu Y, Tang X, McClure
K, Gabel CA, Athar M and Bickers DR: Role of p38 MAPK in
UVB-induced inflammatory responses in the skin of SKH-1 hairless
mice. J Invest Dermatol. 124:1318–1325. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mathiessen A and Conaghan PG: Synovitis in
osteoarthritis: Current understanding with therapeutic
implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bartels YL, van Lent PLEM, van der Kraan
PM, Blom AB, Bonger KM and van den Bosch MHJ: Inhibition of TLR4
signalling to dampen joint inflammation in osteoarthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 63:608–618. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: CytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 4:S4–S11. 2014.
|
|
26
|
Bayly CI, Cieplak P, Cornell W and Kollman
PA: A well-behaved electrostatic potential based method using
charge restraints for deriving atomic charges: The RESP model. J
Phys Chem. 97:10269–10280. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD,
Impey RW and Klein ML: Comparison of simple potential functions for
simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys. 79:926–935. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zakrzewska M, Opalinski L, Haugsten EM,
Otlewski J and Wiedlocha A: Crosstalk between p38 and Erk 1/2 in
downregulation of FGF1-induced signaling. IJMS. 20:18262019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mei S, Gu H, Ward A, Yang X, Guo H, He K,
Liu Z and Cao W: p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)
promotes cholesterol ester accumulation in macrophages through
inhibition of macroautophagy. J Biol Chem. 287:11761–11768. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
National Research Council (US); Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care Use of Laboratory Animals:
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition.
National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
31
|
Hu S, Li H, Jiang H, Liu X, Ke J and Long
X: Macrophage activation in synovitis and osteoarthritis of
temporomandibular joint and its relationship with the progression
of synovitis and bone remodeling. Am J Pathol. 194:296–306. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gynther GW, Dijkgraaf LC, Reinholt FP,
Holmlund AB, Liem RS and de Bont LG: Synovial inflammation in
arthroscopically obtained biopsy specimens from the
temporomandibular joint: A review of the literature and a proposed
histologic grading system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 56:1281–1286.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng M, Yi X and Zhou Q: Overexpression
of HIF-1alpha in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote the
repair of mandibular condylar osteochondral defect in a rabbit
model. J Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 79:345.e1–345.e15. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen Y, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhou B and Yang G:
Diosmetin exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects
on TNF-α-stimulated human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like
synoviocytes through regulating the Akt and NF-κB signaling
pathways. Phytotherapy Research. 34:1310–1319. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Guo G and Dong J: Diosmetin attenuates
oxidative stress-induced damage to lens epithelial cells via the
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Bioengineered.
13:11072–11081. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Yao J, Han C, Yang J, Chaudhry MT,
Wang S, Liu H and Yin Y: Quercetin, inflammation and immunity.
Nutrients. 8:1672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng S, Gao N, Zhang Z, Chen G, Budhraja
A, Ke Z, Son YO, Wang X, Luo J and Shi X: Quercetin induces
tumor-selective apoptosis through downregulation of Mcl-1 and
activation of bax. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5679–5691. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|