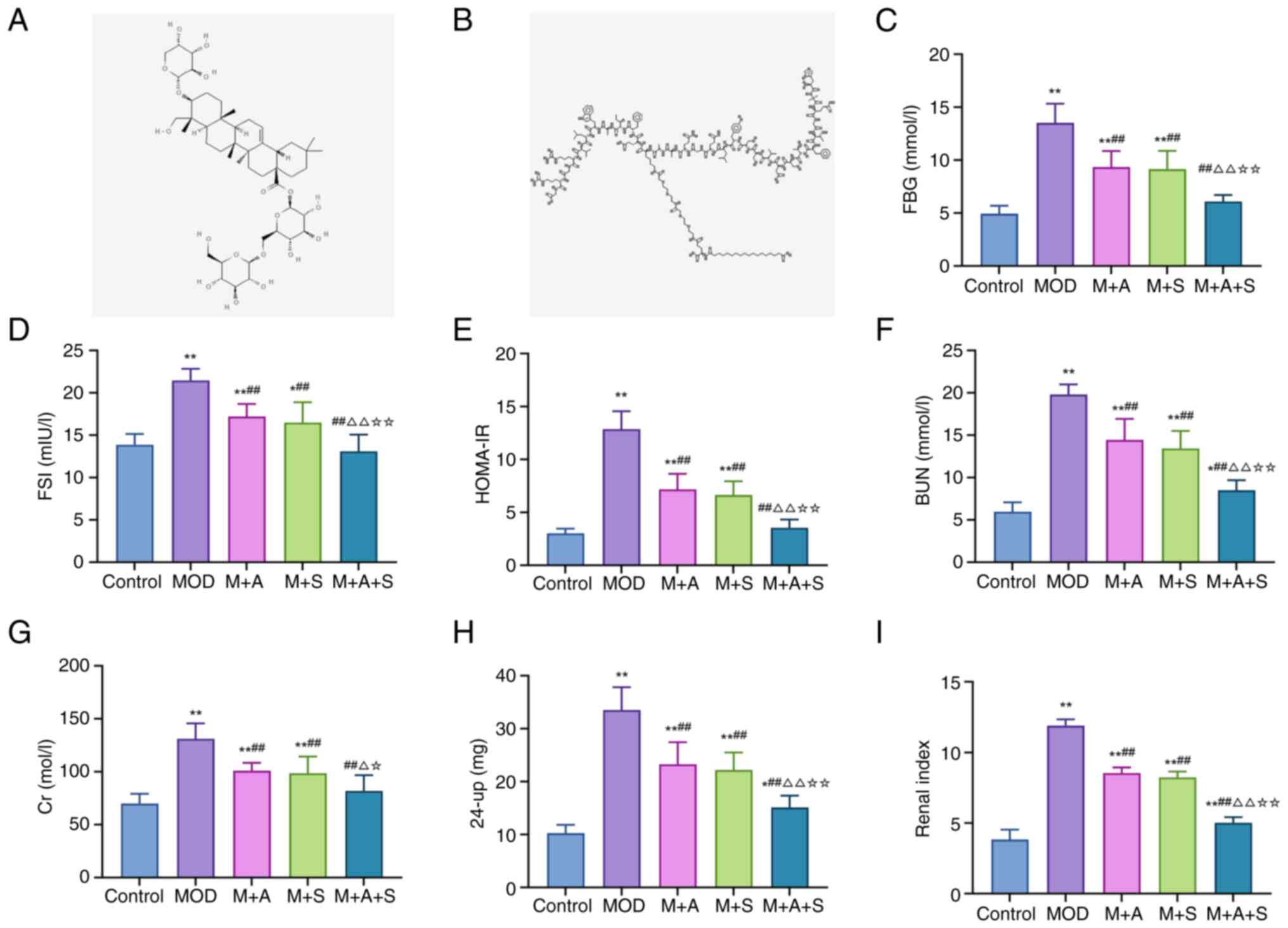
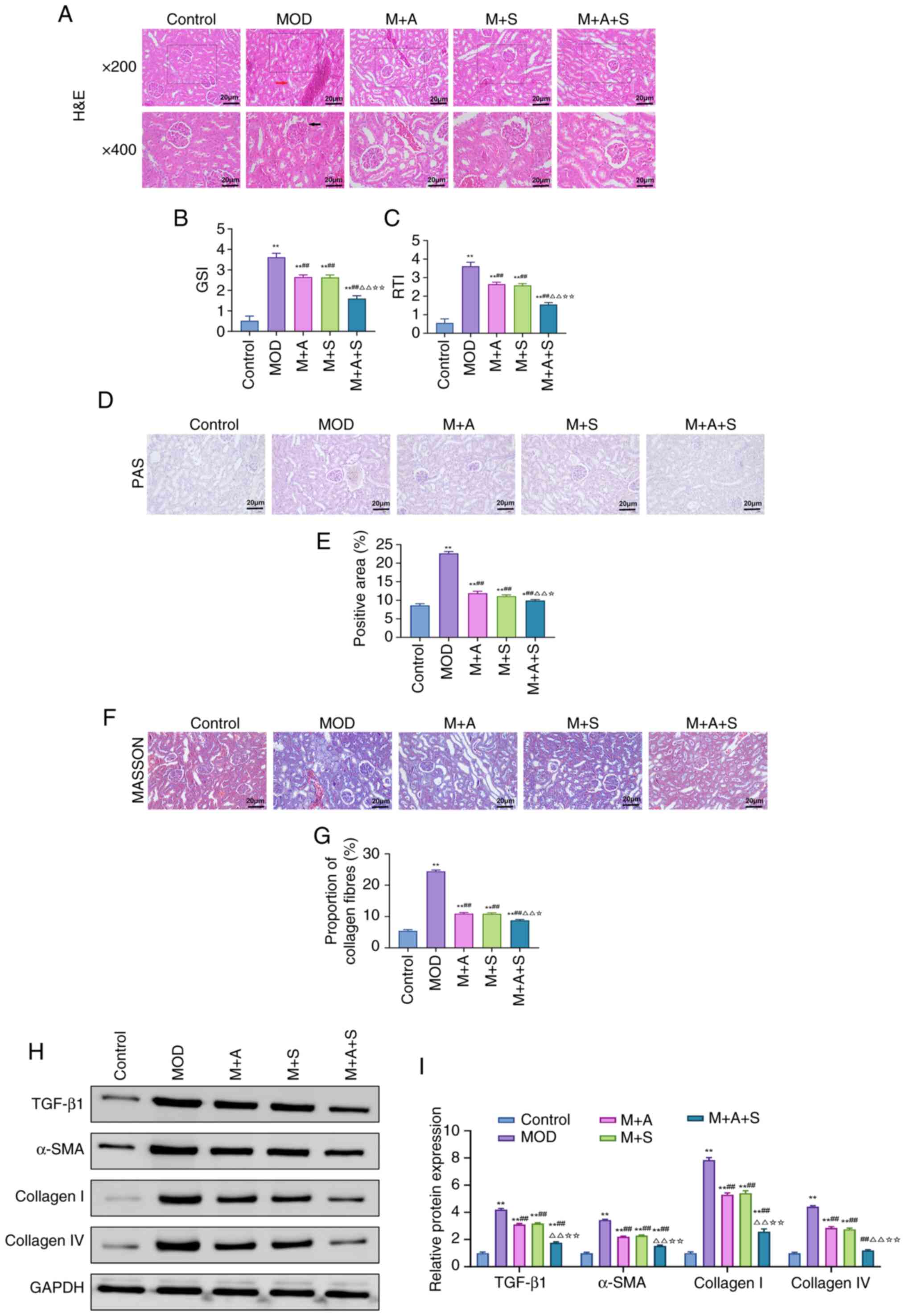
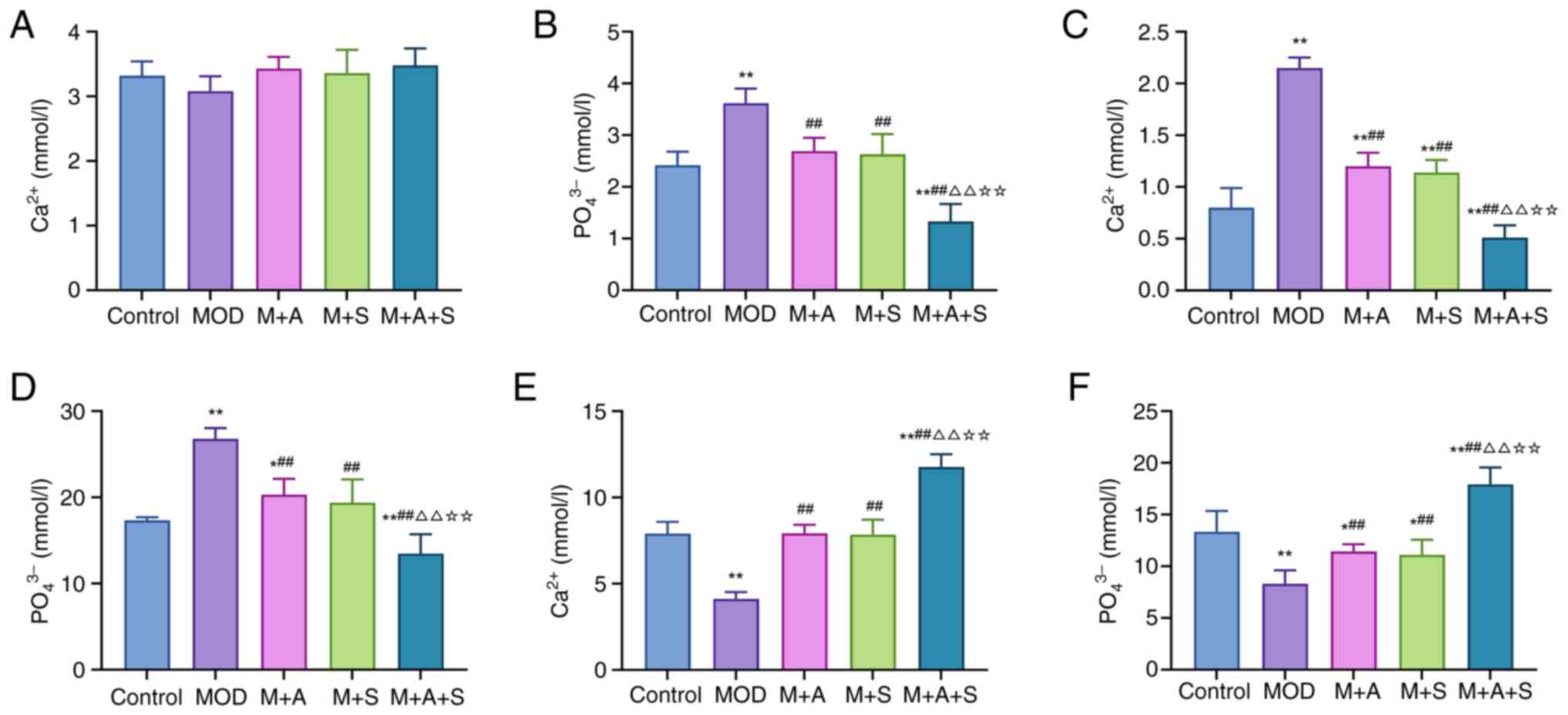
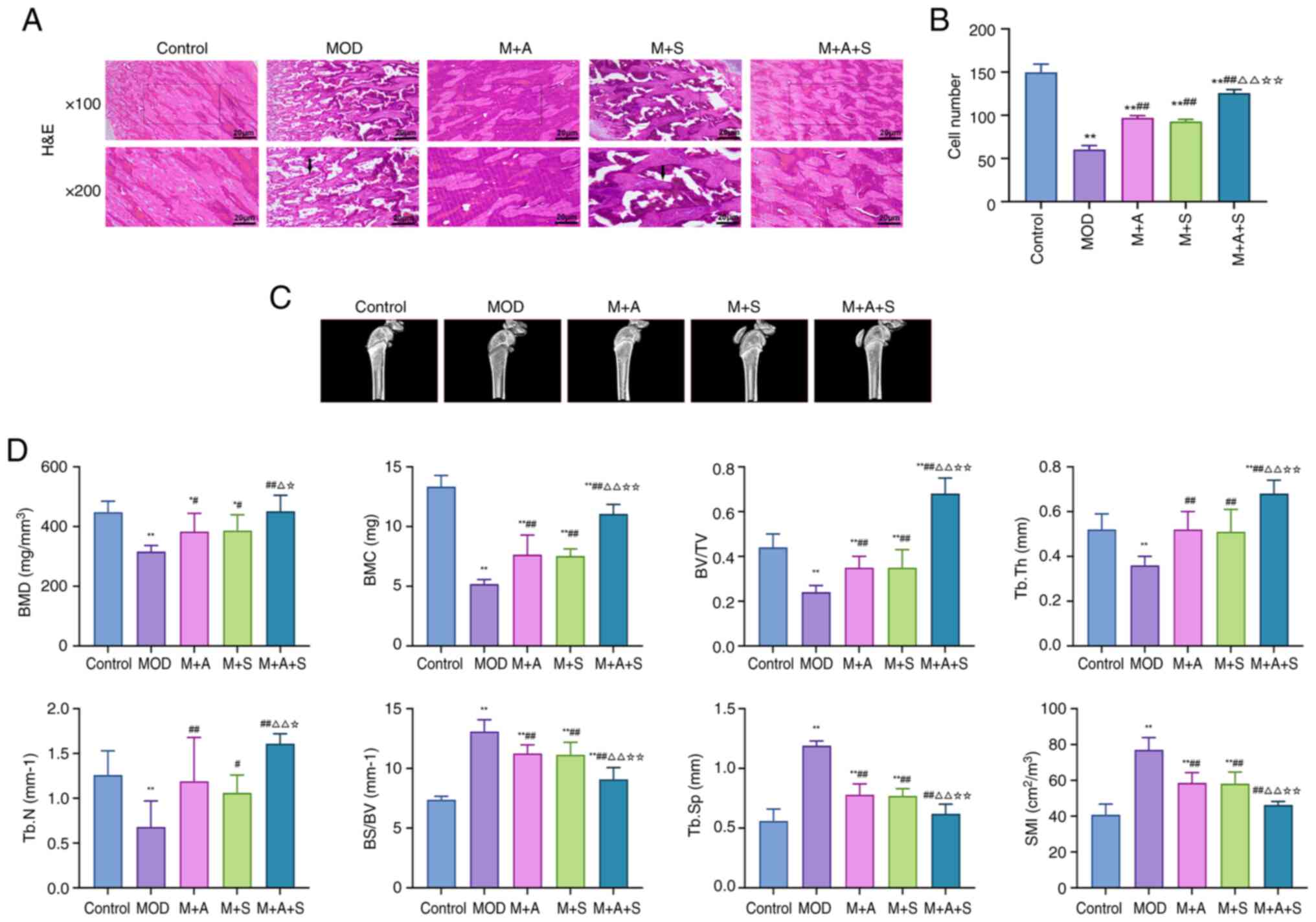
|
1
|
Yang T, Qi F, Guo F, Shao M, Song Y, Ren
G, Linlin Z, Qin G and Zhao Y: An update on chronic complications
of diabetes mellitus: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic
strategies with a focus on metabolic memory. Mol Med. 30:712024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lovic D, Piperidou A, Zografou I, Grassos
H, Pittaras A and Manolis A: The growing epidemic of diabetes
mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 18:104–109. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157:1078432019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Magee C, Grieve DJ, Watson CJ and Brazil
DP: Diabetic nephropathy: A tangled web to unweave. Cardiovasc
Drugs Ther. 31:579–592. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thipsawat S: Early detection of diabetic
nephropathy in patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of
the literature. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 18:147916412110588562021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bao K, Jiao Y, Xing L, Zhang F and Tian F:
The role of wnt signaling in diabetes-induced osteoporosis.
Diabetol Metab Syndr. 15:842023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vestergaard P: Discrepancies in bone
mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type
2 diabetes-a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 18:427–444. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Janghorbani M, Van Dam RM, Willett WC and
Hu FB: Systematic review of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and
risk of fracture. Am J Epidemiol. 166:495–505. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, You W, Jing Z, Wang R, Fu Z and
Wang Y: Increased risk of vertebral fracture in patients with
diabetes: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int Orthop.
40:1299–1307. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xia J, Zhong Y, Huang G, Chen Y, Shi H and
Zhang Z: The relationship between insulin resistance and
osteoporosis in elderly male type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic
nephropathy. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 73:546–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan P, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Miao Y, Gao C
and Wan Q: Association of circulating Omentin-1 with Osteoporosis
in a Chinese Type 2 diabetic population. Mediators Inflamm.
2020:93897202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang S, Hu T, Liu H, Lv YL, Zhang W, Li H,
Xuan L, Gong LL and Liu LH: Akebia saponin D ameliorates metabolic
syndrome (MetS) via remodeling gut microbiota and attenuating
intestinal barrier injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 138:1114412021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xuan L, Yang S, Ren L, Liu H, Zhang W, Sun
Y, Xu B, Gong L and Liu L: Akebia saponin D attenuates allergic
airway inflammation through AMPK activation. J Nat Med. 78:393–402.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gu L, Ye L, Chen Y, Deng C, Zhang X, Chang
J, Feng M, Wei J, Bao X and Wang R: Integrating network
pharmacology and transcriptomic omics reveals that akebia saponin D
attenuates neutrophil extracellular Traps-induced neuroinflammation
via NTSR1/PKAc/PAD4 pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage. FASEB
J. 38:e233942024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gong LL, Yang S, Zhang W, Han FF, Lv YL,
Wan ZR, Liu H, Jia YJ, Xuan LL and Liu LH: Akebia saponin D
alleviates hepatic steatosis through BNip3 induced mitophagy. J
Pharmacol Sci. 136:189–195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kristensen SL, Rorth R, Jhund PS, Docherty
KF, Sattar N, Preiss D, Køber L, Petrie MC and McMurray JJV:
Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor
agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes
Endocrinol. 7:776–785. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao H, Zhang A, Li D, Wu Y, Wang CZ, Wan
JY and Yuan CS: Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor
agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for
type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ.
384:e0764102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Beery AK and Zucker I: Sex bias in
neuroscience and biomedical research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
35:565–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mauvais-Jarvis F: Sex differences in
metabolic homeostasis, diabetes, and obesity. Biol Sex Differ.
6:142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du J, Zhu M, Li H, Liang G, Li Y and Feng
S: Metformin attenuates cardiac remodeling in mice through the
Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 20:838–845. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
O'Neil PM, Birkenfeld AL, McGowan B,
Mosenzon O, Pedersen SD, Wharton S, Carson CG, Jepsen CH, Kabisch M
and Wilding JPH: Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with
liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: A
randomised, Double-blind, placebo and active controlled,
dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 392:637–649. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Davies M, Faerch L, Jeppesen OK,
Pakseresht A, Pedersen SD, Perreault L, Rosenstock J, Shimomura I,
Viljoen A, Wadden TA, et al: Semaglutide 2.4 mg once a week in
adults with overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2): A
randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3
trial. Lancet. 397:971–984. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nair AB and Jacob S: A simple practice
guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin
Pharm. 7:27–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang KC, Chuang PY, Yang TY, Tsai YH, Li
YY and Chang SF: Diabetic rats induced using a High-fat diet and
Low-dose streptozotocin treatment exhibit gut microbiota dysbiosis
and osteoporotic bone pathologies. Nutrients. 16:12202024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu MM, Dong R, Hua Z, Lv NN, Ma Y, Huang
GC, Cheng J and Xu HY: Therapeutic potential of liuwei dihuang pill
against KDM7A and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic
nephropathy-related osteoporosis. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR202017782020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yu X, Wang LN, Du QM, Ma L, Chen L, You R,
Liu L, Ling JJ, Yang ZL and Ji H: Akebia Saponin D attenuates
amyloid β-induced cognitive deficits and inflammatory response in
rats: Involvement of Akt/NF-κB pathway. Behav Brain Res.
235:200–209. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cardiff RD, Miller CH and Munn RJ: Manual
hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold
Spring Harb Protoc. 2014:655–658. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gu LY, Yun S, Tang HT and Xu ZX: Huangkui
capsule in combination with metformin ameliorates diabetic
nephropathy via the Klotho/TGF-beta1/p38MAPK signaling pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 281:1135482021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yaroslavceva MV, Bondarenko ON, El-Taravi
YA, Magerramova ST, Pigarova EA, Ulyanova IN and Galstyan GR:
Etiopathogenetic features of bone metabolism in patients with
diabetes mellitus and Charcot foot. Probl Endokrinol (Mosk).
70:57–64. 2024.In Russian. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma R, Zhu R, Wang L, Guo Y, Liu C, Liu H,
Liu F, Li H, Li Y, Fu M and Zhang D: Diabetic osteoporosis: A
review of its traditional Chinese medicinal use and clinical and
preclinical research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2016:32183132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen F, Wang P, Dai F, Zhang Q, Ying R, Ai
L and Chen Y: Correlation between blood glucose fluctuations and
osteoporosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol.
2025:88894202025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ishtaya GA, Anabtawi YM, Zyoud SH and
Sweileh WM: Osteoporosis knowledge and beliefs in diabetic
patients: A cross sectional study from Palestine. BMC Musculoskelet
Disord. 19:432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Prud'homme GJ and Wang Q:
Anti-Inflammatory role of the klotho protein and relevance to
aging. Cells. 13:14132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Marei HE, Althani A, Afifi N, Hasan A,
Caceci T, Pozzoli G, Morrione A, Giordano A and Cenciarelli C: p53
signaling in cancer progression and therapy. Cancer Cell Int.
21:7032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goyal SN, Reddy NM, Patil KR, Nakhate KT,
Ojha S, Patil CR and Agrawal YO: Challenges and issues with
streptozotocin-induced diabetes-A clinically relevant animal model
to understand the diabetes pathogenesis and evaluate therapeutics.
Chem Biol Interact. 244:49–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Rais N, Ved A, Ahmad R, Parveen K, Gautam
GK, Bari DG, Shukla KS, Gaur R and Singh AP: Model of
Streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced type 2 diabetes: A comparative
review. Curr Diabetes Rev. 18:e1711211980012022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Klinkhammer BM and Boor P: Kidney
fibrosis: Emerging diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Mol
Aspects Med. 93:1012062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu C, Fan G and Wang D: Akebia Saponin D
ameliorated kidney injury and exerted anti-inflammatory and
anti-apoptotic effects in diabetic nephropathy by activation of
NRF2/HO-1 and inhibition of NF-KB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
84:1064672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Moellmann J, Klinkhammer BM, Onstein J,
Stöhr R, Jankowski V, Jankowski J, Lebherz C, Tacke F, Marx N, Boor
P and Lehrke M: Glucagon-Like peptide 1 and its cleavage products
are renoprotective in murine diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes.
67:2410–2419. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Veneti S and Tziomalos K: Is there a role
for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the management of
diabetic nephropathy? World J Diabetes. 11:370–373. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fernandez-Villabrille S, Martin-Carro B,
Martin-Virgala J, Rodríguez-Santamaria MDM, Baena-Huerta F,
Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Fernández-Martín JL, Alonso-Montes C,
Naves-Díaz M, Carrillo-López N and Panizo S: Novel biomarkers of
bone metabolism. Nutrients. 16:6052024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Onoviran OF, Li D, Toombs Smith S and Raji
MA: Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on
comorbidities in older patients with diabetes mellitus. Ther Adv
Chronic Dis. 10:20406223198626912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Herrou J, Mabilleau G, Lecerf JM, Thomas
T, Biver E and Paccou J: Narrative review of effects of
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists on bone health in people
living with obesity. Calcif Tissue Int. 114:86–97. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sun M, Wu X, Yu Y, Wang L, Xie D, Zhang Z,
Chen L, Lu A, Zhang G and Li F: Disorders of calcium and phosphorus
metabolism and the Proteomics/Metabolomics-Based research. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 8:5761102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Winiarska A, Filipska I, Knysak M and
Stompor T: Dietary phosphorus as a marker of mineral metabolism and
progression of diabetic kidney disease. Nutrients. 13:7892021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Buchanan S, Combet E, Stenvinkel P and
Shiels PG: Klotho, Aging, and the failing kidney. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 11:5602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hosseini L, Babaie S, Shahabi P, Fekri K,
Shafiee-Kandjani AR, Mafikandi V, Maghsoumi-Norouzabad L and
Abolhasanpour N: Klotho: Molecular mechanisms and emerging
therapeutics in central nervous system diseases. Mol Biol Rep.
51:9132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kanbay M, Copur S, Ozbek L, Mutlu A, Cejka
D, Ciceri P, Cozzolino M and Haarhaus ML: Klotho: A potential
therapeutic target in aging and neurodegeneration beyond chronic
kidney disease-a comprehensive review from the ERA CKD-MBD working
group. Clin Kidney J. 17:sfad2762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tang A, Zhang Y, Wu L, Lin Y, Lv L, Zhao
L, Xu B, Huang Y and Li M: Klotho's impact on diabetic nephropathy
and its emerging connection to diabetic retinopathy. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:11801692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hejrati A, Zabihi T, Riazi S and Sarv F:
Klotho: A possible diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target in
diabetes complications. Int J Diabetes Developing Countries. 1–16.
2025.
|
|
52
|
Nie F, Wu D, Du H, Yang X, Yang M, Pang X
and Xu Y: Serum klotho protein levels and their correlations with
the progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes
Complications. 31:94–98. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kim SS, Song SH, Kim IJ, Lee EY, Lee SM,
Chung CH, Kwak IS, Lee EK and Kim YK: Decreased plasma alpha-Klotho
predict progression of nephropathy with type 2 diabetic patients. J
Diabetes Complications. 30:887–892. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lahalle A, Lacroix M, De Blasio C, Cisse
MY, Linares LK and Le Cam L: The p53 Pathway and Metabolism: The
tree that hides the forest. Cancers (Basel). 13:1332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kung CP and Murphy ME: The role of the p53
tumor suppressor in metabolism and diabetes. J Endocrinol.
231:R61–R75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|