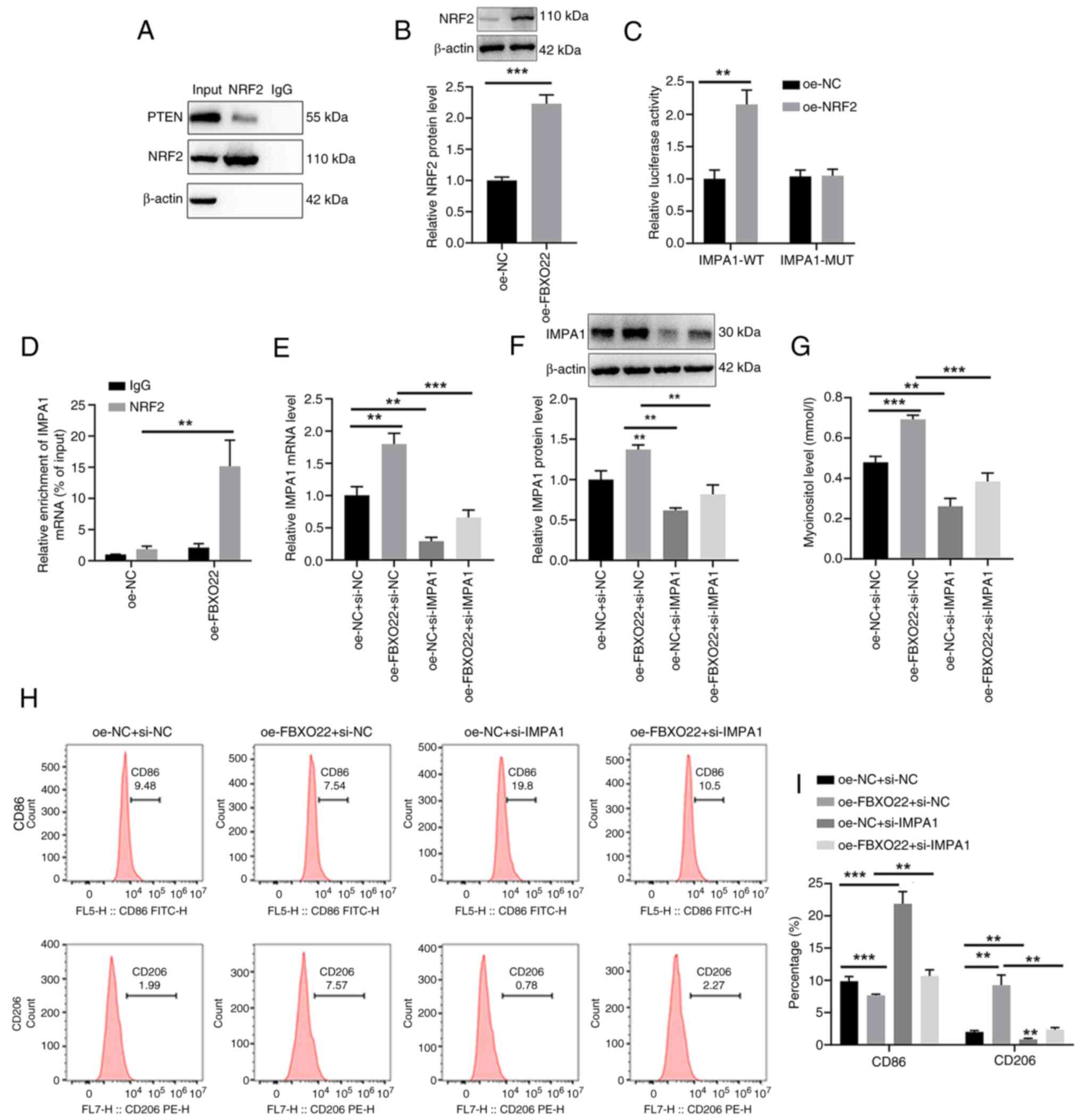
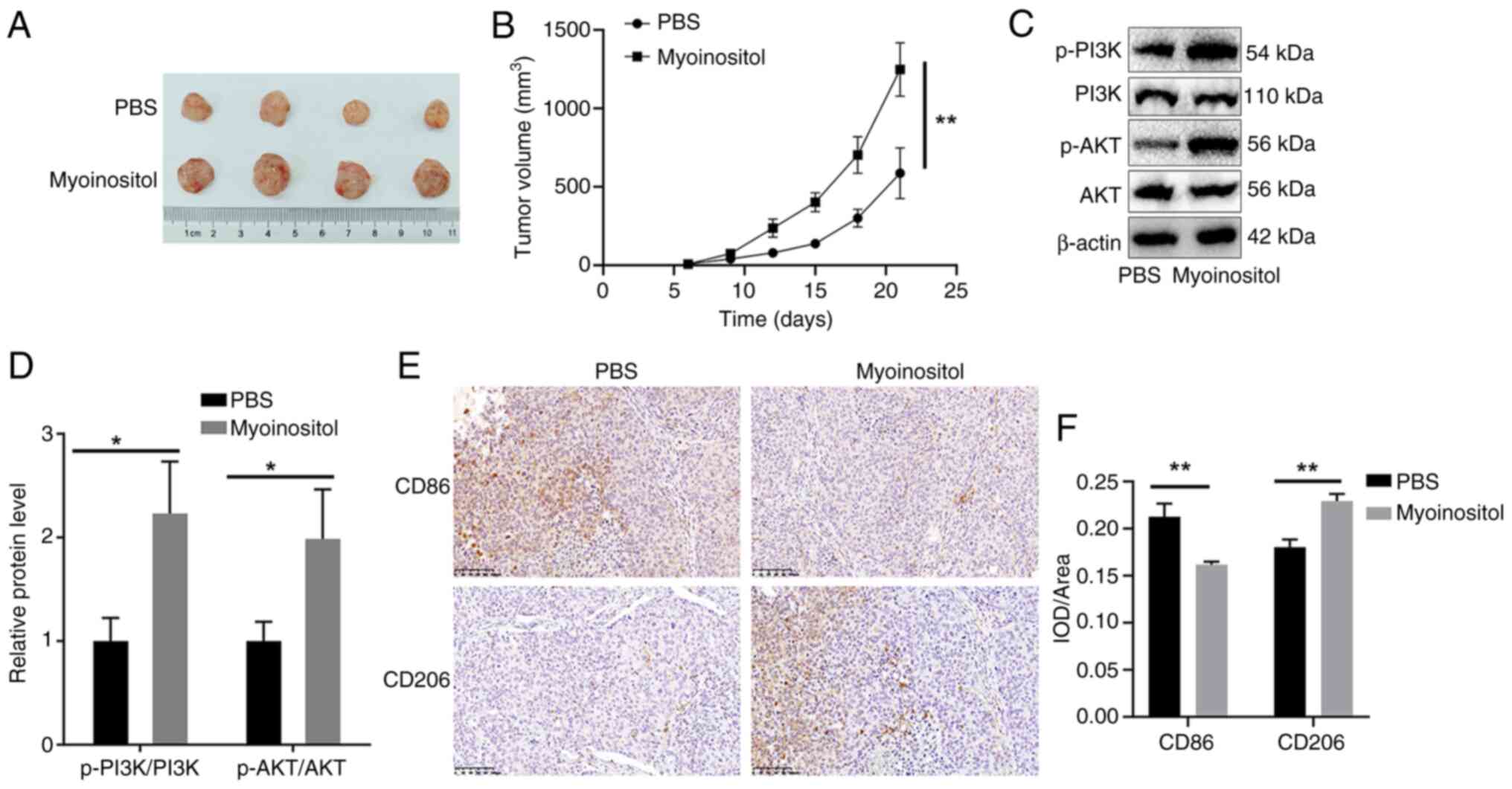
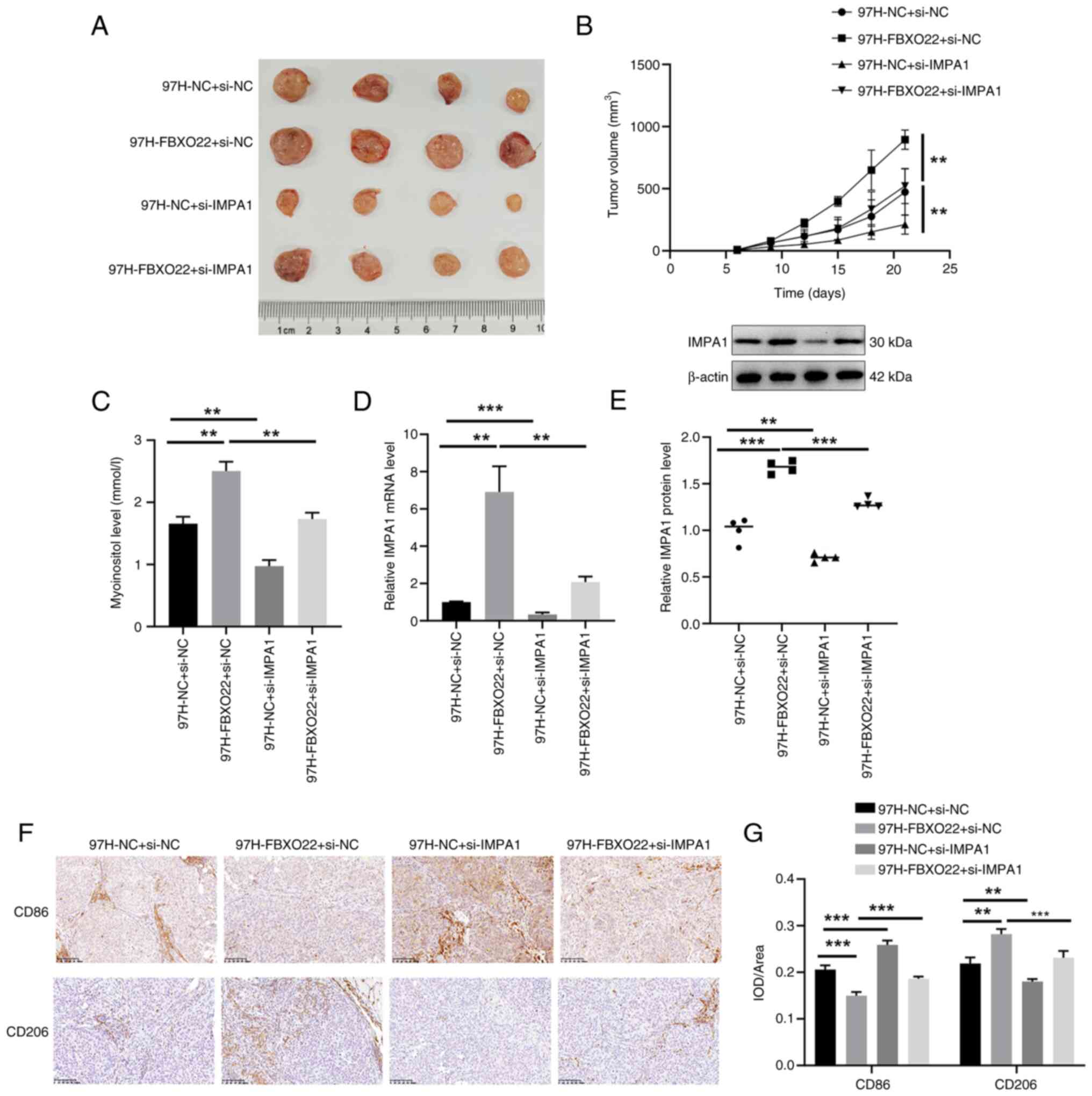
|
1
|
Ferenci P, Fried M, Labrecque D, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): A global perspective. Arab Journal
of Gastroenterology. 11:174–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brown ZJ, Tsilimigras DI, Ruff SM, Mohseni
A, Kamel IR, Cloyd JM and Pawlik TM: Management of hepatocellular
carcinoma A review. JAMA Surg. 158:410–420. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, Kroemer G
and Galluzzi L: Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor
microenvironment. Cell Metab. 30:36–50. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hinshaw DC and Shevde LA: The tumor
microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res.
79:4557–4566. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Z, Wu T, Zheng B and Chen L:
Individualized precision treatment: Targeting TAM in HCC. Cancer
Lett. 458:86–91. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Du M, Sun L, Guo J and Lv H: Macrophages
and tumor-associated macrophages in the senescent microenvironment:
From immunosuppressive TME to targeted tumor therapy. Pharmacol
Res. 204:1071982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Christofides A, Strauss L, Yeo AT, Cao C,
Charest A and Boussiotis V: The complex role of tumor-infiltrating
macrophages. Nat Immunol. 23:1148–1156. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang T, Wang Y, Dai W, Zheng X, Wang J,
Song S, Fang L, Zhou J, Wu W and Gu J: Increased B3GALNT2 in
hepatocellular carcinoma promotes macrophage recruitment via
reducing acetoacetate secretion and elevating MIF activity. J
Hematol Oncol. 11:502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shiau DJ, Kuo WT, Davuluri GVN, Shieh CC,
Tsai PJ, Chen CC, Lin YS, Wu YZ, Hsiao YP and Chang CP:
Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived high mobility group box 1 triggers
M2 macrophage polarization via a TLR2/NOX2/autophagy axis. Sci Rep.
10:135822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nguyen KM and Busino L: The biology of
F-box proteins: The SCF family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1217:111–122. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ho MS, Tsai PI and Chien CT: F-box
proteins: The key to protein degradation. J Biomed Sci. 13:181–191.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan MKM, Lim HJ and Harper JW: SCFFBXO22
regulates histone H3 lysine 9 and 36 methylation levels by
targeting histone demethylase KDM4A for ubiquitin-mediated
proteasomal degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 31:3687–3699. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tian X, Dai S, Sun J, Jin G and Jiang Y,
Meng F, Li Y, Wu D and Jiang Y: F-box protein FBXO22 mediates
polyubiquitination and degradation of KLF4 to promote
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Oncotarget. 6:22767–22775.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Croze ML, Vella RE, Pillon NJ, Soula HA,
Hadji L, Guichardant M and Soulage CO: Chronic treatment with
myo-inositol reduces white adipose tissue accretion and improves
insulin sensitivity in female mice. J Nutr Biochem. 24:457–466.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Food and Drug Administration (FDA):
Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Initial Clinical
Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers. FDA;
Rockville, MD: 2005
|
|
17
|
Toit AD: Post-translational modification:
Sweetening protein quality control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:2952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang S, Osgood AO and Chatterjee A:
Uncovering post-translational modification-associated
protein-protein interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 74:1023522022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park J, Cho J and Song EJ:
Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) as a target for anticancer
treatment. Arch Pharm Res. 43:1144–1161. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brauckhoff A, Ehemann V, Schirmacher P and
Breuhahn K: Reduced expression of the E3-ubiquitin ligase seven in
absentia homologue (SIAH)-1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Verh
Dtsch Ges Pathol. 91:269–277. 2007.In German.
|
|
21
|
Lin XT, Zhang J, Liu ZY, Wu D, Fang L, Li
CM, Yu HQ and Xie CM: Elevated FBXW10 drives hepatocellular
carcinoma tumorigenesis via AR-VRK2 phosphorylation-dependent GAPDH
ubiquitination in male transgenic mice. Cell Rep. 42:1128122023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kipreos ET and Pagano M: The F-box protein
family. Genome Biol. 1:1–7. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Johmura Y, Sun J, Kitagawa K, Nakanishi K,
Kuno T, Naiki-Ito A, Sawada Y, Miyamoto T, Okabe A, Aburatani H, et
al: SCFFbxo22-KDM4A targets methylated p53 for degradation and
regulates senescence. Nat Commun. 7:105742016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Zhang L, Chen J, Ning D, Liu Q, Wang C,
Zhang Z, Chu L, Yu C, Liang HF, Zhang B and Chen X: FBXO22 promotes
the development of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the
ubiquitination and degradation of p21. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:1012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng Y, Chen H, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Liu J,
Pan Y, Bai J and Zhang H: Knockdown of FBXO22 inhibits melanoma
cell migration, invasion and angiogenesis via the HIF-1α/VEGF
pathway. Invest New Drugs. 38:20–28. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lin M, Zhang J, Bouamar H, Wang Z, Sun LZ
and Zhu X: Fbxo22 promotes cervical cancer progression via
targeting p57Kip2 for ubiquitination and degradation. Cell Death
Dis. 13:8052022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Dahia PL: PTEN, a unique tumor suppressor
gene. Endocr Relat Cancer. 7:115–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu L, Long H, Wu Y, Li H, Dong L, Zhong
JL, Liu Z, Yang X, Dai X, Shi L, et al: HRD1-mediated PTEN
degradation promotes cell proliferation and hepatocellular
carcinoma progression. Cell Signal. 50:90–99. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu Y, Zhang D, Ji J and Zhang L: Ubiquitin
ligase MARCH8 promotes the malignant progression of hepatocellular
carcinoma through PTEN ubiquitination and degradation. Mol
Carcinog. 62:1062–1072. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ge MK, Zhang N, Xia L, Zhang C, Dong SS,
Li ZM, Ji Y, Zheng MH, Sun J, Chen GQ and Shen SM: FBXO22 degrades
nuclear PTEN to promote tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 11:17202020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rojo AI, Rada P, Mendiola M, Ortega-Molina
A, Wojdyla K, Rogowska-Wrzesinska A, Hardisson D, Serrano M and
Cuadrado A: The PTEN/NRF2 axis promotes human carcinogenesis.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:2498–2514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ding C, Zou Q, Wu Y, Lu J, Qian C, Li H
and Huang B: EGF released from human placental mesenchymal stem
cells improves premature ovarian insufficiency via NRF2/HO-1
activation. Aging (Albany NY). 12:2992–3009. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lei Z, Luo Y, Lu J, Fu Q, Wang C, Chen Q,
Zhang Z and Zhang L: FBXO22 promotes HCC angiogenesis and
metastasis via RPS5/AKT/HIF-1α/VEGF-A signaling axis. Cancer Gene
Ther. 32:198–213. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choi W, Lee J, Lee J, Lee SH and Kim S:
Hepatocyte growth factor regulates macrophage transition to the M2
Phenotype and promotes murine skeletal muscle regeneration. Front
Physiol. 10:9142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao J, Li H, Zhao S, Wang E, Zhu J, Feng
D, Zhu Y, Dou W, Fan Q, Hu J, et al: Epigenetic silencing of
miR-144/451a cluster contributes to HCC progression via paracrine
HGF/MIF-mediated TAM remodeling. Mol Cancer. 20:462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meng PH, Raynaud C, Tcherkez G, Blanchet
S, Massoud K, Domenichini S, Henry Y, Soubigou-Taconnat L,
Lelarge-Trouverie C, Saindrenan P, et al: Crosstalks between
Myo-Inositol metabolism, programmed cell death and basal immunity
in arabidopsis. PLoS One. 4:e73642009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Antony PJ, Gandhi GR, Stalin A,
Balakrishna K, Toppo E, Sivasankaran K, Ignacimuthu S and Al-Dhabi
NA: Myoinositol ameliorates high-fat diet and
streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats through promoting insulin
receptor signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 88:1098–1113. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang WD, Feng L, Liu Y, et al: Effects of
graded levels of dietary myo-inositol on non-specific immune and
specific immune parameters in juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio
var. Jian). Aquaculture Research. 41:1413–1420. 2010.
|
|
39
|
Ghosh N, Das A, Biswas N, Mahajan SP,
Madeshiya AK, Khanna S, Sen CK and Roy S: Myo-inositol in fermented
sugar matrix improves human macrophage function. Mol Nutr Food Res.
66:e21008522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kassie F, Bagherpoor AJ, Kovacs K and
Seelig D: Combinatory lung tumor inhibition by myo-inositol and
iloprost/rapamycin: Association with immunomodulation.
Carcinogenesis. 43:547–556. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mueller C, Hong H, Sharma AA, Qin H,
Benveniste EN and Szaflarski JP: Brain temperature, brain
metabolites, and immune system phenotypes in temporal lobe
epilepsy. Epilepsia Open. 9:2454–2466. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Niwa T, Sobue G, Maeda K and Mitsuma T:
Myoinositol inhibits proliferation of cultured Schwann cells:
Evidence for neurotoxicity of myoinositol. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
4:662–666. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hofmann BT and Jücker M: Activation of
PI3K/Akt signaling by n-terminal SH2 domain mutants of the p85α
regulatory subunit of PI3K is enhanced by deletion of its
c-terminal SH2 domain. Cell Signal. 24:1950–1954. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Baitsch D, Bock HH, Engel T, Telgmann R,
Müller-Tidow C, Varga G, Bot M, Herz J, Robenek H, von Eckardstein
A and Nofer JR: Apolipoprotein E induces antiinflammatory phenotype
in macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:1160–1168. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|