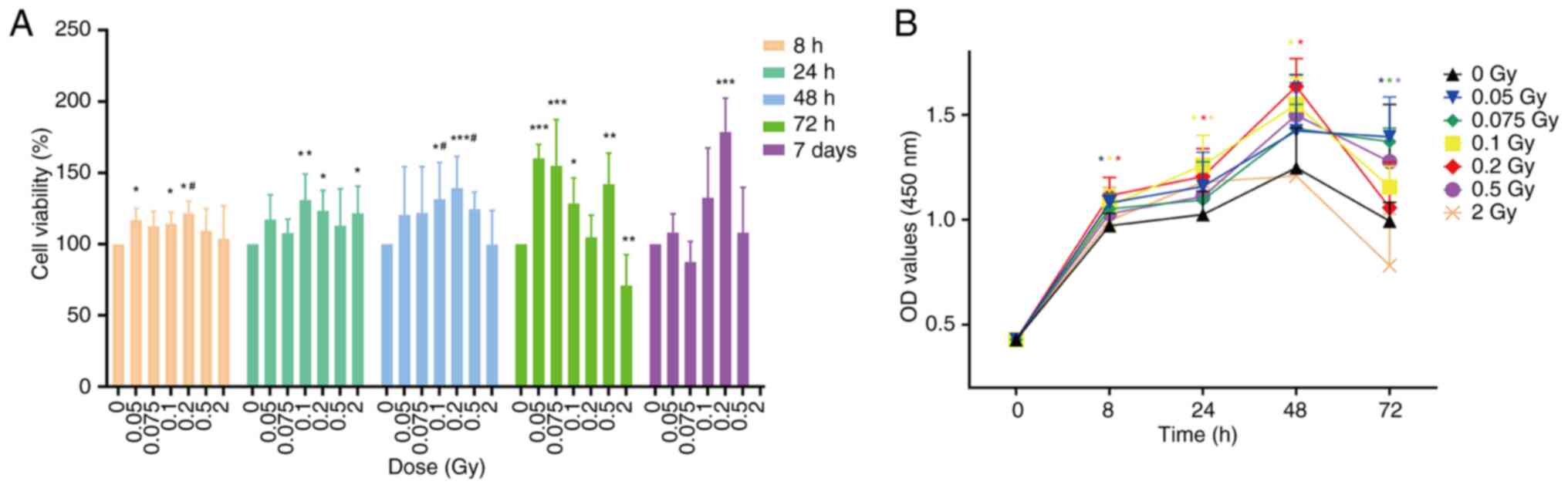
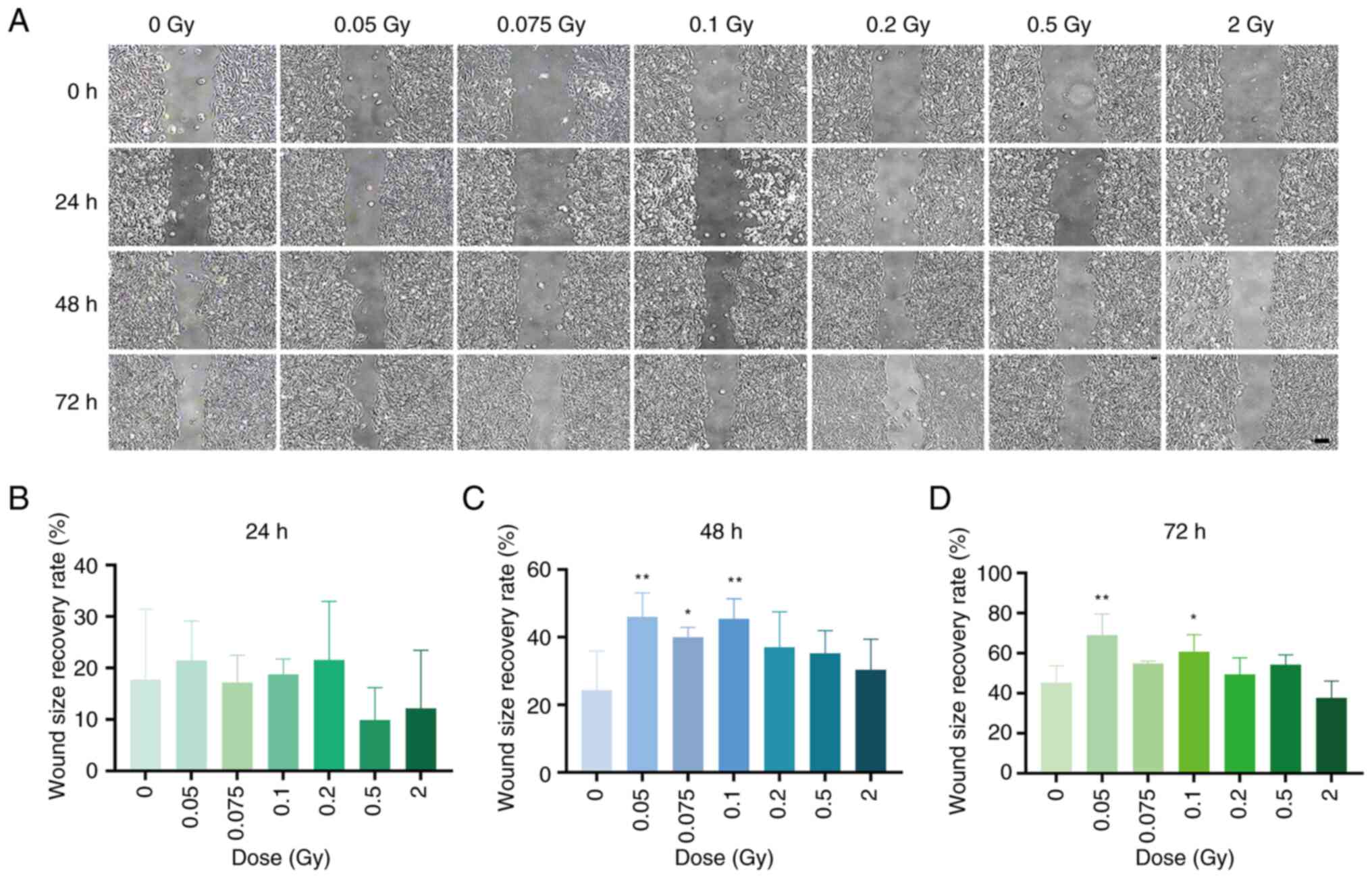
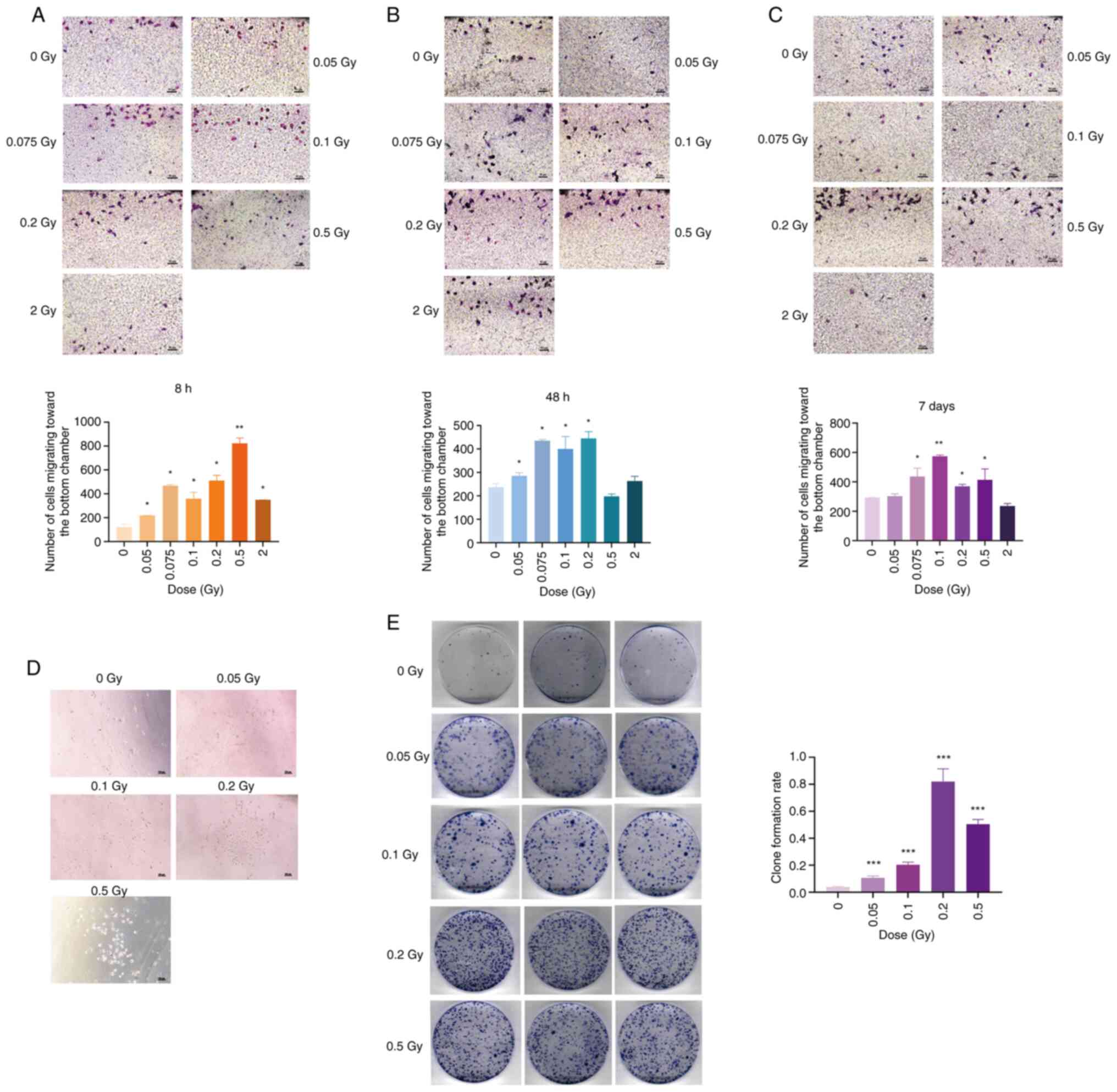
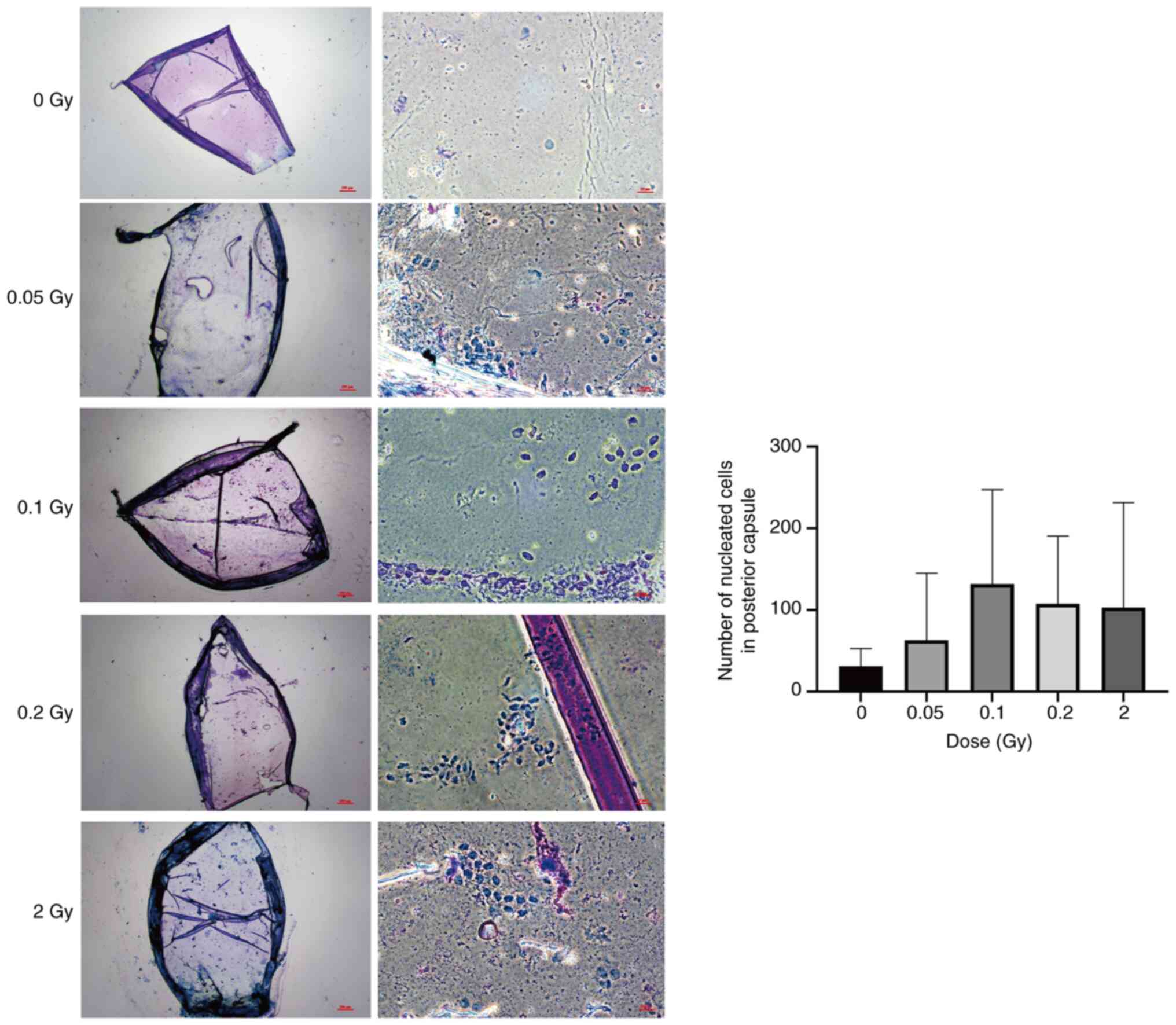
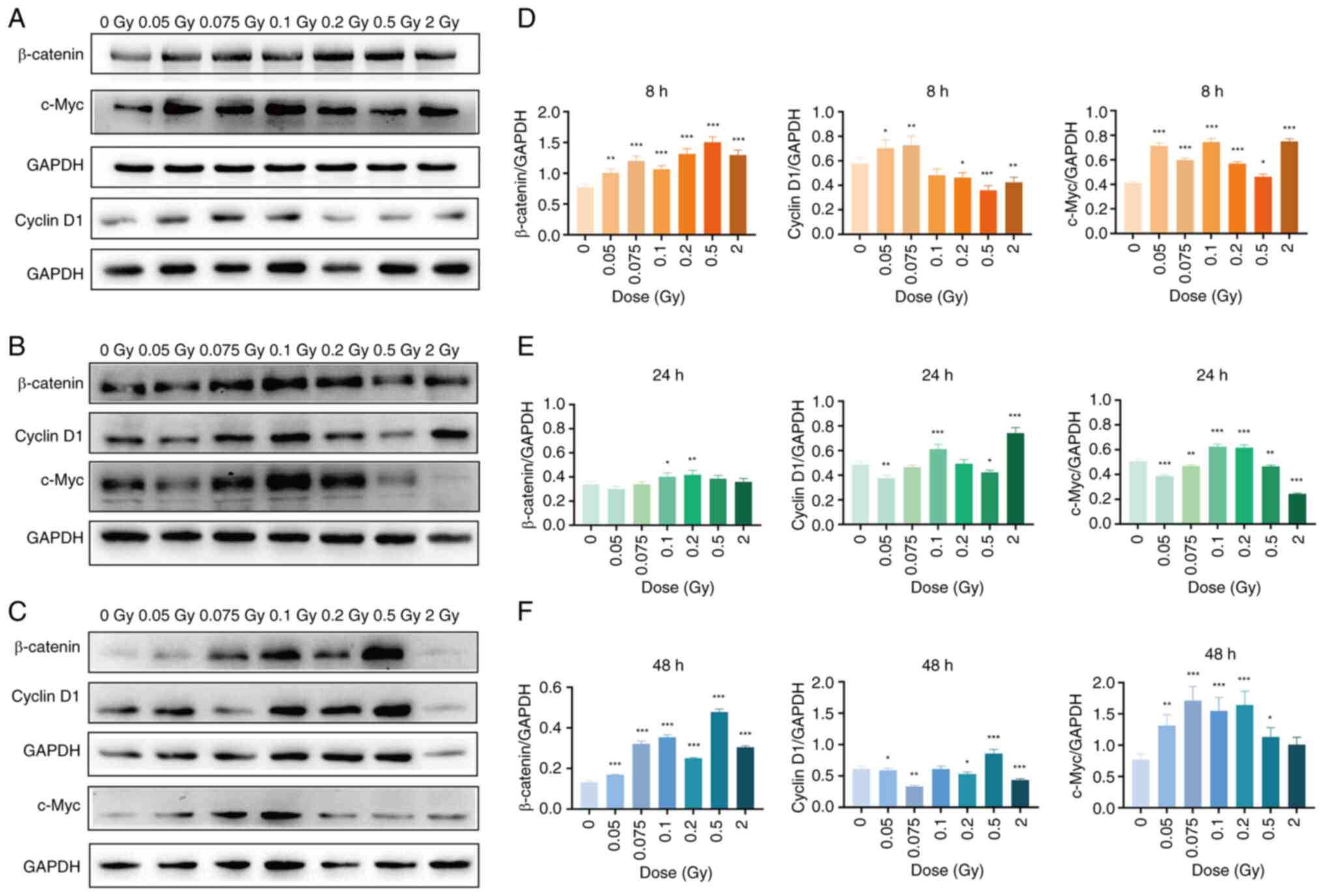
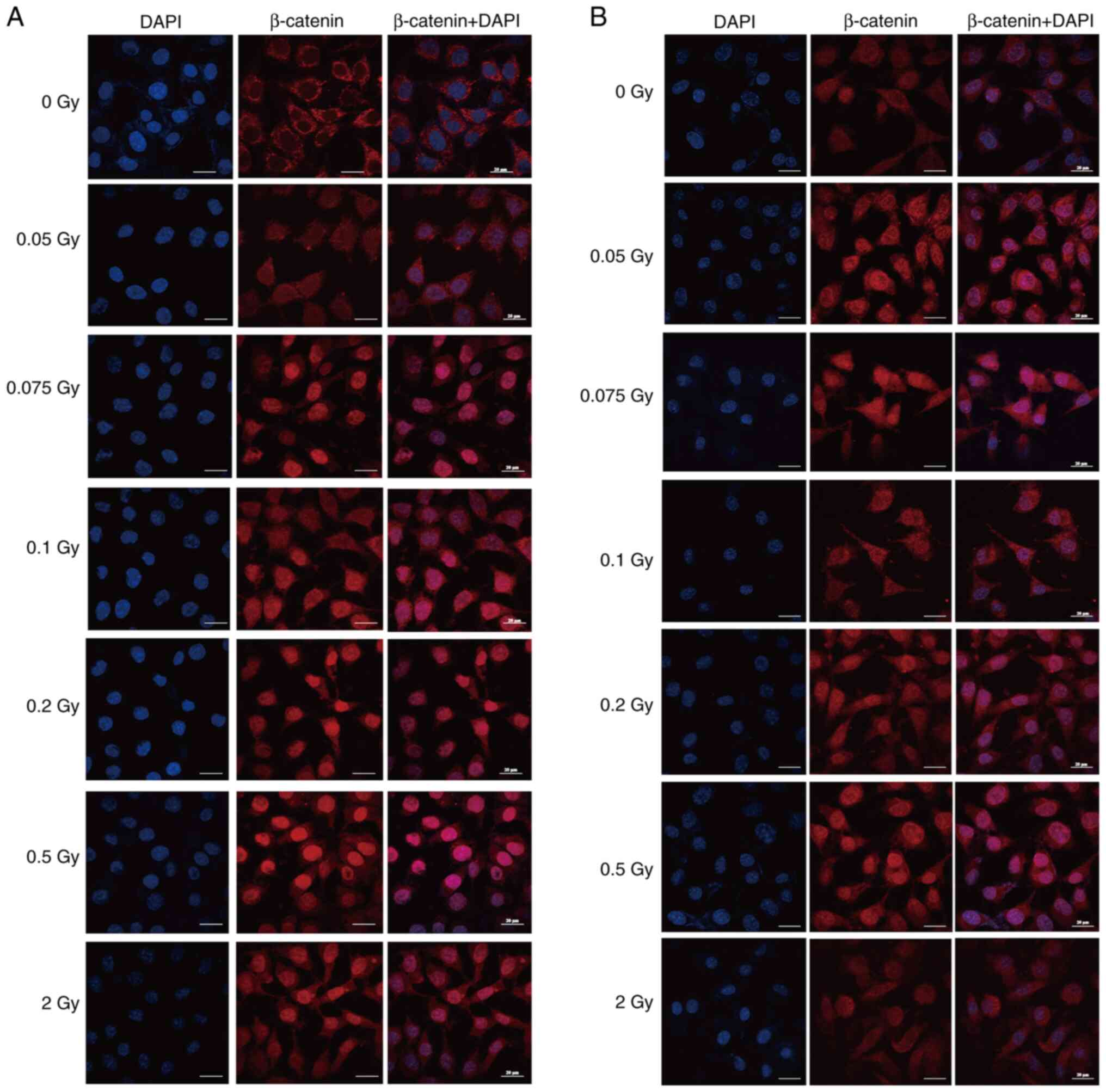
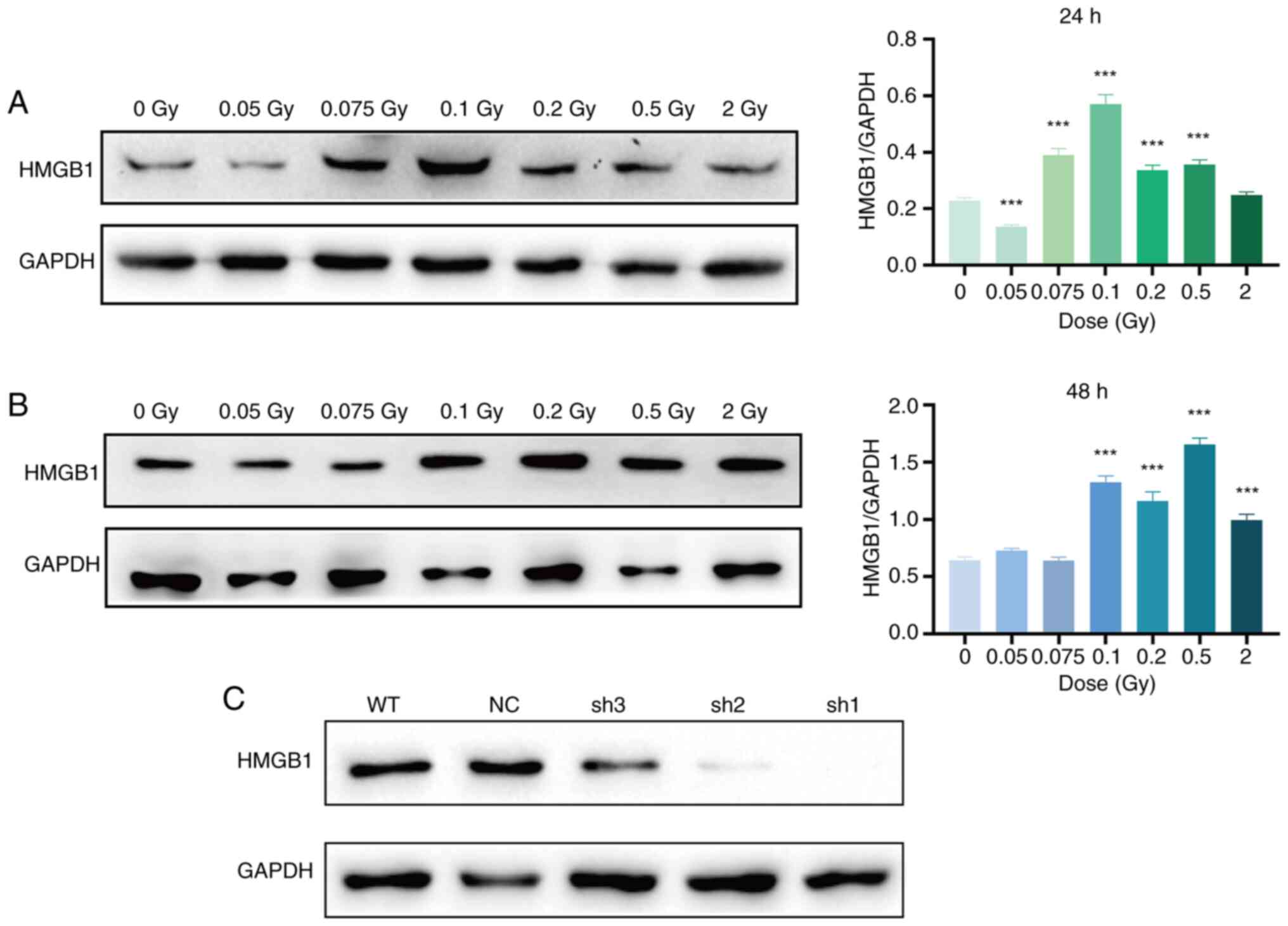
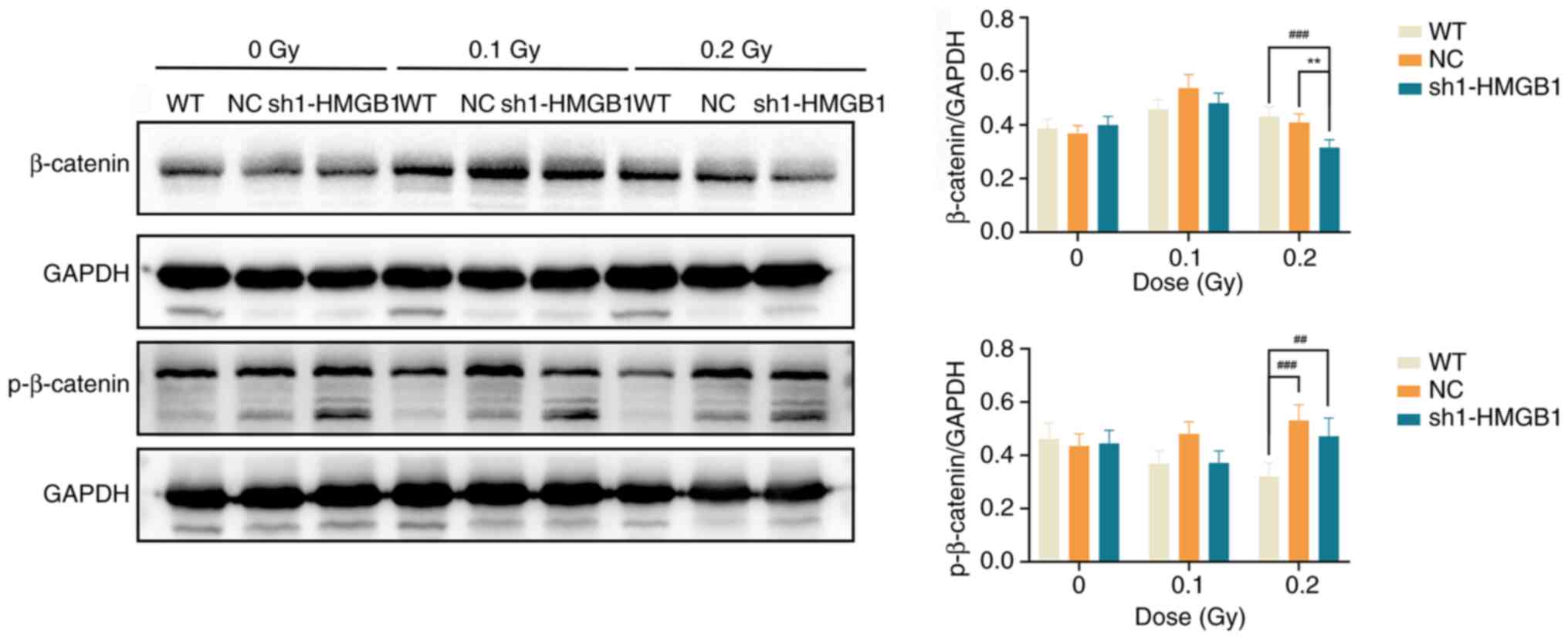
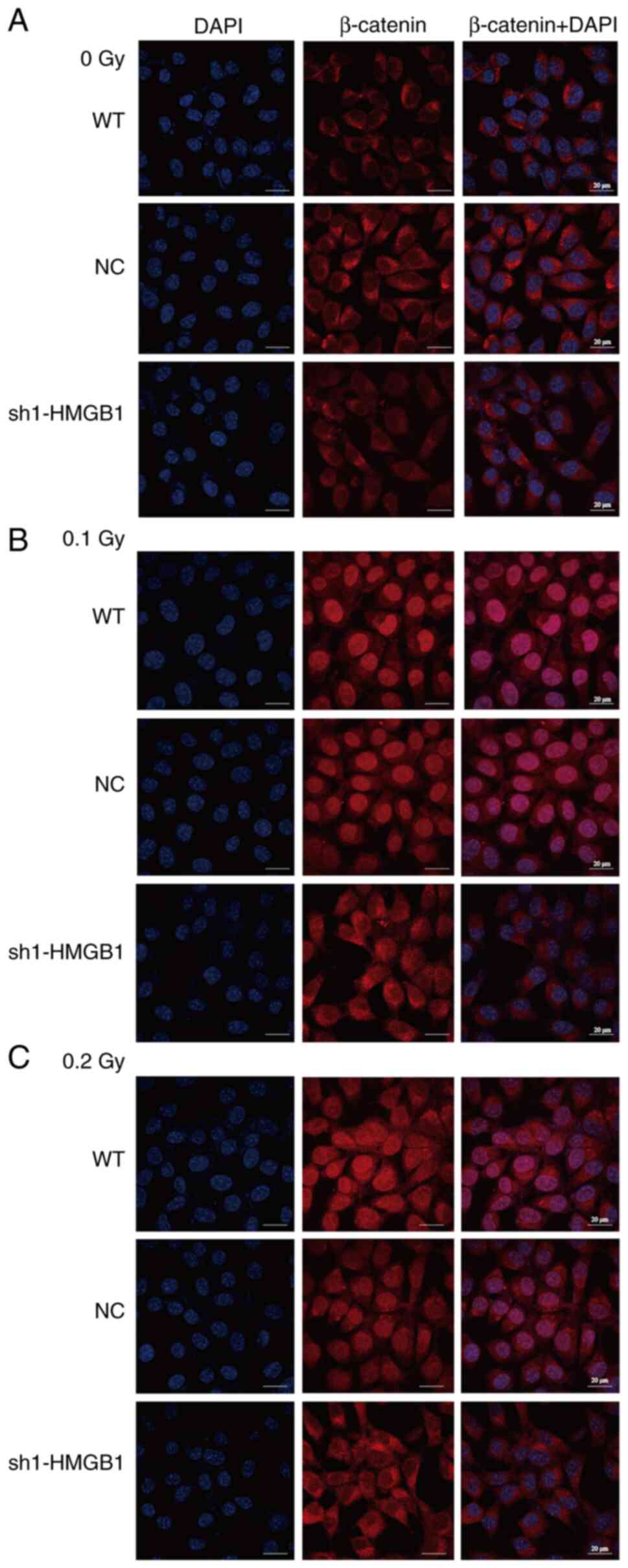
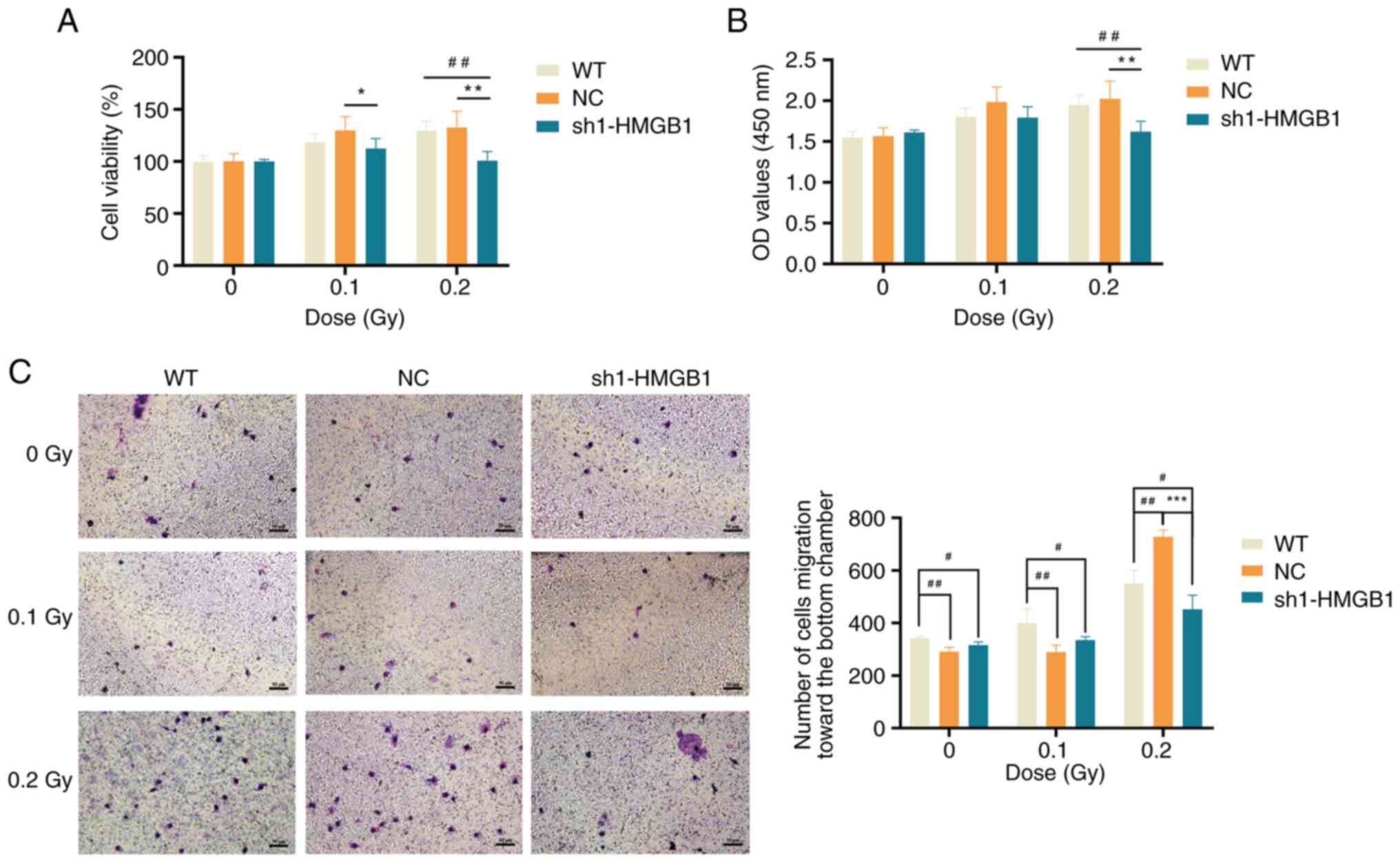
|
1
|
Neriishi K, Nakashima E, Minamoto A,
Fujiwara S, Akahoshi M, Mishima HK, Kitaoka T and Shore RE:
Postoperative cataract cases among atomic bomb survivors: Radiation
dose response and threshold. Radiat Res. 168:404–408. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chodick G, Bekiroglu N, Hauptmann M,
Alexander BH, Freedman DM, Doody MM, Cheung LC, Simon SL, Weinstock
RM, Bouville A and Sigurdson AJ: Risk of cataract after exposure to
low doses of ionizing radiation: A 20-year prospective cohort study
among US radiologic technologists. Am J Epidemiol. 168:620–631.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Azizova TV, Hamada N, Grigoryeva ES and
Bragin EV: Risk of various types of cataracts in a cohort of Mayak
workers following chronic occupational exposure to ionizing
radiation. Eur J Epidemiol. 33:1193–1204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ahmadi M, Barnard S, Ainsbury E and Kadhim
M: Early responses to low-dose ionizing radiation in cellular lens
epithelial models. Radiat Res. 197:78–91. 2022.
|
|
5
|
Barnard S, Uwineza A, Kalligeraki A,
McCarron R, Kruse F, Ainsbury EA and Quinlan RA: Lens epithelial
cell proliferation in response to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res.
197:92–99. 2022.
|
|
6
|
Siddam AD, Gautier-Courteille C,
Perez-Campos L, Anand D, Kakrana A, Dang CA, Legagneux V, Méreau A,
Viet J, Gross JM, et al: The RNA-binding protein Celf1
post-transcriptionally regulates p27Kip1 and Dnase2b to control
fiber cell nuclear degradation in lens development. PLoS Genet.
14:e10072782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kumar B and Reilly MA: The development,
growth, and regeneration of the crystalline lens: A review. Curr
Eye Res. 45:313–326. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang P, Li YW, Lu X, Liu Y, Tian XL, Gao
L, Liu QJ, Fan L and Tian M: Low-dose ionizing radiation: Effects
on the proliferation and migration of lens epithelial cells via
activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol
Environ Mutagen. 888:5036372023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Vigneux G, Pirkkanen J, Laframboise T,
Prescott H, Tharmalingam S and Thome C: Radiation-induced
alterations in proliferation, migration, and adhesion in lens
epithelial cells and implications for cataract development.
Bioengineering (Basel). 9:292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Terrell AM, Anand D and Lachke SA:
Molecular characterization of human lens epithelial cell lines
HLE-B3 and SRA01/04 and their utility to model lens biology. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:40112015.
|
|
11
|
Wang P, Fan L, Lu X, Gao L, Liu Q and Tian
M: Identification of differential mRNA expression profiles in lens
epithelial cells induced by low-dose ionizing radiation. Radiat
Prot. 43:175–185. 2023.In Chinese.
|
|
12
|
Li PF, Borgia F, Custurone P, Vaccaro M,
Pioggia G and Gangemi S: Role of HMGB1 in cutaneous melanoma: State
of the art. Int J Mol Sci. 23:39272022.
|
|
13
|
Shu Z, Miao X, Tang T, Zhan P, Zeng L and
Jiang Y: The GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in
HMGB1-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage matrix
degradation. Int J Mol Med. 45:769–778. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang XH, Zhang SY, Shi M and Xu XP: HMGB1
promotes the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer by
activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
19:15330338209480542020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen YC, Statt S, Wu R, Chang HT, Liao JW,
Wang CN, Shyu WC and Lee CC: High mobility group box 1-induced
epithelial mesenchymal transition in human airway epithelial cells.
Sci Rep. 6:188152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weatherbee B, Barton JR, Siddam AD, Anand
D and Lachke SA: Molecular characterization of the human lens
epithelium-derived cell line SRA01/04. Exp Eye Res. 188:1077872019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin M, Gao D, Wang R, Sik A and Liu K:
Possible involvement of TGF-β-SMAD-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in pro-metastatic property of PAX6. Oncol Rep.
44:555–564. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oharazawa H, Ibaraki N, Lin LR and Reddy
VN: The effects of extracellular matrix on cell attachment,
proliferation and migration in a human lens epithelial cell line.
Exp Eye Res. 69:603–610. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Markiewicz E, Barnard S, Haines J, Coster
M, van Geel O, Wu W, Richards S, Ainsbury E, Rothkamm K, Bouffler S
and Quinlan RA: Nonlinear ionizing radiation-induced changes in eye
lens cell proliferation, cyclin D1 expression and lens shape. Open
Biol. 5:1500112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim W, Kim M and Jho EH: Wnt/β-catenin
signalling: From plasma membrane to nucleus. Biochem J. 450:9–21.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shah K and Kazi JU:
Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of WNT/beta-catenin signaling.
Front Oncol. 12:8587822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamada N: Ionizing radiation sensitivity
of the ocular lens and its dose rate dependence. Int J Radiat Biol.
93:1024–1034. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Andley UP, Rhim JS, Chylack LJ Jr and
Fleming TP: Propagation and immortalization of human lens
epithelial cells in culture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
35:3094–3102. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao Y, Su YP, Li XL, Lei SJ, Chen HF, Cui
SY, Zhang SF, Zou JM, Liu QJ and Sun QF: ATM and TP53 polymorphisms
modified susceptibility to radiation-induced lens opacity in
natural high background radiation area, China. Int J Radiat Biol.
98:1235–1242. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen Y, Feng J, Liu J, Zhou H, Luo H, Xue
C and Gao W: Effects of neutron radiation on Nrf2-regulated
antioxidant defense systems in rat lens. Exp Ther Med. 21:3342021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Mahesh P, Wang Y, Novo SG, Shihan
MH, Hayward-Piatkovskyi B and Duncan MK: Spatiotemporal dynamics of
canonical Wnt signaling during embryonic eye development and
posterior capsular opacification (PCO). Exp Eye Res. 175:148–158.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bao XL, Song H, Chen Z and Tang X: Wnt3a
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and
proliferation of lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 18:1983–1990.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chauhan V, Rowan-Carroll A, Gagné R, Kuo
B, Williams A and Yauk CL: The use of in vitro transcriptional data
to identify thresholds of effects in a human lens epithelial
cell-line exposed to ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol.
95:156–169. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kianian F, Kadkhodaee M, Sadeghipour HR,
Karimian SM and Seifi B: An overview of high-mobility group box 1,
a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine in asthma. J Basic Clin Physiol
Pharmacol. 31:2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ulloa L and Messmer D: High-mobility group
box 1 (HMGB1) protein: Friend and foe. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
17:189–201. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Jiang Z, Yan J and Ying S: HMGB1
as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for malignant
mesothelioma. Dis Markers. 2019:41831572019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang S, Du S, Lv Y, Zhang F and Wang W:
MicroRNA-665 inhibits the oncogenicity of retinoblastoma by
directly targeting high-mobility group box 1 and inactivating the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 11:3111–3123. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Zhou X, Hu X, Xie J, Xu C, Xu W and Jiang
H: Exogenous high-mobility group box 1 protein injection improves
cardiac function after myocardial infarction: Involvement of Wnt
signaling activation. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:7438792012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|