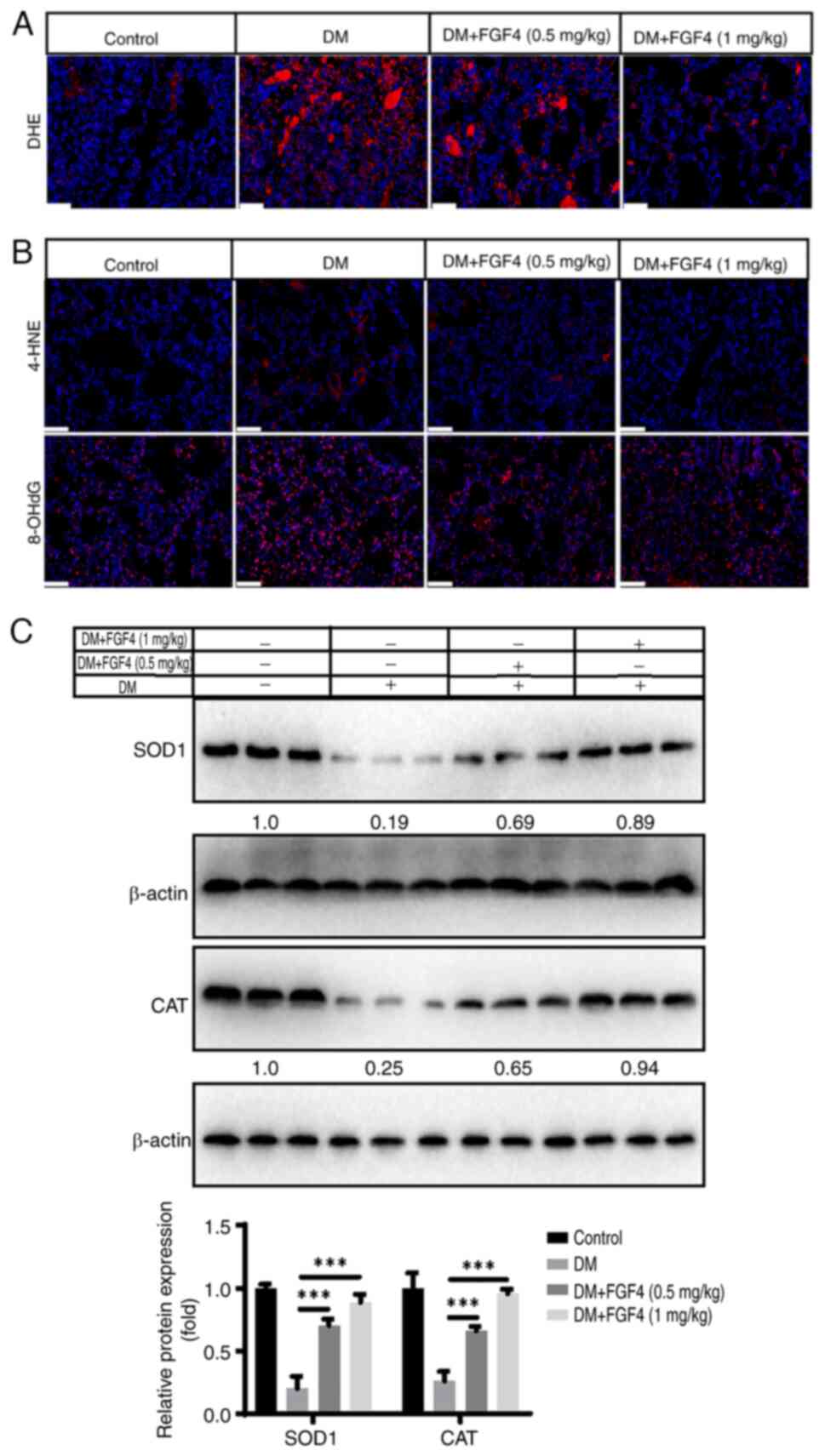
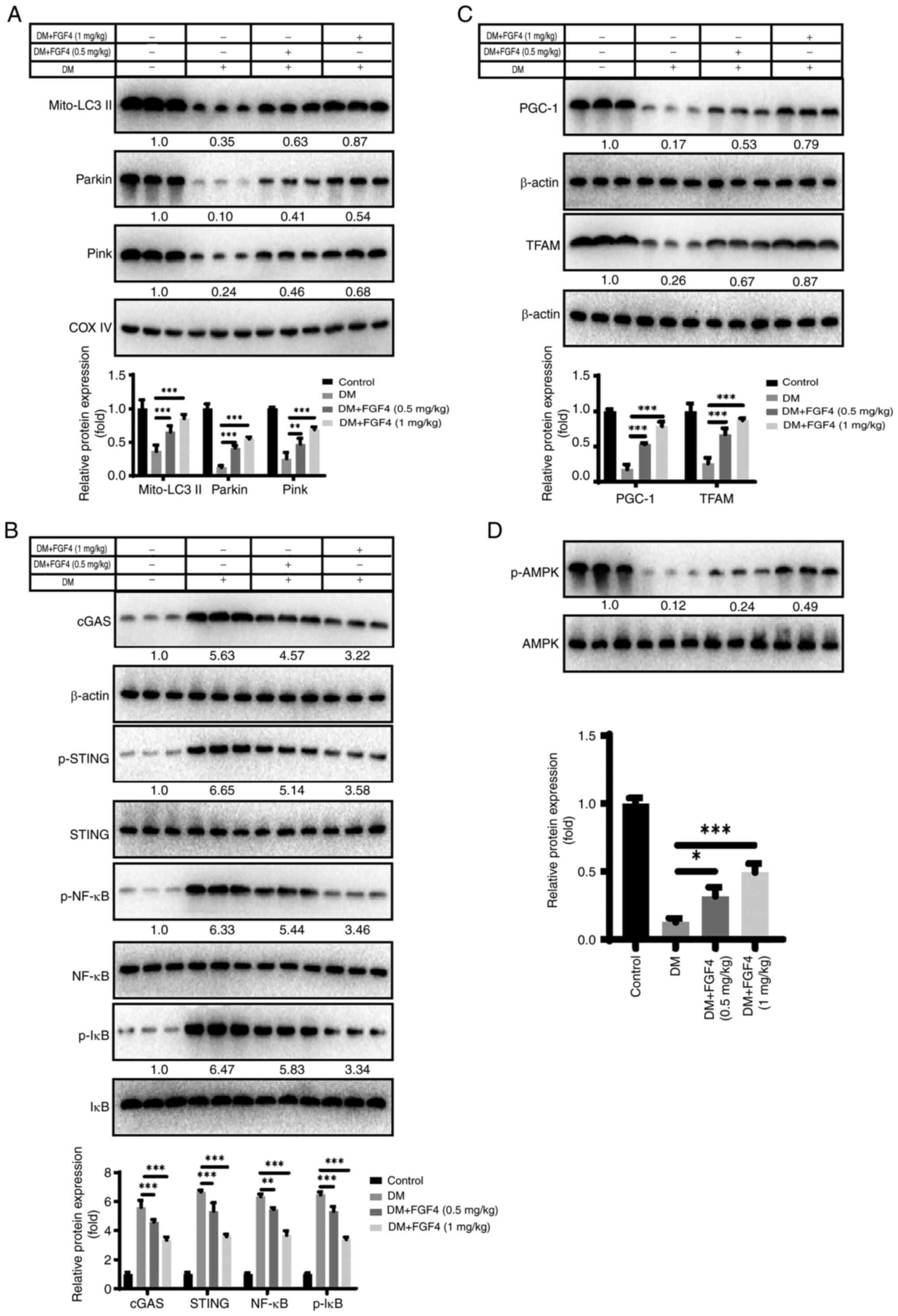
|
1
|
Banday MZ, Sameer AS and Nissar S:
Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview. Avicenna J Med.
10:174–188. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cole JB and Florez JC: Genetics of
diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat Rev Nephrol.
16:377–390. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klein S, Gastaldelli A, Yki-Järvinen H and
Scherer PE: Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 34:11–20.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chan JCN, Lim LL, Wareham NJ, Shaw JE,
Orchard TJ, Zhang P, Lau ESH, Eliasson B, Kong APS, Ezzati M, et
al: The lancet commission on diabetes: Using data to transform
diabetes care and patient lives. Lancet. 396:2019–2082. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Goldman MD: Lung dysfunction in diabetes.
Diabetes Care. 26:1915–1918. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hsia CCW and Raskin P: Lung function
changes related to diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther.
9(Suppl 1): S73–S82. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mameli C, Ghezzi M, Mari A, Cammi G,
Macedoni M, Redaelli FC, Calcaterra V, Zuccotti G and D'Auria E:
The diabetic lung: Insights into pulmonary changes in children and
adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Metabolites. 11:692021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Gent R, Brackel HJ, de Vroede M and
van der Ent CK: Lung function abnormalities in children with type 1
diabetes. Respir Med. 96:976–978. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng H, Wu J, Jin Z and Yan LJ: Potential
biochemical mechanisms of lung injury in diabetes. Aging Dis.
8:7–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang L, Zhou F, Zheng D, Wang D, Li X,
Zhao C and Huang X: FGF/FGFR signaling: From lung development to
respiratory diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 62:94–104. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ghanem M, Archer G, Crestani B and
Mailleux AA: The endocrine FGFs axis: A systemic anti-fibrotic
response that could prevent pulmonary fibrogenesis? Pharmacol Ther.
259:1086692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang X, Zhou L, Ye S, Liu S, Chen L, Cheng
Z, Huang Y, Wang B, Pan M, Wang D, et al: rFGF4 alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the
TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 117:1099232023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Ji J, Zheng S, Wei A, Li D, Shi B,
Han X and Chen X: Senescent lung-resident mesenchymal stem cells
drive pulmonary fibrogenesis through FGF-4/FOXM1 axis. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 15:3092024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sundaram SM, Lenin RR and Janardhanan R:
FGF4 alleviates hyperglycemia in diabetes and obesity conditions.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 34:583–585. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baumgartner-Parzer SM, Wagner L,
Pettermann M, Grillari J, Gessl A and Waldhäusl W:
High-glucose-triggered apoptosis in cultured endothelial cells.
Diabetes. 44:1323–1327. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Blake R and Trounce IA: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and complications associated with diabetes. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1840:1404–1412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yao K, Zhang WW, Yao L, Yang S, Nie W and
Huang F: Carvedilol promotes mitochondrial biogenesis by regulating
the PGC-1/TFAM pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
(HUVECs). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 470:961–966. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khateeb J, Fuchs E and Khamaisi M:
Diabetes and lung disease: An underestimated relationship. Rev
Diabet Stud. 15:1–15. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Xiong XQ, Wang WT, Wang LR, Jin LD and Lin
LN: Diabetes increases inflammation and lung injury associated with
protective ventilation strategy in mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
13:280–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lontchi-Yimagou E, Sobngwi E, Matsha TE
and Kengne AP: Diabetes mellitus and inflammation. Curr Diab Rep.
13:435–444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Forgiarini LA Jr, Kretzmann NA, Porawski
M, Dias AS and Marroni NA: Experimental diabetes mellitus:
Oxidative stress and changes in lung structure. J Bras Pneumol.
35:788–791. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shimizu M and Sato R: Endocrine fibroblast
growth factors in relation to stress signaling. Cells. 11:5052022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Xue Q, Miao L and Cai L: Pulmonary
fibrosis: A possible diabetic complication. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
27:311–317. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: Process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim J, Kim HS and Chung JH: Molecular
mechanisms of mitochondrial DNA release and activation of the
cGAS-STING pathway. Exp Mol Med. 55:510–519. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiménez-Loygorri JI, Villarejo-Zori B,
Viedma-Poyatos Á, Zapata-Muñoz J, Benítez-Fernández R, Frutos-Lisón
MD, Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC, Area-Gómez E, Gomez-Duran A and
Boya P: Mitophagy curtails cytosolic mtDNA-dependent activation of
cGAS/STING inflammation during aging. Nat Commun. 15:8302024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|