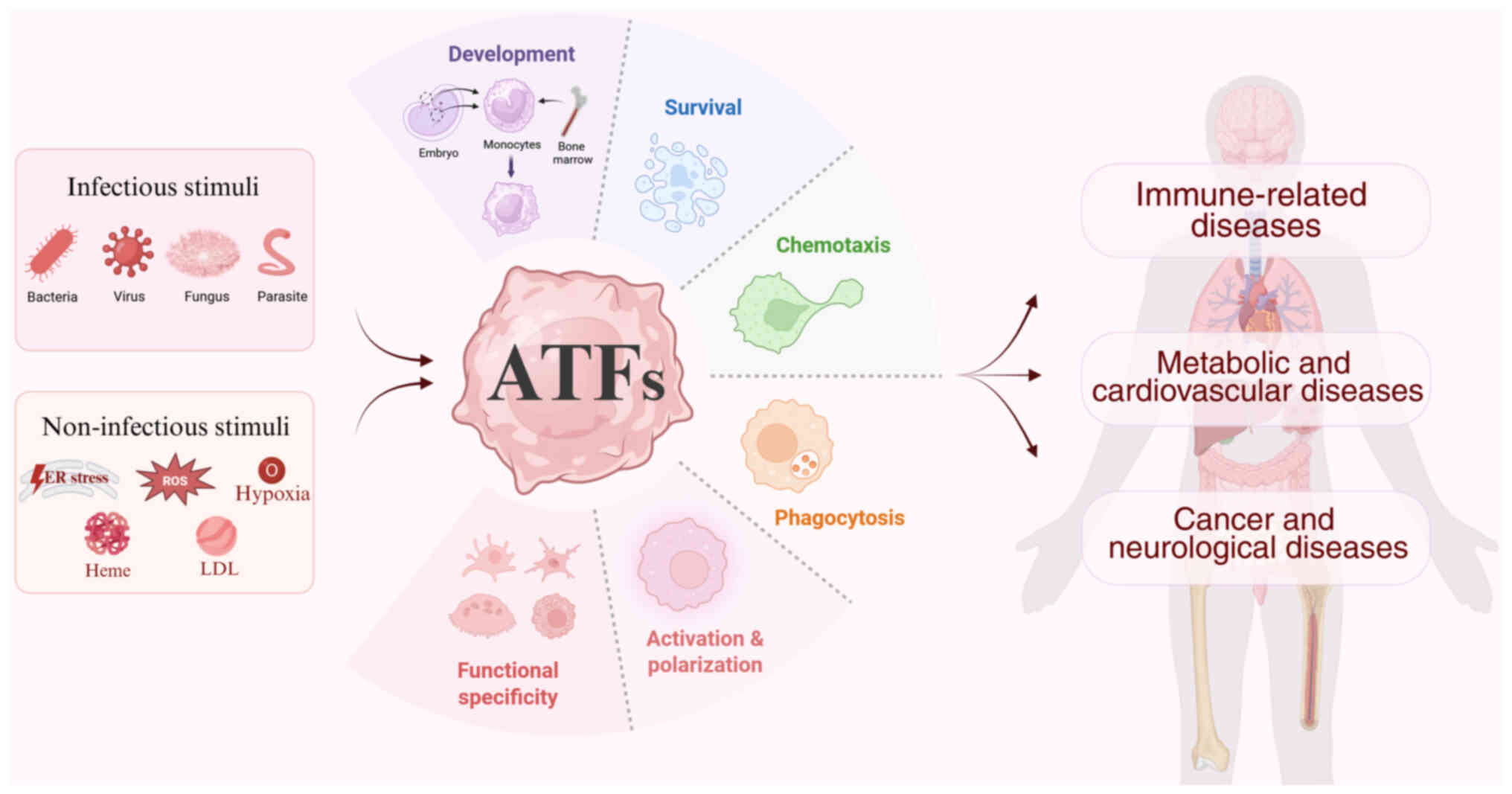
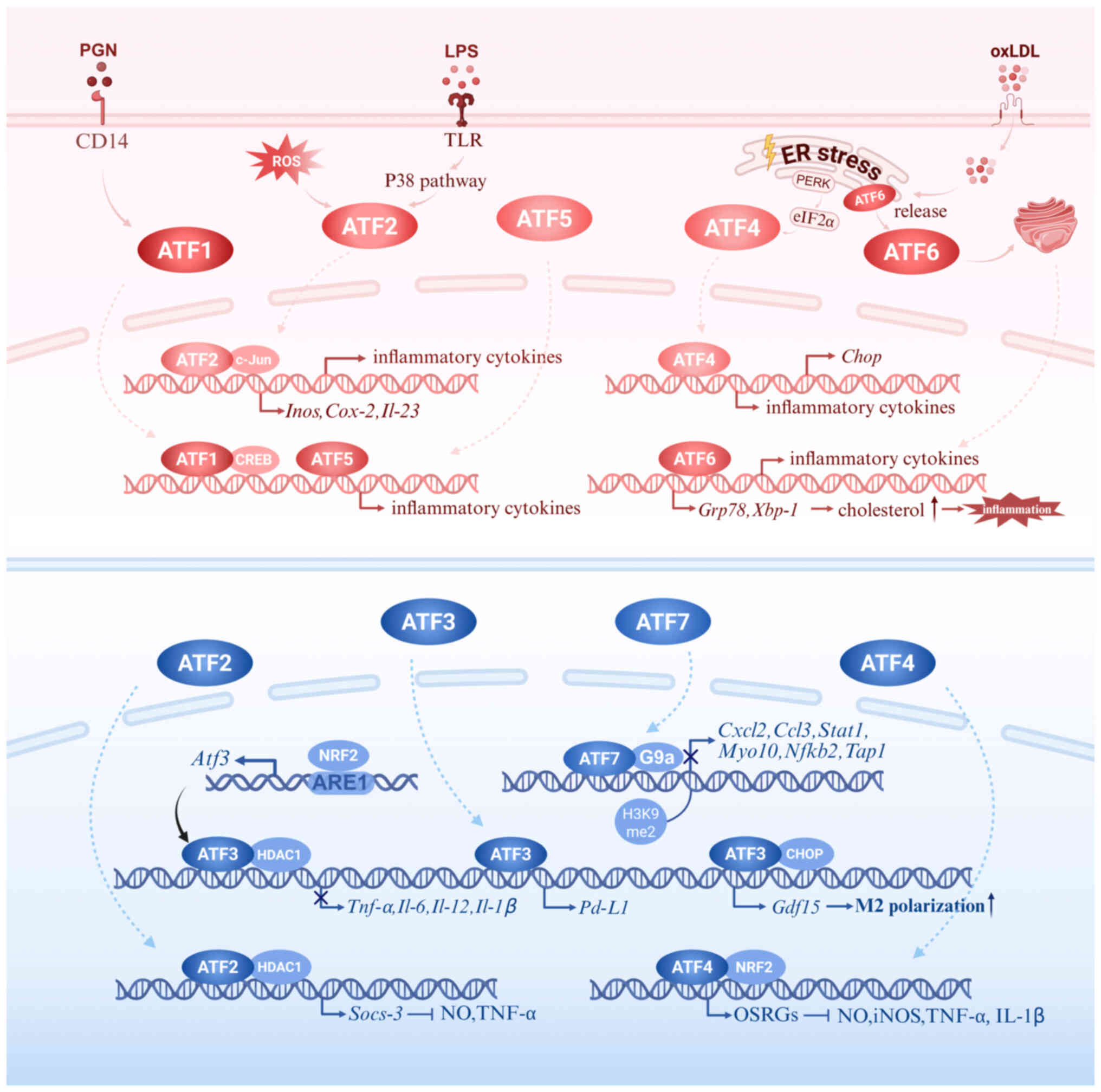
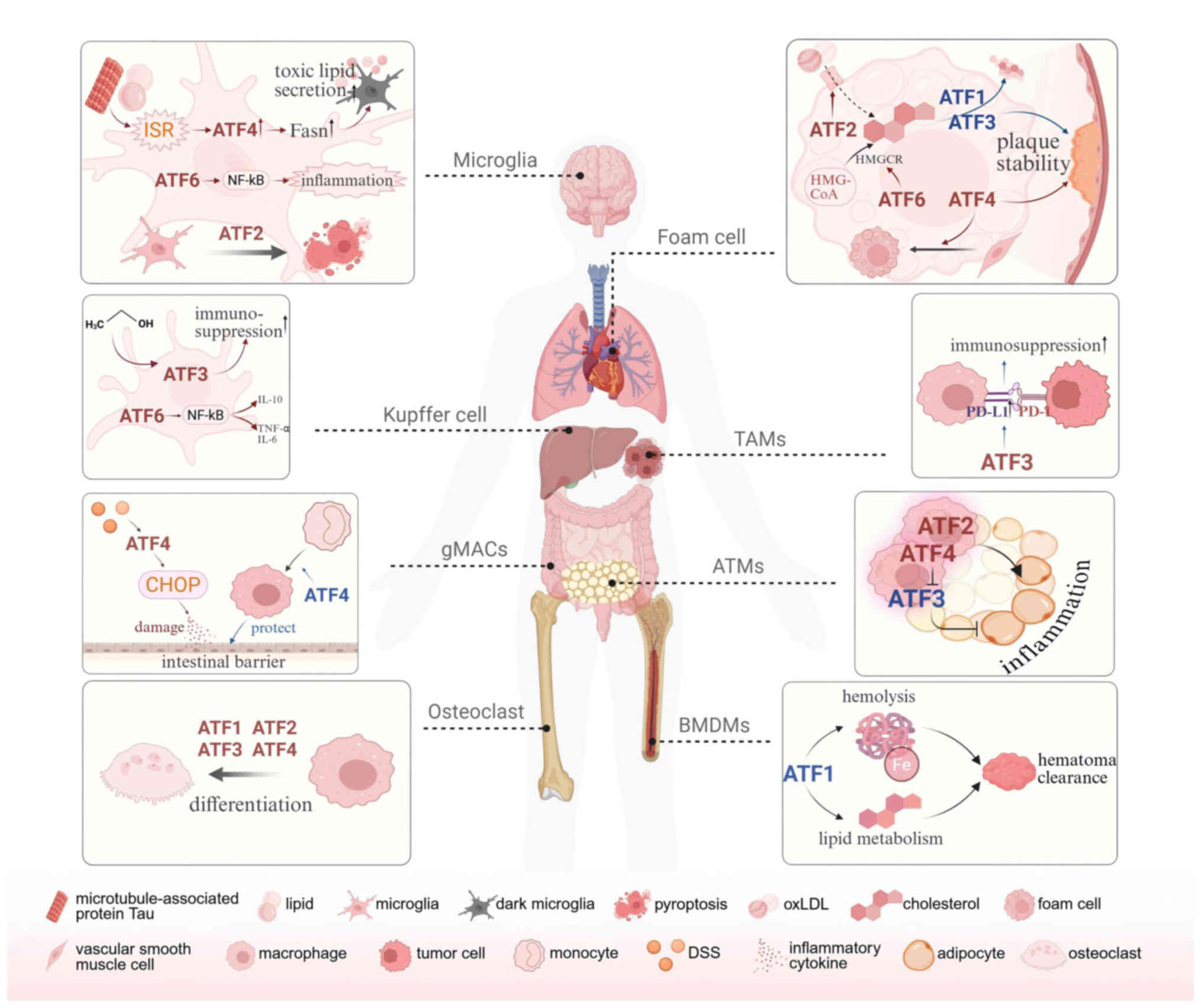
|
1
|
Chen S, Saeed AFUH, Liu Q, Jiang Q, Xu H,
Xiao GG, Rao L and Duo Y: Macrophages in immunoregulation and
therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:2072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mass E, Ballesteros I, Farlik M,
Halbritter F, Günther P, Crozet L, Jacome-Galarza CE, Händler K,
Klughammer J, Kobayashi Y, et al: Specification of tissue-resident
macrophages during organogenesis. Science. 353:aaf42382016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuznetsova T, Prange KHM, Glass CK and de
Winther MPJ: Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of
macrophages in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 17:216–228. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Ajami B, Bennett JL, Krieger C, Tetzlaff W
and Rossi FM: Local self-renewal can sustain CNS microglia
maintenance and function throughout adult life. Nat Neurosci.
10:1538–1543. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bian Z, Gong Y, Huang T, Lee CZW, Bian L,
Bai Z, Shi H, Zeng Y, Liu C, He J, et al: Deciphering human
macrophage development at single-cell resolution. Nature.
582:571–576. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gomez Perdiguero E, Klapproth K, Schulz C,
Busch K, Azzoni E, Crozet L, Garner H, Trouillet C, de Bruijn MF,
Geissmann F and Rodewald HR: Tissue-resident macrophages originate
from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature.
518:547–551. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Guan F, Wang R, Yi Z, Luo P, Liu W, Xie Y,
Liu Z, Xia Z, Zhang H and Cheng Q: Tissue macrophages: Origin,
heterogenity, biological functions, diseases and therapeutic
targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 10:932025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hashimoto D, Chow A, Noizat C, Teo P,
Beasley MB, Leboeuf M, Becker CD, See P, Price J, Lucas D, et al:
Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult
life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes.
Immunity. 38:792–804. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosmus DD, Koch J, Hausmann A, Chiot A,
Arnhold F, Masuda T, Kierdorf K, Hansen SM, Kuhrt H, Fröba J, et
al: Redefining the ontogeny of hyalocytes as yolk sac-derived
tissue-resident macrophages of the vitreous body. J
Neuroinflammation. 21:1682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Masuda T, Amann L, Monaco G, Sankowski R,
Staszewski O, Krueger M, Del Gaudio F, He L, Paterson N, Nent E, et
al: Specification of CNS macrophage subsets occurs postnatally in
defined niches. Nature. 604:740–748. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kazankov K, Jorgensen SMD, Thomsen KL,
Møller HJ, Vilstrup H, George J, Schuppan D and Grønbæk H: The role
of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:145–159. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Appios A, Davies J, Sirvent S, Henderson
S, Trzebanski S, Schroth J, Law ML, Carvalho IB, Pinto MM, Carvalho
C, et al: Convergent evolution of monocyte differentiation in adult
skin instructs Langerhans cell identity. Sci Immunol.
9:eadp03442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hassnain Waqas SF, Noble A, Hoang AC,
Ampem G, Popp M, Strauß S, Guille M and Röszer T: Adipose tissue
macrophages develop from bone marrow-independent progenitors in
Xenopus laevis and mouse. J Leukoc Biol. 102:845–855. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Perdiguero EG and Geissmann F: The
development and maintenance of resident macrophages. Nat Immunol.
17:2–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Sakai M, Troutman TD, Seidman JS, Ouyang
Z, Spann NJ, Abe Y, Ego KM, Bruni CM, Deng Z, Schlachetzki JCM, et
al: Liver-derived signals sequentially reprogram myeloid enhancers
to initiate and maintain kupffer cell identity. Immunity.
51:655–670 e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yona S, Kim KW, Wolf Y, Mildner A, Varol
D, Breker M, Strauss-Ayali D, Viukov S, Guilliams M, Misharin A, et
al: Fate mapping reveals origins and dynamics of monocytes and
tissue macrophages under homeostasis. Immunity. 38:79–91. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TA: Protective and
pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:723–737. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Martinez FO and Gordon S: The M1 and M2
paradigm of macrophage activation: time for reassessment.
F1000Prime Rep. 6:132014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mills CD: Anatomy of a discovery: m1 and
m2 macrophages. Front Immunol. 6:2122015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ
and Hill AM: M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J
Immunol. 164:6166–6173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bosco MC: Macrophage polarization:
Reaching across the aisle? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 143:1348–1350.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Locati M, Curtale G and Mantovani A:
Diversity, Mechanisms, and Significance of Macrophage Plasticity.
Annu Rev Pathol. 15:123–147. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ivashkiv LB: Epigenetic regulation of
macrophage polarization and function. Trends Immunol. 34:216–223.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dong T, Chen X, Xu H, Song Y, Wang H, Gao
Y, Wang J, Du R, Lou H and Dong T: Mitochondrial metabolism
mediated macrophage polarization in chronic lung diseases.
Pharmacol Ther. 239:1082082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gordon S and Martinez FO: Alternative
activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity.
32:593–604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Colin S, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G and Staels B:
Macrophage phenotypes in atherosclerosis. Immunol Rev. 262:153–166.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ruytinx P, Proost P, Van Damme J and
Struyf S: Chemokine-induced macrophage polarization in inflammatory
conditions. Front Immunol. 9:19302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xue J, Schmidt SV, Sander J, Draffehn A,
Krebs W, Quester I, De Nardo D, Gohel TD, Emde M, Schmidleithner L,
et al: Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum
model of human macrophage activation. Immunity. 40:274–288. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yan L, Wang J, Cai X, Liou YC, Shen HM,
Hao J, Huang C, Luo G and He W: Macrophage plasticity: Signaling
pathways, tissue repair, and regeneration. MedComm (2020).
5:e6582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen X, Tang J, Shuai W, Meng J, Feng J
and Han Z: Macrophage polarization and its role in the pathogenesis
of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflamm
Res. 69:883–895. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen R, Zhang H, Tang B, Luo Y, Yang Y,
Zhong X, Chen S, Xu X, Huang S and Liu C: Macrophages in
cardiovascular diseases: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic
targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:1302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Frangogiannis NG: Cardiac fibrosis: Cell
biological mechanisms, molecular pathways and therapeutic
opportunities. Mol Aspects Med. 65:70–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hou P, Fang J, Liu Z, Shi Y, Agostini M,
Bernassola F, Bove P, Candi E, Rovella V, Sica G, et al: Macrophage
polarization and metabolism in atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis.
14:6912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lopez B, Ravassa S, Moreno MU, José GS,
Beaumont J, González A and Díez J: Diffuse myocardial fibrosis:
Mechanisms, diagnosis and therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Cardiol.
18:479–498. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moore KJ and Tabas I: Macrophages in the
pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell. 145:341–355. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Xin W, Hu X, Wang H, Ye X, Xu C,
Nan Y, Wu Z, Ju D and Fan J: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling
ameliorates foam cell formation by promoting autophagy in early
atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis. 14:7402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Byles V, Covarrubias AJ, Ben-Sahra I,
Lamming DW, Sabatini DM, Manning BD and Horng T: The TSC-mTOR
pathway regulates macrophage polarization. Nat Commun. 4:28342013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Castoldi A, Naffah de Souza C, Camara NO
and Moraes-Vieira PM: The macrophage switch in obesity development.
Front Immunol. 6:6372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chawla A, Nguyen KD and Goh YP:
Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat Rev
Immunol. 11:738–749. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Duan H, Jing L, Xiang J, Ju C, Wu Z, Liu
J, Ma X, Chen X, Liu Z, Feng J and Yan X: CD146 Associates with
Gp130 to Control a macrophage pro-inflammatory program that
regulates the metabolic response to obesity. Adv Sci (Weinh).
9:e21037192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang H, Westerterp M, Wang C, Zhu Y and
Ai D: Macrophage mTORC1 disruption reduces inflammation and insulin
resistance in obese mice. Diabetologia. 57:2393–2404. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lu X, Kong X, Wu H, Hao J, Li S, Gu Z,
Zeng X, Shen Y, Wang S, Chen J, et al: UBE2M-mediated neddylation
of TRIM21 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic
disorders. Cell Metab. 35:1390–1405 e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL and Saltiel AR:
Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage
polarization. J Clin Invest. 117:175–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lumeng CN, Deyoung SM, Bodzin JL and
Saltiel AR: Increased inflammatory properties of adipose tissue
macrophages recruited during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes.
56:16–23. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cassetta L and Pollard JW: Targeting
macrophages: Therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
17:887–904. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
De Palma M, Biziato D and Petrova TV:
Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 17:457–474. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB and Ley
K: Macrophage polarization: Different gene signatures in M1(LPS+)
vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. alternatively activated
macrophages. Front Immunol. 10:10842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pombo Antunes AR, Scheyltjens I, Lodi F,
Messiaen J, Antoranz A, Duerinck J, Kancheva D, Martens L, De
Vlaminck K, Van Hove H, et al: Single-cell profiling of myeloid
cells in glioblastoma across species and disease stage reveals
macrophage competition and specialization. Nat Neurosci.
24:595–610. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ruffell B, Chang-Strachan D, Chan V,
Rosenbusch A, Ho CM, Pryer N, Daniel D, Hwang ES, Rugo HS and
Coussens LM: Macrophage IL-10 blocks CD8+ T cell-dependent
responses to chemotherapy by suppressing IL-12 expression in
intratumoral dendritic cells. Cancer Cell. 26:623–637. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Inoue K, Qin Y, Xia Y, Han J, Yuan R, Sun
J, Xu R, Jiang JX, Greenblatt MB and Zhao B: Bone marrow
Adipoq-lineage progenitors are a major cellular source of M-CSF
that dominates bone marrow macrophage development,
osteoclastogenesis, and bone mass. Elife. 12:e821182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kulkarni A, Chandrasekar V, Natarajan SK,
Ramesh A, Pandey P, Nirgud J, Bhatnagar H, Ashok D, Ajay AK and
Sengupta S: A designer self-assembled supramolecule amplifies
macrophage immune responses against aggressive cancer. Nat Biomed
Eng. 2:589–599. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Sathi GA, Farahat M, Hara ES, Taketa H,
Nagatsuka H, Kuboki T and Matsumoto T: MCSF orchestrates branching
morphogenesis in developing submandibular gland tissue. J Cell Sci.
130:1559–1569. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Deng Y, Wang H, Liu X, Yuan H, Xu J, de
Thé H, Zhou J and Zhu J: Zbtb14 regulates monocyte and macrophage
development through inhibiting pu.1 expression in zebrafish. Elife.
11:e807602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Solomon LA, Podder S, He J,
Jackson-Chornenki NL, Gibson K, Ziliotto RG, Rhee J and DeKoter RP:
Coordination of myeloid differentiation with reduced cell cycle
progression by PU.1 induction of MicroRNAs targeting cell cycle
regulators and lipid anabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 37:e00013–17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tu J, Chen W, Fang Y, Han D, Chen Y, Jiang
H, Tan X, Xu Z, Wu X, Wang H, et al: PU.1 promotes development of
rheumatoid arthritis via repressing FLT3 in macrophages and
fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 82:198–211. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Xiao X, Li JX, Li HH and Teng F: ACE2
alleviates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy through inhibiting M1
macrophage via NF-ĸB/STAT1 signals. Cell Biol Toxicol. 40:822024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Jin C, Zhang F, Luo H, Li B, Jiang X,
Pirozzi CJ, Liang C and Zhang M: The CCL5/CCR5/SHP2 axis sustains
Stat1 phosphorylation and activates NF-ĸB signaling promoting M1
macrophage polarization and exacerbating chronic prostatic
inflammation. Cell Commun Signal. 22:5842024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wu Q, Li B, Li J and Sun S, Yuan J and Sun
S: Cancer-associated adipocytes as immunomodulators in cancer.
Biomark Res. 9:22021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gu L, Larson Casey JL, Andrabi SA, Lee JH,
Meza-Perez S, Randall TD and Carter AB: Mitochondrial calcium
uniporter regulates PGC-1α expression to mediate metabolic
reprogramming in pulmonary fibrosis. Redox Biol. 26:1013072019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Yu T, Gan S, Zhu Q, Dai D, Li N, Wang H,
Chen X, Hou D, Wang Y, Pan Q, et al: Modulation of M2 macrophage
polarization by the crosstalk between Stat6 and Trim24. Nat Commun.
10:43532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Deng C, Huo M, Chu H, Zhuang X, Deng G, Li
W, Wei H, Zeng L, He Y, Liu H, et al: Exosome circATP8A1 induces
macrophage M2 polarization by regulating the miR-1-3p/STAT6 axis to
promote gastric cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 23:492024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Choi JY, Seok HJ, Lee DH, Lee E, Kim TJ,
Bae S, Shin I and Bae IH: Tumor-derived miR-6794-5p enhances cancer
growth by promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Cell Commun Signal.
22:1902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lee KA, Hai TY, SivaRaman L, Thimmappaya
B, Hurst HC, Jones NC and Green MR: A cellular protein, activating
transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple
E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
84:8355–8359. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hai T and Hartman MG: The molecular
biology and nomenclature of the activating transcription
factor/cAMP responsive element binding family of transcription
factors: Activating transcription factor proteins and homeostasis.
Gene. 273:1–11. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Vallejo M, Ron D, Miller CP and Habener
JF: C/ATF, a member of the activating transcription factor family
of DNA-binding proteins, dimerizes with CAAT/enhancer-binding
proteins and directs their binding to cAMP response elements. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:4679–4683. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Montminy MR and Bilezikjian LM: Binding of
a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the
somatostatin gene. Nature. 328:175–178. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Moller E, Praz V, Rajendran S, Dong R,
Cauderay A, Xing YH, Lee L, Fusco C, Broye LC, Cironi L, et al:
EWSR1-ATF1 dependent 3D connectivity regulates oncogenic and
differentiation programs in clear cell sarcoma. Nat Commun.
13:22672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hai TW, Liu F, Allegretto EA, Karin M and
Green MR: A family of immunologically related transcription factors
that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev.
2:1216–1226. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Foulkes NS, Borrelli E and Sassone-Corsi
P: CREM gene: Use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates
multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell.
64:739–749. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu H, Deng X, Shyu YJ, Li JJ, Taparowsky
EJ and Hu CD: Mutual regulation of c-Jun and ATF2 by
transcriptional activation and subcellular localization. EMBO J.
25:1058–1069. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
De Cesare D, Vallone D, Caracciolo A,
Sassone-Corsi P, Nerlov C and Verde P: Heterodimerization of c-Jun
with ATF-2 and c-Fos is required for positive and negative
regulation of the human urokinase enhancer. Oncogene. 11:365–376.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sun MH, Jiang WJ, Li XH, Lee SH, Heo G,
Zhou D, Choi JS, Kim KS, Lv W and Cui XS: ATF7-dependent epigenetic
changes induced by high temperature during early porcine embryonic
development. Cell Prolif. 56:e133522023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Liu Y, Maekawa T, Yoshida K, Muratani M,
Chatton B and Ishii S: The transcription factor ATF7 controls
adipocyte differentiation and thermogenic gene programming.
iScience. 13:98–112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Diring J, Camuzeaux B, Donzeau M, Vigneron
M, Rosa-Calatrava M, Kedinger C and Chatton B: A cytoplasmic
negative regulator isoform of ATF7 impairs ATF7 and ATF2
phosphorylation and transcriptional activity. PLoS One.
6:e233512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Tsujino H, Kondo E, Fukuoka T, Dai Y,
Tokunaga A, Miki K, Yonenobu K, Ochi T and Noguchi K: Activating
transcription factor 3 (ATF3) induction by axotomy in sensory and
moto-neurons: A novel neuronal marker of nerve injury. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 15:170–182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rodriguez-Martinez JA, Reinke AW,
Bhimsaria D, Keating AE and Ansari AZ: Combinatorial bZIP dimers
display complex DNA-binding specificity landscapes. Elife.
6:e192722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Tsushima H, Okazaki K, Ishihara K,
Ushijima T and Iwamoto Y: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β promotes
receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa-B ligand (RANKL)
expression and osteoclast formation in the synovium in rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:312015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Huggins CJ, Mayekar MK, Martin N, Saylor
KL, Gonit M, Jailwala P, Kasoji M, Haines DC, Quiñones OA and
Johnson PF: C/EBPү is a critical regulator of cellular stress
response networks through heterodimerization with ATF4. Mol Cell
Biol. 36:693–713. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Dias-Teixeira KL, Calegari-Silva TC,
Medina JM, Vivarini ÁC, Cavalcanti Á, Teteo N, Santana AKM, Real F,
Gomes CM, Pereira RMS, et al: Emerging role for the
PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4 in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Sci Rep.
7:170742017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Newman JR and Keating AE: Comprehensive
identification of human bZIP interactions with coiled-coil arrays.
Science. 300:2097–2101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Glembotski CC, Arrieta A, Blackwood EA and
Stauffer WT: ATF6 as a nodal regulator of proteostasis in the
heart. Front Physiol. 11:2672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yoshida H, Okada T, Haze K, Yanagi H, Yura
T, Negishi M and Mori K: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
formation of transcription factor complex ERSF including NF-Y (CBF)
and activating transcription factors 6alpha and 6beta that
activates the mammalian unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol.
21:1239–1248. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yamamoto K, Sato T, Matsui T, Sato M,
Okada T, Yoshida H, Harada A and Mori K: Transcriptional induction
of mammalian ER quality control proteins is mediated by single or
combined action of ATF6alpha and XBP1. Dev Cell. 13:365–376. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hao Q, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Dong Z, Hu T and
Chen P: Targeting overexpressed activating transcription factor 1
(ATF1) inhibits proliferation and migration and enhances
sensitivity to paclitaxel in esophageal cancer cells. Med Sci Monit
Basic Res. 23:304–312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Meijer BJ, Giugliano FP, Baan B, van der
Meer JHM, Meisner S, van Roest M, Koelink PJ, de Boer RJ, Jones N,
Breitwieser W, et al: ATF2 and ATF7 are critical mediators of
intestinal epithelial repair. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol.
10:23–42. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Maekawa T, Kim S, Nakai D, Takagi T, Ogura
H, Yamada K, Chatton B and Ishii S: Social isolation stress induces
ATF-7 phosphorylation and impairs silencing of the 5-HT 5B receptor
gene. EMBO J. 29:196–208. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Gozdecka M and Breitwieser W: The roles of
ATF2 (activating transcription factor 2) in tumorigenesis. Biochem
Soc Trans. 40:230–234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chen M, Liu Y, Yang Y, Qiu Y, Wang Z, Li X
and Zhang W: Emerging roles of activating transcription factor
(ATF) family members in tumourigenesis and immunity: Implications
in cancer immunotherapy. Genes Dis. 9:981–999. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Yan C and Boyd DD: ATF3 regulates the
stability of p53: A link to cancer. Cell Cycle. 5:926–929. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Hai T, Wolfgang CD, Marsee DK, Allen AE
and Sivaprasad U: ATF3 and stress responses. Gene Expr. 7:321–335.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Giannoudis A, Malki MI, Rudraraju B,
Mohhamed H, Menon S, Liloglou T, Ali S, Carroll JS and Palmieri C:
Activating transcription factor-2 (ATF2) is a key determinant of
resistance to endocrine treatment in an in vitro model of breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 22:1262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Fawcett TW, Martindale JL, Guyton KZ, Hai
T and Holbrook NJ: Complexes containing activating transcription
factor (ATF)/cAMP-responsive-element-binding protein (CREB)
interact with the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP)-ATF
composite site to regulate Gadd153 expression during the stress
response. Biochem J. 339:135–141. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Shahriari-Felordi M, Alikhani HK,
Hashemian SR, Hassan M and Vosough M: Mini review ATF4 and GRP78 as
novel molecular targets in ER-Stress modulation for critical
COVID-19 patients. Mol Biol Rep. 49:1545–1549. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yoshida H, Okada T, Haze K, Yanagi H, Yura
T, Negishi M and Mori K: ATF6 activated by proteolysis binds in the
presence of NF-Y (CBF) directly to the cis-acting element
responsible for the mammalian unfolded protein response. Mol Cell
Biol. 20:6755–6767. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Thuerauf DJ, Morrison LE, Hoover H and
Glembotski CC: Coordination of ATF6-mediated transcription and ATF6
degradation by a domain that is shared with the viral transcription
factor, VP16. J Biol Chem. 277:20734–20739. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Thuerauf DJ, Arnold ND, Zechner D, Hanford
DS, DeMartin KM, McDonough PM, Prywes R and Glembotski CC: p38
Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates the transcriptional
induction of the atrial natriuretic factor gene through a serum
response element. A potential role for the transcription factor
ATF6. J Biol Chem. 273:20636–20643. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Luo R, Lu JF, Hu Q and Maity SN: CBF/NF-Y
controls endoplasmic reticulum stress induced transcription through
recruitment of both ATF6(N) and TBP. J Cell Biochem. 104:1708–1723.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Kokame K, Kato H and Miyata T:
Identification of ERSE-II, a new cis-acting element responsible for
the ATF6-dependent mammalian unfolded protein response. J Biol
Chem. 276:9199–9205. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Haze K, Yoshida H, Yanagi H, Yura T and
Mori K: Mammalian transcription factor ATF6 is synthesized as a
transmembrane protein and activated by proteolysis in response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Biol Cell. 10:3787–3799. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Niwano K, Arai M, Tomaru K, Uchiyama T,
Ohyama Y and Kurabayashi M: Transcriptional stimulation of the eNOS
gene by the stable prostacyclin analogue beraprost is mediated
through cAMP-responsive element in vascular endothelial cells:
Close link between PGI2 signal and NO pathways. Circ Res.
93:523–530. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Xiao X, Chen M, Sang Y, Xue J, Jiang K,
Chen Y, Zhang L, Yu S, Lv W, Li Y, et al: Methylation-mediated
silencing of ATF3 promotes thyroid cancer progression by regulating
prognostic genes in the MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways. Thyroid.
33:1441–1454. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zhang WC, Du LJ, Zheng XJ, Chen XQ, Shi C,
Chen BY, Sun XN, Li C, Zhang YY, Liu Y, et al: Elevated sodium
chloride drives type I interferon signaling in macrophages and
increases antiviral resistance. J Biol Chem. 293:1030–1039. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
106
|
Ranjan K, Hedl M, Sinha S, Zhang X and
Abraham C: Ubiquitination of ATF6 by disease-associated RNF186
promotes the innate receptor-induced unfolded protein response. J
Clin Invest. 131:e1454722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Udompong S, Mankhong S, Jaratjaroonphong J
and Srisook K: Involvement of p38 MAPK and ATF-2 signaling pathway
in anti-inflammatory effect of a novel compound
bis[(5-methyl)2-furyl] (4-nitrophenyl)methane on
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol.
50:6–13. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Herrema H, Guan D, Choi JW, Feng X,
Salazar Hernandez MA, Faruk F, Auen T, Boudett E, Tao R, Chun H and
Ozcan U: FKBP11 rewires UPR signaling to promote glucose
homeostasis in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Cell Metab.
34:1004–1022 e8. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhou S, Zhong Z, Huang P, Xiang B, Li X,
Dong H, Zhang G, Wu Y and Li P: IL-6/STAT3 induced neuron apoptosis
in hypoxia by downregulating ATF6 expression. Front Physiol.
12:7299252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Kwon JW, Kwon HK, Shin HJ, Choi YM, Anwar
MA and Choi S: Activating transcription factor 3 represses
inflammatory responses by binding to the p65 subunit of NF-ĸB. Sci
Rep. 5:144702015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Cui A, Ding D and Li Y: Regulation of
hepatic metabolism and cell growth by the ATF/CREB family of
transcription factors. Diabetes. 70:653–664. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Takii R, Fujimoto M, Tan K, Takaki E,
Hayashida N, Nakato R, Shirahige K and akai A: ATF1 modulates the
heat shock response by regulating the stress-inducible heat shock
factor 1 transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 35:11–25. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
113
|
Karanam B, Wang L, Wang D, Liu X,
Marmorstein R, Cotter R and Cole PA: Multiple roles for acetylation
in the interaction of p300 HAT with ATF-2. Biochemistry.
46:8207–8216. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Nguyen HCB, Adlanmerini M, Hauck AK and
Lazar MA: Dichotomous engagement of HDAC3 activity governs
inflammatory responses. Nature. 584:286–290. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gilchrist M, Thorsson V, Li B, Rust AG,
Korb M, Roach JC, Kennedy K, Hai T, Bolouri H and Aderem A: Systems
biology approaches identify ATF3 as a negative regulator of
Toll-like receptor 4. Nature. 441:173–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Chen BP, Liang G, Whelan J and Hai T: ATF3
and ATF3 delta Zip. Transcriptional repression versus activation by
alternatively spliced isoforms. J Biol Chem. 269:15819–15826. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Sela D, Chen L, Martin-Brown S, Washburn
MP, Florens L, Conaway JW and Conaway RC: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress-responsive transcription factor ATF6alpha directs
recruitment of the mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription and
multiple histone acetyltransferase complexes. J Biol Chem.
287:23035–23045. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Hirose N, Maekawa T, Shinagawa T and Ishii
S: ATF-2 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced transcription in
macrophage cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 385:72–77. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Yoshida K, Maekawa T, Zhu Y,
Renard-Guillet C, Chatton B, Inoue K, Uchiyama T, Ishibashi K,
Yamada T, Ohno N, et al: The transcription factor ATF7 mediates
lipopolysaccharide-induced epigenetic changes in macrophages
involved in innate immunological memory. Nat Immunol. 16:1034–1043.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Baumeister P, Luo S, Skarnes WC, Sui G,
Seto E, Shi Y and Lee AS: Endoplasmic reticulum stress induction of
the Grp78/BiP promoter: Activating mechanisms mediated by YY1 and
its interactive chromatin modifiers. Mol Cell Biol. 25:4529–4540.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ma J, Liu Y, Valladolid-Acebes I,
Recio-López P, Peng G, Li J, Berggren PO, Juntti-Berggren L and
Tong N: ATF5 is a regulator of ER stress and β-cell apoptosis in
different mouse models of genetic- and diet-induced obesity and
diabetes mellitus. Cell Signal. 102:1105352023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Raines LN, Zhao H, Wang Y, Chen HY,
Gallart-Ayala H, Hsueh PC, Cao W, Koh Y, Alamonte-Loya A, Liu PS,
et al: PERK is a critical metabolic hub for immunosuppressive
function in macrophages. Nat Immunol. 23:431–445. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
Wang Y, Zhang X, Fu Y, Fu D, Zhen D, Xing
A, Chen Y, Gong G and Wei C: 1, 8-cineole protects against
ISO-induced heart failure by inhibiting oxidative stress and ER
stress in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 910:1744722021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Hu S, Li R, Gong D, Hu P, Xu J, Ai Y, Zhao
X, Hu C, Xu M, Liu C, et al: Atf3-mediated metabolic reprogramming
in hepatic macrophage orchestrates metabolic dysfunction-associated
steatohepatitis. Sci Adv. 10:eado31412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Brocard M, Lu J, Hall B, Borah K,
Moller-Levet C, Georgana I, Sorgeloos F, Beste DJV, Goodfellow IG
and Locker N: Murine norovirus infection results in
anti-inflammatory response downstream of amino acid depletion in
macrophages. J Virol. 95:e01134212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Huang Y, Ge MX, Li YH, Li JL, Yu Q, Xiao
FH, Ao HS, Yang LQ, Li J, He Y and Kong QP: Longevity-associated
transcription factor ATF7 promotes healthspan by suppressing
cellular senescence and systematic inflammation. Aging Dis.
14:1374–1389. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Liu H, Kuang X, Zhang Y, Ye Y, Li J, Liang
L, Xie Z, Weng L, Guo J, Li H, et al: ADORA1 inhibition promotes
tumor immune evasion by regulating the ATF3-PD-L1 axis. Cancer
Cell. 37:324–339 e8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Liu T, Wen Z, Shao L, Cui Y, Tang X, Miao
H, Shi J, Jiang L, Feng S, Zhao Y, et al: ATF4 knockdown in
macrophage impairs glycolysis and mediates immune tolerance by
targeting HK2 and HIF-1alpha ubiquitination in sepsis. Clin
Immunol. 254:1096982023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Zhang Q, Liu G, Liu R, Liu J, Zeng X, Ren
D, Yan X and Yuan X: Dual role of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-ATF-6 activation in autophagy and apoptosis induced by
cyclic stretch in myoblast. Apoptosis. 28:796–809. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Dai W, Hong L, Xiao W, Zhang L, Sha W, Yu
Z, Liu X, Liu S, Xiao Y, Yang P, et al: The ATF2/miR-3913-5p/CREB5
axis is involved in the cell proliferation and metastasis of
colorectal cancer. Commun Biol. 6:10262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Wang B, Zhang J, Liu X, Chai Q, Lu X, Yao
X, Yang Z, Sun L, Johnson SF, Schwartz RC and Zheng YH: Protein
disulfide isomerases (PDIs) negatively regulate ebolavirus
structural glycoprotein expression in the endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) via the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. Autophagy. 18:2350–2367.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Wen Z, Xiong X, Chen D, Shao L, Tang X,
Shen X, Zhang S, Huang S, Zhang L, Chen Y, et al: Activating
transcription factor 4 protects mice against sepsis-induced
intestinal injury by regulating gut-resident macrophages
differentiation. Chin Med J (Engl). 135:2585–2595. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Rajabalee N, Siushansian H, Weerapura M,
Berton S, Berbatovci F, Hooks B, Geoffrion M, Yang D, Harper ME,
Rayner K, et al: ATF2 orchestrates macrophage differentiation and
activation to promote antibacterial responses. J Leukoc Biol.
114:280–298. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Qin W, Yang H, Liu G, Bai R, Bian Y, Yang
Z and Xiao C: Activating transcription factor 3 is a potential
target and a new biomarker for the prognosis of atherosclerosis.
Hum Cell. 34:49–59. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Nilsson R, Bajic VB, Suzuki H, di Bernardo
D, Björkegren J, Katayama S, Reid JF, Sweet MJ, Gariboldi M,
Carninci P, et al: Transcriptional network dynamics in macrophage
activation. Genomics. 88:133–142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Clement M, Basatemur G, Masters L, Baker
L, Bruneval P, Iwawaki T, Kneilling M, Yamasaki S, Goodall J and
Mallat Z: Necrotic cell sensor clec4e promotes a proatherogenic
macrophage phenotype through activation of the unfolded protein
response. Circulation. 134:1039–1051. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Elbarghati L, Murdoch C and Lewis CE:
Effects of hypoxia on transcription factor expression in human
monocytes and macrophages. Immunobiology. 213:899–908. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Zhao Q, Luo YF, Tian M, Xiao YL, Cai HR
and Li H: Activating transcription factor 3 involved in Pseudomonas
aeruginosa PAO1-induced macrophage senescence. Mol Immunol.
133:122–127. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Li M, Lu H, Wang X, Duan C, Zhu X, Zhang
Y, Ge X, Ji F, Wang X, Su J and Zhang D: Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2)
interacts with activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2) to bridge
glycolysis and pyroptosis in microglia. Mol Immunol. 140:250–266.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Hu Y, Li CS, Li YQ, Liang Y, Cao L and
Chen LA: Perfluorocarbon inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
macrophage inflammatory protein-2 expression and activation of
ATF-2 and c-Jun in A549 pulmonary epithelial cells. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 62:18–24. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Boehlk S, Fessele S, Mojaat A, Miyamoto
NG, Werner T, Nelson EL, Schlöndorff D and Nelson PJ: ATF and Jun
transcription factors, acting through an Ets/CRE promoter module,
mediate lipopolysaccharide inducibility of the chemokine RANTES in
monocytic Mono Mac 6 cells. Eur J Immunol. 30:1102–1112. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Sha H, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Wen Y and Wang Y:
ATF3 promotes migration and M1/M2 polarization of macrophages by
activating tenascin-C via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol Med Rep.
16:3641–3647. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Hu C, Meng X, Huang C, Shen C and Li J:
Frontline Science: ATF3 is responsible for the inhibition of TNF-α
release and the impaired migration of acute ethanol-exposed
monocytes and macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 101:633–642. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Du Y, Ma Z, Zheng J, Huang S, Yang X, Song
Y, Dong D, Shi L and Xu D: ATF3 positively regulates antibacterial
immunity by modulating macrophage killing and migration functions.
Front Immunol. 13:8395022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Mylvaganam S, Freeman SA and Grinstein S:
The cytoskeleton in phagocytosis and macropinocytosis. Curr Biol.
31:R619–R632. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Taka S, Gazouli M, Politis PK, Pappa KI
and Anagnou NP: Transcription factor ATF-3 regulates allele
variation phenotypes of the human SLC11A1 gene. Mol Biol Rep.
40:2263–2271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Middleton JD, Fehlman J, Sivakumar S,
Stover DG and Hai T: Stress-inducible gene Atf3 dictates a
dichotomous macrophage activity in chemotherapy-enhanced lung
colonization. Int J Mol Sci. 22:73562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Xu Y, Li Y, Jadhav K, Pan X, Zhu Y, Hu S,
Chen S, Chen L, Tang Y, Wang HH, et al: Hepatocyte ATF3 protects
against atherosclerosis by regulating HDL and bile acid metabolism.
Nat Metab. 3:59–74. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Raghavan S, Singh NK, Gali S, Mani AM and
Rao GN: Protein Kinase ctheta via activating transcription factor
2-mediated CD36 expression and foam cell formation of Ly6C(hi)
cells contributes to atherosclerosis. Circulation. 138:2395–2412.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Seneviratne A, Han Y, Wong E, Walter ERH,
Jiang L, Cave L, Long NJ, Carling D, Mason JC, Haskard DO and Boyle
JJ: Hematoma resolution in vivo is directed by activating
transcription factor 1. Circ Res. 127:928–944. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Illouz M, Leclercq LD, Dessenne C, Hatfull
G, Daher W and Kremer L and Guérardel Y: Multiple Mycobacterium
abscessus O-acetyltransferases influence glycopeptidolipid
structure and colony morphotype. J Biol Chem. 299:1049792023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Perez-Arques C, Navarro-Mendoza MI, Murcia
L, Lax C, Martínez-García P, Heitman J, Nicolás FE and Garre V:
Mucor circinelloides Thrives inside the phagosome through an
Atf-Mediated germination pathway. mBio. 10:e02765–18. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Gupta D, Wang Q, Vinson C and Dziarski R:
Bacterial peptidoglycan induces CD14-dependent activation of
transcription factors CREB/ATF and AP-1. J Biol Chem.
274:14012–14020. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Shi R, Wang J, Zhang Z, Leng Y and Chen
AF: ASGR1 promotes liver injury in sepsis by modulating
monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation via NF-ĸB/ATF5 pathway. Life
Sci. 315:1213392023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Abe JI, Ko KA, Kotla S, Wang Y,
Paez-Mayorga J, Shin IJ, Imanishi M, Vu HT, Tao Y, Leiva-Juarez MM,
et al: MAGI1 as a link between endothelial activation and ER stress
drives atherosclerosis. JCI Insight. 4:e1255702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Jin Z, Xu H, Zhao W, Zhang K, Wu S, Shu C,
Zhu L, Wang Y, Wang L, Zhang H and Yan B: Macrophage ATF6
accelerates corticotomy-assisted orthodontic tooth movement through
promoting Tnfα transcription. Int J Oral Sci. 17:282025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Xu X, Lei T, Li W and Ou H: Enhanced
cellular cholesterol efflux by naringenin is mediated through
inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress - ATF6 activity in
macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids.
1864:1472–1482. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Rao J, Yue S, Fu Y, Zhu J, Wang X,
Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW, Lu L and Zhai Y: ATF6 mediates a
pro-inflammatory synergy between ER stress and TLR activation in
the pathogenesis of liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J
Transplant. 14:1552–1561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Wang Q, Zhu X, Li Z, Feng M and Liu X:
ATF6 promotes liver fibrogenesis by regulating macrophage-derived
interleukin-1alpha expression. Cell Immunol. 367:1044012021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Wang J, Cheng W, Wang Z, Xin L and Zhang
W: ATF3 inhibits the inflammation induced by Mycoplasma pneumonia
in vitro and in vivo. Pediatr Pulmonol. 52:1163–1170. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Hoetzenecker W, Echtenacher B, Guenova E,
Hoetzenecker K, Woelbing F, Brück J, Teske A, Valtcheva N, Fuchs K,
Kneilling M, et al: ROS-induced ATF3 causes susceptibility to
secondary infections during sepsis-associated immunosuppression.
Nat Med. 18:128–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Bae YA and Cheon HG: Activating
transcription factor-3 induction is involved in the
anti-inflammatory action of berberine in RAW264.7 murine
macrophages. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 20:415–424. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Saha S, Roy S, Dutta A, Jana K and Ukil A:
Leishmania donovani targets host transcription factor NRF2 to
activate antioxidant enzyme HO-1 and transcriptional repressor ATF3
for establishing infection. Infect Immun. 89:e00764202021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Qian L, Zhao Y, Guo L, Li S and Wu X:
Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting the
expression of TL1A. J Cell Physiol. 232:3727–3734. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Cheng CF and Lin H: Acute kidney injury
and the potential for ATF3-regulated epigenetic therapy. Toxicol
Mech Methods. 21:362–366. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Yu T, Moh SH, Kim SB, Yang Y, Kim E, Lee
YW, Cho CK, Kim KH, Yoo BC, Cho JY and Yoo HS: HangAmDan-B, an
ethnomedicinal herbal mixture, suppresses inflammatory responses by
inhibiting Syk/NF-ĸB and JNK/ATF-2 pathways. J Med Food. 16:56–65.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
166
|
Zhang C, He H, Wang L, Zhang N, Huang H,
Xiong Q, Yan Y, Wu N, Ren H, Han H, et al: Virus-triggered ATP
release limits viral replication through facilitating IFN-β
Production in a P2X7-Dependent manner. J Immunol. 199:1372–1381.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Yu T, Yang Y, Kwak YS, Song GG, Kim MY,
Rhee MH and Cho JY: Ginsenoside Rc from Panax ginseng exerts
anti-inflammatory activity by targeting TANK-binding kinase
1/interferon regulatory factor-3 and p38/ATF-2. J Ginseng Res.
41:127–133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Xu X, Xia J, Zhao S, Wang Q, Ge G, Xu F,
Liu X, Zhang W and Yang Y: Qing-Fei-Pai-Du decoction and wogonoside
exert anti-inflammatory action through down-regulating USP14 to
promote the degradation of activating transcription factor 2. FASEB
J. 35:e218702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Park JB, Peters R, Pham Q and Wang TTY:
Javamide-II Inhibits IL-6 without Significant Impact on TNF-alpha
and IL-1beta in macrophage-like cells. Biomedicines. 8:1382020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Kim SM, Park EJ and Lee HJ: Nuciferine
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses by
inhibiting p38 MAPK/ATF2 signaling pathways. Inflammopharmacology.
30:2373–2383. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Endale M, Kim TH, Kwak YS, Kim NM, Kim SH,
Cho JY, Yun BS and Rhee MH: Torilin inhibits inflammation by
limiting TAK1-mediated MAP kinase and NF-ĸB activation. Mediators
Inflamm. 2017:72509682017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Miyata Y, Fukuhara A, Otsuki M and
Shimomura I: Expression of activating transcription factor 2 in
inflammatory macrophages in obese adipose tissue. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 21:731–736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Hu Y, Gu J, Wang Y, Lin J, Yu H, Yang F,
Wu S, Yin J, Lv H, Ji X and Wang S: Promotion effect of EGCG on the
raised expression of IL-23 through the signaling of
STAT3-BATF2-c-JUN/ATF2. J Agric Food Chem. 69:7898–7909. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Sukhorukov VN, Khotina VA, Bagheri Ekta M,
Ivanova EA, Sobenin IA and Orekhov AN: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
in macrophages: The vicious circle of lipid accumulation and
pro-inflammatory response. Biomedicines. 8:2102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Song C, Chen J, Li X, Yang R, Cao X, Zhou
L, Zhou Y, Ying H, Zhang Q and Sun Y: Limonin ameliorates dextran
sulfate sodium-induced chronic colitis in mice by inhibiting
PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway of ER stress and NF-kappaB signaling. Int
Immunopharmacol. 90:1071612021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Luo JH, Wang FX, Zhao JW, Yang CL, Rong
SJ, Lu WY, Chen QJ, Zhou Q, Xiao J, Wang YN, et al: PDIA3 defines a
novel subset of adipose macrophages to exacerbate the development
of obesity and metabolic disorders. Cell Metab. 36:2262–2280 e5.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Boyle JJ, Johns M, Kampfer T, Nguyen AT,
Game L, Schaer DJ, Mason JC and Haskard DO: Activating
transcription factor 1 directs Mhem atheroprotective macrophages
through coordinated iron handling and foam cell protection. Circ
Res. 110:20–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Suganami T, Yuan X, Shimoda Y,
Uchio-Yamada K, Nakagawa N, Shirakawa I, Usami T, Tsukahara T,
Nakayama K, Miyamoto Y, et al: Activating transcription factor 3
constitutes a negative feedback mechanism that attenuates saturated
Fatty acid/toll-like receptor 4 signaling and macrophage activation
in obese adipose tissue. Circ Res. 105:25–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Tang Q, Xie J, Wang Y, Dong C and Sun Q:
Exosomes secreted by ATF3/Nrf2-mediated ferroptotic renal tubular
epithelial cells promote M1/M2 ratio imbalance inducing renal
interstitial fibrosis following ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Front Immunol. 16:15105002025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Bartels HC, Hameed S, Young C, Nabhan M,
Downey P, Curran KM, McCormack J, Fabre A, Kolch W, Zhernovkov V
and Brennan DJ: Spatial proteomics and transcriptomics of the
maternal-fetal interface in placenta accreta spectrum. Transl Res.
274:67–80. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Iwasaki Y, Suganami T, Hachiya R,
Shirakawa I, Kim-Saijo M, Tanaka M, Hamaguchi M, Takai-Igarashi T,
Nakai M, Miyamoto Y and Ogawa Y: Activating transcription factor 4
links metabolic stress to interleukin-6 expression in macrophages.
Diabetes. 63:152–161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Xia HF, Zhu JY, Wang JN, Ren JG, Cai Y,
Wang FQ, Zhang W, Chen G, Zhao YF and Zhao JH: Association of ATF4
expression with tissue hypoxia and M2 macrophage infiltration in
infantile hemangioma. J Histochem Cytochem. 65:285–294. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Chen C, Zong S, Wang Z, Yang R, Guo Y,
Wang Y, Chen X, Li Y and Wang S: FTY720 Attenuates LPS-Induced
inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via the
NF-kappaB and HDAC4/ATF pathways. J Immunol Res. 2023:85716492023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Baek K, Park HJ, Baek JH and Kim HR:
Isoproterenol increases RANKL expression in a ATF4/NFATc1-dependent
manner in mouse osteoblastic cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:22042017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Chattopadhyay A, Kwartler CS, Kaw K, Li Y,
Kaw A, Chen J, LeMaire SA, Shen YH and Milewicz DM:
Cholesterol-induced phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells to
macrophage/fibroblast-like cells is driven by an unfolded protein
response. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 41:302–316. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Kim J, Kwak HJ, Cha JY, Jeong YS, Rhee SD,
Kim KR and Cheon HG: Metformin suppresses lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced inflammatory response in murine macrophages via
activating transcription factor-3 (ATF-3) induction. J Biol Chem.
289:23246–23255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Luo M, Zhao F, Cheng H, Su M and Wang Y:
Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory
diseases. Front Immunol. 15:13529462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Xiang M, Li P, Yue X, Liu L, Wang L, Sun
N, Wang K, Zhang Y and Wang H: Dysregulated macrophage immunity in
Helicobacter pylori infection: unveiling mechanistic insights and
therapeutic implications. Front Immunol. 16:16367682025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Fu YL and Harrison RE: Microbial
phagocytic receptors and their potential involvement in cytokine
induction in macrophages. Front Immunol. 12:6620632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Arango Duque G and Descoteaux A:
Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious
diseases. Front Immunol. 5:4912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Lv K and Liang Q: Macrophages in
sepsis-induced acute lung injury: exosomal modulation and
therapeutic potential. Front Immunol. 15:15180082025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
A-Gonzalez N, Quintana JA, Garcia-Silva S,
Mazariegos M, González de la Aleja A, Nicolás-Ávila JA, Walter W,
Adrover JM, Crainiciuc G, Kuchroo VK, et al: Phagocytosis imprints
heterogeneity in tissue-resident macrophages. J Exp Med.
214:1281–1296. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Ochando J, Mulder WJM, Madsen JC, Netea MG
and Duivenvoorden R: Trained immunity-basic concepts and
contributions to immunopathology. Nat Rev Nephrol. 19:23–37. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
194
|
Nathan C and Ding A: Nonresolving
inflammation. Cell. 140:871–882. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Cheng Y, Marion TN, Cao X, Wang W and Cao
Y: Park 7: A novel therapeutic target for macrophages in
sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Front Immunol. 9:26322018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Jiang Y, Cai R, Huang Y, Zhu L, Xiao L,
Wang C and Wang L: Macrophages in organ fibrosis: From pathogenesis
to therapeutic targets. Cell Death Discov. 10:4872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Ahmad S, Zaki A, Manda K, Mohan A and Syed
MA: Vitamin-D ameliorates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via
augmenting miR-149-5p and downregulating ER stress. J Nutr Biochem.
110:1091302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Zhang S, Meng P, Liu G, Liu K and Che C:
ATF4 involvement in TLR4 and LOX-1-induced host inflammatory
response to aspergillus fumigatus keratitis. J Ophthalmol.
2018:58302022018.
|
|
199
|
Li R, Ren T, Zeng J and Xu H: ALCAM
deficiency alleviates LPS-Induced acute lung injury by inhibiting
inflammatory response. Inflammation. 46:688–699. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Al-Salleeh F and Petro TM: Promoter
analysis reveals critical roles for SMAD-3 and ATF-2 in expression
of IL-23 p19 in macrophages. J Immunol. 181:4523–4533. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Ta HM, Le TM, Ishii H, Takarada-Iemata M,
Hattori T, Hashida K, Yamamoto Y, Mori K, Takahashi R, Kitao Y and
Hori O: Atf6α deficiency suppresses microglial activation and
ameliorates pathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
J Neurochem. 139:1124–1137. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Wellen KE and Hotamisligil GS:
Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue. J Clin
Invest. 112:1785–1788. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Olefsky JM and Glass CK: Macrophages,
inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:219–246.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Liang W, Qi Y, Yi H, Mao C, Meng Q, Wang H
and Zheng C: The roles of adipose tissue macrophages in human
disease. Front Immunol. 13:9087492022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Guria S, Hoory A, Das S, Chattopadhyay D
and Mukherjee S: Adipose tissue macrophages and their role in
obesity-associated insulin resistance: An overview of the complex
dynamics at play. Biosci Rep. 43:BSR202202002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Bai Y and Sun Q: Macrophage recruitment in
obese adipose tissue. Obes Rev. 16:127–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
De Nardo D, Labzin LI, Kono H, Seki R,
Schmidt SV, Beyer M, Xu D, Zimmer S, Lahrmann C, Schildberg FA, et
al: High-density lipoprotein mediates anti-inflammatory
reprogramming of macrophages via the transcriptional regulator
ATF3. Nat Immunol. 15:152–160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Xu J, Ding L, Mei J, Hu Y, Kong X, Dai S,
Bu T, Xiao Q and Ding K: Dual roles and therapeutic targeting of
tumor-associated macrophages in tumor microenvironments. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 10:2682025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Takayanagi H: Osteoimmunology: Shared
mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat
Rev Immunol. 7:292–304. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Sun Y, Li J, Xie X, Gu F, Sui Z, Zhang K
and Yu T: Macrophage-osteoclast associations: Origin, polarization,
and subgroups. Front Immunol. 12:7780782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Nakashima T, Hayashi M and Takayanagi H:
New insights into osteoclastogenic signaling mechanisms. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 23:582–590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Perrone M, Chiodoni C, Lecchi M, Botti L,
Bassani B, Piva A, Jachetti E, Milani M, Lecis D, Tagliabue E, et
al: ATF3 reprograms the bone marrow niche in response to early
breast cancer transformation. Cancer Res. 83:117–129. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
213
|
Gao C, Jiang J, Tan Y and Chen S:
Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanism and potential
therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3592023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Fleiss B, Van Steenwinckel J, Bokobza C, I
KS, Ross-Munro E and Gressens P: Microglia-mediated
neurodegeneration in perinatal brain injuries. Biomolecules.
11:992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Flury A, Aljayousi L, Park HJ, Khakpour M,
Mechler J, Aziz S, McGrath JD, Deme P, Sandberg C, González Ibáñez
F, et al: A neurodegenerative cellular stress response linked to
dark microglia and toxic lipid secretion. Neuron. 113:554–571 e14.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
216
|
Liu LL, Xiao YS, Huang WM, Liu S, Huang
LX, Zhong JH, Jia P and Liu WY: ATF1/miR-214-5p/ITGA7 axis promotes
osteoclastogenesis to alter OVX-induced bone absorption. Mol Med.
28:562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Kim HN, Baek JK, Park SB, Kim JD, Son HJ,
Park GH, Eo HJ, Park JH, Jung HS and Jeong JB: Anti-inflammatory
effect of Vaccinium oldhamii stems through inhibition of NF-kappaB
and MAPK/ATF2 signaling activation in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7
cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 19:2912019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
218
|
Comarita IK, Vilcu A, Constantin A,
Procopciuc A, Safciuc F, Alexandru N, Dragan E, Nemecz M, Filippi
A, Chiţoiu L, et al: Therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived
extracellular vesicles on atherosclerosis-induced vascular
dysfunction and its key molecular players. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10:8171802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Ho HH, Antoniv TT, Ji JD and Ivashkiv LB:
Lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases
in human monocytes is suppressed by IFN-gamma via superinduction of
ATF-3 and suppression of AP-1. J Immunol. 181:5089–5097. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Ishida M, Ueki M, Morishita J, Ueno M,
Shiozawa S and Maekawa N: T-5224, a selective inhibitor of
c-Fos/activator protein-1, improves survival by inhibiting serum
high mobility group box-1 in lethal lipopolysaccharide-induced
acute kidney injury model. J Intensive Care. 3:492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Kubryn N, Fijalkowski L, Nowaczyk J, Jamil
A and Nowaczyk A: PROTAC technology as a new tool for modern
pharmacotherapy. Molecules. 30:21232025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Hu Z and Crews CM: Recent developments in
PROTAC-mediated protein degradation: From bench to clinic.
Chembiochem. 23:e2021002702022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
223
|
Bekes M, Langley DR and Crews CM: PROTAC
targeted protein degraders: The past is prologue. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 21:181–200. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Ai M, Ma H, He J, Xu F, Ming Y, Ye Z,
Zheng Q, Luo D, Yang K, Li J, et al: Targeting oncogenic
transcriptional factor c-myc by oligonucleotide PROTAC for the
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Med Chem.
280:1169782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Simpson LM, Glennie L, Brewer A, Zhao JF,
Crooks J, Shpiro N and Sapkota GP: Target protein localization and
its impact on PROTAC-mediated degradation. Cell Chem Biol.
29:1482–1504 e7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Liu Z, Hu M, Yang Y, Du C, Zhou H, Liu C,
Chen Y, Fan L, Ma H, Gong Y and Xie Y: An overview of PROTACs: A
promising drug discovery paradigm. Mol Biomed. 3:462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Liu J, Chen H, Kaniskan HU, Xie L, Chen X,
Jin J and Wei W: TF-PROTACs enable targeted degradation of
transcription factors. J Am Chem Soc. 143:8902–8910. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Ji J, Ma S, Zhu Y, Zhao J, Tong Y, You Q
and Jiang Z: ARE-PROTACs enable co-degradation of an Nrf2-MafG
heterodimer. J Med Chem. 66:6070–6081. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Wang D, Liu Y, Chen Y, Dai C, Hu W, Han J,
Li Z, Yin F, Zhang Y and Shi C: EGFR targeted liposomal PROTAC
assisted with epigenetic regulation as an efficient strategy for
osimertinib-resistant lung cancer therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh).
12:e101972025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Chen S, Chen E, Su J, Gong Y, Tang S, Qin
A, Shen A, Tang S and Zhang L: Magnetically navigated nano-PROTAC
ameliorates acute lung injury. J Nanobiotechnology. 23:6222025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Zhao L, Zhao J, Zhong K, Tong A and Jia D:
Targeted protein degradation: Mechanisms, strategies and
application. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Kronke J, Udeshi ND, Narla A, Grauman P,
Hurst SN, McConkey M, Svinkina T, Heckl D, Comer E, Li X, et al:
Lenalidomide causes selective degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in
multiple myeloma cells. Science. 343:301–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
233
|
Greene LA, Zhou Q, Siegelin MD and
Angelastro JM: Targeting transcription factors ATF5, CEBPB and
CEBPD with cell-penetrating peptides to treat brain and other
cancers. Cells. 12:5812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Sun X, Angelastro JM, Merino D, Zhou Q,
Siegelin MD and Greene LA: Dominant-negative ATF5 rapidly depletes
survivin in tumor cells. Cell Death Dis. 10:7092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Rui Y, Eppler HB, Yanes AA and Jewell CM:
Tissue-targeted drug delivery strategies to promote
antigen-specific immune tolerance. Adv Healthc Mater.
12:e22022382023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
236
|
Chen W, Schilperoort M, Cao Y, Shi J,
Tabas I and Tao W: Macrophage-targeted nanomedicine for the
diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol.
19:228–249. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
237
|
Zhao G, Xue L, Geisler HC, Xu J, Li X,
Mitchell MJ and Vaughan AE: Precision treatment of viral pneumonia
through macrophage-targeted lipid nanoparticle delivery. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 121:e23147471212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Hai T, Wolford CC and Chang YS: ATF3, a
hub of the cellular adaptive-response network, in the pathogenesis
of diseases: Is modulation of inflammation a unifying component?
Gene Expr. 15:1–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Nguyen CT, Kim EH, Luong TT, Pyo S and
Rhee DK: ATF3 confers resistance to pneumococcal infection through
positive regulation of cytokine production. J Infect Dis.
210:1745–1754. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Bekeredjian-Ding I, Stein C and Uebele J:
The innate immune response against staphylococcus aureus. Curr Top
Microbiol Immunol. 409:385–418. 2017.
|
|
241
|
Nguyen CT, Kim EH, Luong TT, Pyo S and
Rhee DK: TLR4 mediates pneumolysin-induced ATF3 expression through
the JNK/p38 pathway in Streptococcus pneumoniae-infected RAW 264.7
cells. Mol Cells. 38:58–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
242
|
Guo B, Stein JL, van Wijnen AJ and Stein
GS: ATF1 and CREB trans-activate a cell cycle regulated histone H4
gene at a distal nuclear matrix associated promoter element.
Biochemistry. 36:14447–14455. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Watson G, Ronai ZA and Lau E: ATF2, a
paradigm of the multifaceted regulation of transcription factors in
biology and disease. Pharmacol Res. 119:347–357. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Lau E and Ronai ZA: ATF2 - at the
crossroad of nuclear and cytosolic functions. J Cell Sci.
125:2815–2824. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Claps G, Cheli Y, Zhang T, Scortegagna M,
Lau E, Kim H, Qi J, Li JL, James B, Dzung A, et al: A
transcriptionally inactive ATF2 variant drives melanomagenesis.
Cell Rep. 15:1884–1892. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Hashimoto Y, Zhang C, Kawauchi J, Imoto I,
Adachi MT, Inazawa J, Amagasa T, Hai T and Kitajima S: An
alternatively spliced isoform of transcriptional repressor ATF3 and
its induction by stress stimuli. Nucleic Acids Res. 0:2398–2406.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
247
|
Chan JYW, Tsui JCC, Law PTW, So WKW, Leung
DYP, Sham MMK, Tsui SKW and Chan CWH: RNA-Seq revealed
ATF3-regulated inflammation induced by silica. Toxicology.
393:34–41. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
248
|
Jeong BC, Kim JH, Kim K, Kim I, Seong S
and Kim N: ATF3 modulates calcium signaling in osteoclast
differentiation and activity by associating with c-Fos and NFATc1
proteins. Bone. 95:33–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|