|
1
|
Zhang M and Zhang S: T cells in fibrosis
and fibrotic diseases. Front Immunol. 11:11422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei L, Liu L, Bai M, Ning X and Sun S:
CircRNAs: Versatile players and new targets in organ fibrosis. Cell
Commun Signal. 21:902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Horowitz JC and Thannickal VJ: Mechanisms
for the resolution of organ fibrosis. Physiology (Bethesda).
34:43–55. 2019.
|
|
4
|
Hohn J, Tan W, Carver A, Barrett H and
Carver W: Roles of exosomes in cardiac fibroblast activation and
fibrosis. Cells. 10:29332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao X, Kwan JYY, Yip K, Liu PP and Liu
FF: Targeting metabolic dysregulation for fibrosis therapy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 19:57–75. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Henderson NC, Rieder F and Wynn TA:
Fibrosis: From mechanisms to medicines. Nature. 587:555–566. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hao Y: Chinese medicine as a therapeutic
option for pulmonary fibrosis: Clinical efficacies and underlying
mechanisms. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li X, Li L, Lei W, Chua HZ, Li Z, Huang X,
Wang Q, Li N and Zhang H: Traditional Chinese medicine as a
therapeutic option for cardiac fibrosis: Pharmacology and
mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 142:1119792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen YL, Wang SJ, Rahman K, Zhang LJ and
Zhang H: Chinese herbal formulas and renal fibrosis: An overview.
Curr Pharm Des. 24:2774–2781. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Lu Y, Nian M, Sheng Q, Zhang C, Han
C, Dou X and Ding Y: Therapeutic potential and mechanism of Chinese
herbal medicines in treating fibrotic liver disease. Chin J Natl
Med. 21:643–657. 2023.
|
|
11
|
Li X, Liu Z, Liao J, Chen Q, Lu X and Fan
X: Network pharmacology approaches for research of traditional
Chinese medicines. Chin J Natl Med. 21:323–332. 2023.
|
|
12
|
Xie J, Xiong J, Ding LS, Chen L, Zhou H,
Liu L, Zhang ZF, Hu XM, Luo P and Qing LS: A efficient method to
identify cardioprotective components of Astragali Radix using a
combination of molecularly imprinted polymers-based knockout
extract and activity evaluation. J Chromatogr A. 1576:10–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bi Y, Bao H, Zhang C, Yao R and Li M:
Quality control of radix astragali (The Root of Astragalus
membranaceus var. mongholicus) along its value chains. Front
Pharmacol. 11:5623762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gong F, Qu R, Li Y, Lv Y and Dai J:
Astragalus mongholicus: A review of its anti-fibrosis properties.
Front Pharmacol. 13:9765612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shan H, Zheng X and Li M: The effects of
astragalus membranaceus active extracts on autophagy-related
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 20:19042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu Y, Chai Y, Xiao G, Liu Y, Xie X, Xiao
W, Zhou P, Ma W, Zhang C and Li L: Astragalus and its formulas as a
therapeutic option for fibrotic diseases: Pharmacology and
mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 13:10403502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu M, Lan L, Li G and Sun G:
Multi-dimensional profiles combined with antioxidant activity and
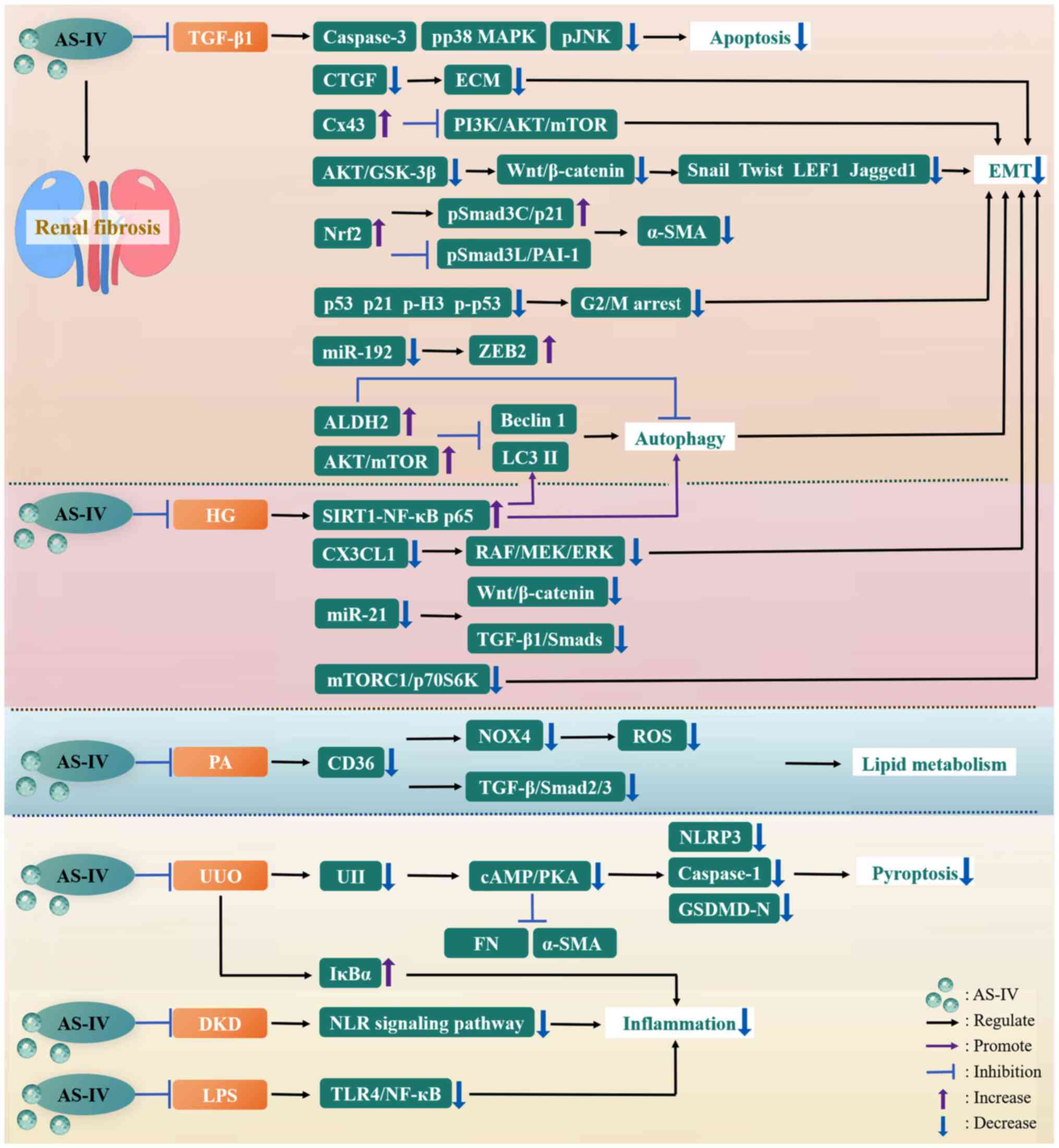
fingerprint-efficacy relationship to analyze the quality of
Astragali Radix from different sources. Food Chemi. 461:1408482024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Wu C, Gao L, Du G and Qin X:
Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research
review on the pharmacological effects. Adv Pharmacol. 87:89–112.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi Y, Shi X, Zhao M, Ma S and Zhang Y:
Pharmacological potential of astragali radix for the treatment of
kidney diseases. Phytomedicine. 123:1551962024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Song SS, Wang RY, Li ZH, Yang Y, Wang TT,
Qing LS and Luo P: Role of simulated in vitro gastrointestinal
digestion on biotransformation and bioactivity of astragalosides
from Radix Astragali. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 231:1154142023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang Y, Chen B, Liang D, Quan X, Gu R,
Meng Z, Gan H, Wu Z, Sun Y, Liu S and Dou G: Pharmacological
effects of astragaloside IV: A review. Molecules. 28:61182023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan YQ, Chen HW and Li J: Astragaloside
IV: An effective drug for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:3731–3746. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
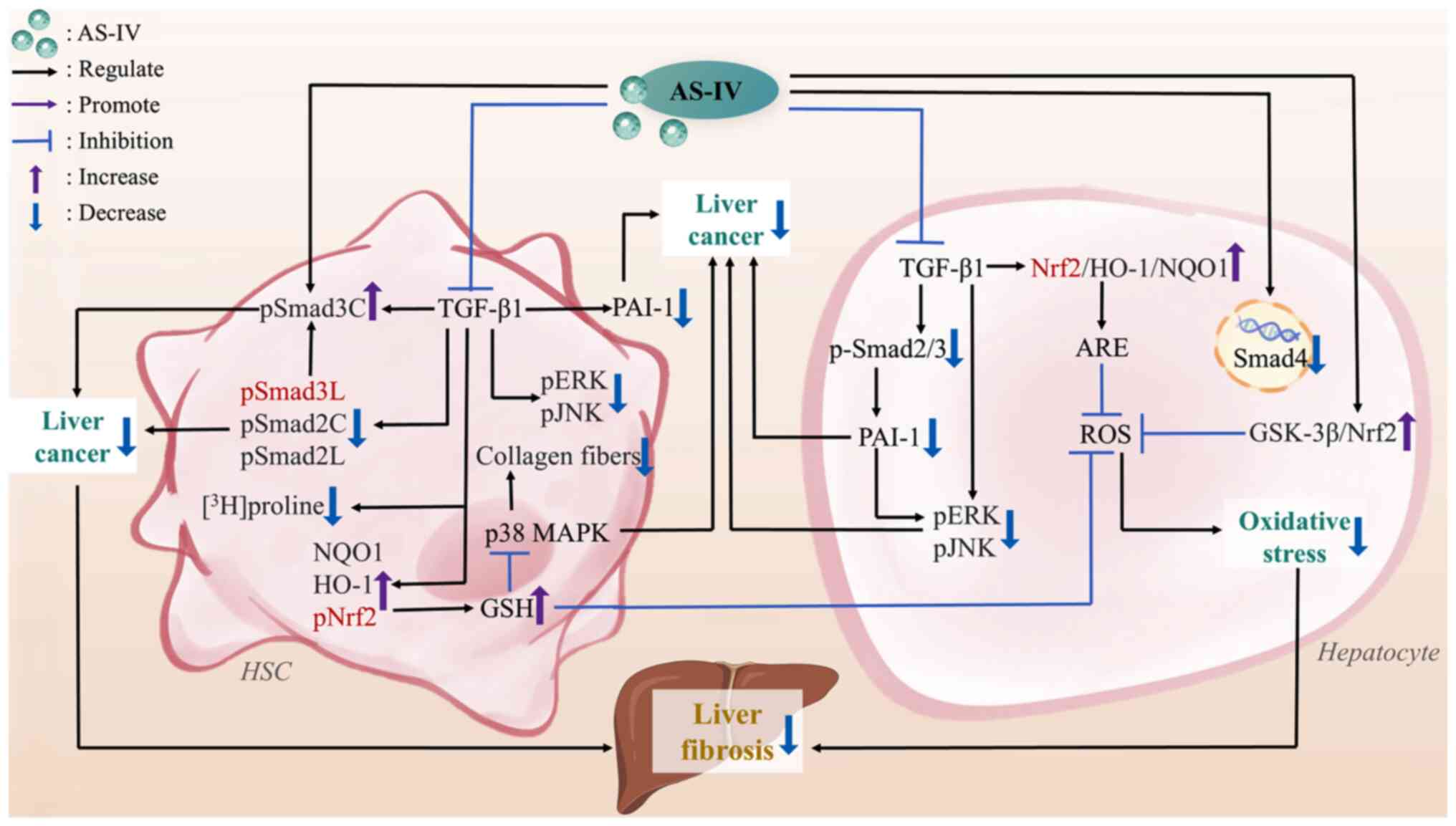
|
|
23
|
Ren S, Zhang H, Mu Y, Sun M and Liu P:
Pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV: A literature review. J
Tradit Chin Med. 33:413–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li L, Hou X, Xu R, Liu C and Tu M:
Research review on the pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV.
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 31:17–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li K, Cui LJ, Cao YX, Li SY, Shi LX, Qin
XM and Du YG: UHPLC Q-exactive MS-based serum metabolomics to
explore the effect mechanisms of immunological activity of
astragalus polysaccharides with different molecular weights. Front
Pharmacol. 11:5956922020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li M, Han B, Zhao H, Xu C, Xu D,
Sieniawska E, Lin X and Kai G: Biological active ingredients of
Astragali Radix and its mechanisms in treating cardiovascular and
cerebrovascular diseases. Phytomedicine. 98:1539182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li L, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Meng X, Pan G, Zhang
H, Li Y and Zhang B: The molecular basis of the anti-inflammatory
property of astragaloside IV for the treatment of diabetes and its
complications. Drug Des Devel Ther. 17:771–790. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Hu J, Chen X, Lei X, Feng H, Wan F
and Tan L: Traditional Chinese medicine monomers: Novel strategy
for endogenous neural stem cells activation after stroke. Front
Cell Neurosci. 15:6281152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Indu P, Arunagirinathan N, Rameshkumar MR,
Sangeetha K, Divyadarshini A and Rajarajan S: Antiviral activity of
astragaloside II, astragaloside III and astragaloside IV compounds
against dengue virus: Computational docking and in vitro studies.
Microb Pathog. 152:1045632021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kang X, Su S, Hong W, Geng W and Tang H:
Research progress on the ability of astragaloside IV to protect the
brain against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Neurosci.
15:7559022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun L, Han R, Guo F, Chen H, Wang W, Chen
Z, Liu W, Sun X and Gao C: Antagonistic effects of IL-17 and
astragaloside IV on cortical neurogenesis and cognitive behavior
after stroke in adult mice through Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Cell Death
Discov. 6:742020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li R, Shi C, Wei C, Wang C, Du H, Hong Q
and Chen X: Fufang shenhua tablet, astragali radix and its active
component astragaloside IV: Research progress on anti-inflammatory
and immunomodulatory mechanisms in the kidney. Front Pharmacol.
14:11316352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meng P, Yang R, Jiang F, Guo J, Lu X, Yang
T and He Q: Molecular mechanism of astragaloside IV in improving
endothelial dysfunction of cardiovascular diseases mediated by
oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:14812362021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li L, Zheng S, Brinckmann JA, Fu J, Zeng
R, Huang L and Chen S: Chemical and genetic diversity of Astragalus
mongholicus grown in different eco-climatic regions. PLoS One.
12:e01847912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu SY, Ouyang HT, Yang JY, Huang XL, Yang
T, Duan JP, Cheng JP, Chen YX, Yang YJ and Qiong P: Subchronic
toxicity studies of Radix Astragali extract in rats and dogs. J
Ethnopharmacol. 21:352–355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zang Y, Wan J, Zhang Z, Huang S, Liu X and
Zhang W: An updated role of astragaloside IV in heart failure.
Biomed Pharmacother. 126:1100122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiangbo Z, Xuying W, Yuping Z, Xili M,
Yiwen Z and Tianbao Z: Effect of astragaloside IV on the
embryo-fetal development of Sprague-Dawley rats and New Zealand
White rabbits. J Appl Toxicol. 29:381–385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xuying W, Jiangbo Z, Yuping Z, Xili M,
Yiwen Z, Tianbao Z and Weidong Z: Effect of astragaloside IV on the
general and peripartum reproductive toxicity in sprague-dawley
rats. Int J Toxicol. 29:505–516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu M, Yin J, Xie L, Zhang J, Zou C, Zou J,
Liu F, Ju W and Li P: Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of toal
astragalosides after intravenous infusion of astragalosides
injection in healthy Chinese volunteers. Phytomedicine.
20:1105–1111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Frangogiannis NG: Cardiac fibrosis.
Cardiovasc Res. 117:1450–1488. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Wan Y, Xu L, Wang Y, Tuerdi N, Ye M and Qi
R: Preventive effects of astragaloside IV and its active sapogenin
cycloastragenol on cardiac fibrosis of mice by inhibiting the NLRP3
inflammasome. Eur J Pharmacol. 833:545–554. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei Y, Wu Y, Feng K, Zhao Y, Tao R, Xu H
and Tang Y: Astragaloside IV inhibits cardiac fibrosis via
miR-135a-TRPM7-TGF-β/Smads pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
249:1124042020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lu J, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Lu XC, Liu YH, Wu Y,
Guo Q, Ma YT and Tang YQ: AstragalosideⅣ against cardiac fibrosis
by inhibiting TRPM7 channel. Phytomedicine. 30:10–17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu J, Qi J, Yin P, Liu Y, You J, Lin L,
Zhou M and Wang L: Cardiovascular disease mortality-China, 2019.
China CDC Wkly. 3:323–326. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang X, Qu H, Yang T, Kong X and Zhou H:
Regulation and functions of NLRP3 inflammasome in cardiac fibrosis:
Current knowledge and clinical significance. Biomed Pharmacother.
143:1122192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kawaguchi M, Takahashi M, Hata T, Kashima
Y, Usui F, Morimoto H, Izawa A, Takahashi Y, Masumoto J, Koyama J,
et al: Inflammasome activation of cardiac fibroblasts is essential
for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation.
123:594–604. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chai C, Sun Y, Chi R, Yang H, Yang B and
Li B: Astragaloside IV alleviates LPS-induced cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy and collagen expression associated with CCL2-mediated
activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
693:1493672024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Feng Y, Ye D, Wang Z, Pan H, Lu X, Wang M,
Xu Y, Yu J, Zhang J, Zhao M, et al: The role of interleukin-6
family members in cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med.
9:8188902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ushakov A, Ivanchenko V and Gagarina A:
Regulation of myocardial extracellular matrix dynamic changes in
myocardial infarction and postinfarct remodeling. Curr Cardiol Rev.
16:11–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Jia G, Leng B, Wang H and Dai H:
Inhibition of cardiotrophin-1 overexpression is involved in the
anti-fibrotic effect of Astrogaloside IV. Mol Med Rep.
16:8365–8370. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cui Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Li D, Zhang F, Jin X,
Li M, Zhang J and Liu Z: Protective effects of ginsenoside F2 on
isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction by activating the
Nrf2/HO-1 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Phytomedicine.
129:1556372024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhao T, Kee HJ, Bai L, Kim MK, Kee SJ and
Jeong MH: Selective HDAC8 inhibition attenuates
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis via p38 MAPK
pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12:6777572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dai H, Jia G, Lu M, Liang C, Wang Y and
Wang H: Astragaloside IV inhibits isoprenaline-induced cardiac
fibrosis by targeting the reactive oxygen species/mitogen-activated
protein kinase signaling axis. Mol Med Rep. 15:1765–1770. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guo Y, Zhou F, Fan J, Wu T, Jia S, Li J
and Chen N: Swimming alleviates myocardial fibrosis of type II
diabetic rats through activating miR-34a-mediated
SIRT1/PGC-1α/FNDC5 signal pathway. PLoS One. 19:e03101362024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Cong X, Zhu X, Zhang X and Ning Z:
Astragaloside IV inhibits angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrosis
and atrial fibrillation by SIRT1/PGC-1α/FNDC5 pathway. Heliyon.
10:e309842024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Nakamura K, Miyoshi T, Yoshida M, Akagi S,
Saito Y, Ejiri K, Matsuo N, Ichikawa K, Iwasaki K, Naito T, et al:
Pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy and heart
failure in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci.
23:35872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang Z, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Ji T and
Li W and Li W: Protective effects of AS-IV on diabetic
cardiomyopathy by improving myocardial lipid metabolism in rat
models of T2DM. Biomed Pharmacother. 127:1100812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Vasudevan SO, Behl B and Rathinam VA:
Pyroptosis-induced inflammation and tissue damage. Semin Immunol.
69:1017812024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Zhang X, Qu H, Yang T, Liu Q and Zhou H:
Astragaloside IV attenuate MI-induced myocardial fibrosis and
cardiac remodeling by inhibiting ROS/caspase-1/GSDMD signaling
pathway. Cell Cycle. 21:2309–2322. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Birch J and Gil J: Senescence and the
SASP: Many therapeutic avenues. Genes Dev. 34:1565–1576. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Campbell RA, Docherty MH, Ferenbach DA and
Mylonas KJ: The role of ageing and parenchymal senescence on
macrophage function and fibrosis. Front Immunol. 12:7007902021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shi L, Deng J, He J, Zhu F, Jin Y, Zhang
X, Ren Y and Du X: Integrative transcriptomics and proteomics
analysis reveal the protection of Astragaloside IV against
myocardial fibrosis by regulating senescence. Eur J Pharmacol.
975:1766322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ok CY, Park S, Jang HO, Takata T, Lee OH,
Bae MK and Bae SK: FK866 Protects human dental pulp cells against
oxidative stress-induced cellular senescence. Antioxidants (Basel).
10:2712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Purnomo Y, Piccart Y, Coenen T, Prihadi JS
and Lijnen PJ: Oxidative stress and transforming growth
factor-1-induced cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug
Targets. 13:165–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen P, Xie Y, Shen E, Li GG, Yu Y, Zhang
CB, Yang Y, Zou Y, Ge J, Chen R and Chen H: Astragaloside IV
attenuates myocardial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1 signaling in
coxsackievirus B3-induced cardiomyopathy. Eur J Pharmacol.
658:168–174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xu H, Yang F and Bao Z: Gut microbiota and
myocardial fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 5:1753552023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Czibik G, Mezdari Z, Altintas DM, Bréhat
J, Pini M, d'Humières T, Delmont T, Radu C, Breau M, Liang H, et
al: Dysregulated phenylalanine catabolism plays a key role in the
trajectory of cardiac aging. Circulation. 144:559–574. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Du XQ, Shi LP, Chen ZW, Hu JY, Zuo B,
Xiong Y and Cao WF: Astragaloside IV ameliorates
isoprenaline-induced cardiac fibrosis in mice via modulating gut
microbiota and fecal metabolites. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
12:8361502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Huang WJ and Tang XX: Virus infection
induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Transl Med. 19:4962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Guan Y, Zhang J, Cai X, Cai Y, Song Z,
Huang Y, Qian W, Pan Z and Zhang X: Astragaloside IV inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis via
lncRNA-ATB/miR-200c/ZEB1 signaling pathway. Gene. 897:1480402024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Sgalla G, Iovene B, Calvello M, Ori M,
Varone F and Richeldi L: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis:
Pathogenesis and management. Respir Res. 19:322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li LC and Kan LD: Traditional Chinese
medicine for pulmonary fibrosis therapy: Progress and future
prospects. J Ethnopharmacol. 198:45–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Savin IA, Zenkova MA and Sen'kova AV:
Bronchial asthma, airway remodeling and lung fibrosis as successive
steps of one process. Int J Mol Sci. 24:160422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wiertz IA, Wuyts WA, van Moorsel CHM,
Vorselaars ADM, Van Es HW, Van Oosterhout MFM and Grutters JC:
Unfavourable outcome of glucocorticoid treatment in suspected
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology. 23:311–317. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Richeldi L,
Thomson CC, Inoue Y, Johkoh T, Kreuter M, Lynch DA, Maher TM,
Martinez FJ, et al: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (an Update) and
progressive pulmonary fibrosis in adults: An official
ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 205:e18–e47. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bai X, Zhao G, Chen Q, Li Z, Gao M, Ho W,
Xu X and Zhang XQ: Inhaled siRNA nanoparticles targeting IL11
inhibit lung fibrosis and improve pulmonary function post-bleomycin
challenge. Sci Adv. 8:eabn71622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li N, Wu K, Feng F, Wang L, Zhou X and
Wang W: Astragaloside IV alleviates silica-induced pulmonary
fibrosis via inactivation of the TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Med. 47:162021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Li N, Feng F, Wu K, Zhang H, Zhang W and
Wang W: Inhibitory effects of astragaloside IV on silica-induced
pulmonary fibrosis via inactivating TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling. Biomed
Pharmacother. 119:1093872019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Hou Y, Zhen Y, Xue Q and Wang W:
Astragaloside IV attenuates TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of pulmonary fibrosis via suppressing NLRP3 expression
in vitro. Pharmazie. 76:97–102. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yu WN, Sun LF and Yang H: Inhibitory
effects of astragaloside IV on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation.
Inflammation. 39:1835–1841. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang G, Zhao G, Chao X, Xie L and Wang H:
The characteristic of virulence, biofilm and antibiotic resistance
of klebsiella pneumoniae. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
17:62782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Li L, Guan J, Lin R, Wang F, Ma H, Mao C,
Guo X, Qu Z and Guan R: Astragaloside IV alleviates lung
inflammation in Klebsiella pneumonia rats by suppressing
TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 56:e122032023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Gao L, Bai Y, Liang C, Han T, Liu Y, Zhou
J, Guo J, Wu J and Hu D: Celastrol-Ligustrazine compound proven to
be a novel drug candidate for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by
intervening in the TGF-β1 mediated pathways-an experimental in
vitro and vivo study. Mol Divers. 29:3957–3973. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Qian W, Cai X, Qian Q, Zhang W and Wang D:
Astragaloside IV modulates TGF-β1-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med.
22:4354–4365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zheng M, Liu K, Li L, Feng C and Wu G:
Traditional Chinese medicine inspired dual-drugs loaded inhalable
nano-therapeutics alleviated idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by
targeting early inflammation and late fibrosis. J Nanobiotechnol.
22:142024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Catrina SB and Zheng X: Hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factors in diabetes and its complications.
Diabetologia. 64:709–716. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xi J, Ma Y, Liu D and Li R: Astragaloside
IV restrains pyroptosis and fibrotic development of pulmonary
artery smooth muscle cells to ameliorate pulmonary artery
hypertension through the PHD2/HIF1α signaling pathway. BMC Pulm
Med. 23:3862023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Elamaa H, Kaakinen M, Nätynki M, Szabo Z,
Ronkainen VP, Äijälä V, Mäki JM, Kerkelä R, Myllyharju J and Eklund
L: PHD2 deletion in endothelial or arterial smooth muscle cells
reveals vascular cell type-specific responses in pulmonary
hypertension and fibrosis. Angiogenesis. 25:259–274. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Li X, Zhang M, Ling C, Sha H, Zou G and
Liang H: Molecular characterization and response of prolyl
hydroxylase domain (PHD) Genes to hypoxia stress in
hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Animals (Basel). 12:1312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yuan S, Zuo B, Zhou SC, Wang M, Tan KY,
Chen ZW and Cao WF: Integrating network pharmacology and
experimental validation to explore the pharmacological mechanism of
astragaloside IV in treating bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 17:1289–1302. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ma J, Xu Y, Li W, Zhou Y, Wang D, Yang M,
Wang B and Chen W: High-mobility group box 1 promotes
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in crystalline silica induced
pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Toxicol Lett. 330:134–143.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li LC, Xu L, Hu Y, Cui WJ, Cui WH, Zhou WC
and Kan LD: Astragaloside IV improves bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis in rats by attenuating extracellular matrix deposition.
Front Pharmacol. 8:5132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jin H, Park SY, Lee JE, Park H, Jeong M,
Lee H, Cho J and Lee YS: GTSE1-driven ZEB1 stabilization promotes
pulmonary fibrosis through the epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Mol Ther. 32:4138–4157. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bridges MC, Daulagala AC and Kourtidis A:
LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J Cell Biol.
220:e2020090452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Volpe MC, Ciucci G, Zandomenego G, Vuerich
R, Ring NAR, Vodret S, Salton F, Marchesan P, Braga L, Marcuzzo T,
et al: Flt1 produced by lung endothelial cells impairs ATII cell
transdifferentiation and repair in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death
Dis. 14:4372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Xu Q, Yao W, Wu Q, Yuan J,
Yan W, Xu T, Ji X and Ni C: Long non-coding RNA-ATB promotes EMT
during silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by competitively binding
miR-200c. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864:420–431. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Guan Y, Ma J and Song W: Identification of
circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gastric cancer by analysis
of microarray data. Cancer Cell Int. 19:1832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhu M, Zhao L, Zhang X and Zhao R:
Astragaloside IV restrains pulmonary fibrosis progression via the
circ_0008898/miR-211-5p/HMGB1 axis. Chem Biol Drug Des.
103:e145082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Gan W, Song W, Gao Y, Zheng X, Wang F,
Zhang Z, Zen K, Liang H and Yan X: Exosomal circRNAs in the plasma
serve as novel biomarkers for IPF diagnosis and progression
prediction. J Transl Med. 22:2642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ye Z, Xian W, Ling G, Zihang LI, Jingtian
Z, Wenkai W, Liang Z and Mei X: Efficacy of Danggui Buxue decoction
on diabetic nephropathy-induced renal fibrosis in rats and possible
mechanism. J Tradit Chin Med. 43:507–513. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Tong J, Wu Z, Wang Y, Hao Q, Liu H, Cao F
and Jiao Y: Astragaloside IV synergizing with ferulic acid
ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021:1–9. 2021.
|
|
102
|
Yue YL, Zhang MY, Liu JY, Fang LJ and Qu
YQ: The role of autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: From
mechanisms to therapies. Ther Adv Respir Dis.
16:1753466622114092022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Li T, Gao X, Jia R, Sun Y, Ding Y, Wang F
and Wang Y: Astragaloside IV inhibits idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
through activation ofautophagy by miR-21-mediated
PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
70:128–136. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Mo Y, Zhang Y, Wan R, Jiang M, Xu Y and
Zhang Q: miR-21 mediates nickel nanoparticle-induced pulmonary
injury and fibrosis. Nanotoxicology. 14:1175–1197. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Deleyto-Seldas N and Efeyan A: The
mTOR-autophagy axis and the control of metabolism. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:6557312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yehia L, Keel E and Eng C: The clinical
spectrum of PTEN mutations. Annu Rev Med. 71:103–116. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Dubey S, Dubey PK, Umeshappa CS, Ghebre YT
and Krishnamurthy P: Inhibition of RUNX1 blocks the differentiation
of lung fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. J Cell Physiol.
237:2169–2182. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Tian H, Zhang Y, Li W, Xie G, Wu J and Liu
J: Astragaloside IV inhibits lung injury and fibrosis induced by
PM2.5 by targeting RUNX1 through miR-362-3p. Mol Biotechnol.
67:4167–4177. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Al-Tamari HM, Dabral S, Schmall A, Sarvari
P, Ruppert C, Paik J, DePinho RA, Grimminger F, Eickelberg O,
Guenther A, et al: FoxO3 an important player in fibrogenesis and
therapeutic target for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. EMBO Mol Med.
10:276–293. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
110
|
Kurebayashi Y, Baba Y, Minowa A, Nadya NA,
Azuma M, Yoshimura A, Koyasu S and Nagai S: TGF-β-induced
phosphorylation of Akt and Foxo transcription factors negatively
regulates induced regulatory T cell differentiation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 480:114–119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Cui H, Liu X, Zhang J, Zhang K, Yao D,
Dong S, Feng S, Yang L, Li Y, Wang H, et al: Rhodiola rosea L.
Attenuates cigarette smoke and lipopolysaccharide-induced COPD in
rats via inflammation inhibition and antioxidant and antifibrosis
pathways. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2:61031582021.
|
|
112
|
Su J, Morgani SM, David CJ, Wang Q, Er EE,
Huang YH, Basnet H, Zou Y, Shu W, Soni RK, et al: TGF-β
orchestrates fibrogenic and developmental EMTs via the RAS effector
RREB1. Nature. 577:566–571. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhang M, Wang W, Liu K, Jia C, Hou Y and
Bai G: Astragaloside IV protects against lung injury and pulmonary
fibrosis in COPD by targeting GTP-GDP domain of RAS and
downregulating the RAS/RAF/FoxO signaling pathway. Phytomedicine.
120:1550662023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Mzimela N, Dimba N, Sosibo A and Khathi A:
Evaluating the impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on pulmonary
vascular function and the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:14314052024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Guo J, Zhang Y, Zhou R, Hao Y, Wu X, Li G
and Du Q: Deciphering the molecular mechanism of Bu Yang Huan Wu
Decoction in interference with diabetic pulmonary fibrosis via
regulating oxidative stress and lipid metabolism disorder. J Pharm
Biomed Anal. 243:1160612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D,
Neuen BL and Perkovic V: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet.
398:786–802. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Johnson HN and Prasad-Reddy L: Updates in
chronic kidney disease. J Pharm Pract. 37:1380–1390. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Kovesdy CP: Epidemiology of chronic kidney
disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 12:7–11. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Liu Y, Kors L, Butter LM, Stokman G,
Claessen N, Zuurbier CJ, Girardin SE, Leemans JC, Florquin S,
Tammaro A, et al: NLRX1 prevents M2 macrophage polarization and
excessive renal fibrosis in chronic obstructive nephropathy. Cells.
13:232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhang L, Wang X, He S, Zhang F and Li Y:
Gypenosides suppress fibrosis of the renal NRK-49F cells by
targeting miR-378a-5p through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 311:1164662023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Fogo AB and Harris RC: Crosstalk between
glomeruli and tubules. Nat Rev Nephrol. 21:189–199. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Patera F, Gatticchi L, Cellini B,
Chiasserini D and Reboldi G: Kidney Fibrosis and oxidative stress:
From molecular pathways to new pharmacological opportunities.
Biomolecules. 14:1372024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Li D, Liu Y, Zhan Q, Zeng Y, Peng Z, He Q,
Tan Q, Cao W, Wang S and Wang J: Astragaloside IV blunts
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and G2/M arrest to alleviate
renal fibrosis via regulating ALDH2-mediated autophagy. Cells.
12:17772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Ruiz-Ortega M, Lamas S and Ortiz A:
Antifibrotic agents for the management of CKD: A review. Am J
Kidney Dis. 80:251–263. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Su Y, Chen Q, Ma K, Ju Y, Ji T, Wang Z and
Li W and Li W: Astragaloside IV inhibits palmitate-mediated
oxidative stress and fibrosis in human glomerular mesangial cells
via downregulation of CD36 expression. Pharmacol Rep. 71:319–329.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Nath A, Li I, Roberts LR and Chan C:
Elevated free fatty acid uptake via CD36 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 5:147522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Du N, Xu Z, Gao M, Liu P, Sun B and Cao X:
Combination of Ginsenoside Rg1 and Astragaloside IV reduces
oxidative stress and inhibits TGF-β1/Smads signaling
cascade on renal fibrosis in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 12:3517–3524. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
128
|
Zhang Y, Tao C, Xuan C, Jiang J and Cao W:
Transcriptomic analysis reveals the protection of astragaloside IV
against diabetic nephropathy by modulating inflammation. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2020:1–17. 2020.
|
|
129
|
Wang S, Qin S, Cai B, Zhan J and Chen Q:
Promising therapeutic mechanism for Chinese herbal medicine in
ameliorating renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:9326492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Lu Q, Ji XJ, Zhou YX, Yao XQ, Liu YQ,
Zhang F and Yin XX: Quercetin inhibits the mTORC1/p70S6K
signaling-mediated renal tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol Res.
99:237–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Chen X, Yang Y, Liu C, Chen Z and Wang D:
Astragaloside IV ameliorates high glucose-induced renal tubular
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by blocking mTORC1/p70S6K
signaling in HK-2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 43:709–716. 2018.
|
|
132
|
Herman-Edelstein M, Thomas MC,
Thallas-Bonke V, Saleem M, Cooper ME and Kantharidis P: A model for
diabetic podocytopathy. Diabetes. 60:1779–1788. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Qiu Y, Kang N, Wang X, Yao Y, Cui J, Zhang
X and Zheng L: Loss of Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) accelerates
dysregulated glucose and renal injury in db/db mice. PeerJ.
11:e161552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Fujii R, Yamada H, Munetsuna E, Yamazaki
M, Ohashi K, Ishikawa H, Maeda K, Hagiwara C, Ando Y, Hashimoto S,
et al: Associations of circulating MicroRNAs (miR-17, miR-21, and
miR-150) and chronic kidney disease in a Japanese Population. J
Epidemiol. 30:177–182. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
135
|
Wang X, Gao Y, Tian N, Zou D, Shi Y and
Zhang N: Astragaloside IV improves renal function and fibrosis via
inhibition of miR-21-induced podocyte dedifferentiation and
mesangial cell activation in diabetic mice. Drug Des Devel Ther.
12:2431–2442. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Teh YM, Mualif SA and Lim SK: A
comprehensive insight into autophagy and its potential signaling
pathways as a therapeutic target in podocyte injury. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 143:1061532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Wang X, Gao Y, Tian N, Wang T, Shi Y, Xu J
and Wu B: Astragaloside IV inhibits glucose-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of podocytes through autophagy
enhancement via the SIRT-NF-κB p65 axis. Sci Rep. 9:3232019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Wang X, Gao Y, Tian N, Zhu Z, Wang T, Xu
J, Wu B and Zhang N: Astragaloside IV represses high
glucose-induced mesangial cells activation by enhancing autophagy
via SIRT1 deacetylation of NF-κB P65 subunit. Drug Des Devel Ther.
12:2971–2980. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
139
|
Shah R, Matthews GJ, Shah RY, McLaughlin
C, Chen J, Wolman M, Master SR, Chai B, Xie D, Rader DJ, et al:
Serum fractalkine (CX3CL1) and cardiovascular outcomes and
diabetes: Findings from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort
(CRIC) study. Am J Kidney Dis. 66:266–273. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Wang C, Ren C, Hu Q, Shen X, Wang M, Yang
Z, Xu E, Wang X, Li Z, Yu H, et al: Histidine-rich calcium binding
protein promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration,
invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Raf/MEK/ERK
signaling. J Cancer. 13:1073–1085. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Hu Y, Tang W, Liu W, Hu Z and Pan C:
Astragaloside IV alleviates renal tubular epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via CX3CL1-RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in diabetic
kidney disease. Drug Des Devel Ther. 16:1605–1620. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Yang Y, Song M, Liu Y, Liu H, Sun L, Peng
Y, Liu F, Venkatachalam MA and Dong Z: Renoprotective approaches
and strategies in acute kidney injury. Pharmacol Ther. 163:58–73.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Zhou X, Sun X, Gong X, Yang Y, Chen C,
Shan G and Yao Q: Astragaloside IV from Astragalus membranaceus
ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation
via TLR4/NF-кB in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 42:18–24.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Pang J, Peng H, Wang S, Xu X, Xu F, Wang
Q, Chen Y, Barton LA, Chen Y, Zhang Y and Ren J: Mitochondrial
ALDH2 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial
contractile dysfunction by suppression of ER stress and autophagy.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1865:1627–1641. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Liu F: Transforming growth factor-beta1 in
diabetic kidney disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:1872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Wang L, Chi YF, Yuan ZT, Zhou WC, Yin PH,
Zhang XM, Peng W and Cai H: Astragaloside IV inhibits renal
tubulointerstitial fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad signaling
pathway in vivo and in vitro. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
239:1310–1324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Lian Y, Li C, Li J, Xie Y, Liu Q, Wu M,
Shi W and Meng L: Astragaloside IV attenuated TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial cells
via connexin43 and Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Tissue Cell.
77:1018312021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Sun X, Huang K, Haiming X, Lin Z, Yang Y,
Zhang M, Liu P and Huang H: Connexin 43 prevents the progression of
diabetic renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis by regulating the
SIRT1-HIF-1α signaling pathway. Clin Sci (Lond). 134:1573–1592.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Yuan R, Fan Q, Liang X, Han S, He J, Wang
QQ, Gao H, Feng Y and Yang S: Cucurbitacin B inhibits
TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in NSCLC
through regulating ROS and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Chin Med.
17:242022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Yu X, Xiao Q, Yu X, Cheng Y, Lin H and
Xiang Z: A network pharmacology-based study on the mechanism of
astragaloside IV alleviating renal fibrosis through the AKT1/GSK-3β
pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 297:1155352022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Wang L, Chi YF, Yuan ZT, Zhou WC, Yin PH,
Zhang XM and Peng W: Astragaloside IV inhibits the up-regulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in rats with unilateral ureteral
obstruction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1316–1328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Che X, Wang Q, Xie Y, Xu W, Shao X, Mou S
and Ni Z: Astragaloside IV suppresses transforming growth factor-β1
induced fibrosis of cultured mouse renal fibroblasts via inhibition
of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:1260–1266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Ma T, Li H, Liu H, Peng Y, Lin T, Deng Z,
Jia N, Chen Z and Wang P: Neat1 promotes acute kidney injury to
chronic kidney disease by facilitating tubular epithelial cells
apoptosis via sequestering miR-129-5p. Mol Ther. 30:3313–3332.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Wang D, Warner GM, Yin P, Knudsen BE,
Cheng J, Butters KA, Lien KR, Gray CE, Garovic VD, Lerman LO, et
al: Inhibition of p38 MAPK attenuates renal atrophy and fibrosis in
a murine renal artery stenosis model. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
304:F938–F947. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Xu W, Shao X, Tian L, Gu L, Zhang M, Wang
Q, Wu B, Wang L, Yao J, Xu X, et al: Astragaloside IV ameliorates
renal fibrosis via the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein
kinases and antiapoptosis in vivo and in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 350:552–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Meng L, Tang J, Wang Y, Zhao JR, Shang MY,
Zhang M, Liu SY, Qu L, Cai SQ and Li XM: Astragaloside IV
synergizes with ferulic acid to inhibit renal tubulointerstitial
fibrosis in rats with obstructive nephropathy. Br J Pharmacol.
162:1805–1818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Huang A, Palmer LS, Hom D, Valderrama E
and Trachtman H: The role of nitric oxide in obstructive
nephropathy. J Urol. 163:1276–1281. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Deb DK, Bao R and Li YC: Critical role of
the cAMP-PKA pathway in hyperglycemia-induced epigenetic activation
of fibrogenic program in the kidney. Faseb J. 31:2065–2075. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Pan H, Lin Y, Dou J, Fu Z, Yao Y, Ye S,
Zhang S, Wang N, Liu A, Li X, et al: Wedelolactone facilitates
Ser/Thr phosphorylation of NLRP3 dependent on PKA signalling to
block inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Cell Prolif.
53:e128682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Zhang L, Liu W, Li S, Wang J, Sun D, Li H,
Zhang Z, Hu Y and Fang J: Astragaloside IV alleviates renal
fibrosis by inhibiting renal tubular epithelial cell pyroptosis
induced by urotensin II through regulating the cAMP/PKA signaling
pathway. PLoS One. 19:e03043652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Keyhanmanesh R, Hamidian G, Lotfi H,
Zavari Z, Seyfollahzadeh M, Ghadiri A, Ahmadi M, Bahari F and Bavil
FM: Troxerutin affects nephropathy signaling events in the kidney
of type-1 diabetic male rats. Avicenna J Phytomed. 12:109–115.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Cao Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, Fan Q and Cong Y:
Astragaloside IV attenuates renal fibrosis through repressing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting microRNA-192
expression: In vivo and in vitro studies. Am J Transl Res.
11:5029–5038. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Kato M, Zhang J, Wang M, Lanting L, Yuan
H, Rossi JJ and Natarajan R: MicroRNA-192 in diabetic kidney
glomeruli and its function in TGF-beta-induced collagen expression
via inhibition of E-box repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:3432–3437. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Csak T and Bernstein D: Hepatorenal
syndrome. Clin Liver Dis. 26:165–179. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Wang Q, Xu J, Li M, Chen Y, Xu Y, Li L,
Gong Y and Yang Y: Nrf2 knockout attenuates the astragaloside IV
therapeutic effect on kidney fibrosis from liver cancer by
regulating pSmad3C/3L pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 397:1687–1700. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Gong Y, Li D, Li L, Yang J, Ding H, Zhang
C, Wen G, Wu C, Fang Z, Hou S and Yang Y: Smad3 C-terminal
phosphorylation site mutation attenuates the hepatoprotective
effect of salvianolic acid B against hepatocarcinogenesis. Food
Chem Toxicol. 147:1119122021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Zhang C, Li L, Hou S, Shi Z, Xu W, Wang Q,
He Y, Gong Y, Fang Z and Yang Y: Astragaloside IV inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma by continually suppressing the development
of fibrosis and regulating pSmad3C/3L and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. J
Ethnopharmacol. 279:1143502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Liang R, Yan D, Zhang X, Chen X, Zhang W
and Jia H: Kidney Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate
cisplatin-induced kidney injury and apoptosis in rats. Tissue Cell.
80:1019982023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Wang Y, Luo P and Wuren T: Narrative
review of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in renal diseases:
Mechanisms, clinical applications, and future directions. Stem
Cells Int. 2024:86582462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Raming R, Cordasic N, Kirchner P, Ekici
AB, Fahlbusch FB, Woelfle J, Hilgers KF, Hartner A and
Menendez-Castro C: Neonatal nephron loss during active
nephrogenesis results in altered expression of renal developmental
genes and markers of kidney injury. Physiol Genomics. 53:509–517.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Berumen J, Baglieri J, Kisseleva T and
Mekeel K: Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology and clinical
implications. WIREs Mech Dis. 13:e14992021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Altamirano-Barrera A, Barranco-Fragoso B
and Méndez-Sánchez N: Management strategies for liver fibrosis. Ann
Hepatol. 16:48–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Cinar R, Iyer MR, Liu Z, Cao Z, Jourdan T,
Erdelyi K, Godlewski G, Szanda G, Liu J, Park JK, et al: Hybrid
inhibitor of peripheral cannabinoid-1 receptors and inducible
nitric oxide synthase mitigates liver fibrosis. JCI Insight.
1:e873362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Lee YA, Wallace MC and Friedman SL:
Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: A translational success story. Gut.
64:830–841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Wu J, Zhang M, Xia S, Han P, Zhao K, Peng
K, Zhou W, Tian D, Liao J and Liu J: Hepatic HRC induces hepatocyte
pyroptosis and HSCs activation via NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. J Mol
Med (Berl). 100:1787–1799. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
El-Ashmawy NE, Al-Ashmawy GM, Fakher HE
and Khedr NF: The role of WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway and
glutamine metabolism in the pathogenesis of CCl4-induced liver
fibrosis: Repositioning of niclosamide and concerns about lithium.
Cytokine. 136:1552502020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Xu XY, Geng Y, Xu HX, Ren Y, Liu DY and
Mao Y: Antrodia camphorata-derived antrodin C inhibits liver
fibrosis by blocking TGF-beta and PDGF signaling pathways. Front
Mol Biosci. 9:8355082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Pastore M, Gitto
S and Marra F: Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying liver
fibrosis regression. Cells. 10:27592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Schuppan D: Liver fibrosis: Common
mechanisms and antifibrotic therapies. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 39:S51–S59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Mohs A, Otto T, Schneider KM, Peltzer M,
Boekschoten M, Holland CH, Hudert CA, Kalveram L, Wiegand S,
Saez-Rodriguez J, et al: Hepatocyte-specific NRF2 activation
controls fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis in steatohepatitis. J
Hepatol. 74:638–648. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Boye A, Wu C, Jiang Y, Wang J, Wu J, Yang
X and Yang Y: Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extracts
modulate MAPK-regulated TGF-β/Smad signaling in hepatocellular
carcinoma by multi-target mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol. 169:219–228.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Wang Z, Li Q, Xiang M, Zhang F, Wei D, Wen
Z and Zhou Y: Astragaloside alleviates hepatic fibrosis function
via par2 signaling pathway in diabetic rats. Cell Physiol Biochem.
41:1156–1166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Matkowski A, Jamiołkowska-Kozlowska W and
Nawrot I: Chinese medicinal herbs as source of antioxidant
compounds-where tradition meets the future. Curr Med Chem.
20:984–1004. 2013.
|
|
184
|
Zhao XM, Zhang J, Liang YN and Niu YC:
Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to alleviate hepatic
fibrosis in bile duct-ligated cirrhotic rats. Dig Dis Sci.
65:2925–2936. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Dong H, Guo H, Liang Y, Wang X and Niu Y:
Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to suppress hepatic
stellate cells activation in vitro. Free Radic Res. 51:167–178.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Bleser PJD, Xu G, Rombouts K, Rogiers V
and Geerts A: Glutathione levels discriminate between oxidative
stress and transforming growth factor-beta signaling in activated
rat hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem. 26:33881–33887. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Li X, Wang X, Han C, Wang X, Xing G, Zhou
L, Li G and Niu Y: Astragaloside IV suppresses collagen production
of activated hepatic stellate cells via oxidative stress-mediated
p38 MAPK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 60:168–176. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Dhar D, Baglieri J, Kisseleva T and
Brenner DA: Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver
cancer. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 245:96–108. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Baba Y, Saeki K, Onodera T and Doi K:
Serological and immunohistochemical studies on
porcine-serum-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Exp Mol Pathol.
79:229–235. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Liu H, Wei W, Sun W and Li X: Protective
effects of astragaloside IV on porcine-serum-induced hepatic
fibrosis in rats and in vitro effects on hepatic stellate cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 122:502–508. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Xie M, Xia B, Xiao L, Yang D, Li Z, Wang
H, Wang X, Zhang X and Peng Q: Astragaloside IV ameliorates
peritoneal fibrosis by promoting PGC-1α to reduce apoptosis in
vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol Med. 27:2945–2955. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Shan Y, Yu M, Dai H, Zhu X, Wang F, You Y,
Cao H, Sheng L, Zhao J, Tang L, et al: The role of
macrophage-derived exosomes in reversing peritoneal fibrosis:
Insights from Astragaloside IV. Phytomedicine. 129:1556832024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Davies SJ, Bryan J, Phillips L and Russell
GI: Longitudinal changes in peritoneal kinetics: The effects of
peritoneal dialysis and peritonitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
11:498–506. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Ditsawanon P and Aramwit P: Preserving the
peritoneal membrane in long-term peritoneal dialysis patients. J
Clin Pharm Ther. 40:508–516. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Dong P,
Poornajaf Y, Hussen BM, Taheri M and Dilmaghani NA: Emerging
functions and clinical applications of exosomal microRNAs in
diseases. Noncoding RNA Res. 8:350–362. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Tkach M and Théry C: Communication by
extracellular vesicles: Where we are and where we need to go. Cell.
164:1226–1232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Wang J, Wang Y, Zhang H, Gao W, Lu M, Liu
W, Li Y and Yin Z: Forkhead box C1 promotes the pathology of
osteoarthritis by upregulating β-catenin in synovial fibroblasts.
FEBS J. 287:3065–3087. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Qi Q, Mao Y, Yi J, Li D, Zhu K and Cha X:
Anti-Fibrotic effects of astragaloside IV in systemic sclerosis.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:2105–2116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Chen X, Peng LH, Li N, Li QM, Li P, Fung
KP, Leung PC and Gao JQ: The healing and anti-scar effects of
astragaloside IV on the wound repair in vitro and in vivo. J
Ethnopharmacol. 139:721–727. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Chen X, Peng LH, Shan YH, Li N, Wei W, Yu
L, Li QM, Liang WQ and Gao JQ: Astragaloside IV-loaded
nanoparticle-enriched hydrogel induces wound healing and anti-scar
activity through topical delivery. Int J Pharm. 447:171–181. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Peng LH, Chen X, Chen L, Li N, Liang WQ
and Gao JQ: Topical astragaloside IV-releasing hydrogel improves
healing of skin wounds in vivo. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:881–888. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Shan YH, Peng LH, Liu X, Chen X, Xiong J
and Gao JQ: Silk fibroin/gelatin electrospun nanofibrous dressing
functionalized with astragaloside IV induces healing and anti-scar
effects on burn wound. Int J Pharm. 479:291–301. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Kasetti RB, Maddineni P, Kodati B,
Nagarajan B and Yacoub S: Astragaloside IV attenuates ocular
hypertension in a mouse model of TGFβ2 induced primary open angle
glaucoma. Int J Mol Sci. 22:125082021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Ashok A, Chaudhary S, Kritikos AE, Kang
MH, McDonald D, Rhee DJ and Singh N: TGFβ2-hepcidin feed-forward
loop in the trabecular meshwork implicates iron in glaucomatous
pathology. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 61:242020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Zhou XT, Zou JJ, Ao C, Gong DY, Chen X and
Ma YR: Renal protective effects of astragaloside IV, in diabetes
mellitus kidney damage animal models: A systematic review,
meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res. 160:1051922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Ren Y, Liang H, Xie M and Zhang M: Natural
plant medications for the treatment of retinal diseases: The
blood-retinal barrier as a clue. Phytomedicine. 130:1555682024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Zaman Q, Zhang D, Reddy OS, Wong WT and
Lai WF: Roles and mechanisms of astragaloside IV in combating
neuronal aging. Aging Dis. 13:18452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Gu Y, Wang G, Pan G, Fawcett JP, Jiye A
and Sun J: Transport and bioavailability studies of astragaloside
IV, an active ingredient in radix astragali. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 95:295–298. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Huang CR, Wang GJ, Wu XL, Li H, Xie HT, Lv
H and Sun JG: Absorption enhancement study of astragaloside IV
based on its transport mechanism in Caco-2 cells. Eur J Drug Metab
Pharmacokinet. 31:5–10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Yang J, Jiang H, Wu C, Lin Y, Tan G, Zhan
J, Han L, Zhu Y, Shang P, Liu L and Liu H: Copper silicate
nanoparticle-mediated delivery of astragaloside-IV for
osteoarthritis treatment by remodeling the articular cartilage
microenvironment. J Control Release. 381:1135832025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Li X, Zhang X, Qi Y, Jin W, Wen Z, Zhao Y,
Li X, Yao X, Shen Z, Zhang F, et al: Conductive bioadhesive
hydrogel with controlled astragaloside IV release for
ferroptosis-mediated cardiac repair. J Control Release.
384:1138742025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Wu S, Zhou M, Zhou H, Han L and Liu H:
Astragaloside IV-loaded biomimetic nanoparticles target IκBα to
regulate neutrophil extracellular trap formation for sepsis
therapy. J Nanobiotechnol. 23:1552025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
213
|
Wei L, Wang H, Ye X, Yue J, Guo H, Mao D,
Li X, Sun Y, Liu C, Liu Y and Chen Y: Oxymatrine and astragaloside
IV co-loaded liposomes: Scale-up purposes and their enhancement of
anti-PD-1 efficacy against breast cancer. Mater Today Bio.
32:1016342025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Yu S, Peng W, Qiu F and Zhang G: Research
progress of astragaloside IV in the treatment of atopic diseases.
Biomed Pharmacother. 156:1139892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Qing LS, Chen TB, Sun WX, Chen L, Luo P,
Zhang ZF and Ding LS: Pharmacokinetics comparison, intestinal
absorption and acute toxicity assessment of a novel water-soluble
astragaloside IV derivative (Astragalosidic Acid, LS-102). Eur J
Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 44:251–259. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|