|
1
|
Bhaskaran M and Mohan M: MicroRNAs:
History, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development
and disease. Vet Pathol. 51:759–774. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Bhatti JS and Reddy
PH: MicroRNAs as peripheral biomarkers in aging and age-related
diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 146:47–94. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
Elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of MicroRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
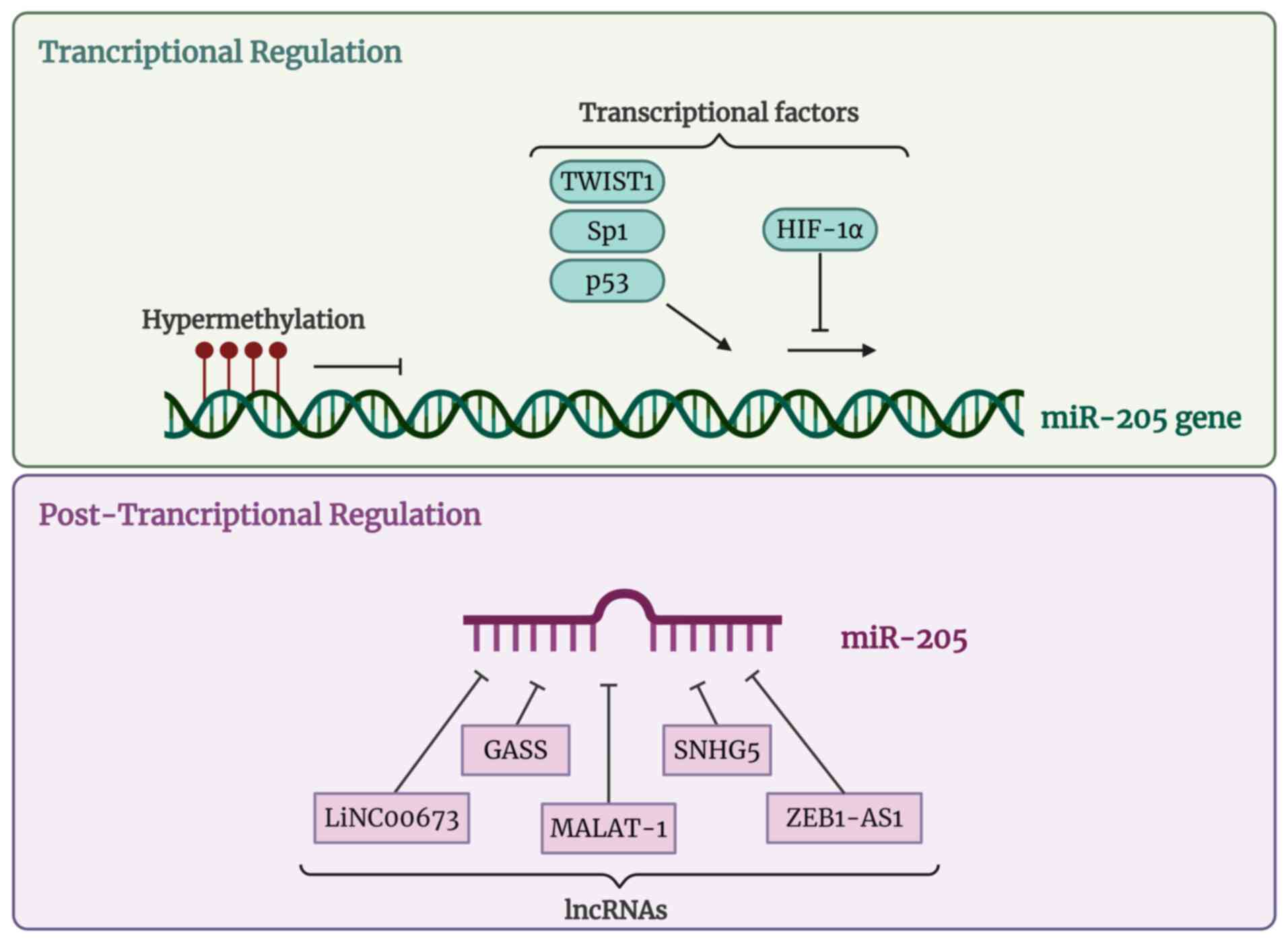
Wang L, Dong F, Reinach PS, He D, Zhao X,
Chen X, Hu DN and Yan D: MicroRNA-182 suppresses HGF/SF-Induced
increases in retinal pigment epithelial cell proliferation and
migration through targeting c-Met. PLoS One. 11:e01676842016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tasharrofi N, Kouhkan F, Soleimani M,
Soheili ZS, Kabiri M, Mahmoudi Saber M and Dorkoosh FA: Survival
improvement in human retinal pigment epithelial cells via fas
receptor targeting by MiR-374a. J Cell Biochem. 118:4854–4861.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hao Y, Zhou Q, Ma J, Zhao Y and Wang S:
MiR-146a Is upregulated during retinal pigment epithelium
(RPE)/Choroid aging in mice and represses IL-6 and VEGF-A
expression in RPE cells. J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 7:5622016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou Q, Gallagher R, Ufret-Vincenty R, Li
X, Olson EN and Wang S: Regulation of angiogenesis and choroidal
neovascularization by members of MicroRNA-23~27~24 Clusters. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:8287–8292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin H, Qian J, Castillo AC, Long B, Keyes
KT, Chen G and Ye Y: Effect of MiR-23 on oxidant-induced injury in
human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
52:6308–6314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li K, Du Y, Jiang BL and He JF: Increased
MicroRNA-155 and Decreased MicroRNA-146a may promote ocular
inflammation and proliferation in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Med Sci
Monit. 20:639–643. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ying SY, Chang DC and Lin SL: The
MicroRNA. Methods Mol Biol. 1733:1–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yi R, Qin Y, Macara IG and Cullen BR:
Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of Pre-MicroRNAs and short
hairpin RNAs. Genes Dev. 17:3011–3016. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A and Green R:
miRNA-Mediated gene silencing by translational repression followed
by mRNA deadenylation and decay. Science. 336:237–240. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Turchinovich A, Tonevitsky AG and
Burwinkel B: Extracellular MiRNA: A collision of two paradigms.
Trends Biochem Sci. 41:883–892. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand
M, Lee JJ and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and
microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 9:654–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guiot J, Struman I, Louis E, Louis R,
Malaise M and Njock MS: Exosomal miRNAs in lung diseases: From
biologic function to therapeutic targets. J Clin Med. 8:13452019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ingenito F, Roscigno G, Affnito A, Nuzzo
S, Scognamiglio I, Quintavalle C and Condorelli G: The role of
Exo-miRNAs in cancer: A focus on therapeutic and diagnostic
applications. Int J Mol Sci. 20:46872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Naeli P, Yousefi F, Ghasemi Y,
Savardashtaki A and Mirzaei H: The role of MicroRNAs in lung
cancer: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Curr Mol Med.
20:90–101. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vishwakarma S and Kaur I: Molecular
mediators and regulators of retinal angiogenesis. Semin Ophthalmol.
38:124–133. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in life, disease
and medicine. Nature. 438:932–936. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
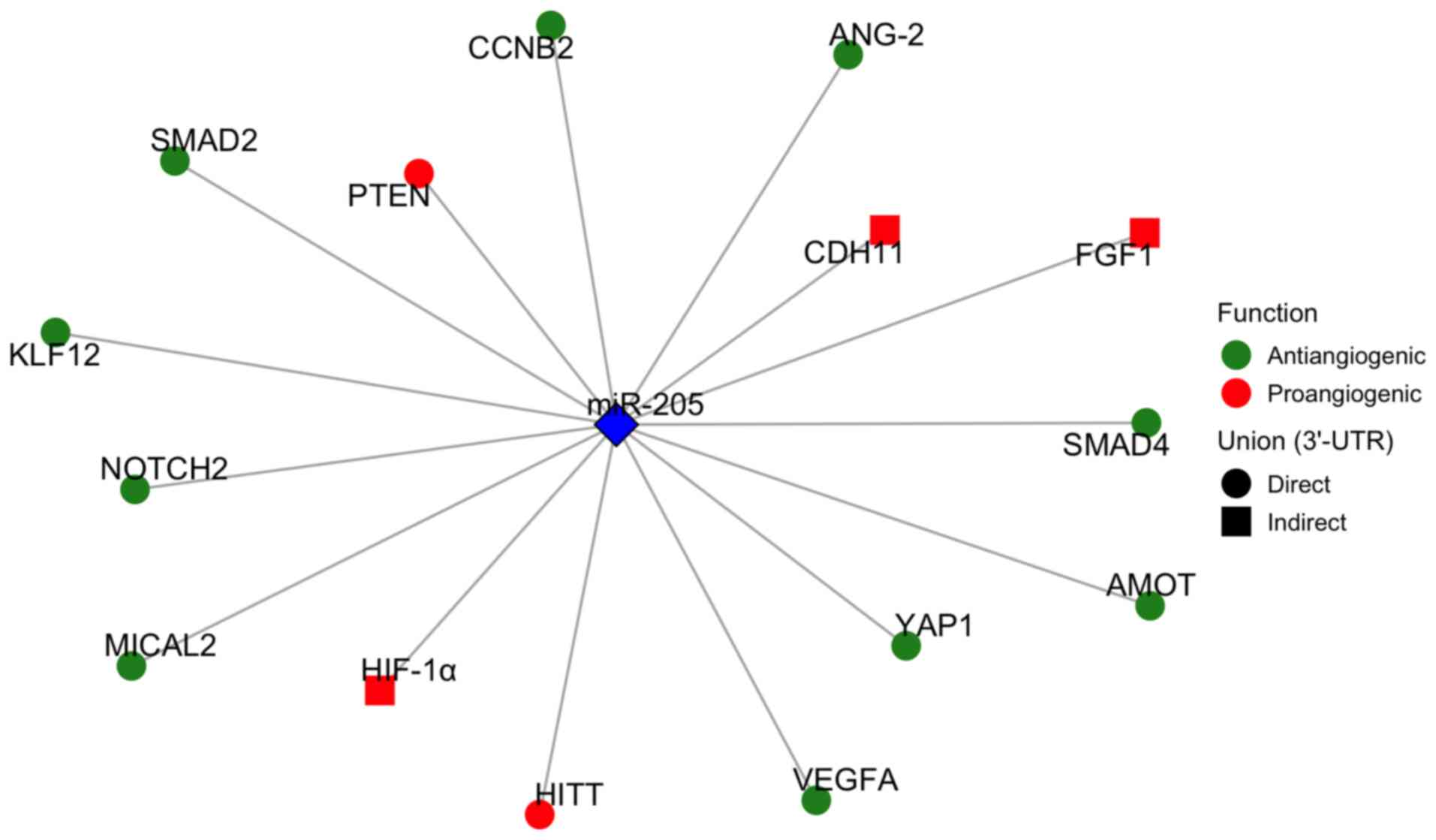
Oltra M, Vidal-Gil L, Maisto R,
Sancho-Pelluz J and Barcia JM: Oxidative stress-induced
angiogenesis is mediated by miR-205-5p. J Cell Mol Med.
24:1428–1436. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xue Y, Liu Y, Bian X, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhang
Q and Yin M: miR-205-5p inhibits psoriasis-associated proliferation
and angiogenesis: Wnt/β-catenin and mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathway are involved. J Dermatol. 47:882–892.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun LL, Xiao L, Du XL, Hong L, Li CL, Jiao
J, Li WD and Li XQ: MiR-205 promotes endothelial progenitor cell
angiogenesis and deep vein thrombosis recanalization and resolution
by targeting PTEN to regulate Akt/autophagy pathway and MMP2
expression. J Cell Mol Med. 23:8493–8504. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Li L, Zhao K, Lin Q, Li H, Xue X,
Ge W, He H, Liu D, Xie H, et al: A novel LncRNA HITT forms a
regulatory loop with HIF-1α to modulate angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell Death Differ. 27:1431–1446. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Martínez-Santos M, Ybarra M, Oltra M,
Muriach M, Romero FJ, Pires ME, Sancho-Pelluz J and Barcia JM: Role
of exosomal miR-205-5p cargo in angiogenesis and cell migration.
Int J Mol Sci. 25:9342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vosgha H, Salajegheh A, Smith RA and Lam
AK: The important roles of miR-205 in normal physiology, cancers
and as a potential therapeutic target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
14:621–637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang D, Zhang Z, O'Loughlin E, Wang L, Fan
X, Lai EC and Yi R: MicroRNA-205 controls neonatal expansion of
skin stem cells by modulating the PI(3)K pathway. Nat Cell Biol.
15:1153–1163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Darnell DK, Kaur S, Stanislaw S, Konieczka
JH, Yatskievych TA and Antin PB: MicroRNA expression during chick
embryo development. Dev Dyn. 235:3156–3165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shingara J, Keiger K, Shelton J,
Laosinchai-Wolf W, Powers P, Conrad R, Brown D and Labourier E: An
optimized isolation and labeling platform for accurate microRNA
expression profiling. RNA. 11:1461–1470. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mouillet JF, Chu T, Nelson DM, Mishima T
and Sadovsky Y: MiR-205 silences MED1 in hypoxic primary human
trophoblasts. FASEB J. 24:2030–2039. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Farmer DT, Finley JK, Chen FY,
Tarifeño-Saldivia E, McNamara NA, Knox SM and McManus MT: MiR-205
is a critical regulator of lacrimal gland development. Dev Biol.
427:12–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu J, Peng H, Ruan Q, Fatima A, Getsios S
and Lavker RM: MicroRNA-205 promotes keratinocyte migration via the
lipid phosphatase SHIP2. FASEB J. 24:3950–3959. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Teta M, Choi YS, Okegbe T, Wong G, Tam OH,
Chong MM, Seykora JT, Nagy A, Littman DR, Andl T and Millar SE:
Inducible deletion of epidermal dicer and drosha reveals multiple
functions for miRNAs in postnatal skin. Development. 139:1405–1416.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Farmer DT, Shariat N, Park CY, Liu HJ,
Mavropoulos A and McManus MT: Partially penetrant postnatal
lethality of an epithelial specific MicroRNA in a mouse knockout.
PLoS One. 8:e766342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tellez CS, Juri DE, Do K, Bernauer AM,
Thomas CL, Damiani LA, Tessema M, Leng S and Belinsky SA: Tumor and
stem cell biology EMT and stem cell-like properties associated with
miR-205 and miR-200 epigenetic silencing are early manifestations
during carcinogen-induced transformation of human lung epithelial
cells. Cancer Res. 71:3087–3097. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee JY, Park MK, Park JH, Lee HJ, Shin DH,
Kang Y, Lee CH and Kong G: Loss of the polycomb protein Mel-18
enhances the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by ZEB1 and ZEB2
expression through the downregulation of MiR-205 in breast cancer.
Oncogene. 33:1325–1335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
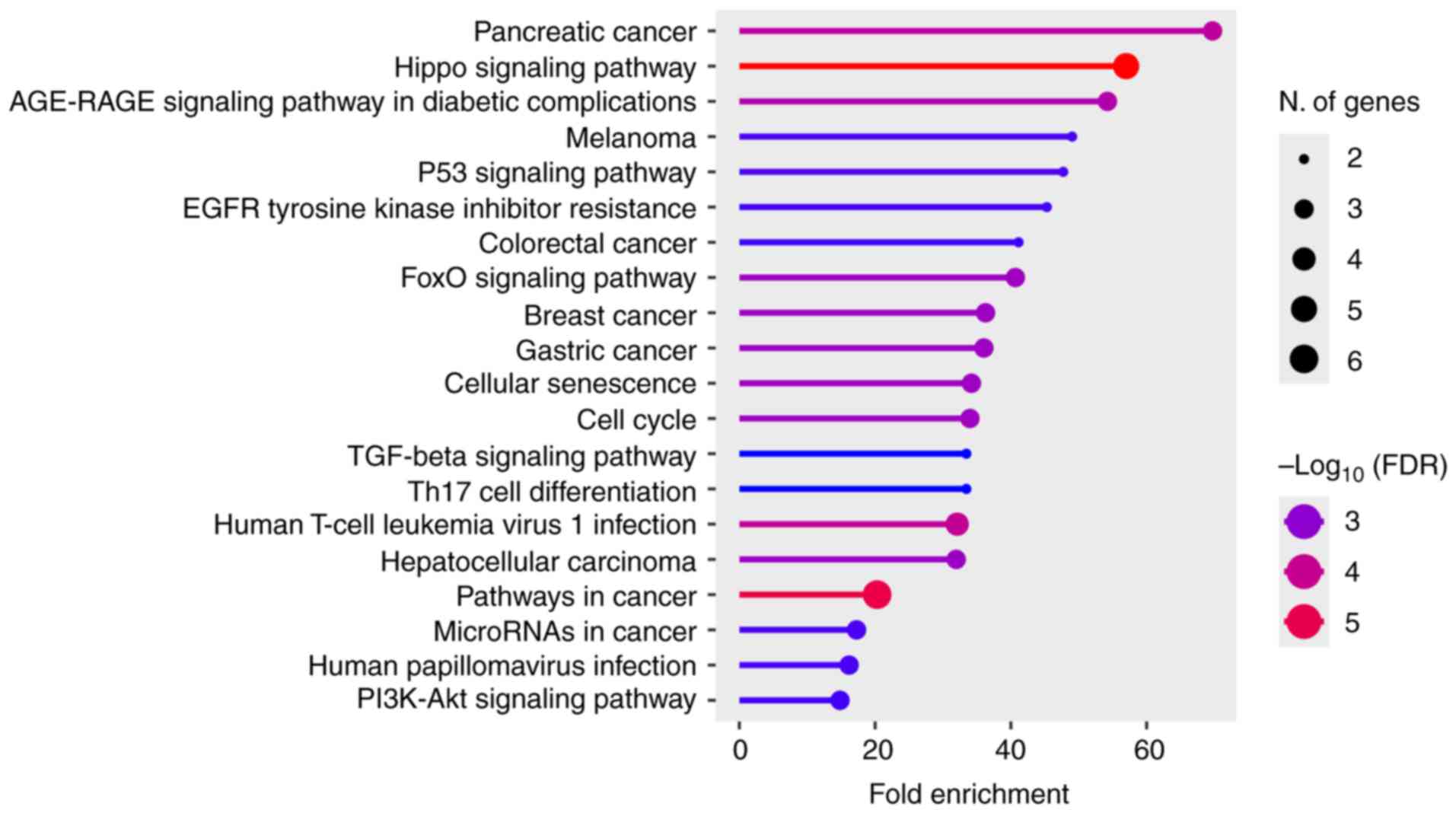
Ferrari E and Gandellini P: Unveiling the
ups and downs of miR-205 in physiology and cancer: Transcriptional
and post-transcriptional mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 11:9802020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hulf T, Sibbritt T, Wiklund ED, Patterson
K, Song JZ, Stirzaker C, Qu W, Nair S, Horvath LG, Armstrong NJ, et
al: Epigenetic-induced repression of microRNA-205 is associated
with MED1 activation and a poorer prognosis in localized prostate
cancer. Oncogene. 32:2891–2899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shaw PH: The Role of P53 in cell cycle
regulation. Pathol Res Pract. 192:669–675. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Piovan C, Palmieri D, Di Leva G, Braccioli
L, Casalini P, Nuovo G, Tortoreto M, Sasso M, Plantamura I, Triulzi
T, et al: Oncosuppressive role of P53-Induced miR-205 in triple
negative breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:458–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gandellini P, Giannoni E, Casamichele A,
Taddei ML, Callari M, Piovan C, Valdagni R, Pierotti MA, Zaffaroni
N and Chiarugi P: MiR-205 hinders the malignant interplay between
prostate cancer cells and associated fibroblasts. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:1045–1059. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Jain RK: Antiangiogenesis strategies
revisited: From starving tumors to alleviating hypoxia. Cancer
Cell. 26:605–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pan F, Mao H, Bu F, Tong X, Li J, Zhang S,
Liu X, Wang L, Wu L, Chen R, et al: Sp1-Mediated transcriptional
activation of miR-205 promotes radioresistance in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:5735–5752. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjøt
L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS,
Borre M, et al: Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200
family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer.
128:1327–1334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhang L, Hung GC, Meng S, Evans R and Xu
J: LncRNA MALAT1 regulates hyperglycemia induced EMT in
keratinocyte via miR-205. Noncoding RNA. 9:142023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li Q, Pan X, Wang X, Jiao X, Zheng J, Li Z
and Huo Y: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes cell proliferation
through suppressing miR-205 and promoting SMAD4 expression in
osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 8:106648–106660. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Gao Q and Wang Y: Long noncoding RNA
MALAT1 regulates apoptosis in ischemic stroke by sponging
miR-205-3p and modulating PTEN expression. Am J Transl Res.
12:2738–2748. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu W, Zhang H, Niu Y, Wu Y, Sun W, Li H,
Kong J, Ding K, Shen HM, Wu H, et al: Long non-coding RNA Linc00673
regulated non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, migration,
invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition by sponging
miR-150-5p. Mol Cancer. 16:1182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
He B, Bai Y, Kang W, Zhang X and Jiang X:
LncRNA SNHG5 regulates imatinib resistance in chronic myeloid
leukemia via acting as a CeRNA against MiR-205-5p. Am J Cancer Res.
7:1704–1713. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang W, Hong L, Xu X, Wang Q, Huang J and
Jiang L: LncRNA GAS5 suppresses the tumorigenesis of cervical
cancer by downregulating miR-196a and miR-205. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177113152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jin Z and Chen B: LncRNA ZEB1-AS1
regulates colorectal cancer cells by MiR-205/YAP1 axis. Open Med
(Wars). 15:175–184. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang X, Zeng X, Xia N, Xie X and Long Y:
Circ_0003520/MiR-205-5p/CUL4B axis drives the progression of clear
cell renal carcinoma. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 39:e702632025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang X, Zhang H, Jiao K, Zhao C, Liu H,
Meng Q, Wang Z, Feng C and Li Y: Effect of miR-205 on proliferation
and migration of thyroid cancer cells by targeting CCNB2 and the
mechanism. Oncol Lett. 19:2568–2574. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Guan B, Li Q, Shen L, Rao Q, Wang Y, Zhu
Y, Zhou XJ and Li XH: MicroRNA-205 directly targets krüppel-like
factor 12 and is involved in invasion and apoptosis in basal-like
breast carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 49:720–734. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang H and Fan Q: MicroRNA-205 inhibits
the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer by regulating AMOT
expression. Oncol Rep. 34:2163–2170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dudley AC and Griffioen AW: Pathological
angiogenesis: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Angiogenesis.
26:313–347. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M,
Ruhrberg C, Lundkvist A, Abramsson A, Jeltsch M, Mitchell C,
Alitalo K, Shima D and Betsholtz C: VEGF guides angiogenic
sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol.
161:1163–1177. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Marech I, Leporini C, Ammendola M,
Porcelli M, Gadaleta CD, Russo E, De Sarro G and Ranieri G:
Classical and non-classical proangiogenic factors as a target of
antiangiogenic therapy in tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett.
380:216–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
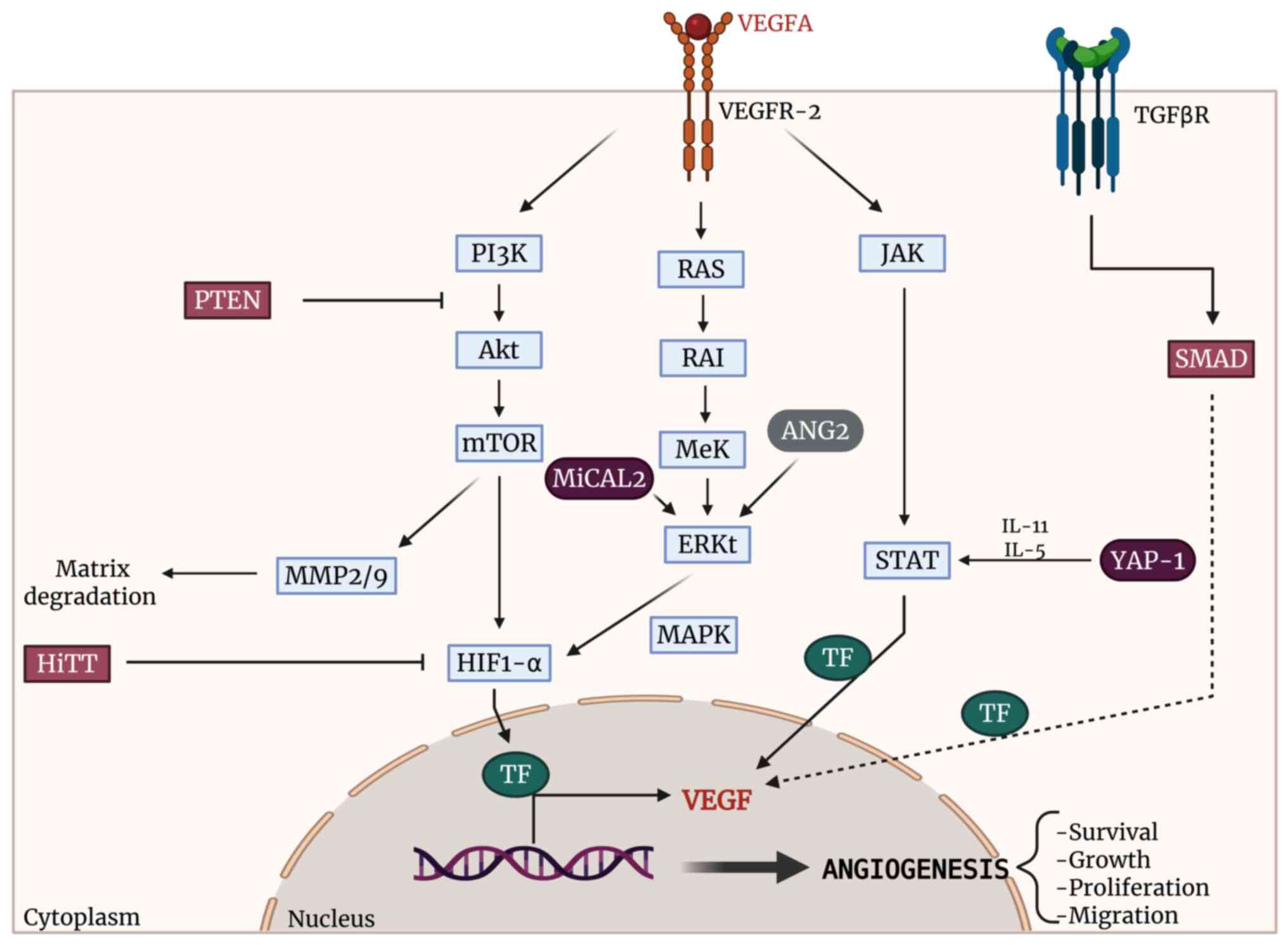
Roskoski R Jr: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 62:179–213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lamalice L, Houle F and Huot J:
Phosphorylation of Tyr 1214 within VEGFR-2 triggers the recruitment
of nck and activation of fyn leading to SAPK2/P38 activation and
endothelial cell migration in response to VEGF. J Biol Chem.
281:34009–34020. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Laddha AP and Kulkarni YA: VEGF and FGF-2:
Promising targets for the treatment of respiratory disorders.
Respir Med. 156:33–46. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu Y, Liu Y, Deng J, Li W and Nie X:
Fibroblast growth factor in diabetic foot ulcer: Progress and
therapeutic prospects. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:7448682021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Goumans MJ, Valdimarsdottir G, Itoh S,
Rosendahl A, Sideras P and Ten Dijke P: Balancing the activation
state of the endothelium via two distinct TGF-Beta type I
receptors. EMBO J. 21:1743–1753. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tabruyn SP, Hansen S, Ojeda-Fernández ML,
Bovy N, Zarrabeitia R, Recio-Poveda L, Bernabéu C, Martial JA,
Botella LM and Struman I: MiR-205 is downregulated in hereditary
hemorrhagic telangiectasia and impairs TGF-Beta signaling pathways
in endothelial cells. Angiogenesis. 16:877–887. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Di Benedetto P, Ruscitti P, Berardicurti
O, Panzera N, Grazia N, Di Vito Nolfi M, Di Francesco B, Navarini
L, Maurizi A, Rucci N, et al: Blocking Jak/STAT signalling using
tofacitinib inhibits angiogenesis in experimental arthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 23:2132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang X, Song Y, Wu Y, Dong Y, Lai L,
Zhang J, Lu B, Dai F, He L, Liu M and Yi Z: Indirubin inhibits
tumor growth by antitumor angiogenesis via blocking VEGFR2-Mediated
JAK/STAT3 signaling in endothelial cell. Int J Cancer.
129:2502–2511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gong W, Wang L, Yao JC, Ajani JA, Wei D,
Aldape KD, Xie K, Sawaya R and Huang S: Expression of activated
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 predicts
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in and angiogenic
phenotype of human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1386–1393.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tan A, Li T, Ruan L, Yang J, Luo Y, Li L
and Wu X: Knockdown of Malat1 alleviates high-glucose-induced
angiogenesis through regulating miR-205-5p/VEGF-A axis. Exp Eye
Res. 207:1085852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ybarra M, Martínez-Santos M, Oltra M,
Muriach M, Pires ME, Ceresoni C, Sancho-Pelluz J and Barcia JM:
MiR-205-5p modulates high glucose-induced VEGFA levels in diabetic
mice and ARPE-19 cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 14:2182025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zeng Y, Zhu J, Shen D, Qin H, Lei Z, Li W,
Huang JA and Liu Z: Repression of Smad4 by MiR-205 moderates
TGF-β-Induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cell lines.
Int J Oncol. 49:700–708. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Du YE, Tu G, Yang G, Li G, Yang D, Lang L,
Xi L, Sun K, Chen Y, Shu K, et al: MiR-205/YAP1 in activated
fibroblasts of breast tumor promotes VEGF-independent angiogenesis
through STAT3 signaling. Theranostics. 7:3972–3988. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cai J, Fang L, Huang Y, Li R, Yuan J, Yang
Y, Zhu X, Chen B, Wu J and Li M: MiR-205 Targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to
augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5402–5415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yao L, Shi W and Gu J: Micro-RNA 205-5p is
involved in the progression of gastric cancer and targets
phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in SGC-7901 human gastric
cancer cells. Med Sci Monit. 25:6367–6377. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Salajegheh A, Vosgha H, Md Rahman A, Amin
M, Smith RA and Lam AK: Modulatory role of miR-205 in angiogenesis
and progression of thyroid cancer. J Mol Endocrinol. 55:183–196.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Vosgha H, Ariana A, Smith RA and Lam AK:
miR-205 targets angiogenesis and EMT concurrently in anaplastic
thyroid carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 25:323–337. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhang J, Zhang J, Pang X, Chen Z, Zhang Z,
Lei L, Xu H, Wen L, Zhu J, Jiang Y, et al: MiR-205-5p suppresses
angiogenesis in gastric cancer by downregulating the expression of
VEGFA and FGF1. Exp Cell Res. 404:1125792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang HY, Zhang QY, Liu Q, Feng SG, Ma Y,
Wang FS, Zhu Y, Yao J and Yan B: Exosome-loading miR-205: A
two-pronged approach to ocular neovascularization therapy. J
Nanobiotechnology. 23:362025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhu L, Zhong Q, Yang T and Xiao X:
Improved therapeutic effects on diabetic foot by human mesenchymal
stem cells expressing MALAT1 as a sponge for microRNA-205-5p. Aging
(Albany NY). 11:12236–12245. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gao C, Zhang CC, Yang HX and Hao YN:
MALAT1 protected the angiogenesis function of human brain
microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) under oxygen glucose
deprivation/re-oxygenation (OGD/R) challenge by interacting with
MiR-205-5p/VEGFA pathway. Neuroscience. 435:135–145. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Krebs M, Kotlyar MJ, Fahl J, Janaki Raman
S, Röhrig F, Marquardt A, Kübler H, Kneitz B, Schulze A and
Kalogirou C: Metformin regulates the miR-205/VEGFA axis in renal
cell carcinoma cells: Exploring a clinical synergism with tyrosine
kinase inhibitors. Urol Int. 108:49–59. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Ouyang Z, Tan T, Zhang X, Wan J, Zhou Y,
Jiang G, Yang D and Liu T: LncRNA ENST00000563492 promoting the
osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling process in bone mesenchymal stem
cells (BMSCs) by functions as a ceRNA for miR-205-5p. Cell Death
Dis. 11:4862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Botella LM, Albiñana V, Ojeda-Fernandez L,
Recio-Poveda L and Bernabéu C: Research on potential biomarkers in
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Front Genet. 6:1152015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ribatti D: Napoleone ferrara and the saga
of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endothelium. 15:1–8. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Hammes HP, Lin J, Wagner P, Feng Y, Vom
Hagen F, Krzizok T, Renner O, Breier G, Brownlee M and Deutsch U:
Angiopoietin-2 causes pericyte dropout in the normal retina:
Evidence for involvement in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes.
53:1104–1110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Biel NM and Siemann DW: Targeting the
angiopoietin-2/Tie-2 axis in conjunction with VEGF signal
interference. Cancer Lett. 380:525–533. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Abouaitah K, Hassan HA, Swiderska-Sroda A,
Gohar L, Shaker OG, Wojnarowicz J, Opalinska A, Smalc-Koziorowska
J, Gierlotka S and Lojkowski W: Targeted nano-drug delivery of
colchicine against colon cancer cells by means of mesoporous silica
nanoparticles. Cancers (Basel). 12:1442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Guo X, Niu Y, Han W, Han X, Chen Q, Tian
S, Zhu Y, Bai D and Li K: The ALK1-Smad1/5-ID1 pathway participates
in tumour angiogenesis induced by low-dose photodynamic therapy.
Int J Oncol. 62:552023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
89
|
Seystahl K, Tritschler I, Szabo E,
Tabatabai G and Weller M: Differential regulation of TGF-β-Induced,
ALK-5-Mediated VEGF release by SMAD2/3 versus SMAD1/5/8 signaling
in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 17:254–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Duan Y and Chen Q: TGF-Β1 Regulating
MiR-205/MiR-195 expression affects the TGF-β signal pathway by
respectively targeting SMAD2/SMAD7. Oncol Rep. 36:1837–1844. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA and
Massagué J: Integration of smad and forkhead pathways in the
control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation.
Cell. 117:211–223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Qi J, Liu Y, Hu K, Zhang Y, Wu Y and Zhang
X: MicroRNA-205-5p regulates extracellular matrix production in
hyperplastic scars by targeting Smad2. Exp Ther Med. 17:2284–2290.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Mariotti S, Barravecchia I, Vindigni C,
Pucci A, Balsamo M, Libro R, Senchenko V, Dmitriev A, Jacchetti E,
Cecchini M, et al: MICAL2 is a novel human cancer gene controlling
mesenchymal to epithelial transition involved in cancer growth and
invasion. Oncotarget. 7:1808–1825. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
94
|
Hou ST, Nilchi L, Li X, Gangaraju S, Jiang
SX, Aylsworth A, Monette R and Slinn J: Semaphorin3A elevates
vascular permeability and contributes to cerebral ischemia-induced
brain damage. Sci Rep. 5:78902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Evans IM, Kennedy SA, Paliashvili K,
Santra T, Yamaji M, Lovering RC, Britton G, Frankel P, Kolch W and
Zachary IC: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) promotes
assembly of the P130Cas interactome to drive endothelial
chemotactic signaling and angiogenesis. Mol Cell Proteomics.
16:168–180. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
96
|
Wang Y, Deng W, Zhang Y, Sun S, Zhao S,
Chen Y, Zhao X, Liu L and Du J: MICAL2 promotes breast cancer cell
migration by maintaining epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
stability and EGFR/P38 signalling activation. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
2222018.
|
|
97
|
Ho JR, Chapeaublanc E, Kirkwood L, Nicolle
R, Benhamou S, Lebret T, Allory Y, Southgate J, Radvanyi F and Goud
B: Deregulation of Rab and Rab effector genes in bladder cancer.
PLoS One. 2012(7): e394692012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Barravecchia I, Mariotti S, Pucci A,
Scebba F, De Cesari C, Bicciato S, Tagliafico E, Tenedini E,
Vindigni C, Cecchini M, et al: MICAL2 is expressed in cancer
associated neo-angiogenic capillary endothelia and it is required
for endothelial cell viability, motility and VEGF response. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1865:2111–2124. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Tao W, Sun W, Zhu H and Zhang J:
MiR-205-5p suppresses pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation by targeting MICAL2-mediated Erk1/2 signaling.
Microvasc Res. 124:43–50. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Taylor KL, Henderson AM and Hughes CC:
Notch activation during endothelial cell network formation in vitro
targets the basic HLH Transcription factor HESR-1 and downregulates
VEGFR-2/KDR expression. Microvasc Res. 64:372–383. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ho RX, Meyer RD, Chandler KB, Ersoy E,
Park M, Bondzie PA, Rehimi N, Xu H, Costello CE and Rahimi N:
MINAR1 Is a Notch2-binding protein that inhibits angiogenesis and
breast cancer growth. J Mol Cell Biol. 10:195–204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ramasamy SK, Kusumbe AP, Wang L and Adams
RH: Endothelial notch activity promotes angiogenesis and
osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 507:376–380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Jiang W, Zhu P, Zhang T, Liao F, Yu Y, Liu
Y, Shen H, Zhao Z, Huang X and Zhou N: MicroRNA-205 mediates
endothelial progenitor functions in distraction osteogenesis by
targeting the transcription regulator NOTCH2. Stem Cell Res Ther.
12:1012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Piccolo S, Dupont S and Cordenonsi M: The
biology of YAP/TAZ: Hippo signaling and beyond. Physiol Rev.
94:1287–1312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Li D, Wang Q, Li N and Zhang S: miR-205
targets YAP1 and inhibits proliferation and invasion in thyroid
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 18:1674–1681. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Xian XS, Wang YT and Jiang XM: Propofol
inhibits proliferation and invasion of stomach cancer cells by
regulating Mir-205/Yap1 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:10771–10779.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Han N, Tian W, Yu N and Yu L: YAP1 Is
required for the angiogenesis in retinal microvascular endothelial
cells via the inhibition of MALAT1-mediated miR-200b-3p in high
glucose-induced diabetic retinopathy. J Cell Physiol.
235:1309–1320. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Giordano NJ, Jansson PS, Young MN, Hagan
KA and Kabrhel C: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, stratification,
and natural history of pulmonary embolism. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol.
20:135–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Li WD and Li XQ: Endothelial progenitor
cells accelerate the resolution of deep vein thrombosis. Vascul
Pharmacol. 83:10–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Li WD, Hu N, Lei FR, Wei S, Rong JJ,
Zhuang H and Li XQ: Autophagy inhibits endothelial progenitor cells
migration via the regulation of MMP2, MMP9 and UPA under normoxia
condition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 466:376–380. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A and
Testa JR: Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: Implications for
therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 94:29–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yanagi S, Kishimoto H, Kawahara K, Sasaki
T, Sasaki M, Nishio M, Yajima N, Hamada K, Horie Y, Kubo H, et al:
Pten controls lung morphogenesis, bronchioalveolar stem cells, and
onset of lung adenocarcinomas in mice. J Clin Invest.
117:2929–2940. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Karaayvaz M, Zhang C, Liang S, Shroyer KR
and Ju J: Prognostic significance of miR-205 in endometrial cancer.
PLoS One. 7:e351582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Unwith S, Zhao H, Hennah L and Ma D: The
potential role of HIF on tumour progression and dissemination. Int
J Cancer. 136:2491–2503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
El-Naggar AM, Veinotte CJ, Cheng H,
Grunewald TG, Negri GL, Somasekharan SP, Corkery DP, Tirode F,
Mathers J, Khan D, et al: Translational activation of HIF1α by YB-1
promotes sarcoma metastasis. Cancer Cell. 27:682–697. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Auyeung KK and Ko JK: Angiogenesis and
oxidative stress in metastatic tumor progression: pathogenesis and
novel therapeutic approach of colon cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
23:3952–3961. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Heidarzadeh M, Gürsoy-Özdemir Y, Kaya M,
Eslami Abriz A, Zarebkohan A, Rahbarghazi R and Sokullu E: Exosomal
Delivery of Therapeutic Modulators through the Blood-Brain Barrier;
Promise and Pitfalls. Cell Biosci. 11:1422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Chen Y, Kleeff J and Sunami Y: Pancreatic
cancer cell- and cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomes in
disease progression, metastasis, and therapy. Discov Oncol.
15:2532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kamerkar S, Lebleu VS, Sugimoto H, Yang S,
Ruivo CF, Melo SA, Lee JJ and Kalluri R: Exosomes facilitate
therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer.
Nature. 546:498–503. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Mendt M, Kamerkar S, Sugimoto H, McAndrews
KM, Wu CC, Gagea M, Yang S, Blanko EVR, Peng Q, Ma X, et al:
Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic
cancer. JCI Insight. 3:e992632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ateeq M, Broadwin M, Sellke FW and Abid
MR: Extracellular vesicles' role in angiogenesis and altering
angiogenic signaling. Med Sci (Basel). 12:42024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Todorova D, Simoncini S, Lacroix R,
Sabatier F and Dignat-George F: Extracellular vesicles in
angiogenesis. Circ Res. 120:1658–1673. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Wang T, Li T, Niu X, Hu L, Cheng J, Guo D,
Ren H, Zhao R, Ji Z, Liu P, et al: ADSC-derived exosomes attenuate
myocardial infarction injury by promoting MiR-205-Mediated cardiac
angiogenesis. Biol Direct. 18:62023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Yang W, Tan S, Yang L, Chen X, Yang R,
Oyang L, Lin J, Xia L, Wu N, Han Y, et al: Exosomal MiR-205-5p
enhances angiogenesis and nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis by
targeting desmocollin-2. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 24:612–623. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
He L, Zhu W, Chen Q, Yuan Y, Wang Y, Wang
J and Wu X: Ovarian cancer cell-secreted exosomal miR-205 promotes
metastasis by inducing angiogenesis. Theranostics. 9:8206–8220.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Qu Q, Liu L, Wang L, Cui Y, Liu C, Jing X
and Xu X: Exosomes derived from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells
restore ovarian function by enhancing angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 15:4962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Liu J, Wang J, Fu W, Wang X, Chen H, Wu X,
Lao G, Wu Y, Hu M, Yang C, et al: MiR-195-5p and MiR-205-5p in
extracellular vesicles isolated from diabetic foot ulcer wound
fluid decrease angiogenesis by inhibiting VEGFA expression. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:19805–19821. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zhuang D, Wang S, Liu G, Liu P, Deng H,
Sun J, Liu C, Leng X, Zhang Q, Bai F, et al: Phenformin suppresses
angiogenesis through the regulation of exosomal microRNA-1246 and
MicroRNA-205 levels derived from oral squamous cell carcinoma
cells. Front Oncol. 12:9434772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Lin D, Halilovic A, Yue P, Bellner L, Wang
K, Wang L and Zhang C: Inhibition of miR-205 impairs the
wound-healing process in human corneal epithelial cells by
targeting KIR4.1 (KCNJ10). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:6167–6178.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Fu JY, Yu XF, Wang HQ, Lan JW, Shao WQ and
Huo YN: MiR-205-3p protects human corneal epithelial cells from
ultraviolet damage by inhibiting autophagy via targeting TLR4/NF-κB
signaling. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 12:6494–6504. 2020.
|
|
131
|
Hughes AE, Bradley DT, Campbell M, Lechner
J, Dash DP, Simpson DA and Willoughby CE: Mutation altering the
miR-184 seed region causes familial keratoconus with cataract. Am J
Hum Genet. 89:628–633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Asal M, Koçak G, Sarı V, Reçber T, Nemutlu
E, Utine CA and Güven S: Development of lacrimal gland organoids
from iPSC derived multizonal ocular cells. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10:10588462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Urbán P, Pöstyéni E, Czuni L, Herczeg R,
Fekete C, Gábriel R and Kovács-Valasek A: miRNA profiling of
developing rat retina in the first three postnatal weeks. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 43:2963–2974. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
CATT Research Group; Martin DF, Maguire
MG, Ying GS, Grunwald JE, Fine SL and Jaffe GJ: Ranibizumab and
bevacizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N
Engl J Med. 364:1897–1908. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Fine HF, Baffi J, Reed GF, Csaky KG and
Nussenblatt RB: Aqueous humor and plasma vascular endothelial
growth factor in uveitis-associated cystoid macular edema. Am J
Ophthalmol. 132:794–796. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Kozak I, Shoughy SS and Stone DU:
Intravitreal antiangiogenic therapy of uveitic macular edema: A
review. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 33:235–239. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Massa H, Pipis SY, Adewoyin T, Vergados A,
Patra S and Panos GD: Macular edema associated with non-infectious
uveitis: Pathophysiology, etiology, prevalence, impact and
management challenges. Clin Ophthalmol. 13:1761–1777. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Içme G, Yilmaz A, Dinç E, Görür A, Fidanci
ŞB and Tamer L: Assessment of miR-182, miR-183, miR-184, and
miR-221 expressions in primary pterygium and comparison with the
normal conjunctiva. Eye Contact Lens. 45:208–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Blasiak J, Watala C, Tuuminen R, Kivinen
N, Koskela A, Uusitalo-Järvinen H, Tuulonen A, Winiarczyk M,
Mackiewicz J, Zmorzyński S, et al: Expression of VEGFA-regulating
MiRNAs and mortality in wet AMD. J Cell Mol Med. 23:8464–8471.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Li JH, Sun SS, Li N, Lv P, Xie SY and Wang
PY: MiR-205 as a promising biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis
of lung cancer. Oncotarget. 8:91938–91949. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Piccinno E, Schirizzi A, Scalavino V, De
Leonardis G, Donghia R, Fantasia A, Ricci AD, Lotesoriere C,
Giannelli G, Serino G and D'Alessandro R: Circulating miR-23b-3p,
miR-30e-3p, and miR-205-5p as novel predictive biomarkers for
ramucirumab-paclitaxel therapy outcomes in advanced gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 25:134982024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Gallant-Behm CL, Piper J, Dickinson BA,
Dalby CM, Pestano LA and Jackson AL: A synthetic microRNA-92a
inhibitor (MRG-110) accelerates angiogenesis and wound healing in
diabetic and nondiabetic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 26:311–323.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Viridian Therapeutics Inc.: MiRagen
announces new clinical data showing MRG-110 positively impacted
tissue repair and new blood vessel growth. https://investors.viridiantherapeutics.com/news/news-details/2019/miRagen-Announces-New-Clinical-Data-Showing-MRG-110-Positively-Impacted-Tissue-Repair-and-New-Blood-Vessel-Growth-10-16-2019/default.aspx.
Accessed October 13, 2025
|