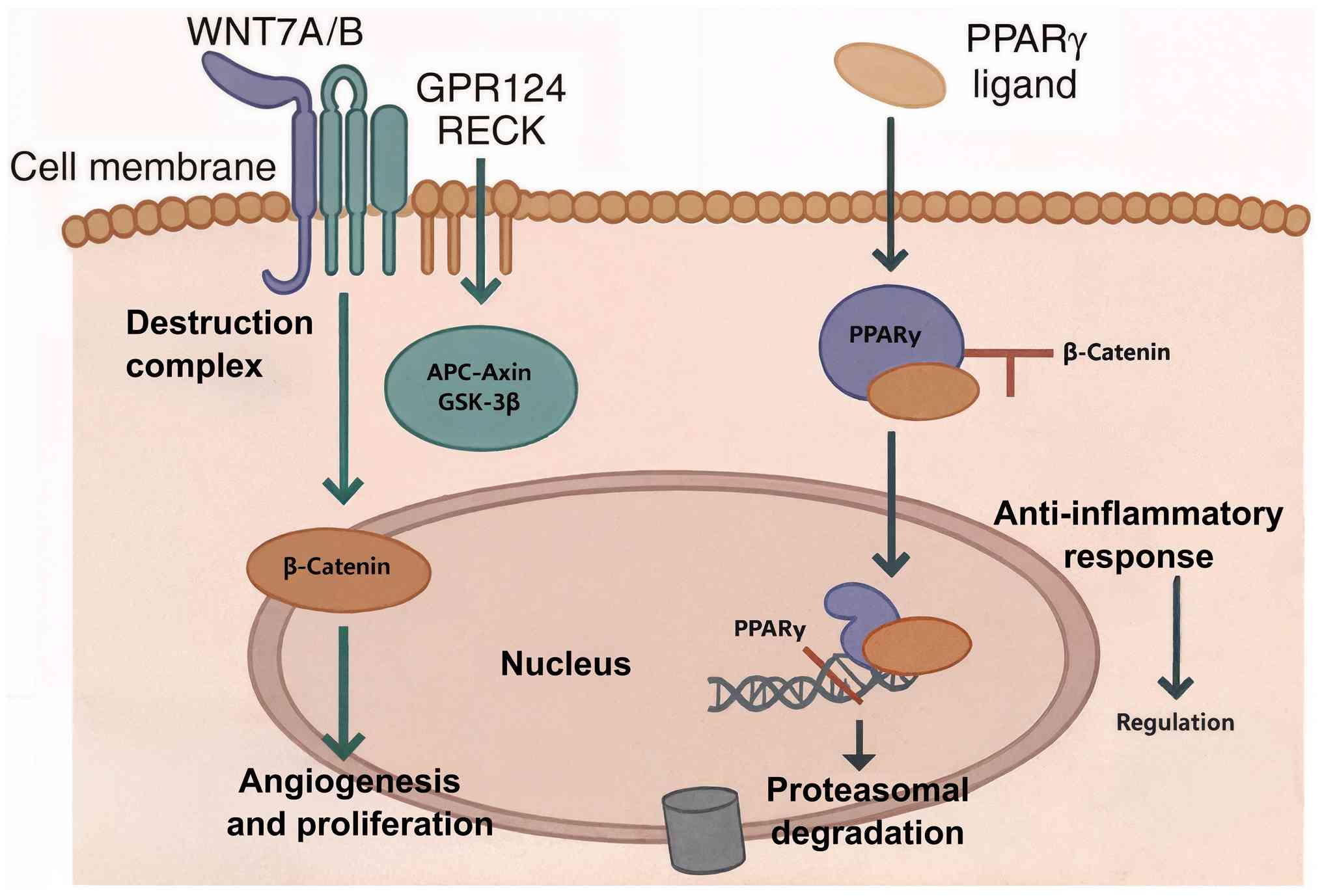
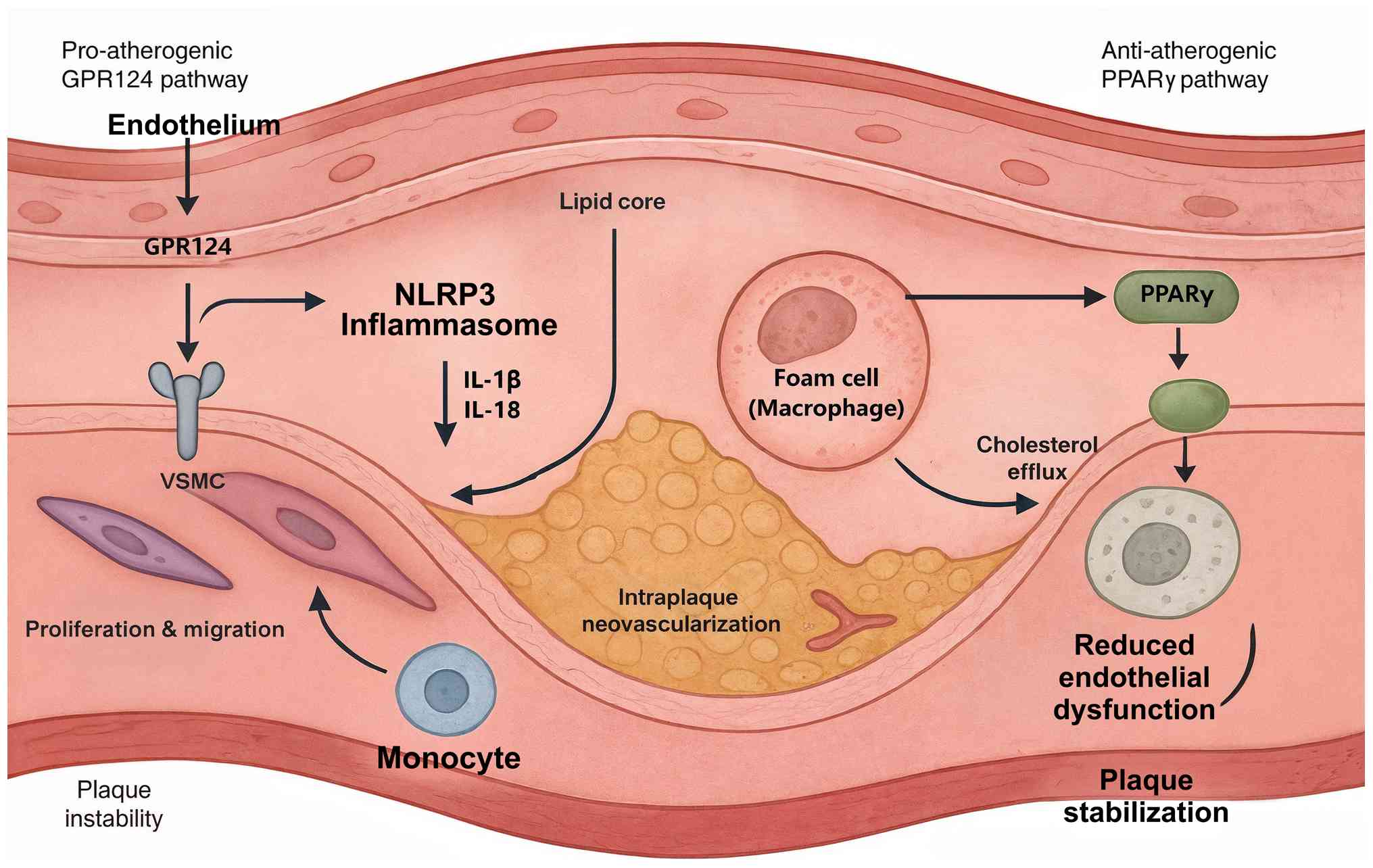
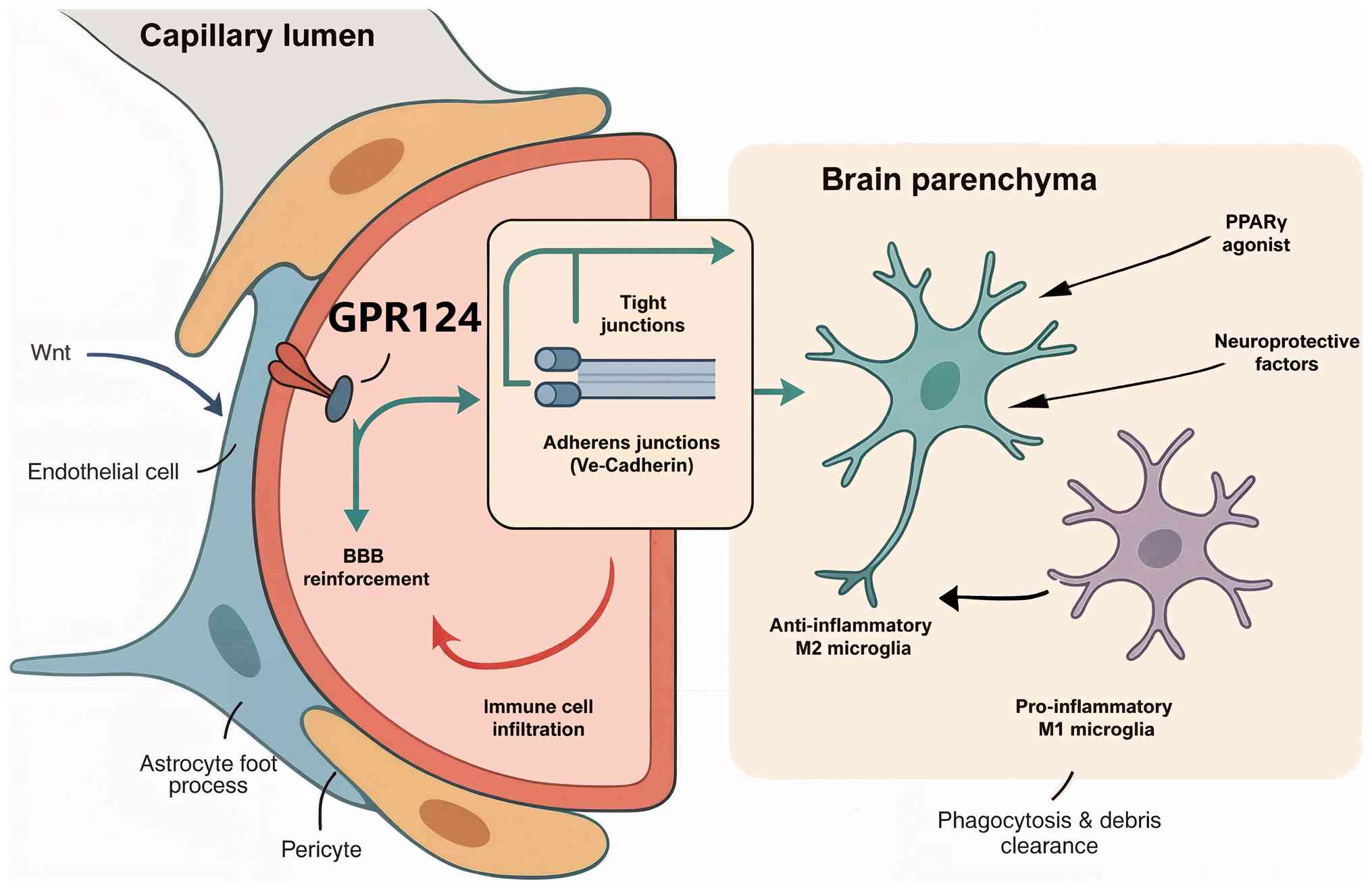
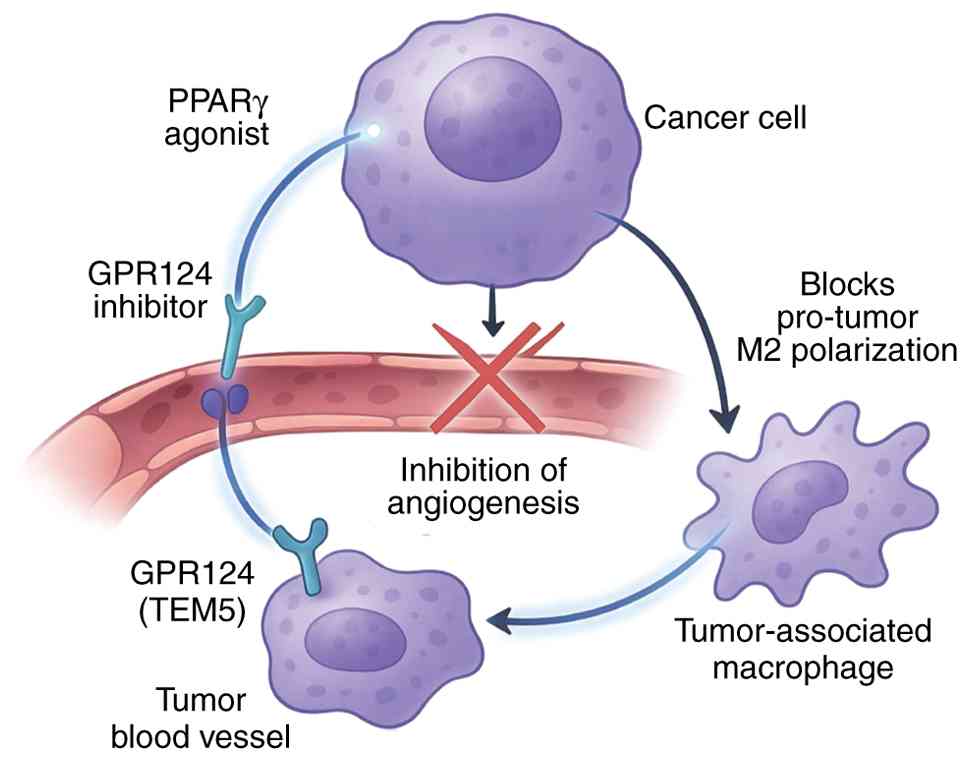
|
1
|
Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng
J, Li Y, Wang X and Zhao L: Inflammatory responses and
inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget.
9:7204–7218. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hotamisligil GS: Inflammation,
metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. 542:177–185.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lecarpentier Y, Claes V, Vallée A and
Hébert JL: Interactions between PPAR gamma and the canonical
Wnt/Beta-catenin pathway in type 2 diabetes and colon cancer. PPAR
Res. 2017:58790902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y, Guillevin R and
Vallée JN: Opposite interplay between the canonical WNT/β-Catenin
pathway and PPAR Gamma: A potential therapeutic target in gliomas.
Neurosci Bull. 34:573–588. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Anderson KD, Pan L, Yang XM, Hughes VC,
Walls JR, Dominguez MG, Simmons MV, Burfeind P, Xue Y, Wei Y, et
al: Angiogenic sprouting into neural tissue requires Gpr124, an
orphan G protein-coupled receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:2807–2812. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kuhnert F, Mancuso MR, Shamloo A, Wang HT,
Choksi V, Florek M, Su H, Fruttiger M, Young WL, Heilshorn SC and
Kuo CJ: Essential regulation of CNS angiogenesis by the orphan G
protein-coupled receptor GPR124. Science. 330:985–989. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Duan Y, Chu Q, Lv H, Li J, Guo X,
Gao Y, Liu M, Tang W, Hu H, et al: G-protein coupled receptor
GPR124 protects against podocyte senescence and injury in diabetic
kidney disease. Kidney Int. 107:652–665. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Tischfield M, Williams J,
Smallwood PM, Rattner A, Taketo MM and Nathans J: Canonical WNT
signaling components in vascular development and barrier formation.
J Clin Invest. 124:3825–3846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Posokhova E, Shukla A, Seaman S, Volate S,
Hilton MB, Wu B, Morris H, Swing DA, Zhou M, Zudaire E, et al:
GPR124 functions as a WNT7-specific coactivator of canonical
β-catenin signaling. Cell Rep. 10:123–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mal S, Dwivedi AR and Kumar V, Kumar N,
Kumar B and Kumar V: Role of peroxisome Proliferator-activated
receptor gamma (PPARγ) in different disease states: Recent updates.
Curr Med Chem. 28:3193–3215. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tu CC, Hsieh TH, Chu CY, Lin YC, Lin BJ
and Chen CH: Targeting PPARγ via SIAH1/2-mediated
ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation as a new therapeutic approach in
luminal-type bladder cancer. Cell Death Dis. 15:9082024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jangra A, Babu B, Divakar S, Gowramma B,
Rajan S, Jangra S and Malakar V: An in-depth review of PPARγ
modulators as anti-diabetes therapeutics. Drug Metab Rev.
57:311–337. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chi T, Wang M, Wang X, Yang K, Xie F, Liao
Z and Wei P: PPAR-γ Modulators as current and potential cancer
treatments. Front Oncol. 11:7377762021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jansson EA, Are A, Greicius G, Kuo IC,
Kelly D, Arulampalam V and Pettersson S: The Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling pathway targets PPARgamma activity in colon cancer cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:1460–1465. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xue C, Chu Q, Shi Q, Zeng Y, Lu J and Li
L: Wnt signaling pathways in biology and disease: Mechanisms and
therapeutic advances. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 10:1062025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bostaille N, Gauquier A, Twyffels L and
Vanhollebeke B: Molecular insights into Adgra2/Gpr124 and Reck
intracellular trafficking. Biol Open. 5:1874–1881. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang J, Mancuso MR, Maier C, Liang X,
Yuki K, Yang L, Kwong JW, Wang J, Rao V, Vallon M, et al: Gpr124 is
essential for blood-brain barrier integrity in central nervous
system disease. Nat Med. 23:450–460. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Gastfriend BD, Nishihara H, Canfield SG,
Foreman KL, Engelhardt B, Palecek SP and Shusta EV: Wnt signaling
mediates acquisition of blood-brain barrier properties in naïve
endothelium derived from human pluripotent stem cells. ELife.
10:e709922021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhou Y and Nathans J: Gpr124 controls CNS
angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier integrity by promoting
ligand-specific canonical wnt signaling. Dev Cell. 31:248–256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu H, Kohno S, Voon DC, Hussein NH, Zhang
Y, Nakayama J, Takegami Y and Takahashi C: RECK/GPR124-driven WNT
signaling in pancreatic and gastric cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
115:3013–3025. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
America M, Bostaille N, Eubelen M, Martin
M, Stainier DYR and Vanhollebeke B: An integrated model for Gpr124
function in Wnt7a/b signaling among vertebrates. Cell Rep.
39:1109022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Cho SG, Wu X, Siwko S and Liu M:
G-protein coupled receptor 124 (GPR124) in endothelial cells
regulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced tumor
angiogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 14:543–554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kroker AJ and Bruning JB: Review of the
structural and dynamic mechanisms of PPARγ partial agonism. PPAR
Res. 2015:8168562015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lefterova MI, Haakonsson AK, Lazar MA and
Mandrup S: PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:293–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Z, Luo L, Yu W, Li P, Ou D, Liu J, Ma
H, Sun Q, Liang A, Huang C, et al: PPARγ phase separates with RXRα
at PPREs to regulate target gene expression. Cell Discov. 8:372022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ahmadian M, Suh JM, Hah N, Liddle C,
Atkins AR, Downes M and Evans RM: PPARγ signaling and metabolism:
The good, the bad and the future. Nat Med. 19:557–566. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bougarne N, Paumelle R, Caron S, Hennuyer
N, Mansouri R, Gervois P, Staels B, Haegeman G and De Bosscher K:
PPARalpha blocks glucocorticoid receptor alpha-mediated
transactivation but cooperates with the activated glucocorticoid
receptor alpha for transrepression on NF-kappaB. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:7397–7402. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Basil MC and Levy BD: Specialized
pro-resolving mediators: Endogenous regulators of infection and
inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 16:51–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gao Z, Xu X, Li Y, Sun K, Yang M, Zhang Q,
Wang S, Lin Y, Lou L, Wu A, et al: Mechanistic insight into PPARγ
and tregs in atherosclerotic immune inflammation. Front Pharmacol.
12:7500782021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
O'Neill LA and Pearce EJ: Immunometabolism
governs dendritic cell and macrophage function. J Exp Med.
213:15–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Kasprzak A: Angiogenesis-related functions
of wnt signaling in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel).
12:36012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sidrat T, Rehman ZU, Joo MD, Lee KL and
Kong IK: Wnt/β-catenin Pathway-mediated PPARδ expression during
embryonic development differentiation and disease. Int J Mol Scie.
22:18542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
van Kappel EC and Maurice MM: Molecular
regulation and pharmacological targeting of the β-catenin
destruction complex. Br J Pharmacol. 174:4575–4588. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lecarpentier Y, Schussler O, Hébert JL and
Vallée A: Multiple targets of the canonical WNT/β-Catenin signaling
in cancers. Front Oncol. 9:12482019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sabatino L, Pancione M, Votino C,
Colangelo T, Lupo A, Novellino E, Lavecchia A and Colantuoni V:
Emerging role of the β-catenin-PPARγ axis in the pathogenesis of
colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 20:7137–7151. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Liu J, Wang H, Zuo Y and Farmer SR:
Functional interaction between peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma and beta-catenin. Mol Cell Biol. 26:5827–5837. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y and Vallée JN:
Interplay of opposing effects of the WNT/β-Catenin pathway and
PPARγ and implications for SARS-CoV2 treatment. Front Immunol.
12:6666932021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cui H, Wang Y, Huang H, Yu W, Bai M, Zhang
L, Bryan BA, Wang Y, Luo J, Li D, et al: GPR126 protein regulates
developmental and pathological angiogenesis through modulation of
VEGFR2 receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 289:34871–34885. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shen Y, Lian Y, Xiao L, Miu Y, Niu J and
Cui Q: GPR124 promotes trophoblast proliferation, migration, and
invasion and inhibits trophoblast cell apoptosis and inflammation
via JNK and P38 MAPK pathways. J Cell Physiol. 239:e312982024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Westerweel PE and Verhaar MC: Protective
actions of PPAR-gamma activation in renal endothelium. PPAR Res.
2008:6356802008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Audano M, Pedretti S, Caruso D, Crestani
M, De Fabiani E and Mitro N: Regulatory mechanisms of the early
phase of white adipocyte differentiation: An overview. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 79:1392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Luan J, Ji X and Liu L: PPARγ in
atherosclerotic endothelial dysfunction: Regulatory compounds and
PTMs. Int J Mol Sci. 24:144942023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Patial S, Sharma A, Raj K and Shukla G:
Atherosclerosis: Progression, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment,
probiotics and synbiotics as a new prophylactic hope. The Microbe.
5:1002122024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lin WY, Dong YL, Lin Y, Sunchuri D and Guo
ZL: Potential role of G protein-coupled receptor 124 in
cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease (review). Exp Ther Med.
29:22025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lu N, Cheng W, Liu D, Liu G, Cui C, Feng C
and Wang X: NLRP3-Mediated inflammation in atherosclerosis and
associated therapeutics. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8233872022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chai Q, Guo C, Li L, Cao J, Liu H and Lu
Z: Association of angiogenesis-associated genes with
atherosclerotic plaque progression, intraplaque hemorrhage, and
immune infiltration. Heliyon. 10:e326922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR,
Kruth HS, Weber DK, Farb A, Guerrero LJ, Hayase M, Kutys R, et al:
Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N Engl
J Med. 349:2316–2325. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yu L, Gao Y, Aaron N and Qiang L: A
glimpse of the connection between PPARγ and macrophage. Front
Pharmacol. 14:12543172023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bäck M, Yurdagul A Jr, Tabas I, Öörni K
and Kovanen PT: Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis:
Mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cardiol.
16:389–406. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Beyer AM, Baumbach GL, Halabi CM, Modrick
ML, Lynch CM, Gerhold TD, Ghoneim SM, de Lange WJ, Keen HL, Tsai
YS, et al: Interference with PPARgamma signaling causes cerebral
vascular dysfunction, hypertrophy, and remodeling. Hypertension.
51:867–871. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chawla A, Boisvert WA, Lee CH, Laffitte
BA, Barak Y, Joseph SB, Liao D, Nagy L, Edwards PA, Curtiss LK, et
al: A PPAR gamma-LXR-ABCA1 pathway in macrophages is involved in
cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis. Mol Cell. 7:161–171. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Iwasaki H, Yagyu H and Shimano H: A
Comprehensive analysis of diabetic complications and advances in
management strategies. J Atheroscler Thromb. 32:550–559. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Xing X, Li M, Liu Y, Xu A
and Zhang J: Podocyte injury of diabetic nephropathy: Novel
mechanism discovery and therapeutic prospects. Biomed Pharmacother.
168:1156702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li L and Liu Y: Podocyte aging and
diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 107:596–598. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wan J, Hou X, Zhou Z, Geng J, Tian J, Bai
X and Nie J: WT1 ameliorates podocyte injury via repression of
EZH2/β-catenin pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic Biol
Med. 108:280–299. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang Y, Yang M, Wang X, Zou H, Chen X and
Yuan R: Role of Gpr124 in the migration and proliferation of
retinal microvascular endothelial cells and microangiopathies in
diabetic retinopathy. Mol Biotechnol. 67:2467–2480. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Al-Latayfeh M, Silva PS, Sun JK and Aiello
LP: Antiangiogenic therapy for ischemic retinopathies. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0064112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Villacorta L, Schopfer FJ, Zhang J,
Freeman BA and Chen YE: PPARgamma and its ligands: Therapeutic
implications in cardiovascular disease. Clin Sci (Lond).
116:205–218. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ding Y, Kang J, Liu S, Xu Y and Shao B:
The protective effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma in cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion injury. Front
Neurol. 11:5885162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chaudhari N, Talwar P, Parimisetty A,
Lefebvre d'Hellencourt C and Ravanan P: A molecular web:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Front Cell Neurosci. 8:2132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Dantzer R: Neuroimmune interactions: From
the brain to the immune system and vice versa. Physiol Rev.
98:477–504. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wong CK, McLean BA, Baggio LL, Koehler JA,
Hammoud R, Rittig N, Yabut JM, Seeley RJ, Brown TJ and Drucker DJ:
Central glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor activation inhibits
Toll-like receptor agonist-induced inflammation. Cell Metab.
36:130–143.e5. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Ho LT, Fang YW, Hsu PS, Wang JT and Tsai
MH: Association between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist
therapy and respiratory illness in patients with type 2 diabetes: A
retrospective observational cohort study. Sci Rep. 15:356252025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Thangavel N, Al Bratty M, Akhtar Javed S,
Ahsan W and Alhazmi HA: Targeting peroxisome Proliferator-activated
receptors using thiazolidinediones: Strategy for design of novel
antidiabetic drugs. Int J Med Chem. 2017:10697182017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kapadia R, Yi JH and Vemuganti R:
Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of
PPAR-gamma agonists. Front Biosci. 13:1813–1826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Adamu A, Li S, Gao F and Xue G: The role
of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: Current
understanding and future therapeutic targets. Front Aging Neurosci.
16:13479872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lochhead JJ, Yang J, Ronaldson PT and
Davis TP: Structure, function, and regulation of the Blood-brain
barrier tight junction in central nervous system disorders. Front
Physiol. 11:9142020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Hashimoto Y, Greene C, Munnich A and
Campbell M: The CLDN5 gene at the blood-brain barrier in health and
disease. Fluids Barriers CNS. 20:222023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liebner S, Dijkhuizen RM, Reiss Y, Plate
KH, Agalliu D and Constantin G: Functional morphology of the
blood-brain barrier in health and disease. Acta Neuropathol.
135:311–336. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhang S, Gao Y, Zhao Y, Huang TY, Zheng Q
and Wang X: Peripheral and central neuroimmune mechanisms in
Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Mol Neurodegener. 20:222025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen DY, Sun NH, Lu YP, Hong LJ, Cui TT,
Wang CK, Chen XH, Wang SS, Feng LL, Shi WX, et al: GPR124
facilitates pericyte polarization and migration by regulating the
formation of filopodia during ischemic injury. Theranostics.
9:5937–5955. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Nicolakakis N and Hamel E: The nuclear
receptor PPARgamma as a therapeutic target for cerebrovascular and
brain dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci.
2:212021.
|
|
73
|
Shao F, Wang X, Wu H, Wu Q and Zhang J:
Microglia and neuroinflammation: Crucial pathological mechanisms in
traumatic brain Injury-Induced Neurodegeneration. Front Aging
Neurosci. 14:8250862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Corona JC and Duchen MR: PPARγ as a
therapeutic target to rescue mitochondrial function in neurological
disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 100:153–163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bhatti JS, Bhatti GK and Reddy PH:
Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic
disorders-A step towards mitochondria based therapeutic strategies.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:1066–1077. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Greten FR and Grivennikov SI: Inflammation
and cancer: Triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity.
51:27–41. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
de Visser KE and Joyce JA: The evolving
tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic
outgrowth. Cancer Cell. 41:374–403. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cullen M, Elzarrad MK, Seaman S, Zudaire
E, Stevens J, Yang MY, Li X, Chaudhary A, Xu L, Hilton MB, et al:
GPR124, an orphan G protein-coupled receptor, is required for
CNS-specific vascularization and establishment of the blood-brain
barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5759–5764. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Olsen JJ, Pohl S, Deshmukh A, Visweswaran
M, Ward NC, Arfuso F, Agostino M and Dharmarajan A: The role of wnt
signalling in angiogenesis. Clin Biochem Rev. 38:131–142. 2017.
|
|
80
|
Cherry AE, Vicente JJ, Xu C, Morrison RS,
Ong SE, Wordeman L and Stella N: GPR124 regulates microtubule
assembly, mitotic progression, and glioblastoma cell proliferation.
Glia. 67:1558–1570. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hosea R, Hillary S, Naqvi S, Wu S and
Kasim V: The two sides of chromosomal instability: Drivers and
brakes in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:752024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hernández-Vásquez MN, Adame-García SR,
Hamoud N, Chidiac R, Reyes-Cruz G, Gratton JP, Côté JF and
Vázquez-Prado J: Cell adhesion controlled by adhesion G
protein-coupled receptor GPR124/ADGRA2 is mediated by a protein
complex comprising intersectins and Elmo-Dock. J Biol Chem.
292:12178–12191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhao W, Zhang Z, Xie M, Ding F, Zheng X,
Sun S and Du J: Exploring tumor-associated macrophages in
glioblastoma: From diversity to therapy. NPJ Precis Oncol.
9:1262025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Peters JJ, Teng C, Peng K and Li X:
Deciphering the blood-brain barrier paradox in brain metastasis
development and therapy. Cancers (Basel). 17:2982025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Hernandez-Quiles M, Broekema MF and
Kalkhoven E: PPARgamma in metabolism, immunity, and cancer: Unified
and diverse mechanisms of action. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
12:6241122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Sainis I, Vareli K, Karavasilis V and
Briasoulis E: PPARgamma: The portrait of a target ally to cancer
chemopreventive agents. PPAR Res. 2008:4364892008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Yang XY, Wang LH and Farrar WL: A role for
PPARgamma in the regulation of cytokines in immune cells and
cancer. PPAR Res. 2008:9617532008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li H, Weiser-Evans MC and Nemenoff R:
Anti- and protumorigenic effects of PPARγ in lung cancer
progression: A Double-edged sword. PPAR Res. 2012:3620852012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Sun J, Yu L, Qu X and Huang T: The role of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in the tumor
microenvironment, tumor cell metabolism, and anticancer therapy.
Front Pharmacol. 14:11847942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Liu X, Kang X, Kang H and Yan H: The
immunosuppressive role of MDSCs in HCC: Mechanisms and therapeutic
opportunities. Cell Commun Signal. 23:1552025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Post Y, Lu C, Fletcher RB, Yeh WC, Nguyen
H, Lee SJ and Li Y: Design principles and therapeutic applications
of novel synthetic WNT signaling agonists. iScience. 27:1099382024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Cho C, Smallwood PM and Nathans J: Reck
and Gpr124 are essential receptor cofactors for
Wnt7a/Wnt7b-Specific signaling in mammalian CNS angiogenesis and
Blood-brain barrier regulation. Neuron. 95:1056–1073.e5. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Nguyen H, Lee SJ and Li Y: Selective
activation of the Wnt-Signaling pathway as a novel therapy for the
treatment of diabetic retinopathy and other retinal vascular
diseases. Pharmaceutics. 14:24762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Liu GH, Chen T, Zhang X, Ma XL and Shi HS:
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the cancers. MedComm (2020).
3:e1812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wei W and Wan Y: Thiazolidinediones on
PPARγ: The roles in bone remodeling. PPAR Res. 2011:8671802011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Blackburn GL: From bench to bedside: Novel
mechanisms and therapeutic advances through the development of
selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
modulators. PPAR Res. 91(Suppl): 251S–253S. 2010.
|
|
97
|
Xie X, Chen W, Zhang N, Yuan M, Xu C,
Zheng Z, Li H and Wang L: Selective tissue distribution mediates
Tissue-Dependent PPARγ activation and insulin sensitization by
INT131, a selective PPARγ modulator. Front Pharmacol. 8:3172017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Hirschfield GM, Shiffman ML, Gulamhusein
A, Kowdley KV, Vierling JM, Levy C, Kremer AE, Zigmond E, Andreone
P, Gordon SC, et al: Seladelpar efficacy and safety at 3 months in
patients with primary biliary cholangitis: ENHANCE, a phase 3,
randomized, Placebo-controlled study. Hepatology. 78:397–415. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Landreth G, Jiang Q, Mandrekar S and
Heneka M: PPARgamma agonists as therapeutics for the treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. Neurotherapeutics. 5:481–489. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Spite M, Clària J and Serhan CN:
Resolvins, specialized proresolving lipid mediators, and their
potential roles in metabolic diseases. Cell Metab. 19:21–36. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Xie X, Yu T, Li X, Zhang N, Foster LJ,
Peng C, Huang W and He G: Recent advances in targeting the
'undruggable' proteins: From drug discovery to clinical trials.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3352023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Wang R, Hu B, Pan Z, Mo C, Zhao X, Liu G,
Hou P, Cui Q, Xu Z, Wang W, et al: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs):
Current and future biopharmaceuticals. J Hematol Oncol. 18:512025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Gregor S, Saumur TM, Crosby LD, Powers J
and Patterson KK: Study paradigms and principles investigated in
motor learning research after stroke: A scoping review. Arch
Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 3:1001112021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Soccio RE, Chen ER, Rajapurkar SR,
Safabakhsh P, Marinis JM, Dispirito JR, Emmett MJ, Briggs ER, Fang
B, Everett LJ, et al: Genetic variation determines PPARγ function
and Anti-diabetic drug response in vivo. Cell. 162:33–44. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Priya SS, Sankaran R, Ramalingam S, Sairam
T and Somasundaram LS: Genotype phenotype correlation of genetic
polymorphism of PPAR gamma gene and therapeutic response to
pioglitazone in type 2 diabetes Mellitus-A pilot study. J Clin
Diagn Res. 10:FC11–FC14. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Konig S, Jayarajan V, Wray S, Kamm R and
Moeendarbary E: Mechanobiology of the blood-brain barrier during
development, disease and ageing. Nat Commun. 16:72332025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Suchý T, Zieschang C, Popkova Y, Kaczmarek
I, Weiner J, Liebing AD, Çakir MV, Landgraf K, Gericke M,
Pospisilik JA, et al: The repertoire of Adhesion G protein-coupled
receptors in adipocytes and their functional relevance. Int J Obes
(Lond). 44:2124–2136. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Vanhollebeke B, Stone OA, Bostaille N, Cho
C, Zhou Y, Maquet E, Gauquier A, Cabochette P, Fukuhara S,
Mochizuki N, et al: Tip cell-specific requirement for an atypical
Gpr124- and Reck-dependent Wnt/β-catenin pathway during brain
angiogenesis. ELife. 4:e064892015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Amato AA and de Assis Rocha Neves F:
Idealized PPARγ-Based therapies: Lessons from bench and bedside.
PPAR Res. 2012:9786872012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
St Croix B, Rago C, Velculescu V, Traverso
G, Romans KE, Montgomery E, Lal A, Riggins GJ, Lengauer C,
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Genes expressed in human tumor
endothelium. Science. 289:1197–1202. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wang M, Zhang S, Li R and Zhao Q:
Unraveling the specialized metabolic pathways in medicinal plant
genomes: A review. Front Plant Sci. 15:14595332024. View Article : Google Scholar
|