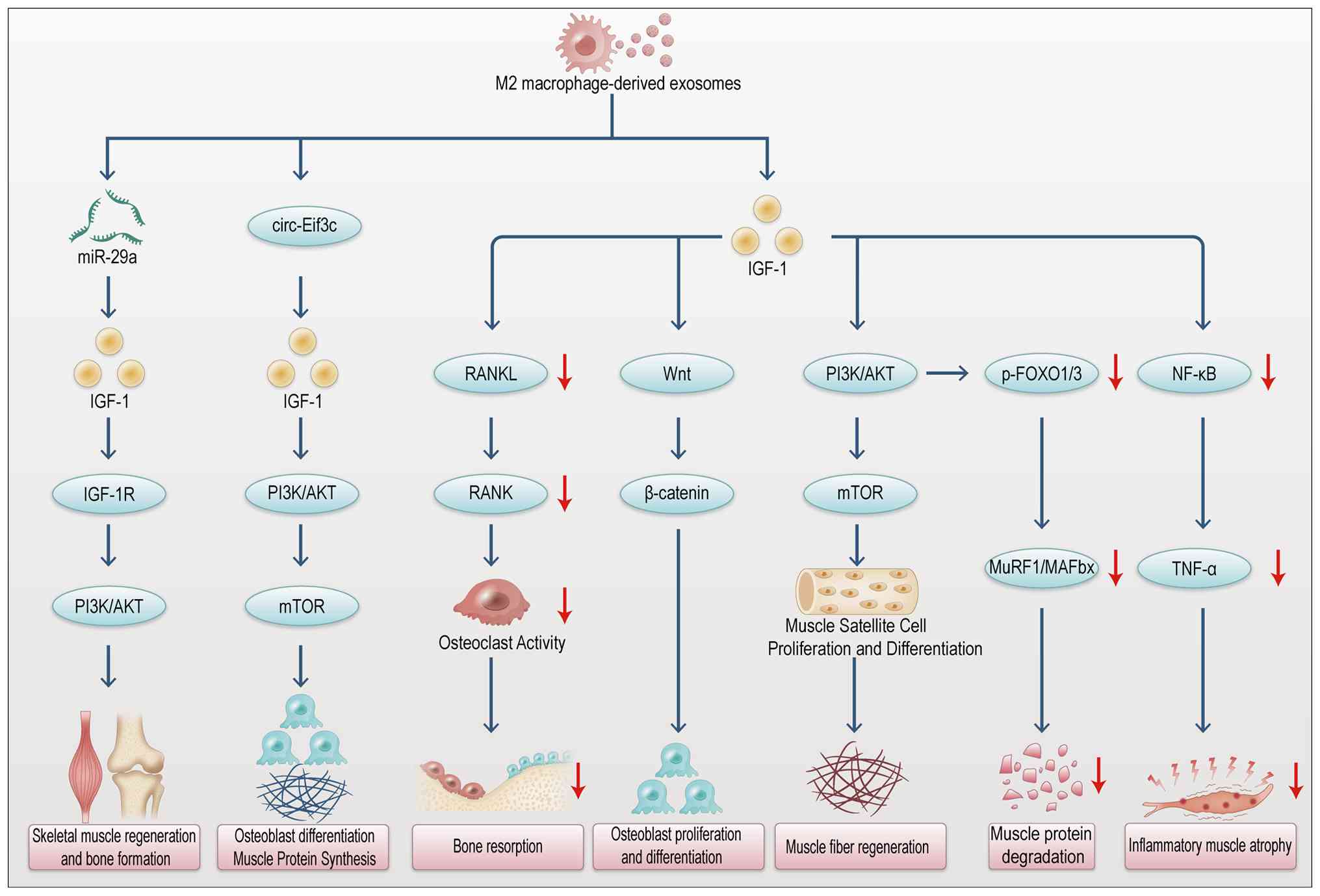
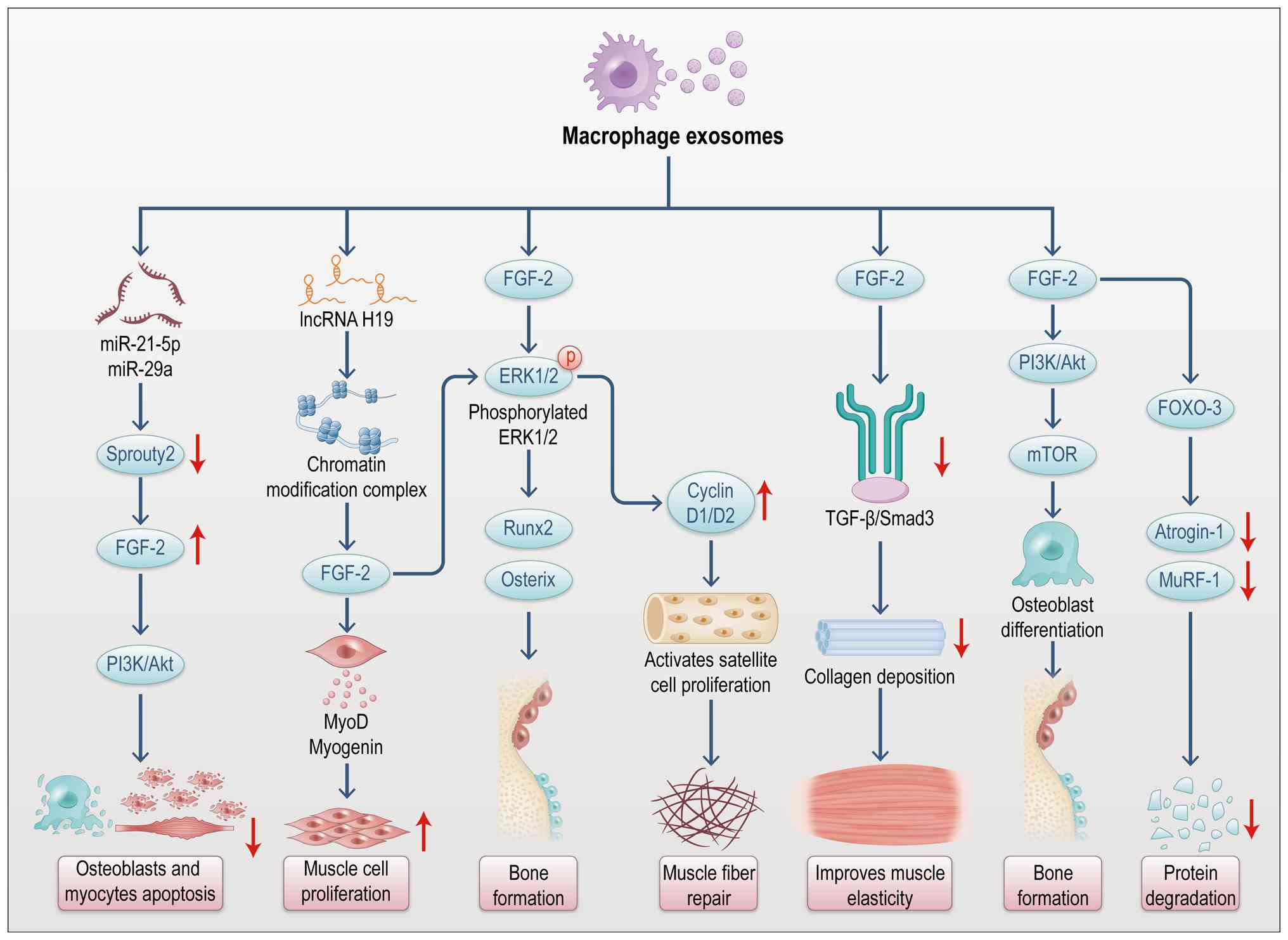
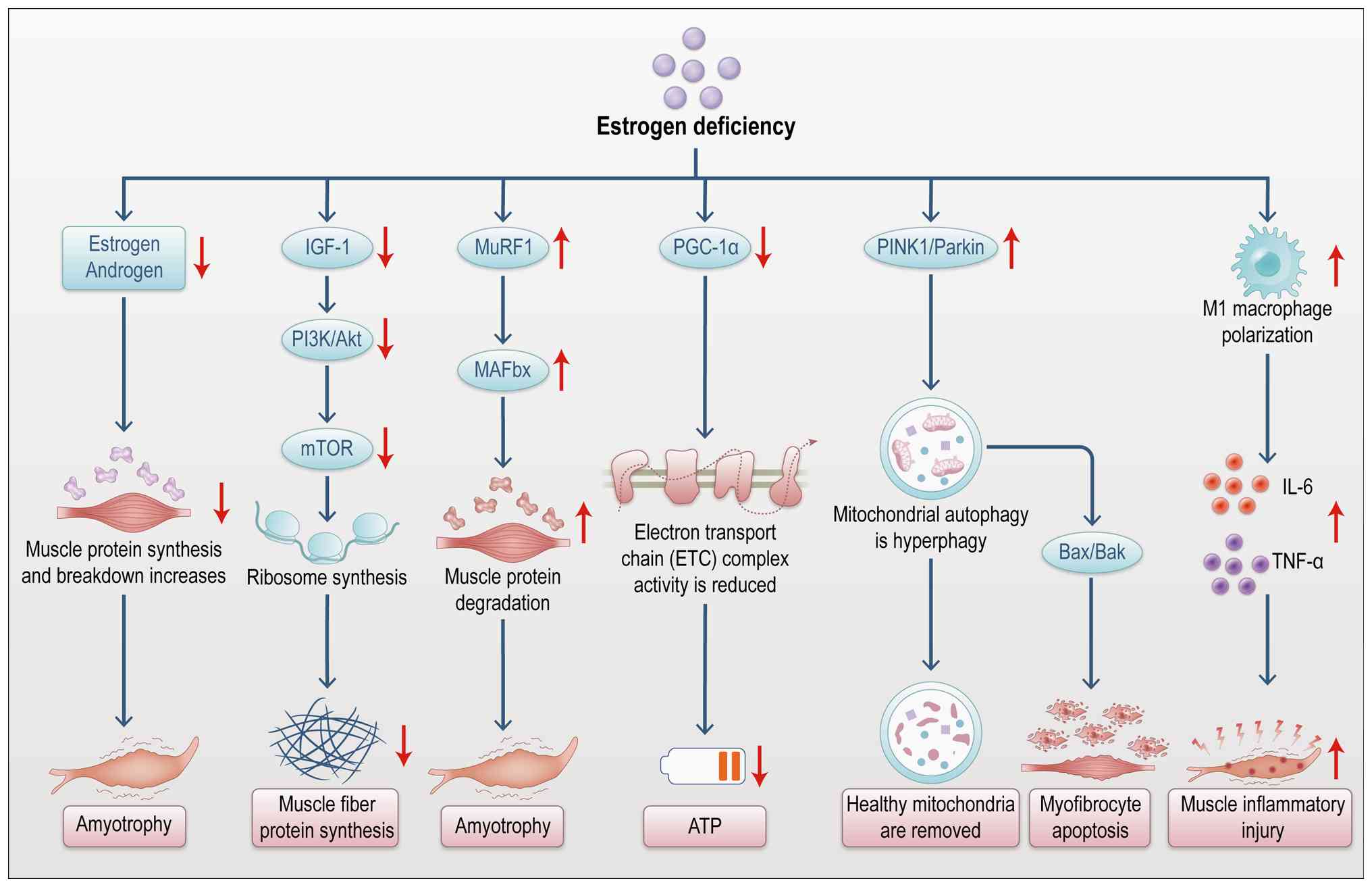
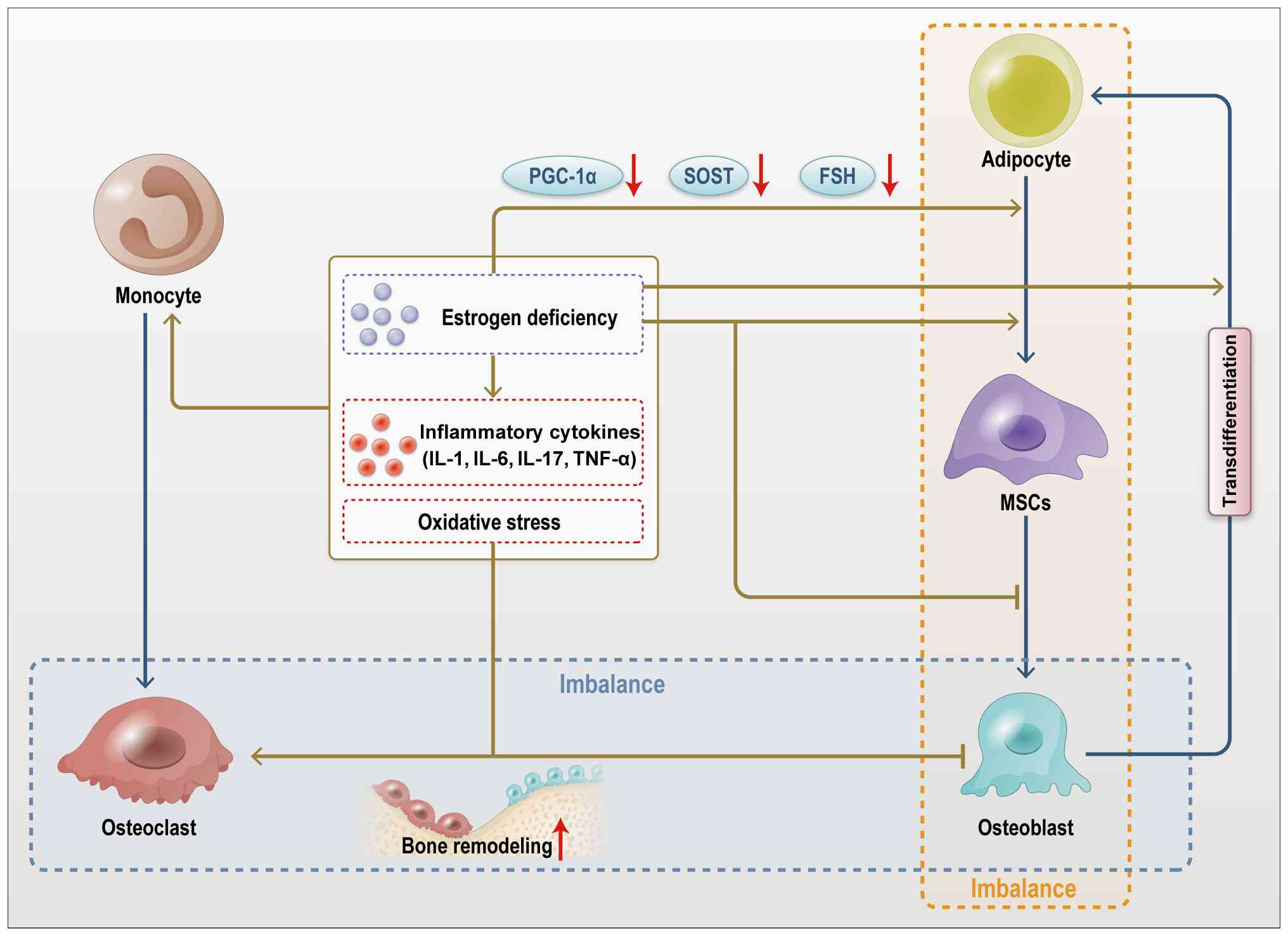
|
1
|
Kirk B, Lombardi G and Duque G: Bone and
muscle crosstalk in ageing and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
21:375–390. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shirvani H, Shamsoddini A, Bazgir B,
McAinch AJ, Najjari A and Arabzadeh E: Metabolic crosstalk between
skeletal muscle and cartilage tissue: Insights into myokines in
osteoarthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 52:9572025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chuang YH, Chuang WL, Huang SP and Huang
CH: Expression of epidermal growth factor, basic fibroblast growth
factor and insulin growth factor-1 and relation to myocyte
regeneration of obstructed ureters in rats. Scand J Urol Nephrol.
39:7–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cecerska-Heryć E, Goszka M, Serwin N,
Roszak M, Grygorcewicz B, Heryć R and Dołęgowska B: Applications of
the regenerative capacity of platelets in modern medicine. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 64:84–94. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gries KJ, Zysik VS, Jobe TK, Griffin N,
Leeds BP and Lowery JW: Muscle-derived factors influencing bone
metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 123:57–63. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pieters BCH, Cappariello A, van den Bosch
MHJ, van Lent PLEM, Teti A and van de Loo FAJ: Macrophage-derived
extracellular vesicles as carriers of alarmins and their potential
involvement in bone homeostasis. Front Immunol. 10:19012019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Y, Liu H, He Y, Yang B, Lu W and Dai
Z: Roles for exosomes in the pathogenesis, drug delivery and
therapy of psoriasis. Pharmaceutics. 17:512025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yue Y, Cao S, Cao F, Wei Y, Li A, Wang D,
Liu P, Zeng H and Lin J: Unveiling research hotspots: A
bibliometric study on macrophages in musculoskeletal diseases.
Front Immunol. 16:15193212025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng A, Liu H, Yin G and Xie Q:
Macrophage-derived exosomes in autoimmune diseases: Mechanistic
insights and therapeutic implications. Immunol Res. 73:1712025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fan C, Wang W, Yu Z, Wang J, Xu W, Ji Z,
He W, Hua D, Wang W, Yao L, et al: M1 macrophage-derived exosomes
promote intervertebral disc degeneration by enhancing nucleus
pulposus cell senescence through LCN2/NF-κB signaling axis. J
Nanobiotechnology. 22:3012024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wen Z, Li S, Liu Y, Liu X, Qiu H, Che Y,
Bian L and Zhou M: An engineered M2 macrophage-derived
exosomes-loaded electrospun biomimetic periosteum promotes cell
recruitment, immunoregulation, and angiogenesis in bone
regeneration. Bioact Mater. 50:95–115. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu M, Ng M, Phu T, Bouchareychas L,
Feeley BT, Kim HT, Raffai RL and Liu X: Polarized macrophages
regulate fibro/adipogenic progenitor (FAP) adipogenesis through
exosomes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14:3212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou M, Li B, Liu C, Hu M, Tang J, Min J,
Cheng J and Hong L: M2 Macrophage-derived exosomal miR-501
contributes to pubococcygeal muscle regeneration. Int
Immunopharmacol. 101(Pt B): 1082232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan Z, Jiang D, Yang M, Tao J, Hu X, Yang
X and Zeng Y: Emerging roles of macrophage polarization in
osteoarthritis: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Orthop Surg.
16:532–550. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ascenzi F, Barberi L, Dobrowolny G, Villa
Nova Bacurau A, Nicoletti C, Rizzuto E, Rosenthal N, Scicchitano BM
and Musarò A: Effects of IGF-1 isoforms on muscle growth and
sarcopenia. Aging Cell. 18:e129542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park SH, Park J, Yoo JY, Kim HS, Lee M and
Kim OK: Humulus japonicus enhances bone growth and
microarchitecture in rats: Potential Involvement of IGF-1
signaling. J Med Food. 28:542–552. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qiu Y, Yu B, Jiang C, Yin H, Meng J, Wang
H, Chen L, Cai Y, Ren T, Qin Q, et al: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells overexpressing FGF-2 loaded onto a decellularized
extracellular matrix hydrogel for the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Biomater Sci. 14:9–30. 2026. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jaśkiewicz Ł, Romaszko-Wojtowicz A,
Chmielewski G, Kuna J and Krajewska-Włodarczyk M: Effect of
myokines on bone tissue metabolism: a systematic review. Bone.
201:1176542025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhao Z, Yan K, Guan Q, Guo Q and Zhao C:
Mechanism and physical activities in bone-skeletal muscle
crosstalk. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:12879722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin L, Lu L, Lin X and Wang X: Crucial
role of androgen receptor in resistance and endurance
trainings-induced muscle hypertrophy through
IGF-1/IGF-1R-PI3K/Akt-mTOR pathway. NutrMetab (Lond). 17:262020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Fu S, Yin L, Lin X, Lu J and Wang X:
Effects of cyclic mechanical stretch on the proliferation of L6
myoblasts and its mechanisms: PI3K/Akt and MAPK signal pathways
regulated by IGF-1 receptor. Int J Mol Sci. 19:16492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen L, Li Y and Zhao H: Fibroblast growth
factor signaling in macrophage polarization: Impact on health and
diseases. Front Immunol. 15:13904532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Cao F, Liang D, Pan M, Lu WW, Lyu
H, Xie Y, Zhang L and Tang P: Mechanical effects in aging of the
musculoskeletal system: Molecular signaling and spatial scale
alterations. J Orthop Translat. 52:464–477. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mao Y, Jin Z, Yang J, Xu D, Zhao L, Kiram
A, Yin Y, Zhou D, Sun Z, Xiao L, et al: Muscle-bone cross-talk
through the FNIP1-TFEB-IGF2 axis is associated with bone metabolism
in human and mouse. Sci Transl Med. 16:eadk98112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin P, Chen M, Rao M, Lin Y, Zhang M, Xu
R, Hu X, Chen R, Chai W, Huang X, et al: Deciphering immune
landscape remodeling unravels the underlying mechanism for
synchronized muscle and bone aging. Adv Sci (Weinh).
11:e23040842024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gómez-Bruton A, Matute-Llorente Á,
González-Agüero A, Casajús JA and Vicente-Rodríguez G: Plyometric
exercise and bone health in children and adolescents: A systematic
review. World J Pediatr. 13:112–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han J, Zhang J, Zhang X, Luo W, Liu L, Zhu
Y, Liu Q and Zhang XA: Emerging role and function of Hippo-YAP/TAZ
signaling pathway in musculoskeletal disorders. Stem Cell Res Ther.
15:3862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schiaffino S, Reggiani C, Akimoto T and
Blaauw B: molecular mechanisms of skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J
Neuromuscul Dis. 8:169–183. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Von den Hoff JW, Carvajal Monroy PL,
Ongkosuwito EM, van Kuppevelt TH and Daamen WF: Muscle fibrosis in
the soft palate: Delivery of cells, growth factors and
anti-fibrotics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 146:60–76. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Savadipour A, Palmer D, Ely EV, Collins
KH, Garcia-Castorena JM, Harissa Z, Kim YS, Oestrich A, Qu F,
Rashidi N and Guilak F: The role of PIEZO ion channels in the
musculoskeletal system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 324:C728–C740.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kirk B, Feehan J, Lombardi G and Duque G:
Muscle, bone, and fat crosstalk: The biological role of myokines,
osteokines, and adipokines. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 18:388–400. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo L, Quan M, Pang W, Yin Y and Li F:
Cytokines and exosomal miRNAs in skeletal muscle-adipose crosstalk.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 34:666–681. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Calejo I, Costa-Almeida R, Reis RL and
Gomes ME: A physiology-inspired multifactorial toolbox in
soft-to-hard musculoskeletal interface tissue engineering. Trends
Biotechnol. 38:83–98. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Adamičková A, Chomaničová N, Gažová A,
Maďarič J, Červenák Z, Valášková S, Adamička M and Kyselovic J:
Effect of atorvastatin on angiogenesis-related genes VEGF-A, HGF
and IGF-1 and the modulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR transcripts in
bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
45:2326–2337. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xu L, Zhao Q, Li K, Zhang Y, Wang C, Hind
K, Wang L, Liu Y and Cheng X: The role of sex hormones on bone
mineral density, marrow adiposity, and muscle adiposity in
middle-aged and older men. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
13:8174182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Tang Y, Guo X, Gao Q, Shao
Y, Wang J, Tian R and Shi Y: Sodium benzoate inhibits osteoblast
differentiation and accelerates bone loss by regulating the
FGF2/p38/RUNX2 pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 73:13891–13901. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ogura H, Nakamura T, Ishii T, Saito A,
Onodera S, Yamaguchi A, Nishii Y and Azuma T: Mechanical
stress-induced FGF-2 promotes proliferation and consequently
induces osteoblast differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 684:1491452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bakker AD and Jaspers RT: IL-6 and IGF-1
signaling within and between muscle and bone: How important is the
mTOR pathway for bone metabolism? Curr Osteoporos Rep. 13:131–139.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshida T and Delafontaine P: Mechanisms
of IGF-1-mediated regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and
atrophy. Cells. 9:19702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chai J, Xu L and Liu N: miR-23b-3p
regulates differentiation of osteoclasts by targeting PTEN via the
PI3k/AKT pathway. Arch Med Sci. 18:1542–1557. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Liu L, Chen K, Sun L, Li W and
Zhang S: Huaier shows anti-cancer activities by inhibition of cell
growth, migration and energy metabolism in lung cancer through
PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 25:2228–2237. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hang K, Wang Y, Bai J, Wang Z, Wu W, Zhu
W, Liu S, Pan Z, Chen J and Chen W: Chaperone-mediated autophagy
protects the bone formation from excessive inflammation through
PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. FASEB J. 38:e236462024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Peifer C, Oláh T, Venkatesan JK, Goebel L,
Orth P, Schmitt G, Zurakowski D, Menger MD, Laschke MW, Cucchiarini
M and Madry H: locally directed recombinant adeno-associated
virus-mediated igf-1 gene therapy enhances osteochondral repair and
counteracts early osteoarthritis in vivo. Am J Sports Med.
52:1336–1349. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang C, Wang J, Xie Y, Wang L, Yang L, Yu
J, Miyamoto A and Sun F: Development of FGF-2-loaded electrospun
waterborne polyurethane fibrous membranes for bone regeneration.
Regen Biomater. 8:rbaa0462020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kogure K, Hasuike A, Kurachi R, Igarashi
Y, Idesawa M and Sato S: Effect of a recombinant human basic
fibroblast growth factor 2 (rhFGF-2)-Impregnated atelocollagen
sponge on vertical guided bone regeneration in a rat calvarial
model. Dent J (Basel). 13:1772025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu X, Qi Y, Zhao T, Fang J, Liu X, Xu T,
Yang Q and Dai X: NGF increases FGF2 expression and promotes
endothelial cell migration and tube formation through PI3K/Akt and
ERK/MAPK pathways in human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
27:526–534. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yin J, Qiu S, Shi B, Xu X, Zhao Y, Gao J,
Zhao S and Min S: Controlled release of FGF-2 and BMP-2 in tissue
engineered periosteum promotes bone repair in rats. Biomed Mater.
13:0250012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wu H, Yin G, Pu X, Wang J, Liao X and
Huang Z: Inhibitory effects of combined bone morphogenetic protein
2, vascular endothelial growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth
factor on osteoclast differentiation and activity. Tissue Eng Part
A. 27:1387–1398. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lötvall J, Hill AF, Hochberg F, Buzás EI,
Di Vizio D, Gardiner C, Gho YS, Kurochkin IV, Mathivanan S,
Quesenberry P, et al: Minimal experimental requirements for
definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A
position statement from the International Society for Extracellular
Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 3:269132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Akbar N, Paget D and Choudhury RP:
Extracellular vesicles in innate immune cell programming.
Biomedicines. 9:7132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Garzetti L, Menon R, Finardi A, Bergami A,
Sica A, Martino G, Comi G, Verderio C, Farina C and Furlan R:
Activated macrophages release microvesicles containing polarized M1
or M2 mRNAs. J Leukoc Biol. 95:817–825. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guan X, Li C, Wang X, Yang L, Lu Y and Guo
Z: Engineered M2 macrophage-derived exosomes: mechanisms and
therapeutic potential in inflammation regulation and regenerative
medicine. Acta Biomater. 203:38–58. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mäki-Mantila K, Niskanen EA, Kainulainen
K, Pardas LP, Aaltonen N, Wahbi W, Takabe P, Rönkä A, Rilla K and
Pasonen-Seppänen S: Extracellular vesicles derived from
pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages induce an inflammatory and invasive
phenotype in melanoma cells. Cell Commun Signal. 24:102025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Vizoso FJ, Eiro N, Cid S, Schneider J and
Perez-Fernandez R: Mesenchymal stem cell secretome: Toward
cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Int J
Mol Sci. 18:18522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu S, Chen J, Shi J, Zhou W, Wang L, Fang
W, Zhong Y, Chen X, Chen Y, Sabri A and Liu S: M1-like
macrophage-derived exosomes suppress angiogenesis and exacerbate
cardiac dysfunction in a myocardial infarction microenvironment.
Basic Res Cardiol. 115:222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li Z, Wang Y, Li S and Li Y: Exosomes
derived from M2 macrophages facilitate osteogenesis and reduce
adipogenesis of BMSCs. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:6803282021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Y, Liang Y and Zhou Y: M2
polarization of RAW264.7-derived exosomes inhibits osteoclast
differentiation and inflammation via PKM2/HIF-1α axis. Immunol
Invest. 54:1195–1209. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Huang R, Wang X, Zhou Y and Xiao Y:
RANKL-induced M1 macrophages are involved in bone formation. Bone
Res. 5:170192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kang M, Huang CC, Lu Y, Shirazi S,
Gajendrareddy P, Ravindran S and Cooper LF: Bone regeneration is
mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone.
141:1156272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ge X, Tang P, Rong Y, Jiang D, Lu X, Ji C,
Wang J, Huang C, Duan A, Liu Y, et al: Exosomal miR-155 from
M1-polarized macrophages promotes Endo MT and impairs mitochondrial
function via activating NF-κB signaling pathway in vascular
endothelial cells after traumatic spinal cord injury. Redox Biol.
41:1019322021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hu Y, Wang Y, Chen T, Hao Z, Cai L and Li
J: Exosome: Function and application in inflammatory bone diseases.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:63249122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pajarinen J, Lin T, Gibon E, Kohno Y,
Maruyama M, Nathan K, Lu L, Yao Z and Goodman SB: Mesenchymal stem
cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials.
196:80–89. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Paschalidi P, Gkouveris I, Soundia A,
Kalfarentzos E, Vardas E, Georgaki M, Kostakis G, Erovic BM,
Tetradis S, Perisanidis C and Nikitakis NG: The role of M1 and M2
macrophage polarization in progression of medication-related
osteonecrosis of the jaw. Clin Oral Investig. 25:2845–2857. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Boldin MP and Baltimore D: MicroRNAs, new
effectors and regulators of NF-κB. Immunol Rev. 246:205–220. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Salhotra A, Shah HN, Levi B and Longaker
MT: Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 21:696–711. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang Z, Zhu H, Shi H, Zhao H, Gao R, Weng
X, Liu R, Li X, Zou Y, Hu K, et al: Exosomes derived from M1
macrophages aggravate neointimal hyperplasia following carotid
artery injuries in mice through miR-222/CDKN1B/CDKN1C pathway. Cell
Death Dis. 10:4222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Qi Y, Zhu T, Zhang T, Wang X, Li W, Chen
D, Meng H and An S: M1 macrophage-derived exosomes transfer miR-222
to induce bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis. Lab Invest.
101:1318–1326. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li L, Zheng B, Zhang F, Luo X, Li F, Xu T,
Zhao H, Shi G, Guo Y, Shi J and Sun J: LINC00370 modulates
miR-222-3p-RGS4 axis to protect against osteoporosis progression.
Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 97:1045052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Jiang C, Xia W, Wu T, Pan C, Shan H, Wang
F, Zhou Z and Yu X: Inhibition of microRNA-222 up-regulates TIMP3
to promotes osteogenic differentiation of MSCs from fracture rats
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cell Mol Med. 24:686–694. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Yu L, Hu M, Cui X, Bao D, Luo Z, Li D, Li
L, Liu N, Wu Y, Luo X and Ma Y: M1 macrophage-derived exosomes
aggravate bone loss in postmenopausal osteoporosis via a
microRNA-98/DUSP1/JNK axis. Cell Biol Int. 45:2452–2463. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Peng S, Yan Y, Li R, Dai H and Xu J:
Extracellular vesicles from M1-polarized macrophages promote
inflammation in the temporomandibular joint via miR-1246 activation
of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1503:48–59. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
He XT, Li X, Yin Y, Wu RX, Xu XY and Chen
FM: The effects of conditioned media generated by polarized
macrophages on the cellular behaviours of bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 22:1302–1315. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Xia Y, He XT, Xu XY, Tian BM, An Y and
Chen FM: Exosomes derived from M0, M1 and M2 macrophages exert
distinct influences on the proliferation and differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ. 8:e89702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Schlundt C, Fischer H, Bucher CH,
Rendenbach C, Duda GN and Schmidt-Bleek K: The multifaceted roles
of macrophages in bone regeneration: A story of polarization,
activation and time. Acta Biomater. 133:46–57. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wei F, Zhou Y, Wang J, Liu C and Xiao Y:
The immunomodulatory role of BMP-2 on macrophages to accelerate
osteogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A. 24:584–594. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wang J, Xue Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Hu S, Zhao
H, Gu Q, Yang H, Huang L, Zhou X and Shi Q: BMP-2 functional
polypeptides relieve osteolysis via bi-regulating bone formation
and resorption coupled with macrophage polarization. NPJ Regen Med.
8:62023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bouchareychas L, Duong P, Covarrubias S,
Alsop E, Phu TA, Chung A, Gomes M, Wong D, Meechoovet B, Capili A,
et al: Macrophage exosomes resolve atherosclerosis by regulating
hematopoiesis and inflammation via microRNA cargo. Cell Rep.
32:1078812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yu S, Geng Q, Pan Q, Liu Z, Ding S, Xiang
Q, Sun F, Wang C, Huang Y and Hong A: miR-690, a Runx2-targeted
miRNA, regulates osteogenic differentiation of C2C12 myogenic
progenitor cells by targeting NF-kappaB p65. Cell Biosci. 6:102016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yang Y, Guo Z, Chen W, Wang X, Cao M, Han
X, Zhang K, Teng B, Cao J, Wu W, et al: M2 macrophage-derived
exosomes promote angiogenesis and growth of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma by targeting E2F2. Mol Ther. 29:1226–1238. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
80
|
Xu T, Luo Y, Wang J, Zhang N, Gu C, Li L,
Qian D, Cai W, Fan J and Yin G: Exosomal miRNA128-3pfrom
mesenchymal stem cells of aged rats regulates osteogenesis and bone
fracture healing by targeting Smad5. J Nanobiotechnology.
18:472020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Zhang D, Wu Y, Li Z, Chen H, Huang S, Jian
C and Yu A: miR-144-5p, an exosomal miRNA from bone marrow-derived
macrophage in type 2 diabetes, impairs bone fracture healing via
targeting Smad1. J Nanobiotechnology. 19:2262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Huang X, Xiong X, Liu J, Zhao Z and Cen X:
MicroRNAs-containing extracellular vesicles in bone remodeling:
anemerging frontier. Life Sci. 254:1178092020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Luo ML, Jiao Y, Gong WP, Li Y, Niu LN, Tay
FR and Chen JH: Macrophages enhance mesenchymal stem cell
osteogenesis via down-regulation of reactive oxygen species. J
Dent. 94:1032972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ren Q, Xing W, Jiang B, Feng H, Hu X, Suo
J, Wang L and Zou W: Tenascin-C promotes bone regeneration via
inflammatory macrophages. Cell Death Differ. 32:763–775. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Halper J, Dolfi B, Ivanov S, Madel MB and
Blin-Wakkach C: Macrophages and osteoclasts: Similarity and
divergence between bone phagocytes. Front Immunol. 16:16838722025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hao W, Chen S, Chao H, Li Z, Yang H, Chen
D, Li S, Zhang S, Zhang J, Wang J, et al: IL-33-Induced TREM2(+)
macrophages promote pathological new bone formation through
CREG1-IGF2R axis in ankylosing spondylitis. Adv Sci (Weinh).
12:e25009522025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Choi JS, Yoon HI, Lee KS, Choi YC, Yang
SH, Kim IS and Cho YW: Exosomes from differentiating human skeletal
muscle cells trigger myogenesis of stem cells and provide
biochemical cues for skeletal muscle regeneration. J Control
Release. 222:107–115. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Forterre A, Jalabert A, Berger E, Baudet
M, Chikh K, Errazuriz E, De Larichaudy J, Chanon S, Weiss-Gayet M,
Hesse AM, et al: Proteomic analysis of C2C12 myoblast and myotube
exosome-like vesicles: A new paradigm for myoblast-myotube cross
talk? PLoS One. 9:e841532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mobley CB, Mumford PW, McCarthy JJ, Miller
ME, Young KC, Martin JS, Beck DT, Lockwood CM and Roberts MD: Whey
protein-derived exosomes increase protein synthesis and hypertrophy
in C2-C12 myotubes. J Dairy Sci. 100:48–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yin J, Qian Z, Chen Y, Li Y and Zhou X:
MicroRNA regulatory networks in the pathogenesis of sarcopenia. J
Cell Mol Med. 24:4900–4912. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gopal Krishnan PD, Lee WX, Goh KY, Choy
SM, Turqueza LRR, Lim ZH and Tang HW: Transcriptional regulation of
autophagy in skeletal muscle stem cells. Dis Model Mech.
18:DMM0520072025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Chen W, Chen Y, Liu Y and Wang X:
Autophagy in muscle regeneration: Potential therapies for
myopathies. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 13:1673–1685. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Guescini M, Canonico B, Lucertini F,
Maggio S, Annibalini G, Barbieri E, Luchetti F, Papa S and Stocchi
V: Muscle releases alpha-sarcoglycan positive extracellular
vesicles carrying miRNAs in the bloodstream. PLoS One.
10:e01250942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Chaturvedi P, Kalani A, Medina I,
Familtseva A and Tyagi SC: Cardiosome mediated regulation of MMP9
in diabetic heart: Role of mir29b and mir455 in exercise. J Cell
Mol Med. 19:2153–2161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kalluri R and LeBleu VS: The biology,
function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science.
367:eaau69772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Qin W and Dallas SL: Exosomes and
extracellular RNA in muscle and bone aging and crosstalk. Curr
Osteoporos Rep. 17:548–559. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Herrmann M, Engelke K, Ebert R,
Müller-Deubert S, Rudert M, Ziouti F, Jundt F, Felsenberg D and
Jakob F: Interactions between muscle and bone-where physics meets
biology. Biomolecules. 10:4322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Li G, Zhang L, Wang D, AIQudsy L, Jiang
JX, Xu H and Shang P: Muscle-bone crosstalk and potential therapies
for sarco-osteoporosis. J Cell Biochem. 120:14262–14273. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Xu Q, Cui Y, Luan J, Zhou X, Li H and Han
J: Exosomes from C2C12 myoblasts enhance osteogenic differentiation
of MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts by delivering miR-27a-3p. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 498:32–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Kitase Y, Vallejo JA, Gutheil W, Vemula H,
Jähn K, Yi J, Zhou J, Brotto M and Bonewald LF: β-aminoiso-butyric
acid, 1-BAIBA, is a muscle-derived osteocyte survival factor. Cell
Rep. 22:1531–1544. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Li Y, Wang X, Pan C, Yuan H, Li X, Chen Z
and He H: Myoblast-derived exosomal Prrx2 attenuates osteoporosis
via transcriptional regulation of lncRNA-MIR22HG to activate Hippo
pathway. Mol Med. 29:542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Li H, Lin X, Yang D, Chen Z, Wang X, Re F,
Wei J and Chen J: Cancer-associated fibroblasts support bone tropic
metastasis by acting as coordinators between the tumor
microenvironment and bone matrix in breast cancer. Neoplasma.
68:10–22. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Zheng YL, Song G, Guo JB, Su X, Chen YM,
Yang Z, Chen PJ and Wang XQ: Interactions among lncRNA/circRNA,
miRNA, and mRNA in musculoskeletal degenerative diseases. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:7539312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Toita R, Shimizu Y, Shimizu E, Deguchi T,
Tsuchiya A, Kang JH, Kitamura M, Kato A, Yamada H, Yamaguchi S and
Kasahara S: Collagen patches releasing phosphatidylserine liposomes
guide M1-to-M2 macrophage polarization and accelerate simultaneous
bone and muscle healing. Acta Biomater. 187:51–65. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wehbe Z, Wehbe M, Al Khatib A, Dakroub AH,
Pintus G, Kobeissy F and Eid AH: Emerging understandings of the
role of exosomes in atherosclerosis. J Cell Physiol.
240:e314542025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
106
|
An F, Wang X, Wang C, Liu Y, Sun B, Zhang
J, Gao P and Yan C: Research progress on the role of lncRNA-miRNA
networks in regulating adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:12106272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Liu K, Luo X, Lv ZY, Zhang YJ, Meng Z, Li
J, Meng CX, Qiang HF, Hou CY, Hou L, et al: Macrophage-derived
exosomes promote bone mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblastic
fate through microRNA-21a-5p. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
9:8014322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Xiong Y, Tang Y, Fan F, Zeng Y, Li C, Zhou
G, Hu Z, Zhang L and Liu Z: Exosomal hsa-miR-21-5p derived from
growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma promotes abnormal bone
formation in acromegaly. Transl Res. 215:1–16. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Choi SH, Chung KY, Johnson BJ, Go GW, Kim
KH, Choi CW and Smith SB: Co-culture of bovine muscle satellite
cells with preadipocytes increases PPARү and C/EBPβ gene expression
in differentiated myoblasts and increases GPR43 gene expression in
adipocytes. J Nutr Biochem. 24:539–543. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Yuan R and Li J: Role of macrophages
andtheir exosomes in orthopedic diseases. Peer J.
12:e171462024.
|
|
111
|
Li K, Yan G, Huang H, Zheng M, Ma K, Cui
X, Lu D, Zheng L, Zhu B, Cheng J and Zhao J: Anti-inflammatory and
immunomodulatory effects of the extracellular vesicles derived from
human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on osteoarthritis via
M2 macrophages. J Nanobiotechnology. 20:382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Pu P, Wu S, Zhang K, Xu H, Guan J, Jin Z,
Sun W, Zhang H and Yan B: Mechanical force induces
macrophage-derived exosomal UCHL3 promoting bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cell osteogenesis by targeting SMAD1. J Nanobiotechnology.
21:882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhdanov VP: Interplay of cellular mRNA,
miRNA and Viral miRNA during infection of a cell. Int J Mol Sci.
24:1222022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Bin-Bin Z, Da-Wa ZX, Chao L, Lan-Tao Z,
Tao W, Chuan L, Chao-Zheng L, De-Chun L, Chang F, Shu-Qing W, et
al: M2 macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-26a-5p induces osteogenic
differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res.
17:1372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Qi L, Hong S, Zhao T, Yan J, Ge W, Wang J,
Fang X, Jiang W, Shen SG and Zhang L: DNA Tetrahedron Delivering
miR-21-5p promotes senescent bone defects repair through
synergistic regulation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Adv
Healthc Mater. 13:e24012752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Hrdlicka HC, Pereira RC, Shin B, Yee SP,
Deymier AC, Lee SK and Delany AM: Inhibition of miR-29-3p isoforms
via tough decoy suppresses osteoblast function in homeostasis but
promotes intermittent parathyroid hormone-induced bone anabolism.
Bone. 143:1157792021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Gu Y, Ma L, Song L, Li X, Chen D and Bai
X: miR-155 inhibits mouse Osteoblast differentiation by suppressing
SMAD5 expression. Biomed Res Int. 2017:18935202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Lan S and Albinsson S: Regulation of
IRS-1, insulin signaling and glucose uptake by miR-143/145 in
vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
529:119–125. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Hade MD, Suire CN and Suo Z: Mesenchymal
stem cell-derived exosomes: Applications in regenerative medicine.
Cells. 10:19592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Mezil Y, Obeid J, Raha S, Hawke TJ and
Timmons BW: The Systemic Effects of Exercise on Regulators of
Muscle and Bone in Girls and Women. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 32:117–123.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zhang J, Rong Y, Luo C and Cui W: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent
osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization.
Aging (Albany NY). 12:25138–25152. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Qin M, Zhu J, Xing L, Fan Y, Luo J, Sun J,
Chen T, Zhang Y and Xi Q: Adipose-derived exosomes ameliorate
skeletal muscle atrophy via miR-146a-5p/IGF-1R signaling. J
Nanobiotechnology. 22:7542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Hu GF, Wang C, Hu GX, Wu G, Zhang C, Zhu
W, Chen C, Gu Y, Zhang H and Yang Z: AZD3463, an IGF-1R inhibitor,
suppresses breast cancer metastasis to bone via modulation of the
PI3K-Akt pathway. Ann Transl Med. 8:3362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Cao D, Lei Y, Ye Z, Zhao L, Wang H, Zhang
J, He F, Huang L, Shi D, Liu Q, et al: Blockade of IGF/IGF-1R
signaling axis with soluble IGF-1R mutants suppresses the cell
proliferation and tumor growth of human osteosarcoma. Am J Cancer
Res. 10:3248–3266. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Song X, Xue Y, Fan S, Hao J and Deng R:
Lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages regulate the osteogenic
differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through
exosomes. PeerJ. 10:e134422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Shu C, Smith SM, Little CB and Melrose J:
Use of FGF-2 and FGF-18 to direct bone marrow stromal stem cells to
chondrogenic and osteogenic lineages. Future Sci OA. 2:FSO1422016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Adhikary S, Choudhary D, Tripathi AK,
Karvande A, Ahmad N, Kothari P and Trivedi R: FGF-2 targets
sclerostin in bone and myostatin in skeletal muscle to mitigate the
deleterious effects of glucocorticoid on musculoskeletal
degradation. Life Sci. 229:261–276. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Le Blanc S, Simann M, Jakob F, Schütze N
and Schilling T: Fibroblast growth factors 1 and 2 inhibit
adipogenesis of human bone marrow stromal cells in 3D collagen
gels. Exp Cell Res. 338:136–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Yang F, Chen C, Yang C, Chen R, Liu Z, Wen
L, Xiao H, Zhou L, Geng B and Xia Y: Exosome-mediated perturbation
of the immune-bone metabolism axis: A mechanistic investigation
into bone loss in a simulated microgravity environment. Artif Cells
Nanomed Biotechnol. 53:494–513. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Hu K and Olsen BR: Osteoblast-derived VEGF
regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone
repair. J Clin Invest. 126:509–526. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Jiménez-Ortega RF, Ortega-Meléndez AI,
Patiño N, Rivera-Paredez B, Hidalgo-Bravo A and Velázquez-Cruz R:
The involvement of microRNAs in bone remodeling signaling pathways
and their role in the development of osteoporosis. Biology (Basel).
13:5052024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Geng Z, Sun T, Yu J, Wang N, Jiang Q, Wang
P, Yang G, Li Y, Ding Y, Zhang J, et al: cinobufagin suppresses
lipid peroxidation and inflammation in osteoporotic mice by
promoting the delivery of miR-3102-5p by macrophage-derived
exosomes. Int J Nanomedicine. 19:10497–10512. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Hosseinpour S, Dai H, Walsh LJ and Xu C:
Mesoporous core-cone silica nanoparticles can deliver mirna-26a to
macrophages to exert immunomodulatory effects on osteogenesis in
vitro. Nanomaterials (Basel). 13:17552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Liu J, Sun Z, You Y, Zhang L, Hou D, Gu G,
Chen Y and Jiao G: M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-486-5p
influences the differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells and osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 15:9499–9520. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhao W, Zhang S, Wang B, Huang J, Lu WW
and Chen D: Runx2 and microRNA regulation in bone and cartilage
diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1383:80–87. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Faraldi M, Sansoni V and Lombardi G:
Recent advances in the role of miRNAs in bone disease. Curr Opin
Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 32:149–155. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Chen G, Deng C and Li YP: TGF-β and BMP
signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J
Biol Sci. 8:272–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
138
|
Kuroyanagi G, Tokuda H, Fujita K, Kawabata
T, Sakai G, Kim W, Hioki T, Tachi J, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Otsuka
T, et al: Upregulation of TGF-β-induced HSP27 by HSP90 inhibitors
in osteoblasts. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 23:4952022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Wu Y, Zhang C and Lv C: Direct and
indirect regulation of bone metabolism by lactoferrin. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 16:16603122025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Méndez-Mancilla A, Turiján-Espinoza E,
Vega-Cárdenas M, Hernández-Hernández GE, Uresti-Rivera EE,
Vargas-Morales JM and Portales-Pérez DP: miR-21, miR-221, miR-29
and miR-34 are distinguishable molecular features of a
metabolically unhealthy phenotype in young adults. PLoS One.
19:e03004202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Fu X, Li Y, Huang T, Yu Z, Ma K, Yang M,
Liu Q, Pan H, Wang H, Wang J and Guan M: Runx2/Osterix and zinc
uptake synergize to orchestrate osteogenic differentiation and
citrate containing bone apatite formation. Adv Sci (Weinh).
5:17007552018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Luo K: Signaling cross talk between
TGF-β/Smad and other signaling pathways. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 9:a0221372017.
|
|
143
|
Zou ML, Chen ZH, Teng YY, Liu SY, Jia Y,
Zhang KW, Sun ZL, Wu JJ, Yuan ZD, Feng Y, et al: The Smad Dependent
TGF-beta and BMP signaling pathway in bone remodeling and
therapies. Front Mol Biosci. 8:5933102021.
|
|
144
|
Zhang B, Zhang X, Xiao J, Zhou X, Chen Y
and Gao C: Neuropeptide Y upregulates Runx2 and osterix and
enhances osteogenesis in mouse MC3T3-E1 cells via an autocrine
mechanism. Mol Med Rep. 22:4376–4382. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Chen M, Li Y, Yang Z, Chen M, Li J, Bao G,
Ma L and Hu J: M2-exo promote orthodontic bone remodeling via the
MeCP2-TCF20-HDAC1 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 16:5692025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Fu XH, Li JP, Li XY, Tan Y, Zhao M, Zhang
SF, Wu XD and Xu JG: M2-Macrophage-Derived exosomes promote
meningioma progression through TGF-β signaling pathway. J Immunol
Res. 2022:83265912022.
|
|
147
|
Li H, Yang Y, Gao Y, Li B, Yang J, Liu P,
Zhang M and Ning G: Exosomes derived from hypoxia-preconditioned M2
macrophages alleviate degeneration in knee osteoarthritis through
the miR-124-3p/STAT3 axis. J Transl Med. 23:7722025.
|
|
148
|
Xie Q, Wei W, Ruan J, Ding Y, Zhuang A, Bi
X, Sun H, Gu P, Wang Z and Fan X: Effects of miR-146a on the
osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone
regeneration. Sci Rep. 7:428402017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Ding S, Ma Y, Yang J, Tang Y, Jin Y, Li L
and Ma C: MiR-224-5p inhibits osteoblast differentiation and
impairs bone formation by targeting Runx2 and Sp7. Cytotechnology.
75:505–516. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Liao X, Yang Z, Li Y, Cui Y, Ma L, Liang
C, Guan Z and Hu J: M2 macrophage-derived exosome facilitates
aerobic glycolysis and osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs by
regulating TRIM26-induced PKM ubiquitination. Free Radic Biol Med.
237:88–100. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Le G, Wen R, Fang H, Huang Z, Wang Y and
Luo H: Exosomal miR-122 derived from M2 macrophages induces
osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in
the treatment of alcoholic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J
Orthop Surg Res. 20:1072025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Xu Y, Jin Y, Hong F, Ma Y, Yang J, Tang Y,
Zhu Z, Wu J, Bao Q, Li L, et al: MiR-664-3p suppresses osteoblast
differentiation and impairs bone formation via targeting Smad4 and
Osterix. J Cell Mol Med. 25:5025–5037. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Sun WL, Wang N and Xu Y: Impact of
miR-302b on calcium-phosphorus metabolism and vascular
calcification of rats with chronic renal failure by regulating
BMP-2/Runx2/Osterix signaling pathway. Arch Med Res. 49:164–171.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Ling F, Bai J, Xie J, Liu J, Lu Q, Yuan L,
Li H and Qian Z: Biomimetic periosteum combining BMP-2-loaded M2
macrophage-derived exosomes for enhanced bone defect repair. Front
Bioeng Biotechnol. 13:16393942025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Yan CP, Wang XK, Jiang K, Yin C, Xiang C,
Wang Y, Pu C, Chen L and Li YL: β-Ecdysterone enhanced bone
regeneration through the BMP-2/SMAD/RUNX2/Osterix signaling
pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8832282022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Zhang Y, Yu T, Xiang Q, van den Tillaart
F, Ma J, Zhuang Z, Stessuk T, Wang H and van den Beucken JJJP:
Osteoclasts drive bone formation in ectopic and orthotopic
environments. Biomaterials. 322:1233772025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Chen X, Wan Z, Yang L, Song S, Fu Z, Tang
K, Chen L and Song Y: Exosomes derived from reparative M2-like
macrophages prevent bone loss in murine periodontitis models via
IL-10 mRNA. J Nanobiotechnology. 20:1102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Udagawa N, Koide M, Nakamura M, Nakamichi
Y, Yamashita T, Uehara S, Kobayashi Y, Furuya Y, Yasuda H, Fukuda C
and Tsuda E: Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling
pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 39:19–26. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Kim HJ, Kang WY, Seong SJ, Kim SY, Lim MS
and Yoon YR: Follistatin-like 1 promotes osteoclast formation via
RANKL-mediated NF-ĸB activation and M-CSF-induced precursor
proliferation. Cell Signal. 28:1137–1144. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Nakao Y, Fukuda T, Zhang Q, Sanui T,
Shinjo T, Kou X, Chen C, Liu D, Watanabe Y, Hayashi C, et al:
Exosomes from TNF-alpha-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance
M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta
Biomater. 122:306–324. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Chen S, Liu J and Zhu L: M2-like
macrophage-derived exosomes inhibit osteoclastogenesis via
releasing miR-1227-5p. Immunobiology. 230:1528612025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Takeda T, Tsubaki M, Genno S, Tomita K and
Nishida S: RANK/RANKL axis promotes migration, invasion, and
metastasis of osteosarcoma via activating NF-ĸB pathway. Exp Cell
Res. 436:1139782024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Guo W, Li H, Lou Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Qian
M, Wei H, Xiao J and Xu Y: Tyloxapol inhibits RANKL-stimulated
osteoclastogenesis and ovariectomized-induced bone loss by
restraining NF-ĸB and MAPK activation. J OrthopTranslat.
28:148–158. 2021.
|
|
164
|
Fan YS, Li Q, Hamdan N, Bian YF, Zhuang S,
Fan K and Liu ZJ: Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside regulates
proliferation, differentiation, and OPG/RANKL/M-CSF expression in
MC3T3-E1 Cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Molecules. 23:23062018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Drissi H and Sanjay A: The multifaceted
osteoclast; far and beyond bone resorption. J Cell Biochem.
117:1753–1756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Guo ZY, Yin NN, Li XF, Wang MM, Sui XN,
Jiang CD, Xu MH, Jia XE, Fu CJ, Chen TL and Liu X: Exosomes
secreted from M2-polarized macrophages inhibit osteoclast
differentiation via CYLD. Tissue Cell. 93:1026452025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Yasuda H: Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG
system. J Bone Miner Metab. 39:2–11. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Hakki SS, Batoon L, Koh AJ, Kannan R,
Mendoza-Reinoso V, Rubin J, Mccauley LK and Roca H: The effects
ofpreosteoblast-derived exosomes on macrophages and bone in mice. J
Cell Mol Med. 28:e180292024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Gebraad A, Kornilov R, Kaur S, Miettinen
S, Haimi S, Peltoniemi H, Mannerström B and Seppänen-Kaijansinkko
R: Monocyte-derived extracellular vesicles stimulate cytokine
secretion and gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases by
mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. FEBS J. 285:2337–2359. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Zhu S, Yao F, Qiu H, Zhang G, Xu H and Xu
J: Coupling factors and exosomal packaging microRNAs involved in
the regulation of bone remodelling. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc.
93:469–480. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Liu S, Yan X, Guo J, An H, Li X, Yang L,
Yu X and Li S: Periodontal ligament-associated protein-1 knockout
mice regulate the differentiation of osteoclasts and osteoblasts
through TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol.
239:e310622024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Stevenson J; medical advisory council of
the British Menopause Society: Prevention and treatment of
osteoporosis in women. Post Reprod Health. 29:11–14. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
173
|
Händel MN, Cardoso I, von Bülow C, Rohde
JF, Ussing A, Nielsen SM, Christensen R, Body JJ, Brandi ML,
Diez-Perez A, et al: Fracture risk reduction and safety by
osteoporosis treatment compared with placebo or active comparator
in postmenopausal women: systematic review, network meta-analysis,
and meta-regression analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ.
381:e0680332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Tagliaferri C, Wittrant Y, Davicco MJ,
Walrand S and Coxam V: Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues.
Ageing Res Rev. 21:55–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Chen K, Jiao Y, Liu L, Huang M, He C, He
W, Hou J, Yang M, Luo X and Li C: communications between bone
marrow macrophages and bone cells in bone remodeling. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 8:5982632020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Li Q, Gao H, Ma X, Wang Z, Zhao L and Xiao
W: Exosome-mediated crosstalk between the cardiovascular and
musculoskeletal systems: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 56:1292025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
177
|
Hou C, Zhang Y, Lv Z, Luan Y, Li J, Meng
C, Liu K, Luo X, Chen L and Liu F: Macrophage exosomes modified by
miR-365-2-5p promoted osteoblast osteogenic differentiation by
targeting OLFML1. Regen Biomater. 11:rbae0182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Hossain MA, Adithan A, Alam MJ, Kopalli
SR, Kim B, Kang CW, Hwang KC and Kim JH: IGF-1 facilitates
cartilage reconstruction by regulating PI3K/AKT, MAPK, and NF-kB
signaling in rabbit osteoarthritis. J Inflamm Res. 14:3555–3568.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Fuentes EN, Björnsson BT, Valdés JA,
Einarsdottir IE, Lorca B, Alvarez M and Molina A: IGF-I/PI3K/Akt
and IGF-I/MAPK/ERK pathways in vivo in skeletal muscle are
regulated by nutrition and contribute to somatic growth in the fine
flounder. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 300:R1532–R1542.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Sudha S, Upmanyu A, Saraswat D and Singh
M: Pharmacological impacts of tanshinone on osteogenesis and
osteoclastogenesis: A review. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
398:135–146. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Luo L, Avery SJ and Waddington RJ:
Exploring a chemotactic role for EVs from progenitor cell
populations of human exfoliated deciduous teeth for promoting
migration of naïve BMSCs in bone repair process. Stem Cells Int.
2021:66817712021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Olivieri F, Prattichizzo F, Giuliani A,
Matacchione G, Rippo MR, Sabbatinelli J and Bonafè M: miR-21 and
miR-146a: The microRNAs of inflammaging and age-related diseases.
Ageing Res Rev. 70:1013742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Jann J, Gascon S, Roux S and Faucheux N:
Influence of the TGF-β superfamily on osteoclasts/osteoblasts
balance in physiological and pathological bone conditions. Int J
Mol Sci. 21:75972020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Yu Y, Cai W, Xu Y and Zuo W:
Down-regulation of miR-19b-3p enhances IGF-1 expression to induce
osteoblast differentiation and improve osteoporosis. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 68:160–168. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Sabbieti MG, Agas D, Marchetti L, Coffin
JD, Xiao L and Hurley MM: BMP-2 differentially modulates FGF-2
isoform effects in osteoblasts from newborn transgenic mice.
Endocrinology. 154:2723–2733. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Zhang C, Yang J, Zhu Z, Qin J, Yang L,
Zhao X, Su W, Cai Y, Yang J, Wang F, et al: Exosomal lncRNA HOTAIR
promotes osteoclast differentiation by targeting
TGF-beta/PTHrP/RANKL pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
132:242–252. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Wang J, Li X, Wang S, Cui J, Ren X and Su
J: Bone-targeted exosomes: Strategies and applications. Adv Healthc
Mater. 12:e22033612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Sayer AA and Cruz-Jentoft A: Sarcopenia
definition, diagnosis and treatment: consensus is growing. Age
Ageing. 51:afac2202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Jun L, Robinson M, Geetha T, Broderick TL
and Babu JR: Prevalence and mechanisms of skeletal muscle atrophy
in metabolic conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 24:29732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Dong Q, Li D, Zhang K, Shi H, Cai M, Li Y,
Zhao R and Qin D: Muscle-bone biochemical crosstalk in
osteosarcopenia: Focusing on mechanisms and potential therapeutic
strategies. J Endocrinol. 266:e2502342025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Zhang H, Du Y, Tang W, Chen M, Yu W, Ke Z,
Dong S and Cheng Q: Eldecalcitol prevents muscle loss and
osteoporosis in disuse muscle atrophy via NF-ĸB signaling in mice.
Skelet Muscle. 13:222023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Bettis T, Kim BJ and Hamrick MW: Impact of
muscle atrophy on bone metabolism and bone strength: Implications
for muscle-bone crosstalk with aging and disuse. Osteoporos Int.
29:1713–1720. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Rong S, Wang L, Peng Z, Liao Y, Li D, Yang
X, Nuessler AK, Liu L, Bao W and Yang W: The mechanisms and
treatments for sarcopenia: Could exosomes be a perspective research
strategy in the future? J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 11:348–365.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Chu R, Li M, Xie Y, Du Y and Ni T:
Exercise interventions and serum IGF-1 levels in older adults with
frailty and/or sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta analysis.
Front Public Health. 13:16606942025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
195
|
Zhu J, Fan J, Xia Y, Wang H, Li Y, Feng Z
and Fu C: Potential therapeutic targets of macrophages in
inhibiting immune damage and fibrotic processes in musculoskeletal
diseases. Front Immunol. 14:12194872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Hu S, Wang S, Yang X, Li P, Li Z, Luo B,
Liang Y and Pan X: Exosomes promise better bone regeneration. Regen
Ther. 30:389–402. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Liu W, Li L, Rong Y, Qian D, Chen J, Zhou
Z, Luo Y, Jiang D, Cheng L, Zhao S, et al: Hypoxic mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer
of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 103:196–212. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Holliday LS, McHugh KP, Zuo J, Aguirre JI,
Neubert JK and Rody WJ Jr: Exosomes: Novel regulators of bone
remodelling and potential therapeutic agents for orthodontics.
Orthod Craniofac Res. 20(Suppl 1): S95–S99. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Hatakeyama J, Inoue S, Jiang H, Yokoi R
and Moriyama H: Exercise-induced interactions between skeletal
muscle and bone via myokines and osteokine in mice: Role of
FNDC5/irisin, IGF-1, and osteocalcin. Bone. 190:1173142025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Krylova SV and Feng D: The machinery of
exosomes: Biogenesis, release, and uptake. Int J Mol Sci.
24:13372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Fridman E, Ginini L, Gil Z and Milman N:
The purification and characterization of exosomes from macrophages.
Methods Mol Biol. 2184:77–90. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Xu WM, Li A, Chen JJ and Sun EJ: Research
development on exosome separation technology. J Membr Biol.
256:25–34. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Auquière M, Muccioli GG and des Rieux A:
methods and challenges in purifying drug-loaded extracellular
vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 14:e700972025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Yousaf I, Kegler U, Hofner M and Noehammer
C: Evaluation of commercially available kits for parallel DNA and
microRNA isolation suitable for epigenetic analyses from cell-free
saliva and salivary extracellular vesicles. Int J Mol Sci.
26:63652025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Coughlan C, Bruce KD, Burgy O, Boyd TD,
Michel CR, Garcia-Perez JE, Adame V, Anton P, Bettcher BM, Chial
HJ, et al: Exosome isolation by ultracentrifugation and
precipitation and techniques for downstream analyses. Curr Protoc
Cell Biol. 88:e1102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Sidhom K, Obi PO and Saleem A: Review of
exosomal isolation methods: Is size exclusion chromatography the
best option? Int J Mol Sci. 21:64662020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Gao M, Cai J, Zitkovsky HS, Chen B and Guo
L: comparison of yield, purity, and functional properties of
large-volume exosome isolation using ultrafiltration and
polymer-based precipitation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 149:638–649.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Greening DW, Xu R, Ji H, Tauro BJ and
Simpson RJ: A protocol for exosome isolation and characterization:
Evaluation of ultracentrifugation, density-gradient separation, and
immunoaffinity capture methods. Methods Mol Biol. 1295:179–209.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Contreras-Naranjo JC, Wu HJ and Ugaz VM:
Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: Enabling liquid
biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab Chip. 17:3558–3577. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Tang YT, Huang YY, Zheng L, Qin SH, Xu XP,
An TX, Xu Y, Wu YS, Hu XM, Ping BH and Wang Q: Comparison of
isolationmethods of exosomes and exosomal RNA from cell culture
medium and serum. Int J Mol Med. 40:834–844. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Huang Y, Liu Y, Huang Q, Sun S, Ji Z,
Huang L, Li Z, Huang X, Deng W and Li T: TMT-Based quantitative
proteomics analysis of synovial fluid-derived exosomes in
inflammatory arthritis. Front Immunol. 13:8009022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Huang LH, Rau CS, Wu SC, Wu YC, Wu CJ,
Tsai CW, Lin CW, Lu TH and Hsieh CH: Identification and
characterization of hADSC-derived exosome proteins from different
isolation methods. J Cell Mol Med. 25:7436–7450. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Lai JJ, Chau ZL, Chen SY, Hill JJ, Korpany
KV, Liang NW, Lin LH, Lin YH, Liu JK, Liu YC, et al: Exosome
processing and characterization approaches for research and
technology development. Adv Sci (Weinh). 9:e21032222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
D'Acunzo P, Kim Y, Ungania JM,
Pérez-González R, Goulbourne CN and Levy E: Isolation of
mitochondria-derived mitovesicles and subpopulations of
microvesicles and exosomes from brain tissues. Nat Protoc.
17:2517–2549. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Doyle LM and Wang MZ: Overview of
extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and
methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells. 8:7272019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Veerman RE, Teeuwen L, Czarnewski P,
Güclüler Akpinar G, Sandberg A, Cao X, Pernemalm M, Orre LM,
Gabrielsson S and Eldh M: Molecular evaluation of five different
isolation methods for extracellular vesicles reveals different
clinical applicability and subcellular origin. J Extracell
Vesicles. 10:e121282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Zhao R, Zhao T, He Z, Cai R and Pang W:
Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose
tissue-derived exosomes. Adipocyte. 10:587–604. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Corona ML, Hurbain I, Raposo G and van
Niel G: Characterization of extracellular vesicles by transmission
electron microscopy and immunolabeling electron microscopy. Methods
Mol Biol. 2668:33–43. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Wu X, Showiheen SAA, Sun AR, Crawford R,
Xiao Y, Mao X and Prasadam I: Exosomes extraction and
identification. Methods Mol Biol. 2054:81–91. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Chen Z, Luo L, Ye T, Zhou J, Niu X, Yuan
J, Yuan T, Fu D, Li H, Li Q and Wang Y: Identification of specific
markers for human pluripotent stem cell-derived small extracellular
vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 13:e124092024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Rahmatinejad F, Kharat Z, Jalili H, Renani
MK and Mobasheri H: Comparison of morphology, protein
concentration, and size distribution of bone marrow and Wharton's
jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells exosomes isolated by
ultracentrifugation and polymer-based precipitation techniques.
Tissue Cell. 88:1024272024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Kim J, Lyu HZ, Jung C, Lee KM, Han SH, Lee
JH and Cha M: Osteogenic response of MC3T3-E1 and Raw264.7 in the
3D-encapsulated co-culture environment. Tissue Eng Regen Med.
18:387–397. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Wragg NM, Mosqueira D, Blokpeol-Ferreras
L, Capel A, Player DJ, Martin NRW, Liu Y and Lewis MP: Development
of a 3D tissue-engineered skeletal muscle and bone co-culture
system. Biotechnol J. 15:e19001062020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
224
|
Ostrovidov S, Ahadian S, Ramon-Azcon J,
Hosseini V, Fujie T, Parthiban SP, Shiku H, Matsue T, Kaji H,
Ramalingam M, et al: Three-dimensional co-culture of C2C12/PC12
cells improves skeletal muscle tissue formation and function. J
Tissue Eng Regen Med. 11:582–595. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Liu J, Yang D, Shi S, Lin L, Xiao M, Yuan
Z and Yu M: Overexpression of vasostatin-1 protects
hypoxia/reoxygenation injuries in cardiomyocytes-endothelial cells
transwell co-culture system. Cell Biol Int. 38:26–31. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
226
|
Liu M, Han Y, Wang J, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Chu
Q, Yang C, Chen B and Sun G: Skeletal muscle-derived IL-33 mediates
muscle-to-bone crosstalk and regulates bone metabolism via CD8(+) T
cell-secreted CCL5. EBioMedicine. 122:1060242025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Le VL, Chang CY, Chuang CW, Syu SH, Shih
HJ, Nguyen Vo HP, Van MN and Huang CJ: Therapeutic effects of
engineered exosomes from RAW264.7 Cells Overexpressing
hsa-let-7i-5p against Sepsis in Mice-A comparative study with human
placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. J Pers Med.
14:6192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Bier A, Berenstein P, Kronfeld N,
Morgoulis D, Ziv-Av A, Goldstein H, Kazimirsky G, Cazacu S, Meir R,
Popovtzer R, et al: Placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and
their exosomes exert therapeutic effects in Duchenne muscular
dystrophy. Biomaterials. 174:67–78. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Cai H and Guo H: Mesenchymal stem cells
and their exocytotic vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 24:20852023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Zha Y, Li Y, Lin T, Chen J, Zhang S and
Wang J: Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids
enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large
segmental bone defects. Theranostics. 11:397–409. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Tenkumo T, Aobulikasimu A, Asou Y, Shirato
M, Shishido S, Kanno T, Niwano Y, Sasaki K and Nakamura K:
Proanthocyanidin-rich grape seed extract improves bone loss, bone
healing, and implant osseointegration in ovariectomized animals.
Sci Rep. 10:88122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Halloran D, Pandit V, Chukwuocha K and
Nohe A: Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin restores aberrant bone
morphogenetic protein 2-signaling in bone marrow stromal cells
obtained from aged C57BL/6 Mice. J Dev Biol. 12:302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Yashima N, Minamizono W, Matsunaga H, Lyu
J, Fujikawa K, Suito H, Okunuki T, Nakai S and Ohsako M:
Non-contact electrical stimulation via a Vector-potential
transformer promotes bone healing in drill-hole injury model. J
Bone Miner Metab. 43:348–359. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Muwanga GPB, Siliezar-Doyle J, Ortiz AA,
Kaslow J, Haight ES and Tawfik VL: The tibial fracture-pin model: A
clinically relevant mouse model of orthopedic injury. J Vis Exp.
28: View Article : Google Scholar : 2022.
|
|
235
|
Wang BW, Jiang Y, Yao ZL, Chen PS, Yu B
and Wang SN: Aucubin protects chondrocytes against IL-1β-Induced
apoptosis in vitro and inhibits osteoarthritis in mice model. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 13:3529–3538. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
236
|
Suh HR, Cho HY and Han HC: Development of
a novel model of intervertebral disc degeneration by the
intradiscal application of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) in rat.
Spine J. 22:183–192. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
237
|
Li Y, Qiao X, Feng Y, Zhou R, Zhang K, Pan
Y, Yan T, Yan L, Yang S, Wei X, et al: Characterization of the gut
microbiota and fecal metabolome in the osteosarcoma mouse model.
Aging (Albany NY). 16:10841–10859. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Ferrena A, Wang J, Zhang R,
Karadal-Ferrena B, Al-Hardan W, Singh S, Borjihan H, Schwartz EL,
Zhao H, Oktay MH, et al: SKP2 knockout in Rb1/p53-Deficient mouse
models of osteosarcoma induces immune infiltration and drives a
transcriptional program with a favorable prognosis. Mol Cancer
Ther. 23:223–234. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
239
|
Wang C, Luo D, Zheng L and Zhao M:
Anti-diabetic mechanism and potential bioactive peptides of casein
hydrolysates in STZ/HFD-induced diabetic rats. J Sci Food Agric.
104:2947–2958. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
240
|
Yao Y, Cai X, Chen Y, Zhang M and Zheng C:
Estrogen deficiency-mediated osteoimmunity in postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Med Res Rev. 45:561–575. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
241
|
Rangel LBA, de Siqueira D, Soares ODR,
Santana HS, Miguel EC, da Cunha M, Oliveira ALA, Pedrosa DF,
Resgala LCR, Neto HAR, et al: Vitamin K supplementation modulates
bone metabolism and ultra-structure of ovariectomized mice. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 51:356–374. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Chen MY, Zhao FL, Chu WL, Bai MR and Zhang
DM: A review of tamoxifen administration regimen optimization for
Cre/loxp system in mouse bone study. Biomed Pharmacother.
165:1150452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Gelles K, Butylina M and Pietschmann P:
Animal models for age-related osteoporosis. Gerontology. 71:1–29.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Rong K, Chen P, Lang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z,
Wen F and Lu L: Morinda officinalis polysaccharide attenuates
osteoporosis in rats underwent bilateral ovariectomy by suppressing
the PGC-1α/PPARү pathway. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).
30:102255362211308242022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
245
|
Liu Y, Dimango E, Bucovsky M, Agarwal S,
Nishiyama K, Guo XE, Shane E and Stein EM: Abnormal
microarchitecture and stiffness in postmenopausal women using
chronic inhaled glucocorticoids. Osteoporos Int. 29:2121–2127.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Abdi S, Javanmehr N, Ghasemi-Kasman M,
Bali HY and Pirzadeh M: Stem cell-based therapeutic and diagnostic
approaches in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Neuropharmacol.
20:1093–1115. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Henderson S, Ibe I, Cahill S, Chung YH and
Lee FY: Bone quality and fracture-healing in type-1 and type-2
diabetes mellitus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 101:1399–1410. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Castillo ÍMP, Argilés JM, Rueda R, Ramírez
M and Pedrosa JML: Skeletal muscle atrophy and dysfunction in
obesity and type-2 diabetes mellitus: Myocellular mechanisms
involved. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 26:815–836. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Edgar L, Akbar N, Braithwaite AT,
Krausgruber T, Gallart-Ayala H, Bailey J, Corbin AL, Khoyratty TE,
Chai JT, Alkhalil M, et al: Hyperglycemia induces trained immunity
in macrophages and their precursors and promotes atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 144:961–982. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Kishore A and Petrek M: roles of
macrophage polarization and macrophage-derived miRNAs in pulmonary
fibrosis. Front Immunol. 12:6784572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Cazzanelli P, Lamoca M, Hasler J, Hausmann
ON, Mesfin A, Puvanesarajah V, Hitzl W and Wuertz-Kozak K: The role
of miR-155-5p in inflammation and mechanical loading during
intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Commun Signal. 22:4192024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Adamopoulos IE: Inflammation in bone
physiology and pathology. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 30:59–64. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
253
|
Sun Y, Kuek V, Liu Y, Tickner J, Yuan Y,
Chen L, Zeng Z, Shao M, He W and Xu J: MiR-214 is an important
regulator of the musculoskeletal metabolism and disease. J Cell
Physiol. 234:231–245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Ma-On C, Sanpavat A, Whongsiri P,
Suwannasin S, Hirankarn N, Tangkijvanich P and Boonla C: Oxidative
stress indicated by elevated expression of Nrf2 and 8-OHdG promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Med Oncol. 34:572017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Palma FR, Gantner BN, Sakiyama MJ, Kayzuka
C, Shukla S, Lacchini R, Cunniff B and Bonini MG: ROS production by
mitochondria: Function or dysfunction? Oncogene. 43:295–303. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
256
|
Song Y and Chung J: Aging aggravates
periodontal inflammatory responses and alveolar bone resorption by
porphyromonas gingivalis infection. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
45:6593–6604. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Liu J, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Yao X and Hang R:
Exosomes derived from macrophages upon Zn ion stimulation promote
osteoblast and endothelial cell functions. J Mater Chem B.
9:3800–3807. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Zhu Y, Zhao S, Cheng L, Lin Z, Zeng M,
Ruan Z, Sun B, Luo Z, Tang Y and Long H: Mg2+-mediated
autophagy-dependent polarization of macrophages mediates the
osteogenesis of bone marrow stromal stem cells by interfering with
macrophage-derived exosomes containing miR-381. J Orthop Res.
40:1563–1576. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Wei F, Li M, Crawford R, Zhou Y and Xiao
Y: Exosome-integrated titanium oxide nanotubes for targeted bone
regeneration. Acta Biomater. 86:480–492. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Bai X, Gao M, Syed S, Zhuang J, Xu X and
Zhang XQ: Bioactive hydrogels for bone regeneration. Bioact Mater.
3:401–417. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Moura MLA, Fugimoto M, Kawachi APM, de
Oliveira ML, Lazaretti-Castro M and Reginato RD: Estrogen therapy
associated with mechanical vibration improves bone
microarchitecture and density in osteopenic female mice. J Anat.
233:715–723. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Vilaca T, Eastell R and Schini M:
Osteoporosis in men. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 10:273–283. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Cauley JA: Estrogen and bone health in men
and women. Steroids. 99(Pt A): 11–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Pellegrino A, Tiidus PM and Vandenboom R:
Mechanisms of estrogen influence on skeletal muscle: Mass,
regeneration, and mitochondrial function. Sports Med. 52:2853–2869.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Alexander SE, Pollock AC and Lamon S: The
effect of sex hormones on skeletal muscle adaptation in females.
Eur J Sport Sci. 22:1035–1045. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
266
|
Jardí F, Laurent MR, Dubois V, Kim N,
Khalil R, Decallonne B, Vanderschueren D and Claessens F: Androgen
and estrogen actions on male physical activity: A story beyond
muscle. J Endocrinol. 238:R31–R52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Unger CA, Aladhami AK, Hope MC, Cotham WE,
Nettles KW, Clegg DJ, Velázquez KT and Enos RT: skeletal muscle
endogenous estrogen production ameliorates the metabolic
consequences of a high-fat diet in male mice. Endocrinology.
164:bqad1052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Collins BC, Mader TL, Cabelka CA, Iñigo
MR, Spangenburg EE and Lowe DA: Deletion of estrogen receptor α in
skeletal muscle results in impaired contractility in female mice. J
Appl Physiol (1985). 124:980–992. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Tramunt B, Smati S, Grandgeorge N, Lenfant
F, Arnal JF, Montagner A and Gourdy P: Sex differences in metabolic
regulation and diabetes susceptibility. Diabetologia. 63:453–461.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
270
|
O'Reilly J, Ono-Moore KD, Chintapalli SV,
Rutkowsky JM, Tolentino T, Lloyd KCK, Olfert IM and Adams SH: Sex
differences in skeletal muscle revealed through fiber type,
capillarity, and transcriptomics profiling in mice. Physiol Rep.
9:e150312021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Farhat F, Amérand A, Simon B, Guegueniat N
and Moisan C: Gender-dependent differences of mitochondrial
function and oxidative stress in rat skeletal muscle at rest and
after exercise training. Redox Rep. 22:508–514. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Clynes MA, Gregson CL, Bruyère O, Cooper C
and Dennison EM: Osteosarcopenia: Where osteoporosis and sarcopenia
collide. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:529–537. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
273
|
Gálvez I, Navarro MC, Martín-Cordero L,
Otero E, Hinchado MD and Ortega E: The influence of obesity and
weight loss on the bioregulation of innate/inflammatory responses:
Macrophages and immunometabolism. Nutrients. 14:6122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Jin Z, Huang Q, Peng J, Liu Z, Hu R, Wu J
and Wang F: MiR-125a-3p alleviates hyperproliferation of
keratinocytes and psoriasis-like inflammation by targeting
TLR4/NF-ĸB pathway. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 40:447–461. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
275
|
Paoli A, Cenci L, Pompei P, Sahin N,
Bianco A, Neri M, Caprio M and Moro T: Effects of two months of
very low carbohydrate ketogenic diet on body composition, muscle
strength, muscle area, and blood parameters in competitive natural
body builders. Nutrients. 13:3742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
276
|
Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Dong Y,
Birmingham A, Seo JB, Ofrecio JM, Wollam J, Hernandez-Carretero A,
Fu W, et al: Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miRNAs can
modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell.
171:372–384.e12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
277
|
Gao X, Chen Y, Wang J, Xu J, Wan H, Li X
and Shi Y: Mitochondria-Rich extracellular vesicles from bone
marrow stem cells mitigate muscle degeneration in rotator cuff
tears in a rat model through macrophage M2 phenotype conversion.
Arthroscopy. 41:3487–3499. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Trentini M, D'Amora U, Ronca A, Lovatti L,
Calvo-Guirado JL, Licastro D, Monego SD, Delogu LG, Wieckowski MR,
Barak S, et al: Bone regeneration revolution: Pulsed
electromagnetic field modulates macrophage-derived exosomes to
attenuate osteoclastogenesis. Int J Nanomedicine. 19:8695–8707.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Hu XM, Wang CC, Xiao Y, Liu Y, Huang HR,
Jiang P, Wang YK, Lin YJ, Li LC and Qi ZQ: Non-clinical safety
evaluation of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells in cynomolgus monkeys. Int J Nanomedicine.
19:4923–4939. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
280
|
Li JJ, Wang B, Kodali MC, Chen C, Kim E,
Patters BJ, Lan L, Kumar S, Wang X, Yue J and Liao FF: In vivo
evidence for the contribution of peripheral circulating
inflammatory exosomes to neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation.
15:82018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
281
|
Wang Y, Kong Y, Du J, Qi L, Liu M, Xie S,
Hao J, Li M, Cao S, Cui H, et al: Injection of human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells exosomes for the treatment of knee
osteoarthritis: From preclinical to clinical research. J Transl
Med. 23:6412025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
282
|
Muraca M and Cappariello A: The role of
extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the epigenetic regulation of bone
metabolism and osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 21:86822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
283
|
Rohm TV, Castellani Gomes Dos Reis F,
Isaac R, Murphy C, Rocha KCE, Bandyopadhyay G, Gao H, Libster AM,
Zapata RC, Lee YS, et al: Adipose tissue macrophages secrete small
extracellular vesicles that mediate rosiglitazone-induced insulin
sensitization. Nat Metab. 6:880–898. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
284
|
Ying W, Gao H, Dos Reis FCG, Bandyopadhyay
G, Ofrecio JM, Luo Z, Ji Y, Jin Z, Ly C and Olefsky JM: MiR-690, an
exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves
insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Cell Metab. 33:781–790.e5. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
285
|
Wang Y, Zhang X, Wang J, Zhang Y, Ye Q,
Wang Y, Fei D and Wang Q: Inflammatory periodontal ligament stem
cells drive m1 macrophage polarization via exosomal
miR-143-3p-Mediated regulation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling. Stem
Cells. 41:184–199. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
286
|
Chen Y, Dong J, Li J, Li J, Lu Y, Dong W,
Zhang D and Dang X: Engineered macrophage-derived exosomes via
click chemistry for the treatment of osteomyelitis. J Mater Chem B.
12:10593–10604. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|