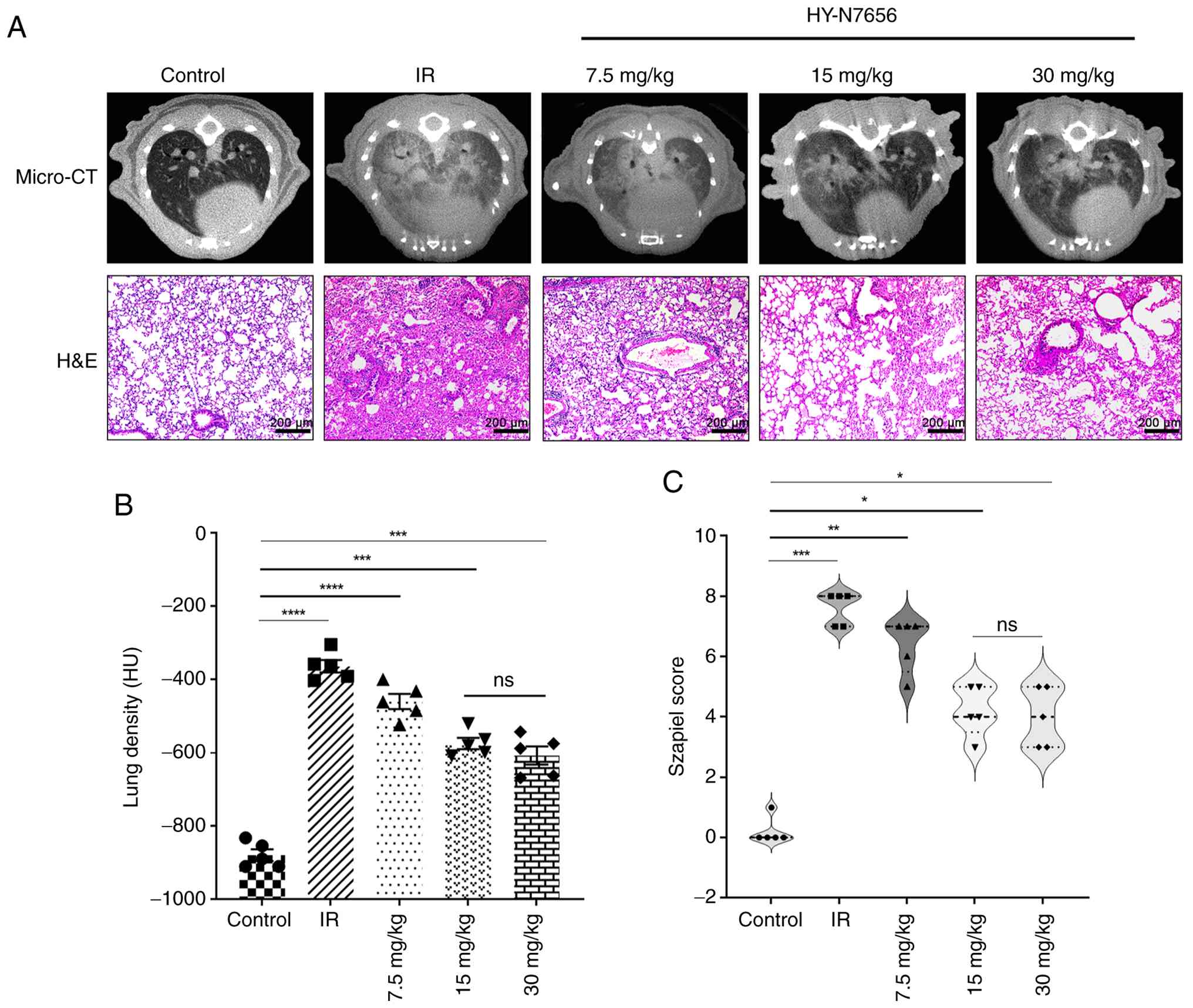
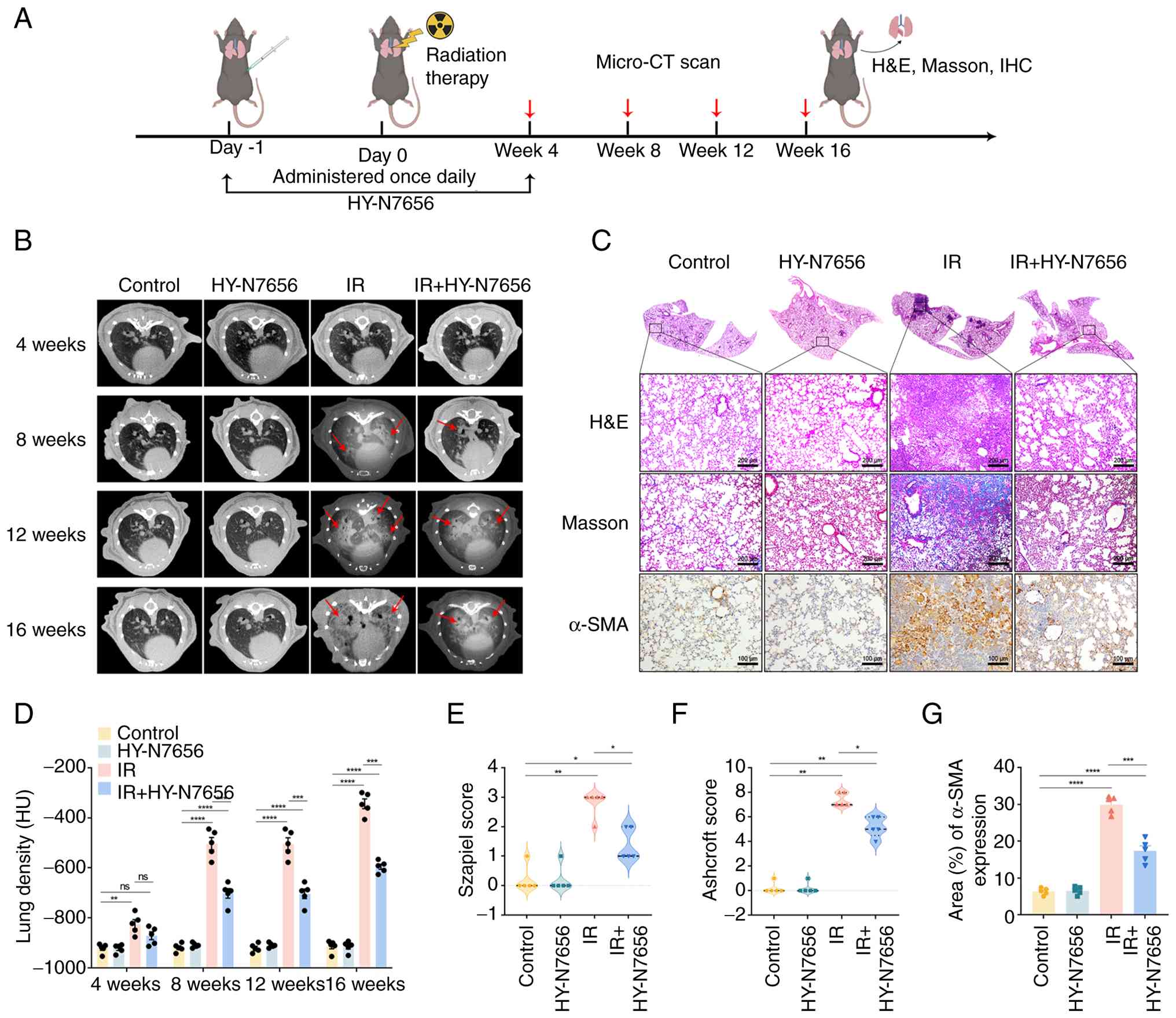
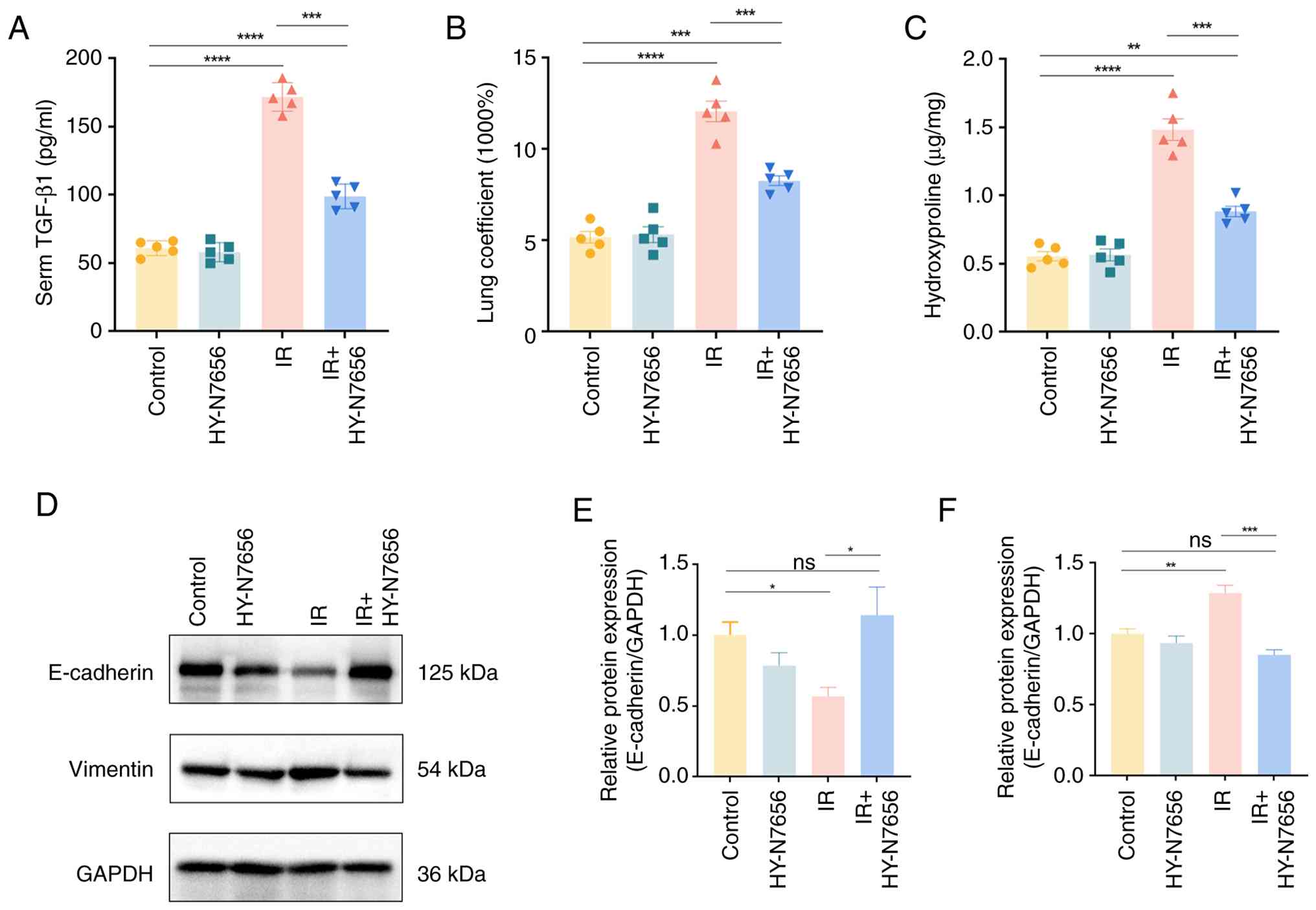
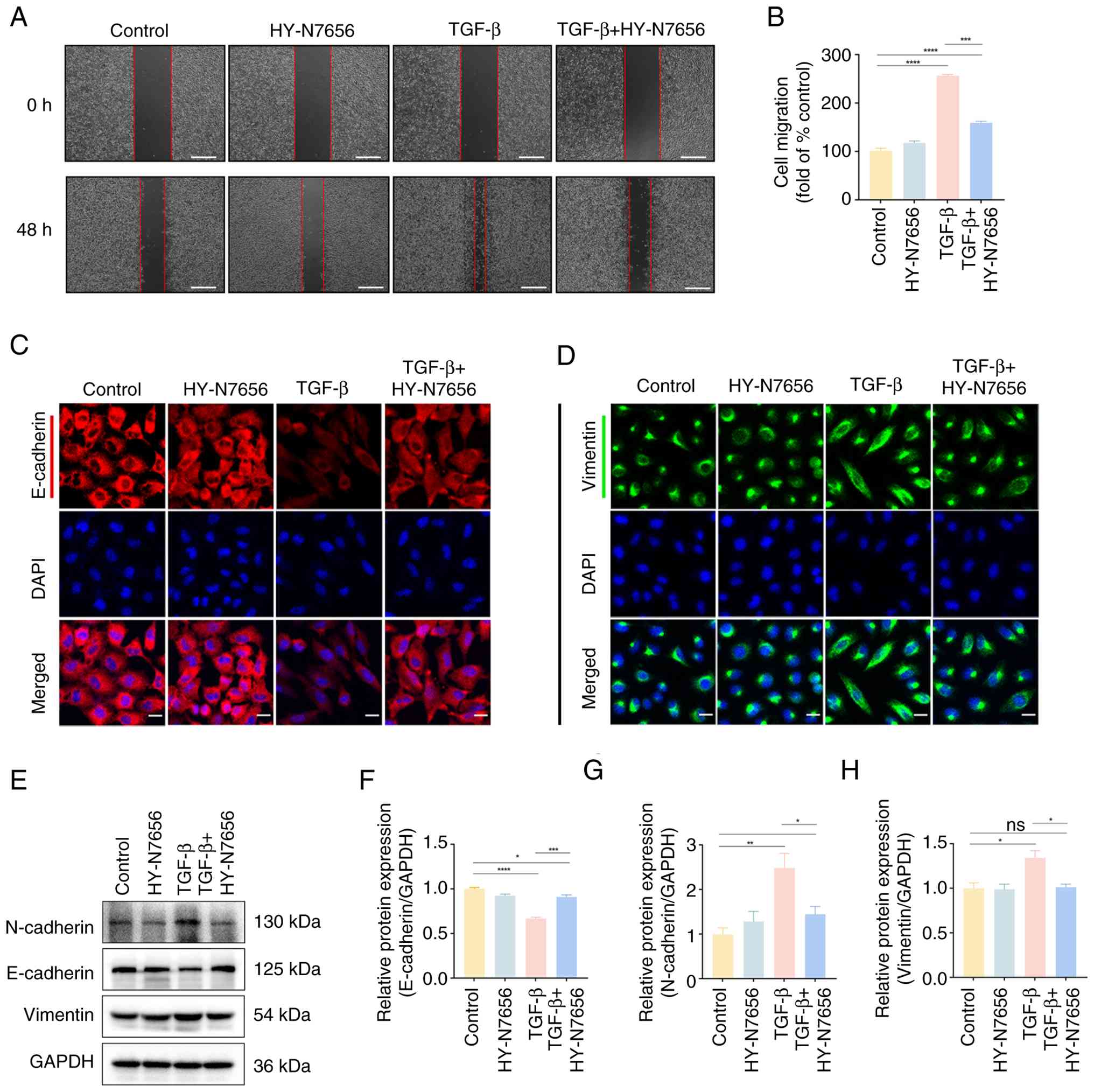
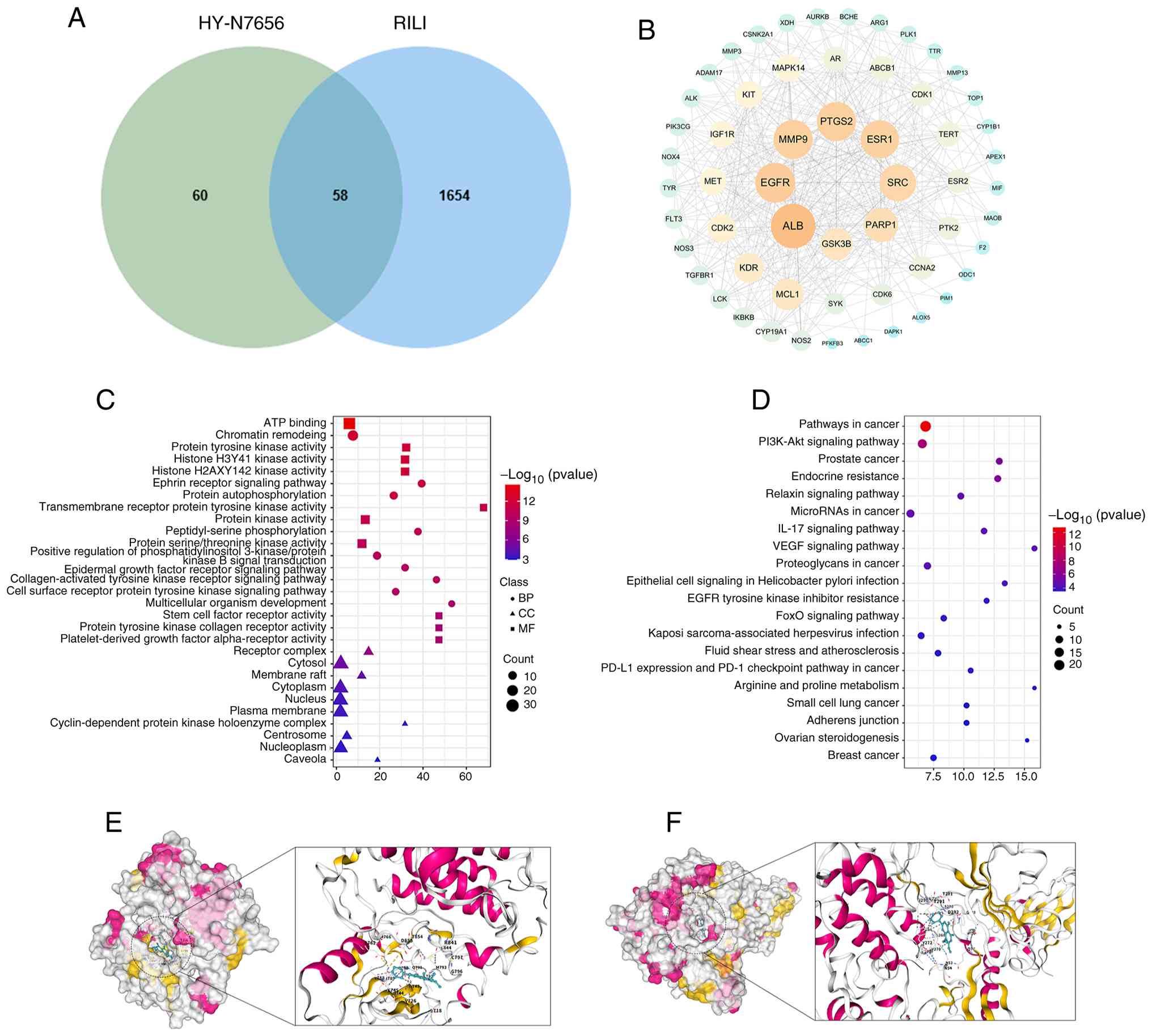
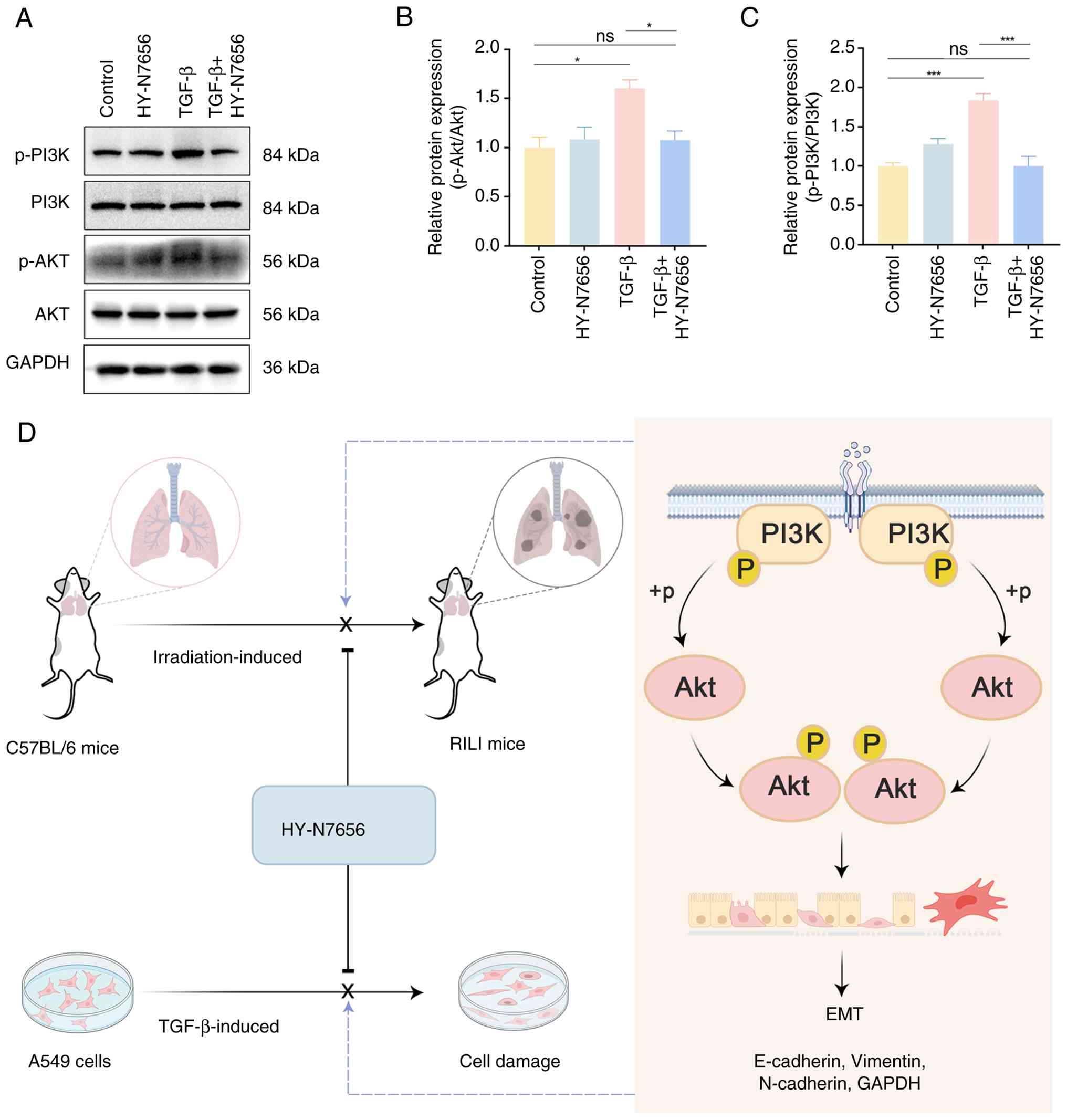
|
1
|
Xu T, Zhang Y, Chang P, Gong S, Shao L and
Dong L: Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for radiation-induced
lung injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bradley JD, Paulus R, Komaki R, Masters G,
Blumenschein G, Schild S, Bogart J, Hu C, Forster K, Magliocco A,
et al: Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with
concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or
without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB
non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): A randomised, two-by-two
factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 16:187–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharma GP, Fish BL, Frei AC, Narayanan J,
Gasperetti T, Scholler D, Pierce L, Szalewski N, Blue N, Medhora M
and Himburg HA: Pharmacologic ACE-inhibition mitigates
radiation-induced pneumonitis by suppressing ACE-expressing lung
myeloid cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 113:177–191. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Onishi H, Marino K, Yamashita H, Terahara
A, Onimaru R, Kokubo M, Shioyama Y, Kozuka T, Matsuo Y, Aruga T and
Hiraoka M: Case series of 23 patients who developed fatal radiation
pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer.
Technol Cancer Res Treat. 17:15330338188013232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meng Y, Yang H, Wang W, Tang X, Jiang C,
Shen Y and Luo W: Excluding PTV from lung volume may better predict
radiation pneumonitis for intensity modulated radiation therapy in
lung cancer patients. Radiat Oncol. 14:72019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu S, Liu C and Ji HL: Concise review:
Therapeutic potential of the mesenchymal stem cell derived
secretome and extracellular vesicles for radiation-induced lung
injury: Progress and hypotheses. Stem Cells Transl Med. 8:344–354.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giuranno L, Ient J, De Ruysscher D and
Vooijs MA: Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI). Front Oncol.
9:8772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bledsoe TJ, Nath SK and Decker RH:
Radiation pneumonitis. Clin Chest Med. 38:201–208. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng Y, Xia X, Zhao Y, Zhao Z, Martinez C,
Yin W, Yao J, Hang Q, Wu W, Zhang J, et al: Glucocorticoid receptor
regulates PD-L1 and MHC-I in pancreatic cancer cells to promote
immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance. Nat Commun.
12:70412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L, Wu D, Deng S, Li J, Zhang F, Zou Y,
Zhang T and Xu Y: NVP-AUY922 alleviates radiation-induced lung
injury via inhibition of autophagy-dependent ferroptosis. Cell
Death Discov. 8:862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simone CB II: Thoracic radiation normal
tissue injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 27:370–377. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Froese AR, Shimbori C, Bellaye PS, Inman
M, Obex S, Fatima S, Jenkins G, Gauldie J, Ask K and Kodlb M:
Stretch-induced activation of transforming growth factor-β1 in
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 194:84–96. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh V, Torricelli AA, Nayeb-Hashemi N,
Agrawal V and Wilson SE: Mouse strain variation in SMA(+)
myofibroblast development after corneal injury. Exp Eye Res.
115:27–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tatler AL and Jenkins G: TGF-β activation
and lung fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 9:130–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim KK, Kugler MC, Wolters PJ, Robillard
L, Galvez MG, Brumwell AN, Sheppard D and Chapman HA: Alveolar
epithelial cell mesenchymal transition develops in vivo during
pulmonary fibrosis and is regulated by the extracellular matrix.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:13180–13185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park HR, Jo SK and Jung U: Ionizing
radiation promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung
epithelial cells by TGF-β-producing M2 macrophages. In Vivo.
33:1773–1784. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sohn SH, Lee JM, Park S, Yoo H, Kang JW,
Shin D, Jung KH, Lee YS, Cho J and Bae H: The inflammasome
accelerates radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in
mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 39:917–926. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moghbeli M: PI3K/AKT pathway as a pivotal
regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung tumor cells.
Cancer Cell Int. 24:1652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bustamante A, Baritaki S, Zaravinos A and
Bonavida B: Relationship of signaling pathways between RKIP
expression and the inhibition of EMT-inducing transcription factors
SNAIL1/2, TWIST1/2 and ZEB1/2. Cancers (Basel). 16:31802024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan Z, Zhu J, Liu Y, Li Z, Liang X, Zhou
S, Hou Y, Chen H, Zhou L, Wang P, et al: DNA-PKcs/AKT1 inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition during radiation-induced
pulmonary fibrosis by inducing ubiquitination and degradation of
Twist1. Clin Transl Med. 14:e16902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Conte E, Fruciano M, Fagone E, Gili E,
Caraci F, Iemmolo M, Crimi N and Vancheri C: Inhibition of PI3K
prevents the proliferation and differentiation of human lung
fibroblasts into myofibroblasts: the role of class I P110 isoforms.
PLoS One. 6:e246632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang XL, Xing RG, Chen L, Liu CR and Miao
ZG: PI3K/Akt signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Med Rep. 14:5699–5706. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang B, Wei J, Meng L, Wang H, Qu C, Chen
X, Xin Y and Jiang X: Advances in pathogenic mechanisms and
management of radiation-induced fibrosis. Biomed Pharmacother.
121:1095602020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lin B, Zhang P and Lang J: Clinical
observation of Huaxian decociton on preventing 70 cases of
radio-pulmonarylesion. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. 30:76–78. 2012.In
Chinese.
|
|
25
|
Lin B, Zhang P and Lang J: Experimental
research of using Huaxian decociton to prevent and treating
radiation fibrosis of lung. J Sichuan Tradit Chin Med. 33:54–57.
2015.In Chinese.
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Zou P, Fang Z, Gong C, Yin J, Chen
M, Lin B and Lang J: Hua Xian Fang alleviates radiation-induced
pulmonary fibrosis by upregulating the level of IFN-γ in blood and
tissues. Chin J Radiat Oncol. 33:554–561. 2024.In Chinese.
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Zou P, Quan L, Gong C, Fang Z, Lin
B, Lang J and Chen M: Huaxian formula prevents the progression of
radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the pro-fibrotic
effects of macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 338:1190262025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gong C, Chen J, Zou P, Fang Z, Quan L,
Wang J, Yin J, Lin B, Lang J and Chen M: Serum pharmacochemistry
and network pharmacology reveal active compounds and mechanisms of
the huaxian formula in alleviating radiation-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 19:627–644. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen DY, Juang SH, Kuo PC, Huang GJ, Chan
YY, Damu AG and Wu TS: Chemical constituents from andrographis
echioides and their anti-inflammatory activity. Int J Mol Sci.
14:496–514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Travis EL, Rachakonda G, Zhou X, Korhonen
K, Sekhar KR, Biswas S and Freeman ML: NRF2 deficiency reduces life
span of mice administered thoracic irradiation. Free Radic Biol
Med. 51:1175–1183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Niu S and Zhang Y, Cong C, Wu Z, Wang Z,
Sun M, Yao C and Zhang Y: Comparative study of radiation-induced
lung injury model in two strains of mice. Health Phys. 122:579–585.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lierova A, Kasparova J, Pejchal J,
Kubelkova K, Jelicova M, Palarcik J, Korecka L, Bilkova Z and
Sinkorova Z: Attenuation of radiation-induced lung injury by
hyaluronic acid nanoparticles. Front Pharmacol. 11:11992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gattinoni L, Caironi P, Pelosi P and
Goodman LR: What has computed tomography taught us about the acute
respiratory distress syndrome? Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
164:1701–1711. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hübner RH, Gitter W, El Mokhtari NE,
Mathiak M, Both M, Bolte H, Freitag-Wolf S and Bewig B:
Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological
samples. Biotechniques. 44:507–511. 514–517. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Missiuro PV, Liu K, Zou L, Ross BC, Zhao
G, Liu JS and Ge H: Information flow analysis of interactome
networks. PLoS Comput Biol. 5:e10003502009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Y, Yang X, Gan J, Chen S, Xiao ZX and
Cao Y: CB-Dock2: Improved protein-ligand blind docking by
integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template
fitting. Nucleic Acids Res. 50:W159–W164. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kang SK, Rabbani ZN, Folz RJ, Golson ML,
Huang H, Yu D, Samulski TS, Dewhirst MW, Anscher MS and Vujaskovic
Z: Overexpression of extracellular superoxide dismutase protects
mice from radiation-induced lung injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 57:1056–1066. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Travis EL, Down JD, Holmes SJ and Hobson
B: Radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis in mouse lung assayed by
respiratory frequency and histology. Radiat Res. 84:133–143. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li X, Ma L, Huang K, Wei Y, Long S, Liu Q,
Zhang D, Wu S, Wang W, Yang G, et al: Regorafenib-attenuated,
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the TGF-β1
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 22:19852021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yang K, Palm J, König J, Seeland U,
Rosenkranz S, Feiden W, Rübe C and Rübe CE:
Matrix-metallo-proteinases and their tissue inhibitors in
radiation-induced lung injury. Int J Radiat Biol. 83:665–676. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim SB, Ly P, Kaisani A, Zhang L, Wright
WE and Shay JW: Mitigation of radiation-induced damage by targeting
EGFR in noncancerous human epithelial cells. Radiat Res.
180:259–267. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen ZY, Xiao HW, Dong JL, Li Y, Wang B,
Fan SJ and Cui M: Gut microbiota-derived PGF2α fights against
radiation-induced lung toxicity through the MAPK/NF-κB pathway.
Antioxidants (Basel). 11:652021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
He G, Tang A, Xie M, Xia W, Zhao P, Wei J,
Lai Y, Tang X, Zou YM and Liu H: Blood gene expression profile
study revealed the activation of apoptosis and p53 signaling
pathway may be the potential molecular mechanisms of ionizing
radiation damage and radiation-induced bystander effects. Dose
Response. 18:15593258209141842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lieverse RIY, Van Limbergen EJ, Oberije
CJG, Troost EGC, Hadrup SR, Dingemans AC, Hendriks LEL, Eckert F,
Hiley C, Dooms C, et al: Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy
(SABR) combined with immunotherapy (L19-IL2) versus standard of
care in stage IV NSCLC patients, ImmunoSABR: A multicentre,
randomised controlled open-label phase II trial. BMC Cancer.
20:5572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hou G, Li J, Liu W, Wei J, Xin Y and Jiang
X: Mesenchymal stem cells in radiation-induced lung injury: From
mechanisms to therapeutic potential. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10:11003052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Konkol M, Śniatała P and Milecki P:
Radiation-induced lung injury - what do we know in the era of
modern radiotherapy? Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 27:552–565.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Drishya S, Dhanisha SS, Raghukumar P and
Guruvayoorappan C: Amomum subulatum mitigates experimental thoracic
radiation-induced lung injury by regulating antioxidant status and
inflammatory responses. Food Funct. 14:1545–1559. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fox MS, Ouriadov A, Thind K, Hegarty E,
Wong E, Hope A and Santyr GE: Detection of radiation induced lung
injury in rats using dynamic hyperpolarized (129)Xe magnetic
resonance spectroscopy. Med Phys. 41:0723022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kun C, Tao L, Leiyuan H, Yunhao F, Ning W,
Zhe L, Yuanyuan C, Xiao L, Hongran Q, Jianming C, et al:
Heat-killed Salmonella typhimurium mitigated radiation-induced lung
injury. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 46:1084–1091. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim JS, Son Y, Jung MG, Jeong YJ, Kim SH,
Lee SJ, Lee YJ and Lee HJ: Geranylgeranylacetone alleviates
radiation-induced lung injury by inhibiting
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition signaling. Mol Med Rep.
13:4666–4670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang X, Li M, Yin J, Fang J, Ying Y, Ye T,
Zhang F, Ma S, Qin H and Liu X: Emetine dihydrochloride alleviated
radiation-induced lung injury through inhibiting EMT. J Cell Mol
Med. 27:3839–3850. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nagaraja SS and Nagarajan D:
Radiation-induced pulmonary epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A
review on targeting molecular pathways and mediators. Curr Drug
Targets. 19:1191–1204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Qu H, Liu L, Liu Z, Qin H, Liao Z, Xia P,
Yang Y, Li B, Gao F and Cai J: Blocking TBK1 alleviated
radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition through Akt-Erk inactivation. Exp Mol Med. 51:1–17.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wang J, Bao L, Yu B, Liu Z, Han W, Deng C
and Guo C: Interleukin-1β promotes epithelial-derived alveolar
elastogenesis via αvβ6 integrin-dependent TGF-β activation. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:2198–2216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wang M, Feng Y, Zhang P, Shen K, Su J,
Zhong Y, Yang X, Lin S and Lu J: Jiawei Maxing Shigan Tang
alleviates radiation-induced lung injury via TGF-β1/Smad signaling
pathway mediated by regulatory T cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
320:1173892024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Chen H, Chen N, Li F, Sun L, Du J, Chen Y,
Cheng F, Li Y, Tian S, Jiang Q, et al: Repeated radon exposure
induced lung injury and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells and
mice. Toxicol Lett. 334:4–13. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Polimeni M, Gulino GR, Gazzano E, Kopecka
J, Marucco A, Fenoglio I, Cesano F, Campagnolo L, Magrini A,
Pietroiusti A, et al: Multi-walled carbon nanotubes directly induce
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelial
cells via the TGF-β-mediated Akt/GSK-3β/SNAIL-1 signalling pathway.
Part Fibre Toxicol. 13:272016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Qian W, Cai X, Qian Q, Zhang W and Wang D:
Astragaloside IV modulates TGF-β1-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med.
22:4354–4365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses
HL and Arteaga CL: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is
required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem.
275:36803–38610. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li Y, Shen Z, Jiang X, Wang Y, Yang Z, Mao
Y, Wu Z, Li G and Chen H: Mouse mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomal miR-466f-3p reverses EMT process through inhibiting
AKT/GSK3β pathway via c-MET in radiation-induced lung injury. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 41:1282022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Karimi Roshan M, Soltani A, Soleimani A,
Rezaie Kahkhaie K, Afshari AR and Soukhtanloo M: Role of AKT and
mTOR signaling pathways in the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) process. Biochimie. 165:229–234. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhao DY, Qu HJ, Guo JM, Zhao HN, Yang YY,
Zhang P, Cao K, Lei X, Cui JG, Liu C, et al: Protective effects of
myrtol standardized against radiation-induced lung injury. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 38:619–634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yang C, Song C, Wang Y, Zhou W, Zheng W,
Zhou H, Deng G, Li H, Xiao W, Yang Z, et al: Re-Du-Ning injection
ameliorates radiation-induced pneumonitis and fibrosis by
inhibiting AIM2 inflammasome and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Phytomedicine. 102:1541842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu X, Shao C and Fu J: Promising
biomarkers of radiation-induced lung injury: A review.
Biomedicines. 9:11812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wu N, Li Z, Wang J, Geng L, Yue Y, Deng Z,
Wang Q and Zhang Q: Low molecular weight fucoidan attenuating
pulmonary fibrosis by relieving inflammatory reaction and
progression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Carbohydr Polym.
273:1185672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang M, Che Y, Li K, Fang Z, Li S, Wang M,
Zhang Y, Xu Z, Luo L, Wu C, et al: [Detection and quantitative
analysis of tumor-associated tertiary lymphoid structures]. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 24:779–795. 2023.In English, Chinese.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhou X, Bao WA, Zhu X, Lin J, Fan JF, Yang
Y, Du XH and Wang YZ: 3,3'-Diindolylmethane attenuates inflammation
and fibrosis in radiation-induced lung injury by regulating
NF-κB/TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. Exp Lung Res. 48:103–113.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|