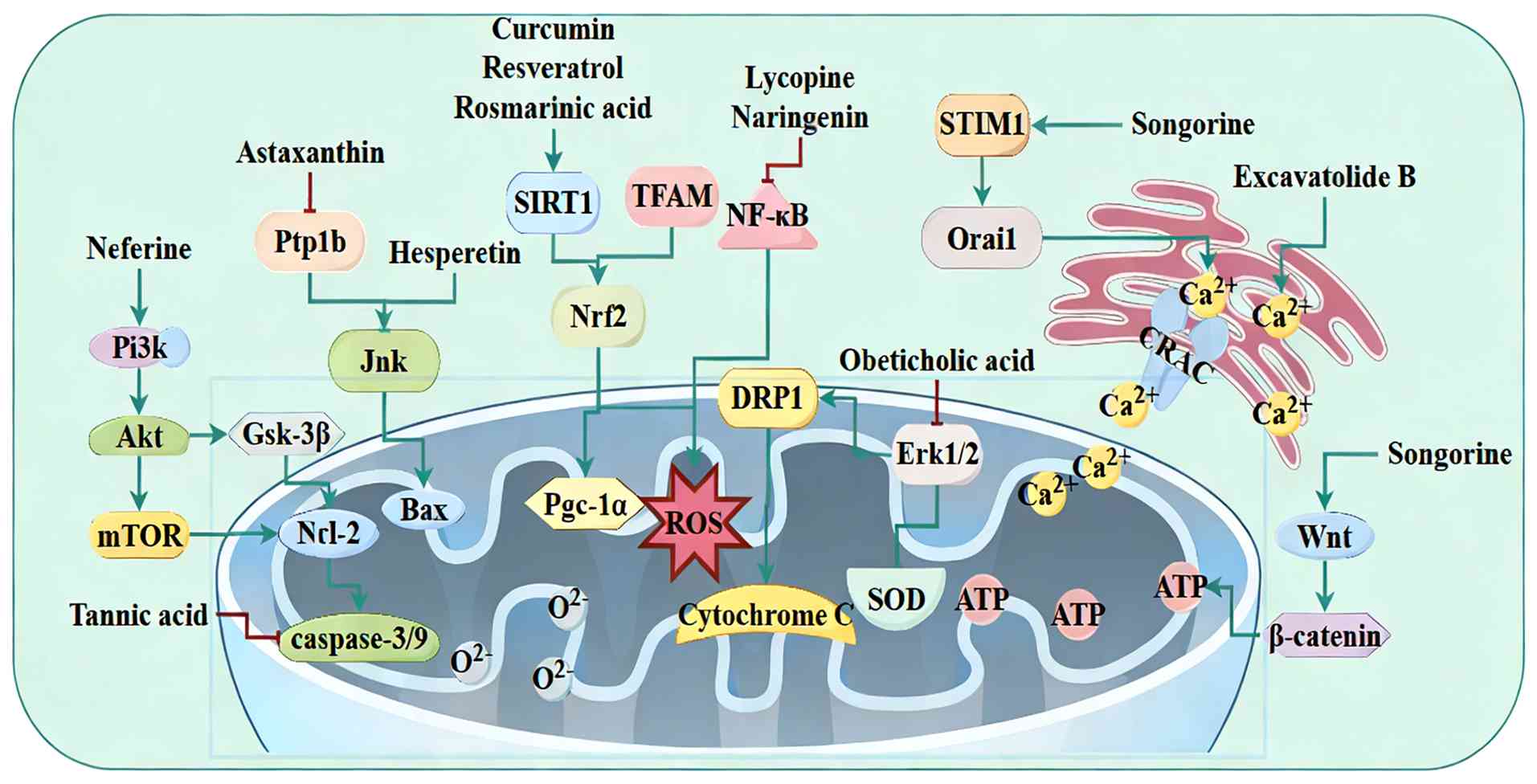
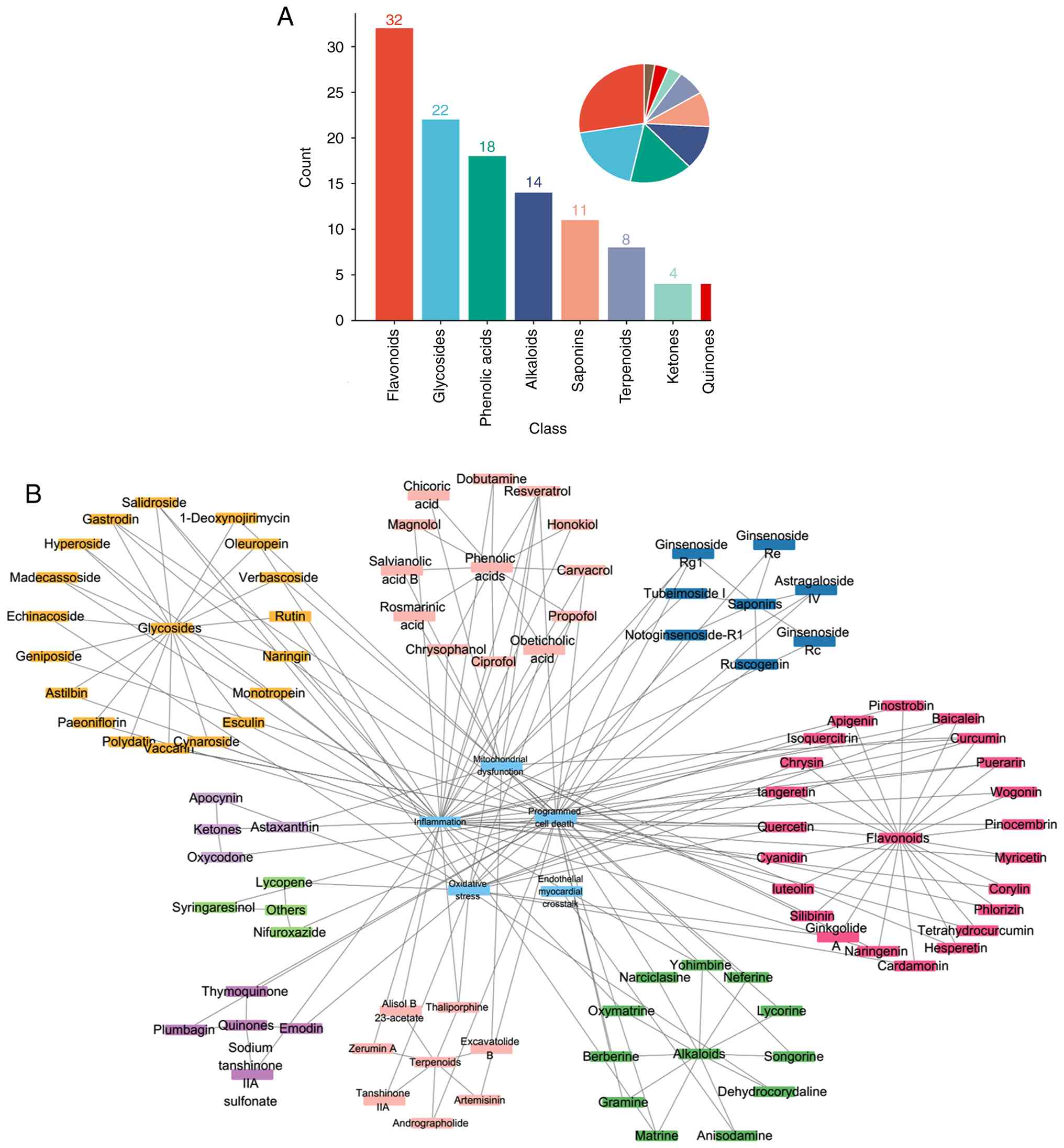
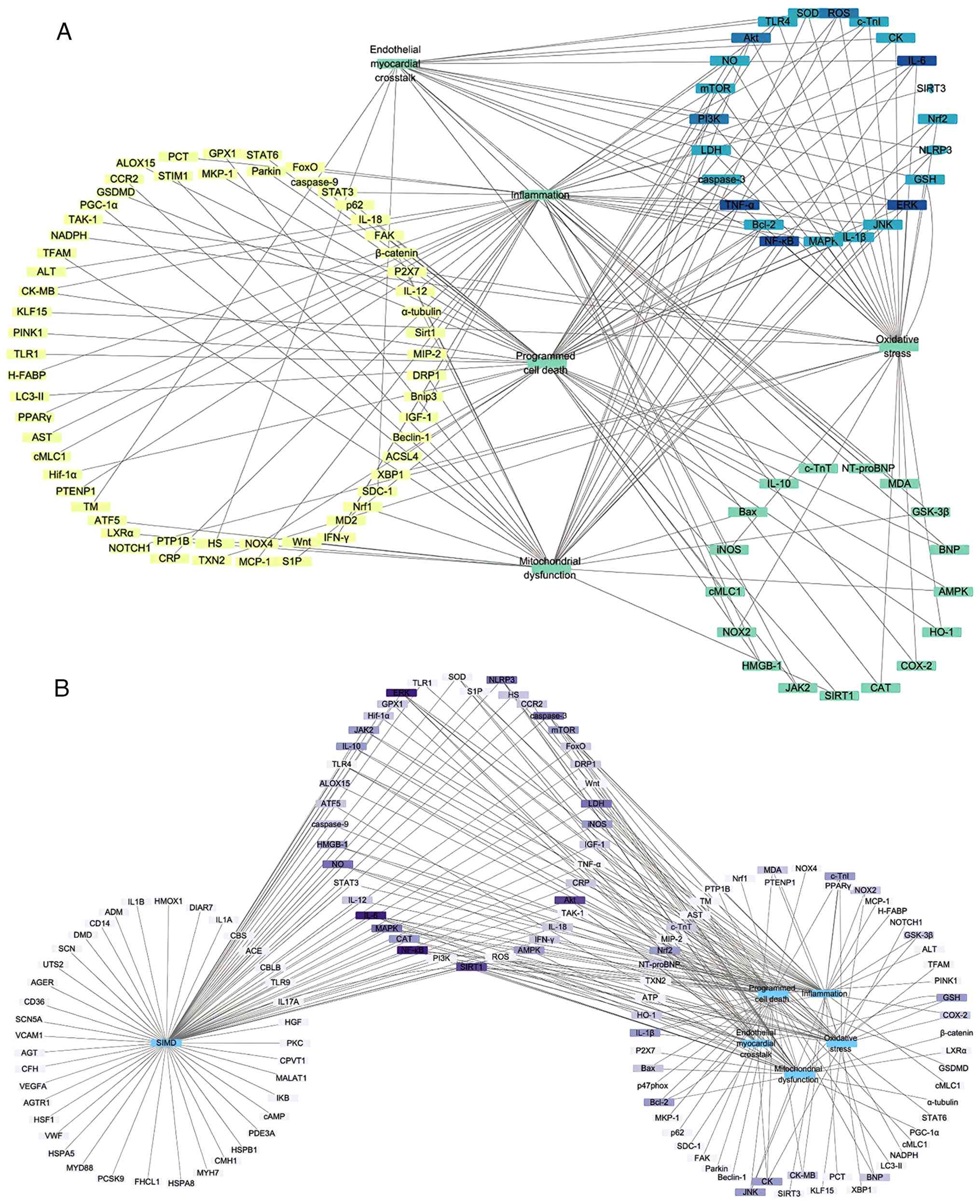
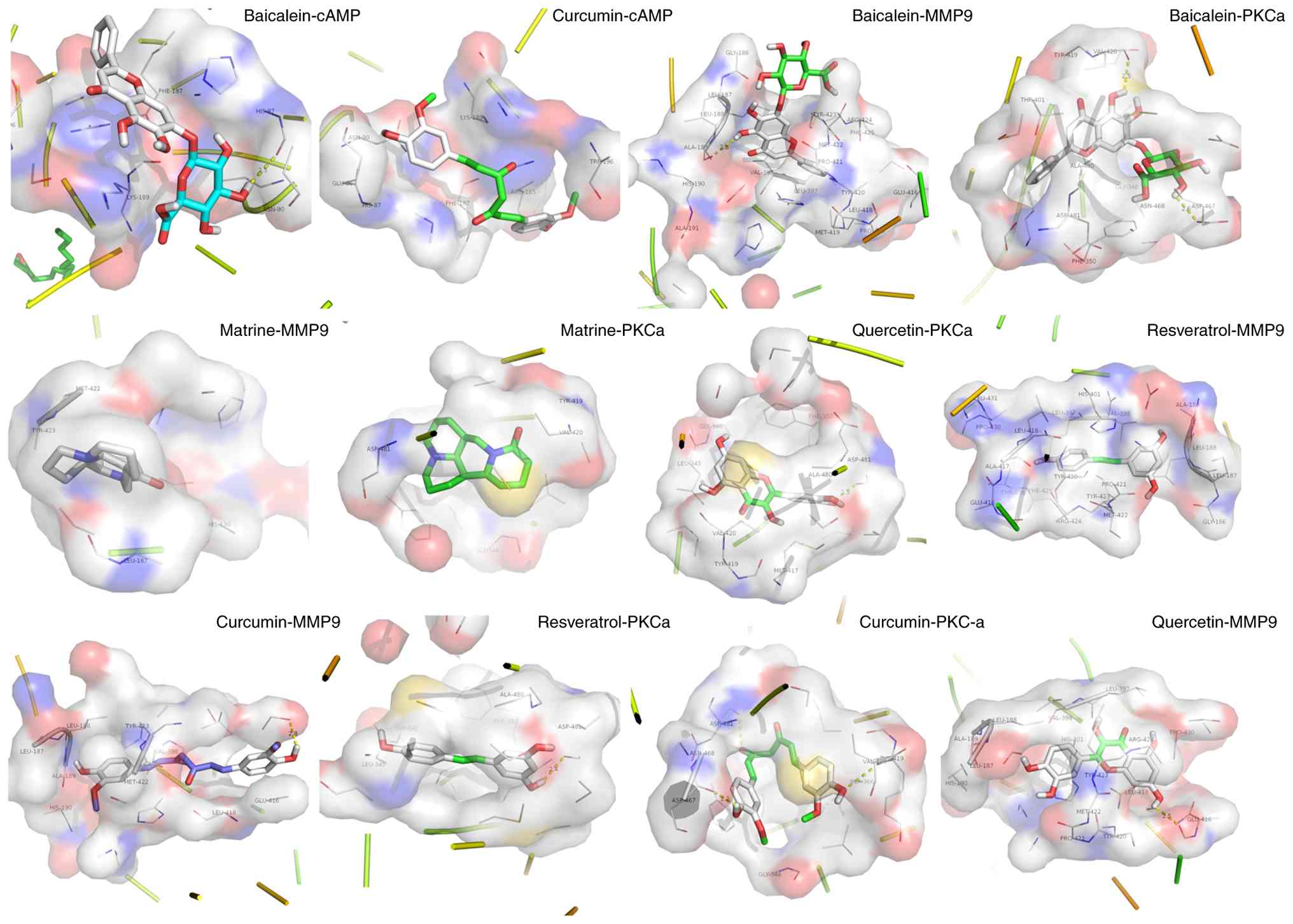
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Angus DC and van der Poll T: Severe sepsis
and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 369:840–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yan J, Li Z, Li Y and Zhang Y: Sepsis
induced cardiotoxicity by promoting cardiomyocyte cuproptosis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 690:1492452024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M and Rhodes A:
Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 392:75–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iyer S, Kennedy JN, Jentzer JC, Senussi MH
and Seymour CW: Cardiac function before sepsis and clinical
outcomes. JAMA. 331:1496–1499. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van der Poll T and van Deventer SJ:
Cytokines and anticytokines in the pathogenesis of sepsis. Infect
Dis Clin North Am. 13:413–426. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Li J, Tian P, Guli B, Weng G, Li L
and Cheng Q: H2S attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via
a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Exp Ther Med. 17:4064–4072.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang F, Zhang JN, Xu LY, Zhao XL, Wan F,
Ao H and Peng C: Endothelial-derived exosomes: A novel therapeutic
strategy for LPS-induced myocardial damage with anisodamine. Int J
Biol Macromol. 282:1369932024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang X, Zhang C, Tian T, Dai X, Xing Y,
Wang Y, Yang D, Li H, Wang Y, Lv X and Wang H: Posttreatment with
dexmedetomidine aggravates LPS-induced myocardial dysfunction
partly via activating cardiac endothelial α2A-AR in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 116:1097242023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tang F, Liu D, Zhang L, Xu LY, Zhang JN,
Zhao XL, Ao H and Peng C: Targeting endothelial cells with golden
spice curcumin: A promising therapy for cardiometabolic
multimorbidity. Pharmacol Res. 197:1069532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Y, Weng D, Shi W, Wei S, Ji W, Wang
X, Xu Y, Wang X, Mei X and Guo S: Integrative network pharmacology
and multi-omics reveal anisodamine hydrobromide's multi-target
mechanisms in sepsis. Sci Rep. 15:279962025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Palmieri V, Innocenti F, Guzzo A, Guerrini
E, Vignaroli D and Pini R: Left ventricular systolic longitudinal
function as predictor of outcome in patients with sepsis. Circ
Cardiovasc Imaging. 8:e0038652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan R, Liu H and Liang Q: Roles and
therapeutic targeting of exosomes in Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.
J Cell Mol Med. 29:e705592025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Antonucci E, Fiaccadori E, Donadello K,
Taccone FS, Franchi F and Scolletta S: Myocardial depression in
sepsis: From pathogenesis to clinical manifestations and treatment.
J Crit Care. 29:500–511. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Repessé X, Charron C and Vieillard-Baron
A: Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function revisited in
septic shock. Crit Care. 17:1642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aissaoui N, Boissier F, Chew M, Singer M
and Vignon P: Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J.
46:3339–3353. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parker MM, Shelhamer JH, Bacharach SL,
Green MV, Natanson C, Frederick TM, Damske BA and Parrillo JE:
Profound but reversible myocardial depression in patients with
septic shock. Ann Intern Med. 100:483–490. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zaky A, Deem S, Bendjelid K and Treggiari
MM: Characterization of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis: An ongoing
challenge. Shock. 41:12–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
ver Elst KM, Spapen HD, Nguyen DN, Garbar
C, Huyghens LP and Gorus FK: Cardiac troponins I and T are
biological markers of left ventricular dysfunction in septic shock.
Clin Chem. 46:650–657. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sheyin O, Davies O, Duan W and Perez X:
The prognostic significance of troponin elevation in patients with
sepsis: A meta-analysis. Heart Lung. 44:75–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Clerico A, Iervasi G and Mariani G:
Pathophysiologic relevance of measuring the plasma levels of
cardiac natriuretic peptide hormones in humans. Horm Metab Res.
31:487–498. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chua G and Kang-Hoe L: Marked elevations
in N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide levels in septic shock.
Crit Care. 8:R248–R250. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Roch A, Allardet-Servent J, Michelet P,
Oddoze C, Forel JM, Barrau K, Loundou A, Perrin G, Auffray JP,
Portugal H and Papazian L: NH2 terminal pro-brain natriuretic
peptide plasma level as an early marker of prognosis and cardiac
dysfunction in septic shock patients. Crit Care Med. 33:1001–1007.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alam ML, Katz R, Bellovich KA, Bhat ZY,
Brosius FC, de Boer IH, Gadegbeku CA, Gipson DS, Hawkins JJ,
Himmelfarb J, et al: Soluble ST2 and Galectin-3 and Progression of
CKD. Kidney Int Rep. 4:103–111. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang X, Guo Y, Wang J, Liu J, Ma Y, Lu Q
and Han Y: Heart-type fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP) as an
early biomarker in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: A prospective
observational study. Lipids Health Dis. 23:2832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weinberger J, Klompas M and Rhee C: What
is the utility of measuring lactate levels in patients with sepsis
and septic shock? Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 42:650–661. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Benz F, Roy S, Trautwein C, Roderburg C
and Luedde T: Circulating MicroRNAs as biomarkers for sepsis. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Manetti AC, Maiese A, Paolo MD, De Matteis
A, La Russa R, Turillazzi E, Frati P and Fineschi V: MicroRNAs and
Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: A systematic review. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:3212020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ketelut-Carneiro N and Fitzgerald KA:
Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and Necroptosis-Oh My! The many ways a cell
can die. J Mol Biol. 434:1673782022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Communal C, Sumandea M, de Tombe P, Narula
J, Solaro RJ and Hajjar RJ: Functional consequences of caspase
activation in cardiac myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:6252–6256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nevière R, Fauvel H, Chopin C, Formstecher
P and Marchetti P: Caspase inhibition prevents cardiac dysfunction
and heart apoptosis in a rat model of sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 163:218–225. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu H, Tian M, Ding C and Yu S: The C/EBP
Homologous protein (CHOP) Transcription factor functions in
endoplasmic reticulum Stress-induced apoptosis and microbial
infection. Front Immunol. 9:30832018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li L, Peng X, Guo L, Zhao Y and Cheng Q:
Sepsis causes heart injury through endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
13:964–971. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu X, Liu Q, He S, Zhao J, Wang N, Han X
and Guo Y: Qiang-Xin 1 formula prevents Sepsis-induced apoptosis in
murine cardiomyocytes by suppressing endoplasmic Reticulum- and
Mitochondria-associated pathways. Front Pharmacol. 9:8182018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zheng X, Chen W, Gong F, Chen Y and Chen
E: The role and mechanism of pyroptosis and potential therapeutic
targets in sepsis: A review. Front Immunol. 12:7119392021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xue Z, Xi Q, Liu H, Guo X, Zhang J, Zhang
Z, Li Y, Yang G, Zhou D, Yang H, et al: miR-21 promotes NLRP3
inflammasome activation to mediate pyroptosis and endotoxic shock.
Cell Death Dis. 10:4612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei
J, Gu S, Gao F, Zhu N, Yin X, et al: Ferroptosis as a target for
protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:2672–2680. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li W, Li W, Leng Y, Xiong Y and Xia Z:
Ferroptosis is involved in diabetes myocardial Ischemia/reperfusion
injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress. DNA Cell Biol.
39:210–225. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Parzych KR and Klionsky DJ: An overview of
autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:460–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Liu AB, Li SJ, Yu YY, Zhang JF and Ma L:
Current insight on the mechanisms of programmed cell death in
sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Front Cell Dev Biol.
11:13097192023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Denk S, Perl M and Huber-Lang M: Damage-
and pathogen-associated molecular patterns and alarmins: Keys to
sepsis? Eur Surg Res. 48:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vénéreau E, Ceriotti C and Bianchi ME:
DAMPs from cell death to new life. Front Immunol. 6:4222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hobai IA, Morse JC, Siwik DA and Colucci
WS: Lipopolysaccharide and cytokines inhibit rat cardiomyocyte
contractility in vitro. J Surg Res. 193:888–901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang YY and Ning BT: Signaling pathways
and intervention therapies in sepsis. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
6:4072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fujimura K, Karasawa T, Komada T, Yamada
N, Mizushina Y, Baatarjav C, Matsumura T, Otsu K, Takeda N,
Mizukami H, et al: NLRP3 inflammasome-driven IL-1β and IL-18
contribute to lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiomyopathy. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 180:58–68. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Busch K, Kny M, Huang N, Klassert TE,
Stock M, Hahn A, Graeger S, Todiras M, Schmidt S, Chamling B, et
al: Inhibition of the NLRP3/IL-1β axis protects against
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.
12:1653–1668. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kumar V: Toll-like receptors in
sepsis-associated cytokine storm and their endogenous negative
regulators as future immunomodulatory targets. Int Immunopharmacol.
89:1070872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hoover DB, Ozment TR, Wondergem R, Li C
and Williams DL: Impaired heart rate regulation and depression of
cardiac chronotropic and dromotropic function in polymicrobial
sepsis. Shock. 43:185–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
49
|
Nolfi-Donegan D, Braganza A and Shiva S:
Mitochondrial electron transport chain: Oxidative phosphorylation,
oxidant production, and methods of measurement. Redox Biol.
37:1016742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen YR and Zweier JL: Cardiac
mitochondria and reactive oxygen species generation. Circ Res.
114:524–537. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sun F, Huo X, Zhai Y, Wang A, Xu J, Su D,
Bartlam M and Rao Z: Crystal structure of mitochondrial respiratory
membrane protein complex II. Cell. 121:1043–1057. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tsolaki V, Makris D, Mantzarlis K and
Zakynthinos E: Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: Oxidative
implications in the initiation and resolution of the damage. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2017:73935252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen YR, Chen CL, Yeh A, Liu X and Zweier
JL: Direct and indirect roles of cytochrome b in the mediation of
superoxide generation and NO catabolism by mitochondrial
succinate-cytochrome c reductase. J Biol Chem. 281:13159–13168.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Takasu O, Gaut JP, Watanabe E, To K,
Fagley RE, Sato B, Jarman S, Efimov IR, Janks DL, Srivastava A, et
al: Mechanisms of cardiac and renal dysfunction in patients dying
of sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 187:509–517. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Vanasco V, Saez T, Magnani ND, Pereyra L,
Marchini T, Corach A, Vaccaro MI, Corach D, Evelson P and Alvarez
S: Cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis in endotoxemia is not
accompanied by mitochondrial function recovery. Free Radic Biol
Med. 77:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Haileselassie B, Mukherjee R, Joshi AU,
Napier BA, Massis LM, Ostberg NP, Queliconi BB, Monack D, Bernstein
D and Mochly-Rosen D: Drp1/Fis1 interaction mediates mitochondrial
dysfunction in septic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
130:160–169. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wagner S, Schürmann S, Hein S, Schüttler J
and Friedrich O: Septic cardiomyopathy in rat LPS-induced
endotoxemia: Relative contribution of cellular diastolic Ca(2+)
removal pathways, myofibrillar biomechanics properties and action
of the cardiotonic drug levosimendan. Basic Res Cardiol.
110:5072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lin Y, Xu Y and Zhang Z: Sepsis-induced
myocardial dysfunction (SIMD): The pathophysiological mechanisms
and therapeutic strategies targeting mitochondria. Inflammation.
43:1184–1200. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ravikumar N, Sayed MA, Poonsuph CJ, Sehgal
R, Shirke MM and Harky A: Septic cardiomyopathy: From basics to
management choices. Curr Probl Cardiol. 46:1007672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cao T, Ni R, Ding W, Ji X, Fan GC, Zhang Z
and Peng T: Nicotinamide mononucleotide as a therapeutic agent to
alleviate multi-organ failure in sepsis. J Transl Med. 21:8832023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Furian T, Aguiar C, Prado K, Ribeiro RV,
Becker L, Martinelli N, Clausell N, Rohde LE and Biolo A:
Ventricular dysfunction and dilation in severe sepsis and septic
shock: Relation to endothelial function and mortality. J Crit Care.
27:319.e9–e15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Kacimi R, Karliner JS, Koudssi F and Long
CS: Expression and regulation of adhesion molecules in cardiac
cells by cytokines: Response to acute hypoxia. Circ Res.
82:576–586. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tang F, Zhao XL, Xu LY, Zhang JN, Ao H and
Peng C: Endothelial dysfunction: Pathophysiology and therapeutic
targets for sepsis-induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.
Biomed Pharmacother. 178:1171802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhan JH, Wei J, Liu YJ, Wang PX and Zhu
XY: Sepsis-associated endothelial glycocalyx damage: A review of
animal models, clinical evidence, and molecular mechanisms. Int J
Biol Macromol. 295:1395482025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Burg N, Malpass R, Alex L, Tran M,
Englebrecht E, Kuo A, Pannelini T, Minett M, Athukorala K and
Worgall T: Endothelial cell sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1
restrains VE-cadherin cleavage and attenuates experimental
inflammatory arthritis. JCI Insight. 9:e1714672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
de Oliveira J and Miranda CH: Doxycycline
protects against sepsis-induced endothelial glycocalyx shedding.
Sci Rep. 14:104772024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
van de Sandt AM, Windler R, Gödecke A,
Ohlig J, Zander S, Reinartz M, Graf J, van Faassen EE, Rassaf T,
Schrader J, et al: Endothelial NOS (NOS3) impairs myocardial
function in developing sepsis. Basic Res Cardiol. 108:3302013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zeng N, Xu J, Yao W, Li S, Ruan W and Xiao
F: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates septic myocardial
dysfunction via eNOS/NO pathway in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:17214342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hong G, Zheng D, Zhang L, Ni R, Wang G,
Fan GC, Lu Z and Peng T: Administration of nicotinamide riboside
prevents oxidative stress and organ injury in sepsis. Free Radic
Biol Med. 123:125–137. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Mirna M, Paar V, Rezar R, Topf A, Eber M,
Hoppe UC, Lichtenauer M and Jung C: MicroRNAs in inflammatory heart
diseases and Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: A potential scope
for the future? Cells. 8:13522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Gao M, Wang X, Zhang X, Ha T, Ma H, Liu L,
Kalbfleisch JH, Gao X, Kao RL, Williams DL and Li C: Attenuation of
cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis by MicroRNA-146a is
mediated via targeting of IRAK1 and TRAF6 expression. J Immunol.
195:672–682. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ma H, Wang X, Ha T, Gao M, Liu L, Wang R,
Yu K, Kalbfleisch JH, Kao RL, Williams DL and Li C: MicroRNA-125b
prevents cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis by targeting
TRAF6-Mediated nuclear factor κB activation and p53-Mediated
apoptotic signaling. J Infect Dis. 214:1773–1783. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yao Y, Sun F and Lei M: miR-25 inhibits
sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targetting PTEN. Biosci
Rep. 38:BSR201715112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li Z, Yi N, Chen R, Meng Y, Wang Y, Liu H,
Cao W, Hu Y, Gu Y, Tong C, et al: miR-29b-3p protects
cardiomyocytes against endotoxin-induced apoptosis and inflammatory
response through targeting FOXO3A. Cell Signal. 74:1097162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Long X, Huang Y, He J, Zhang X, Zhou Y,
Wei Y, Tang Y and Liu L: Upregulation of miR-335 exerts protective
effects against sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Mol Med Rep.
24:8062021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
76
|
Liang L, Liu S, Wu Q, Chen R, Jiang S and
Yang Z: m6A-mediated upregulation of miRNA-193a aggravates
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammatory response in sepsis-induced
cardiomyopathy via the METTL3/miRNA-193a/BCL2L2 pathway. Exp Cell
Res. 430:1137122023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
He Z, Xu L, Zeng X, Yang B, Liu P, Han D,
Xue H and Luo B: circROCK1 Promotes septic myocardial injury
through regulating miR-96-5p/OXSR1 axis. Acta Biochim Pol.
70:567–574. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wang H, Bei Y, Shen S, Huang P, Shi J,
Zhang J, Sun Q, Chen Y, Yang Y, Xu T, et al: miR-21-3p controls
sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 94:43–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ge C, Liu J and Dong S: miRNA-214 protects
Sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Shock. 50:112–118. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Li Y, Sun G and Wang L: MiR-21
participates in LPS-induced myocardial injury by targeting Bcl-2
and CDK6. Inflamm Res. 71:205–214. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhu XG, Zhang TN, Wen R and Liu CF:
Overexpression of miR-150-5p alleviates apoptosis in Sepsis-induced
myocardial depression. Biomed Res Int. 2020:30231862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang L, Li B, Li W, Jiang J, Chen W, Yang
H and Pan D: miR-107 attenuates Sepsis-induced myocardial injury by
targeting PTEN and activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cells
Tissues Organs. 212:523–534. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Sun F, Yuan W, Wu H, Chen G, Sun Y, Yuan
L, Zhang W and Lei M: LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 attenuates sepsis-induced
myocardial injury via regulating miR-192-5p/XIAP axis. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 245:620–630. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chen DD, Wang HW and Cai XJ: Long
non-coding RNA ZFAS1 alleviates sepsis-induced myocardial injury
via target miR-34b-5p/SIRT1. Innate Immun. 27:377–387. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Xu LJ, Yang Y, Yuan LF, Liu H, Xu NP, Yang
Y and Huang L: SP1-stimulated miR-208a-5p aggravates sepsis-induced
myocardial injury via targeting XIAP. Exp Cell Res. 435:1139052024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li Y, Shao Y, Su J and Dong S: MiR-383-3p
attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial ferroptosis by targeting ATF4
and inhibiting the ATF4-CHOP-CHAC1 signaling axis. Cell Signal.
136:1121692025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang J, Wei T, Zhang W, Chu Y, Zhang D,
Zhang M, Hu J, Ji Z and Hao Q: Inhibition of miR-194-5p avoids
DUSP9 downregulation thus limiting sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.
Sci Rep. 14:203132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Liang D, Jin Y, Lin M, Xia X, Chen X and
Huang A: Down-regulation of Xist and Mir-7a-5p improves LPS-induced
myocardial injury. Int J Med Sci. 17:2570–2577. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Gong M, Tao L and Li X:
MicroRNA-21-3p/Rcan1 signaling axis affects apoptosis of
cardiomyocytes of sepsis rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. 42:217–227.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Dao L, Liu H, Xiu R, Yao T, Tong R and Xu
L: Gramine improves sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by
binding to NF-κB p105 and inhibiting its ubiquitination.
Phytomedicine. 125:1553252024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Chen D, Wang H and Cai X: Curcumin
interferes with sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via TLR1
inhibition. Rev Port Cardiol. 42:209–221. 2023.In English,
Portuguese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang J, Zhu D, Wang Y and Ju Y:
Andrographolide attenuates LPS-induced cardiac malfunctions through
Inhibition of IκB phosphorylation and apoptosis in mice. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:1619–1628. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Wang YY, Li HM, Wang HD, Peng XM, Wang YP,
Lu DX, Qi RB, Hu CF and Jiang JW: Pretreatment with berberine and
yohimbine protects against LPS-induced myocardial dysfunction via
inhibition of cardiac I-[kappa]B[alpha] phosphorylation and
apoptosis in mice. Shock. 35:322–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Meng YY, Liu Y, Hu ZF, Zhang Y, Ni J, Ma
ZG, Liao HH, Wu QQ and Tang QZ: Sanguinarine attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis by inhibiting
the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Curr Med Sci.
38:204–211. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhong L, Zhou XL, Liu YS, Wang YM, Ma F,
Guo BL, Yan ZQ and Zhang QY: Estrogen receptor α mediates the
effects of notoginsenoside R1 on endotoxin-induced inflammatory and
apoptotic responses in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep.
12:119–126. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Sun B, Xiao J, Sun XB and Wu Y:
Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates cardiac dysfunction in endotoxemic
mice: An insight into oestrogen receptor activation and PI3K/Akt
signalling. Br J Pharmacol. 168:1758–1770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
97
|
Zhu H, Zhang L, Jia H, Xu L, Cao Y, Zhai
M, Li K, Xia L, Jiang L, Li X, et al: Tetrahydrocurcumin improves
lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial dysfunction by inhibiting
oxidative stress and inflammation via JNK/ERK signaling pathway
regulation. Phytomedicine. 104:1542832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Xie WJ, Hou G, Wang L, Wang SS and Xiong
XX: Astaxanthin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial
injury by regulating MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR/GSK3β signaling. Mol
Med Rep. 22:3338–3346. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Jiang L, Zhang L, Yang J, Shi H, Zhu H,
Zhai M, Lu L, Wang X, Li XY, Yu S, et al: 1-Deoxynojirimycin
attenuates septic cardiomyopathy by regulating oxidative stress,
apoptosis, and inflammation via the JAK2/STAT6 signaling pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 155:1136482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Su Y, Yin X, Huang X, Guo Q, Ma M and Guo
L: Astragaloside IV ameliorates sepsis-induced myocardial
dysfunction by regulating NOX4/JNK/BAX pathway. Life Sci.
310:1211232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhang T, Yan T, Du J, Wang S and Yang H:
Apigenin attenuates heart injury in lipopolysaccharide-induced
endotoxemic model by suppressing sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine
1-phosphate signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 233:46–55. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yu H, Du Q, Wu J, Feng F, Hou S, Liu M,
Wang S, Liu X, Wang C and Xu K: Gastrodin regulates H3K14la through
the CDT2-KAT2A axis to treat sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.
Int Immunopharmacol. 161:1150652025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wang RY, Wang MG, Tang HZ, Du H, Luo Y, Li
Q, Zhang XH, Fu J and Lv CZ: The protective effects of ruscogenin
against Lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury in septic
mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 84:175–187. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhu XX, Meng XY, Zhang AY, Zhao CY, Chang
C, Chen TX, Huang YB, Xu JP, Fu X, Cai WW, et al: Vaccarin
alleviates septic cardiomyopathy by potentiating NLRP3
palmitoylation and inactivation. Phytomedicine. 131:1557712024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Long H, Xu B, Luo Y and Luo K: Artemisinin
protects mice against burn sepsis through inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome activation. Am J Emerg Med. 34:772–777. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Liu H, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Yang G, Guo L, Zhao
Y and Pei Z: Role of thymoquinone in cardiac damage caused by
sepsis from BALB/c mice. Inflammation. 42:516–525. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Wei A, Liu J, Li D, Lu Y, Yang L, Zhuo Y,
Tian W and Cong H: Syringaresinol attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac
dysfunction by inhibiting inflammation and pyroptosis in mice. Eur
J Pharmacol. 913:1746442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Luo M, Yan D, Sun Q, Tao J, Xu L, Sun H
and Zhao H: Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and
inflammation via the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. J Cell Biochem.
121:2994–3004. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Shao F, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Chen H, Zhang Y
and Guan Z: Gastrodin alleviates inflammatory injury of
cardiomyocytes in septic shock mice via inhibiting NLRP3
expression. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 57:571–581. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Khodir AE, Samra YA and Said E: A novel
role of nifuroxazide in attenuation of sepsis-associated acute lung
and myocardial injuries; role of TLR4/NLPR3/IL-1β signaling
interruption. Life Sci. 256:1179072020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Song P, Shen DF, Meng YY, Kong CY, Zhang
X, Yuan YP, Yan L, Tang QZ and Ma ZG: Geniposide protects against
sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction through AMPKα-dependent
pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 152:186–196. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Dai S, Ye B, Chen L, Hong G, Zhao G and Lu
Z: Emodin alleviates LPS-induced myocardial injury through
inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Phytother Res.
35:5203–5213. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Du R, Yun Q, Wang Y, Dou X, Ye H, Wang J
and Gao Q: Plumbagin protect against sepsis-induced myocardial
injury in mice by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway to
reduce cardiomyocyte pyroptosis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
44:2209–2219. 2024.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Joshi S, Kundu S, Priya VV, Kulhari U,
Mugale MN and Sahu BD: Anti-inflammatory activity of carvacrol
protects the heart from lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac
dysfunction by inhibiting pyroptosis via NLRP3/Caspase1/Gasdermin D
signaling axis. Life Sci. 324:1217432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang Y, Feng W, Li S, Liu C, Jia L, Wang
P, Li L, Du H and Yu W: Oxycodone attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting
inflammation, oxidation and pyroptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 signalling
pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 51:e139102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wu B, Song H, Fan M, You F, Zhang L, Luo
J, Li J, Wang L, Li C and Yuan M: Luteolin attenuates
sepsis-induced myocardial injury by enhancing autophagy in mice.
Int J Mol Med. 45:1477–1487. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Shiroorkar PN, Afzal O, Kazmi I, Al-Abbasi
FA, Altamimi ASA, Gubbiyappa KS and Sreeharsha N: Cardioprotective
effect of tangeretin by inhibiting PTEN/AKT/mTOR axis in
experimental Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Molecules.
25:56222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Cardenas H, Arango D, Nicholas C, Duarte
S, Nuovo GJ, He W, Voss OH, Gonzalez-Mejia ME, Guttridge DC,
Grotewold E and Doseff AI: Dietary apigenin exerts
Immune-regulatory activity in vivo by reducing NF-κB activity,
halting leukocyte infiltration and restoring normal metabolic
function. Int J Mol Sci. 17:3232016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Li F, Lang F, Zhang H, Xu L, Wang Y, Zhai
C and Hao E: Apigenin alleviates Endotoxin-induced myocardial
toxicity by modulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and
autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:23028962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Chang X, He Y, Wang L, Luo C, Liu Y and Li
R: Puerarin alleviates LPS-induced H9C2 cell injury by inducing
mitochondrial autophagy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 80:600–608. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Tang R, Jia L, Li Y, Zheng J and Qi P:
Narciclasine attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by
modulating autophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 13:15151–15163. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Yuan X, Chen G, Guo D, Xu L and Gu Y:
Polydatin alleviates septic myocardial injury by promoting
SIRT6-mediated autophagy. Inflammation. 43:785–795. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Yu YW, Chen X, Yan JY, Hu J, Huang KY, Ji
KT and Cai HL: Phlorizin, a novel caloric restriction mimetic,
stimulates hypoxia and protects cardiomyocytes through activating
autophagy via modulating the Hif-1α/Bnip3 axis in sepsis-induced
myocardial dysfunction. Int Immunopharmacol. 126:1112412024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Zhou B, Zhang J, Chen Y, Liu Y, Tang X,
Xia P, Yu P and Yu S: Puerarin protects against sepsis-induced
myocardial injury through AMPK-mediated ferroptosis signaling.
Aging (Albany NY). 14:3617–3632. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Lin X, Zhao X, Chen Q, Wang X, Wu Y and
Zhao H: Quercetin ameliorates ferroptosis of rat cardiomyocytes via
activation of the SIRT1/p53/SLC7A11 signaling pathway to alleviate
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Med. 52:1162023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
126
|
Xiao Y, Yu Y, Hu L, Yang Y, Yuan Y, Zhang
W, Luo J and Yu L: Matrine alleviates Sepsis-induced myocardial
injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and apoptosis. Inflammation.
46:1684–1696. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Lin LQ, Mao FK, Lin J, Guo L, Yuan WR and
Wang BY: Ginsenoside Rg1 induces ferroptosis by regulating the
focal adhesion kinase/protein kinase B-forkhead box O3A signaling
pathway and alleviates sepsis-induced myocardial damage. J Physiol
Pharmacol. 75:2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Wang X, Simayi A, Fu J, Zhao X and Xu G:
Resveratrol mediates the miR-149/HMGB1 axis and regulates the
ferroptosis pathway to protect myocardium in endotoxemia mice. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 323:e21–e32. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Tang R, Jiang M, Tang X, Chen S, Xu H, Pan
Y, Lin B, Wei X, Ye Q, Wu M and Qi P: Narciclasine mitigates
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by enhancing BNIP3-mediated
mitophagy and suppressing ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
238:220–234. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zeng Y, Cao G, Lin L, Zhang Y, Luo X, Ma
X, Aiyisake A and Cheng Q: Resveratrol attenuates Sepsis-induced
cardiomyopathy in rats through Anti-Ferroptosis via the Sirt1/Nrf2
pathway. J Invest Surg. 36:21575212023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Ye H, Wu L, Liu YM, Zhang JX, Hu HT, Dong
ML and Ren J: Wogonin attenuates septic cardiomyopathy by
suppressing ALOX15-mediated ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
46:2407–2422. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Guan F, Du H, Li J, Ren H and Dong A:
Quercetin alleviates LPS-stimulated myocardial injury through
regulating ALOX5/PI3K/AKT pathway in sepsis. Cardiovasc Toxicol.
24:1116–1124. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Huang SH, Xu M, Wu HM, Wan CX, Wang HB, Wu
QQ, Liao HH, Deng W and Tang QZ: Isoquercitrin attenuated cardiac
dysfunction via AMPKα-Dependent pathways in LPS-Treated mice. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 62:e18009552018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Wei X, Meng X, Yuan Y, Shen F, Li C and
Yang J: Quercetin exerts cardiovascular protective effects in
LPS-induced dysfunction in vivo by regulating inflammatory cytokine
expression, NF-κB phosphorylation, and caspase activity. Mol Cell
Biochem. 446:43–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Zhou Q, Zeng X, Kang W, Pan X, Wang L and
Xia Z: Ciprofol attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy via α7
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-dependent modulation of myocardial
inflammation and NF-κB/STAT3 signaling. Eur J Pharmacol.
1003:1779832025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Huang X, Zhang MZ, Liu B, Ma SY, Yin X and
Guo LH: Astragaloside IV Attenuates polymicrobial Sepsis-induced
cardiac dysfunction in rats via IKK/NF-κB pathway. Chin J Integr
Med. 27:825–831. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Chen S and Fan B: Myricetin protects
cardiomyocytes from LPS-induced injury. Herz. 43:265–274. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Zhang N, Feng H, Liao HH, Chen S, Yang Z,
Deng W and Tang QZ: Myricetin attenuated LPS induced cardiac injury
in vivo and in vitro. Phytother Res. 32:459–470. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Xianchu L, Lan PZ, Qiufang L, Yi L,
Xiangcheng R, Wenqi H and Yang D: Naringin protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac injury in mice. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 48:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Sun LJ, Qiao W, Xiao YJ, Cui L, Wang X and
Ren WD: Naringin mitigates myocardial strain and the inflammatory
response in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction through
regulation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
75:1057822019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Fang Z, Wang G, Huang R, Liu C,
Yushanjiang F, Mao T and Li J: Astilbin protects from
sepsis-induced cardiac injury through the NRF2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-κB
pathway. Phytother Res. 38:1044–1058. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Su Z, Gao M, Weng L and Xu T: Esculin
targets TLR4 to protect against LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy.
Int Immunopharmacol. 131:1118972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Shaojun Z, Yanyan X, Jian C, Xia Z, Qiang
F and Saiping J: Effects of puerarin on lipopolysaccharide-induced
myocardial dysfunction in isolated rat hearts. Pak J Pharm Sci.
30:1195–1202. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Xing C, Xu L and Yao Y: Beneficial role of
oleuropein in sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Possible
Involvement of GSK-3β/NF-κB pathway. Acta Cir Bras. 36:e3601072021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Shyni GL, Renjitha J, B Somappa S and
Raghu KG: Zerumin A attenuates the inflammatory responses in
LPS-stimulated H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
35:1–11. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Yan C, Kuang W, Jin L, Wang R, Niu L, Xie
C, Ding J, Liao Y, Wang L, Wan H and Ma G: Carvacrol protects mice
against LPS-induced sepsis and attenuates inflammatory response in
macrophages by modulating the ERK1/2 pathway. Sci Rep.
13:128092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Tang J, Hu JJ, Lu CH, Liang JN, Xiao JF,
Liu YT, Lin CS and Qin ZS: Propofol inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression
and myocardial depression through decreasing the generation of
superoxide anion in cardiomyocytes. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2014:1573762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Li C, Wan W, Ye T, Sun Y, Chen X, Liu X,
Shi S, Zhang Y, Qu C, Yang B, et al: Pinocembrin alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury and cardiac
dysfunction in rats by inhibiting p38/JNK MAPK pathway. Life Sci.
277:1194182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Cao W, Li XQ, Zhang XN, Hou Y, Zeng AG,
Xie YH and Wang SW: Madecassoside suppresses LPS-induced TNF-alpha
production in cardiomyocytes through inhibition of ERK, p38, and
NF-kappaB activity. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:723–729. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Wang B, Chen L, Dai L, Fang W and Wang H:
Alisol B 23-Acetate ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac
dysfunction by suppressing Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/NADPH
Oxidase 2 (NOX2) signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:8472–8481.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Zhang M, Wang X, Wang X, Hou X, Teng P,
Jiang Y, Zhang L, Yang X, Tian J, Li G, et al: Oxymatrine protects
against myocardial injury via inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling in
rat septic shock. Mol Med Rep. 7:1293–1299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Zhang M, Wang X, Bai B, Zhang R, Li Y and
Wang Y: Oxymatrine protects against sepsis-induced myocardial
injury via inhibition of the TNF-α/p38-MAPK/caspase-3 signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 14:551–559. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Zhao P, Wang Y, Zeng S, Lu J, Jiang TM and
Li YM: Protective effect of astragaloside IV on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction via downregulation
of inflammatory signaling in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
37:428–433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Zhai J and Guo Y: Paeoniflorin attenuates
cardiac dysfunction in endotoxemic mice via the inhibition of
nuclear factor-κB. Biomed Pharmacother. 80:200–206. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Shang X, Lin K, Yu R, Zhu P, Zhang Y, Wang
L, Xu J and Chen K: Resveratrol protects the myocardium in sepsis
by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases
(PI3K)/AKT/Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway and
inhibiting the nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Med Sci
Monit. 25:9290–9298. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Lee AS, Chen WP, Kuo YL, Ho YJ, Lee SS and
Su MJ: Thaliporphine preserves cardiac function of endotoxemic
rabbits by both directly and indirectly attenuating NFκB signaling
pathway. PLoS One. 7:e391742012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
He H, Chang X, Gao J, Zhu L, Miao M and
Yan T: Salidroside mitigates Sepsis-Induced myocarditis in rats by
regulating IGF-1/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling. Inflammation.
38:2178–2184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Li C, Hou D, Huang Y, Liu Y, Li Y and Wang
C: Corylin alleviated sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via
attenuating inflammation through downregulation of microRNA-214-5p.
Toxicol Res (Camb). 13:tfae0812024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Zhang J, Liu Y and Liu L: Hyperoside
prevents sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction through regulating
cardiomyocyte viability and inflammation via inhibiting miR-21.
Biomed Pharmacother. 138:1115242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Liu Y, Liu L and Zhang J: Protective role
of matrine in sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction through
regulating the lncRNA PTENP1/miR-106b-5p axis. Biomed Pharmacother.
134:1111122021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Zhao H, Wang Y and Zhu X: Chrysophanol
exerts a protective effect against sepsis-induced acute myocardial
injury through modulating the microRNA-27b-3p/Peroxisomal
proliferating-activated receptor gamma axis. Bioengineered.
13:12673–12690. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Athapaththu A, Lee KT, Kavinda MHD, Lee S,
Kang S, Lee MH, Kang CH, Choi YH and Kim GY: Pinostrobin
ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation and
endotoxemia by inhibiting LPS binding to the TLR4/MD2 complex.
Biomed Pharmacother. 156:1138742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Feng J, Liu Z, Chen H, Zhang M, Ma X, Han
Q, Lu D and Wang C: Protective effect of cynaroside on
sepsis-induced multiple organ injury through Nrf2/HO-1-dependent
macrophage polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 911:1745222021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Jinzhong Wang MS and Jian Fu MS:
STAT3/FoxO3a/Sirt1 pathway inhibition by ginsenoside Rc ameliorates
cardiomyocyte damage in septic cardiomyopathy by altering
macrophage polarization. J Mol Histol. 56:1482025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Li F, Lang F, Wang Y, Zhai C, Zhang C,
Zhang L and Hao E: Cyanidin ameliorates endotoxin-induced
myocardial toxicity by modulating inflammation and oxidative stress
through mitochondria and other factors. Food Chem Toxicol.
120:104–111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Chen HM, Liou SF, Hsu JH, Chen TJ, Cheng
TL, Chiu CC and Yeh JL: Baicalein inhibits HMGB1 release and
MMP-2/-9 expression in lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac
hypertrophy. Am J Chin Med. 42:785–797. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Wu W, Wang J, Wang G, Wang F, Yang Y, Liu
Z, Song Q, Chen S and Chen H: Monotropein inhibits MMP9-mediated
cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation, matrix degradation and
apoptosis in a mouse and cell line models of septic cardiac injury.
Mol Biol Rep. 52:3292025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Cao W, Zhang W, Liu J, Wang Y, Peng X, Lu
D, Qi R, Wang Y and Wang H: Paeoniflorin improves survival in
LPS-challenged mice through the suppression of TNF-α and IL-1β
release and augmentation of IL-10 production. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:172–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Liu A, Xun S, Zhou G, Zhang Y and Lin L:
Honokiol alleviates sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via
attenuating inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 75:397–406. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Tang X, Xu Y, Dai X, Xing Y, Yang D, Huang
Q, Li H, Lv X, Wang Y, Lu D and Wang H: The Long-term effect of
dobutamine on intrinsic myocardial function and myocardial injury
in septic rats with myocardial dysfunction. Shock. 56:582–592.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Tsai YC, Cheng PY, Kung CW, Peng YJ, Ke
TH, Wang JJ and Yen MH: Beneficial effects of magnolol in a rodent
model of endotoxin shock. Eur J Pharmacol. 641:67–73. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Meng ZJ, Wang C, Meng LT, Bao BH, Wu JH
and Hu YQ: Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate attenuates cardiac
dysfunction and improves survival of rats with cecal ligation and
puncture-induced sepsis. Chin J Nat Med. 16:846–855.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Dörtbudak MB, Demircioğlu M and Kapucuk
FS: Micromeria congesta alleviates LPS-Induced inflammation,
apoptosis, oxidative stress and DNA damage in rat heart and
kidneys. Vet Med Sci. 11:e702642025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Pan J, Meng L, Li R, Wang Z, Yuan W, Li Y,
Chen L, Shen Q, Liu W and Zhu L: Naringenin protects against septic
cardiomyopathy in mice by targeting HIF-1α. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 704:1496132024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Cheng Z, Lv D, Luo M, Wang R, Guo Y, Yang
X, Huang L, Li X, Li C, Shang FF, et al: Tubeimoside I protects
against sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via SIRT3. Eur J
Pharmacol. 905:1741862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Wang Y, Yu X, Wang F, Wang Y, Wang Y, Li
H, Lv X, Lu D and Wang H: Yohimbine promotes cardiac NE release and
prevents LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction via blockade of
presynaptic α2A-adrenergic receptor. PLoS One. 8:e636222013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Duzen IV, Oguz E, Yilmaz R, Taskin A,
Vuruskan E, Cekici Y, Bilgel ZG, Goksuluk H, Candemir B and Sucu M:
Lycopene has a protective effect on septic shock-induced cardiac
injury in rats. Bratisl Lek Listy. 120:919–923. 2019.
|
|
178
|
Ben-Shaul V, Lomnitski L, Nyska A,
Zurovsky Y, Bergman M and Grossman S: The effect of natural
antioxidants, NAO and apocynin, on oxidative stress in the rat
heart following LPS challenge. Toxicol Lett. 123:1–10. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Li X, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Yin Y, Yuan X, You
X and Wu J: Echinacoside prevents Sepsis-induced myocardial damage
via targeting SOD2. J Med Food. 27:123–133. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Xianchu L, Lan Z, Ming L and Yanzhi M:
Protective effects of rutin on lipopolysaccharide-induced heart
injury in mice. J Toxicol Sci. 43:329–337. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Yang C, Wu K, Li SH and You Q: Protective
effect of curcumin against cardiac dysfunction in sepsis rats.
Pharm Biol. 51:482–487. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Sompamit K, Kukongviriyapan U, Nakmareong
S, Pannangpetch P and Kukongviriyapan V: Curcumin improves vascular
function and alleviates oxidative stress in non-lethal
lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxaemia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
616:192–199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Kukongviriyapan U, Sompamit K,
Pannangpetch P, Kukongviriyapan V and Donpunha W: Preventive and
therapeutic effects of quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced
oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction in mice. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 90:1345–1353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Hao E, Lang F, Chen Y, Zhang H, Cong X,
Shen X and Su G: Resveratrol alleviates endotoxin-induced
myocardial toxicity via the Nrf2 transcription factor. PLoS One.
8:e694522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Xingyue L, Shuang L, Qiang W, Jinjuan F
and Yongjian Y: Chrysin ameliorates Sepsis-induced cardiac
dysfunction through upregulating Nfr2/Heme oxygenase 1 pathway. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 77:491–500. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Tan Y, Wan HH, Sun MM, Zhang WJ, Dong M,
Ge W, Ren J and Peng H: Cardamonin protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction in
mice through Nrf2-regulated mechanism. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
42:404–413. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
187
|
Li Y, Zhang L, Zhang P and Hao Z:
Dehydrocorydaline protects against Sepsis-induced myocardial injury
through modulating the TRAF6/NF-κB pathway. Front Pharmacol.
12:7096042021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Lee YM, Cheng PY, Chim LS, Kung CW, Ka SM,
Chung MT and Sheu JR: Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria
baicalensis Georgi, improves cardiac contractile function in
endotoxaemic rats via induction of heme oxygenase-1 and suppression
of inflammatory responses. J Ethnopharmacol. 135:179–185. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Cheng PY, Lee YM, Wu YS, Chang TW, Jin JS
and Yen MH: Protective effect of baicalein against endotoxic shock
in rats in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 73:793–804. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Chen WP, Tzeng HJ, Ku HC, Ho YJ, Lee SS
and Su MJ: Thaliporphine ameliorates cardiac depression in
endotoxemic rats through attenuating TLR4 signaling in the
downstream of TAK-1 phosphorylation and NF-κB signaling. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 382:441–453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Chen RC, Wang J, Yang L, Sun GB and Sun
XB: Protective effects of ginsenoside Re on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction in mice. Food Funct.
7:2278–2287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Chen L, Liu P, Feng X and Ma C:
Salidroside suppressing LPS-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting
ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol
Med. 21:3178–3189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Xie L, Zhao M, Zong L and Yue Y: Propofol
ameliorates Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction via
Anti-Apoptotic, Anti-Oxidative properties, and mTOR signaling.
Discov Med. 36:2088–2097. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Wang L, Zhao Y, Su Z, Zhao K, Li P and Xu
T: Ginkgolide A targets forkhead box O1 to protect against
lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiomyopathy. Phytother Res.
37:3309–3322. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Huang L, Zheng M, Zhou Y, Zhu J, Zhu M,
Zhao F and Cui S: Tanshinone IIA attenuates cardiac dysfunction in
endotoxin-induced septic mice via inhibition of NADPH oxidase
2-related signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:444–449. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Hou D, Liao H, Hao S, Liu R, Huang H and
Duan C: Curcumin simultaneously improves mitochondrial dynamics and
myocardial cell bioenergy after sepsis via the SIRT1-DRP1/PGC-1α
pathway. Heliyon. 10:e285012024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Smeding L, Leong-Poi H, Hu P, Shan Y,
Haitsma JJ, Horvath E, Furmli S, Masoom H, Kuiper JW, Slutsky AS,
et al: Salutary effect of resveratrol on sepsis-induced myocardial
depression. Crit Care Med. 40:1896–1907. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Peng K, Yang F, Qiu C, Yang Y and Lan C:
Rosmarinic acid protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac
dysfunction via activating Sirt1/PGC-1α pathway to alleviate
mitochondrial impairment. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 50:218–227.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Li Y, Feng YF, Liu XT, Li YC, Zhu HM, Sun
MR, Li P, Liu B and Yang H: Songorine promotes cardiac
mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2 induction during sepsis. Redox
Biol. 38:1017712021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Yang Z, Liu Y, Deng W, Dai J, Li F, Yuan
Y, Wu Q, Zhou H, Bian Z and Tang Q: Hesperetin attenuates
mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced H9C2
cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep. 9:1941–1946. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Yang YP, Zhao JQ, Gao HB, Li JJ, Li XL,
Niu XL, Lei YH and Li X: Tannic acid alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced H9C2 cell apoptosis by suppressing
reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol
Med Rep. 24:5352021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
202
|
Xie WJ, Liu M, Zhang X, Zhang YG, Jian ZH
and Xiong XX: Astaxanthin suppresses LPS-induced myocardial
apoptosis by regulating PTP1B/JNK pathway in vitro. Int
Immunopharmacol. 127:1113952024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Ye G, Wang M, Liu D, Cheng L, Yin X, Zhang
Q and Liu W: Mechanism of naringenin blocking the protection of
LTB4/BLT1 receptor against septic cardiac dysfunction. Ann Clin Lab
Sci. 50:769–774. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Zhao H, Chen Y, Qian L, Du L, Wu X, Tian
Y, Deng C, Liu S, Yang W, Lu C, et al: Lycorine protects against
septic myocardial injury by activating AMPK-related pathways. Free
Radic Biol Med. 197:1–14. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Miao H, Tang X, Cui Y, Shi J, Xiong X,
Wang C and Zhang Y: Obeticholic acid inhibit mitochondria
dysfunction via regulating ERK1/2-DRP pathway to exert protective
effect on lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury. Adv Biol
(Weinh). 8:e23005762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Qi Z, Wang R, Liao R, Xue S and Wang Y:
Neferine ameliorates Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction through
Anti-apoptotic and antioxidative effects by regulating the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12:7062512021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Liu Z, Pan H, Zhang Y, Zheng Z, Xiao W,
Hong X, Chen F, Peng X, Pei Y, Rong J, et al: Ginsenoside-Rg1
attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by modulating
mitochondrial damage via the P2X7 receptor-mediated Akt/GSK-3β
signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 36:e228852022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Zhu X, Sun M, Guo H, Lu G, Gu J, Zhang L,
Shi L, Gao J, Zhang D, Wang W, et al: Verbascoside protects from
LPS-induced septic cardiomyopathy via alleviating cardiac
inflammation, oxidative stress and regulating mitochondrial
dynamics. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 233:1133272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Lu C, Lei W, Sun M, Wu X, Liu Q, Liu J,
Yang Y, Yang W, Zhang Z, Li X, et al: Identification of CCR2 as a
hub in septic myocardial injury and cardioprotection of silibinin.
Free Radic Biol Med. 197:46–57. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Sun M, Zhao H, Jin Z, Lei W, Deng C, Yang
W, Lu C, Hou Y, Zhang Y, Tang R, et al: Silibinin protects against
sepsis and septic myocardial injury in an NR1H3-dependent pathway.
Free Radic Biol Med. 187:141–157. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Sun HJ, Zheng GL, Wang ZC, Liu Y, Bao N,
Xiao PX, Lu QB and Zhang JR: Chicoric acid ameliorates
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy via regulating macrophage metabolism
reprogramming. Phytomedicine. 123:1551752024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
212
|
Chen M, Huang S, Weng S, Weng J, Guo R,
Shi B and Liu D: Songorine ameliorates LPS-induced sepsis
cardiomyopathy by Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway-mediated
mitochondrial biosynthesis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
397:4713–4725. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
213
|
Hwang HR, Tai BY, Cheng PY, Chen PN, Sung
PJ, Wen ZH and Hsu CH: Excavatolide B modulates the
electrophysiological characteristics and calcium homeostasis of
atrial myocytes. Mar Drugs. 15:252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Chen R, Zheng A, Wang Y, Guo L, Dou H, Lu
L, Rafiq M, Li P, Chen X and Xiao Q: Salvianolic acid B improves
mitochondrial dysfunction of septic cardiomyopathy via enhancing
ATF5-mediated mitochondrial unfolded protein response. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 491:1170722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Nong Y, Lu J, Yu D and Wei X:
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-induced
vascular endothelium dysfunction by regulating antioxidant
capacity. Immun Inflamm Dis. 12:e701072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Tang F, Liu D, Wan F, Zhang L, Xu LY,
Zhang JN, Zhao XL, Ao H and Peng C: Ameliorative effect of
anisodamine (654-1/654-2) against myocardial dysfunction induced by
septic shock via the NF-κB/NLRP-3 or the PI3K-AKT/NF-κB pathway.
Phytomedicine. 123:1552772024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
217
|
Chiorcea-Paquim AM: Electrochemistry of
flavonoids: A comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 24:156672023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Billowria K, Ali R, Rangra NK, Kumar R and
Chawla PA: Bioactive flavonoids: A comprehensive review on
pharmacokinetics and analytical aspects. Crit Rev Anal Chem.
54:1002–1016. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
219
|
Jomova K, Alomar SY, Valko R, Liska J,
Nepovimova E, Kuca K and Valko M: Flavonoids and their role in
oxidative stress, inflammation, and human diseases. Chem Biol
Interact. 413:1114892025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Patel S: Plant-derived cardiac glycosides:
Role in heart ailments and cancer management. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:1036–1041. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
de Araújo FF, de Paulo Farias D, Neri-Numa
IA and Pastore GM: Polyphenols and their applications: An approach
in food chemistry and innovation potential. Food Chem.
338:1275352021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Cinelli MA and Jones AD: Alkaloids of the
genus datura: Review of a rich resource for natural product
discovery. Molecules. 26:26292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Jolly A, Hour Y and Lee YC: An outlook on
the versatility of plant saponins: A review. Fitoterapia.
174:1058582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Huang S, Liu D, Sun J, Zhang H, Zhang J,
Wang Q, Gan L, Qu G, Qiu J, Deng J, et al: Tim-3 regulates
sepsis-induced immunosuppression by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling
pathway in CD4 T cells. Mol Ther. 30:1227–1238. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Chen XS, Wang SH, Liu CY, Gao YL, Meng XL,
Wei W, Shou ST, Liu YC and Chai YF: Losartan attenuates
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by regulating macrophage polarization
via TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Pharmacol Res.
185:1064732022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
226
|
Yang Q, Wang Y, Cao G, Li X and Zhao T:
Anti-sepsis effect of Xiaochaihu decoction based on the
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway. Heliyon. 10:e267122024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
227
|
Huang L, Li Y, Cheng Z, Lv Z, Luo S and
Xia Y: PCSK9 promotes endothelial dysfunction during sepsis via the
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and NLRP3 Pathways. Inflammation. 46:115–128.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
228
|
Wu Y, Wang Q, Li M, Lao J, Tang H, Ming S,
Wu M, Gong S, Li L, Liu L and Huang X: SLAMF7 regulates the
inflammatory response in macrophages during polymicrobial sepsis. J
Clin Invest. 133:e1502242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Al-Kadi A, Anter AF, Rofaeil RR,
Sayed-Ahmed MM, Hafez S and Ahmed AF: Endothelin system blockade
extenuates Sepsis-induced acute heart and kidney injuries via
modulating ET-1/Klotho/p38-MAPK. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
52:e700422025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Wang Y, Yu W, Shi C and Hu P: Crocetin
attenuates Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via regulation of
inflammatory response and mitochondrial function. Front Physiol.
11:5142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Li J, Wang L, Wang B, Zhang Z, Jiang L,
Qin Z, Zhao Y and Su B: NOX4 is a potential therapeutic target in
septic acute kidney injury by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction
and inflammation. Theranostics. 13:2863–2878. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Pan T, Sun S, Chen Y, Tian R, Chen E, Tan
R, Wang X, Liu Z, Liu J and Qu H: Immune effects of
PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α-regulated glycolysis in polymorphonuclear
neutrophils during sepsis. Crit Care. 26:292022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Ma L, Zhang R, Li D, Qiao T and Guo X:
Fluoride regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy via
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact.
349:1096592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Lee J, Kim J, Lee JH, Choi YM, Choi H, Cho
HD, Cha GH, Lee YH, Jo EK, Park BH and Yuk JM: SIRT1 promotes host
protective immunity against toxoplasma gondii by controlling the
FoxO-autophagy axis via the AMPK and PI3K/AKT signalling pathways.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:135782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Yin Z, Tian L, Kou W, Cao G, Wang L, Xia
Y, Lin Y, Tang S, Zhang J and Yang H: Xiyangshen Sanqi Danshen
granules attenuated D-gal-induced C57BL/6J mouse aging through the
AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 136:1562132025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
236
|
Chen Y, Chen J, Xing Z, Peng C and Li D:
Autophagy in neuroinflammation: A focus on epigenetic regulation.
Aging Dis. 15:739–754. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
237
|
Lu SM, Yang B, Tan ZB, Wang HJ, Xie JD,
Xie MT, Jiang WH, Huang JZ, Li J, Zhang L, et al: TaoHe ChengQi
decoction ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through
anti-ferroptosis via the Nrf2 pathway. Phytomedicine.
129:1555972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Tang F, Yan YM, Yan HL, Wang LX, Hu CJ,
Wang HL, Ao H, Peng C and Tan YZ: Chuanxiongdiolides R4 and R5,
phthalide dimers with a complex polycyclic skeleton from the aerial
parts of Ligusticum chuanxiong and their vasodilator activity.
Bioorg Chem. 107:1045232021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
239
|
Zhang T, Lu M, Yang Y, Ji X, Gu H, Sun Y,
Chen C and Sun T: Cold-adapted nanozymes. Adv Healthc Mater.
14:e25012112025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Li S, Wang F, Hao L, Zhang P, Song G,
Zhang Y, Wang C, Wang Z and Wu Q: Enhancing peroxidase activity of
NiCo2O4 nanoenzyme by Mn doping for catalysis of
CRISPR/Cas13a-mediated non-coding RNA detection. Int J Biol
Macromol. 283:1375942024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
241
|
Meng X, Fan K and Yan X: Nanozymes: An
emerging field bridging nanotechnology and enzymology. Sci China
Life Sci. 62:1543–1546. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Cao X, Jiang H, Huang X, Sun D and Qi G:
Hydrogel patch doped with nanoenzyme for SERS detection of hydrogen
peroxide in complex body fluids. Talanta. 285:1273282025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
243
|
Jiang C, Shi Q, Yang J, Ren H, Zhang L,
Chen S, Si J, Liu Y, Sha D, Xu B and Ni J: Ceria nanozyme
coordination with curcumin for treatment of sepsis-induced cardiac
injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and inflammation. J Adv Res.
63:159–170. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
244
|
Li S, Wang K, Jiang K, Xing D, Deng R, Xu
Y, Ding Y, Guan H, Chen LL, Wang D, et al: Brazilin-Ce
nanoparticles attenuate inflammation by de/anti-phosphorylation of
IKKβ. Biomaterials. 305:1224662024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
245
|
Mai BT, Fernandes S, Balakrishnan PB and
Pellegrino T: Nanosystems based on magnetic nanoparticles and
thermo\or pH-Responsive polymers: An update and future
perspectives. Acc Chem Res. 51:999–1013. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
De Jong WH and Borm PJ: Drug delivery and
nanoparticles: Applications and hazards. Int J Nanomedicine.
3:133–149. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
247
|
Wang J, Wang H, Zhu R, Liu Q, Fei J and
Wang S: Anti-inflammatory activity of Curcumin-loaded solid lipid
nanoparticles in IL-1β transgenic mice subjected to the
lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. Biomaterials. 53:475–483. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
248
|
Rattis BAC, Piva HL, Duarte A, Gomes
FGFLR, Lellis JR, Soave DF, Ramos SG, Tedesco AC and Celes MRN:
Modulation of the mTOR pathway by curcumin in the heart of septic
mice. Pharmaceutics. 14:22772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Tian B, Hua S and Liu J:
Cyclodextrin-based delivery systems for chemotherapeutic anticancer
drugs: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 232:1158052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Sahu KM, Patra S and Swain SK: Host-guest
drug delivery by β-cyclodextrin assisted polysaccharide vehicles: A
review. Int J Biol Macromol. 240:1243382023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
251
|
Heimfarth L, Dos Santos KS, Monteiro BS,
de Souza Oliveira AK, Coutinho HDM, Menezes IRA, Dos Santos MRV, de
Souza Araújo AA, Picot L, de Oliveira Júnior RG, et al: The
protective effects of naringenin, a citrus flavonoid, non-complexed
or complexed with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin against multiorgan
damage caused by neonatal endotoxemia. Int J Biol Macromol.
264:1305002024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
252
|
Penalva R, González-Navarro CJ, Gamazo C,
Esparza I and Irache JM: Zein nanoparticles for oral delivery of
quercetin: Pharmacokinetic studies and preventive anti-inflammatory
effects in a mouse model of endotoxemia. Nanomedicine. 13:103–110.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
253
|
Wang S, Tan KS, Beng H, Liu F, Huang J,
Kuai Y, Zhang R and Tan W: Protective effect of isosteviol sodium
against LPS-induced multiple organ injury by regulating of
glycerophospholipid metabolism and reducing macrophage-driven
inflammation. Pharmacol Res. 172:1057812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Liu S, Yao C, Xie J, Liu H, Wang H, Lin Z,
Qin B, Wang D, Lu W, Ma X, et al: Effect of an Herbal-based
injection on 28-Day mortality in patients with sepsis: The EXIT-SEP
randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 183:647–655. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Zhang H, Wei L, Zhao G, Liu S, Zhang Z,
Zhang J and Yang Y: Protective effect of Xuebijing injection on
myocardial injury in patients with sepsis: A randomized clinical
trial. J Tradit Chin Med. 36:706–710. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Wu X, He C, Liu C, Xu X, Chen C, Yang H,
Shi H, Fei Y, Sun Y, Zhou S and Fang B: Mechanisms of JinHong
Formula on treating sepsis explored by randomized controlled trial
combined with network pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol.
305:1160402023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
257
|
Huang N, Tam YH, Zhang Z, Kao X, Yang Z,
Xu W, Yuan K, He M and Chen J: Efficacy and safety of Dachaihu
decoction for sepsis: A randomized controlled trial. Phytomedicine.
136:1563112025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
258
|
Liao J, Qin C, Wang Z, Gao L, Zhang S,
Feng Y, Liu J and Tao L: Effect of shenfu injection in patients
with septic shock: A systemic review and meta-analysis for
randomized clinical trials. J Ethnopharmacol. 320:1174312024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Yu Y, Zhu C, Hong Y, Chen L, Huang Z, Zhou
J, Tian X, Liu D, Ren B, Zhang C, et al: Effectiveness of
anisodamine for the treatment of critically ill patients with
septic shock: A multicentre randomized controlled trial. Crit Care.
25:3492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Zhang F, Mei X, Zhou P, Tian YP, Liu JX,
Dong X, Yuan DS, Lin ZF, Zhang L, Lin JH, et al: Anisodamine
hydrobromide in the treatment of critically ill patients with
septic shock: A multi-center randomized controlled trial. Ann Med.
55:22643182023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
261
|
Guo X, Luo W, Wu L, Zhang L, Chen Y, Li T,
Li H, Zhang W, Liu Y, Zheng J and Wang Y: Natural products from
herbal medicine Self-Assemble into advanced bioactive materials.
Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e24033882024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Li J, Sun S, Zhu D, Mei X, Lyu Y, Huang K,
Li Y, Liu S, Wang Z, Hu S, et al: Inhalable stem cell exosomes
promote heart repair after myocardial infarction. Circulation.
150:710–723. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Yuan Y, Mei Z, Qu Z, Li G, Yu S, Liu Y,
Liu K, Shen Z, Pu J, Wang Y, et al: Exosomes secreted from
cardiomyocytes suppress the sensitivity of tumor ferroptosis in
ischemic heart failure. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:1212023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Tirziu D, Giordano FJ and Simons M: Cell
communications in the heart. Circulation. 122:928–937. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Hu Y, Chen H, Zhang L, Lin X, Li X, Zhuang
H, Fan H, Meng T, He Z, Huang H, et al: The AMPK-MFN2 axis
regulates MAM dynamics and autophagy induced by energy stresses.
Autophagy. 17:1142–1156. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
266
|
Wu S, Lu Q, Ding Y, Wu Y, Qiu Y, Wang P,
Mao X, Huang K, Xie Z and Zou MH: Hyperglycemia-driven inhibition
of AMP-activated protein kinase α2 induces diabetic cardiomyopathy
by promoting mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum
membranes in vivo. Circulation. 139:1913–1936. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Zhou ZK, Yu MM, Shou ST, Chai YF and Liu
YC: Interaction between gut-heart axis in sepsis-induced
cardiomyopathy. Pharmacol Res. 217:1078062025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Yuzefpolskaya M, Bohn B, Nasiri M, Zuver
AM, Onat DD, Royzman EA, Nwokocha J, Mabasa M, Pinsino A, Brunjes
D, et al: Gut microbiota, endotoxemia, inflammation, and oxidative
stress in patients with heart failure, left ventricular assist
device, and transplant. J Heart Lung Transplant. 39:880–890. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|