Introduction
From 1990 to 2017, the incidence of pancreatic
cancer has increased (age-standardized incidence rate, 5.0/100,000
person-years in 1990 to 5.7 in 2017), positioning it among the most
lethal types of human malignancy, largely due to its poor prognosis
(1). Although progress has been
made in contemporary medical practices, the 5-year survival rate
for this disease has improved marginally, rising from <5% in
1990 to ~10% by 2021 (2). This
limited survival benefit is primarily associated with delayed
detection, as a majority of patients are diagnosed at a later stage
of the disease. In cases where early diagnosis is achieved, ~20% of
individuals meet the criteria for surgical resection. For those who
undergo surgery, the 5-year survival rate may increase to ~25%
(3). As the risk of pancreatic
cancer is associated with aging, the prevalence of the disease is
projected to escalate in response to the global aging trend
(4). Anatomically, the pancreas
is connected to the gastrointestinal system via the pancreatic
duct, which facilitates the retrograde movement of intestinal
microorganisms into the pancreatic ductal system. This microbial
translocation and resulting dysbiosis may contribute to sustained
inflammatory responses, offering a potential explanation for the
higher frequency of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) in the
pancreatic head compared with its body or tail (5). The gut microbiota, a complex and
essential component of the human organism, comprises
>1×1014 microbial cells (6). Certain bacteria-associated
metabolites, such as nitrosamines, may modulate the immune
landscape and influence resistance to treatment, thereby serving a
role in the development and progression of pancreatic cancer
(7).
The circadian clock is a conserved molecular
feedback loop that regulates signaling pathways, controlling cell
metabolism and immune function (8). Disruption of circadian rhythms
leads to misalignment between external signals and the internal
clock, resulting in metabolic dysregulation (9). A previous study has revealed
circadian rhythm dysfunction in PDAC, which is associated with
tumor progression and poor prognosis (10). Additionally, the gut microbiome
exhibits circadian variations (11). For example, enteric
Enterobacteriaceae in the gastrointestinal tract are sensitive to
melatonin, a neurohormone secreted into the gastrointestinal lumen,
and exhibit circadian patterns of aggregation and motility
(12). Disruption of circadian
rhythms alters the gut microbiota and its metabolites, thereby
promoting cancer development (13). Therefore, circadian rhythm
disturbances may contribute to the development of pancreatic cancer
by affecting the gut microbiota and its metabolites. Previous
reviews have primarily focused on the association between either
circadian rhythms or the gut microbiota and pancreatic cancer
(14,15). To the best of our knowledge,
however, a comprehensive discussion linking circadian rhythm, gut
microbiota and pancreatic cancer has been lacking. The present
review aimed to summarize the impact of circadian rhythm disruption
on the gut microbiota and its metabolites and discuss microbiota
associated with pancreatic cancer, exploring how microbiota and
metabolites influence pancreatic cancer progression. The aim of the
present study is to enhance understanding and application of gut
microbiota in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Methods
PubMed (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and Web of Science
(clarivate.com/academia-government/scientific-and-academic-research/research-discovery-and-referencing/web-of-science/)
databases were searched from inception to October 2025 for relevant
literature, with the language restricted to English. The search
strategy focused on the association between circadian rhythm, gut
microbiota and pancreatic cancer. Key words included 'circadian
rhythm', 'circadian disruption', 'gut microbiota', 'microbial
metabolites', 'pancreatic cancer', 'pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma', as well as mechanism-related terms such as 'LPS',
'SCFAs', 'immune suppression', and 'TLRs'.
The present study included original studies
(including in vitro and in vivo experiments, animal
studies, clinical observations and trials) that explored the
association between pancreatic cancer, circadian rhythm disruption,
gut microbiota and their metabolites, immune regulation, tumor
microenvironment, gut-pancreas axis or microbiota-mediated drug
resistance. In addition, high-quality review articles were used to
supplement background information and theoretical frameworks.
Excluded studies included those not clearly
involving the mechanisms of circadian rhythm or gut microbiota in
non-pancreatic cancer research, non-English publications,
conference abstracts, non-peer reviewed preprints, incomplete case
reports and commentaries or editorials with low relevance to the
review topic.
A total of two authors independently conducted the
initial screening and full-text review of all retrieved articles.
Disagreements were resolved through discussion, with arbitration by
a third reviewer when necessary.
The present review did not conduct a meta-analysis
due to substantial heterogeneity between the included studies in
terms of study populations, exposure assessment and outcome
definitions, as well as partial overlap among cohorts. Under such
conditions, a quantitative synthesis may lead to inappropriate
weighting or potential double-counting of results. The present
study extracted and reported the effect sizes and corresponding
uncertainty measures from the original publications, including odds
ratio (OR), hazard ratios (HRs), standardized incidence ratios
(SIRs), areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve
(AUROCs), 95% confidence intervals (95% CI), as well as the study
designs and population characteristics for each study.
Disruption of circadian rhythm and
pancreatic cancer risk
Sleep disorders include conditions such as insomnia,
narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (16). Engaging in shift work, which
requires activity during usual sleep periods, can disturb circadian
rhythms (17). As reported by
the International Agency for Research on Cancer in 2019, such
circadian disruption is associated with elevated cancer risk
(17). Gu et al (18) suggested that residents of the
western regions of the United States, where there is a temporal
discrepancy between natural sunlight exposure and internal
biological clocks, may face an increased likelihood of circadian
rhythm misalignment. This misalignment is a potential contributor
to the development of diseases such as pancreatic cancer (18). In a study by Parent et al
(19), data from 3,137 male
patients with cancer patients were analyzed, revealing that those
with a history of night shift employment exhibited a notably higher
risk of pancreatic cancer (OR: 2.27, 95% CI: 1.24-4.15), although
no significant association was observed between cancer risk and the
total duration of night shift work. Moreover, findings from a Cox
proportional hazards model based on 464,371 individuals indicate
that those residing in areas with increased nighttime light
exposure have a 27% greater risk of developing PDAC compared with
individuals exposed to lower levels of night lighting (HR: 1.24,
95% CI: 1.03-1.49) (20).
Additionally, Mendelian randomization analysis by Titova et
al (21) demonstrated that a
genetic tendency toward shorter sleep duration is associated with a
heightened risk of pancreatic cancer (OR: 2.18, 95% CI: 1.32-3.62).
In the US National Institutes of health-American association of
retired persons diet and health study prospective cohort, nighttime
light exposure assessed by satellite remote sensing was positively
associated with PDAC incidence, with the with individuals in the
highest exposure quartile having an increased risk of PDAC compared
with those in the lowest quartile (HR 1.24, 95% CI 1.03-1.49; male,
HR 1.21, 95% CI 0.96-1.53; female, HR 1.28, 95% CI 0.94-1.75),
suggesting that environmental circadian disruption may promote PDAC
development (20). A
case-control study from Canada based on 3,137 male patients with
cancer showed that those who had ever worked night shifts had a
notably increased risk of pancreatic cancer (adjusted OR 2.27, 95%
CI 1.24-4.15), and this association is not increased by longer
cumulative duration of night shift work, suggesting that the
exposure is more important than duration (19). Using a German health insurance
database, a case-control study with propensity score matching
included 37,161 gastrointestinal cancer cases and an equal number
of controls; having a recorded sleep disorder in the year before
diagnosis was associated with an increased overall odds of
gastrointestinal cancer (OR 1.20, 95% CI 1.08-1.34), and
site-specific analyses suggested higher odds for pancreatic cancer
in the year preceding diagnosis, supporting a short-term
association between sleep disorders and cancer that may reflect
bidirectional interactions between circadian disruption and early
tumorigenesis (22). An
ecological analysis using longitude position within a time zone as
a proxy for social jetlag covered 607 counties across 11 US states
and showed that moving from the eastern to the western edge of the
same time zone was associated with higher age-standardized
incidence rates for overall malignancy and several site-specific
cancers (risk gradients evaluated/5 degrees of longitude and
remaining significant after multiple-comparison adjustments);
although a distinct estimate for pancreatic cancer was not
significant, this general pattern supports incorporating circadian
disruption into etiological frameworks for pancreatic cancer
(18). By contrast with the
aforementioned positive signals, a meta-analysis pooling data from
>8.4 million individuals across prospective and case-control
studies found no significant increase in overall pancreatic cancer
risk when comparing ever vs. never night shift work (pooled OR
1.007, 95% CI 0.910-1.104; pancreatic cancer k=6; heterogeneity
I2 3.2%), suggesting that discrepancies between studies
may reflect differences in exposure metrics, occupational
composition and confounding control, highlighting the need for more
objective circadian measures to identify high-risk groups (23). Mendelian randomization analysis
indicates that genetic predisposition to short sleep is associated
with higher pancreatic cancer risk (OR 2.18, 95% CI 1.32-3.62),
whereas genetic predisposition to long sleep is associated with
lower risk (OR 0.44, 95% CI 0.25-0.79), but these associations are
not significant after multiple testing correction and not
replicated in external two-sample analyses, implying that the
causal role of sleep duration in PDAC requires larger samples and
stronger instruments for confirmation (21).
In sum, epidemiological signals linking circadian
disruption to pancreatic cancer are modest and heterogeneous.
Across cohorts, satellite-derived light at night shows small excess
risks (highest vs. lowest exposure HR, 1.2-1.3), single
case-control estimates for ever night shift work can be larger (OR
~2.3), whereas meta-analytic pooling under mixed exposure
definitions demonstrate a pooled OR close to 1.0, indicating no
clear overall association. Mendelian randomization analysis
(21) using genetic variants as
proxies for short sleep suggest risk but does not withstand
multiple-testing and lacks replication. Heterogeneity may reflect
exposure misclassification, occupational mix and incomplete control
of smoking, adiposity and diabetes, and short-term elevations in
sleep disorder diagnoses before cancer raise the possibility of
reverse causation. Clinically, these data support pragmatic
mitigation of circadian misalignment and incorporation of objective
circadian metrics into risk stratification, using study designs
that account for the induction and latency period between exposure
and cancer diagnosis to clarify timing; peri-therapeutically,
actigraphy-guided light and sleep alignment may be piloted
alongside standard care to test whether circadian calibration
improves treatment tolerance and clinical outcomes.
Circadian regulation of gut barrier
microbiota and immunity in pancreatic cancer
The circadian clock is a multilayered temporal
control system that synchronizes daily oscillations of the
gastrointestinal barrier, immune response and metabolic pathways
(24). Multiple studies indicate
that disruption of host circadian rhythms reshapes both the
composition and rhythmicity of the gut microbiota, alters systemic
exposure to key microbial metabolites such as lipopolysaccharide
(LPS) and short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), promotes chronic
inflammation and immune imbalance within the tumor microenvironment
and influences pancreatic cancer phenotypes (24,25). Conversely, selected microbial
metabolites (such as SCFAs, acetate, propionate and butyrate)
modulate core clock machinery in the host, which implies a
bidirectional loop (26).
Host clock disruption reshapes microbiota
and compromises the barrier in pancreatic cancer
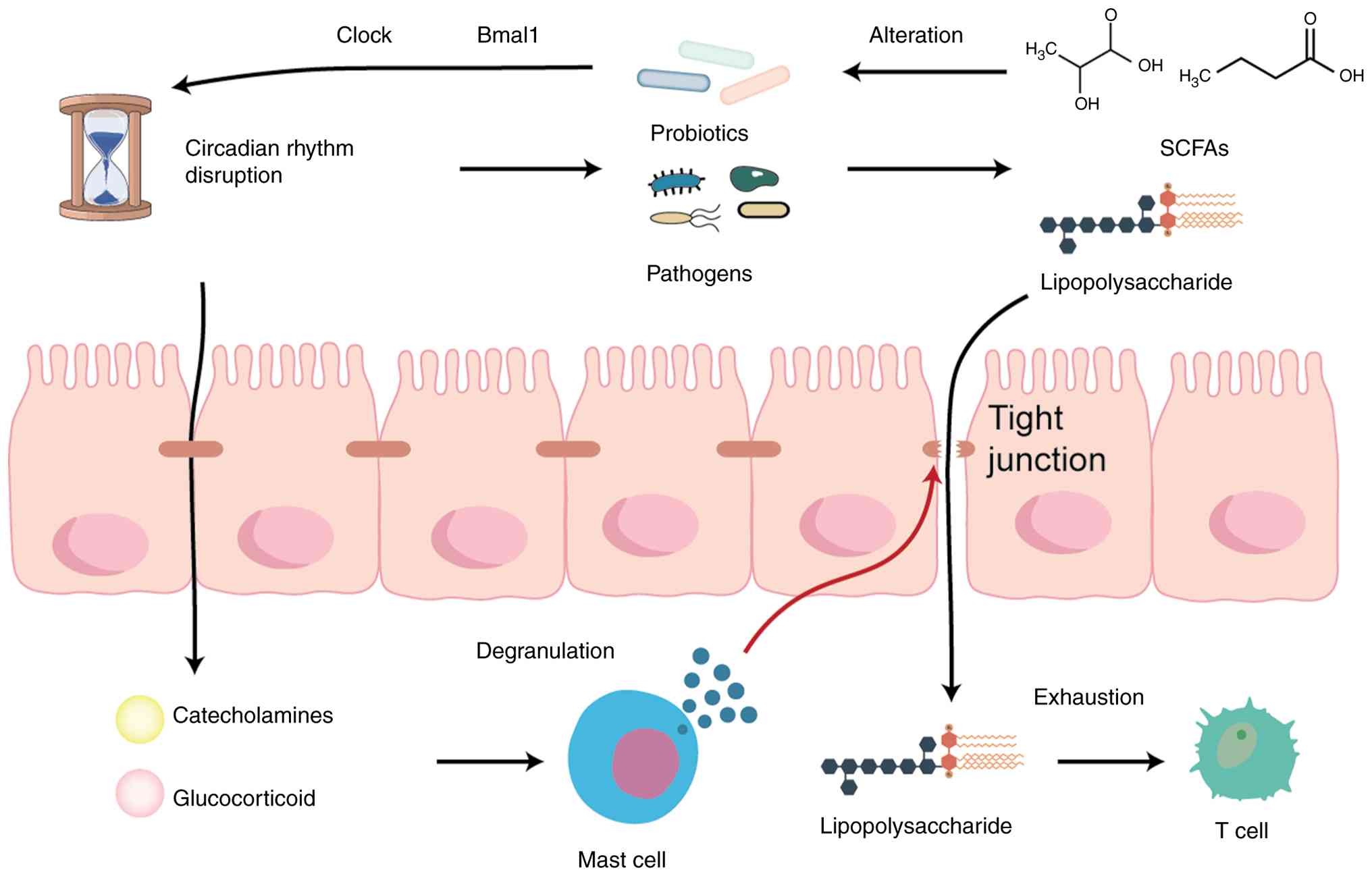
Circadian rhythm disturbances may influence
pancreatic cancer through alterations in the gut microbiome
(Fig. 1). In mice, deletion of
the core clock gene BMAL1 abolishes the diurnal oscillation of the
phylum Bacteroidetes and decreases its absolute abundance relative
to controls, indicating that host clock genes directly shape
microbial rhythmicity and abundance structure (24). On a broader scale, the gut
microbiota as a whole exhibits marked daily oscillations. Disrupted
feeding rhythms and experimental jet lag disturb these oscillations
and produce transferable metabolic imbalance, demonstrating that
behavioral and environmental cues act through the microbiota to
influence host metabolic outcomes (25). Evidence linking the upper
gastrointestinal microbiome with pancreatic cancer comes from study
of duodenal fluid and bile (22). In a prospective cohort, patients
with PDAC who have shorter survival show enrichment of oral and
opportunistic taxa in duodenal fluid, especially members of
Fusobacteria and the genus Rothia, suggesting that upstream
dysbiosis is associated with poor prognosis (22). Patients with severe obstructive
sleep apnea have significantly higher fecal Fusobacterium levels
and its abundance is positively associated with the apnea hypopnea
index (AHI) (27). This suggests
that sleep fragmentation and intermittent hypoxia selectively
enrich proinflammatory taxa, a feature that may be shared with the
unfavorable pancreatic tumor microenvironment (in linear
regression, AHI is positively associated with the relative
abundance of Fusobacterium, β=0.538) (27).
Circadian imbalance also directly impairs the
intestinal epithelial barrier. Both genetic clock disruption and
environmental light and dark phase misalignment increase epithelial
permeability, facilitate endotoxin translocation and trigger
systemic inflammatory responses, thereby creating an anatomical
route for gut-derived molecules to enter the circulation (28). Classical sleep deprivation model
further shows that progressively sleep restricted rats develop
cultivable bacteria in tissue that is normally sterile, which
supports translocation of microbes and their components across
compromised barriers (29).
Human study demonstrates that partial nocturnal sleep loss raises
circulating norepinephrine and epinephrine levels, reflecting
heightened sympathetic activity that is associated with
inflammatory susceptibility (30). At the mucosal level, mast cell
tryptase activates epithelial protease-activated receptor 2 to
increase paracellular permeability, providing a cellular basis for
stress-induced tight junction disruption and barrier leak (31). These barrier and inflammatory
alterations align with pancreatic tumor biology. In a mouse model
of PDAC, increased gut permeability elevates LPS levels in both the
circulation and tumor tissue. The rise in LPS coincides with T cell
infiltration while simultaneously inducing T cell exhaustion and
loss of effector function, together establishing an
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (P<0.05) (32).
Bidirectional coupling of microbial
metabolites and the host clock in pancreatic cancer
Circadian disruption due to sleep disorders alters
the microbial metabolic profile. Patients with severe obstructive
sleep apnea show notably higher plasma D lactate levels, along with
enrichment of proinflammatory gut taxa, suggesting that microbially
derived lactate stereoisomers may serve as surrogate indicators of
systemic metabolic stress (27).
In mice, fecal microbiota transplantation from sleep deprived
donors to healthy recipients reproduces colonic dysbiosis
characterized by increased Aeromonas and endotoxins in serum
and colon, and reduced butyrate levels, which indicates that
circadian disruption drives inflammatory phenotypes through
transferable microbe and metabolite consortia (33). In the aforementioned
transplantation model, melatonin supplementation reverses
dysbiosis, restores canonical butyrate producers including the
Ruminococcaceae NK4A136 (an uncultured Ruminococcaceae clade)
group, the Eubacterium xylanophilum group, Ruminococcus 1 and
Ruminococcaceae A2, and alleviates inflammation. These findings
imply that circadian signals improve host inflammatory status by
rebuilding butyrate-producing niches (33). Functionally, SCFAs, especially
butyrate, regulate immune cell and tumor cell phenotypes through G
protein-coupled receptors and histone deacetylase pathways. SCFAs
serve as metabolic substrates and epigenetic regulators and show
anti-inflammatory and antitumor potential in cancer (26).
LPS, a Gram-negative cell wall component, is a key
metabolite-associated mediator that links microbial rhythm
disruption to systemic inflammation (28). LPS traverses the injured
intestinal barrier and activates mucosal and systemic immunity,
driving chemotaxis, adhesion molecule expression and cytokine
cascades that provide sustained stimuli for immune exhaustion and
fibrosis in pancreatic tumors (32). Endotoxin exposure and host
responses show clear diurnal features. In healthy volunteers, fever
and neuroendocrine responses to low dose endotoxin depend on time
of day, indicating that human systemic sensitivity to LPS varies
across the circadian cycle (34). At the cellular level, mRNA
expression of several toll-like receptors (TLRs), including TLR4,
oscillates in splenic adherent immune cells over the 24-h cycle.
LPS given at different times of day elicits distinct cytokine
profiles, indicating that innate immune recognition is under
circadian clock control (35).
Consistently, the macrophage clock modulates LPS-induced NF-κB
signaling and cytokine production through BMAL1 and microRNA (miRNA
or miR)-155, imparting temporal specificity to endotoxin responses
(36). Barrier dysfunction
caused by circadian disruption increases exposure to
microbiota-derived LPS in the circulation (28,37). In a light shift model, microbial
community structure and function are altered, with enrichment of
pathways involved in LPS biosynthesis, which suggests rhythm
disturbance may both increase endotoxin supply and modify host
responsiveness (38). Taken
together, these observations indicate that the circadian clock
interfaces with gut-derived LPS signaling in the pancreatic cancer
microenvironment through regulation of epithelial permeability and
time selective responsiveness of innate TLR4 pathways. The
coexistence of dysbiosis and circadian misalignment may intensify
immunosuppression in PDAC and confer temporal sensitivity to
immunotherapy strategies such as PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade (39,40).
Microbial metabolites feed back onto host clock
genes. Dietary choline is converted by gut microbes to
trimethylamine and oxidized in the liver to trimethylamine N-oxide
(TMAO) (41). In endothelial
cell models in vitro, TMAO upregulates circadian locomotor
output cycles kaput (CLOCK) and brain and muscle ARNT-like 1
(BMAL1) and modulates cell proliferation rhythms by coupling with
long non-coding RNA and MAPK pathways, which suggests that certain
metabolites remodel peripheral clocks (41,42). In summary, circadian disruption
shapes a pancreatic tumor microenvironment in which proinflammatory
immunity coexists with immune exhaustion through alteration of
butyrate-producing niches and increased endotoxin exposure.
Metabolites such as butyrate and TMAO influence host clock gene
networks through receptor-mediated and epigenetic pathways. This
bidirectional coupling provides tractable entry points for
mechanistic studies and intervention strategies (26,41).
Evidence across genetic, behavioral and clinical
models supports a coherent chain from host clock disruption to
dysbiosis, barrier leak and time-dependent immune dysfunction in
pancreatic cancer. Loss of microbial rhythmicity following BMAL1
deletion (24) coincides with
community shifts in humans, including enrichment of oral taxa in
proximal gut among short-survival PDAC cases with measurable
α-diversity decrease and β-diversity separation (22). Sleep fragmentation and
intermittent hypoxia show a proinflammatory effect on fecal
communities, exemplified by a positive association between AHI and
Fusobacterium abundance in regression analyses (β=0.538) (27). Independent lines of evidence
indicate barrier compromise and systemic activation, with partial
sleep loss elevating catecholamine levels (30) and PDAC models linking increased
permeability with higher circulating and intratumoral LPS alongside
T cell infiltration with functional exhaustion (32). Metabolite-clock crosstalk is
bidirectional, as butyrate depletion and enrichment of LPS pathway
are associated with circadian misalignment (38), while TMAO upregulates CLOCK and
BMAL1 in vitro (41), and
melatonin restores canonical butyrate producers following dysbiosis
transfer (33). These
observations support clinical frameworks that integrate objective
circadian phenotyping with multi-site microbiome and metabolite
readouts, and pilot peri-therapeutic ecological calibration and
time-informed immunotherapy scheduling to test translatability
(40).
Gut microbiota and pancreatic cancer
The gut microbiota is a complex and finely balanced
ecosystem, constituting the largest microbial community in the
human body. It serves essential roles in protecting the host from
infection, aiding digestion and regulating the immune system
(43). Dysbiosis, or imbalance
in the gut microbiota, is associated with a number of diseases,
particularly metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2
diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome.
Gut microbiota can reach the pancreas through the circulatory
system and pancreatic ducts, suggesting a potential involvement in
pancreatic pathophysiology (44). Antibiotic-mediated depletion of
gut microbiota in mice increases the number of anti-tumor T cells
[such as T helper (Th)1 and type 1 cytotoxic T cells], reduce
pro-tumor cell populations (such as IL-17A and IL-10-producing T
cells) and enhance the infiltration of effector T cells into
pancreatic tumors, thereby boosting the immune system capacity to
combat pancreatic cancer (45).
These findings highlight the role of gut microbiota in modulating
pancreatic cancer development through immune regulation, though the
exact mechanisms remain to be elucidated.
Role of gut microbiota in pancreatic
cancer development
Heliobacter pylori
Meta-analysis has demonstrated a notable association
between serum positivity for H. pylori and an increased risk
of pancreatic cancer, although no significant association was
identified specifically for positivity with the
cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) strain (pooled adjusted OR,
1.38, 95% CI 1.08-1.75) (46).
These findings indicate that the effect of H. pylori
infection on pancreatic cancer risk may depend on bacterial strain
variation. Schulte et al (47) showed that individuals infected
with CagA− H. pylori strains exhibit a notably
elevated risk of developing pancreatic cancer (OR 1.30; 95% CI
1.02-1.65), whereas those with CagA+ strains exhibit a
reduced risk (OR 0.78; 95% CI 0.67-0.91). Consistent with these
results, a meta-analysis involving 3,033 participants found a
significant yet modest association between H. pylori
infection and pancreatic cancer incidence. However, the
aforementioned analysis did not reveal a significant association
between the presence of CagA+ strains and the occurrence
of pancreatic cancer (overall pooled OR 1.47, 95% CI 1.22-1.77),
and this association persisted when the analysis was restricted to
the studies of higher methodological quality, defined as those
scoring ≥6 on the Newcastle-Ottawa scale (high-quality subset OR
1.28, 95% CI 1.01-1.63). By contrast, the subgroup analysis limited
to CagA+ strains did not show a significant association
with pancreatic cancer (OR 1.42, 95% CI 0.79-2.57) (48). The aforementioned studies suggest
that the risk of pancreatic cancer may vary depending on the
specific strain of H. pylori, although further investigation
is needed to define the relationship (47). Beyond H. pylori strains,
the ABO genotype may also play a role in this process. ABO blood
group antigens are expressed in the gastrointestinal epithelium and
influence H. pylori adhesion, thereby regulating gastric and
pancreatic secretion functions, which may impact pancreatic
carcinogenesis related to dietary and smoking-associated
nitrosamine exposure, thus influencing pancreatic cancer risk
(49). H. pylori damages
the gastric mucosa, leading to the formation of gastric ulcers.
Gastric ulcers are typically associated with hypochlorhydria,
creating an environment conducive to the accumulation of nitrites
(50), which are carcinogenic
and increase the risk of pancreatic cancer (51). This may explain why patients with
untreated gastric ulcer face a heightened risk of pancreatic
cancer. During years 3-38 of follow-up after ulcer diagnosis, the
SIR was 1.20 (95% CI 1.10-1.40); at 15 years of follow-up, the SIR
was 1.50 (95% CI 1.10-2.10); and 20 years after gastric resection,
the SIR was 2.10 (95% CI 1.40-3.10) (52). Alcohol consumption may also play
a role in H. pylori-induced pancreatic cancer, as infection
with H. pylori may increase pancreatic cancer risk in
low-alcohol consumers (overall adjusted OR 1.25, 95% CI 0.75-2.09;
never smokers-adjusted OR 3.81, 95% CI 1.06-13.63; low-alcohol
consumers-adjusted OR 2.13, 95% CI 0.97-4.69) (53).
Fusobacterium
A cohort study detected Fusobacterium DNA in
pancreatic cancer tissue and linked its presence to poor prognosis;
patients with Fusobacterium-positive tumors show
significantly shorter survival, supporting its potential as an
adverse prognostic biomarker (multivariable HR for overall
mortality 2.57, 95% CI 1.01-6.58; multivariable HR for
cancer-specific mortality 2.16, 95% CI 1.02-4.59) (54). Mechanistically, mouse and human
data indicate that intratumoral Fusobacterium nucleatum
augments chemokine signaling and recruits granulocytes, thereby
intensifying inflammatory conditions and promoting pancreatic
cancer progression; activation of CXCL1 and its receptor CXCR2 is a
key pathway (tumor tissue detection rate 15.5%) (55). Upstream sources may involve the
upper gastrointestinal tract: Duodenal fluid analysis has shown
that show enrichment of Fusobacteria and oral taxa such as Rothia
in short-survival patients, suggesting oral-gut translocation and
dysbiosis of the upper gut as a microbial reservoir for pancreatic
colonization (discovery cohort n=308 with PDAC n=74; enrichment
determined by differential abundance testing) (56). Intratumoral bacteria typically
localize intracellularly within immune and cancer cells, a
distribution that may facilitate immune evasion and direct
crosstalk with host signaling networks (57). The pancreatic cancer microbiome
induces suppression of innate and adaptive immunity, including
polarization of tumor-associated macrophages toward
immunosuppressive states and inhibition of T cell activation,
thereby creating a niche favorable for pro-inflammatory colonizers
such as Fusobacterium (antibiotic-mediated microbial
depletion significantly decreases orthotopic tumor growth and
myeloid suppressor populations and increases
CD4+/CD8+ T cell infiltration) (58). The detection rate of F.
nucleatum in pancreatic cancer is associated with prognosis and
immune escape, further supporting its feasibility as an
intervention target (59).
Veillonella and Streptococcus
A multi-center fecal metagenomic study developed
specific pancreatic cancer classification models in which
oral-associated genera including Veillonella and
Streptococcus repeatedly emerge as discriminative features
and retain stable performance in independent validation,
underscoring their key roles in disease-associated communities
(fecal metagenomic classifier AUROC up to 0.84; combination with
CA19-9 increases AUROC to 0.94; external disease-specificity tested
in 25 datasets at 90% specificity with low false-positive rates)
(60). An independent Israeli
amplicon-based study similarly reported increased relative
abundance of Veillonellaceae and Akkermansia in feces
from patients with pancreatic cancer, along with depletion of
families common in healthy controls such as Clostridiaceae,
Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae, and achieved an
AUC of 82.5% for distinguishing patients with pancreatic cancer
from healthy controls (61). A
prospective Chinese fecal study further showed decreased overall α
diversity and enrichment of inflammation-related functions such as
LPS biosynthesis, and highlighted associations between
Streptococcus and intestinal bile factors, suggesting
potential interactions between altered bile dynamics and expansion
of oral taxa (62). Multi-site
sampling combined with fluorescence in situ hybridization
(FISH) confirms that characteristic oral-gut taxa can be detected
in pancreatic tumor tissue in situ, strengthening the
biological continuity between oral-gut sources and pancreatic
colonization (60).
Akkermansia muciniphila and
butyrate-associated commensal organisms
Metagenomic analysis of long-term survivors has
revealed enrichment of commensal organisms associated with
antitumor immunity, most notably Faecalibacterium
prausnitzii and A. muciniphila, relative to typical
pancreatic cancer cases; both taxa are associated with favorable
responses to immunotherapy in other types of malignancy, suggesting
they may modulate pancreatic cancer progression by promoting
antitumor immunity (significant enrichment of F. prausnitzii
and A. muciniphila reported with metagenomic testing)
(63). A cross-cohort stool and
tissue study identified Akkermansia as a recurrent feature in
diagnostic models, with in-tumor validation by FISH, consistent
with potential migration from the gut and niche adaptation within
the pancreas (fecal AUROC up to 0.84, rising to 0.94 with CA19-9)
(60). Concordant with Israeli
amplicon data, pancreatic cancer cohorts frequently show higher
levels of Akkermansia and Veillonellaceae alongside decreased
levels of Ruminococcaceae and other butyrate-associated families, a
directional shift aligned with perturbations in mucosal barrier
integrity, SCFA homeostasis and immune regulation (AUC 82.5% for a
taxa-based classifier) (61). At
the tissue level, the intratumoral microbiome is coupled with the
host immune landscape; tumors from long-term survivors harbor more
diverse microbial networks that are associated with features of T
cell activation, including increased intratumoral CD3+
and CD8+ T cell infiltration and higher numbers of
granzyme B-positive cytotoxic T cells, providing histological
support for the hypothesis that butyrate-associated commensal
organisms shape antitumor immunity via metabolic and
antigen-presentation pathways (64). Systemically, immunosuppression
driven by the pancreatic cancer microbiome is partially reversed by
microbiota depletion, in line with the enrichment of beneficial
commensal organisms in long-term survivors and supporting
microbiome-based strategies to improve antitumor immune responses
(antibiotics decrease tumor burden and reprogram myeloid/T cell
compartments) (58).
Porphyromonas gingivalis and oral-gut
translocation
Oral pathobionts are associated with pancreatic
cancer (60,65). Mechanistically, P.
gingivalis can colonize pancreatic tumors and accelerate the
growth of orthotopic and ectopic pancreatic cancer by inducing
tumor-associated neutrophils to secrete neutrophil elastase,
thereby establishing a neutrophil-dominated pro-inflammatory
microenvironment (65).
Detection of this oral pathogen in both tumor tissue and the oral
cavity reinforces the anatomical route for oral-gut translocation
and distal colonization, and implies that periodontal disease
control may have practical relevance for pancreatic cancer
prevention and peri-therapeutic management (65). Elevated intratumoral microbial
loads coexisting with immune suppression may provide a niche that
permits the persistence of oral taxa, consistent with findings that
microbial depletion activates antitumor immunity and restrains
tumor growth (58). Moreover,
multi-site sequencing and ISH confirm that characteristic gut and
oral bacteria can be directly visualized within pancreatic tissue,
providing anatomical evidence for the involvement of oral microbes
in pancreatic cancer progression (fecal classifier AUROC up to 0.84
with tissue-level FISH validation in a subset) (60).
Microbial communities within the
pancreas
In the context of pancreatic cystic lesions,
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is reported as a
potential precursor to invasive pancreatic cancer (66). Notably, in patients with IPMN
with high-grade dysplasia and cancer, bacterial 16S rDNA copy
numbers and IL-1β protein levels in cystic fluid are significantly
higher compared with patients with non-IPMN pancreatic cystic
neoplasm (16S rDNA geometric mean 17.7-fold higher in IPMN with
high-grade dysplasia vs. IPMN with low-grade dysplasia; IL-1β
103.2-fold higher) (66). This
suggests that an increase in intra-pancreatic bacteria may be
associated with pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. Riquelme et
al (64)demonstrated that
pancreatic tissue from long-term survival patients with PDAC
exhibit notably higher α-diversity in their pancreatic microbiomes.
Additionally, specific microbial taxa (Pseudoxanthomonas,
Streptomyces, Saccharopolyspora and Bacillus clauii) within
the tumor microbiome are significantly associated with prolonged
survival (64). These findings
indicate that not only do specific microbial communities exist
within pancreatic cancer tissue, but they also exhibit distinct
patterns depending on the disease state. The pancreatic duct and
the intestine are anatomically connected, with interactions between
the pancreas and the gut facilitated by the pancreatic duct. FISH
with 16S rRNA probes and quantitative PCR results indicate that the
bacterial population in the pancreas of patients with pancreatic
cancer is 1,000 times higher than that in healthy pancreatic tissue
(67). Certain bacteria migrate
through the pancreatic duct and accumulate in pancreatic cancer
tissue (67). In the adult gut
microbiome, Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes are dominant, while
Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria and
Verrucomicrobia are present at lower levels (68). However, in the gut microbiota of
patients with pancreatic cancer, the relative abundance of
Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria
and Verrucomicrobia is notably increased. Correspondingly,
an abnormal increase in Proteobacteria is also detected in
the pancreatic microbiota of these patients, with the abundance of
Proteobacteria associated with pancreatic cancer progression
(58). These findings suggest
that the gut microbiota influences the abundance of microbial
communities within the pancreas and may serve a role in the
development of pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, the microbial
communities within pancreatic cancer tissue selectively activate
TLRs, triggering immune tolerance responses that contribute to
immune evasion in pancreatic cancer (69). For examples, the abundance of
B. pseudolongum in both pancreatic cancer tissue and the gut
of patients with PDAC is increased. The cell-free extracts of B.
pseudolongum selectively activate TLR2 and TLR5, promoting
macrophage polarization and subsequent secretion of
immune-suppressive cytokines, such as IL-10, which provide immune
protection for the tumor (58).
In addition, the presence of Gammaproteobacteria in pancreatic
cancer tissue has been reported (70). These bacteria secrete enzymes,
such as cytosine deaminase, which convert gemcitabine, a
chemotherapeutic agent used for PDAC, into its inactive form,
2',2'-difluorodeoxyuridine (70). This results in the development of
gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic tumors, which is reversed by
ciprofloxacin treatment (70).
Moreover, H. pylori DNA is detected in 75% of pancreatic
tissue samples and 60% of duodenal samples from patients with
exocrine pancreatic cancer. This suggests H. pylori may be
transmitted from the digestive tract to the pancreas, potentially
promoting the development of pancreatic cancer and chronic
pancreatitis (71). H.
pylori stimulates pancreatic cancer cells to secrete IL-8,
VEGF, NF-κB, activator protein 1 and serum response element, which
enhance immune responses, angiogenesis and promote cancer cell
proliferation and survival (72). Additionally, F. nucleatum,
a bacterium associated with periodontal disease, has been detected
in pancreatic cancer tissue (prevalence, 8.8%) (54). Patients with Fusobacterium
positivity have notably higher cancer-specific mortality rates,
suggesting that the presence of Fusobacterium in pancreatic tissue
is independently associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic
cancer (54).
Collectively, oral-gut pathobionts expand along the
oral/duodenal/pancreatic continuum and align with adverse
phenotypes (56). Intratumoral
Fusobacterium is associated with shorter survival after adjustment
for clinical covariates, with HR of ~2 two, and tumor positivity is
observed in a minority of cases, suggesting a high-risk microbial
subset rather than a ubiquitous marker (54). H. pylori shows
strain-contingent signals, with pooled ORs for seropositivity in
the range of 1.3-1.5, a higher risk with CagA-negative strains near
1.30 and a lower risk with CagA-positive strains near 0.78
(47). Long-term gastric ulcer
carries standardized incidence ratios between 1.2 and 2.1 across
latency windows, consistent with nitrosation-associated pathways
that may intersect with pancreatic carcinogenesis (52). Diagnostic modeling adds
convergent support (60). Stool
classifiers that elevate oral taxa such as Veillonella and
Streptococcus have AUC values near 0.84 and approach 0.94
when combined with CA19-9, with external disease specificity
maintained at high specificity thresholds (60), while an independent amplicon
study reports an AUC near 0.825 (61). By contrast, commensal organisms
linked to barrier integrity and immune tone, including
Akkermansia and butyrate-associated families, concentrate in
long-survivor networks and track with T cell-active tissue states
(64).
These findings suggest complementary avenues for
translation. Biomarker development may use stool or tumor microbial
signatures together with clinical markers such as CA19-9 to support
risk stratification and prognostic assessment across settings
(60). In parallel,
peri-therapeutic ecological modulation can be tested through
mechanism-guided hypotheses, including inhibition of the CXCL1 and
CXCR2 chemokine axis to limit neutrophil recruitment (55), reprogramming of macrophages
through TLR-based signaling (58) and mitigation of microbe-mediated
drug metabolism (70). However,
most available studies are associative and sensitive to sampling
site and batch structure, and effect estimates vary with exposure
definitions and host context. More persuasive mechanistic
inferences require converging evidence that traces microbial
sources to in-tumor localization, delineates immune consequences
and demonstrates reversibility under intervention, accompanied by
clear reporting of effect sizes and heterogeneity to clarify
magnitude and generalizability.
Hepatitis viruses and pancreatic cancer
Patients with chronic liver disease associated with
hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) commonly
exhibit marked disturbances of the gut microbiota (73). Epidemiological evidence indicates
that chronic HBV/HCV infection is associated with an increased risk
of pancreatic cancer, positioning viral hepatitis as a key link
between gut microbiota alterations and pancreatic cancer
progression (74).
HBV and HCV, is a leading cause of death due to
viral hepatitis (75). HBV and
HCV are not only detected in the liver but also in extrahepatic
tissue such as the pancreas (76). For example, Yoshimura et
al (77) demonstrated
hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positivity in the pancreatic
tissue of patients with pancreatic lesions, and electron microscopy
reveals structures resembling HBV core particles in both the
nucleus and cytoplasm. Jin et al (78) demonstrated that HBsAg and HBcAg
are expressed in both pancreatic cancer tissue (21%, 34/162) and
non-tumorous pancreatic tissue (29%, 47/162) and that both HBsAg
and HBcAg are significantly associated with the occurrence of
chronic pancreatitis (78). The
aforementioned study also revealed the presence of the S, C, and X
genes of HBV in pancreatic cancer (20%, 6/30) and non-cancerous
pancreatic tissue samples (26.9%, 7/26). Notably, HBV DNA and
anti-HBc antibody positivity are significantly higher in patients
with pancreatic cancer compared with healthy controls (78). Taranto et al (79) suggested that mild pancreatic
injury, indicated by elevated pancreatic amylase levels, may occur
during the early stages of acute viral hepatitis. Chronic HBV
infection and the presence of HBsAg notably increase the risk of
pancreatic cancer (80).
Similarly, Iloeje et al (81) found that chronic HBV infection
may be associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer, with
a notably higher risk in HBsAg-positive patients with HBV DNA ≥300
copies/ml, compared with those with HBV DNA <300 copies/ml.
Additionally, the rate of synchronous liver metastasis in
HBsAg-positive patients and those with chronic HBV infection is
significantly lower than in HBsAg-negative patients and non-HBV
infection groups, suggesting that HBV infection may influence the
occurrence of liver metastasis and serve as an independent
prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer (82). Given the higher detectability of
HBV DNA in patients with pancreatic cancer, this suggests a
potential role of latent HBV infection in pancreatic cancer
progression. Latent HBV infection may not only serve as a reservoir
for HBV following HBsAg clearance but could also trigger a mild yet
prolonged necrotic inflammatory process, promoting the development
of pancreatic cancer (78). A
meta-analysis has shown that HBsAg positivity is associated with an
increased risk of pancreatic cancer, while anti-HBc positivity also
suggests an elevated risk, though the findings are not
statistically significant, indicating the need for further studies
to clarify the association between chronic HBV infection and
pancreatic cancer (83). Beyond
HBV and HCV, torque teno virus (TTV), a liver-tropic virus first
isolated from a patient with acute post-transfusion hepatitis in
1997, is considered a pathogenic factor in acute hepatitis
(84). TTV has been detected not
only in the liver but also in the pancreas: TTV DNA has been found
in patients with unexplained hepatitis who later develop pancreatic
cancer, suggesting a potential link between TTV and pancreatic
cancer (85). However, further
research is needed to confirm this association (85).
The role of hepatitis viruses in pancreatic cancer
development may be associated with inflammation, as HBsAg and HBcAg
positivity in pancreatic tissue significantly increases the
incidence of chronic pancreatitis (78). Following liver transplantation,
pancreatic inflammation occurs is often associated with acute HBV
infection in the transplanted liver (86), supporting the hypothesis that HBV
may induce pancreatic cancer through inflammatory mechanisms.
Additionally, a previous study suggests a notable interaction
between a history of diabetes and chronic HBV infection, further
increasing the risk of PDAC (80). There is a higher incidence of
latent HBV infection in diabetic patients compared with healthy
controls, which may be linked to the high incidence of primary
hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients (87). The pathogenesis of type 2
diabetes also involves pancreatitis (88), supporting the potential role of
HBV in promoting pancreatic cancer through inflammation. Moreover,
hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) expression upregulates ErbB4 and
TGF-α expression, activating the PI3K/AKT, MAPK, and ERK signaling
pathways, thereby promoting the proliferation and invasion of
pancreatic cancer cells. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway
reverses the effects of HBx in PDAC cell lines (89). Therefore, HBx may promote
pancreatic cancer progression by modulating these pathways
(89).
Mechanisms of gut microbiota-mediated
pancreatic cancer progression
Microbial-induced inflammatory
pathways
Pancreatic inflammation serves a key role in the
development of pancreatic cancer, with evidence indicating a
significantly higher risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with
chronic pancreatitis (90).
Increasing evidence suggests that microbial infection contributes
to the progression of pancreatitis (91,92). Dysbiosis in the gastrointestinal
microbiota leads to the proliferation of harmful bacteria, which
disrupt the epithelial barrier, allowing pathogenic bacteria to
migrate to the pancreas. The colonization of these harmful bacteria
in the pancreas triggers pancreatic inflammation (92). Serra et al (93) showed that Gram-negative bacteria
contribute to the promotion of tumor-associated inflammatory
responses.
The pro-inflammatory effects of microbes involve
pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and their associated signaling
molecules. NOD-like receptors (NLRs), which are cytosolic PRRs,
activate NF-κB signaling pathways upon recognition of
microbial-associated molecular patterns (Fig. 2). This activation not only
triggers NF-κB signaling but also promotes inflammasome formation
(94). One of the key components
of activated inflammasomes is caspase-1, which facilitates the
cleavage and maturation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as
IL-1β and IL-18 (95).
Inflammasomes are key regulators of the host defense against
pathogen invasion and maintaining intestinal microbial balance.
Mice lacking NLRs exhibit alterations in gut microbiota and
microbial dysbiosis, which leads to the development of inflammatory
disease (96). Mice with NOD1,
Nlrp3 or caspase-1 knockout show reduced acute pancreatitis induced
by cerulein, indicating the key role of inflammasomes in the
promotion of pancreatitis (97).
Moreover, NOD1 responds to gut microbiota and promotes the
activation of NF-κB and STAT3. Activation of these pathways
enhances the production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
(MCP-1), which recruits C-C chemokine receptor type 2-posotive
(CCR2+) inflammatory cells to the pancreas, thereby
initiating pancreatitis (98).
STAT3 is a key participant in pancreatitis and is activated in
cerulein-challenged mice. In wild-type mice, STAT3 activation is
transient and returns to baseline as the pancreas recovers from
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. However, in KC mice (mice with
KRAS mutations in pancreatic epithelial cells), STAT3 activation
persists due to the recruitment of myeloid cells, which secrete
IL-6, activating STAT3 in the pancreas (99,100). Persistent STAT3 activation
promotes the expression of cytokines, chemokines and other
mediators, such as IL-6 and COX2, further driving pancreatic cancer
progression (100,101). Additionally, STAT3 induces the
expression of MMP-7, which facilitates tumor metastasis (99). Germ-free mice exhibit fewer
gastrointestinal malignancies, potentially due to decreased
tumor-associated inflammation (102). This anti-tumor effect was also
confirmed in mice treated with antibiotics to decrease
gastrointestinal microbiota (102). Although the aforementioned
studies have not been verified in pancreatic cancer models, similar
evidence suggests that antibiotic-induced gut sterilization
alleviates acute pancreatitis (91).
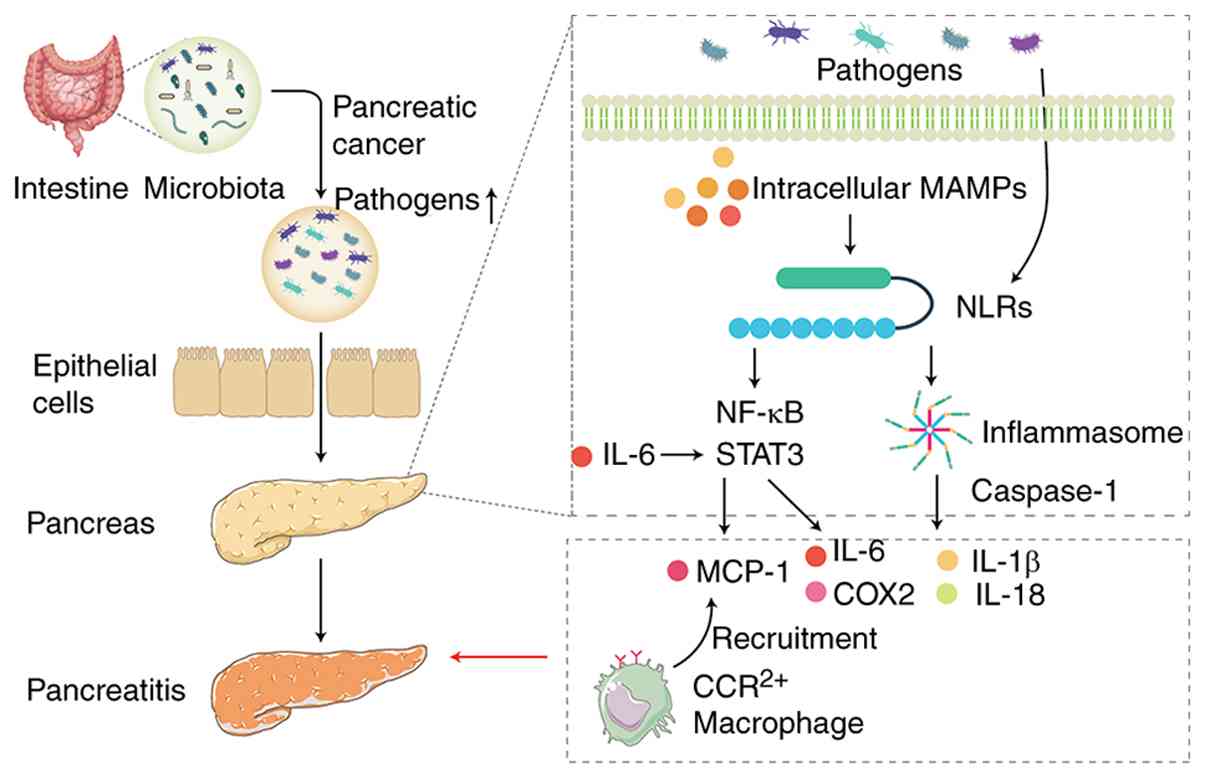 | Figure 2Microbial infection and inflammatory
pathways in pancreatitis and cancer development. Dysbiosis of the
gut microbiota leads to the proliferation of harmful bacteria,
disrupting the intestinal epithelial barrier and allowing
pathogenic bacteria to migrate to the pancreas, triggering an
inflammatory response. NLRs activate the NF-κB signaling pathway
and promote inflammasome formation following recognition of MAMPs.
A key component of inflammasomes, caspase-1, facilitates the
maturation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-18,
exacerbating the inflammatory response. NOD1 responds to gut
microbiota and activates the NF-κB and STAT3 pathways, leading to
the production of MCP-1, which recruits CCR2+
inflammatory cells to the pancreas. Persistent activation of STAT3
promotes the production of cytokines and chemokines such as IL-6
and COX2. Figure created using Adobe Illustrator 2025 (Adobe,
Inc.). MAMP, microbial-associated molecular pattern; NLR, Nod-like
receptor; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; CCR, C-C
chemokine receptor. |
Gut microbiota regulation of the immune
system in pancreatic cancer
Changes in the gut microbiota present within
pancreatic cancer tissue contribute to immune suppression within
the tumor microenvironment (Fig.
3). Pushalkar et al (58) demonstrated that administering
oral antibiotics to eliminate gut microbiota effectively inhibits
tumor progression. However, this effect is not observed in
recombination activating gene 1 (Rag1) knockout mice, suggesting
that the immune system is essential for gut microbiota-mediated
regulation of tumor development (45). Furthermore, depletion of gut
microbiota led to a marked increase in T cells producing IFN-γ,
while the populations of T cells secreting IL-17A and IL-10 are
notably decreased (45). In the
pancreatic cancer tumor microenvironment, the Th2/Th1 ratio is
considered an independent prognostic marker for patient survival. A
decrease in this ratio is associated with notably prolonged overall
survival (103). This suggests
that the removal of gut microbiota inhibits tumor growth by
increasing Th1 responses and decreasing Th17 and regulatory T cell
responses. Thomas et al (104) investigated the effects of
microbiota depletion in KrasG12D/PTENlox/+
mice, showing that microbiota-depleted mice exhibit fewer poorly
differentiated tumors. Furthermore, in a xenograft model of PDAC in
non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD-SCID)
mice, tumor growth is inhibited in microbiota-depleted mice
compared with microbiota-intact controls (104). The aforementioned study also
observed a notable increase in CD45+ immune cells within
PDAC xenografts derived from mice subjected to gut microbiota
depletion, implying intestinal microbiota may contribute to the
suppression of innate immune responses (104). Pushalkar et al (58) demonstrated that in KC mice (Kras;
p48Cre), the decrease in gut microbiota resulted in
diminished infiltration of myeloid-derived suppressor cells within
tumor tissues. This microbial alteration also facilitates the
polarization of tumor-associated macrophages toward the
pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype and supports the differentiation of
CD4+ Th cells toward the Th1 subtype. Additionally,
microbiota depletion leads to a significant rise in the expression
of PD-1 on effector T cells (58). Fecal bacteria from PDAC mice
inhibit the tumor-protective effects observed in
microbiota-depleted KC mice, whereas fecal bacteria from normal
mice do not have this effect (58). The immunosuppressive effects of
PDAC-associated bacterial extracts are abolished in macrophages
lacking TLR signaling (58).
These observations indicate that manipulating the gut microbiota
may affect the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy
and they offer strong evidence for the role of gut microbes in
reprogramming immune responses through TLR signaling pathways. TLRs
are well-studied PRRs that detect pathogen- and damage-associated
molecular patterns (DAMPs). When TLR activation is not properly
regulated, it may result in impairments in immune function
(105). Following activation,
TLRs recruit signaling molecules such as MyD88 or
TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF), further
activating the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. In patients with pancreatic
cancer and mouse models, the expression of TLR4 and TLR7 is
upregulated (106,107). The upregulated TLRs bind to
DAMPs, promoting immune cell release of inflammatory mediators,
which alter the tumor microenvironment and promote pancreatic
cancer progression (106).
Blocking MyD88 can inhibit the immunosuppressive effects of
fecal-derived extracts from KC mice, evidenced by the activation of
CD4+ T cells and the upregulation of immune mediators
such as lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1), CD44, TNF
and IFN-γ (58,107). These data support the
hypothesis that gut microbiota mediates immune suppression and
promotes tumor proliferation via TLRs, particularly TLR2 and TLR5
pathways and downstream MyD88 signaling.
Regulation of pancreatic cancer by
microbial metabolites
SCFAs and pancreatic cancer
Microbes are key regulators of metabolic processes
and studies have shown that microbial metabolites can impact both
gut and systemic homeostasis, thereby influencing tumorigenesis
(62,108) (Fig. 4). Evidence has outlined the
primary categories of microbial metabolites and their potential
association with pancreatic cancer (Table I) (110-115,117-119,123). Among these metabolites, SCFAs
are a key group generated by the fermentation of indigestible
carbohydrates through gut microbial activity (109). These include lactate, acetate
and butyrate. Data obtained through single-cell RNA sequencing have
identified a negative association between lactate metabolism
markers and anti-tumor immune responses, along with disruptions in
immune cell infiltration patterns (109). By contrast, these markers have
shown a positive association with signaling pathways that support
tumor progression (109).
Furthermore, the elimination of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), a
key enzyme governing lactate production in pancreatic cancer cells,
enhances the activity of CD8+ T cells involved in
anti-tumor immunity and improves the overall effectiveness of
immunotherapy (109). A similar
study (110) suggested that
increased LDHA expression in the tumor microenvironment of PDAC is
a poor prognostic factor for patients with PDAC. In a mouse model
of PDAC enriched with cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), LDHA
depletion inhibits tumor growth (110). The aforementioned study also
found that lactate is taken up by CAFs via monocarboxylate
transporter 1, promoting CAF proliferation. Additionally, lactate
upregulates IL-6 expression in CAFs, which suppresses immune cell
activity (110).
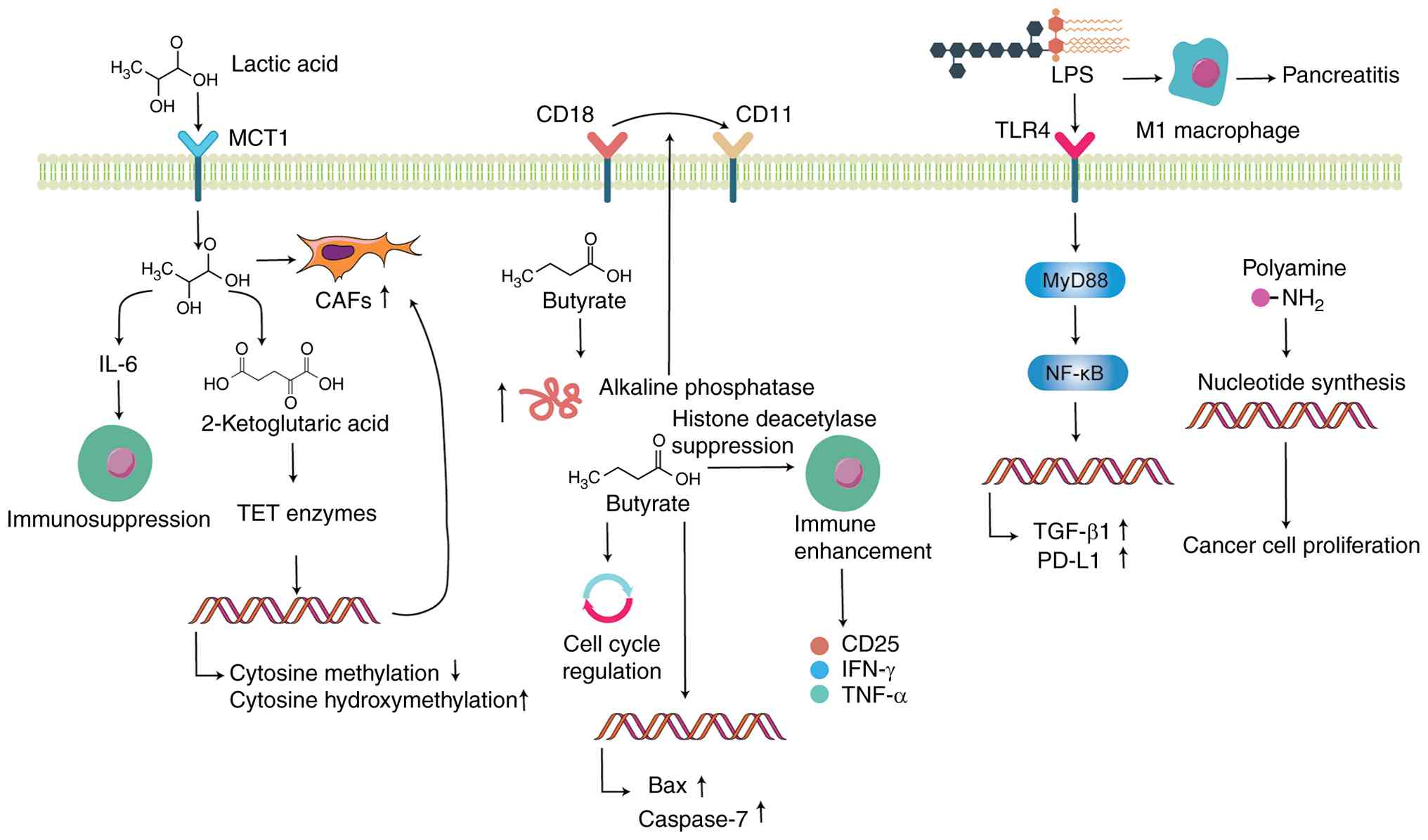 | Figure 4Gut microbiota metabolites and
pancreatic cancer progression. Lactic acid, a short-chain fatty
acid, is absorbed by CAFs via MCT1, promoting CAF proliferation and
upregulating IL-6 expression, which suppresses immune cell activity
and enhances CAF formation via α-ketoglutarate-dependent TET
enzymes. Butyrate increases alkaline phosphatase activity,
facilitating the conversion of CD18 to CD11 cells. Additionally,
butyrate inhibits the cell cycle progression, increases the
expression of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and caspase-7 and
suppresses pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Butyrate enhances
immune cell activity and stimulates the production of immune
factors such as CD25, IFN-γ and TNF-α. LPS, via the
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway, elevates the production of
PD-L1 and TGF-β1 in tumor cells, promoting pancreatic cancer
progression. LPS promotes M1 polarization of macrophages,
contributing to pancreatic inflammation. Polyamines drive tumor
proliferation by promoting the synthesis of purine and pyrimidine
nucleotides. Figure created using Adobe Illustrator 2025 (Adobe,
Inc.). CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; MCT, monocarboxylate
transporter; TET, 10-11 translocation; LPS, lipopolysaccharide;
TLR, toll-like receptor. |
 | Table IMicrobial metabolites and their
associations with pancreatic cancer progression. |
Table I
Microbial metabolites and their
associations with pancreatic cancer progression.
| Authors, year | Metabolite | Model |
Effect/mechanism | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Kitamura et
al, 2023 | Lactic acid | CAF-rich murine
PDAC | CAFs take up
lactate and promote their own proliferation via the TCA cycle;
lactate stimulates CAFs to express IL-6 and inhibits the activity
of cytotoxic immune cells | (110) |
| Bhagat et
al, 2019 | | PDAC cells with
CAFs | Lactate stimulates
the production of α-KG in MSCs, activating TET enzyme, which
decreases cytosine methylation and increases hydroxymethylation,
promoting MSC differentiation into CAFs and boosting PDAC
invasiveness | (111) |
| Mullins et
al, 1991 | Butyrate | HPAF cell line | Increased alkaline
phosphatase activity notably promotes the transition of CD18 to
CD11 cells, facilitates the differentiation of pancreatic cancer
cell lines and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of PDAC
cells | (112) |
| Pellizzaro et
al, 2008 | | MIA PaCa-2
cells | Arrests the cell
cycle at G0/G1 and G2/M phases, upregulates pro-apoptotic proteins
Bax and caspase-7, downregulates angiogenesis-associated proteins
VEGF-A165 and VEGF-D and inhibits proliferation of pancreatic
cancer cells | (113) |
| Kanika et
al, 2015 | Sodium
butyrate | Wistar rat | Inhibits
L-arginine-induced pancreatic fibrosis and pancreatic injury | (114) |
| Luu et al,
2021 | Valerate and
butyrate | CTLs and CAR T
cells | Inhibits the
activity of class I histone deacetylase, enhances the
anti-pancreatic cancer tumor activity of CTLs and CAR T cells,
increases the expression of effector molecules such as CD25, IFN-γ
and TNF-α | (115) |
| Sivam et al,
2023 |
Lipopolysaccharide | PDAC cells and RAW
264.7 macrophages | Promotes the
activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, increases the expression of IL-1β
and TNF-α, facilitates the formation of a pro-inflammatory
microenvironment and enhances the survival of PDAC cells | (117) |
| Peng et al,
2023 | | C57BL/6J mouse | Promotes macrophage
M1 polarization and exacerbates pancreatitis via the MLKL/CXCL10
pathway | (118) |
| Sun et al,
2018 | | Sprague-Dawley
rat | Increases TGF-β1
production by activating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway,
promoting the development of chronic pancreatitis | (119) |
| Mendez et
al, 2020 | Polyamine | KPC mouse | Metabolic pathways
associated with polyamine biosynthesis are upregulated in the gut
microbiota of PDAC mice and mice with PanIN show increased serum
polyamine levels | (123) |
Lactate induces the production of α-ketoglutarate
in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). This activates 10-11
translocation enzymes, resulting in decreased DNA methylation and
increased hydroxymethylation, an epigenetic modification that
promotes MSC differentiation into CAFs, contributing to the
invasive behavior of PDAC (111). Butyrate enhance alkaline
phosphatase activity and facilitates the transformation of CD18
into CD11 cells, which contributes to the differentiation of
pancreatic cancer cell lines and suppression of PDAC cell
proliferation and invasion (112). Moreover, a butyrate compound
conjugated with hyaluronic acid induces cell cycle arrest at both
the G0/G1 and G2/M phases. This compound also promotes the
expression of pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bax and caspase-7,
while concurrently reducing the levels of angiogenesis-associated
factors including VEGF-A165 and VEGF-D, thereby inhibiting the
proliferation of the MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cell line
(113). In a study by Ren et
al (62), gut microbiota
profiles of patients with pancreatic cancer and healthy controls
were compared using MiSeq sequencing. The results indicated a
higher abundance of pathogenic and LPS-producing bacteria in
patients with pancreatic cancer patients, whereas levels of
beneficial microbes, including butyrate-producing species and
probiotics, are diminished (62). These findings are in line with
the research by Kanika et al (114), who reported that sodium
butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, decreases pancreatic
fibrosis and injury induced by L-arginine in Wistar rats.
Additionally, an in vitro study (115) has shown that treating cytotoxic
T lymphocytes and chimeric antigen receptor T cells with pentanoate
and butyrate can enhance their anti-tumor functions against
pancreatic cancer. This is achieved through inhibition of class I
histone deacetylase activity and upregulation of effector molecules
such as CD25, IFN-γ and TNF-α (115). The aforementioned studies
suggest that different SCFA components may have distinct effects on
pancreatic cancer. Future research should focus on modulating the
gut microbiota, such as decreasing levels of lactate-producing
microbes and increasing levels of butyrate-producing microbes, to
regulate pancreatic cancer progression. However, further
experimental studies are needed.
Role of LPS in pancreatic cancer
LPS, a notable component of the outer membrane of
Gram-negative bacteria, is released into the surrounding
environment under the action of antibiotics or host immune cells
(116). In a co-culture system
involving PDAC cells and macrophages (RAW 264.7), stimulation with
LPS activates the NLRP3 inflammasome. This leads to elevated
expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α, which
contribute to the formation of a pro-inflammatory tumor
microenvironment and enhanced PDAC cell survival (117). Notably, this effect is
mitigated by MCC950, a selective inhibitor of the NLRP3
inflammasome (117). Peng et
al (118) established an
acute pancreatitis model in C57BL/6J mice using cerulein combined
with LPS. The results showed a marked increase in the expression of
mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) and phosphorylated
MLKL in pancreatic acinar cells, accompanied by a rise in M1-type
macrophage polarization. Disruption of MLKL or neutralization of
the chemokine CXCL10 decreases M1 macrophage polarization and
alleviates the severity of acute pancreatitis in cerulein and
LPS-induced acute pancreatitis C57BL/6J mice (118). Additionally, LPS has been shown
to enhance the production of TGF-β1 via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB
signaling pathway, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of
chronic pancreatitis (119). In
PDAC tissue, LPS also upregulates PD-L1 expression through the same
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway, facilitating tumor immune escape
mechanisms (40). The
aforementioned studies indicate that LPS promotes macrophage M1
polarization and contributes to the formation of an inflammatory
pancreatic microenvironment, which accelerates the progression of
pancreatic cancer, primarily via the NLRP3 inflammasome,
MLKL/CXCL10 pathway and TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling.
Polyamines in pancreatic cancer
progression
Polyamines are small polycationic molecules that
serve various biological roles, including gene regulation, stress
resistance and cell proliferation and differentiation (120). Polyamines promote synthesis of
purine and pyrimidine nucleotides by providing amino groups, which
supports rapid cell proliferation, making them potential biomarkers
for tumor progression (121).
The gut microbiota is associated with polyamine concentrations and
serves an essential role in regulating human gut polyamine levels
(122). In PDAC mice, notable
upregulation of the metabolic pathways associated with polyamine
biosynthesis in the gut microbiota is observed (123). Serum analysis shows increased
polyamine concentrations in mice with pancreatic intraepithelial
neoplasia, even without observable tumors (123). The aforementioned study also
detected Lactobacillus in the gut microbiota of 4-month-old
LSL-KrasG12D/+; LSL-Trp53R172H/+; Pdx1-Cre)
mice and metabolomic analysis demonstrates an association between
Lactobacillus and polyamine metabolism (123). This confirms the role of
polyamines as microbial metabolites in promoting pancreatic cancer
progression. Similar finding has been reported in gastric cancer,
where H. pylori regulates polyamine metabolism to facilitate
tumor progression (124). The
aforementioned studies suggest that gut microbiota imbalances, such
as an increase in Lactobacillus, promote polyamine
synthesis, thereby serving a notable role in pancreatic cancer
progression. Future research should focus on the inhibition of
polyamine metabolism and its association with pancreatic cancer to
enhance microbiota modulation strategies for pancreatic cancer
therapy.
Extracellular polymeric substance
(EPS)
In the clinical context of malignant biliary
obstruction due to pancreatic cancer, intraductal drains and stents
provide artificial surfaces that facilitate microbial adhesion and
colonization (125). These
conditions promote production of EPS and subsequent biofilm
formation. EPS, which comprises polysaccharides, protein and
extracellular DNA (eDNA), constitute the structural and functional
core of biofilms (126). This
matrix governs adhesion, antimicrobial tolerance, immune evasion
and mechanical stability, thereby influencing the control of
jaundice, the incidence of cholangitis and the timing and efficacy
of systemic anticancer therapy (127,128). Before and after surgery, as
well as during palliative treatment, >60% of pancreatic cancer
cases arise in the pancreatic head, invade the bile duct and
produce obstructive jaundice that necessitates endoscopic
transpapillary stent placement (129). Multispecies communities and
matrix-like EPS deposits emerge rapidly within the stent lumen.
These changes form the pathological basis for stent re-occlusion
and infection (129). Biliary
stents retrieved from malignant obstruction associated with
pancreatic cancer demonstrate that proteins and polysaccharides are
the predominant, quantifiable components of the biofilm matrix.
This implies a material basis linking EPS burden to stent failure
(130). Metagenomic and
culture-based investigation further shows that among patients
undergoing pancreatic surgery or stent placement, biofilms within
biliary stents are enriched with bacteria of oral and intestinal
origin and contain gene clusters associated with biofilm formation
and antimicrobial resistance (125). These findings indicate that
diverse microorganisms in the biliary environment rely on EPS for
adhesion, cooperative community behavior and drug tolerance
(125). Consistent with these
results, prospective cohort data show that plastic biliary stents
are almost invariably colonized by bacterial and fungal biofilms
with broad resistance spectra (131). This suggests that systemic
antimicrobial therapy alone is unlikely to eradicate organisms
embedded within biofilms, a limitation associated with the barrier
function of EPS (131). With
regard to clinical outcomes, in patients with gastrointestinal
malignancy complicated by malignant biliary obstruction, the
presence of cholangitis before percutaneous or endoscopic biliary
drainage is associated with notably worse overall survival. This
association indicates that biofilm-associated infection narrows the
therapeutic window for systemic treatment in pancreatic cancer,
with EPS-mediated barriers to both antimicrobials and host defenses
as key etiological factors (132). Within EPS, polysaccharides and
proteins crosslink through electrostatic and hydrophobic
interactions to form a three-dimensional network. This network
confers high viscoelasticity and low permeability, limits bacterial
detachment under bile flow shear and restricts the diffusion of
bile acids, antibiotics and complement. The resulting
physicochemical shield provides the microscopic basis for biliary
stent re-occlusion (133).
eDNA, a key scaffold component of EPS, binds multivalent cations
and cationic antimicrobial peptides, thereby depleting local
divalent ions. This upregulates bacterial membrane modification
pathways and increases the minimum inhibitory concentrations of
aminoglycosides and cationic peptides by several-fold (134). This chemical antagonism has
been demonstrated in vitro and may explain the persistence
of biofilm-associated resistance in clinical settings (134). In a polymicrobial in
vitro model, exogenous DNase alone or in combination with
protease markedly weakens biofilm structure, decreases colony
viability and improves antibiotic penetration (135). These findings suggest that
enzymatic strategies targeting EPS degradation may serve as
intrastent or locally irrigated adjuncts for infection associated
with biliary stents in pancreatic cancer. Nevertheless, biliary
safety and pharmacokinetics require clinical validation (136). Beyond common members of
Enterobacteriaceae and enterococci, biliary stent biofilms may
accumulate oral streptococci and actinomycetes (125). Features of the biofilm
microbiota, such as polymicrobial community structure, dominance of
taxa including Streptococcus anginosus, Escherichia
coli and Enterococcus faecalis, and enrichment of
biofilm and antimicrobial resistance genes, are associated with
time to re-occlusion, which provides new evidence to support
individualized stent management and materials science-based
improvements in patients with pancreatic cancer (137).
Taken together, biliary obstruction resulting from
pancreatic cancer and the use of drainage devices supply a stable
substratum for microbial adhesion. EPS-driven biofilms exert system
level effects on infection, re-occlusion, limit the access of host
immune cells and soluble mediators to the stent surface and
surrounding tissue, and alter drug permeability. These phenomena
define a strategic bridge between device management in the biliary
tract and the overall effectiveness of comprehensive therapy for
pancreatic cancer.
Gut microbiota and chemotherapy
resistance in pancreatic cancer
Surgical resection followed by adjuvant
chemotherapy is the preferred treatment strategy for early-stage
pancreatic cancer. However, drug resistance to chemotherapy notably
contributes to poor clinical prognosis (138). Gemcitabine is the first-line
chemotherapy drug for patients with pancreatic cancer not eligible
for surgical resection (139).
Evidence (70) has shown that
certain bacteria, such as Gammaproteobacteria including
Escherichia coli, in pancreatic tissue contribute to drug
resistance by expressing long-form cytidine deaminase. This enzyme
converts gemcitabine (2,2-difluorodeoxycytidine) into its inactive
form (2,2-difluorodeoxyuridine), thereby leading to drug resistance
(70). This finding is
consistent with research by Bengala et al (140), which reported that high
expression of cytidine deaminase (CDA) in patients with advanced
pancreatic cancer is associated with significantly higher rates of
early disease progression and shorter overall survival. In
addition, Mycoplasma hyorhinis infection is implicated in
various types of cancer in humans, including gastric and colon
carcinoma, esophageal and lung cancers, breast cancer and gliomas
(141). Gemcitabine is
converted into its inactive form in tumor cell extracts from M.
hyorhinis-infected cells (142). Furthermore, the use of cytidine
deaminase inhibitors restores the activity of gemcitabine in these
cells, indicating that M. hyorhinis produces mycoplasma
cytidine deaminase, which facilitates the metabolism of gemcitabine
(142). Weniger et al
(143) discovered that
gemcitabine therapy improved progression-free survival in patients
with pancreatic cancer negative for Klebsiella pneumoniae,
but no significant improvement was observed in patients positive
for this bacterium. Additionally, the use of quinolone antibiotics
in K. pneumoniae-positive patients notably improved their
overall survival. These findings suggest that K. pneumoniae
may serve a key role in the development of gemcitabine resistance
in pancreatic cancer (143).
Moreover, in a type 2 diabetes mouse model, the development of
hyperglycemia leads to significant changes in the gut microbiota,
resulting in a poorer response of pancreatic cancer tumors to
gemcitabine/paclitaxel treatment. Genomic analysis reveals that the
microbiota in the diabetic group is enriched with bacteria involved
in menadione biosynthesis (144). By increasing the concentration
of menadione, these bacteria protect tumor cells from oxidative
damage caused by chemotherapy, contributing to the development of
drug resistance (144). F.
nucleatum has been reported to promote pancreatic cancer
progression (145). In
colorectal cancer, F. nucleatum activates autophagy via the
TLR4/MyD88 pathway and selectively inhibits certain miRNAs (such as
miR-18a-3p and miR-4802), thereby leading to resistance to
capecitabine (146).
Udayasuryan et al (145)
identified Bacteroides ovatus and Bacteroides
xylanisolvens as positively associated with therapeutic
efficacy. Oral administration of B. ovatus and B.
xylanisolvens enhances the efficacy of erlotinib in a lung
cancer mouse model (147). The
aforementioned studies highlight that gut microbiota can influence
the metabolism of chemotherapy drugs in the host and, through
metabolic reprogramming, affect the efficacy of the drugs, leading
to the development of drug resistance. This provides a direction
for future research to improve chemotherapy efficacy by modulating
specific gut microbiota.
Conclusion
The present review systematically explores how
circadian rhythm disruption influences pancreatic cancer
development by regulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites.
With the increasing incidence of pancreatic cancer and its high
mortality rate, there is need to gain a deeper understanding of its
underlying pathological mechanisms to identify effective preventive
and therapeutic strategies. Circadian rhythm disruption increases
the risk of pancreatic cancer, with this heightened risk associated
with changes in the gut microbiota. Disruption of circadian rhythms
leads to an increased risk of H. pylori infection, which is
associated with pancreatic cancer, and induces alterations in the
abundance of microbiota associated with pancreatic cancer. This
includes changes in the levels of microbial metabolites and
disruption of the intestinal barrier, which allows pathogens,
including LPS, to enter the systemic circulation. These pathogens
and LPS promote the progression of pancreatitis, a risk factor for
pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, gut microbiota also contributes to
immune suppression in the host through TLRs. Metabolites from the
microbiota, such as SCFAs, LPS and polyamines, regulate the
progression of pancreatic cancer. Specific gut microbes are
involved in the degradation of chemotherapy drugs, leading to the
development of drug resistance. Integrating these findings, the
present review proposes a coherent, bidirectional mechanistic
framework: circadian disruption may promote the development of
pancreatic cancer by reshaping the gut microbiota and its
metabolites, while microbial metabolites such as butyrate and TMAO,
in turn, regulate core clock components (CLOCK and BMAL1),
potentially creating a feed-forward loop that reinforces circadian
misalignment and tumor progression.
The gut microbiota is associated with risk factors
for PDAC, such as diabetes, obesity and diet. Future research
should focus on clarifying whether changes in the microbiota are
primary initiators of cancer progression or responses to these
factors. Future studies should investigate the dominant microbial
communities in the gut and pancreatic tissue of patients with
pancreatic cancer and analyze the relationship between gut and
pancreatic microbiota. Such studies may facilitate the application
of gut microbiota modulation in pancreatic cancer treatment.
Additionally, considering the role of intra-pancreatic microbes in
drug resistance, further research should explore the association
between the dominant microbial communities in the pancreas and
chemotherapy drug metabolism to improve the application of gut
microbiota modulation in overcoming pancreatic cancer chemotherapy
resistance.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
YaL and YoL performed the literature review and
wrote the manuscript. HM, SD and CC constructed figures and tables.
Data authentication is not applicable. All authors have read and
approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of
Hubei Province (grant no. 2023AFB991).
References
|
1
|
GBD 2017 Pancreatic Cancer Collaborators:
The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and
its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories,
1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease
study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:934–947. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He J, Ahuja N, Makary MA, Cameron JL,
Eckhauser FE, Choti MA, Hruban RH, Pawlik TM and Wolfgang CL: 2564
resected periampullary adenocarcinomas at a single institution:
Trends over three decades. HPB (Oxford). 16:83–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zeng L, Wu Z, Yang J, Zhou Y and Chen R:
Association of genetic risk and lifestyle with pancreatic cancer
and their age dependency: A large prospective cohort study in the
UK Biobank. BMC Med. 21:4892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li X and Liang Z: Causal effect of gut
microbiota on pancreatic cancer: A Mendelian randomization and
colocalization study. J Cell Mol Med. 28:e182552024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhatt AP, Redinbo MR and Bultman SJ: The
role of the microbiome in cancer development and therapy. CA Cancer
J Clin. 67:326–344. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li P, Shu Y and Gu Y: The potential role
of bacteria in pancreatic cancer: A systematic review.
Carcinogenesis. 41:397–404. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bass J and Lazar MA: Circadian time
signatures of fitness and disease. Science. 354:994–999. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Allada R and Bass J: Circadian mechanisms
in medicine. N Engl J Med. 384:550–561. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li W, Liu L, Liu D, Lin S, Yang Y, Tang W
and Gong L: Decreased circadian component Bmal1 predicts tumor
progression and poor prognosis in human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 472:156–162. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zarrinpar A, Chaix A, Yooseph S and Panda
S: Diet and feeding pattern affect the diurnal dynamics of the gut
microbiome. Cell Metab. 20:1006–1017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Paulose JK, Wright JM, Patel AG and
Cassone VM: Human gut bacteria are sensitive to melatonin and
express endogenous circadian rhythmicity. PLoS One.
11:e01466432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bishehsari F, Voigt RM and Keshavarzian A:
Circadian rhythms and the gut microbiota: From the metabolic
syndrome to cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 16:731–739. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schwartz PB, Nukaya M, Berres ME,
Rubinstein CD, Wu G, Hogenesch JB, Bradfield CA and
Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM: The circadian clock is disrupted in pancreatic
cancer. PLoS Genet. 19:e10107702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amara S, Yang LV, Tiriveedhi V and
Muzaffar M: Complex role of microbiome in pancreatic tumorigenesis:
Potential therapeutic implications. Cells. 11:19002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Subramanian SK, Brahmbhatt B,
Bailey-Lundberg JM, Thosani NC and Mutha P: Lifestyle medicine for
the prevention and treatment of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
Diagnostics (Basel). 14:6142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
IARC Monographs Vol 124 group:
Carcinogenicity of night shift work. Lancet Oncol. 20:1058–1059.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu F, Xu S, Devesa SS, Zhang F, Klerman
EB, Graubard BI and Caporaso NE: Longitude position in a time zone
and cancer risk in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 26:1306–1311. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Parent M, El-Zein M, Rousseau MC, Pintos J
and Siemiatycki J: Night work and the risk of cancer among men. Am
J Epidemiol. 176:751–759. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao Q, Jones RR, James P and
Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ: Light at night and risk of pancreatic
cancer in the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Cancer Res.
81:1616–1622. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Titova OE, Michaëlsson K, Vithayathil M,
Mason AM, Kar S, Burgess S and Larsson SC: Sleep duration and risk
of overall and 22 site-specific cancers: A mendelian randomization
study. Int J Cancer. 148:914–920. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Loosen S, Krieg S, Krieg A, Leyh C, Luedde
T, Vetter C, Kostev K and Roderburg C: Are sleep disorders
associated with the risk of gastrointestinal cancer?-A case-control
study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:11369–11378. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dun A, Zhao X, Jin X, Wei T, Gao X, Wang Y
and Hou H: Association between night-shift work and cancer risk:
Updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol.
10:10062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang X, Bushman FD and FitzGerald GA:
Rhythmicity of the intestinal microbiota is regulated by gender and
the host circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:10479–10484.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thaiss CA, Zeevi D, Levy M,
Zilberman-Schapira G, Suez J, Tengeler AC, Abramson L, Katz MN,
Korem T, Zmora N, et al: Transkingdom control of microbiota diurnal
oscillations promotes metabolic homeostasis. Cell. 159:514–529.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li S, Duan Y, Luo S, Zhou F, Wu Q and Lu
Z: Short-chain fatty acids and cancer. Trends Cancer. 11:154–168.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li Q, Xu T, Shao C, Gao W, Wang M, Dong Y,
Wang X, Lu F, Li D, Tan H, et al: Obstructive sleep apnea is
related to alterations in fecal microbiome and impaired intestinal
barrier function. Sci Rep. 13:7782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Summa KC, Voigt RM, Forsyth CB, Shaikh M,
Cavanaugh K, Tang Y, Vitaterna MH, Song S, Turek FW and
Keshavarzian A: Disruption of the circadian clock in mice increases
intestinal permeability and promotes alcohol-induced hepatic
pathology and inflammation. PLoS One. 8:e671022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Everson CA and Toth LA: Systemic bacterial
invasion induced by sleep deprivation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 278:R905–R916. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Irwin M, Thompson J, Miller C, Gillin JC
and Ziegler M: Effects of sleep and sleep deprivation on
catecholamine and interleukin-2 levels in humans: Clinical
implications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 84:1979–1985.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jacob C, Yang PC, Darmoul D, Amadesi S,
Saito T, Cottrell GS, Coelho AM, Singh P, Grady EF, Perdue M and
Bunnett NW: Mast cell tryptase controls paracellular permeability
of the intestine. Role of protease-activated receptor 2 and
beta-arrestins. J Biol Chem. 280:31936–31948. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Spindler LRB, Luppi AI, Adapa RM, Craig
MM, Coppola P, Peattie ARD, Manktelow AE, Finoia P, Sahakian BJ,
Williams GB, et al: Dopaminergic brainstem disconnection is common
to pharmacological and pathological consciousness perturbation.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e20262891182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang X, Wang Z, Cao J, Dong Y and Chen Y:
Gut microbiota-derived metabolites mediate the neuroprotective
effect of melatonin in cognitive impairment induced by sleep
deprivation. Microbiome. 11:172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pollmächer T, Mullington J, Korth C,
Schreiber W, Hermann D, Orth A, Galanos C and Holsboer F: Diurnal
variations in the human host response to endotoxin. J Infect Dis.
174:1040–1045. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Silver AC, Buckley SM, Hughes ME, Hastings
AK, Nitabach MN and Fikrig E: Daily oscillations in expression and
responsiveness of Toll-like receptors in splenic immune cells.
Heliyon. 4:e005792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Curtis AM, Fagundes CT, Yang G,
Palsson-McDermott EM, Wochal P, McGettrick AF, Foley NH, Early JO,
Chen L, Zhang H, et al: Circadian control of innate immunity in
macrophages by miR-155 targeting Bmal1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:7231–7236. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tran L, Jochum SB, Shaikh M, Wilber S,
Zhang L, Hayden DM, Forsyth CB, Voigt RM, Bishehsari F,
Keshavarzian A and Swanson GR: Circadian misalignment by
environmental light/dark shifting causes circadian disruption in
colon. PLoS One. 16:e02516042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu L, Li G, Shu Y, Hou X, Yang L and Jin
Y: Circadian dysregulation induces alterations of visceral
sensitivity and the gut microbiota in Light/Dark phase shift mice.
Front Microbiol. 13:9359192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yin H, Pu N, Chen Q, Zhang J, Zhao G, Xu
X, Wang D, Kuang T, Jin D, Lou W and Wu W: Gut-derived
lipopolysaccharide remodels tumoral microenvironment and synergizes
with PD-L1 checkpoint blockade via TLR4/MyD88/AKT/NF-κB pathway in
pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 12:10332021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Massoumi RL, Teper Y, Ako S, Ye L, Wang E,
Hines OJ and Eibl G: Direct effects of lipopolysaccharide on human
pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreas. 50:524–528. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu X, Chen L, Zeb F, Huang Y, An J, Ren J,
Yang F and Feng Q: Regulation of circadian rhythms by NEAT1
mediated TMAO-induced endothelial proliferation: A protective role
of asparagus extract. Exp Cell Res. 382:1114512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu A, Zhang Y, Xun S and Sun M:
Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes atherosclerosis via regulating the
enriched abundant transcript 1/miR-370-3p/signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3/flavin-containing monooxygenase-3
axis. Bioengineered. 13:1541–1553. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Lynch SV and Pedersen O: The human
intestinal microbiome in health and disease. N Engl J Med.
375:2369–2379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fan Y and Pedersen O: Gut microbiota in
human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 19:55–71.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sethi V, Kurtom S, Tarique M, Lavania S,
Malchiodi Z, Hellmund L, Zhang L, Sharma U, Giri B, Garg B, et al:
Gut microbiota promotes tumor growth in mice by modulating immune
response. Gastroenterology. 155:33–37.e36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Trikudanathan G, Philip A, Dasanu CA and
Baker WL: Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and
pancreatic cancer. A cumulative meta-analysis. JOP. 12:26–31.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schulte A, Pandeya N, Fawcett J, Fritschi
L, Risch HA, Webb PM, Whiteman DC and Neale RE: Association between
Helicobacter pylori and pancreatic cancer risk: A meta-analysis.
Cancer Causes Control. 26:1027–1035. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiao M, Wang Y and Gao Y: Association
between Helicobacter pylori infection and pancreatic cancer
development: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 8:e755592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Risch HA: Pancreatic cancer: Helicobacter
pylori colonization, N-nitrosamine exposures, and ABO blood group.
Mol Carcinog. 51:109–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Malfertheiner P, Camargo MC, El-Omar E,
Liou JM, Peek R, Schulz C, Smith SI and Suerbaum S: Helicobacter
pylori infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 9:192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Abasse KS, Essien EE, Abbas M, Yu X, Xie
W, Sun J, Akter L and Cote A: Association between dietary nitrate,
nitrite intake, and site-specific cancer risk: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 14:6662022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Luo J, Nordenvall C, Nyrén O, Adami HO,
Permert J and Ye W: The risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with
gastric or duodenal ulcer disease. Int J Cancer. 120:368–372. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lindkvist B, Johansen D, Borgström A and
Manjer J: A prospective study of Helicobacter pylori in relation to
the risk for pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. 8:3212008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mitsuhashi K, Nosho K, Sukawa Y, Matsunaga
Y, Ito M, Kurihara H, Kanno S, Igarashi H, Naito T, Adachi Y, et
al: Association of Fusobacterium species in pancreatic cancer
tissues with molecular features and prognosis. Oncotarget.
6:7209–7220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hayashi M, Ikenaga N, Nakata K, Luo H,
Zhong P, Date S, Oyama K, Higashijima N, Kubo A, Iwamoto C, et al:
Intratumor fusobacterium nucleatum promotes the progression of
pancreatic cancer via the CXCL1-CXCR2 axis. Cancer Sci.
114:3666–3678. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kohi S, Macgregor-Das A, Dbouk M, Yoshida
T, Chuidian M, Abe T, Borges M, Lennon AM, Shin EJ, Canto MI and
Goggins M: Alterations in the duodenal fluid microbiome of patients
with pancreatic cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:e196–e227.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Nejman D, Livyatan I, Fuks G, Gavert N,
Zwang Y, Geller LT, Rotter-Maskowitz A, Weiser R, Mallel G, Gigi E,
et al: The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor
type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science. 368:973–980. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Pushalkar S, Hundeyin M, Daley D,
Zambirinis CP, Kurz E, Mishra A, Mohan N, Aykut B, Usyk M, Torres
LE, et al: The pancreatic cancer microbiome promotes oncogenesis by
induction of innate and adaptive immune suppression. Cancer Discov.
8:403–416. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
D'Antonio DL, Zenoniani A, Umme S,
Piattelli A and Curia MC: Intratumoral fusobacterium nucleatum in
pancreatic cancer: Current and future perspectives. Pathogens.
14:22024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kartal E, Schmidt TSB, Molina-Montes E,
Rodríguez-Perales S, Wirbel J, Maistrenko OM, Akanni WA, Alhamwe
BA, Alves RJ, Carrato K, et al: A faecal microbiota signature with
high specificity for pancreatic cancer. Gut. 71:1359–1372. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Half E, Keren N, Reshef L, Dorfman T,
Lachter I, Kluger Y, Reshef N, Knobler H, Maor Y, Stein A, et al:
Fecal microbiome signatures of pancreatic cancer patients. Sci Rep.
9:168012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ren Z, Jiang J, Xie H, Li A, Lu H, Xu S,
Zhou L, Zhang H, Cui G, Chen X, et al: Gut microbial profile
analysis by MiSeq sequencing of pancreatic carcinoma patients in
China. Oncotarget. 8:95176–95191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kharofa J, Haslam D, Wilkinson R, Weiss A,
Patel S, Wang K, Esslinger H, Olowokure O, Sohal D, Wilson G, et
al: Analysis of the fecal metagenome in long-term survivors of
pancreas cancer. Cancer. 129:1986–1994. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Riquelme E, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Montiel M,
Zoltan M, Dong W, Quesada P, Sahin I, Chandra V, San Lucas A, et
al: Tumor microbiome diversity and composition influence pancreatic
cancer outcomes. Cell. 178:795–806.e712. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tan Q, Ma X, Yang B, Liu Y, Xie Y, Wang X,
Yuan W and Ma J: Periodontitis pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis
promotes pancreatic tumorigenesis via neutrophil elastase from
tumor-associated neutrophils. Gut Microbes. 14:20737852022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Gaiser RA, Halimi A, Alkharaan H, Lu L,
Davanian H, Healy K, Hugerth LW, Ateeb Z, Valente R, Moro CF, et
al: Enrichment of oral microbiota in early cystic precursors to
invasive pancreatic cancer. Gut. 68:2186–2194. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dickson I: Microbiome promotes pancreatic
cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:3282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tojo R, Suárez A, Clemente MG, de los
Reyes-Gavilán CG, Margolles A, Gueimonde M and Ruas-Madiedo P:
Intestinal microbiota in health and disease: Role of bifidobacteria
in gut homeostasis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:15163–15176. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sethi V, Vitiello GA, Saxena D, Miller G
and Dudeja V: The role of the microbiome in immunologic development
and its implication for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy.
Gastroenterology. 156:2097–2115.e2092. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Geller LT, Barzily-Rokni M, Danino T,
Jonas OH, Shental N, Nejman D, Gavert N, Zwang Y, Cooper ZA, Shee
K, et al: Potential role of intratumor bacteria in mediating tumor
resistance to the chemotherapeutic drug gemcitabine. Science.
357:1156–1160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nilsson HO, Stenram U, Ihse I and Wadstrom
T: Helicobacter species ribosomal DNA in the pancreas, stomach and
duodenum of pancreatic cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol.
12:3038–3043. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Takayama S, Takahashi H, Matsuo Y, Okada Y
and Manabe T: Effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on human
pancreatic cancer cell line. Hepatogastroenterology. 54:2387–2391.
2007.
|
|
73
|
Albillos A, de Gottardi A and Rescigno M:
The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for
therapy. J Hepatol. 72:558–577. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Xu JH, Fu JJ, Wang XL, Zhu JY, Ye XH and
Chen SD: Hepatitis B or C viral infection and risk of pancreatic
cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:4234–4241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lanini S, Ustianowski A, Pisapia R, Zumla
A and Ippolito G: Viral hepatitis: Etiology, epidemiology,
transmission, diagnostics, treatment, and prevention. Infect Dis
Clin North Am. 33:1045–1062. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Fiorino S, Cuppini A, Castellani G,
Bacchi-Reggiani ML and Jovine E: HBV- and HCV-related infections
and risk of pancreatic cancer. JOP. 14:603–609. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yoshimura M, Sakurai I, Shimoda T, Abe K,
Okano T and Shikata T: Detection of HBsAg in the pancreas. Acta
Pathol Jpn. 31:711–717. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jin Y, Gao H, Chen H, Wang J, Chen M, Li
G, Wang L, Gu J and Tu H: Identification and impact of hepatitis B
virus DNA and antigens in pancreatic cancer tissues and adjacent
non-cancerous tissues. Cancer Lett. 335:447–454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Taranto D, Carrato A, Romano M, Maio G,
Izzo CM and Del Vecchio Blanco C: Mild pancreatic damage in acute
viral hepatitis. Digestion. 42:93–97. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ben Q, Li Z, Liu C, Cai Q, Yuan Y, Wang K,
Xiao L, Gao J and Zhang H: Hepatitis B virus status and risk of
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A case-control study from China.
Pancreas. 41:435–440. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Jen CL, Su J, Wang LY,
You SL, Lu SN and Chen CJ: Risk of pancreatic cancer in chronic
hepatitis B virus infection: Data from the REVEAL-HBV cohort study.
Liver Int. 30:423–429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Wei XL, Qiu MZ, Chen WW, Jin Y, Ren C,
Wang F, Luo HY, Wang ZQ, Zhang DS, Wang FH, et al: The status of
HBV infection influences metastatic pattern and survival in Chinese
patients with pancreatic cancer. J Transl Med. 11:2492013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Majumder S, Bockorny B, Baker WL and
Dasanu CA: Association between HBsAg positivity and pancreatic
cancer: A meta-analysis. J Gastrointest Cancer. 45:347–352. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhong S, Yeo W, Tang MW, Lin XR, Mo F, Ho
WM, Hui P and Johnson PJ: Gross elevation of TT virus genome load
in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of cancer patients. Ann N
Y Acad Sci. 945:84–92. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tomasiewicz K, Modrzewska R, Lyczak A and
Krawczuk G: TT virus infection and pancreatic cancer: Relationship
or accidental coexistence. World J Gastroenterol. 11:2847–2849.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Camargo CA Jr, Greig PD, Levy GA and
Clavien PA: Acute pancreatitis following liver transplantation. J
Am Coll Surg. 181:249–256. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Demir M, Serin E, Göktürk S, Ozturk NA,
Kulaksizoglu S and Ylmaz U: The prevalence of occult hepatitis B
virus infection in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:668–673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Brooks-Worrell B and Palmer JP: Immunology
in the clinic review series; focus on metabolic diseases:
Development of islet autoimmune disease in type 2 diabetes
patients: potential sequelae of chronic inflammation. Clin Exp
Immunol. 167:40–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
89
|
Chen Y, Bai X, Zhang Q, Wen L, Su W, Fu Q,
Sun X, Lou Y, Yang J, Zhang J, et al: The hepatitis B virus X
protein promotes pancreatic cancer through modulation of the
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 380:98–105. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P, Cavallini G,
Ammann RW, Lankisch PG, Andersen JR, Dimagno EP, Andrén-Sandberg A
and Domellöf L: Pancreatitis and the risk of pancreatic cancer.
International pancreatitis study group. N Engl J Med.
328:1433–1437. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zambirinis CP, Pushalkar S, Saxena D and
Miller G: Pancreatic cancer, inflammation, and microbiome. Cancer
J. 20:195–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Sammallahti H, Kokkola A, Rezasoltani S,
Ghanbari R, Aghdaei HA, Knuutila S, Puolakkainen P and Sarhadi VK:
Microbiota alterations and their association with oncogenomic
changes in pancreatic cancer patients. Int J Mol Sci. 22:129782021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Serra N, Di Carlo P, Gulotta G, d' Arpa F,
Giammanco A, Colomba C, Melfa G, Fasciana T and Sergi C: Bactibilia
in women affected with diseases of the biliary tract and pancreas.
A STROBE guidelines-adherent cross-sectional study in Southern
Italy. J Med Microbiol. 67:1090–1095. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Franchi L, Muñoz-Planillo R and Núñez G:
Sensing and reacting to microbes through the inflammasomes. Nat
Immunol. 13:325–332. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hayward JA, Mathur A, Ngo C and Man SM:
Cytosolic recognition of microbes and pathogens: Inflammasomes in
action. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 82:e00015–e00018. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chen GY and Núñez G: Inflammasomes in
intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology.
141:1986–1999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Hoque R, Sohail M, Malik A, Sarwar S, Luo
Y, Shah A, Barrat F, Flavell R, Gorelick F, Husain S and Mehal W:
TLR9 and the NLRP3 inflammasome link acinar cell death with
inflammation in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 141:358–369.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Tsuji Y, Watanabe T, Kudo M, Arai H,
Strober W and Chiba T: Sensing of commensal organisms by the
intracellular sensor NOD1 mediates experimental pancreatitis.
Immunity. 37:326–338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Fukuda A, Wang SC, Morris JP IV, Folias
AE, Liou A, Kim GE, Akira S, Boucher KM, Firpo MA, Mulvihill SJ and
Hebrok M: Stat3 and MMP7 contribute to pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma initiation and progression. Cancer Cell. 19:441–455.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Lesina M, Kurkowski MU, Ludes K, Rose-John
S, Treiber M, Klöppel G, Yoshimura A, Reindl W, Sipos B, Akira S,
et al: Stat3/Socs3 activation by IL-6 transsignaling promotes
progression of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and development
of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell. 19:456–469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Schwabe RF and Jobin C: The microbiome and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:800–812. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
De Monte L, Reni M, Tassi E, Clavenna D,
Papa I, Recalde H, Braga M, Di Carlo V, Doglioni C and Protti MP:
Intratumor T helper type 2 cell infiltrate correlates with
cancer-associated fibroblast thymic stromal lymphopoietin
production and reduced survival in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med.
208:469–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Thomas RM, Gharaibeh RZ, Gauthier J,
Beveridge M, Pope JL, Guijarro MV, Yu Q, He Z, Ohland C, Newsome R,
et al: Intestinal microbiota enhances pancreatic carcinogenesis in
preclinical models. Carcinogenesis. 39:1068–1078. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Takeuchi O and Akira S: Pattern
recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 140:805–820. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zambirinis CP, Ochi A, Barilla R, Greco S,
Deutsch M and Miller G: Induction of TRIF- or MYD88-dependent
pathways perturbs cell cycle regulation in pancreatic cancer. Cell
Cycle. 12:1153–1154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Thomas RM and Jobin C: Microbiota in
pancreatic health and disease: The next frontier in microbiome
research. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:53–64. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J,
Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W and Pettersson S: Host-gut microbiota
metabolic interactions. Science. 336:1262–1267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Chen D, Liu P, Lu X, Li J, Qi D, Zang L,
Lin J, Liu Y, Zhai S, Fu D, et al: Pan-cancer analysis implicates
novel insights of lactate metabolism into immunotherapy response
prediction and survival prognostication. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
43:1252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Kitamura F, Semba T, Yasuda-Yoshihara N,
Yamada K, Nishimura A, Yamasaki J, Nagano O, Yasuda T, Yonemura A,
Tong Y, et al: Cancer-associated fibroblasts reuse cancer-derived
lactate to maintain a fibrotic and immunosuppressive
microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight. 8:e1630222023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Bhagat TD, Von Ahrens D, Dawlaty M, Zou Y,
Baddour J, Achreja A, Zhao H, Yang L, Patel B, Kwak C, et al:
Lactate-mediated epigenetic reprogramming regulates formation of
human pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts. Elife.
8:e506632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Mullins TD, Kern HF and Metzgar RS:
Ultrastructural differentiation of sodium butyrate-treated human
pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines. Pancreas. 6:578–587. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Pellizzaro C, Speranza A, Zorzet S, Crucil
I, Sava G, Scarlata I, Cantoni S, Fedeli M and Coradini D:
Inhibition of human pancreatic cell line MIA PaCa2 proliferation by
HA-But, a hyaluronic butyric ester: A preliminary report. Pancreas.
36:e15–e23. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Kanika G, Khan S and Jena G: Sodium
butyrate ameliorates L-arginine-induced pancreatitis and associated
fibrosis in wistar rat: Role of inflammation and nitrosative
stress. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 29:349–359. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Luu M, Riester Z, Baldrich A, Reichardt N,
Yuille S, Busetti A, Klein M, Wempe A, Leister H, Raifer H, et al:
Microbial short-chain fatty acids modulate CD8(+) T cell responses
and improve adoptive immunotherapy for cancer. Nat Commun.
12:40772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Avila-Calderón ED, Ruiz-Palma MDS,
Aguilera-Arreola MG, Velázquez-Guadarrama N, Ruiz EA, Gomez-Lunar
Z, Witonsky S and Contreras-Rodríguez A: Outer membrane vesicles of
gram-negative bacteria: An outlook on biogenesis. Front Microbiol.
12:5579022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Sivam HGP, Chin BY, Gan SY, Ng JH,
Gwenhure A and Chan EWL: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation of
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and macrophages activates
the NLRP3 inflammasome that influences the levels of
pro-inflammatory cytokines in a co-culture model. Cancer Biol Ther.
24:22848572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Peng C, Tu G, Wang J, Wang Y, Wu P, Yu L,
Li Z and Yu X: MLKL signaling regulates macrophage polarization in
acute pancreatitis through CXCL10. Cell Death Dis. 14:1552023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Sun L, Xiu M, Wang S, Brigstock DR, Li H,
Qu L and Gao R: Lipopolysaccharide enhances TGF-β1 signalling
pathway and rat pancreatic fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 22:2346–2356.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Tofalo R, Cocchi S and Suzzi G: Polyamines
and gut microbiota. Front Nutr. 6:162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Arruabarrena-Aristorena A, Zabala-Letona A
and Carracedo A: Oil for the cancer engine: The cross-talk between
oncogenic signaling and polyamine metabolism. Sci Adv.
4:eaar26062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Matsumoto M and Benno Y: The relationship
between microbiota and polyamine concentration in the human
intestine: A pilot study. Microbiol Immunol. 51:25–35. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Mendez R, Kesh K, Arora N, Di Martino L,
McAllister F, Merchant N and Banerjee S and Banerjee S: Microbial
dysbiosis and polyamine metabolism as predictive markers for early
detection of pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis. 41:561–570. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
124
|
Di Martino ML, Campilongo R, Casalino M,
Micheli G, Colonna B and Prosseda G: Polyamines: Emerging players
in bacteria-host interactions. Int J Med Microbiol. 303:484–491.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Blanco-Míguez A, Carloni S, Cardenas C,
Dioguardi CC, Lambroia L, Capretti G, Nappo G, Fugazza A, Capogreco
A, Armanini F, et al: Microbial composition associated with biliary
stents in patients undergoing pancreatic resection for cancer. NPJ
Biofilms Microbiomes. 10:352024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Flemming HC, van Hullebusch ED, Neu TR,
Nielsen PH, Seviour T, Stoodley P, Wingender J and Wuertz S: The
biofilm matrix: Multitasking in a shared space. Nat Rev Microbiol.
21:70–86. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Chen L, Wang D, Liu W, Zhou S, Gu Q and
Zhou T: Immunomodulation of exopolysaccharide produced by
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus ZFM216 in cyclophosphamide-induced
immunosuppressed mice by modulating gut microbiota. Int J Biol
Macromol. 283:1376192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Jia K, Wei M, He Y, Wang Y, Wei H and Tao
X: Characterization of novel exopolysaccharides from enterococcus
hirae WEHI01 and its immunomodulatory activity. Foods. 11:35382022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Itonaga M and Kitano M: Endoscopic biliary
drainage for distal bile duct obstruction due to pancreatic cancer.
Clin Endosc. 58:40–52. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
130
|
Vaishnavi C, Samanta J and Kochhar R:
Characterization of biofilms in biliary stents and potential
factors involved in occlusion. World J Gastroenterol. 24:112–123.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Lübbert C, Wendt K, Feisthammel J, Moter
A, Lippmann N, Busch T, Mössner J, Hoffmeister A and Rodloff AC:
Epidemiology and resistance patterns of bacterial and fungal
colonization of biliary plastic stents: A prospective cohort study.
PLoS One. 11:e01554792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Niemelä J, Kallio R, Ohtonen P, Saarnio J
and Syrjälä H: Impact of cholangitis on survival of patients with
malignant biliary obstruction treated with percutaneous
transhepatic biliary drainage. BMC Gastroenterol. 23:912023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Di Martino P: Extracellular polymeric
substances, a key element in understanding biofilm phenotype. AIMS
Microbiol. 4:274–288. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Mulcahy H, Charron-Mazenod L and Lewenza
S: Extracellular DNA chelates cations and induces antibiotic
resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. PLoS Pathog.
4:e10002132008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Tetz GV, Artemenko NK and Tetz VV: Effect
of DNase and antibiotics on biofilm characteristics. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 53:1204–1209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
136
|
Karygianni L, Attin T and Thurnheer T:
Treatment interferes with composition combined dnase and proteinase
and structural integrity of multispecies oral biofilms. J Clin Med.
9:9832020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Gruszecka J and Filip R: Bacterial
biofilms-A threat to biliary stents, understanding their formation,
clinical consequences and management. Medicina (Kaunas).
61:5122025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Zeng S, Pöttler M, Lan B, Grützmann R,
Pilarsky C and Yang H: Chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 20:45042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Fu Y, Ricciardiello F, Yang G, Qiu J,
Huang H, Xiao J, Cao Z, Zhao F, Liu Y, Luo W, et al: The role of
mitochondria in the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells.
Cells. 10:4972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Bengala C, Guarneri V, Giovannetti E,
Lencioni M, Fontana E, Mey V, Fontana A, Boggi U, Del Chiaro M,
Danesi R, et al: Prolonged fixed dose rate infusion of gemcitabine
with autologous haemopoietic support in advanced pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 93:35–40. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Huang S, Li JY, Wu J, Meng L and Shou CC:
Mycoplasma infections and different human carcinomas. World J
Gastroenterol. 7:266–269. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Voorde VJ, Sabuncuoğlu S, Noppen S, Hofer
A, Ranjbarian F, Fieuws S, Balzarini J and Liekens S:
Nucleoside-catabolizing enzymes in mycoplasma-infected tumor cell
cultures compromise the cytostatic activity of the anticancer drug
gemcitabine. J Biol Chem. 289:13054–13065. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Weniger M, Hank T, Qadan M, Ciprani D,
Michelakos T, Niess H, Heiliger C, Ilmer M, D'Haese JG, Ferrone CR,
et al: Influence of Klebsiella pneumoniae and quinolone treatment
on prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg.
108:709–716. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Kesh K, Mendez R, Abdelrahman L and
Banerjee S and Banerjee S: Type 2 diabetes induced microbiome
dysbiosis is associated with therapy resistance in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Microb Cell Fact. 19:752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Udayasuryan B, Ahmad RN, Nguyen TTD, Umaña
A, Roberts LM, Sobol P, Jones SD, Munson JM, Slade DJ and Verbridge
SS: Fusobacterium nucleatum induces proliferation and migration in
pancreatic cancer cells through host autocrine and paracrine
signaling. Sci Signal. 15:eabn49482022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J,
Qian Y, Kryczek I, Sun D, Nagarsheth N, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by
modulating autophagy. Cell. 170:548–563.e516. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Heshiki Y, Vazquez-Uribe R, Li J, Ni Y,
Quainoo S, Imamovic L, Li J, Sørensen M, Chow BKC, Weiss GJ, et al:
Predictable modulation of cancer treatment outcomes by the gut
microbiota. Microbiome. 8:282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|