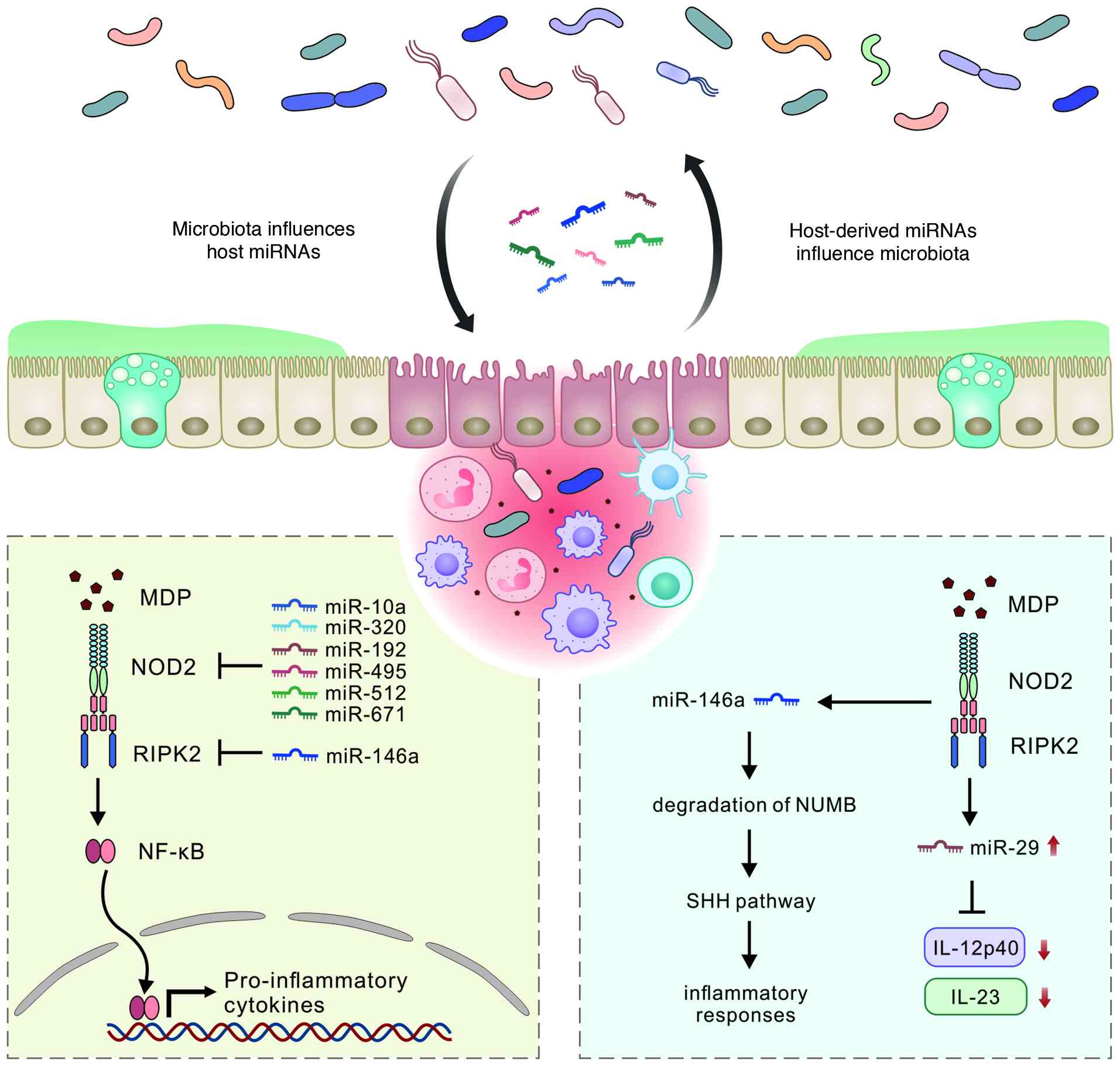
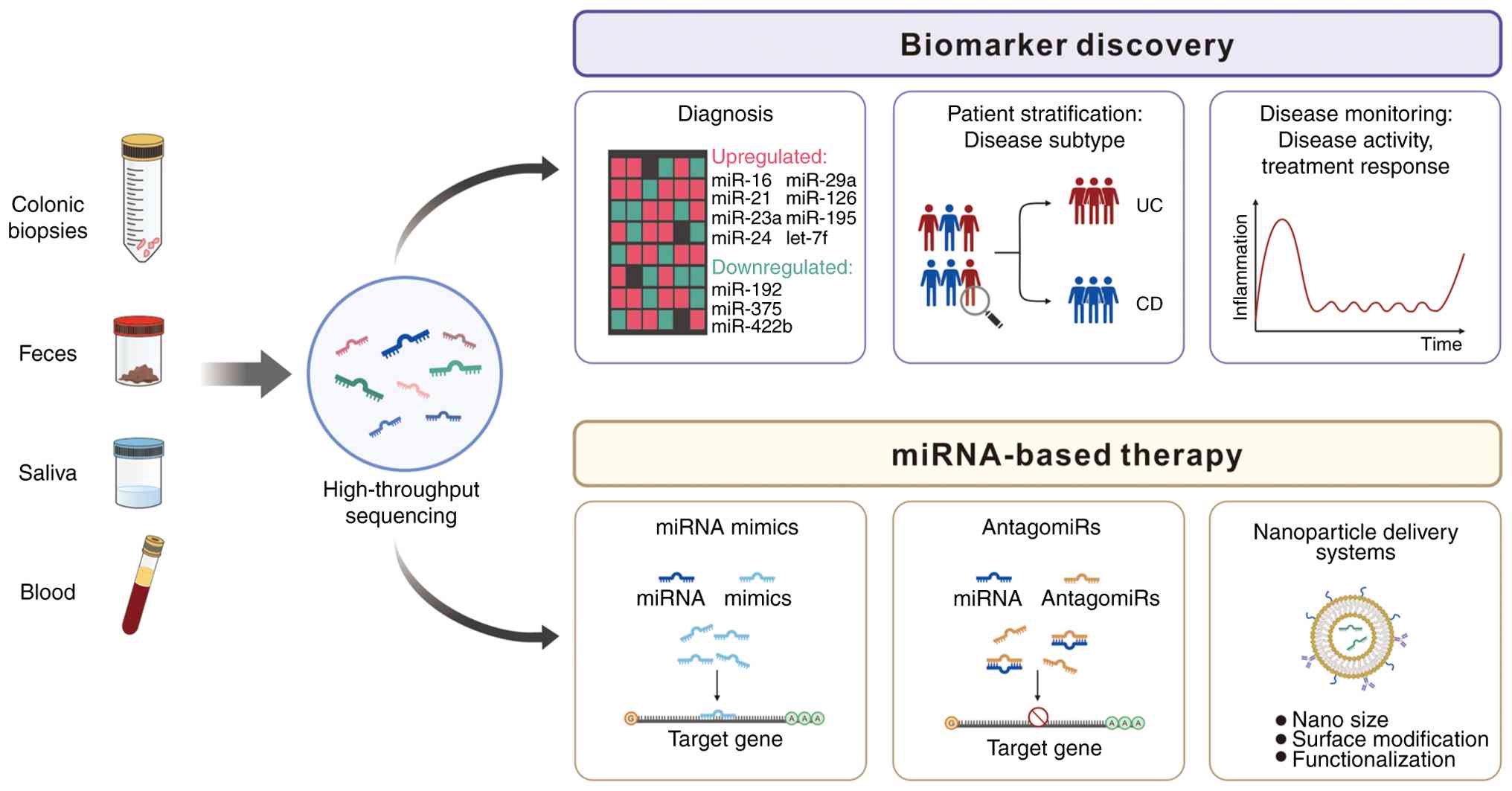
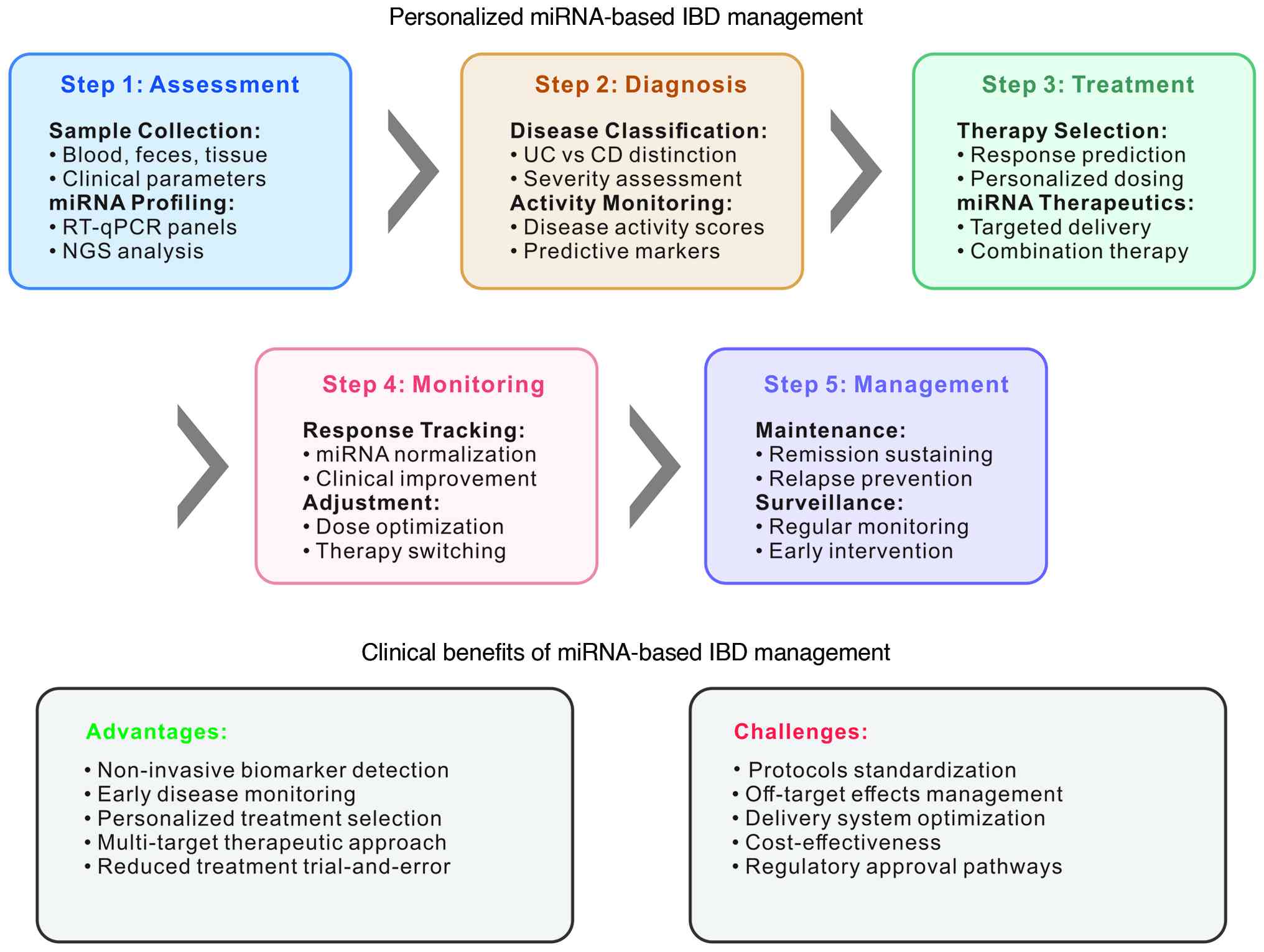
|
1
|
Wan J, Zhou J, Wang Z, Liu D, Zhang H, Xie
S and Wu K: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of
inflammatory bowel disease: Insights from the past two years. Chin
Med J (Engl). 138:763–776. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clarke WT and Feuerstein JD: Colorectal
cancer surveillance in inflammatory bowel disease: Practice
guidelines and recent developments. World J Gastroenterol.
25:4148–4157. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giammona A, Galuzzi BG, Imperia E,
Gervasoni C, Remedia S, Restaneo L, Nespoli M, De Gara L, Tani F,
Cicala M, et al: Chronic gastrointestinal disorders and
miRNA-associated disease: An up-to-date. Int J Mol Sci. 26:4132025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rishik S, Hirsch P, Grandke F, Fehlmann T
and Keller A: miRNATissueAtlas 2025: An update to the uniformly
processed and annotated human and mouse non-coding RNA tissue
atlas. Nucleic Acids Res. 53:D129–D137. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Ramadan YN, Kamel AM, Medhat MA and Hetta
HF: MicroRNA signatures in the pathogenesis and therapy of
inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Med. 24:2172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu XM and Zhang HJ: miRNAs as new
molecular insights into inflammatory bowel disease: Crucial
regulators in autoimmunity and inflammation. World J Gastroenterol.
22:2206–2218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gu H, Zhao C, Zhang T, Liang H, Wang XM,
Pan Y, Chen X, Zhao Q, Li D, Liu F, et al: Salmonella produce
microRNA-like RNA fragment sal-1 in the infected cells to
facilitate intracellular survival. Sci Rep. 7:23922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dalmasso G, Nguyen HT, Yan Y, Laroui H,
Charania MA, Ayyadurai S, Sitaraman SV and Merlin D: Microbiota
modulate host gene expression via MicroRNAs. PLoS One.
6:e192932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pös O, Styk J, Buglyó G, Zeman M, Lukyova
L, Bernatova K, Hrckova Turnova E, Rendek T, Csók Á, Repiska V, et
al: Cross-kingdom interaction of miRNAs and Gut microbiota with
non-invasive diagnostic and therapeutic implications in colorectal
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:105202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Temido MJ, Honap S, Jairath V, Vermeire S,
Danese S, Portela F and Peyrin-Biroulet L: Overcoming the
challenges of overtreating and undertreating inflammatory bowel
disease. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:462–474. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Balakrishnan A, Stearns AT, Park PJ,
Dreyfuss JM, Ashley SW, Rhoads DB and Tavakkolizadeh A: MicroRNA
mir-16 is anti-proliferative in enterocytes and exhibits diurnal
rhythmicity in intestinal crypts. Exp Cell Res. 316:3512–3521.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Panelli S, Epis S, Cococcioni L, Perini M,
Paroni M, Bandi C, Drago L and Zuccotti GV: Inflammatory bowel
diseases, the hygiene hypothesis and the other side of the
microbiota: Parasites and fungi. Pharmacol Res. 159:1049622020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
James JP, Riis LB, Malham M, Høgdall E,
Langholz E and Nielsen BS: MicroRNA biomarkers in IBD-differential
diagnosis and prediction of colitis-associated cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:78932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu S, da Cunha AP, Rezende RM, Cialic R,
Wei Z, Bry L, Comstock LE, Gandhi R and Weiner HL: The host shapes
the gut microbiota via fecal MicroRNA. Cell Host Microbe. 19:32–43.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Witwer KW and Hirschi KD: Transfer and
functional consequences of dietary microRNAs in vertebrates:
concepts in search of corroboration: negative results challenge the
hypothesis that dietary xenomiRs cross the gut and regulate genes
in ingesting vertebrates, but important questions persist.
Bioessays. 36:394–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Witwer KW and Zhang CY: Diet-derived
microRNAs: Unicorn or silver bullet? Genes Nutr. 12:152017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lakkisto P, Dalgaard LT, Belmonte T,
Pinto-Sietsma SJ, Devaux Y and de Gonzalo-Calvo D; EU-CardioRNA
COST Action CA17129: https://cardiorna.eu/. Development of circulating
microRNA-based biomarkers for medical decision-making: A friendly
reminder of what should NOT be done. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 60:pp.
141–152. 2023, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Condrat CE, Thompson DC, Barbu MG, Bugnar
OL, Boboc A, Cretoiu D, Suciu N, Cretoiu SM and Voinea SC: miRNAs
as biomarkers in disease: Latest findings regarding their role in
diagnosis and prognosis. Cells. 9:2762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sokal-Dembowska A, Jarmakiewicz-Czaja S,
Helma K and Filip R: The role of microRNAs in inflammatory bowel
disease. Int J Mol Sci. 26:47502025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Casado-Bedmar M, Roy M, Berthet L, Hugot
JP, Yang C, Manceau H, Peoc'h K, Chassaing B, Merlin D and Viennois
E: Fecal let-7b and miR-21 directly modulate the intestinal
microbiota, driving chronic inflammation. Gut Microbes.
16:23942492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li M, Chen WD and Wang YD: The roles of
the gut microbiota-miRNA interaction in the host pathophysiology.
Mol Med. 26:1012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anzola A, González R, Gámez-Belmonte R,
Ocón B, Aranda CJ, Martínez-Moya P, López-Posadas R,
Hernández-Chirlaque C, Sánchez de Medina F and Martínez-Augustin O:
miR-146a regulates the crosstalk between intestinal epithelial
cells, microbial components and inflammatory stimuli. Sci Rep.
8:173502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu S, Dong TS, Dalal SR, Wu F, Bissonnette
M, Kwon JH and Chang EB: The microbe-derived short chain fatty acid
butyrate targets miRNA-Dependent p21 gene expression in human colon
cancer. PLoS One. 6:e162212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sanchez HN, Moroney JB, Gan H, Shen T, Im
JL, Li T, Taylor JR, Zan H and Casali P: B cell-intrinsic
epigenetic modulation of antibody responses by dietary
fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids. Nat Commun. 11:602020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fardi F, Khasraghi LB, Shahbakhti N,
Salami Naseriyan A, Najafi S, Sanaaee S, Alipourfard I, Zamany M,
Karamipour S, Jahani M, et al: An interplay between non-coding RNAs
and gut microbiota in human health. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
201:1107392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fleishman JS and Kumar S: Bile acid
metabolism and signaling in health and disease: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
9:972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Virtue AT, McCright SJ, Wright JM, Jimenez
MT, Mowel WK, Kotzin JJ, Joannas L, Basavappa MG, Spencer SP, Clark
ML, et al: The gut microbiota regulates white adipose tissue
inflammation and obesity via a family of microRNAs. Sci Transl Med.
11:eaav18922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moloney GM, O'Leary OF, Salvo-Romero E,
Desbonnet L, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Clarke G and Cryan JF: Microbial
regulation of hippocampal miRNA expression: Implications for
transcription of kynurenine pathway enzymes. Behav Brain Res.
334:50–54. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Froy O and Weintraub Y: The circadian
clock, metabolism, and inflammation-the holy trinity of
inflammatory bowel diseases. Clin Sci (Lond). 139:777–790. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Torres M, Becquet D, Franc JL and
François-Bellan AM: Circadian processes in the RNA life cycle.
Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 9:e14672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang M, Zhou C, Li X, Li H, Han Q, Chen
Z, Tang W and Yin J: Interactions between Gut microbiota, host
circadian rhythms, and metabolic diseases. Adv Nutr. 16:1004162025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Van Wijk N, Zohar K and Linial M:
Challenging cellular homeostasis: Spatial and temporal regulation
of miRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 23:161522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hicks SD, Khurana N, Williams J, Dowd
Greene C, Uhlig R and Middleton FA: Diurnal oscillations in human
salivary microRNA and microbial transcription: Implications for
human health and disease. PLoS One. 13:e01982882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Herichová I, Vanátová D, Reis R, Stebelová
K, Olexová L, Morová M, Ghosh A, Baláž M, Štefánik P and Kršková L:
Daily profile of miRNAs in the rat colon and in silico analysis of
their possible relationship to colorectal cancer. Biomedicines.
13:18652025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Muttiah B and Law JX: Milk-derived
extracellular vesicles and gut health. NPJ Sci Food. 9:122025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yi C, Lu L, Li Z, Guo Q, Ou L, Wang R and
Tian X: Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles for microRNA
delivery in cancer treatment. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 15:84–101.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xu Q, Li Y, Qin X, Xin Y, Wang J, Zhang Y,
Xu K, Yang X and Wang X: osa-miR168a, a plant miRNA that survives
the process of in vivo food digestion, attenuates dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis in mice by oral administration. J Agric Food
Chem. 72:25146–25160. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guzmán-Lorite M, Muñoz-Moreno L, Marina
ML, Carmena MJ and García MC: Extraction, detection and
determination of dietary microRNA: A review. Trends in Food Science
& Technology. 135:215–233. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jiang K, Pang X, Li W, Xu X, Yang Y, Shang
C and Gao X: Interbacterial warfare in the human gut: Insights from
Bacteroidales' perspective. Gut Microbes. 17:24735222025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Neurath MF, Artis D and Becker C: The
intestinal barrier: A pivotal role in health, inflammation, and
cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:573–592. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rothschild D, Weissbrod O, Barkan E,
Kurilshikov A, Korem T, Zeevi D, Costea PI, Godneva A, Kalka IN,
Bar N, et al: Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping
human gut microbiota. Nature. 555:210–215. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Flanagan K, Gassner K, Lang M, Ozelyte J,
Hausmann B, Crepaz D, Pjevac P, Gasche C, Berry D, Vesely C and
Pereira FC: Human-derived microRNA 21 regulates indole and
L-tryptophan biosynthesis transcripts in the gut commensal
Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. mBio. 16:e03928242025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Santos AA, Afonso MB, Ramiro RS, Pires D,
Pimentel M, Castro RE and Rodrigues CMP: Host miRNA-21 promotes
liver dysfunction by targeting small intestinal Lactobacillus in
mice. Gut Microbes. 12:1–18. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Teng Y, Ren Y, Sayed M, Hu X, Lei C, Kumar
A, Hutchins E, Mu J, Deng Z, Luo C, et al: Plant-derived exosomal
MicroRNAs shape the gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe.
24:637–652.e8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu S, Rezende RM, Moreira TG, Tankou SK,
Cox LM, Wu M, Song A, Dhang FH, Wei Z, Costamagna G and Weiner HL:
Oral Administration of miR-30d from Feces of MS patients suppresses
MS-like symptoms in mice by expanding akkermansia muciniphila. Cell
Host Microbe. 26:779–794.e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
He L, Zhou X, Liu Y, Zhou L and Li F:
Fecal miR-142a-3p from dextran sulfate sodium-challenge recovered
mice prevents colitis by promoting the growth of Lactobacillus
reuteri. Mol Ther. 30:388–399. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
47
|
Tambaro F, Gallicchio C, Orlando S,
Carnevale S and Muscaritoli M: The conundrum of XenomiRs and human
health. Adv Nutr. 16:1005102025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dickinson B, Zhang Y, Petrick JS, Heck G,
Ivashuta S and Marshall WS: Lack of detectable oral bioavailability
of plant microRNAs after feeding in mice. Nat Biotechnol.
31:965–967. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lang C, Karunairetnam S, Lo KR, Kralicek
AV, Crowhurst RN, Gleave AP, MacDiarmid RM and Ingram JR: Common
variants of the plant microrna-168a exhibit differing silencing
efficacy for human low-density lipoprotein receptor adaptor protein
1 (LDLRAP1). Microrna. 8:166–170. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xu T, Zhu Y, Lin Z, Lei J, Li L, Zhu W and
Wu D: Evidence of Cross-Kingdom gene regulation by plant MicroRNAs
and possible reasons for inconsistencies. J Agric Food Chem.
72:4564–4573. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mayoral RJ, Pipkin ME, Pachkov M, van
Nimwegen E, Rao A and Monticelli S: MicroRNA-221-222 regulate the
cell cycle in mast cells. J Immunol. 182:433–445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Mayoral RJ, Deho L, Rusca N, Bartonicek N,
Saini HK, Enright AJ and Monticelli S: MiR-221 influences effector
functions and actin cytoskeleton in mast cells. PLoS One.
6:e261332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lu TX, Lim EJ, Besse JA, Itskovich S,
Plassard AJ, Fulkerson PC, Aronow BJ and Rothenberg ME: MiR-223
deficiency increases eosinophil progenitor proliferation. J
Immunol. 190:1576–1582. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Khan AU, Chacon-Millan P and Stiuso P:
Potential miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for differentiating
disease states in ulcerative colitis: A systematic review. Int J
Mol Sci. 26:68222025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Neudecker V, Haneklaus M, Jensen O,
Khailova L, Masterson JC, Tye H, Biette K, Jedlicka P, Brodsky KS,
Gerich ME, et al: Myeloid-derived miR-223 regulates intestinal
inflammation via repression of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Exp Med.
214:1737–1752. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lin S, Zheng B, Wu R, Wu Q and Chen X:
Investigation of the mechanism by which miR-223-3p inhibits reflux
esophagitis through targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. BMC
Gastroenterol. 25:3652025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou H, Xiao J, Wu N, Liu C, Xu J, Liu F
and Wu L: MicroRNA-223 regulates the differentiation and function
of intestinal dendritic cells and macrophages by targeting C/EBPβ.
Cell Rep. 13:1149–1160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liao TL, Chen YM, Tang KT, Chen PK, Liu HJ
and Chen DY: MicroRNA-223 inhibits neutrophil extracellular traps
formation through regulating calcium influx and small extracellular
vesicles transmission. Sci Rep. 11:156762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lu ZJ, Wu JJ, Jiang WL, Xiao JH, Tao KZ,
Ma L, Zheng P, Wan R and Wang XP: MicroRNA-155 promotes the
pathogenesis of experimental colitis by repressing SHIP-1
expression. World J Gastroenterol. 23:976–385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Knolle MD, Chin SB, Rana BMJ, Englezakis
A, Nakagawa R, Fallon PG, Git A and McKenzie ANJ: MicroRNA-155
protects group 2 innate lymphoid cells from apoptosis to promote
type-2 immunity. Front Immunol. 9:22322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zeng Y, Zeng Q, Wen Y, Li J, Xiao H, Yang
C, Luo R and Liu W: Apolipoprotein A-I inhibited group II innate
lymphoid cell response mediated by microRNA-155 in allergic
rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. 3:1002122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Trotta R, Chen L, Ciarlariello D, Josyula
S, Mao C, Costinean S, Yu L, Butchar JP, Tridandapani S, Croce CM
and Caligiuri MA: miR-155 regulates IFN-γ production in natural
killer cells. Blood. 119:3478–3485. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Adel RM, Helal H, Ahmed Fouad M and Sobhy
Abd-Elhalem S: Regulation of miRNA-155-5p ameliorates NETosis in
pulmonary fibrosis rat model via inhibiting its target cytokines
IL-1β, TNF-α and TGF-β1. Int Immunopharmacol. 127:1114562024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hawez A, Al-Haidari A, Madhi R, Rahman M
and Thorlacius H: MiR-155 Regulates PAD4-Dependent formation of
neutrophil extracellular traps. Front Immunol. 10:24622019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wu H, Fan H, Shou Z, Xu M, Chen Q, Ai C,
Dong Y, Liu Y, Nan Z, Wang Y, et al: Extracellular vesicles
containing miR-146a attenuate experimental colitis by targeting
TRAF6 and IRAK1. Int Immunopharmacol. 68:204–212. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lyu B, Wei Z, Jiang L, Ma C, Yang G and
Han S: MicroRNA-146a negatively regulates IL-33 in activated group
2 innate lymphoid cells by inhibiting IRAK1 and TRAF6. Genes Immun.
21:37–44. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Hsieh YT, Chou YC, Kuo PY, Tsai HW, Yen
YT, Shiau AL and Wang CR: Down-regulated miR-146a expression with
increased neutrophil extracellular traps and apoptosis formation in
autoimmune-mediated diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. J Biomed Sci.
29:622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zare E, Yaghoubi SM, Khoshnazar M, Jafari
Dargahlou S, Machhar JS, Zheng Z, Duijf PHG and Mansoori B:
MicroRNAs in cancer immunology: Master regulators of the tumor
microenvironment and immune evasion, with therapeutic potential.
Cancers (Basel). 17:21722025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Galbiati V, Lefevre MA, Maddalon A,
Vocanson M, Iulini M, Marinovich M and Corsini E: Role of miR-24-3p
and miR-146a-5p in dendritic cells' maturation process induced by
contact sensitizers. Arch Toxicol. 97:2183–2191. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sonoyama K and Ohsaka F: Role of microRNAs
in the crosstalk between the gut microbiota and intestinal immune
system. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 42:222–228. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Pan Y, Wang D and Liu F: miR-146b
suppresses LPS-induced M1 macrophage polarization via inhibiting
the FGL2-activated NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway in inflammatory
bowel disease. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 77:1000692022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Yousefi MJ, Afshar Y, Amoozadehsamakoosh
A, Naseri A, Soltani F, Yazdanpanah N, Saleki K and Rezaei N:
Interplay between innate-like T-cells and microRNAs in cancer
immunity. Discov Oncol. 16:14252025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li J, Zhang J, Guo H, Yang S, Fan W, Ye N,
Tian Z, Yu T, Ai G, Shen Z, et al: Critical role of alternative M2
Skewing in miR-155 deletion-mediated protection of colitis. Front
Immunol. 9:9042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Quero L, Tiaden AN, Hanser E, Roux J,
Laski A, Hall J and Kyburz D: miR-221-3p Drives the Shift of
M2-macrophages to a pro-inflammatory function by suppressing
JAK3/STAT3 activation. Front Immunol. 10:30872019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Duroux-Richard I, Roubert C, Ammari M,
Présumey J, Grün JR, Häupl T, Grützkau A, Lecellier CH, Boitez V,
Codogno P, et al: miR-125b controls monocyte adaptation to
inflammation through mitochondrial metabolism and dynamics. Blood.
128:3125–3136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu Y, Wu Y, Wang C, Hu W, Zou S, Ren H,
Zuo Y and Qu L: MiR-127-3p enhances macrophagic proliferation via
disturbing fatty acid profiles and oxidative phosphorylation in
atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 193:36–52. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sprenkle NT, Serezani CH and Pua HH:
MicroRNAs in macrophages: Regulators of activation and function. J
Immunol. 210:359–368. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen S, Zhu H and Jounaidi Y:
Comprehensive snapshots of natural killer cells functions,
signaling, molecular mechanisms and clinical utilization. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 9:3022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Alivernini S,
Melchor EG, Elmesmari A, Tolusso B, Tange C, Petricca L, Gilchrist
DS, Di Sante G, Keijzer C, et al: MicroRNA-34a dependent regulation
of AXL controls the activation of dendritic cells in inflammatory
arthritis. Nat Commun. 8:158772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zheng Z, Yang Y, Liu H, Hu M and Chen P:
Inhibition of miR-let-7i Induces DC immature cells and improves
skin graft tolerance. Dis Markers. 2022:86056212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gaál Z: Role of microRNAs in immune
regulation with translational and clinical applications. Int J Mol
Sci. 25:19422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xu SJ, Chen JH, Chang S and Li HL: The
role of miRNAs in T helper cell development, activation, fate
decisions and tumor immunity. Front Immunol. 14:13203052023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Liu SQ, Jiang S, Li C, Zhang B and Li QJ:
miR-17-92 cluster targets phosphatase and tensin homology and
ikaros family zinc finger 4 to promote TH17-mediated inflammation.
J Biol Chem. 289:12446–12456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Singh UP, Murphy AE, Enos RT, Shamran HA,
Singh NP, Guan H, Hegde VL, Fan D, Price RL, Taub DD, et al:
miR-155 deficiency protects mice from experimental colitis by
reducing T helper type 1/type 17 responses. Immunology.
143:478–489. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Shi T, Xie Y, Fu Y, Zhou Q, Ma Z, Ma J,
Huang Z, Zhang J and Chen J: The signaling axis of
microRNA-31/interleukin-25 regulates Th1/Th17-mediated inflammation
response in colitis. Mucosal Immunol. 10:983–995. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Guo M, Mao X, Ji Q, Lang M, Li S, Peng Y,
Zhou W, Xiong B and Zeng Q: miR-146a in PBMCs modulates Th1
function in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Immunol Cell
Biol. 88:555–564. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Qin Z, Wang PY, Wan JJ, Zhang Y, Wei J,
Sun Y and Liu X: MicroRNA124-IL6R mediates the effect of nicotine
in inflammatory bowel disease by shifting Th1/Th2 balance toward
Th1. Front Immunol. 11:2352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sheedy FJ: Turning 21: Induction of miR-21
as a key switch in the inflammatory response. Front Immunol.
6:192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sawant DV, Wu H, Kaplan MH and Dent AL:
The Bcl6 target gene microRNA-21 promotes Th2 differentiation by a
T cell intrinsic pathway. Mol Immunol. 54:435–442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lu TX, Hartner J, Lim EJ, Fabry V, Mingler
MK, Cole ET, Orkin SH, Aronow BJ and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA-21
limits in vivo immune response-mediated activation of the
IL-12/IFN-gamma pathway, Th1 polarization, and the severity of
delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 187:3362–3373. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Czopik AK, McNamee EN, Vaughn V, Huang X,
Bang IH, Clark T, Wang Y, Ruan W, Nguyen T, Masterson JC, et al:
HIF-2α-dependent induction of miR-29a restrains TH1 activity during
T cell dependent colitis. Nat Commun. 15:80422024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Smith KM, Guerau-de-Arellano M, Costinean
S, Williams JL, Bottoni A, Mavrikis Cox G, Satoskar AR, Croce CM,
Racke MK, Lovett-Racke AE and Whitacre CC: miR-29ab1 deficiency
identifies a negative feedback loop controlling Th1 bias that is
dysregulated in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 189:1567–1576. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wu R, Zeng J, Yuan J, Deng X, Huang Y,
Chen L, Zhang P, Feng H, Liu Z, Wang Z, et al: MicroRNA-210
overexpression promotes psoriasis-like inflammation by inducing Th1
and Th17 cell differentiation. J Clin Invest. 128:2551–2568. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Cho S, Wu CJ, Yasuda T, Cruz LO, Khan AA,
Lin LL, Nguyen DT, Miller M, Lee HM, Kuo ML, et al: miR-23~27~24
clusters control effector T cell differentiation and function. J
Exp Med. 213:235–249. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Maschmeyer P, Petkau G, Siracusa F,
Zimmermann J, Zügel F, Kühl AA, Lehmann K, Schimmelpfennig S, Weber
M, Haftmann C, et al: Selective targeting of pro-inflammatory Th1
cells by microRNA-148a-specific antagomirs in vivo. J Autoimmun.
89:41–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
97
|
Holvoet P: miRNAs and T cell-mediated
immune response in disease. Yale J Biol Med. 98:187–202. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cichalewska-Studzinska M, Szymanski J,
Stec-Martyna E, Perdas E, Studzinska M, Jerczynska H,
Kulczycka-Wojdala D, Stawski R and Mycko MP: The role of miR-155 in
modulating gene expression in CD4+ T cells: insights into
alternative immune pathways in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int J
Mol Sci. 25:113552024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lu LF, Thai TH, Calado DP, Chaudhry A,
Kubo M, Tanaka K, Loeb GB, Lee H, Yoshimura A, Rajewsky K and
Rudensky AY: Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive
fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein. Immunity.
30:80–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zhu F, Li H, Liu Y, Tan C, Liu X, Fan H,
Wu H, Dong Y, Yu T, Chu S, et al: miR-155 antagomir protect against
DSS-induced colitis in mice through regulating Th17/Treg cell
balance by Jarid2/Wnt/β-catenin. Biomed Pharmacother.
126:1099092020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
O'Connell RM, Kahn D, Gibson WSJ, Round
JL, Scholz RL, Chaudhuri AA, Kahn ME, Rao DS and Baltimore D:
MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing
inflammatory T cell development. Immunity. 33:607–619. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Hu J, Huang S, Liu X, Zhang Y, Wei S and
Hu X: miR-155: An important role in inflammation response. J
Immunol Res. 2022:74372812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wang L, Wang E, Wang Y, Mines R, Xiang K,
Sun Z, Zhou G, Chen KY, Rakhilin N, Chao S, et al: miR-34a is a
microRNA safeguard for Citrobacter-induced inflammatory colon
oncogenesis. Elife. 7:e394792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Brockmann L, Tran A, Huang Y, Edwards M,
Ronda C, Wang HH and Ivanov II: Intestinal microbiota-specific Th17
cells possess regulatory properties and suppress effector T cells
via c-MAF and IL-10. Immunity. 56:2719–2735.e7. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Mikami Y, Philips RL, Sciumè G, Petermann
F, Meylan F, Nagashima H, Yao C, Davis FP, Brooks SR, Sun HW, et
al: MicroRNA-221 and -222 modulate intestinal inflammatory Th17
cell response as negative feedback regulators downstream of
interleukin-23. Immunity. 54:514–525.e6. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ge Y, Sun M, Wu W, Ma C, Zhang C, He C, Li
J, Cong Y, Zhang D and Liu Z: MicroRNA-125a suppresses intestinal
mucosal inflammation through targeting ETS-1 in patients with
inflammatory bowel diseases. J Autoimmun. 101:109–120. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Cho S, Lee HM, Yu IS, Choi YS, Huang HY,
Hashemifar SS, Lin LL, Chen MC, Afanasiev ND, Khan AA, et al:
Differential cell-intrinsic regulations of germinal center B and T
cells by miR-146a and miR-146b. Nat Commun. 9:27572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Li B, Wang X, Choi IY, Wang YC, Liu S,
Pham AT, Moon H, Smith DJ, Rao DS, Boldin MP and Yang L: miR-146a
modulates autoreactive Th17 cell differentiation and regulates
organ-specific autoimmunity. J Clin Invest. 127:3702–3716. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Honardoost MA, Naghavian R, Ahmadinejad F,
Hosseini A and Ghaedi K: Integrative computational mRNA-miRNA
interaction analyses of the autoimmune-deregulated miRNAs and
well-known Th17 differentiation regulators: An attempt to discover
new potential miRNAs involved in Th17 differentiation. Gene.
572:153–162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Sanctuary MR, Huang RH, Jones AA, Luck ME,
Aherne CM, Jedlicka P, de Zoeten EF and Collins CB: miR-106a
deficiency attenuates inflammation in murine IBD models. Mucosal
Immunol. 12:200–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Wu W, He C, Liu C, Cao AT, Xue X,
Evans-Marin HL, Sun M, Fang L, Yao S, Pinchuk IV, et al: miR-10a
inhibits dendritic cell activation and Th1/Th17 cell immune
responses in IBD. Gut. 64:1755–1764. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Yang W, Chen L, Xu L, Bilotta AJ, Yao S,
Liu Z and Cong Y: MicroRNA-10a negatively regulates CD4+ T Cell
IL-10 production through suppression of Blimp1. J Immunol.
207:985–995. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Yang W, Yu T, Yang H, Yao S, Ma R,
Steinert EM, Ridge KM, Cui W, Chandel NS and Cong Y: Intrinsic
MicroRNA-10a restricts regulatory T cell suppressive function and
intestinal repair by coordinating transcriptional, metabolic, and
epithelial repair pathways. Adv Sci (Weinh). 13:e099532025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Liao K, Chen P, Zhang M, Wang J,
Hatzihristidis T, Lin X, Yang L, Yao N, Liu C, Hong Y, et al:
Critical roles of the miR-17~92 family in thymocyte development,
leukemogenesis, and autoimmunity. Cell Rep. 43:1142612024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Jiang S, Li C, Olive V, Lykken E, Feng F,
Sevilla J, Wan Y, He L and Li QJ: Molecular dissection of the
miR-17-92 cluster's critical dual roles in promoting Th1 responses
and preventing inducible Treg differentiation. Blood.
118:5487–5497. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Fujiwara M, Raheja R, Garo LP, Ajay AK,
Kadowaki-Saga R, Karandikar SH, Gabriely G, Krishnan R, Beynon V,
Paul A, et al: microRNA-92a promotes CNS autoimmunity by modulating
the regulatory and inflammatory T cell balance. J Clin Invest.
132:e1556932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Veryaskina YA, Titov SE, Kovynev IB,
Fyodorova SS, Berezina OV, Zhurakovskij IP, Antonenko OV, Demakov
SA, Demenkov PS, Ruzankin PS, et al: MicroRNAs in diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Biomarkers with prognostic potential.
Cancers (Basel). 17:13002025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Hu YZ, Li Q, Wang PF, Li XP and Hu ZL:
Multiple functions and regulatory network of miR-150 in B
lymphocyte-related diseases. Front Oncol. 13:11408132023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Thai TH, Patterson HC, Pham DH, Kis-Toth
K, Kaminski DA and Tsokos GC: Deletion of microRNA-155 reduces
autoantibody responses and alleviates lupus-like disease in the Fas
(lpr)'mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:20194–20199. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Casali P, Li S, Morales G, Daw CC, Chupp
DP, Fisher AD and Zan H: Epigenetic modulation of class-switch DNA
recombination to IgA by miR-146a through downregulation of Smad2,
Smad3 and Smad4. Front Immunol. 12:7614502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Li J, Tian J and Cai T: Integrated
analysis of miRNAs and mRNAs in thousands of single cells. Sci Rep.
15:16362025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Niderla-Bielińska J, Jankowska-Steifer E
and Włodarski P: Non-Coding RNAs and human diseases: Current status
and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 24:116792023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Săsăran MO and Bănescu C: Role of salivary
miRNAs in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders: A
mini-review of available evidence. Front Genet. 14:12284822023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Layton E, Goldsworthy S, Yang E, Ong WY,
Sutherland TE, Bancroft AJ, Thompson S, Au VB, Griffiths-Jones S,
Grencis RK, et al: An optimised faecal microRNA sequencing pipeline
reveals fibrosis in Trichuris muris infection. Nat Commun.
16:15892025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Ma L, Guo H, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Wang C, Bu J,
Sun T and Wei J: Liquid biopsy in cancer current: Status,
challenges and future prospects. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
9:3362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Dhuppar S and Murugaiyan G: MicroRNA
effects on gut homeostasis: Therapeutic implications for
inflammatory bowel disease. Trends Immunol. 43:917–931. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Fan Y and Pedersen O: Gut microbiota in
human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 19:55–71.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Komatsu S, Kitai H and Suzuki HI: Network
regulation of microRNA biogenesis and target interaction. Cells.
12:3062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Wu F, Zikusoka M, Trindade A, Dassopoulos
T, Harris ML, Bayless TM, Brant SR, Chakravarti S and Kwon JH:
MicroRNAs are differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis and
alter expression of macrophage inflammatory peptide-2α.
Gastroenterology. 135:1624–1635.e24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Chapman CG and Pekow J: The emerging role
of miRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease: A review. Therap Adv
Gastroenterol. 8:4–22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Thorlacius-Ussing G, Schnack Nielsen B,
Andersen V, Holmstrøm K and Pedersen AE: Expression and
localization of miR-21 and miR-126 in mucosal tissue from patients
with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 23:739–752.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Xie X, Liu P, Wu H, Li H, Tang Y, Chen X,
Xu C, Liu X and Dai G: miR-21 antagonist alleviates colitis and
angiogenesis via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in colitis mice induced
by TNBS. Ann Transl Med. 10:4132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Li N, Ouyang Y, Xu X, Yuan Z, Liu C and
Zhu Z: MiR-155 promotes colitis-associated intestinal fibrosis by
targeting HBP1/Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
25:4765–4775. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Masi L, Capobianco I, Magrì C, Marafini I,
Petito V and Scaldaferri F: MicroRNAs as innovative biomarkers for
inflammatory bowel disease and prediction of colorectal cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 23:79912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Willeit P, Zampetaki A, Dudek K, Kaudewitz
D, King A, Kirkby NS, Crosby-Nwaobi R, Prokopi M, Drozdov I,
Langley SR, et al: Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for
platelet activation. Circ Res. 112:595–600. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Xu Q, Qin X, Zhang Y, Xu K, Li Y, Li Y, Qi
B, Li Y, Yang X and Wang X: Plant miRNA bol-miR159 regulates gut
microbiota composition in mice: In vivo evidence of the crosstalk
between plant miRNAs and intestinal microbes. J Agric Food Chem.
71:16160–16173. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Aguilar C, Mano M and Eulalio A: MicroRNAs
at the host-bacteria interface: Host defense or bacterial offense.
Trends Microbiol. 27:206–218. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Abu-Halima M, Keller A, Becker LS, Fischer
U, Engel A, Ludwig N, Kern F, Rounge TB, Langseth H, Meese E and
Keller V: Dynamic and static circulating cancer microRNA biomarkers
- a validation study. RNA Biol. 20:1–9. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Ma C, Chen K, Wang Y, Cen C, Zhai Q and
Zhang J: Establishing a novel colorectal cancer predictive model
based on unique gut microbial single nucleotide variant markers.
Gut Microbes. 13:1–6. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Eftekhari A, Maleki Dizaj S, Sharifi S,
Salatin S, Khalilov R, Samiei M, Zununi Vahed S and Ahmadian E:
Salivary biomarkers in cancer. Adv Clin Chem. 110:171–192. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Guo S, Wang X, Shan D, Xiao Y, Ju L, Zhang
Y, Wang G and Qian K: The detection, biological function, and
liquid biopsy application of extracellular vesicle-associated DNA.
Biomark Res. 12:1232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Wang Y and Yin Z: Prediction of
miRNA-disease association based on multisource inductive matrix
completion. Sci Rep. 14:275032024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Ionescu RF, Enache RM, Cretoiu SM and
Cretoiu D: The interplay between gut microbiota and miRNAs in
cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9:8569012022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Nai S, Song J, Su W and Liu X:
Bidirectional interplay among non-coding RNAs, the microbiome, and
the host during development and diseases. Genes (Basel).
16:2082025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Xue X, Cao AT, Cao X, Yao S, Carlsen ED,
Soong L, Liu CG, Liu X, Liu Z, Duck LW, et al: Downregulation of
microRNA-107 in intestinal CD11c(+) myeloid cells in response to
microbiota and proinflammatory cytokines increases IL-23p19
expression. Eur J Immunol. 44:673–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
146
|
Chen YH, Wu KH and Wu HP: Unraveling the
complexities of toll-like receptors: From molecular mechanisms to
clinical applications. Int J Mol Sci. 25:50372024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Liang H, Zhang L, Hoden B, Qu B, Derubeis
D, Song X and Zhang D: Delineating the role of toll-like receptors
in inflammatory bowel disease. Methods Mol Biol. 2700:221–228.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Moghaddam MM, Behzadi E, Sedighian H,
Goleij Z, Kachuei R, Heiat M and Fooladi AAI: Regulation of immune
responses to infection through interaction between stem
cell-derived exosomes and toll-like receptors mediated by microRNA
cargoes. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 14:13844202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Garo LP, Ajay AK, Fujiwara M, Gabriely G,
Raheja R, Kuhn C, Kenyon B, Skillin N, Kadowaki-Saga R, Saxena S
and Murugaiyan G: MicroRNA-146a limits tumorigenic inflammation in
colorectal cancer. Nat Commun. 12:24192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Schmolka N, Papotto PH, Romero PV, Amado
T, Enguita FJ, Amorim A, Rodrigues AF, Gordon KE, Coroadinha AS,
Boldin M, et al: MicroRNA-146a controls functional plasticity in γδ
T cells by targeting NOD1. Sci Immunol. 3:eaao13922018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Zhu F, Yang T, Ning M, Liu Y, Xia W, Fu Y,
Wen T, Zheng M, Xia R, Qian R, et al: MiR-146a alleviates
inflammatory bowel disease in mice through systematic regulation of
multiple genetic networks. Front Immunol. 15:13663192024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Chen Y, Wang C, Liu Y, Tang L, Zheng M, Xu
C, Song J and Meng X: miR-122 targets NOD2 to decrease intestinal
epithelial cell injury in crohn's disease. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 438:133–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Brain O, Owens BM, Pichulik T, Allan P,
Khatamzas E, Leslie A, Steevels T, Sharma S, Mayer A, Catuneanu AM,
et al: The intracellular sensor NOD2 induces MicroRNA-29 expression
in human dendritic cells to limit IL-23 release. Immunity.
39:521–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Yao XC, Wu JJ, Yuan ST and Yuan FL: Recent
insights and perspectives into the role of the miRNA-29 family in
innate immunity (Review). Int J Mol Med. 55:532025. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
155
|
Ghorpade DS, Sinha AY, Holla S, Singh V
and Balaji KN: NOD2-Nitric Oxide-responsive MicroRNA-146a activates
sonic hedgehog signaling to orchestrate inflammatory responses in
murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. J Biol Chem.
288:33037–33048. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Bras JP, Silva AM, Calin GA, Barbosa MA,
Santos SG and Almeida MI: miR-195 inhibits macrophages
pro-inflammatory profile and impacts the crosstalk with smooth
muscle cells. PLoS One. 12:e01885302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Kankuri E: Deficiency of miRNA-149-3p
shaped gut microbiota and enhanced dextran sulfate sodium-induced
colitis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 31:367–369. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Packwood K, Drewe E, Staples E, Webster D,
Witte T, Litzman J, Egner W, Sargur R, Sewell W, Lopez-Granados E,
et al: NOD2 polymorphisms in clinical phenotypes of common variable
immunodeficiency disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 161:536–541. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Chan SY and Loscalzo J: The emerging
paradigm of network medicine in the study of human disease. Circ
Res. 111:359–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
de Oliveira ECS, Quaglio AEV, Grillo TG,
Di Stasi LC and Sassaki LY: MicroRNAs in inflammatory bowel
disease: What do we know and what can we expect? World J
Gastroenterol. 30:2184–2190. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Zhou R, Qiu P, Wang H, Yang H, Yang X, Ye
M, Wang F and Zhao Q: Identification of microRNA-16-5p and
microRNA-21-5p in feces as potential noninvasive biomarkers for
inflammatory bowel disease. Aging (Albany NY). 13:4634–4646. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Clough J, Colwill M, Poullis A, Pollok R,
Patel K and Honap S: Biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease: A
practical guide. Therap Adv Gastroenterol.
17:175628482412516002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Wohnhaas CT, Schmid R, Rolser M, Kaaru E,
Langgartner D, Rieber K, Strobel B, Eisele C, Wiech F, Jakob I, et
al: Fecal MicroRNAs show promise as noninvasive crohn's disease
biomarkers. Crohns Colitis. 3602:otaa0032020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Schaefer JS, Attumi T, Opekun AR, Abraham
B, Hou J, Shelby H, Graham DY, Streckfus C and Klein JR: MicroRNA
signatures differentiate Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis.
BMC Immunol. 16:52015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Peck BC, Weiser M, Lee SE, Gipson GR, Iyer
VB, Sartor RB, Herfarth HH, Long MD, Hansen JJ, Isaacs KL, et al:
MicroRNAs classify different disease behavior phenotypes of Crohn's
disease and may have prognostic utility. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
21:2178–2187. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Mohammadi A, Kelly OB, Smith MI,
Kabakchiev B and Silverberg MS: Differential miRNA expression in
ileal and colonic tissues reveals an altered immunoregulatory
molecular profile in individuals with Crohn's disease versus
healthy subjects. J Crohns Colitis. 13:1459–1469. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Chen S and Liu L: The
landscape of miRNA-mRNA regulatory network and cellular sources in
inflammatory bowel diseases: Insights from text mining and single
cell RNA sequencing analysis. Front Immunol. 15:14545322024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Zhang J, Guo Z, Wang Z, Zhu W and Li Q:
Fecal miR-223 is a noninvasive biomarker for estimating Crohn's
disease activity. Immun Inflamm Dis. 11:e11312023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Shumway AJ, Shanahan MT, Hollville E, Chen
K, Beasley C, Villanueva JW, Albert S, Lian G, Cure MR, Schaner M,
et al: Aberrant miR-29 is a predictive feature of severe phenotypes
in pediatric Crohn's disease. JCI Insight. 9:e1688002024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Wang H, Zhang S, Yu Q, Yang G, Guo J, Li
M, Zeng Z, He Y, Chen B and Chen M: Circulating MicroRNA223 is a
new biomarker for inflammatory bowel disease. Medicine (Baltimore).
95:e27032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Viennois E, Zhao Y, Han MK, Xiao B, Zhang
M, Prasad M, Wang L and Merlin D: Serum miRNA signature diagnoses
and discriminates murine colitis subtypes and predicts ulcerative
colitis in humans. Sci Rep. 7:25202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Tran F, Scharmacher A, Baran N, Mishra N,
Wozny M, Chavez SP, Bhardwaj A, Hinz S, Juzenas S, Bernardes JP, et
al: Dynamic changes in extracellular vesicle-associated miRNAs
elicited by ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Sci
Rep. 14:109252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Shen Q, Huang Z, Ma L, Yao J, Luo T, Zhao
Y, Xiao Y and Jin Y: Extracellular vesicle miRNAs promote the
intestinal microenvironment by interacting with microbes in
colitis. Gut Microbes. 14:21286042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Morilla I, Uzzan M, Laharie D,
Cazals-Hatem D, Denost Q, Daniel F, Belleannee G, Bouhnik Y,
Wainrib G, Panis Y, et al: Colonic MicroRNA profiles, identified by
a deep learning algorithm, that predict responses to therapy of
patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 17:905–913. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Batra SK, Heier CR, Diaz-Calderon L, Tully
CB, Fiorillo AA, van den Anker J and Conklin LS: Serum miRNAs are
pharmacodynamic biomarkers associated with therapeutic response in
pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
26:1597–1606. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Cerutti C, Edwards LJ, de Vries HE,
Sharrack B, Male DK and Romero IA: MiR-126 and miR-126* regulate
shear-resistant firm leukocyte adhesion to human brain endothelium.
Sci Rep. 7:452842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Han Z, Estephan RJ, Wu X, Su C, Yuan YC,
Qin H, Kil SH, Morales C, Schmolze D, Sanchez JF, et al: MicroRNA
regulation of T-Cell exhaustion in cutaneous T cell lymphoma. J
Invest Dermatol. 142:603–612.e7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Innocenti T, Bigagli E, Lynch EN, Galli A
and Dragoni G: MiRNA-based therapies for the treatment of
inflammatory bowel disease: What are we still missing? Inflamm
Bowel Dis. 29:308–323. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Ye D, Guo S, Al-Sadi R and Ma TY: MicroRNA
regulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability.
Gastroenterology. 141:1323–1333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Rawat M, Govindappa PK, Gupta Y and Ma TY:
MicroRNA in intestinal tight junction regulation. NPJ Gut Liver.
2:112025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Rawat M, Nighot M, Al-Sadi R, Gupta Y,
Viszwapriya D, Yochum G, Koltun W and Ma TY: IL1B increases
intestinal tight junction permeability by up-regulation of
MIR200C-3p, which degrades occludin mRNA. Gastroenterology.
159:1375–1389. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Mansouri P, Mansouri P, Behmard E,
Najafipour S, Kouhpayeh A and Farjadfar A: Novel targets for
mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Int
Immunopharmacol. 144:1135442025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Popa ML, Ichim C, Anderco P, Todor SB and
Pop-Lodromanean D: MicroRNAs in the diagnosis of digestive
diseases: A comprehensive review. J Clin Med. 14:20542025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Xia X, Yang Q, Han X, Du Y, Guo S, Hua M,
Fang F, Ma Z, Ma H, Yuan H, et al: Explore on the mechanism of
miRNA-146a/TAB1 in the regulation of cellular apoptosis and
inflammation in ulcerative colitis based on NF-κB Pathway. Curr Mol
Med. 25:330–342. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
He S, Lv Y, Jiang Y, Tao H, Chen X and
Peng L: Recombination of miR-146b by lactococcus lactis for
remolding macrophages and the microbiome in the treatment of murine
colitis. J Agric Food Chem. 73:13427–13438. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Zhang Y, Zhuang H, Chen K, Zhao Y, Wang D,
Ran T and Zou D: Intestinal fibrosis associated with inflammatory
bowel disease: Known and unknown. Chin Med J (Engl). 138:883–893.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Brillante S, Volpe M and Indrieri A:
Advances in MicroRNA therapeutics: From preclinical to clinical
studies. Hum Gene Ther. 35:628–648. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Liu Z, Huang Z, Wang Y, Xiong S, Lin S, He
J, Tan J, Liu C, Wu X, Nie J, et al: Intestinal strictures in
Crohn's disease: An update from 2023. United European Gastroenterol
J. 12:802–813. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Yang J, Zhou CZ, Zhu R, Fan H, Liu XX,
Duan XY, Tang Q, Shou ZX and Zuo DM: miR-200b-containing
microvesicles attenuate experimental colitis associated intestinal
fibrosis by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 32:1966–1974. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Nijhuis A, Curciarello R, Mehta S, Feakins
R, Bishop CL, Lindsay JO and Silver A: MCL-1 is modulated in
Crohn's disease fibrosis by miR-29b via IL-6 and IL-8. Cell Tissue
Res. 368:325–335. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Yin J, Ye YL, Hu T, Xu LJ, Zhang LP, Ji
RN, Li P, Chen Q, Zhu JY and Pang Z: Hsa_circRNA_102610
upregulation in Crohn's disease promotes transforming growth
factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via sponging of
hsa-miR-130a-3p. World J Gastroenterol. 26:3034–3055. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Kaz AM and Venu N: Diagnostic methods and
biomarkers in inflammatory bowel disease. Diagnostics (Basel).
15:13032025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Rojas-Feria M, Romero-García T, Fernández
Caballero-Rico JÁ, Pastor Ramírez H, Avilés-Recio M,
Castro-Fernandez M, Chueca Porcuna N, Romero-Gόmez M, García F,
Grande L and Del Campo JA: Modulation of faecal metagenome in
Crohn's disease: Role of microRNAs as biomarkers. World J
Gastroenterol. 24:5223–5233. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Chen G and Shen J: Artificial intelligence
enhances studies on inflammatory bowel disease. Front Bioeng
Biotechnol. 9:6357642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Segal M and Slack FJ: Challenges
identifying efficacious miRNA therapeutics for cancer. Expert Opin
Drug Discov. 15:987–992. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Sabour S, Sadeghi Koupaei H, Ghasemi H,
Amin M and Azimi T: Anaerobic gut bacteria and their potential role
in the initiation, exacerbation, and development of human
colorectal cancer: A narrative review. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
15:15590012025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Nanni L, Murgiano M, Hsu CE, Khalili S,
Cammarota G, Papa A, Gasbarrini A, Scaldaferri F and Lopetuso LR:
Gut microbial healing in IBD: Visionary approach or evidence-based
reality? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:833–851. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Rawat M, Nara S, Gupta Y, Ma TY and
Parasher G: Lipid membrane-camouflaged biomimetic nanoparticle for
MicroRNA based therapeutic delivery to intestinal epithelial cells.
Sci Rep. 15:313632025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Seyhan AA: Trials and tribulations of
MicroRNA therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 25:14692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Wang JY, Xiao L and Wang JY:
Posttranscriptional regulation of intestinal epithelial integrity
by noncoding RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 8: View Article : Google Scholar : 2017.
|
|
201
|
Pandey S and Yadav P: Exploring the
therapeutic potential of microRNAs: Targeted gene regulation
strategies for enhanced cancer therapy. J Genet Eng Biotechnol.
23:1005562025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Salunkhe SS, Ghatage T and Prabhakar BS:
Multi-oncogene targeting in cancer therapy: A miRNA-driven
pharmacological approach. Biochem Pharmacol. 242:1174172025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Niu J, Zhu J, Li Z, Wang H, Gao Y, Wei B,
Li Y, Wang H, Qian Y, Jing G, et al: MiR-29a-loaded nanoparticles
alleviate inflammatory bowel disease via Sgk1/Foxo3a axis. J
Control Release. 387:1141752025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Rojo Arias JE and Busskamp V: Challenges
in microRNAs' targetome prediction and validation. Neural Regen
Res. 14:1672–1677. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Cui S, Yu S, Huang HY, Lin YC, Huang Y,
Zhang B, Xiao J, Zuo H, Wang J, Li Z, et al: miRTarBase 2025:
Updates to the collection of experimentally validated
microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 53:D147–D156.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Aggeletopoulou I, Mouzaki A, Thomopoulos K
and Triantos C: miRNA molecules-late breaking treatment for
inflammatory bowel diseases? Int J Mol Sci. 24:22332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Furey TS, Sethupathy P and Sheikh SZ:
Redefining the IBDs using genome-scale molecular phenotyping. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:296–311. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
D'Argenio V: The high-throughput analyses
era: Are we ready for the data struggle? High Throughput. 7:82018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Bracken CP, Scott HS and Goodall GJ: A
network-biology perspective of microRNA function and dysfunction in
cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 17:719–732. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Bruscadin JJ, Cardoso TF, Conteville LC,
da Silva JV, Ibelli AMG, Pena GAC, Porto T, de Oliveira PSN,
Andrade BGN, Zerlotini A and Regitano LCA: HolomiRA: A reproducible
pipeline for miRNA binding site prediction in microbial genomes.
BMC Bioinformatics. 26:2362025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Zhang Z: Expanding bioinformatics: Toward
a paradigm shift from data to theory. Fundam Res. Dec 3–2024.Epub
ahead of print.
|
|
212
|
Rahmati R, Zarimeidani F, Ahmadi F,
Yousefi-Koma H, Mohammadnia A, Hajimoradi M, Shafaghi S and Nazari
E: Identification of novel diagnostic and prognostic microRNAs in
sarcoma on TCGA dataset: bioinformatics and machine learning
approach. Sci Rep. 15:75212025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Stafford IS, Gosink MM, Mossotto E, Ennis
S and Hauben M: A systematic review of artificial intelligence and
machine learning applications to inflammatory bowel disease, with
practical guidelines for interpretation. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
28:1573–1583. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Stankovic B, Kotur N, Nikcevic G, Gasic V,
Zukic B and Pavlovic S: Machine learning modeling from omics data
as prospective tool for improvement of inflammatory bowel disease
diagnosis and clinical classifications. Genes (Basel). 12:14382021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Luo Y, Peng L, Shan W, Sun M, Luo L and
Liang W: Machine learning in the development of targeting microRNAs
in human disease. Front Genet. 13:10881892022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
216
|
Luna Buitrago D, Lovering RC and Caporali
A: Insights into online microRNA bioinformatics tools. Noncoding
RNA. 9:182023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Lou Y, Wang Y, Lu J and Chen X:
MicroRNA-targeted nanoparticle delivery systems for cancer therapy:
Current status and future prospects. Nanomedicine (Lond).
20:1181–1194. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Telkoparan-Akillilar P, Chichiarelli S,
Tucci P and Saso L: Integration of MicroRNAs with nanomedicine:
Tumor targeting and therapeutic approaches. Front Cell Dev Biol.
13:15691012025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Zhu Z, Liao L, Gao M and Liu Q:
Garlic-derived exosome-like nanovesicles alleviate dextran sulphate
sodium-induced mouse colitis via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway and
gut microbiota modulation. Food Funct. 14:7520–7534. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Tian Y, Xu J, Li Y, Zhao R, Du S, Lv C, Wu
W, Liu R, Sheng X, Song Y, et al: MicroRNA-31 reduces inflammatory
signaling and promotes regeneration in colon epithelium, and
delivery of mimics in microspheres reduces colitis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 156:2281–2296.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Fukata T, Mizushima T, Nishimura J,
Okuzaki D, Wu X, Hirose H, Yokoyama Y, Kubota Y, Nagata K,
Tsujimura N, et al: The supercarbonate apatite-MicroRNA complex
inhibits dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 12:658–671. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Yang R, Xu K, Li H, Feng Y, Xiang G, Zhou
X and Zhang C: Laminarin-mediated oral delivery of miRNA-223 for
targeted macrophage polarization in inflammatory bowel disease. Int
J Biol Macromol. 311:1430522025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Long J, Liang X, Ao Z, Tang X, Li C, Yan
K, Yu X, Wan Y, Li Y, Li C and Zhou M: Stimulus-responsive drug
delivery nanoplatforms for inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Acta
Biomater. 188:27–47. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Zhao G, Zeng Y, Cheng W, Karkampouna S,
Papadopoulou P, Hu B, Zang S, Wezenberg E, Forn-Cuní G,
Lopes-Bastos B, et al: Peptide-modified lipid nanoparticles boost
the antitumor efficacy of RNA therapeutics. ACS Nano.
19:13685–13704. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Haque MA, Shrestha A, Mikelis CM and
Mattheolabakis G: Comprehensive analysis of lipid nanoparticle
formulation and preparation for RNA delivery. Int J Pharm X.
8:1002832024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Martino MTD, Tagliaferri P and Tassone P:
MicroRNA in cancer therapy: Breakthroughs and challenges in early
clinical applications. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 44:1262025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Sundaram V and Aryal S: Emerging
biomimetic drug delivery nanoparticles inspired by extracellular
vesicles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol.
17:e700252025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Qiu S, Zhu F and Tong L: Application of
targeted drug delivery by cell membrane-based biomimetic
nanoparticles for inflammatory diseases and cancers. Eur J Med Res.
29:5232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Beuzelin D and Kaeffer B: Exosomes and
miRNA-Loaded biomimetic nanovehicles, a focus on their potentials
preventing type-2 diabetes linked to metabolic Syndrome. Front
Immunol. 9:27112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Cui C, Wang Y, Liu J, Zhao J, Sun P and
Wang S: A fungal pathogen deploys a small silencing RNA that
attenuates mosquito immunity and facilitates infection. Nat Commun.
10:42982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Mathur M, Nair A and Kadoo N:
Plant-pathogen interactions: MicroRNA-mediated trans-kingdom gene
regulation in fungi and their host plants. Genomics. 112:3021–3035.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Wong-Bajracharya J, Singan VR, Monti R,
Plett KL, Ng V, Grigoriev IV, Martin FM, Anderson IC and Plett JM:
The ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus microcarpus encodes a
microRNA involved in cross-kingdom gene silencing during symbiosis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 119:e21035271192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Li L, Li C, Lv M, Hu Q, Guo L and Xiong D:
Correlation between alterations of gut microbiota and miR-122-5p
expression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Transl
Med. 8:14812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Gupta P, O'Neill H, Wolvetang EJ,
Chatterjee A and Gupta I: Advances in single-cell long-read
sequencing technologies. NAR Genom Bioinform. 6:lqae0472024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Duan D, Wang M, Han J, Li M, Wang Z, Zhou
S, Xin W and Li X: Advances in multi-omics integrated analysis
methods based on the gut microbiome and their applications. Front
Microbiol. 15:15091172025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Moisoiu T, Dragomir MP, Iancu SD,
Schallenberg S, Birolo G, Ferrero G, Burghelea D, Stefancu A, Cozan
RG, Licarete E, et al: Combined miRNA and SERS urine liquid biopsy
for the point-of-care diagnosis and molecular stratification of
bladder cancer. Mol Med. 28:392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Dave VP, Ngo TA, Pernestig AK, Tilevik D,
Kant K, Nguyen T, Wolff A and Bang DD: MicroRNA amplification and
detection technologies: Opportunities and challenges for point of
care diagnostics. Lab Invest. 99:452–469. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
238
|
Akbarian P, Asadi F and Sabahi A:
Developing mobile health applications for inflammatory bowel
disease: A systematic review of features and technologies. Middle
East J Dig Dis. 16:2112024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
239
|
De Deo D, Dal Buono A, Gabbiadini R,
Nardone OM, Ferreiro-Iglesias R, Privitera G, Bonifacio C,
Barreiro-de Acosta M, Bezzio C and Armuzzi A: Digital biomarkers
and artificial intelligence: A new frontier in personalized
management of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol.
16:16371592025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Asadi F, Hosseini A and Daeechini AH:
Designing the essential informational needs of a smartphone
application for self-management of patients with inflammatory bowel
disease. Health Sci Rep. 7:e701862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Yarani R, Shojaeian A, Palasca O, Doncheva
NT, Jensen LJ, Gorodkin J and Pociot F: Differentially expressed
miRNAs in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Front Immunol.
13:8657772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Wu F, Zhang S, Dassopoulos T, Harris ML,
Bayless TM, Meltzer SJ, Brant SR and Kwon JH: Identification of
microRNAs associated with ileal and colonic Crohn's disease.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 16:1729–1738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Lederer T, Hipler NM, Thon C, Kupcinskas J
and Link A: Comparison of fecal MicroRNA isolation using various
total RNA isolation kits. Genes (Basel). 15:4982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Tam S, Tsao MS and McPherson JD:
Optimization of miRNA-seq data preprocessing. Brief Bioinform.
16:950–963. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Rashid H, Hossain B, Siddiqua T, Kabir M,
Noor Z, Ahmed M and Haque R: Fecal MicroRNAs as potential
biomarkers for screening and diagnosis of intestinal diseases.
Front Mol Biosci. 7:1812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Drago L, De La Motte LR, Deflorio L,
Sansico DF, Salvatici M, Micaglio E, Biazzo M and Giarritiello F:
Systematic review of bidirectional interaction between gut
microbiome, miRNAs, and human pathologies. Front Microbiol.
16:15409432025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Cuinat C, Pan J and Comelli EM:
Host-dependent alteration of the gut microbiota: the role of
luminal microRNAs. Microbiome Res Rep. 4:152025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Lv Y, Zhen C, Liu A, Hu Y, Yang G, Xu C,
Lou Y, Cheng Q, Luo Y, Yu J, et al: Profiles and interactions of
gut microbiome and intestinal microRNAs in pediatric Crohn's
disease. mSystems. 9:e00783242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Metwaly A, Kriaa A, Hassani Z, Carraturo
F, Druart C; IHMCSA Consortium; Arnauts K, Wilmes P, Walter J,
Rosshart S, et al: A Consensus Statement on establishing causality,
therapeutic applications and the use of preclinical models in
microbiome research. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:343–356.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
What will it take to get miRNA therapies
to market? Nat Biotechnol. 42:1623–1624. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Diener C, Keller A and Meese E: Emerging
concepts of miRNA therapeutics: From cells to clinic. Trends Genet.
38:613–626. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Monaghan TM, Seekatz AM, Markham NO, Yau
TO, Hatziapostolou M, Jilani T, Christodoulou N, Roach B, Birli E,
Pomenya O, et al: Fecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent
clostridioides difficile infection associates with functional
alterations in circulating microRNAs. Gastroenterology.
161:255–270.e4. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Brusnic O, Adrian B, Sorin-Radu F, Grama
B, Sofonea F, Roman-Filip C, Roman-Filip I, Solomon A, Bîrsan S,
Dura H, et al: Importance of fecal microbiota transplantation and
molecular regulation as therapeutic strategies in inflammatory
bowel diseases. Nutrients. 16:44112024. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
254
|
Cerrotti G, Buratta S, Latella R, Calzoni
E, Cusumano G, Bertoldi A, Porcellati S, Emiliani C and Urbanelli
L: Hitting the target: Cell signaling pathways modulation by
extracellular vesicles. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids.
5:527–552. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Yan Y, Nguyen LH, Franzosa EA and
Huttenhower C: Strain-level epidemiology of microbial communities
and the human microbiome. Genome Med. 12:712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Iacomino G: miRNAs: The Road from Bench to
Bedside. Genes (Basel). 14:3142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Jones CH, Androsavich JR, So N, Jenkins
MP, MacCormack D, Prigodich A, Welch V, True JM and Dolsten M:
Breaking the mold with RNA-a 'RNAissance' of life science. NPJ
Genom Med. 9:22024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
258
|
Santo J, Gineste P, Scherrer D, Nitcheu J,
Ehrlich H, Sands BE and Vermeire S: P001 Obefazimod upregulates
miR-124 and downregulates the expression of some cytokines in blood
and rectal biopsies of patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative
colitis. J Crohns Colitis. 17:i169–i170. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Vermeire S, Sands BE, Tilg H, Tulassay Z,
Kempinski R, Danese S, Bunganič I, Nitcheu J, Santo J, Scherrer D,
et al: ABX464 (obefazimod) for moderate-to-severe, active
ulcerative colitis: A phase 2b, double-blind, randomised,
placebo-controlled induction trial and 48 week, open-label
extension. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:1024–1035. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Abivax: Abivax announces positive phase 3
results from both ABTECT 8-week induction trials investigating
obefazimod its first-in-class oral miΡ-124 enhancer in moderate to
severely active ulcerative colitis. 2025.
|
|
261
|
Zendjabil M: Preanalytical, analytical and
postanalytical considerations in circulating microRNAs measurement.
Biochem Med (Zagreb). 34:0205012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Sandau US, Wiedrick JT, McFarland TJ,
Galasko DR, Fanning Z, Quinn JF and Saugstad JA: Analysis of the
longitudinal stability of human plasma miRNAs and implications for
disease biomarkers. Sci Rep. 14:21482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Link J, Thon C, Petkevicius V,
Steponaitiene R, Malfertheiner P, Kupcinskas J and Link A: The
translational impact of plant-derived Xeno-miRNA miR-168 in
gastrointestinal cancers and preneoplastic conditions. Diagnostics
(Basel). 13:27012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Tembo KM, Wang X, Bolideei M, Liu Q,
Baboni F, Mehran MJ, Sun F and Wang CY: Exploring the bioactivity
of MicroRNAs originated from plant-derived exosome-like
nanoparticles (PELNs): Current perspectives. J Nanobiotechnology.
23:5632025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
265
|
Zheng Y, Ji B, Song R, Wang S, Li T, Zhang
X, Chen K, Li T and Li J: Accurate detection for a wide range of
mutation and editing sites of microRNAs from small RNA
high-throughput sequencing profiles. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:e1232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Kern F, Krammes L, Danz K, Diener C, Kehl
T, Küchler O, Fehlmann T, Kahraman M, Rheinheimer S,
Aparicio-Puerta E, et al: Validation of human microRNA target
pathways enables evaluation of target prediction tools. Nucleic
Acids Res. 49:127–144. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
267
|
Witkos TM, Koscianska E and Krzyzosiak WJ:
Practical aspects of microRNA target prediction. Curr Mol Med.
11:93–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Oliveira ECS, Quaglio AEV, Magro DO, Di
Stasi LC and Sassaki LY: Intestinal microbiota and miRNA in IBD: A
narrative review about discoveries and perspectives for the future.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:71762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Liu Y, Zhao Z and Li M: Overcoming the
cellular barriers and beyond: Recent progress on cell penetrating
peptide modified nanomedicine in combating physiological and
pathological barriers. Asian J Pharm Sci. 17:523–543.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Singh D: Next-generation miRNA
therapeutics: From computational design to translational
engineering. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. Aug 15–2025.Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
271
|
Casado-Bedmar M and Viennois E: MicroRNA
and gut microbiota: Tiny but mighty-novel insights into their
cross-talk in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis and
therapeutics. J Crohns Colitis. 16:992–1005. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
272
|
Chodur GM and Steinberg FM: Human
MicroRNAs modulated by diet: A scoping review. Adv Nutr.
15:1002412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Campbell K: Do the microRNAs we eat affect
gene expression? Nature. 582:S10–S11. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
274
|
Jouve de la Barreda N: From transgenesis
to gene edition. Bioethical and applied considerations. Cuad Bioet.
31:387–401. 2020.In Spanish. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
275
|
Shin A and Xu H: Privacy risks in
microbiome research: Public perspectives before and during a global
pandemic. Ethics Hum Res. 44:2–13. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|