Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is defined as kidney
damage resulting from diabetes. In total, ~40% of patients with
diabetes will eventually develop DKD (1,2).
Moreover, with disease progression, patients with DKD experience a
decline in renal function, ultimately culminating in kidney failure
and end-stage kidney disease (3). Under the pathological condition of
DKD, metabolic dysregulation can trigger oxidative stress (4-7),
inflammatory cascades (8),
tubulointerstitial injury (9,10) and glomerular endothelial
dysfunction via fenestration alterations (11). Therefore, there is an urgent
requirement to fully understand the pathological changes in
different regions of DKD and explore effective diagnostic and
therapeutic approaches.
Metabolomics is an omics technology that enables the
comprehensive analysis of metabolites in organisms (12). Classic metabolomics methods focus
on identifying and quantifying metabolites, providing a global
metabolic pathway profile that captures systemic alterations under
physiological or pathological conditions (13,14). This enables the identification of
metabolic disparities across diverse sample cohorts (15,16). However, data obtained by these
methods lack information on the spatial distribution of metabolites
within tissues. This limitation has driven the development of
spatial metabolomics.
Spatial metabolomics is a technology developed over
the past two decades, and its application scope has been
continuously expanded in the last 5 years with the advancement of
technical methodologies (17,18). This technique integrates
metabolomics with spatial biology, offering a novel approach to
explore the heterogeneity of metabolites within tissue
microenvironments under disease conditions. Recent studies on
cancer types such as hepatocellular carcinoma have reported that
the spatial distribution patterns of immune cells can more
accurately predict diseases than gene expression levels alone
(19-22). This highlights the importance of
spatial location information in disease research. Currently,
spatial metabolomics has demonstrated great potential in several
fields, including neuroscience (23,24), microbiology (25), plant science (26), drug development (27) and clinical applications (28). Notably, the application of
spatial metabolomics in kidney research is still in its
developmental stage, with most existing studies concentrating on
the heterogeneity between the renal cortex and medulla (29-31).
The present review discusses the fundamental
principles and advantages of spatial metabolomics technology,
summarizing recent advancements in its application to metabolic
disorders in DKD. The focus is on characteristics associated with
carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, amino acid metabolism
and nucleic acid metabolism within cortical and medullary regions.
Finally, the review outlines potential future research directions,
aiming to provide valuable insights and contributions to
researchers in the fields of DKD and related pathophysiology.
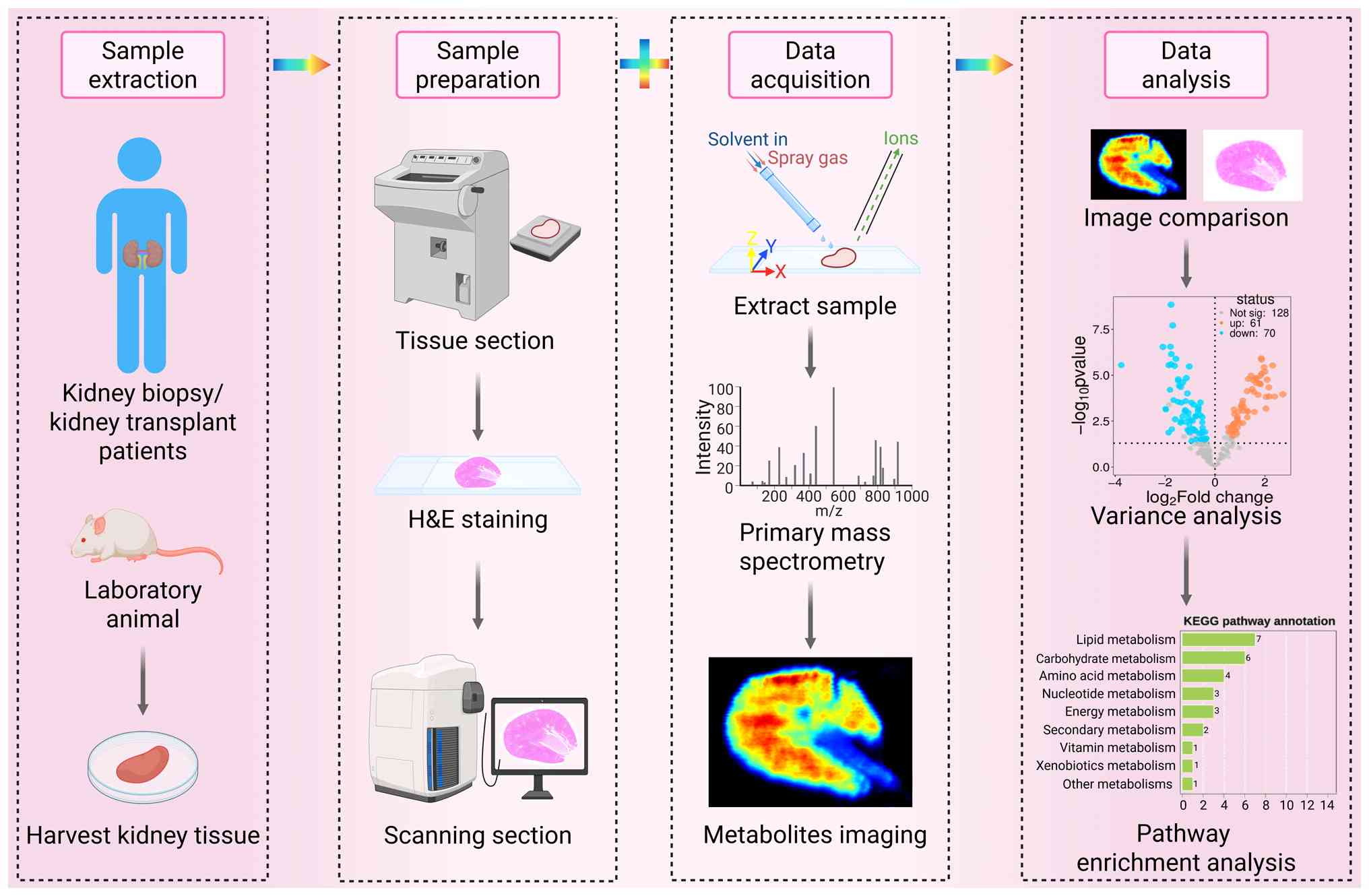
Spatial metabolomics represents a cutting-edge
technology that integrates mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) with the
principles of metabolomics. The fundamental working principle
involves employing specific ionization methods to ionize
metabolites present in tissue sections of samples (32). Currently, three primary
ionization techniques are widely utilized in spatial metabolomics:
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI)-MSI, desorption
electrospray ionization (DESI)-MSI and secondary ion (SIMS)-MSI
(33-38). These ionized metabolites are then
sent to a mass spectrometer for mass analysis, where they are
analyzed to obtain information on their mass-to-charge ratio. At
the same time, the spatial distribution images of metabolites in
the tissue sections are reconstructed by combining the mass
spectrometry data with the spatial coordinate information of the
tissue samples (32,39,40). To enable co-localization
analysis, previous studies spatially aligned consecutive kidney
sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin with MSI data (41,42) (Fig. 1).
The core advantage of spatial metabolomics is its
capability to resolve spatial information, enabling in situ
localization of metabolites within biological tissues. This is
particularly valuable in kidney research, where the average
cellular diameter is ~10 μm (43). MALDI-MSI boasts high sensitivity
and the capability to detect low-abundance metabolites, thus
occupying a dominant position in the field of spatial metabolomics.
Using MALDI-MSI with a spatial resolution of 20 μm, the
overall metabolic heterogeneity distribution from the cortex to the
medulla in DKD kidney sections can be clearly visualized, revealing
metabolic gradient changes in different functional regions under
disease conditions (31). By
contrast, employing a higher resolution of 5 μm with
MALDI-MSI and isotope labeling enables in situ,
cell-type-specific dynamic metabolic measurements, uncovering
cellular metabolism within the tissue structure (44). A key advantage of DESI-MSI is its
compatibility with fresh tissues, facilitating rapid detection of
clinical samples. Operating at room temperature and atmospheric
pressure, DESI-MSI requires no complex sample pretreatment
(45,46). With a typical spatial resolution
of 50-200 μm (47) and a
moderate detectable molecular weight range, it is more suitable for
imaging large tissue regions. This facilitates the investigation of
the pervasive metabolic landscape in advanced DKD, a condition
often characterized by extensive interstitial fibrosis. SIMS-MSI
operates under high-vacuum conditions and has stringent temperature
requirements. While SIMS-MSI achieves an ultra-high spatial
resolution of <1 μm, it has the narrowest detectable
molecular weight range among all the discussed techniques.
Nevertheless, it provides the highest spatial resolution among the
technologies addressed here, making it ideally suited for
single-cell metabolomics research (35,37). Therefore, the selection of an
appropriate spatial metabolomics technique for DKD research
necessitates a trade-off between its spatial resolution and
metabolite coverage. Future studies may integrate multiple
technologies to obtain more comprehensive metabolic information,
thereby enhancing our in-depth understanding of disease
mechanisms.
The kidney is a vital excretory and regulatory
organ, whose functions rely on the sophisticated structure and
division of labor between the renal cortex and medulla (48,49). The renal cortex, composed
primarily of abundant renal corpuscles and proximal tubules, is
principally responsible for blood filtration, reabsorption and
secretion of substances (50,51). By contrast, the renal medulla,
through the loops of Henle and collecting ducts, maintains internal
environmental homeostasis by regulating water-electrolyte balance
and urine concentration (52,53). Owing to these functional
distinctions between the two regions, there are notable differences
in their demand for and utilization of metabolites (54).
In the onset and progression of DKD, the
dysregulation of regional metabolic functions is particularly
critical, and metabolomics research provides an essential
technological approach for systematically elucidating its molecular
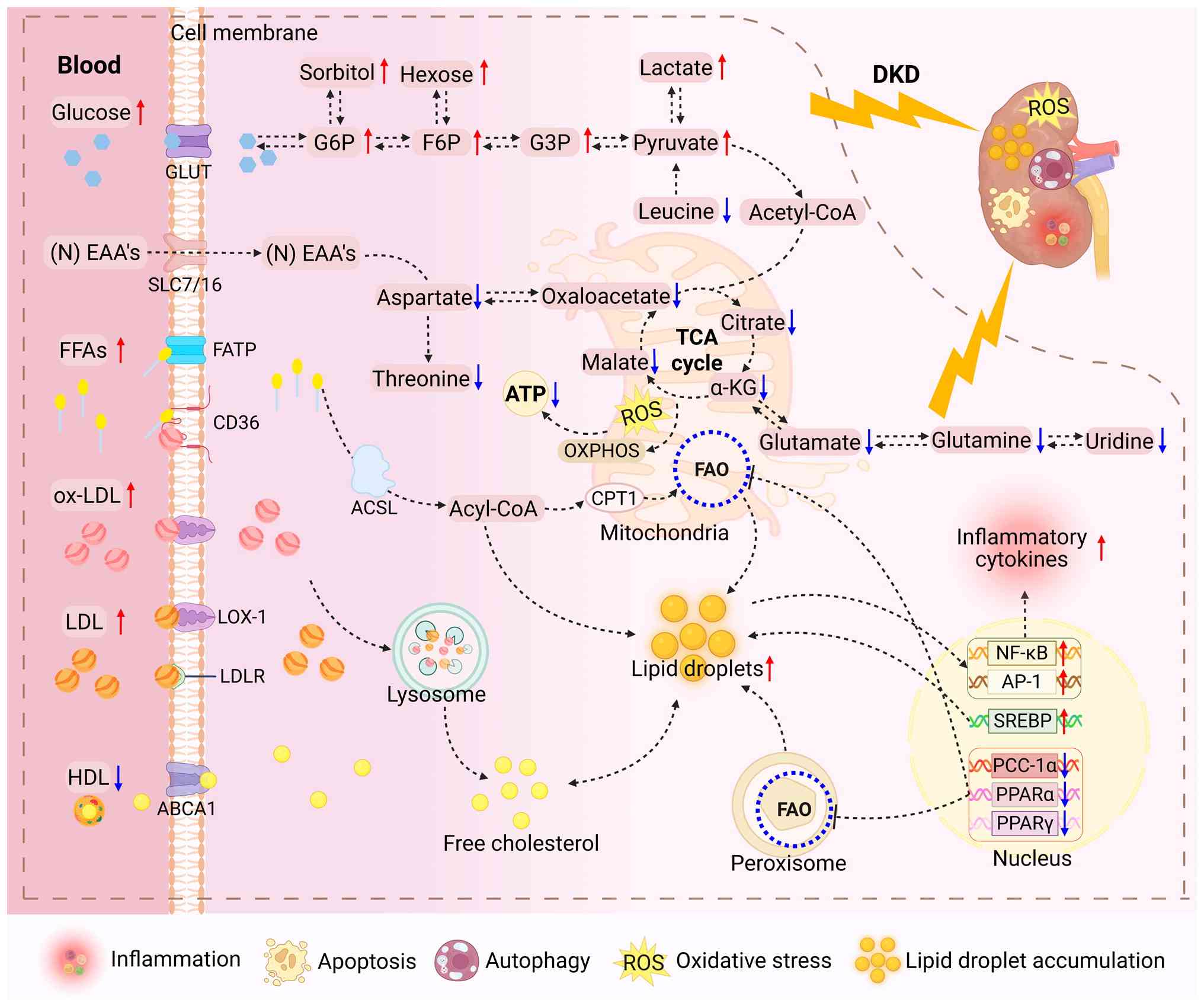
mechanisms (55,56). Classical metabolomics, through
the synergistic application of non-targeted metabolic profiling and
targeted metabolite quantification strategies, has systematically
constructed a comprehensive molecular map of the metabolic network
of the kidney (Fig. 2),
revealing ATP depletion driven by mitochondrial dysfunction,
imbalance of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates and
inhibition of fatty acid oxidation (FAO), which ultimately leads to
apoptosis, autophagy, oxidative stress and lipid droplet
accumulation (57,58). Therefore, the integration of
spatial metabolomics has enabled unprecedented precision in
regional metabolite localization (59,60).
A hyperglycemic environment can induce an imbalance
in energy metabolism homeostasis, characterized by mitochondrial
oxidative phosphorylation dysfunction and metabolic reprogramming
(61,62). Notably, the renal medulla mainly
relies on glucose for energy (63,64). Previous research reported that
the levels of hexoses in the cortical tissue increased when male
C57BL/6J-Ins2Akita mice reached 17 weeks of age (65). When DKD rats were 24 and 28 weeks
old, respectively, the kidney glucose levels exhibited a marked
global increase, with particularly pronounced elevations observed
in the cortex region (31,66). By contrast, rats subjected to
prolonged feeding exhibited notably reduced glucose levels in the
renal medulla region (66).
However, it should be noted that these findings reflect the
complexity of metabolic heterogeneity across different regions and
time points. The discrepancies in glucose levels between the renal
cortex and medulla have led to varied interpretations of the
pathophysiological mechanisms of DKD, highlighting the necessity of
considering tissue specificity and its potential impacts on overall
disease progression when investigating metabolic alterations.
The distribution of TCA cycle intermediates also
exhibits spatial heterogeneity. Clinical studies have reported
that, compared with healthy controls, succinic acid and malic acid
are markedly reduced in kidney biopsies of patients with type 1
diabetes across several kidney regions, suggesting subclinical
mitochondrial dysfunction (67).
These spatial distribution abnormalities are highly congruent with
the global findings of classical metabolomics. In individuals with
DKD, enzymes involved in glycolytic, sorbitol, methylglyoxal and
mitochondrial pathways have been reported to exhibit reduced
expression and activity. Moreover, pyruvate kinase M2 demonstrates
marked decreases in both its transcriptional expression and
enzymatic activity (68). From
the perspective of metabolic pathways, the accumulation of TCA
cycle intermediates induces a burst of mitochondrial reactive
oxygen species, driving the progression of DKD (69,70). Table I consolidates information on
spatially resolved metabolic alterations in carbohydrate and TCA
cycle intermediates.
Classical metabolomics studies have systematically
characterized the systemic lipid metabolic dysregulation in DKD,
elucidating imbalances in cholesterol esterification, phospholipid
remodeling and triglyceride (TG) accumulation (71-73). Moreover, spatial metabolomics has
revealed notable regional variations in phospholipids and TGs in
DKD kidneys (66,74). Phospholipids are key components
of cell membranes and are associated with the pathogenesis of DKD
(75). Lysophosphatidic acid
(LPA), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), lysophosphatidylethanolamine
(LPE) and lycerylphosphorylethanolamine (GPE) are all lipid
metabolites derived from phospholipids. In DKD model mice, the
levels of LPA, LPC, LPE and GPE in the cortex were reported to be
markedly elevated (65,76,77). Moreover, changes in the
phosphatidylcholine (PC)/phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) ratio have
been reported to have an impact on cellular processes associated
with health and disease (77).
In cardiovascular disease patients at risk of insulin resistance,
changes in the PC/PE ratio affect cellular processes related to
cardiovascular health and disease progression by regulating
inflammatory responses and the physiological state of
cardiomyocytes (78). Notably,
in db/db mice, the levels of PC/PE ratio in the cortex and medulla
showed opposite changes, indicating that metabolic responses in
different kidney regions during disease progression are both
complex and region-specific (66). TGs are subject to rapid turnover
and re-arrangement of fatty acids (FAs) (79). A recent spatial multi-omics study
of long-term DKD reported a marked accumulation of TG in the
medullary region (74).
Furthermore, in DKD rats at 24 weeks of age, renal cortical oleic
acid levels were elevated, whilst polyunsaturated FAs, including
linoleic acid, were markedly reduced (31).
Spatial metabolomics has advanced the understanding
of lipid changes in the kidneys of DKD to the level of proximal
tubular cells. Under physiological conditions, the kidney tubules
predominantly utilize FAs (64,80,81), and this utilization requires
carnitine as a carrier, facilitating the transport of long-chain
fatty acids into the mitochondria via the carnitine shuttle system
(82). Spatial metabolomics and
multi-omics analyses of human kidney samples reported that the
detection of acylcarnitines in cortical samples was insufficiently
sensitive (83). This
observation is consistent with the known downregulation of FAO in
chronic kidney disease, indicating impaired FAO in proximal tubular
cells of patients with kidney disease (84). Detailed lipid changes are
presented in Table II.
It should be noted that the inherent differences in
sample size, animal model selection and experimental methodologies
among the aforementioned studies may impose significant constraints
on the reproducibility and generalizability of the results.
Although spatial metabolomics has successfully revealed the
regional heterogeneity of lipid distribution in the kidney,
existing research is mostly confined to single-species models
(e.g., db/db mice and DKD rats). Moreover, the sample size used for
spatial metabolomics analysis is only up to 6 animals per group,
coupled with the lack of dynamic tracking data across different
disease stages. This may not only induce biases in interpreting the
causal relationship between lipid metabolic disorders and the
pathological progression of DKD, but may also hinder the accurate
reflection of the clinical metabolic characteristics of human DKD.
Therefore, future studies should prioritize optimizing experimental
designs by expanding sample sizes, diversifying animal models and
conducting dynamic monitoring across multiple disease stages, so as
to more comprehensively elucidate the metabolic response mechanisms
of distinct renal regions during DKD progression.
The dysregulation of amino acid metabolism in DKD is
not merely a consequence of renal dysfunction, but an active driver
of pathogenesis (85,86). Spatial metabolomics techniques
have revealed changes in amino acids in specific regions of the
kidney. In db/db mice, glutamate, spermine, taurine and spermidine
were notably reduced in both the cortex and medulla, whilst
histamine, putrescine and indoxyl sulfate markedly accumulated in
the cortex (66,87,88). Notably, spermidine has been
reported to exhibit multiple pharmacological effects, including
anti-aging, anti-oxidation, anti-inflammation and cardiovascular
protection (89-92). Sulfate is a protein-binding
gut-derived uremic toxin that has been reported to be closely
associated with podocyte loss in DKD (93). Our previous research demonstrated
that Tangshen formula can effectively decrease the concentration of
sulfate during the treatment of DKD (94). Furthermore, compared with that in
db/db mice, glutamate was reported to be similarly reduced in the
cortex and medulla of high-fat diet and STZ-induced DKD rats
(31,66). Additionally, glutamine,
aspartate, threonine and leucine/isoleucine were reported to be
markedly reduced (31,66,95). The heterogeneity of amino acid
and related metabolism in the cortex and medulla of DKD revealed by
spatial metabolomics is summarized in Table III.
Classic metabolomic studies have demonstrated that
after inducing diabetes in rats via injection of alloxan, the
levels of purine metabolites in their bodies are significantly
elevated, including uric acid (the end product of purine
metabolism) and metabolic intermediates such as xanthine,
hypoxanthine, adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and inosine (96-98). Notably, a large-scale clinical
metabolomics study, involving 4,503 healthy controls and 1,875
patients with DKD, reported that the levels of uracil in patients
with DKD were markedly reduced (99). These phenomena suggest unique
nucleic acid metabolic disturbances. However, to clarify their
local in situ distribution and pathological significance
within the kidney, spatial metabolomics is required.
Spatially resolved analyses have elucidated
compartment-specific nucleotide dysregulation, offering mechanistic
insights into DKD pathology (31,100). In db/db mice, the level of AMP,
a key intermediate in purine nucleotide metabolism, was reported to
be notably elevated across all renal regions (66). Moreover, in DKD rats, the levels
of AMP and guanosine monophosphate (GMP) were reported to be
markedly increased in the cortex, whilst they showed a decreasing
trend in the medulla (31).
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) integrates growth factor and
insulin signaling pathways to orchestrate critical cellular
processes, including cell proliferation, motility, survival,
protein synthesis, autophagy and transcriptional regulation
(101). In DKD, abnormal
activation of the mTOR pathway can mediate metabolic reprogramming,
with adenine reported to drive kidney pathological progression
through this pathway. Spatial metabolomics studies reveal that in
normal kidneys, adenine is primarily localized in the glomeruli and
vascular regions (102,103). However, in the pathology of
DKD, adenine diffusely increases throughout the entire tissue
section, particularly in the regions of sclerotic vessels, mildly
sclerotic glomeruli, atrophic renal tubules and areas of
interstitial inflammation (102). The importance of adenine in
rescue and targeted therapies has been elucidated using multimodal
omics approaches (104). As the
most abundant modified nucleoside in several RNA species,
pseudouridine has been recognized as a new biomarker demonstrating
better performance than creatinine in chronic kidney disease
stratification (105). Previous
studies have reported that diabetic mice exhibit relatively high
levels of pseudouridine in the cortex tissue (65). Table IV summarizes spatial
metabolomics research revealing dysregulation of nucleotide and
purine metabolism in kidneys of organisms with DKD.
In-depth analyses of metabolic remodeling and
pathological mechanisms in the renal microenvironment is the
theoretical cornerstone for developing new targeted intervention
strategies for DKD. The present review systematically summarizes
the cutting-edge advancements in spatial metabolomics in this
field. Its core contribution lies in overcoming the limitations of
traditional global tissue analysis, revealing the fundamental
spatial heterogeneity of metabolic regulation along the
cortical-medullary axis and within specific pathological
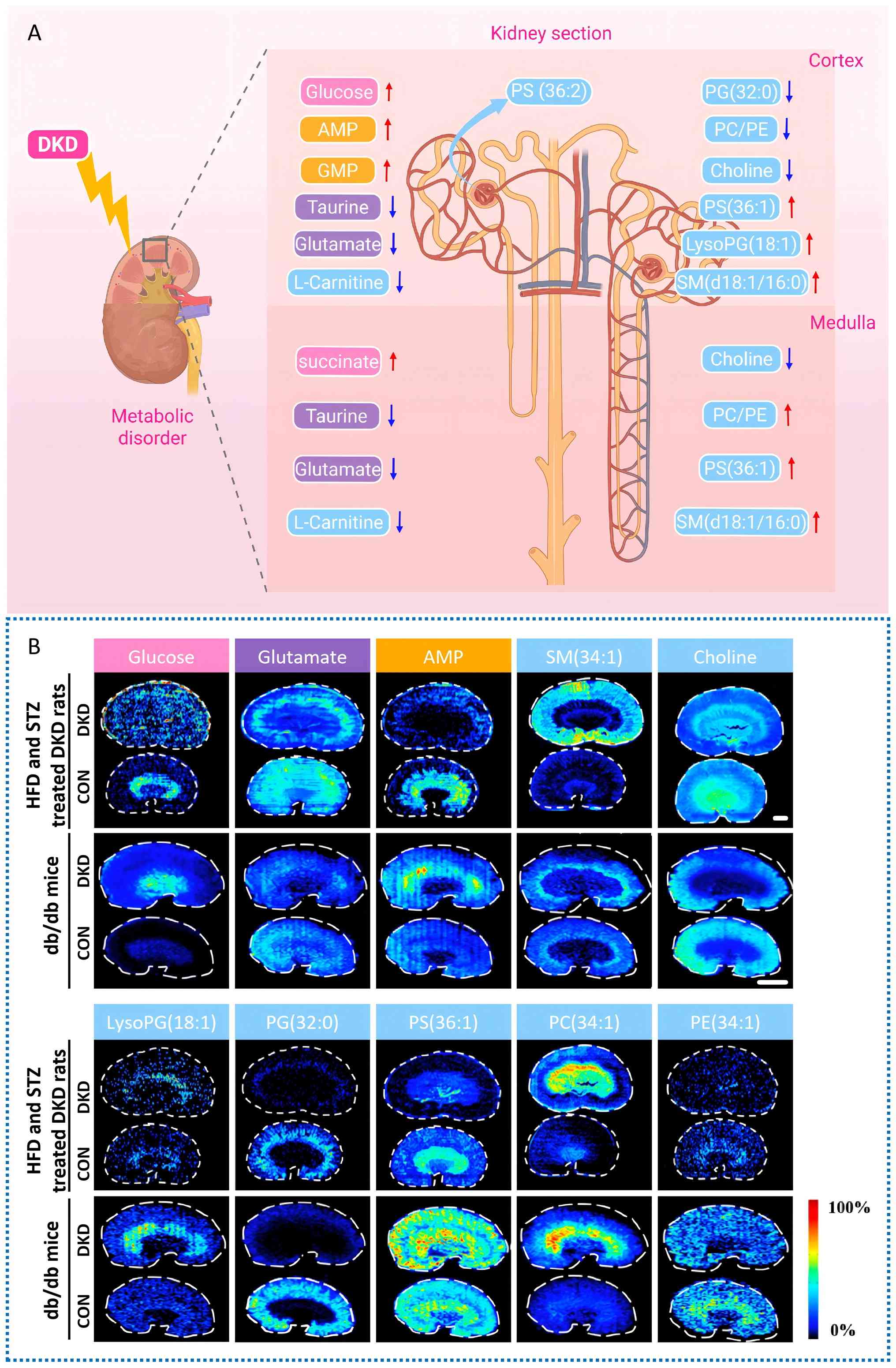
structures. Synthesizing existing research findings, the metabolite
profiles in the renal cortex and medulla exhibit marked
region-specific dysregulation across multiple DKD animal models. In
the cortex region, the levels of glucose, AMP, GMP, PS(36:2),
PS(36:1), LysoPG(18:1) and SM(d18:1/16:0) are significantly
upregulated; concurrently, the levels of taurine, glutamate,
L-carnitine, PG(32:0), PC/PE and choline are notably downregulated.
In the medulla region, the levels of succinate, PS(36:1),
SM(d18:1/16:0) and PC/PE show significant elevation; meanwhile, the
levels of taurine, glutamate, L-carnitine and choline also display
a decreasing trend. Fig. 3
offers an intuitive visual overview and acts as a reference for
identifying regional or global metabolic targets in subsequent
targeted interventions. Metabolites exhibit similar or opposite
distribution and regional accumulation in different functional
areas of the kidney. These are key spatial details that traditional
tissue homogenate-based metabolomics cannot capture. Conventional
methods provide overall averages, masking contrasting trends across
anatomical regions. This obscures the true picture of metabolic
disorders.
The core value of spatial metabolomics lies in
addressing the 'where' and 'how' questions that conventional
techniques cannot resolve, thereby revealing the molecular
mechanisms and causal relationships driving pathological processes.
It is known that metabolic disorders disrupt cellular energy
homeostasis; for example, in the renal hyperglycemic environment,
the pentose phosphate, polyol and hexosamine pathways are
activated, leading to the local accumulation of toxic metabolites,
which in turn activate key signaling pathways and ultimately
trigger core pathological processes such as inflammation, oxidative
stress and fibrosis (106,107). However, classical metabolomics
cannot clearly illustrate in which region of the kidney these
metabolic disorders and signaling pathway activations occur, nor
how the spatial distribution of metabolites drives pathological
processes. This is where spatial metabolomics demonstrates its
unique value, and the research on endogenous adenine metabolism is
a prime example. The accumulation of adenine in specific regions
inhibits 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase whilst activating the
mTORC1-S6K signaling axis, thereby translating metabolic
dysregulation into typical pathological phenotypes such as cellular
hypertrophy and tissue fibrosis (108-111). By integrating spatial
metabolomics and spatial proteomics, research has reported that
metformin acts in the cortical-medullary outer zone, upregulating
nephrosis 2 and inhibiting IL-17 signaling (112). This specifically reverses
purine metabolic imbalance, thereby blocking glomerulosclerosis and
interstitial fibrosis (112).
This intuitively shows how the three-dimensional spatial coupling
of metabolism, transcription and proteins precisely remodels the
pathological microenvironment. Nevertheless, notably, knowledge
gaps remain regarding the regional dynamics of metabolites and the
precise mechanisms by which they promote renal pathology at the
molecular and cellular levels. The key direction for future
research should shift from current descriptive associations to
systematic functional validation and mechanistic exploration of
these spatially anchored metabolites.
As a pivotal methodology for investigating the
spatial distribution of metabolites in vivo, spatial
metabolomics is an indispensable component of spatial multi-omics
research. This technology not only provides a novel spatial
perspective for understanding DKD but also deepens the
comprehension of disease-specific metabolic processes. However, its
application in the field of DKD still faces several pressing
challenges that need to be addressed, for example: i) There are
limitations in technical sensitivity and resolution. Low-abundance
metabolites are prone to loss in imaging (113). Most existing studies only
localize metabolites to large anatomical regions, such as the
cortex or medulla, and they struggle to accurately depict the true
distribution of these metabolites within fine functional units,
such as glomeruli and specific tubular segments. If the resolution
is enhanced, the acquisition speed may consequently be reduced
(114). ii) The identification
and annotation of metabolites often lack sufficient precision. When
annotating metabolites, certain metabolites, such as isomers,
cannot be annotated with absolute certainty (17,115,116). iii) Data analysis and
interpretation present challenges. Crucial challenges exist in data
and signal processing, data comparability and the need for
optimization tailored to each tissue type (117). These challenges indicate that
engineers and researchers need to address the shortcomings to
provide more accurate spatial metabolic maps for the mechanistic
analysis of complex diseases such as DKD.
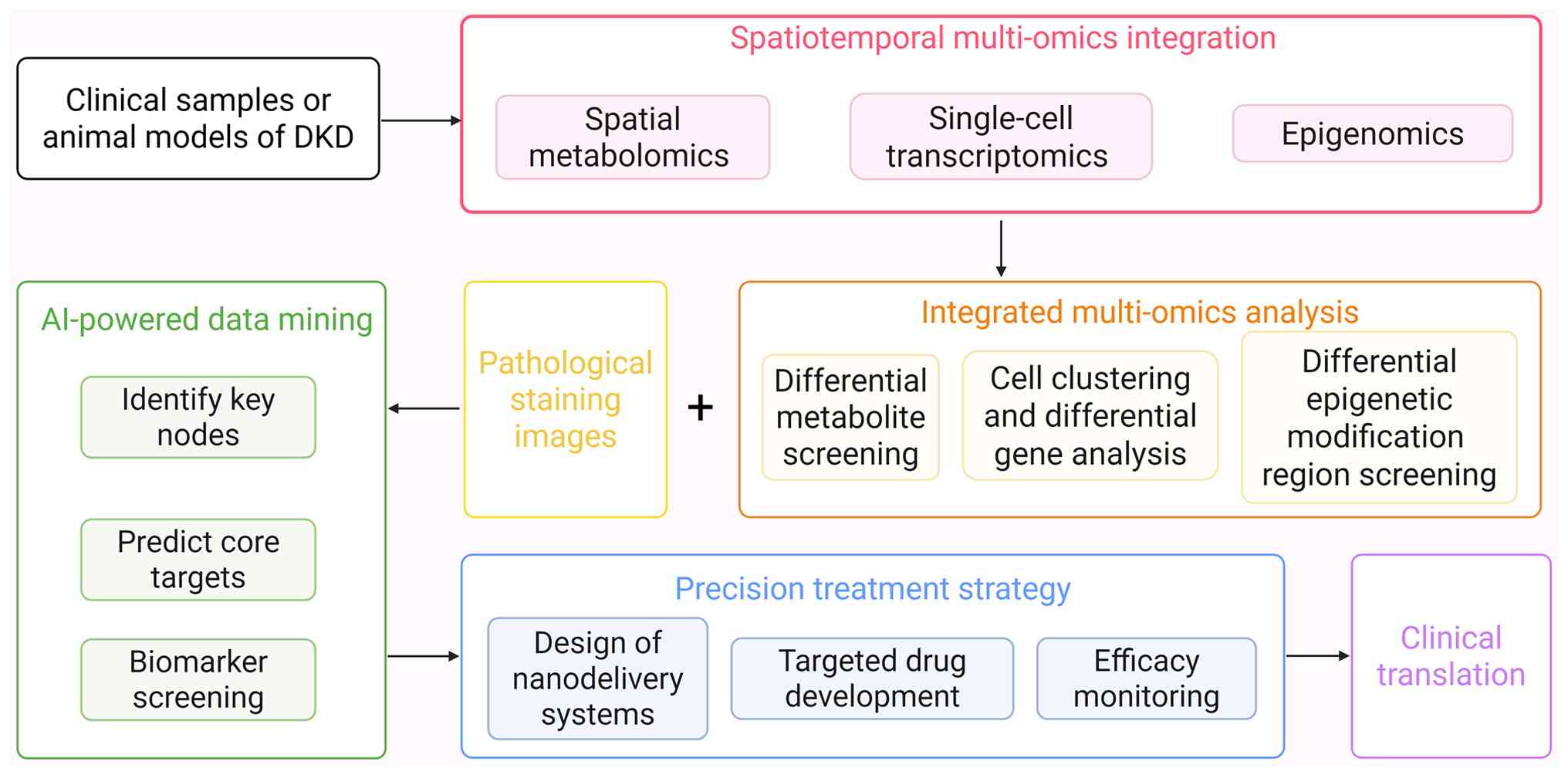
Moreover, spatial metabolomics can directly present
actual biochemical activities and functional metabolic outcomes,
offering new opportunities for DKD research: Firstly, applying
integrated spatial multi-omics to establish causal mechanisms. As
life science research progresses, single-omics approaches are
increasingly inadequate for comprehensively deciphering complex
biological processes. The integration of spatial metabolomics with
transcriptomics and proteomics has become more prevalent (118). By integrating data from spatial
metabolomics and spatial transcriptomics, researchers can associate
changes in metabolite levels with alterations in gene expression,
enabling a deeper exploration of the molecular mechanisms
underlying metabolic regulation (119). Secondly, targeted strategies
can address regional metabolic heterogeneity. This moves beyond
conventional treatment, enabling precision medicine. Spatial
metabolomics technology can assess changes in the distribution of
metabolites after drug intervention, effectively evaluate DKD
drugs, clarify the mechanism of drug treatment and monitor
treatment responses, thereby helping to further optimize treatment
regimens (31). By combining
nanotechnology with drug targeted delivery systems, precise
treatment can be implemented for specific regions of metabolic
heterogeneity (120). The
combined application of these technologies could provide new
possibilities for formulating personalized DKD treatment plans and
achieving accurate prognostic assessment for patients with DKD
(Fig. 4).
The present review systematically examines the
regional metabolic characteristics of DKD, and it highlights the
unique value of spatial metabolomics in elucidating the
pathological mechanisms of DKD. With continuous improvements in
spatial resolution and quantitative analytical techniques, this
technology is expected to serve a critical role in the precision
diagnosis and treatment of DKD. Future research may delve deeper
into the cellular level, focusing on elucidating the more refined
spatial localization and functional associations of specific
metabolites. With the continuous advancement of multi-center data
accumulation and clinical trial validation, region-specific
metabolites or key enzymes are expected to be translated into
reliable diagnostic biomarkers and intervenable therapeutic
targets. Such initiatives will enable the tailored development of
individualized therapies, ultimately boosting early diagnostic
efficiency and optimizing long-term outcomes for patients with
DKD.
Not applicable.
HL made substantial contributions to writing the
original draft, reviewing and editing the manuscript, acquiring
resources, conducting investigation, developing the
conceptualization and performing visualization. TZ participated in
reviewing and editing the manuscript, carrying out investigation,
securing funding acquisition and conceptualization. DF contributed
to reviewing and editing the manuscript, as well as
conceptualization. YL and BZ both took part in reviewing and
editing the manuscript, and visualization. WC and GM were involved
in visualization and investigation. JR made contributions to
writing the original draft and visualization. SD participated in
investigation and visualization. All authors have read and approved
the final manuscript. Data authentication is not applicable.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Not applicable.
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant no. 82374224), the Beijing Natural
Science Foundation (grant no. 7252270), the Noncommunicable Chronic
Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project (grant no.
2023ZD0509306), National High Level Hospital Clinical Research
Funding (grant no. 2024-NHLHCRF-PY I-07) and National High Level
Hospital Clinical Research Funding (grant no.
2024-NHLHCRF-JBGS-ZH-01).
|
1
|
GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators: Global,
regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with
projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the
Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 402:203–234. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Joumaa JP, Raffoul A, Sarkis C, Chatrieh
E, Zaidan S, Attieh P, Harb F, Azar S and Ghadieh HE: Mechanisms,
biomarkers, and treatment approaches for diabetic kidney disease:
Current insights and future perspectives. J Clin Med. 14:7272025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johansen KL, Gilbertson DT, Li SL, Li S,
Liu J, Roetker NS, Ku E, Schulman IH, Greer RC, Chan K, et al: US
renal data system 2023 annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney
disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 83:A8–A13. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vartak T, Godson C and Brennan E:
Therapeutic potential of pro-resolving mediators in diabetic kidney
disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 178:1139652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cleveland KH and Schnellmann RG:
Pharmacological targeting of mitochondria in diabetic kidney
disease. Pharmacol Rev. 75:250–262. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tuttle KR, Agarwal R, Alpers CE, Bakris
GL, Brosius FC, Kolkhof P and Uribarri J: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int.
102:248–260. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sharma V, Khokhar M, Panigrahi P, Gadwal
A, Setia P and Purohit P: Advancements, Challenges, and clinical
implications of integration of metabolomics technologies in
diabetic nephropathy. Clin Chim Acta. 561:1198422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rayego-Mateos S, Rodrigues-Diez RR,
Fernandez-Fernandez B, Mora-Fernández C, Marchant V, Donate-Correa
J, Navarro-González JF, Ortiz A and Ruiz-Ortega M: Targeting
inflammation to treat diabetic kidney disease: The road to 2030.
Kidney Int. 103:282–296. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xu F, Jiang H, Li X, Pan J, Li H, Wang L,
Zhang P, Chen J, Qiu S, Xie Y, et al: Discovery of PRDM16-Mediated
TRPA1 induction as the mechanism for low Tubulo-interstitial
fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease. Adv Sci (Weinh).
11:e23067042024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu D, Chen X, He W, Lu M, Li M, Zhang S,
Xie J, Zhang Y and Wang W: Update on the pathogenesis, diagnosis,
and treatment of diabetic tubulopathy. Integrat Med Nephrol Androl.
11:e23–00029. 2024.
|
|
11
|
Empitu MA, Rinastiti P and
Kadariswantiningsih IN: Targeting endothelin signaling in podocyte
injury and diabetic nephropathy-diabetic kidney disease. J Nephrol.
38:49–60. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Muthubharathi BC, Gowripriya T and
Balamurugan K: Metabolomics: Small molecules that matter more. Mol
Omics. 17:210–229. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou M, Sun W, Gao Y, Jiang B, Sun T, Xu
R, Zhang X, Wang Q, Xuan Q and Ma S: Metabolomic profiling reveals
interindividual metabolic variability and its association with
cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome risk. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
24:3152025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barovic M, Hahn JJ, Heinrich A, Adhikari
T, Schwarz P, Mirtschink P, Funk A, Kabisch S, Pfeiffer AFH, Blüher
M, et al: Proteomic and metabolomic signatures in prediabetes
progressing to diabetes or reversing to normoglycemia within 1
year. Diabetes Care. 48:405–415. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pereira PR, Carrageta DF, Oliveira PF,
Rodrigues A, Alves MG and Monteiro MP: Metabolomics as a tool for
the early diagnosis and prognosis of diabetic kidney disease. Med
Res Rev. 42:1518–1544. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Md Dom ZI, Moon S, Satake E, Hirohama D,
Palmer ND, Lampert H, Ficociello LH, Abedini A, Fernandez K, Liang
X, et al: Urinary Complement proteome strongly linked to diabetic
kidney disease progression. Nat Commun. 16:72912025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alexandrov T: Spatial metabolomics and
imaging mass spectrometry in the age of artificial intelligence.
Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 3:61–87. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sharma K, Hansen J, Susztak K, Eberlin L,
Anderton CR, Alexandrov T and Iyengar R: Spatial metabolomics and
multiomics integration for breakthroughs in precision medicine for
kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. Oct 9–2025. View Article : Google Scholar : Epub ahead of
print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Najumudeen AK and Vande voorde J: Spatial
metabolomics to unravel cellular metabolism. Nat Rev Genet.
26:2282025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Allam M and Coskun AF: Combining spatial
metabolomics and proteomics profiling of single cells. Nat Rev
Immunol. 24:7012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun N, Krauss T, Seeliger C, Kunzke T,
Stöckl B, Feuchtinger A, Zhang C, Voss A, Heisz S, Prokopchuk O, et
al: Inter-organ cross-talk in human cancer cachexia revealed by
spatial metabolomics. Metabolism. 161:1560342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jia G, He P, Dai T, Goh D, Wang J, Sun M,
Wee F, Li F, Lim JCT, Hao S, et al: Spatial immune scoring system
predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Nature.
640:1031–1041. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang X, Li T, Zhou Y, Wang X, Dan Z,
Huang J and He J: A new direction in metabolomics: Analysis of the
central nervous system based on spatially resolved metabolomics.
TrAC Trends Analytical Chemist. 165:1171032023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Miller A, York EM, Stopka SA,
Martínez-François JR, Hossain MA, Baquer G, Regan MS, Agar NYR and
Yellen G: Spatially resolved metabolomics and isotope tracing
reveal dynamic metabolic responses of dentate granule neurons with
acute stimulation. Nat Metab. 5:1820–1835. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dean DA, Klechka L, Hossain E, Parab AR,
Eaton K, Hinsdale M and McCall LI: Spatial metabolomics reveals
localized impact of influenza virus infection on the lung tissue
metabolome. mSystems. 7:e00353222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu X, Liu Z and Sun X: Single-cell and
spatial multi-omics in the plant sciences: Technical advances,
applications, and perspectives. Plant Commun. 4:1005082023.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Wang X, Zhang J, Zheng K, Du Q, Wang G,
Huang J, Zhou Y, Li Y, Jin H and He J: Discovering metabolic
vulnerability using spatially resolved metabolomics for antitumor
small molecule-drug conjugates development as a precise cancer
therapy strategy. J Pharm Anal. 13:776–787. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bag S, Oetjen J, Shaikh S, Chaudhary A,
Arun P and Mukherjee G: Impact of spatial metabolomics on
immune-microenvironment in oral cancer prognosis: A clinical
report. Mol Cell Biochem. 479:41–49. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
He T, Lin K, Xiong L, Zhang W, Zhang H,
Duan C, Li X and Zhang J: Disorder of phospholipid metabolism in
the renal cortex and medulla contributes to acute tubular necrosis
in mice after cantharidin exposure using integrative lipidomics and
spatial metabolomics. J Pharm Anal. 15:1012102025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qiu S, Wang Z, Wang X, Guo S, Cai Y, Xie
D, Hu Z, Wang S, Yang Q and Zhang A: Spatial metabolomics
identifies riboflavin metabolism as a therapeutic target of Huangqi
Guizhi Wuwu decoction in diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Chromatogr.
39:e702392025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Fu W, Huo M, He B, Liu Y, Tian L,
Li W, Zhou Z, Wang B, Xia J, et al: Spatial-resolved metabolomics
reveals tissue-specific metabolic reprogramming in diabetic
nephropathy by using mass spectrometry imaging. Acta Pharm Sin B.
11:3665–3677. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Min X, Zhao Y, Yu M, Zhang W, Jiang X, Guo
K, Wang X, Huang J, Li T, Sun L and He J: Spatially resolved
metabolomics: From metabolite mapping to function visualizing. Clin
Transl Med. 14:e700312024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tuck M, Grélard F, Blanc L and Desbenoit
N: MALDI-MSI towards multimodal imaging: Challenges and
perspectives. Front Chem. 10:9046882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kumar BS: Desorption electrospray
ionization mass spectrometry imaging (DESI-MSI) in disease
diagnosis: An overview. Anal Methods. 15:3768–3784. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang S, Wang Z, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhang H,
Wang Z, Zhou Z and Abliz Z: Dual mass spectrometry imaging and
spatial metabolomics to investigate the metabolism and
nephrotoxicity of nitidine chloride. J Pharm Anal. 14:1009442024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song X, Zang Q, Li C, Zhou T and Zare RN:
Immuno-desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging
identifies functional macromolecules by using
Microdroplet-cleavable mass tags. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
62:e2022169692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lockyer NP, Aoyagi S, Fletcher JS, Gilmore
I, van der heide P, Moore KL, Tyler BJ and Weng LT: Secondary ion
mass spectrometry. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 4:322024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Coello Y, Jones AD, Gunaratne TC and
Dantus M: Atmospheric pressure femtosecond laser imaging mass
spectrometry. Anal Chem. 82:2753–2758. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen H, Durand S, Bawa O, Bourgin M,
Montégut L, Lambertucci F, Motiño O, Li S, Nogueira-Recalde U,
Anagnostopoulos G, et al: Biomarker identification in liver cancers
using desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
(DESI-MS) imaging: An approach for spatially resolved metabolomics.
Methods Mol Biol. 2769:199–209. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
He MJ, Pu W, Wang X, Zhong X, Zhao D, Zeng
Z, Cai W, Liu J, Huang J, Tang D and Dai Y: Spatial metabolomics on
liver cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer
Cell Int. 22:3662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lakkimsetty SS, Weber A, Bemis KA, Stehl
V, Bronsert P, Föll MC and Vitek O: MSIreg: An R package for
unsupervised coregistration of mass spectrometry and H&E
images. Bioinformatics. 40:btae6242024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zickuhr GM, Um IH, Laird A, Harrison DJ
and Dickson AL: DESI-MSI-guided exploration of metabolic-phenotypic
relationships reveals a correlation between PI 38:3 and
proliferating cells in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via
single-section co-registration of multimodal imaging. Anal Bioanal
Chem. 416:4015–4028. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang G, Heijs B, Kostidis S, Rietjens RGJ,
Koning M, Yuan L, Tiemeier GL, Mahfouz A, Dumas SJ, Giera M, et al:
Spatial dynamic metabolomics identifies metabolic cell fate
trajectories in human kidney differentiation. Cell Stem Cell.
29:1580–1593.e7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang G, Heijs B, Kostidis S, Mahfouz A,
Rietjens RGJ, Bijkerk R, Koudijs A, van der Pluijm LAK, van den
Berg CW, Dumas SJ, et al: Analyzing cell-type-specific dynamics of
metabolism in kidney repair. Nat Metab. 4:1109–1118. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lin J, Lin H, Li C, Liao N, Zheng Y, Yu X,
Sun Y and Wu L: Unveiling characteristic metabolic accumulation
over enzymatic-catalyzed process of Tieguanyin oolong tea
manufacturing by DESI-MSI and multiple-omics. Food Res Int.
181:1141362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Banerjee S, Wong AC, Yan X, Wu B, Zhao H,
Tibshirani RJ, Zare RN and Brooks JD: Early detection of unilateral
ureteral obstruction by desorption electrospray ionization mass
spectrometry. Sci Rep. 9:110072019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qi K, Wu L, Liu C and Pan Y: Recent
advances of ambient mass spectrometry imaging and its applications
in lipid and metabolite analysis. Metabolites. 11:7802021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Blanc T, Goudin N, Zaidan M, Traore MG,
Bienaime F, Turinsky L, Garbay S, Nguyen C, Burtin M, Friedlander
G, et al: Three-dimensional architecture of nephrons in the normal
and cystic kidney. Kidney Int. 99:632–645. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li H, Li D and Humphreys BD: Chromatin
conformation and histone modification profiling across human kidney
anatomic regions. Sci Data. 11:7972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang SY and Mahler GJ: A glomerulus and
proximal tubule microphysiological system simulating renal
filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and toxicity. Lab Chip.
23:272–284. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Fan G, Jiang C, Huang Z, Tian M, Pan H,
Cao Y, Lei T, Luo Q and Yuan J: 3D autofluorescence imaging of
hydronephrosis and renal anatomical structure using
cryo-micro-optical sectioning tomography. Theranostics.
13:4885–4904. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hinze C, Karaiskos N, Boltengagen A,
Walentin K, Redo K, Himmerkus N, Bleich M, Potter SS, Potter AS,
Eckardt KU, et al: Kidney Single-cell transcriptomes predict
spatial corticomedullary gene expression and tissue osmolality
gradients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 32:291–306. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
53
|
Gao G, Sumrall ES, Pitchiaya S, Bitzer M,
Alberti S and Walter NG: Biomolecular condensates in kidney
physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 19:756–770. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ding Y, Zhao F, Hu J, Zhao Z, Shi B and Li
S: A conjoint analysis of renal structure and omics characteristics
reveal new insight to yak high-altitude hypoxia adaptation.
Genomics. 116:1108572024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gurung RL, Zheng H, Tan JLI, Liu S, Chan
C, Ang K, Tan C, Liu JJ, Subramaniam T, Sum CF and Lim SC:
Integrative metabolomic and proteomic analysis of diabetic kidney
disease progression with younger-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 27:7454–7463. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jiang X, Liu X, Qu X, Zhu P, Wo F, Xu X,
Jin J, He Q and Wu J: Integration of metabolomics and peptidomics
reveals distinct molecular landscape of human diabetic kidney
disease. Theranostics. 13:3188–3203. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Fan X, Yang M, Lang Y, Lu S, Kong Z, Gao
Y, Shen N, Zhang D and Lv Z: Mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming
in diabetic kidney disease. Cell Death Dis. 15:4422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li S and Susztak K: Mitochondrial
dysfunction has a central role in diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 21:77–78. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Poorna R, Chen WW, Qiu P and Cicerone MT:
Toward Gene-correlated spatially resolved metabolomics with
fingerprint coherent Raman imaging. J Phys Chem B. 127:5576–5587.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Alexandrov T: Spatial metabolomics: From a
niche field towards a driver of innovation. Nat Metabolism.
5:1443–1445. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang J, Wu T, Li C and Du J: A
glycopolymersome strategy for 'drug-free' treatment of diabetic
nephropathy. J Control Release. 372:347–361. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Luo A, Wang R, Gong J, Wang S, Yun C, Chen
Z, Jiang Y, Liu X, Dai H, Liu H and Zheng Y: Syntaxin 17
translocation mediated mitophagy switching drives
hyperglycemia-induced vascular injury. Adv Sci (Weinh).
12:e24149602025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Rebelos E, Mari A, Oikonen V, Iida H,
Nuutila P and Ferrannini E: Evaluation of renal glucose uptake with
[18F] FDG-PET: Methodological advancements and metabolic
outcomes. Metabolism. 141:1553822023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Liu X, Du H, Sun Y and Shao L: Role of
abnormal energy metabolism in the progression of chronic kidney
disease and drug intervention. Ren Fail. 44:790–805. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang G, Zhang J, DeHoog RJ, Pennathur S,
Anderton CR, Venkatachalam MA, Alexandrov T, Eberlin LS and Sharma
K: DESI-MSI and METASPACE indicates lipid abnormalities and altered
mitochondrial membrane components in diabetic renal proximal
tubules. Metabolomics. 16:112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang X, Liu Y, Yang S, Gao X, Wang S,
Wang Z, Zhang C, Zhou Z, Chen Y, Wang Z and Abliz Z: Comparison of
local metabolic changes in diabetic rodent kidneys using mass
spectrometry imaging. Metabolites. 13:3242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang G, Liu L, Tamayo IM, De Leon NGP,
Vigers TB, Tommerdahl KL, Nelson RG, Ladd PE, Alexandrov T,
Birznieks C, et al: 406-P: Spatial metabolomics of human kidney
tissues reveal impaired tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle turnover in
type 1 Diabetes (T1D). Diabetes. 72:4062023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Qi W, Keenan HA, Li Q, Ishikado A, Kannt
A, Sadowski T, Yorek MA, Wu IH, Lockhart S, Coppey LJ, et al:
Pyruvate kinase M2 activation may protect against the progression
of diabetic glomerular pathology and mitochondrial dysfunction. Nat
Med. 23:753–762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hasegawa S and Inagi R: Harnessing
metabolomics to describe the pathophysiology underlying progression
in diabetic kidney disease. Curr Diab Rep. 21:212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Murphy DP, Wolfson J, Reule S, Johansen
KL, Ishani A and Drawz PE: A cohort study of sodium-glucose
cotransporter-2 inhibitors after acute kidney injury among Veterans
with diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 106:126–135. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang Y, Liu T, Wu Y, Wang L, Ding S, Hou
B, Zhao H, Liu W and Li P: Lipid homeostasis in diabetic kidney
disease. Int J Biol Sci. 20:3710–3724. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Mitrofanova A, Merscher S and Fornoni A:
Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in
chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 19:629–645. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Iizuka K: Commentary: Comprehensive
lipidome profiling of the kidney in early-stage diabetic
nephropathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:10153052022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang YR, Piao HL and Chen D:
Identification of spatial specific lipid metabolic signatures in
Long-standing diabetic kidney disease. Metabolites. 14:6412024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hao Y, Fan Y, Feng J, Zhu Z, Luo Z, Hu H,
Li W, Yang H and Ding G: ALCAT1-mediated abnormal cardiolipin
remodelling promotes mitochondrial injury in podocytes in diabetic
kidney disease. Cell Commun Signal. 22:262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Grove KJ, Voziyan PA, Spraggins JM, Wang
S, Paueksakon P, Harris RC, Hudson BG and Caprioli RM: Diabetic
nephropathy induces alterations in the glomerular and tubule lipid
profiles. J Lipid Res. 55:1375–1385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
McCrimmon A, Corbin S, Shrestha B, Roman
G, Dhungana S and Stadler K: Redox phospholipidomics analysis
reveals specific oxidized phospholipids and regions in the diabetic
mouse kidney. Redox Biol. 58:1025202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Vianello E, Ambrogi F, Kalousová M,
Badalyan J, Dozio E, Tacchini L, Schmitz G, Zima T, Tsongalis GJ
and Corsi-Romanelli MM: Circulating perturbation of
phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is
associated to cardiac remodeling and NLRP3 inflammasome in
cardiovascular patients with insulin resistance risk. Exp Mol
Pathol. 137:1048952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wunderling K, Zurkovic J, Zink F,
Kuerschner L and Thiele C: Triglyceride cycling enables
modification of stored fatty acids. Nat Metab. 5:699–709. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Darshi M, Tumova J, Saliba A, Kim J, Baek
J, Pennathur S and Sharma K: Crabtree effect in kidney proximal
tubule cells via late-stage glycolytic intermediates. Iscience.
26:1064622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hall AM: Protein handling in kidney
tubules. Nat Rev Nephrol. 21:241–252. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Panov AV, Mayorov VI, Dikalova AE and
Dikalov SI: Long-Chain and Medium-Chain fatty acids in energy
metabolism of murine kidney mitochondria. Int J Mol Sci.
24:3792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Li H, Li D, Ledru N, Xuanyuan Q, Wu H,
Asthana A, Byers LN, Tullius SG, Orlando G, Waikar SS and Humphreys
BD: Transcriptomic, epigenomic, and spatial metabolomic cell
profiling redefines regional human kidney anatomy. Cell Metab.
36:1105–1125.e10. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kang HM, Ahn SH, Choi P, Ko YA, Han SH,
Chinga F, Park AS, Tao J, Sharma K, Pullman J, et al: Defective
fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key
role in kidney fibrosis development. Nat Med. 21:37–46. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Li C, Gao L, Lv C, Li Z, Fan S, Liu X,
Rong X, Huang Y and Liu J: Active role of amino acid metabolism in
early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Front
Nutr. 10:12398382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu L, Xu J, Zhang Z, Ren D, Wu Y, Wang D,
Zhang Y, Zhao S, Chen Q and Wang T: Metabolic homeostasis of amino
acids and diabetic kidney disease. Nutrients. 15:1842023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Linnan B, Yanzhe W, Ling Z, Yuyuan L,
Sijia C, Xinmiao X, Fengqin L and Xiaoxia W: In situ metabolomics
of metabolic reprogramming involved in a mouse model of type 2
diabetic kidney disease. Front Physiol. 12:7796832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Han J, Li P, Sun H, Zheng Y, Liu C, Chen
X, Guan S, Yin F and Wang X: Integrated metabolomics and mass
spectrometry imaging analysis reveal the efficacy and mechanism of
Huangkui capsule on type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Phytomedicine.
138:1563972025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Castoldi F, Kroemer G and Pietrocola F:
Spermidine rejuvenates T lymphocytes and restores anticancer
immunosurveillance in aged mice. Oncoimmunology. 11:21468552022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zou D, Zhao Z, Li L, Min Y, Zhang D, Ji A,
Jiang C, Wei X and Wu X: A comprehensive review of spermidine:
Safety, health effects, absorption and metabolism, food materials
evaluation, physical and chemical processing, and bioprocessing.
Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 21:2820–2842. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Aihara S, Torisu K, Uchida Y, Imazu N,
Nakano T and Kitazono T: Spermidine from arginine metabolism
activates Nrf2 and inhibits kidney fibrosis. Commun Biol.
6:6762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li X, Zhou X, Liu X, Li X, Jiang X, Shi B
and Wang S: Spermidine protects against acute kidney injury by
modulating macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome activation and
mitochondrial respiration in an eIF5A hypusination-related pathway.
Mol Med. 28:1032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jia M, Lin L, Xun K, Li D, Wu W, Sun S,
Qiu H and Jin D: Indoxyl sulfate aggravates podocyte damage through
the TGF-β1/Smad/ROS signalling pathway. Kidney Blood Press Res.
49:385–396. 2024.
|
|
94
|
Zhao T, Zhang H, Yin X, Zhao H, Ma L, Yan
M, Peng L, Wang Q, Dong X and Li P: Tangshen formula modulates gut
Microbiota and reduces gut-derived toxins in diabetic nephropathy
rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 129:1103252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hejazi L, Sharma S, Ruiz A, Zhang G, Tucci
FC and Sharma K: Spatial metabolomics analysis by MSI-DeepPath
identifies key pathways in ZDF diabetic kidney disease model.
Diabetes. 72(Suppl 1): 400–P. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Varadaiah YGC, Sivanesan S, Nayak SB and
Thirumalarao KR: Purine metabolites can indicate diabetes
progression. Arch Physiol Biochem. 128:87–91. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Zubaidi SN, Wong PL, Qadi WSM, Dawoud EAD,
Hamezah HS, Baharum SN, Jam FA, Abas F, Moreno A and Mediani A:
Deciphering the mechanism of Annona muricata leaf extract in
alloxan-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rat model with 1H-NMR-based
metabolomics approach. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 260:1168062025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Shen XL, Liu H, Xiang H, Qin XM, Du GH and
Tian JS: Combining biochemical with (1)H NMR-based metabolomics
approach unravels the antidiabetic activity of genipin and its
possible mechanism. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 129:80–89. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yuan Y, Huang L, Yu L, Yan X, Chen S, Bi
C, He J, Zhao Y, Yang L, Ning L, et al: Clinical metabolomics
characteristics of diabetic kidney disease: A meta-analysis of 1875
cases with diabetic kidney disease and 4503 controls. Diabetes
Metab Res Rev. 40:e37892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Jung I, Nam S, Lee DY, Park SY, Yu JH, Seo
JA, Lee DH and Kim NH: Association of succinate and adenosine
nucleotide metabolic pathways with diabetic kidney disease in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J.
48:1126–1134. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Mohandes S, Doke T, Hu H, Mukhi D, Dhillon
P and Susztak K: Molecular pathways that drive diabetic kidney
disease. J Clin Invest. 133:e1656542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Sharma K, Zhang GS, Hansen J, Bjornstad P,
Lee HJ, Menon R, Hejazi L, Liu JJ, Franzone A, Looker HC, et al:
Endogenous adenine mediates kidney injury in diabetic models and
predicts diabetic kidney disease in patients. J Clin Invest.
133:e1703412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Ragi N and Sharma K: Deliverables from
metabolomics in kidney disease: Adenine, new insights, and
implication for clinical Decision-making. Am J Nephrol. 55:421–438.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Drexler Y and Fornoni A: Adenine crosses
the biomarker bridge: From 'omics to treatment in diabetic kidney
disease. J Clin Invest. 133:e1740152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Hocher B and Adamski J: Metabolomics for
clinical use and research in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 13:269–284. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Efiong EE, Maedler K, Effa E, Osuagwu UL,
Peters E, Ikebiuro JO, Soremekun C, Ihediwa U, Niu J, Fuchs M, et
al: Decoding diabetic kidney disease: A comprehensive review of
interconnected pathways, molecular mediators, and therapeutic
insights. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 17:1922025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Sinha SK and Nicholas SB: Pathomechanisms
of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Med. 12:73492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Huynh C, Ryu J, Lee J, Inoki A and Inoki
K: Nutrient-sensing mTORC1 and AMPK pathways in chronic kidney
diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 19:102–122. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Zhang J, Fuhrer T, Ye H, Kwan B,
Montemayor D, Tumova J, Darshi M, Afshinnia F, Scialla JJ, Anderson
A, et al: High-throughput metabolomics and diabetic kidney disease
progression: Evidence from the chronic renal insufficiency (CRIC)
study. Am J Nephrol. 53:215–225. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Hong YA and Nangaku M: Endogenous adenine
as a key player in diabetic kidney disease progression: An
integrated multiomics approach. Kidney Int. 105:918–920. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Demko J, Saha B, Takagi E, Manis A,
Richman P and Pearce D: Renal tubule mTORC2 deletion increases
gluconeogenesis and urinary glucose excretion. Physiology.
38:57350392023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Qiu S, Xie D, Guo S, Wang Z, Wang X, Cai
Y, Lin C, Yao H, Guan Y, Zhao Q, et al: Spatially segregated
multiomics decodes metformin-mediated function-specific metabolic
characteristics in diabetic kidney disease. Life Metabolism.
4:loaf0192025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Wu Q, Chu JL, Rubakhin SS, Gillette MU and
Sweedler JV: Dopamine-modified TiO2 monolith-assisted LDI MS
imaging for simultaneous localization of small metabolites and
lipids in mouse brain tissue with enhanced detection selectivity
and sensitivity. Chem Sci. 8:3926–3938. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Spraggins JM, Rizzo DG, Moore JL, Noto MJ,
Skaar EP and Caprioli RM: Next-generation technologies for spatial
proteomics: Integrating ultra-high speed MALDI-TOF and high mass
resolution MALDI FTICR imaging mass spectrometry for protein
analysis. Proteomics. 16:1678–1689. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Neumann EK, Migas LG, Allen JL, Caprioli
RM, Van de Plas R and Spraggins JM: Spatial metabolomics of the
human kidney using MALDI trapped ion mobility imaging mass
spectrometry. Anal Chem. 92:13084–13091. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Fu T, Oetjen J, Chapelle M, Verdu A,
Szesny M, Chaumot A, Degli-Esposti D, Geffard O, Clément Y,
Salvador A and Ayciriex S: In situ isobaric lipid mapping by
MALDI-ion mobility separation-mass spectrometry imaging. J Mass
Spectrom. 55:e45312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Spatial Omics DataBase (SODB): Increasing
accessibility to spatial omics data. Nat Methods. 20:359–360. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Vandergrift GW, Veličković M, Day LZ,
Gorman BL, Williams SM, Shrestha B and Anderton CR: Untargeted
spatial metabolomics and spatial proteomics on the same tissue
section. Anal Chem. 97:392–400. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Abedini A, Levinsohn J, Klötzer KA,
Dumoulin B, Ma Z, Frederick J, Dhillon P, Balzer MS, Shrestha R,
Liu H, et al: Single-cell multi-omic and spatial profiling of human
kidneys implicates the fibrotic microenvironment in kidney disease
progression. Nat Genet. 56:1712–1724. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Chuang AE, Chen YL, Chiu HJ, Nguyen HT and
Liu CH: Nasal administration of polysaccharides-based nanocarrier
combining hemoglobin and diferuloylmethane for managing diabetic
kidney disease. Int J Biol Macromol. 282:1365342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|