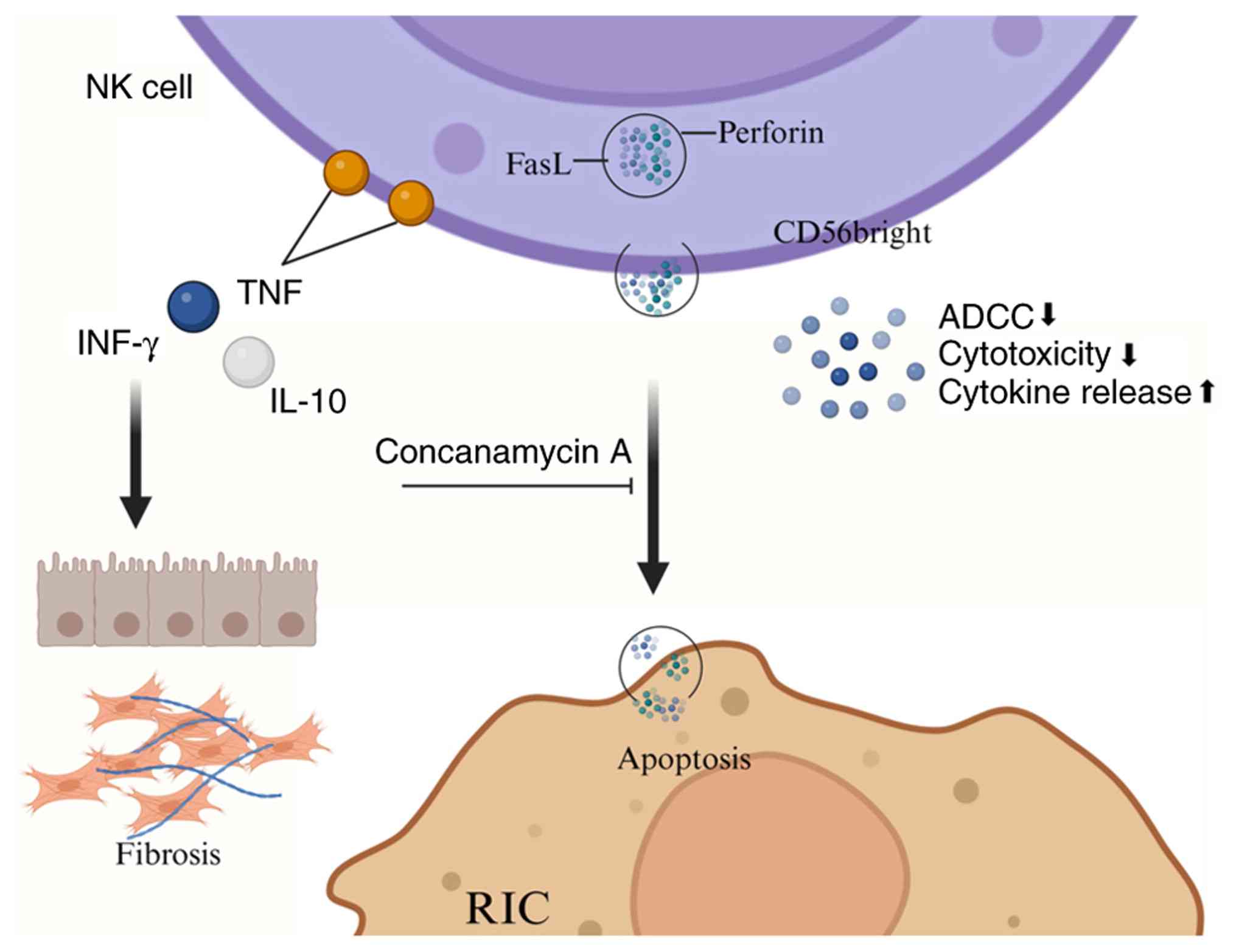
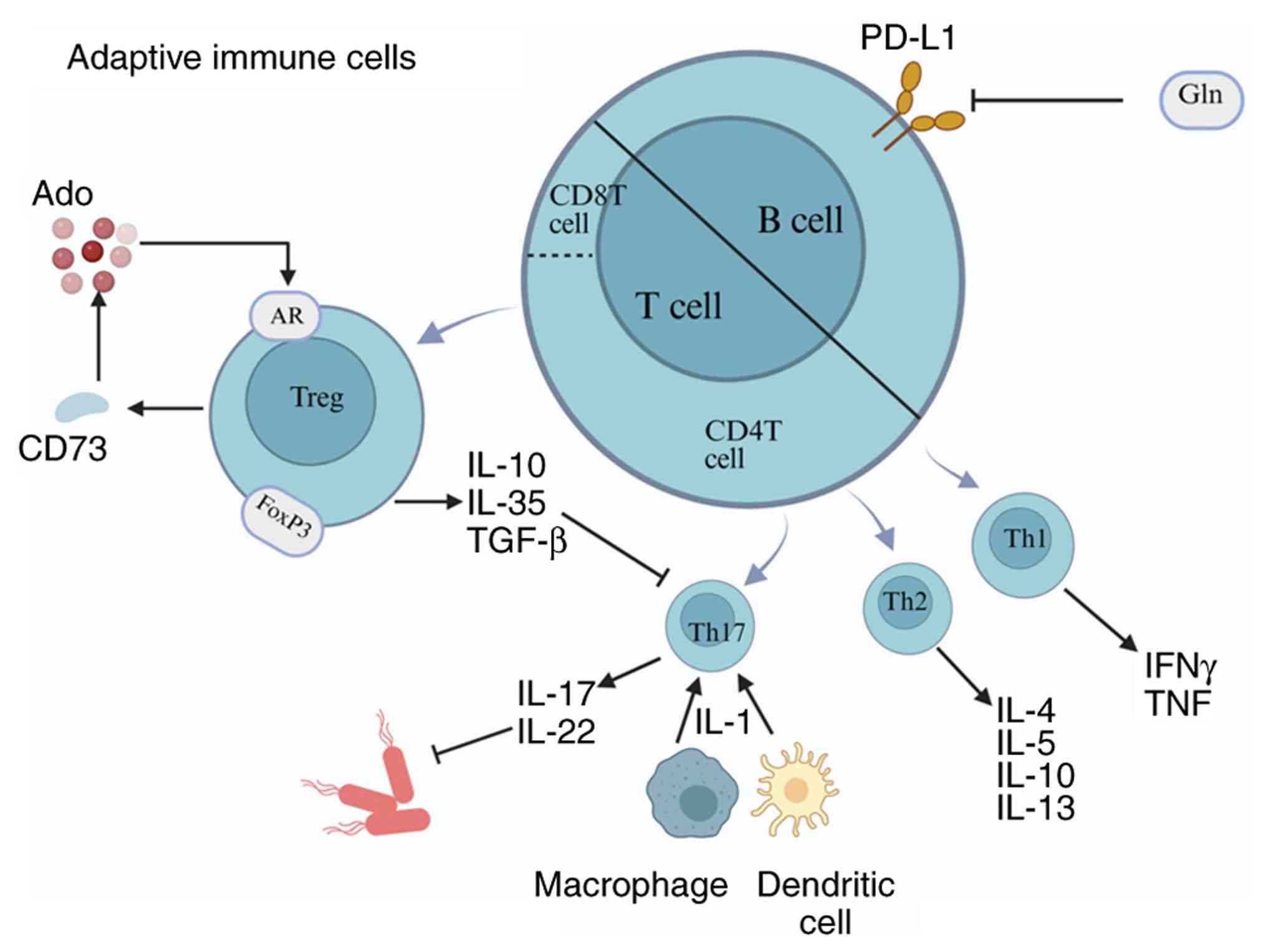
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seymour CW, Kennedy JN, Wang S, Chang CH,
Elliott CF, Xu Z, Berry S, Clermont G, Cooper G, Gomez H, et al:
Derivation, validation, and potential treatment implications of
novel clinical phenotypes for sepsis. JAMA. 321:2003–2017. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu D, Huang SY, Sun JH, Zhang HC, Cai QL,
Gao C, Li L, Cao J, Xu F, Zhou Y, et al: Sepsis-induced
immunosuppression: Mechanisms, diagnosis and current treatment
options. Mil Med Res. 9:562022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang D, Sun T and Liu Z: Sepsis-associated
acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Res. 3:251–258. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS,
Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, et al:
Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational,
multicenter study. JAMA. 294:813–818. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Balkrishna A, Sinha S, Kumar A, Arya V,
Gautam AK, Valis M, Kuca K, Kumar D and Amarowicz R:
Sepsis-mediated renal dysfunction: Pathophysiology, biomarkers and
role of phytoconstituents in its management. Biomed Pharmacother.
165:1151832023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee K, Jang HR and Rabb H: Lymphocytes and
innate immune cells in acute kidney injury and repair. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 20:789–805. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao X, Cai S, Li X and Wu G:
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: Mechanisms, biomarkers and
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 16:15771052025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z and Wang Z: The role of macrophages
polarization in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front Immunol.
14:12094382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwok AJ, Allcock A, Ferreira RC,
Cano-Gamez E, Smee M, Burnham KL, Zurke YX; Emergency Medicine
Research Oxford (EMROx); McKechnie S, Mentzer AJ, et al:
Neutrophils and emergency granulopoiesis drive immune suppression
and an extreme response endotype during sepsis. Nat Immunol.
24:767–779. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qi X, Yu Y, Sun R, Huang J, Liu L, Yang Y,
Rui T and Sun B: Identification and characterization of neutrophil
heterogeneity in sepsis. Crit Care. 25:502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao F, Xiao C, Evans KS, Theivanthiran T,
DeVito N, Holtzhausen A, Liu J, Liu X, Boczkowski D, Nair S, et al:
Paracrine Wnt5a-β-catenin signaling triggers a metabolic program
that drives dendritic cell tolerization. Immunity. 48:147–160.e7.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Flohé SB, Agrawal H, Schmitz D, Gertz M,
Flohé S and Schade FU: Dendritic cells during polymicrobial sepsis
rapidly mature but fail to initiate a protective Th1-type immune
response. J Leukoc Biol. 79:473–481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tang J, Shang C, Chang Y, Jiang W, Xu J,
Zhang L, Lu L, Chen L, Liu X, Zeng Q, et al: Peripheral
PD-1+NK cells could predict the 28-day mortality in
sepsis patients. Front Immunol. 15:14260642024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nascimento DC, Viacava PR, Ferreira RG,
Damaceno MA, Piñeros AR, Melo PH, Donate PB, Toller-Kawahisa JE,
Zoppi D, Veras FP, et al: Sepsis expands a CD39+
plasmablast population that promotes immunosuppression via
adenosine-mediated inhibition of macrophage antimicrobial activity.
Immunity. 54:2024–2041.e8. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kox M, Bauer M, Bos LDJ, Bouma H, Calandra
T, Calfee CS, Chousterman BG, Derde LPG, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ,
Gómez H, et al: The immunology of sepsis: Translating new insights
into clinical practice. Nat Rev Nephrol. 22:30–49. 2026. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dick SA, Wong A, Hamidzada H, Nejat S,
Nechanitzky R, Vohra S, Mueller B, Zaman R, Kantores C, Aronoff L,
et al: Three tissue resident macrophage subsets coexist across
organs with conserved origins and life cycles. Sci Immunol.
7:eabf77772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bell RMB and Conway BR: Macrophages in the
kidney in health, injury and repair. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
367:101–147. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zimmerman KA, Yang Z, Lever JM, Li Z,
Croyle MJ, Agarwal A, Yoder BK and George JF: Kidney resident
macrophages in the rat have minimal turnover and replacement by
blood monocytes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 321:F162–F169. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheung MD, Erman EN, Moore KH, Lever JM,
Li Z, LaFontaine JR, Ghajar-Rahimi G, Liu S, Yang Z, Karim R, et
al: Resident macrophage subpopulations occupy distinct
microenvironments in the kidney. JCI Insight. 7:e1610782022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao J, Andreev I and Silva HM: Resident
tissue macrophages: Key coordinators of tissue homeostasis beyond
immunity. Sci Immunol. 9:eadd19672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qu Z, Chu J, Jin S, Yang C, Zang J, Zhang
J, Xu D and Cheng M: Tissue-resident macrophages and renal
diseases: Landscapes and treatment directions. Front Immunol.
16:15480532025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Burns KD and Douvris A: Protecting the
kidney in sepsis: Resident macrophages to the rescue. Kidney Int.
103:461–463. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu Q, Xiao L, Cheng G, He J, Yin C, Wang
L, Wang Q, Li L, Wei B, Weng Y, et al: Self-maintaining macrophages
within the kidney contribute to salt and water balance by
modulating kidney sympathetic nerve activity. Kidney Int.
104:324–333. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi C and Pamer EG: Monocyte recruitment
during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:762–774.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gong N, Wang W, Fu Y, Zheng X, Guo X, Chen
Y, Chen Y, Zheng S and Cai G: The crucial role of metabolic
reprogramming in driving macrophage conversion in kidney disease.
Cell Mol Biol Lett. 30:722025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Qu X and Zhou G: Role of
the endothelial cell glycocalyx in sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury. Front Med (Lausanne). 12:15356732025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chousterman BG, Boissonnas A, Poupel L,
Baudesson de Chanville C, Adam J, Tabibzadeh N, Licata F,
Lukaszewicz AC, Lombès A, Deterre P, et al: Ly6Chigh monocytes
protect against kidney damage during sepsis via a CX3CR1-dependent
adhesion mechanism. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:792–803. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Gao Z, Lu L and Chen X: Release of HMGB1
in podocytes exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney
injury. Mediators Inflamm. 2021:52202262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kounatidis D, Tzivaki I, Daskalopoulou S,
Daskou A, Adamou A, Rigatou A, Sdogkos E, Karampela I, Dalamaga M
and Vallianou NG: Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: What's new
regarding its diagnostics and therapeutics? Diagnostics (Basel).
14:28452024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jia P, Xu S, Wang X, Wu X, Ren T, Zou Z,
Zeng Q, Shen B and Ding X: Chemokine CCL2 from proximal tubular
epithelial cells contributes to sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 323:F107–F119. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu W, Hou H, Yang W, Tang W and Sun L:
Immunologic role of macrophages in sepsis-induced acute liver
injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 143:1134922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nie J, Zhou L, Tian W, Liu X, Yang L, Yang
X, Zhang Y, Wei S, Wang DW and Wei J: Deep insight into cytokine
storm: From pathogenesis to treatment. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 10:1122025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ovali MA and Percin S: Sepsis-associated
immunosuppression: Mechanistic Insights, Biomarkers, and
therapeutic perspectives. Mol Biol Rep. 53:1482025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu C, Wei W, Huang Y, Fu P, Zhang L and
Zhao Y: Metabolic reprogramming in septic acute kidney injury:
Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Metabolism.
158:1559742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Freemerman AJ, Johnson AR, Sacks GN,
Milner JJ, Kirk EL, Troester MA, Macintyre AN, Goraksha-Hicks P,
Rathmell JC and Makowski L: Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages:
glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1)-mediated glucose metabolism drives a
proinflammatory phenotype. J Biol Chem. 289:7884–7896. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morris M and Li L: Molecular mechanisms
and pathological consequences of endotoxin tolerance and priming.
Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 60:13–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Gauthier T and Chen W: Modulation of
macrophage immunometabolism: A new approach to fight infections.
Front Immunol. 13:7808392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pålsson-McDermott EM and O'Neill LAJ:
Targeting immunometabolism as an anti-inflammatory strategy. Cell
Res. 30:300–314. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu B, Liu Y, Li N and Geng Q: Lactate and
lactylation in macrophage metabolic reprogramming: Current progress
and outstanding issues. Front Immunol. 15:13957862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kieler M, Hofmann M and Schabbauer G: More
than just protein building blocks: How amino acids and related
metabolic pathways fuel macrophage polarization. FEBS J.
288:3694–3714. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Munder M, Eichmann K and Modolell M:
Alternative metabolic states in murine macrophages reflected by the
nitric oxide synthase/arginase balance: Competitive regulation by
CD4+ T cells correlates with Th1/Th2 phenotype. J Immunol.
160:5347–5354. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rath M, Müller I, Kropf P, Closs EI and
Munder M: Metabolism via arginase or nitric oxide synthase: Two
competing arginine pathways in macrophages. Front Immunol.
5:5322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bronte V and Zanovello P: Regulation of
immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol.
5:641–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu PS, Wang H, Li X, Chao T, Teav T,
Christen S, Di Conza G, Cheng WC, Chou CH, Vavakova M, et al:
α-ketoglutarate orchestrates macrophage activation through
metabolic and epigenetic reprogramming. Nat Immunol. 18:985–994.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shan X, Hu P, Ni L, Shen L, Zhang Y, Ji Z,
Cui Y, Guo M, Wang H, Ran L, et al: Serine metabolism orchestrates
macrophage polarization by regulating the IGF1-p38 axis. Cell Mol
Immunol. 19:1263–1278. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mussbacher M, Derler M, Basílio J and
Schmid JA: NF-κB in monocytes and macrophages-an inflammatory
master regulator in multitalented immune cells. Front Immunol.
14:11346612023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ekihiro S and David AB: NF-κB. Signaling
Pathways in Liver Diseases. 2015.
|
|
49
|
Wang J, Zhao X, Wang Q, Zheng X, Simayi D,
Zhao J, Yang P, Mao Q and Xia H: FAM76B regulates
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB-mediated M1 macrophage polarization by influencing
the stability of PIK3CD mRNA. Cell Mol Life Sci. 81:1072024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Geng H, Zhang H, Cheng L and Dong S:
Sivelestat ameliorates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by
activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 128:1114662024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
He J, Zhao S and Duan M: The Response of
macrophages in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. J Clin Med.
12:11012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Androulidaki A, Iliopoulos D, Arranz A,
Doxaki C, Schworer S, Zacharioudaki V, Margioris AN, Tsichlis PN
and Tsatsanis C: The kinase Akt1 controls macrophage response to
lipopolysaccharide by regulating microRNAs. Immunity. 31:220–231.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zeng Y, Yuan W, Feng C, Peng L, Xie X,
Peng F, Li T, Lin M, Zhang H and Dai H: Trametinib alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting
macrophage polarization through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Transpl
Immunol. 89:1021832025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu C, Li B, Tang K, Dong X, Xue L, Su G
and Jin Y: Aquaporin 1 alleviates acute kidney injury via
PI3K-mediated macrophage M2 polarization. Inflamm Res. 69:509–521.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xue C, Yao Q, Gu X, Shi Q, Yuan X, Chu Q,
Bao Z, Lu J and Li L: Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling
pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 8:2042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cai B, Cai JP, Luo YL, Chen C and Zhang S:
The specific roles of JAK/STAT signaling pathway in sepsis.
Inflammation. 38:1599–1608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xin P, Xu X, Deng C, Liu S, Wang Y, Zhou
X, Ma H, Wei D and Sun S: The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway
and its inhibitors in diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 80:1062102020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lee SH, Kim KH, Lee SM, Park SJ, Lee S,
Cha RH, Lee JW, Kim DK, Kim YS, Ye SK and Yang SH: STAT3 blockade
ameliorates LPS-induced kidney injury through macrophage-driven
inflammation. Cell Commun Signal. 22:4762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhu H, Wang X, Wang X, Liu B, Yuan Y and
Zuo X: Curcumin attenuates inflammation and cell apoptosis through
regulating NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway against acute
kidney injury. Cell Cycle. 19:1941–1951. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yan X, Cheng X, He X, Zheng W, Yuan X and
Chen H: HO-1 overexpressed mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate
sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by activating JAK/stat3
pathway. Cell Mol Bioeng. 11:509–518. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sawoo R and Bishayi B: TLR4/TNFR1 blockade
suppresses STAT1/STAT3 expression and increases SOCS3 expression in
modulation of LPS-induced macrophage responses. Immunobiology.
229:1528402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang M, Liu S, Wu Z, Wang C, Zhang H,
Yang J, Guo C, Dai M, Wang X and Ren W: Porcine GWAS identifies
ACOT11 as regulator for macrophage IL-1β maturation via IFNGR2
palmitoylation. Sci China Life Sci. 68:3037–3050. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fan W, Wang C, Xu K, Liang H and Chi Q:
Ccl5+ Macrophages drive pro-inflammatory responses and
neutrophil recruitment in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.
Int Immunopharmacol. 143:1133392024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Shi Y, Zhang Q, Bi H, Lu M, Tan Y, Zou D,
Ge L, Chen Z, Liu C, Ci W and Ma L: Decoding the multicellular
ecosystem of vena caval tumor thrombus in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma by single-cell RNA sequencing. Genome Biol. 23:872022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Nalio Ramos R, Missolo-Koussou Y,
Gerber-Ferder Y, Bromley CP, Bugatti M, Núñez NG, Tosello Boari J,
Richer W, Menger L, Denizeau J, et al: Tissue-resident
FOLR2+ macrophages associate with CD8+ T cell
infiltration in human breast cancer. Cell. 185:1189–1207.e25. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Mitsi E, Kamng'ona R, Rylance J, Solórzano
C, Jesus Reiné J, Mwandumba HC, Ferreira DM and Jambo KC: Human
alveolar macrophages predominately express combined classical M1
and M2 surface markers in steady state. Respir Res. 19:662018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sezginer O and Unver N: Dissection of
pro-tumoral macrophage subtypes and immunosuppressive cells
participating in M2 polarization. Inflamm Res. 73:1411–1423. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fuchs AL, Costello SM, Schiller SM, Tripet
BP and Copié V: Primary human M2 macrophage subtypes are
distinguishable by aqueous metabolite profiles. Int J Mol Sci.
25:24072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang LX, Zhang SX, Wu HJ, Rong XL and Guo
J: M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J Leukoc
Biol. 106:345–358. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Di X, Li Y, Wei J, Li T and Liao B:
Targeting fibrosis: From molecular mechanisms to advanced
therapies. Adv Sci (Weinh). 12:e24104162025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Meng XM, Wang S, Huang XR, Yang C, Xiao J,
Zhang Y, To KF, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY: Inflammatory
macrophages can transdifferentiate into myofibroblasts during renal
fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 7:e24952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kuppe C, Ibrahim MM, Kranz J, Zhang X,
Ziegler S, Perales-Patón J, Jansen J, Reimer KC, Smith JR, Dobie R,
et al: Decoding myofibroblast origins in human kidney fibrosis.
Nature. 589:281–286. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Liu H, Guan Q, Zhao P and Li J:
TGF-β-induced CCR8 promoted macrophage transdifferentiation into
myofibroblast-like cells. Exp Lung Res. 1–14. 2022.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Tang PC, Chung JY, Xue VW, Xiao J, Meng
XM, Huang XR, Zhou S, Chan AS, Tsang AC, Cheng AS, et al: Smad3
promotes cancer-associated fibroblasts generation via
macrophage-myofibroblast transition. Adv Sci (Weinh).
9:e21012352022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Wang L, Tang W, Jiang L, Zhang D, Wang Z,
Guo R, Wang J and Xiao D: Inhibition of USP11 attenuates
sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by downregulating
TGFBR2/Smad3 signaling. Front Mol Biosci. 12:15715932025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liu X, Xu W, Feng J, Wang Y, Li K, Chen Y,
Wang W, Zhao W, Ge S and Li J: Adoptive cell transfer of
piezo-activated macrophage rescues immunosuppressed rodents from
life-threating bacterial infections. Nat Commun. 16:13632025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhuang J, Hai Y, Lu X, Sun B, Fan R, Zhang
B, Wang W, Han B, Luo L, Yang L, et al: A self-assembled metabolic
regulator reprograms macrophages to combat cytokine storm and boost
sepsis immunotherapy. Research (Wash DC). 8:06632025.
|
|
78
|
Li Y, Qu G, Dou G, Ren L, Dang M, Kuang H,
Bao L, Ding F, Xu G, Zhang Z, et al: Engineered extracellular
vesicles driven by erythrocytes ameliorate bacterial sepsis by iron
recycling, toxin clearing and inflammation regulation. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 11:e23068842024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ye M, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Xie R, Tong Y, Sauer
JD and Gong S: NAD(H)-loaded nanoparticles for efficient sepsis
therapy via modulating immune and vascular homeostasis. Nat
Nanotechnol. 17:880–890. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhang S, Xie Y, Zhang L, Qi Y, Liao Q, Xu
C, Yang S, Zhou H, Tan Q and Qi S: A pH-responsive biomimetic
antioxidant nanoplatform with dual renal targeting for synergistic
therapy of acute kidney injury. Adv Sci (Weinh). 13:e156642026.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Wang Y, Wang S, Luo Q, Zhou Y, Li X, Shang
Y, Wang H, Plotnikov EY, Liao X, Feng W, et al: Engineered
macrophage-targeted germacrone-bearing nanosheet achieves
synergistic treatment of acute kidney injury through macrophage
polarization modulation and oxidative stress alleviation. Chem Eng
J. 520:1656022025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Ganesh K and Joshi MB: Neutrophil
sub-types in maintaining immune homeostasis during steady state,
infections and sterile inflammation. Inflamm Res. 72:1175–1192.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xiao W, Lu Z, Liu Y, Hua T, Zhang J, Hu J,
Li H, Xu Y and Yang M: Influence of the initial neutrophils to
lymphocytes and platelets ratio on the incidence and severity of
sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: A double robust estimation
based on a large public database. Front Immunol. 13:9254942022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ma Y, Yabluchanskiy A, Iyer RP, Cannon PL,
Flynn ER, Jung M, Henry J, Cates CA, Deleon-Pennell KY and Lindsey
ML: Temporal neutrophil polarization following myocardial
infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 110:51–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Ohms M, Möller S and Laskay T: An attempt
to polarize human neutrophils toward N1 and N2 phenotypes in vitro.
Front Immunol. 11:5322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Garley M and Jabłońska E: Heterogeneity
among neutrophils. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 66:21–30. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Woodfin A, Beyrau M, Voisin MB, Ma B,
Whiteford JR, Hordijk PL, Hogg N and Nourshargh S:
ICAM-1-expressing neutrophils exhibit enhanced effector functions
in murine models of endotoxemia. Blood. 127:898–907. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
88
|
Herter JM, Rossaint J, Spieker T and
Zarbock A: Adhesion molecules involved in neutrophil recruitment
during sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. J Innate Immun.
6:597–606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wu L, Gokden N and Mayeux PR: Evidence for
the role of reactive nitrogen species in polymicrobial
sepsis-induced renal peritubular capillary dysfunction and tubular
injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:1807–1815. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Bianchi ME and Manfredi AA: High-mobility
group box 1 (HMGB1) protein at the crossroads between innate and
adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev. 220:35–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Leliefeld PH, Wessels CM, Leenen LP,
Koenderman L and Pillay J: The role of neutrophils in immune
dysfunction during severe inflammation. Crit Care. 20:732016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
De Filippo K, Dudeck A, Hasenberg M, Nye
E, van Rooijen N, Hartmann K, Gunzer M, Roers A and Hogg N: Mast
cell and macrophage chemokines CXCL1/CXCL2 control the early stage
of neutrophil recruitment during tissue inflammation. Blood.
121:4930–4937. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sawant KV, Poluri KM, Dutta AK, Sepuru KM,
Troshkina A, Garofalo RP and Rajarathnam K: Chemokine CXCL1
mediated neutrophil recruitment: Role of glycosaminoglycan
interactions. Sci Rep. 6:331232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Molema G, Zijlstra JG, van Meurs M and
Kamps JAAM: Renal microvascular endothelial cell responses in
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 18:95–112.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Aguilar MG, AlHussen HA, Gandhi PD, Kaur
P, Pothacamuri MA, Talikoti MAH, Avula N, Shekhawat P, Silva AB,
Kaur A and Rai M: Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury:
Pathophysiology and treatment modalities. Cureus.
16:e759922024.
|
|
96
|
Tang D, Kang R, Berghe TV, Vandenabeele P
and Kroemer G: The molecular machinery of regulated cell death.
Cell Res. 29:347–364. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Okeke EB, Louttit C, Fry C, Najafabadi AH,
Han K, Nemzek J and Moon JJ: Inhibition of neutrophil elastase
prevents neutrophil extracellular trap formation and rescues mice
from endotoxic shock. Biomaterials. 238:1198362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Li Z, Ludwig N, Thomas K, Mersmann S,
Lehmann M, Vestweber D, Pittet JF, Gomez H, Kellum JA, Rossaint J
and Zarbock A: The pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion induced
acute kidney injury depends on renal neutrophil recruitment whereas
sepsis-induced AKI does not. Front Immunol. 13:8437822022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Singhal A and Kumar S: Neutrophil and
remnant clearance in immunity and inflammation. Immunology.
165:22–43. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Jia Y, Li JH, Hu BC, Huang X, Yang X, Liu
YY, Cai JJ, Yang X, Lai JM, Shen Y, et al: Targeting SLC22A5
fosters mitophagy inhibition-mediated macrophage immunity against
septic acute kidney injury upon CD47-SIRPα axis blockade. Heliyon.
10:e267912024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Borregaard N and Herlin T: Energy
metabolism of human neutrophils during phagocytosis. J Clin Invest.
70:550–557. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Jeon JH, Hong CW, Kim EY and Lee JM:
Current understanding on the metabolism of neutrophils. Immune
Netw. 20:e462020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Stojkov D, Gigon L, Peng S, Lukowski R,
Ruth P, Karaulov A, Rizvanov A, Barlev NA, Yousefi S and Simon HU:
Physiological and pathophysiological roles of metabolic pathways
for NET formation and other neutrophil functions. Front Immunol.
13:8265152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Tan C, Gu J, Chen H, Li T, Deng H, Liu K,
Liu M, Tan S, Xiao Z, Zhang H and Xiao X: Inhibition of Aerobic
glycolysis promotes neutrophil to influx to the infectious site via
CXCR2 in sepsis. Shock. 53:114–123. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Masucci MT, Minopoli M, Del Vecchio S and
Carriero MV: The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps
(NETs) in tumor progression and metastasis. Front Immunol.
11:17492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Kovacs SB, Oh C, Maltez VI, McGlaughon BD,
Verma A, Miao EA and Aachoui Y: Neutrophil caspase-11 is essential
to defend against a cytosol-invasive bacterium. Cell Rep.
32:1079672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Ni Y, Hu BC, Wu GH, Shao ZQ, Zheng Y,
Zhang R, Jin J, Hong J, Yang XH, Sun RH, et al: Interruption of
neutrophil extracellular traps formation dictates host defense and
tubular HOXA5 stability to augment efficacy of anti-Fn14 therapy
against septic AKI. Theranostics. 11:9431–9451. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kaplan MJ and Radic M: Neutrophil
extracellular traps: Double-edged swords of innate immunity. J
Immunol. 189:2689–2695. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wei Z, Wang J, Wang Y, Wang C, Liu X, Han
Z, Fu Y and Yang Z: Effects of neutrophil extracellular traps on
bovine mammary epithelial cells in vitro. Front Immunol.
10:10032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang H, Wang C, Zhao MH and Chen M:
Neutrophil extracellular traps can activate alternative complement
pathways. Clin Exp Immunol. 181:518–527. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Biron BM, Chung CS, Chen Y, Wilson Z,
Fallon EA, Reichner JS and Ayala A: PAD4 deficiency leads to
decreased organ dysfunction and improved survival in a dual insult
model of hemorrhagic shock and sepsis. J Immunol. 200:1817–1828.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Woodfin A, Voisin MB, Beyrau M, Colom B,
Caille D, Diapouli FM, Nash GB, Chavakis T, Albelda SM, Rainger GE,
et al: The junctional adhesion molecule JAM-C regulates polarized
transendothelial migration of neutrophils in vivo. Nat Immunol.
12:761–769. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Garner H and de Visser KE: Neutrophils
take a round-trip. Science. 358:42–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
de Oliveira S, Rosowski EE and
Huttenlocher A: Neutrophil migration in infection and wound repair:
Going forward in reverse. Nat Rev Immunol. 16:378–391. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Bordon Y: Innate immunity: Neutrophil
U-turn fans the flames. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:4982011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zi SF, Wu XJ, Tang Y, Liang YP, Liu X,
Wang L, Li SL, Wu CD, Xu JY, Liu T, et al: Endothelial cell-derived
extracellular vesicles promote aberrant neutrophil trafficking and
subsequent remote lung injury. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e24006472024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Ya-Fen Z, Jing C, Yue-Fei Z and Chang-Ping
D: Reduction in NGAL at 48 h predicts the progression to CKD in
patients with septic associated AKI: A single-center clinical
study. Int Urol Nephrol. 56:607–613. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Showell HJ, Remick
DG, Phan SH, Ward PA and Marks RM: Endothelial cell gene expression
of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1
beta. Science. 243:1467–1469. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zhang A, Cai Y, Wang PF, Qu JN, Luo ZC,
Chen XD, Huang B, Liu Y, Huang WQ, Wu J and Yin YH: Diagnosis and
prognosis of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute
kidney injury with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Crit Care. 20:412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Tavris BS, Morath C, Rupp C, Szudarek R,
Uhle F, Sweeney TE, Liesenfeld O, Fiedler-Kalenka MO, Dubler S,
Zeier M, et al: Complementary role of transcriptomic endotyping and
protein-based biomarkers for risk stratification in
sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 29:1362025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Bagshaw SM, Bennett M, Haase M,
Haase-Fielitz A, Egi M, Morimatsu H, D'amico G, Goldsmith D,
Devarajan P and Bellomo R: Plasma and urine neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin in septic versus non-septic acute
kidney injury in critical illness. Intensive Care Med. 36:452–461.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Mårtensson J, Bell M, Oldner A, Xu S,
Venge P and Martling CR: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
in adult septic patients with and without acute kidney injury.
Intensive Care Med. 36:1333–1340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tuan PNH, Quyen DBQ, Van Khoa H, Loc ND,
Van My P, Dung NH, Toan ND, Quyet D and Thang LV: Serum and urine
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels measured at
admission predict progression to chronic kidney disease in
sepsis-associated acute kidney injury patients. Dis Markers.
2020:88834042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Mathur R, Elsafy S, Press AT, Brück J,
Hornef M, Martin L, Schürholz T, Marx G, Bartneck M, Kiessling F,
et al: Neutrophil hitchhiking enhances liposomal dexamethasone
therapy of sepsis. ACS Nano. 18:28866–28880. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Zhou M, Tang Y, Lu Y, Zhang T, Zhang S,
Cai X and Lin Y: Framework nucleic acid-based and neutrophil-based
nanoplatform loading baicalin with targeted drug delivery for
anti-inflammation treatment. ACS Nano. 19:3455–3469. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Zhou M, Lu Y, Tang Y, Zhang T, Xiao D,
Zhang M, Zhang S, Li J, Cai X and Lin Y: A DNA-based nanorobot for
targeting, hitchhiking, and regulating neutrophils to enhance
sepsis therapy. Biomaterials. 318:1231832025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Chang YT, Lin CY, Chen CJ, Hwang E,
Alshetaili A, Yu HP and Fang JY: Neutrophil-targeted combinatorial
nanosystems for suppressing bacteremia-associated hyperinflammation
and MRSA infection to improve survival rates. Acta Biomater.
174:331–344. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Wu S, Zhou M, Zhou H, Han L and Liu H:
Astragaloside IV-loaded biomimetic nanoparticles target IκBα to
regulate neutrophil extracellular trap formation for sepsis
therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 23:1552025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Liu Z, Liu X, Yang Q, Yu L, Chang Y and Qu
M: Neutrophil membrane-enveloped nanoparticles for the amelioration
of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Acta Biomater.
104:158–166. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Yang Y, Du J, Gan J, Song X, Shu J, An C,
Lu L, Wei H, Che J and Zhao X: Neutrophil-mediated nanozyme
delivery system for acute kidney injury therapy. Adv Healthc Mater.
13:e24011982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Reilly JP, Anderson BJ, Hudock KM, Dunn
TG, Kazi A, Tommasini A, Charles D, Shashaty MG, Mikkelsen ME,
Christie JD and Meyer NJ: Neutropenic sepsis is associated with
distinct clinical and biological characteristics: A cohort study of
severe sepsis. Crit Care. 20:2222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Kurts C: Dendritic cells: Not just another
cell type in the kidney, but a complex immune sentinel network.
Kidney Int. 70:412–414. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Kurts C, Ginhoux F and Panzer U: Kidney
dendritic cells: Fundamental biology and functional roles in health
and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 16:391–407. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Weisheit CK, Engel DR and Kurts C:
Dendritic cells and macrophages: Sentinels in the kidney. Clin J Am
Soc Nephrol. 10:1841–1851. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Sun Y, Oravecz-Wilson K, Bridges S,
McEachin R, Wu J, Kim SH, Taylor A, Zajac C, Fujiwara H, Peltier
DC, et al: miR-142 controls metabolic reprogramming that regulates
dendritic cell activation. J Clin Invest. 129:2029–2042. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Trombetta ES, Ebersold M, Garrett W,
Pypaert M and Mellman I: Activation of lysosomal function during
dendritic cell maturation. Science. 299:1400–1403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Efron P and Moldawer LL: Sepsis and the
dendritic cell. Shock. 20:386–401. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Worbs T, Hammerschmidt SI and Förster R:
Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol.
17:30–48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Carson WF, Cavassani KA, Dou Y and Kunkel
SL: Epigenetic regulation of immune cell functions during
post-septic immunosuppression. Epigenetics. 6:273–283. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
140
|
Fan HY, Qi D, Yu C, Zhao F, Liu T, Zhang
ZK, Yang MY, Zhang LM, Chen DQ and Du Y: Paeonol protects
endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury: Potential mechanism of
inhibiting TLR4-NF-κB signal pathway. Oncotarget. 7:39497–39510.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Naito Y, Tsuji T, Nagata S, Tsuji N,
Fujikura T, Ohashi N, Kato A, Miyajima H and Yasuda H: IL-17A
activated by Toll-like receptor 9 contributes to the development of
septic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
318:F238–F247. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Aksoy E, Taboubi S, Torres D, Delbauve S,
Hachani A, Whitehead MA, Pearce WP, Berenjeno IM, Nock G, Filloux
A, et al: The p110δ isoform of the kinase PI(3)K controls the
subcellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects
from endotoxic shock. Nat Immunol. 13:1045–1054. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Mócsai A, Ruland J and Tybulewicz VLJ: The
SYK tyrosine kinase: A crucial player in diverse biological
functions. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:387–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Al-Harbi NO, Nadeem A, Ahmad SF, Alanazi
MM, Aldossari AA and Alasmari F: Amelioration of sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury through inhibition of inflammatory cytokines
and oxidative stress in dendritic cells and neutrophils
respectively in mice: Role of spleen tyrosine kinase signaling.
Biochimie. 158:102–110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Nadeem A, Ahmad SF, Al-Harbi NO, Ibrahim
KE, Alqahtani F, Alanazi WA, Mahmood HM, Alsanea S and Attia SM:
Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibition attenuates oxidative stress in
systemic immune cells and renal compartment during sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 90:1071232021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Qi C, Liu C, Gong J, Liu D, Wang X, Zhang
P, Qin Y, Ge S, Zhang M, Peng Z, et al: Claudin18.2-specific CAR T
cells in gastrointestinal cancers: Phase 1 trial final results. Nat
Med. 30:2224–2234. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Bol KF, Schreibelt G, Bloemendal M, van
Willigen WW, Hins-de Bree S, de Goede AL, de Boer AJ, Bos KJH,
Duiveman-de Boer T, Olde Nordkamp MAM, et al: Adjuvant dendritic
cell therapy in stage IIIB/C melanoma: The MIND-DC randomized phase
III trial. Nat Commun. 15:16322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Benjamim CF, Lundy SK, Lukacs NW, Hogaboam
CM and Kunkel SL: Reversal of long-term sepsis-induced
immunosuppression by dendritic cells. Blood. 105:3588–3595. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Wang HW, Yang W, Gao L, Kang JR, Qin JJ,
Liu YP and Lu JY: Adoptive transfer of bone marrow-derived
dendritic cells decreases inhibitory and regulatory T-cell
differentiation and improves survival in murine polymicrobial
sepsis. Immunology. 145:50–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
150
|
Piliponsky AM, Acharya M and Shubin NJ:
Mast cells in viral, bacterial, and fungal infection immunity. Int
J Mol Sci. 20:28512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Pundir P, Liu R, Vasavda C, Serhan N,
Limjunyawong N, Yee R, Zhan Y, Dong X, Wu X, Zhang Y, et al: A
connective tissue mast-cell-specific receptor detects bacterial
quorum-sensing molecules and mediates antibacterial immunity. Cell
Host Microbe. 26:114–122.e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Piliponsky AM, Chen CC, Rios EJ, Treuting
PM, Lahiri A, Abrink M, Pejler G, Tsai M and Galli SJ: The chymase
mouse mast cell protease 4 degrades TNF, limits inflammation, and
promotes survival in a model of sepsis. Am J Pathol. 181:875–886.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Sutherland RE, Olsen JS, McKinstry A,
Villalta SA and Wolters PJ: Mast cell IL-6 improves survival from
Klebsiella pneumonia and sepsis by enhancing neutrophil killing. J
Immunol. 181:5598–5605. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Ramos L, Peña G, Cai B, Deitch EA and
Ulloa L: Mast cell stabilization improves survival by preventing
apoptosis in sepsis. J Immunol. 185:709–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Urb M and Sheppard DC: The role of mast
cells in the defence against pathogens. PLoS Pathog.
8:e10026192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Amponnawarat A, Torres MDT, Krishnan R, de
la Fuente-Nunez C and Ali H: Synthetic peptides targeting a mast
cell-specific G protein-coupled receptor MRGPRB2 display
anti-infective potential. Cell Biomaterials. 1:1000882025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Madjene LC, Danelli L, Dahdah A, Vibhushan
S, Bex-Coudrat J, Pacreau E, Vaugier C, Claver J, Rolas L, Pons M,
et al: Mast cell chymase protects against acute ischemic kidney
injury by limiting neutrophil hyperactivation and recruitment.
Kidney Int. 97:516–527. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Blank U, Essig M, Scandiuzzi L, Benhamou M
and Kanamaru Y: Mast cells and inflammatory kidney disease. Immunol
Rev. 217:79–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Summers SA, Chan J, Gan PY, Dewage L,
Nozaki Y, Steinmetz OM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Kitching AR and
Holdsworth SR: Mast cells mediate acute kidney injury through the
production of TNF. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:2226–2236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Wang F, Cui Y, He D, Gong L and Liang H:
Natural killer cells in sepsis: Friends or foes? Front Immunol.
14:11019182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA and Caligiuri MA:
The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol.
22:633–640. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Seki S, Nakashima H, Nakashima M and
Kinoshita M: Antitumor immunity produced by the liver Kupffer
cells, NK cells, NKT cells, and CD8 CD122 T cells. Clin Dev
Immunol. 2011:8683452011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Choi YH, Lim EJ, Kim SW, Moon YW, Park KS
and An HJ: IL-27 enhances IL-15/IL-18-mediated activation of human
natural killer cells. J Immunother Cancer. 7:1682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Maskalenko NA, Zhigarev D and Campbell KS:
Harnessing natural killer cells for cancer immunotherapy:
Dispatching the first responders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 21:559–577.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Fehniger TA, Cooper MA, Nuovo GJ, Cella M,
Facchetti F, Colonna M and Caligiuri MA: CD56bright natural killer
cells are present in human lymph nodes and are activated by T
cell-derived IL-2: A potential new link between adaptive and innate
immunity. Blood. 101:3052–3057. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Brodin P, Kärre K and Höglund P: NK cell
education: Not an on-off switch but a tunable rheostat. Trends
Immunol. 30:143–149. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Uchida T, Seki S and Oda T: Infections,
reactions of natural killer T cells and natural killer cells, and
kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 23:4792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Schuster IS, Sng XYX, Lau CM, Powell DR,
Weizman OE, Fleming P, Neate GEG, Voigt V, Sheppard S, Maraskovsky
AI, et al: Infection induces tissue-resident memory NK cells that
safeguard tissue health. Immunity. 56:2173–2174. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Uchida T, Nakashima H, Ito S, Ishikiriyama
T, Nakashima M, Seki S, Kumagai H and Oshima N: Activated natural
killer T cells in mice induce acute kidney injury with hematuria
through possibly common mechanisms shared by human CD56+
T cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 315:F618–F627. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Sato A, Nakashima H, Kinoshita M,
Nakashima M, Ogawa Y, Shono S, Ikarashi M and Seki S: The effect of
synthetic C-reactive protein on the in vitro immune response of
human PBMCs stimulated with bacterial reagents. Inflammation.
36:781–792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Uchida T, Ito S, Kumagai H, Oda T,
Nakashima H and Seki S: Roles of natural killer T cells and natural
killer cells in kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 20:24872019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Forel JM, Chiche L, Thomas G, Mancini J,
Farnarier C, Cognet C, Guervilly C, Daumas A, Vély F, Xéridat F, et
al: Phenotype and functions of natural killer cells in
critically-ill septic patients. PLoS One. 7:e504462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Tsaganos T,
Spyridaki E, Mouktaroudi M, Plachouras D, Vaki I, Karagianni V,
Antonopoulou A, Veloni V and Giamarellou H: Early changes of
CD4-positive lymphocytes and NK cells in patients with severe
Gram-negative sepsis. Crit Care. 10:R1662006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Tang J, Xie L, Liu H, Wu L, Li X, Du H,
Wang X, Li X and Yang Y: The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis
secondary to lung cancer: A case report. Open Life Sci.
18:202207022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Zhou X, Wang Y, Dou Z, Delfanti G,
Tsahouridis O, Pellegry CM, Zingarelli M, Atassi G, Woodcock MG,
Casorati G, et al: CAR-redirected natural killer T cells
demonstrate superior antitumor activity to CAR-T cells through
multimodal CD1d-dependent mechanisms. Nat Cancer. 5:1607–1621.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Godfrey DI, MacDonald HR, Kronenberg M,
Smyth MJ and Van Kaer L: NKT cells: What's in a name? Nat Rev
Immunol. 4:231–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Liu Y, Wang G, Chai D, Dang Y, Zheng J and
Li H: iNKT: A new avenue for CAR-based cancer immunotherapy. Transl
Oncol. 17:1013422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Ambrosino E, Terabe M, Halder RC, Peng J,
Takaku S, Miyake S, Yamamura T, Kumar V and Berzofsky JA:
Cross-regulation between type I and type II NKT cells in regulating
tumor immunity: A new immunoregulatory axis. J Immunol.
179:5126–5136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Halder RC, Aguilera C, Maricic I and Kumar
V: Type II NKT cell-mediated anergy induction in type I NKT cells
prevents inflammatory liver disease. J Clin Invest. 117:2302–2312.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Kezić A, Stajic N and Thaiss F: Innate
immune response in kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury: Potential
target for therapy. J Immunol Res. 2017:63054392017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Heffernan DS, Chun TT, Monaghan SF, Chung
CS and Ayala A: Invariant natural killer T cells modulate the
peritoneal macrophage response to polymicrobial sepsis. J Surg Res.
300:211–220. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Hu CK, Venet F, Heffernan DS, Wang YL,
Horner B, Huang X, Chung CS, Gregory SH and Ayala A: The role of
hepatic invariant NKT cells in systemic/local inflammation and
mortality during polymicrobial septic shock. J Immunol.
182:2467–2475. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Etogo AO, Nunez J, Lin CY, Toliver-Kinsky
TE and Sherwood ER: NK but not CD1-restricted NKT cells facilitate
systemic inflammation during polymicrobial intra-abdominal sepsis.
J Immunol. 180:6334–6345. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Tang R, Jin P, Shen C, Lin W, Yu L, Hu X,
Meng T, Zhang L, Peng L, Xiao X, et al: Single-cell RNA sequencing
reveals the transcriptomic landscape of kidneys in patients with
ischemic acute kidney injury. Chin Med J (Engl). 136:1177–1187.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Zhang J, Han C, Dai H, Hou J, Dong Y, Cui
X, Xu L, Zhang M and Xia Q: Hypoxia-Inducible factor-2α limits
natural killer T cell cytotoxicity in renal ischemia/reperfusion
injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:92–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Mohammadi H, Sharafkandi N, Hemmatzadeh M,
Azizi G, Karimi M, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Baradaran B and Babaloo Z: The
role of innate lymphoid cells in health and disease. J Cell
Physiol. 233:4512–4529. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Wang L, Tang J, Yang X, Zanvit P, Cui K,
Ku WL, Jin W, Zhang D, Goldberg N, Cain A, et al: TGF-β induces ST2
and programs ILC2 development. Nat Commun. 11:352020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Wang Y, Luo P and Wuren T: Narrative
review of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in renal diseases:
Mechanisms, clinical applications, and future directions. Stem
Cells Int. 2024:86582462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Ryu S, Lee EY, Kim DK, Kim YS, Chung DH,
Kim JH, Lee H and Kim HY: Reduction of circulating innate lymphoid
cell progenitors results in impaired cytokine production by innate
lymphoid cells in patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res
Ther. 22:632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Jacquelot N, Luong K and Seillet C:
Physiological regulation of innate lymphoid cells. Front Immunol.
10:4052019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Gieseck RL III, Wilson MS and Wynn TA:
Type 2 immunity in tissue repair and fibrosis. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:62–76. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Becker M, Gnirck AC and Turner JE: Innate
lymphoid cells in renal inflammation. Front Immunol. 11:722020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Nagashima R and Iyoda M: The roles of
kidney-resident ILC2 in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Front
Immunol. 12:6886472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Akcay A, Nguyen Q, He Z, Turkmen K, Won
Lee D, Hernando AA, Altmann C, Toker A, Pacic A, Ljubanovic DG, et
al: IL-33 exacerbates acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol.
22:2057–2067. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Cao Q, Wang Y, Niu Z, Wang C, Wang R,
Zhang Z, Chen T, Wang XM, Li Q, Lee VWS, et al: Potentiating
tissue-resident type 2 innate lymphoid cells by IL-33 to prevent
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:961–976.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Lai D, Chen W, Zhang K, Scott MJ, Li Y,
Billiar TR, Wilson MA and Fan J: GRK2 regulates group 2 innate
lymphoid cell mobilization in sepsis. Mol Med. 28:322022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Dong X, Tu H, Qin S, Bai X, Yang F and Li
Z: Insights into the roles of B cells in patients with sepsis. J
Immunol Res. 2023:74089672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Sun S, Chen R, Dou X, Dai M, Long J, Wu Y
and Lin Y: Immunoregulatory mechanism of acute kidney injury in
sepsis: A narrative review. Biomed Pharmacother. 159:1142022023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Inaba A, Tuong ZK, Riding AM, Mathews RJ,
Martin JL, Saeb-Parsy K and Clatworthy MR: B lymphocyte-derived
CCL7 augments neutrophil and monocyte recruitment, exacerbating
acute kidney injury. J Immunol. 205:1376–1384. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Han H, Zhu J, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Chen Y, Lu L,
Jin W, Yan X and Zhang R: Renal recruitment of B lymphocytes
exacerbates tubulointerstitial fibrosis by promoting monocyte
mobilization and infiltration after unilateral ureteral
obstruction. J Pathol. 241:80–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Coelho S, Cabral MG, Salvador R, Andrade
C, Martins A, Correia B, Freitas P, Cruzado JM and Jacinto A:
Urinary immune cell phenotype of severe AKI in critically ill
patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 54:2047–2055. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Hu YM, Hsiung YC, Pai MH and Yeh SL:
Glutamine administration in early or late septic phase
downregulates lymphocyte PD-1/PD-L1 expression and the inflammatory
response in mice with polymicrobial sepsis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral
Nutr. 42:538–549. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Liu Z, Dai B, Bao J and Pan Y: T cell
metabolism in kidney immune homeostasis. Front Immunol.
15:14988082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Waterhölter A, Krebs CF and Panzer U: γδ T
cells in immune-mediated kidney disease. Eur J Immunol.
54:e24510692024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Abbas AK, Murphy KM and Sher A: Functional
diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 383:787–793. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Chung Y, Chang SH, Martinez GJ, Yang XO,
Nurieva R, Kang HS, Ma L, Watowich SS, Jetten AM, Tian Q and Dong
C: Critical regulation of early Th17 cell differentiation by
interleukin-1 signaling. Immunity. 30:576–587. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Dong X, Bachman LA, Miller MN, Nath KA and
Griffin MD: Dendritic cells facilitate accumulation of IL-17 T
cells in the kidney following acute renal obstruction. Kidney Int.
74:1294–1309. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Yang XY, Song J, Hou SK, Fan HJ, Lv Q, Liu
ZQ, Ding H, Zhang YZ, Liu JY, Dong WL and Wang X: Ulinastatin
ameliorates acute kidney injury induced by crush syndrome
inflammation by modulating Th17/Treg cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
81:1062652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
D'Alessio FR, Kurzhagen JT and Rabb H:
Reparative T lymphocytes in organ injury. J Clin Invest.
129:2608–2618. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Wardell CM, Boardman DA and Levings MK:
Harnessing the biology of regulatory T cells to treat disease. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 24:93–111. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
211
|
Kinsey GR, Huang L, Jaworska K,
Khutsishvili K, Becker DA, Ye H, Lobo PI and Okusa MD: Autocrine
adenosine signaling promotes regulatory T cell-mediated renal
protection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:1528–1537. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Wang Y and Tao Y: Research progress on
regulatory T cells in acute kidney injury. J Immunol Res.
2015:1741642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T and Ono
M: Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 133:775–787.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Kinsey GR, Sharma R, Huang L, Li L, Vergis
AL, Ye H, Ju ST and Okusa MD: Regulatory T cells suppress innate
immunity in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol.
20:1744–1753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Zhou X, Yao J, Lin J, Liu J, Dong L and
Duan M: Th17/regulatory T-cell imbalance and acute kidney injury in
patients with sepsis. J Clin Med. 11:40272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Shi X, Li J, Han Y, Wang J, Li Q, Zheng Y
and Li W: The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist
PNU-282987 ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in rats. Bosn J Basic Med Sci.
22:882–893. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Li G, Zhang Y, He GL, Hao W and Hu W:
Impaired T lymphocyte subsets early predict acute kidney injury in
sepsis patients. Authorea. 2024.
|
|
218
|
Shih JM, Shih YM, Pai MH, Hou YC, Yeh CL
and Yeh SL: Fish oil-based fat emulsion reduces acute kidney injury
and inflammatory response in antibiotic-treated polymicrobial
septic mice. Nutrients. 8:1652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
de Pablo R, Monserrat J, Prieto A and
Alvarez-Mon M: Role of circulating lymphocytes in patients with
sepsis. Biomed Res Int. 2014:6710872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Guo XL, Lu CX, Luo Y, Wang PP, Su WS, Yang
SJ and Zhan LH: Circulating T-lymphocyte subsets as promising
biomarkers for the identification of sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury. J Chin Med Assoc. 87:1068–1077. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Xu J, Ma X, Yu K, Wang R, Wang S, Liu R,
Liu H, Gao H, Yu K and Wang C: Lactate up-regulates the expression
of PD-L1 in kidney and causes immunosuppression in septic acute
renal injury. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 54:404–410. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Luo C, Luo F, Man X, Liu X, Zhao L, Che L,
Zhang W, Guo J, Cai S, Wang D and Xu Y: Mesenchymal stem cells
attenuate sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by changing the
balance of Th17 cells/Tregs via Gal-9/Tim-3. Curr Stem Cell Res
Ther. 18:540–550. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
223
|
Hou YC, Wu JM, Chen KY, Chen PD, Lei CS,
Yeh SL and Lin MT: Effects of prophylactic administration of
glutamine on CD4+ T cell polarisation and kidney injury
in mice with polymicrobial sepsis. Br J Nutr. 122:657–665. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Nozaki Y, Ri J, Sakai K, Niki K, Funauchi
M and Matsumura I: Protective effects of recombinant human soluble
thrombomodulin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:25192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Singbartl K, Bockhorn SG, Zarbock A,
Schmolke M and Van Aken H: T cells modulate neutrophil-dependent
acute renal failure during endotoxemia: Critical role for CD28. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 16:720–728. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Ma K, Luo L, Yang M and Meng Y: The
suppression of sepsis-induced kidney injury via the knockout of T
lymphocytes. Heliyon. 10:e233112023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
227
|
Cho E, Lee JH, Lim HJ, Oh SW, Jo SK, Cho
WY, Kim HK and Lee SY: Soluble CD25 is increased in patients with
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrology (Carlton).
19:318–324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Patschan D, Heeg M, Brier M, Brandhorst G,
Schneider S, Müller GA and Koziolek MJ: CD4+ lymphocyte adenosine
triphosphate-a new marker in sepsis with acute kidney injury? BMC
Nephrol. 15:2032014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
229
|
Ostermann M, Forni LG, Joannidis M,
Kane-Gill SL, Legrand M, Lumlertgul N, McNicholas B, Meersch M,
Monard C, Pickkers P, et al: State of the art: Renal recovery after
AKI-from basic science to clinical practice. Intensive Care Med.
51:1490–1507. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Borges A and Bento L: Organ crosstalk and
dysfunction in sepsis. Ann Intensive Care. 14:1472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Virzì G, Day S, de Cal M, Vescovo G and
Ronco C: Heart-kidney crosstalk and role of humoral signaling in
critical illness. Crit Care. 18:2012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Li X, Yuan F and Zhou L: Organ crosstalk
in acute kidney injury: Evidence and mechanisms. J Clin Med.
11:66372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|