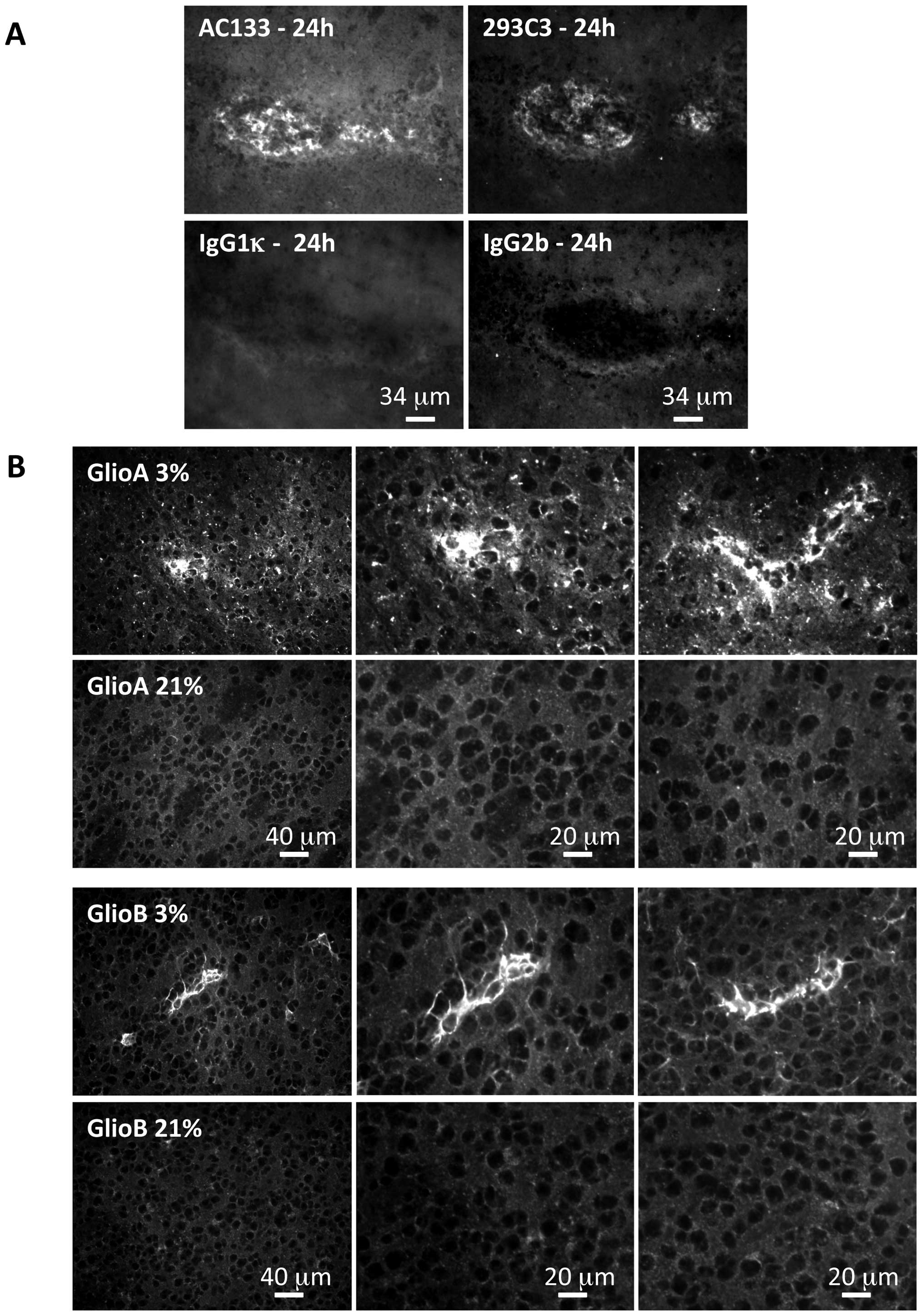
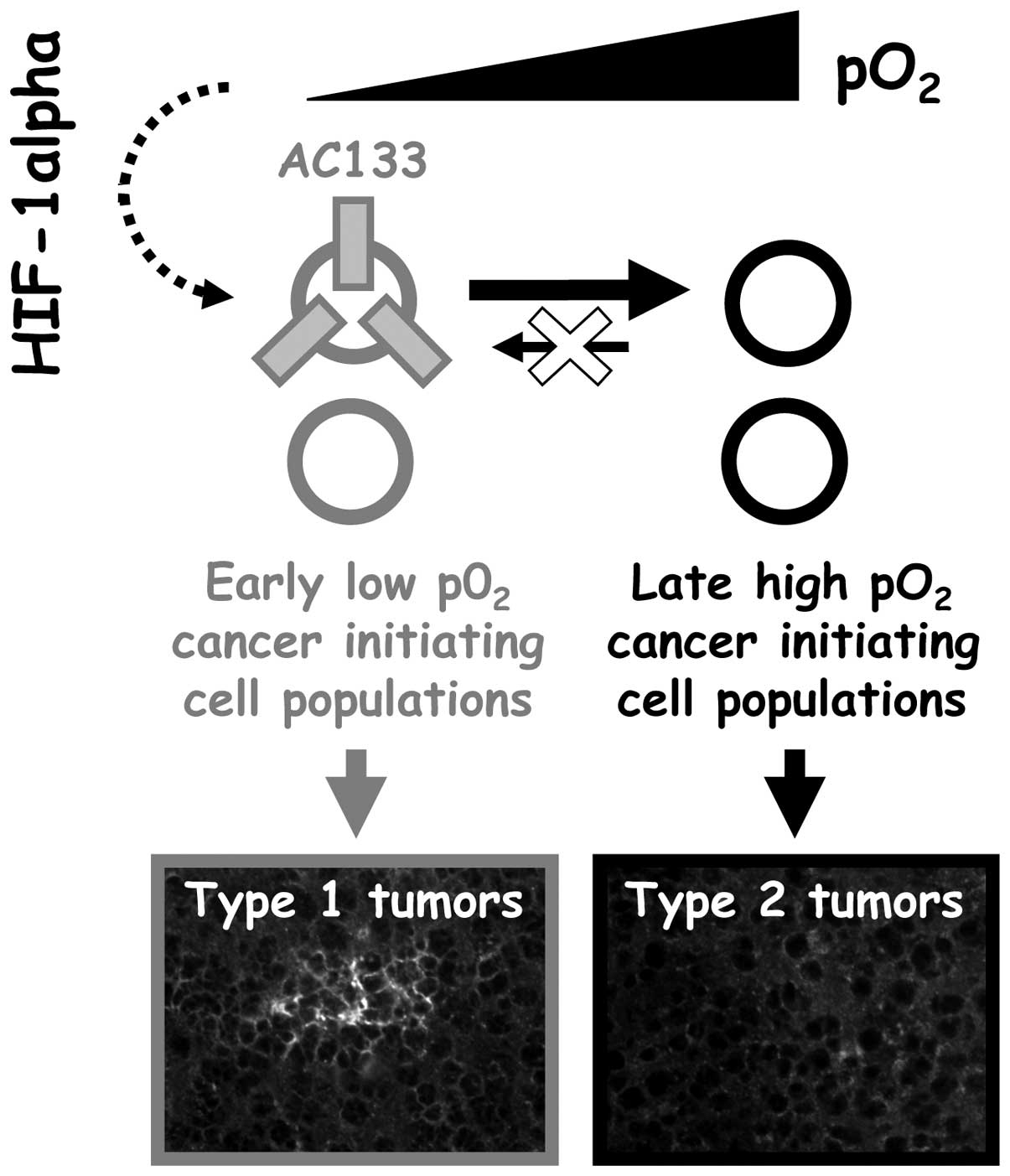
|
1
|
Ignatova TN, Kukekov VG, Laywell ED,
Suslov ON, Vrionis FD and Steindler DA: Human cortical glial tumors
contain neural stem-like cells expressing astroglial and neuronal
markers in vitro. Glia. 39:193–206. 2002.
|
|
2
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, et al:
Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer
Res. 63:5821–5828. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, et al:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004.
|
|
4
|
Jacques TS, Swales A, Brzozowski MJ, et
al: Combinations of genetic mutations in the adult neural stem cell
compartment determine brain tumour phenotypes. EMBO J. 29:222–235.
2010.
|
|
5
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008.
|
|
6
|
Mayol JF, Loeuillet C, Herodin F and Wion
D: Characterisation of normal and cancer stem cells: one
experimental paradigm for two kinds of stem cells. Bioessays.
31:993–1001. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Mao XG, Zhang X, Xue XY, et al: Brain
tumor stem-like cells identified by neural stem cell marker CD15.
Transl Oncol. 2:247–257. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Bao S, Wu Q, Li Z, et al: Targeting cancer
stem cells through L1CAM suppresses glioma growth. Cancer Res.
68:6043–6048. 2008.
|
|
9
|
Miraglia S, Godfrey W, Yin AH, et al: A
novel five-transmembrane hematopoietic stem cell antigen:
isolation, characterization, and molecular cloning. Blood.
90:5013–5021. 1997.
|
|
10
|
Yin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED, et al:
AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and progenitor
cells. Blood. 90:5002–5012. 1997.
|
|
11
|
Corbeil D, Roper K, Weigmann A and Huttner
WB: AC133 hematopoietic stem cell antigen: human homologue of mouse
kidney prominin or distinct member of a novel protein family?
Blood. 91:2625–2626. 1998.
|
|
12
|
Ferrandina G, Petrillo M, Bonanno G and
Scambia G: Targeting CD133 antigen in cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 13:823–837. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, et al: Glioma
stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of
the DNA damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006.
|
|
14
|
Zobalova R, McDermott L, Stantic M,
Prokopova K, Dong LF and Neuzil J: CD133-positive cells are
resistant to TRAIL due to up-regulation of FLIP. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 373:567–571. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, et al: Stem
cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular
endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res. 66:7843–7848. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Zeppernick F, Ahmadi R, Campos B, et al:
Stem cell marker CD133 affects clinical outcome in glioma patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:123–129. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Joo KM, Kim SY, Jin X, et al: Clinical and
biological implications of CD133-positive and CD133-negative cells
in glioblastomas. Lab Invest. 88:808–815. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Garcion E, Naveilhan P, Berger F and Wion
D: Cancer stem cells: Beyond Koch’s postulates. Cancer Lett.
278:3–8. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Scadden DT: The stem-cell niche as an
entity of action. Nature. 441:1075–1079. 2006.
|
|
20
|
Calabrese C, Poppleton H, Kocak M, et al:
A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell.
11:69–82. 2007.
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Bao S, Wu Q, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factors regulate tumorigenic capacity of glioma
stem cells. Cancer Cell. 15:501–513. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Pistollato F, Abbadi S, Rampazzo E, et al:
Intratumoral hypoxic gradient drives stem cells distribution and
MGMT expression in glioblastoma. Stem Cells. 28:851–862. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Panchision DM: The role of oxygen in
regulating neural stem cells in development and disease. J Cell
Physiol. 220:562–568. 2009.
|
|
24
|
Evans SM, Judy KD, Dunphy I, et al:
Hypoxia is important in the biology and aggression of human glial
brain tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 10:8177–8184. 2004.
|
|
25
|
Platet N, Liu SY, Atifi ME, et al:
Influence of oxygen tension on CD133 phenotype in human glioma cell
cultures. Cancer Lett. 258:286–290. 2007.
|
|
26
|
McCord AM, Jamal M, Shankavarum UT, Lang
FF, Camphausen K and Tofilon PJ: Physiologic oxygen concentration
enhances the stem-like properties of CD133+ human
glioblastoma cells in vitro. Mol Cancer Res. 7:489–497. 2009.
|
|
27
|
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, et
al: Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by
geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome
Biol. 3:Research00342002.
|
|
28
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, et al:
Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human
cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835. 1999.
|
|
29
|
Wenger RH, Stiehl DP and Camenisch G:
Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci STKE.
2005:re122005.
|
|
30
|
Tazuke SI, Mazure NM, Sugawara J, et al:
Hypoxia stimulates insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1
(IGFBP-1) gene expression in HepG2 cells: a possible model for
IGFBP-1 expression in fetal hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:10188–10193. 1998.
|
|
31
|
Yuan Y, Hilliard G, Ferguson T and
Millhorn DE: Cobalt inhibits the interaction between
hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha and von Hippel-Lindau protein by
direct binding to hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha. J Biol Chem.
278:15911–15916. 2003.
|
|
32
|
Vordermark D and Brown JM: Evaluation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) as an intrinsic marker
of tumor hypoxia in U87 MG human glioblastoma: in vitro and
xenograft studies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 56:1184–1193.
2003.
|
|
33
|
Csete M: Oxygen in the cultivation of stem
cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1049:1–8. 2005.
|
|
34
|
Vaupel P, Kelleher DK and Hockel M: Oxygen
status of malignant tumors: pathogenesis of hypoxia and
significance for tumor therapy. Semin Oncol. 28:29–35. 2001.
|
|
35
|
Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, et al:
Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured in bFGF and
EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of primary
tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell. 9:391–403.
2006.
|
|
36
|
Shervington A and Lu C: Expression of
multidrug resistance genes in normal and cancer stem cells. Cancer
Invest. 26:535–542. 2008.
|
|
37
|
Huang X, Le QT and Giaccia AJ:
MiR-210-micromanager of the hypoxia pathway. Trends Mol Med.
16:230–237. 2010.
|
|
38
|
Pistollato F, Chen HL, Rood BR, et al:
Hypoxia and HIF1alpha repress the differentiative effects of BMPs
in high-grade glioma. Stem Cells. 27:7–17. 2009.
|
|
39
|
Dringen R, Pfeiffer B and Hamprecht B:
Synthesis of the antioxidant glutathione in neurons: supply by
astrocytes of CysGly as precursor for neuronal glutathione. J
Neurosci. 19:562–569. 1999.
|
|
40
|
King FW, Ritner C, Liszewski W, et al:
Subpopulations of human embryonic stem cells with distinct
tissue-specific fates can be selected from pluripotent cultures.
Stem Cells Dev. 18:1441–1450. 2009.
|
|
41
|
Wu Y and Wu PY: CD133 as a marker for
cancer stem cells: progresses and concerns. Stem Cells Dev.
18:1127–1134. 2009.
|
|
42
|
Alcantara Llaguno S, Chen J, Kwon CH, et
al: Malignant astrocytomas originate from neural stem/progenitor
cells in a somatic tumor suppressor mouse model. Cancer Cell.
15:45–56. 2009.
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Yang J, Zheng H, et al: Expression
of mutant p53 proteins implicates a lineage relationship between
neural stem cells and malignant astrocytic glioma in a murine
model. Cancer Cell. 15:514–526. 2009.
|
|
44
|
Hill RP: Identifying cancer stem cells in
solid tumors: case not proven. Cancer Res. 66:1890–1895. 2006.
|
|
45
|
Adams JM and Strasser A: Is tumor growth
sustained by rare cancer stem cells or dominant clones? Cancer Res.
68:4018–4021. 2008.
|
|
46
|
Piccirillo SG, Reynolds BA, Zanetti N, et
al: Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit the tumorigenic potential
of human brain tumour-initiating cells. Nature. 444:761–765.
2006.
|
|
47
|
Ogden AT, Waziri AE, Lochhead RA, et al:
Identification of A2B5+CD133−
tumor-initiating cells in adult human gliomas. Neurosurgery.
62:505–514. 2008.
|
|
48
|
Wang J, Sakariassen PO, Tsinkalovsky O, et
al: CD133 negative glioma cells form tumors in nude rats and give
rise to CD133 positive cells. Int J Cancer. 122:761–768. 2008.
|
|
49
|
Soeda A, Park M, Lee D, et al: Hypoxia
promotes expansion of the CD133-positive glioma stem cells through
activation of HIF-1alpha. Oncogene. 28:3949–3959. 2009.
|
|
50
|
Bar EE, Lin A, Mahairaki V, Matsui W and
Eberhart CG: Hypoxia increases the expression of stem-cell markers
and promotes clonogenicity in glioblastoma neurospheres. Am J
Pathol. 177:1491–1502. 2010.
|
|
51
|
Matsumoto K, Arao T, Tanaka K, et al: mTOR
signal and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha regulate CD133
expression in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:7160–7164. 2009.
|
|
52
|
Heddleston JM, Li Z, McLendon RE,
Hjelmeland AB and Rich JN: The hypoxic microenvironment maintains
glioblastoma stem cells and promotes reprogramming towards a cancer
stem cell phenotype. Cell Cycle. 8:3274–3284. 2009.
|
|
53
|
Lopez-Barneo J, Pardal R and Ortega-Saenz
P: Cellular mechanism of oxygen sensing. Annu Rev Physiol.
63:259–287. 2001.
|
|
54
|
Arany Z, Foo SY, Ma Y, et al:
HIF-independent regulation of VEGF and angiogenesis by the
transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha. Nature. 451:1008–1012.
2008.
|
|
55
|
Liu L, Cash TP, Jones RG, Keith B,
Thompson CB and Simon MC: Hypoxia-induced energy stress regulates
mRNA translation and cell growth. Mol Cell. 21:521–531. 2006.
|
|
56
|
Tabu K, Sasai K, Kimura T, et al: Promoter
hypomethylation regulates CD133 expression in human gliomas. Cell
Res. 18:1037–1046. 2008.
|
|
57
|
Yi JM, Tsai HC, Glockner SC, et al:
Abnormal DNA methylation of CD133 in colorectal and glioblastoma
tumors. Cancer Res. 68:8094–8103. 2008.
|
|
58
|
Wion D, Christen T, Barbier EL and Coles
JA: PO(2) matters in stem cell culture. Cell Stem Cell. 5:242–243.
2009.
|
|
59
|
Lillien L and Raphael H: BMP and FGF
regulate the development of EGF-responsive neural progenitor cells.
Development. 127:4993–5005. 2000.
|
|
60
|
Chen R, Nishimura MC, Bumbaca SM, et al: A
hierarchy of self-renewing tumor-initiating cell types in
glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 17:362–375. 2010.
|
|
61
|
Kemper K, Sprick MR, De Bree M, et al: The
AC133 epitope, but not the CD133 protein, is lost upon cancer stem
cell differentiation. Cancer Res. 70:719–729. 2010.
|
|
62
|
Campos B, Wan F, Farhadi M, et al:
Differentiation therapy exerts antitumor effects on stem-like
glioma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2715–2728. 2010.
|
|
63
|
Soda Y, Marumoto T, Friedmann-Morvinski D,
et al: Trans-differentiation of glioblastoma cells into vascular
endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:4274–4280. 2011.
|