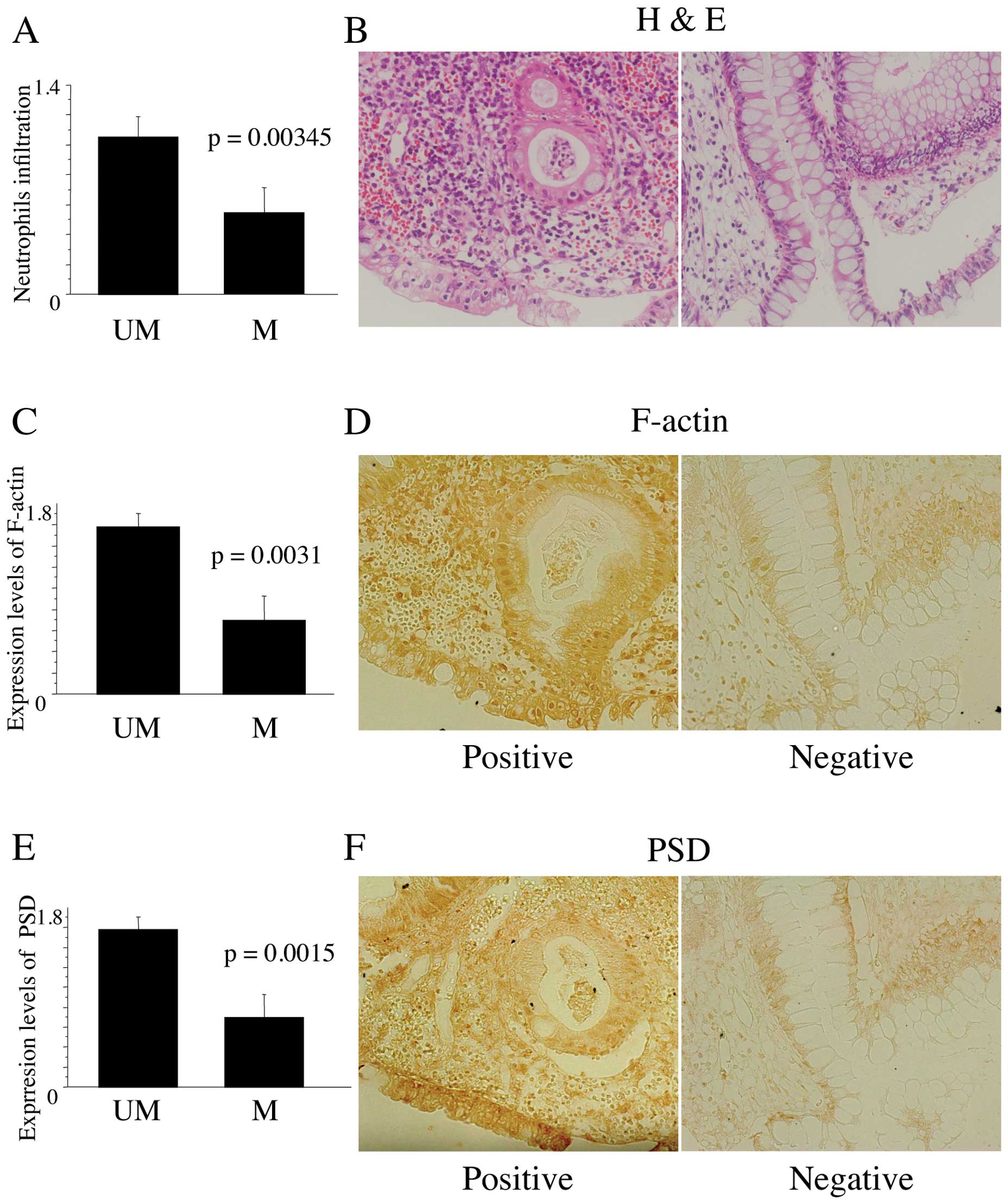
|
1
|
Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M and Adami HO:
Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. a population-based study.
N Engl J Med. 323:1228–1233. 1990.
|
|
2
|
Lashner BA, Silverstein MD and Hanauer SB:
Hazard rates for dysplasia and cancer in ulcerative colitis.
Results from a surveillance program. Dig Dis Sci. 34:1536–1541.
1989.
|
|
3
|
Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, et al: A
genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory
bowel disease gene. Science. 314:1461–1463. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Franke A, Balschun T, Karlsen TH, et al:
Replication of signals from recent studies of Crohn’s disease
identifies previously unknown disease loci for ulcerative colitis.
Nat Genet. 40:713–715. 2008.
|
|
5
|
Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H, et al:
Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with
susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature. 411:599–603. 2001.
|
|
6
|
Barrett JC, Hansoul S, Nicolae DL, et al:
Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct
susceptibility loci for Crohn’s disease. Nat Genet. 40:955–962.
2008.
|
|
7
|
Hampe J, Franke A, Rosenstiel P, et al: A
genome-wide association scan of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a
susceptibility variant for Crohn disease in ATG16L1. Nat Genet.
39:207–211. 2007.
|
|
8
|
Rioux JD, Xavier RJ, Taylor KD, et al:
Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci
for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis.
Nat Genet. 39:596–604. 2007.
|
|
9
|
Barrett JC, Lee JC, Lees CW, et al:
Genome-wide association study of ulcerative colitis identifies
three new susceptibility loci, including the HNF4A region. Nat
Genet. 41:1330–1334. 2009.
|
|
10
|
Stoll M, Corneliussen B, Costello CM, et
al: Genetic variation in DLG5 is associated with inflammatory bowel
disease. Nat Genet. 36:476–480. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Humbert P, Russell S and Richardson H:
Dlg, Scribble and Lgl in cell polarity, cell proliferation and
cancer. Bioessays. 25:542–553. 2003.
|
|
12
|
Wakabayashi M, Ito T, Mitsushima M, et al:
Interaction of lp-dlg/KIAA0583, a membrane-associated guanylate
kinase family protein, with vinexin and beta-catenin at sites of
cell-cell contact. J Biol Chem. 278:21709–21714. 2003.
|
|
13
|
Okada S, Suzuki K, Kato T, et al: Aberrant
methylation of the Pleckstrin and Sec7 domain-containing gene is
implicated in ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis through
its inhibition of apoptosis. Int J Oncol. DOI:
10.3892/ijo.2011.1231. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Eom YW, Yoo MH, Woo CH, et al: Implication
of the small GTPase Rac1 in the apoptosis induced by UV in Rat-2
fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 285:825–829. 2001.
|
|
15
|
Gulbins E, Coggeshall KM, Brenner B,
Schlottmann K, Linderkamp O and Lang F: Fas-induced apoptosis is
mediated by activation of a Ras and Rac protein-regulated signaling
pathway. J BiolChem. 271:26389–26394. 1996.
|
|
16
|
Esteve P, Embade N, Perona R, et al:
Rho-regulated signals induce apoptosis in vitro and in vivo by a
p53-independent, but Bcl2 dependent pathway. Oncogene.
17:1855–1869. 1998.
|
|
17
|
Servant G, Weiner OD, Herzmark P, Balla T,
Sedat JW and Bourne HR: Polarization of chemoattractant receptor
signaling during neutrophil chemotaxis. Science. 287:1037–1040.
2000.
|
|
18
|
Servant G, Weiner OD, Neptune ER, Sedat JW
and Bourne HR: Dynamics of a chemoattractant receptor in living
neutrophils during chemotaxis. Mol Biol Cell. 10:1163–1178.
1999.
|
|
19
|
Wang F, Herzmark P, Weiner OD, Srinivasan
S, Servant G and Bourne HR: Lipid products of PI(3)Ks maintain
persistent cell polarity and directed motility in neutrophils. Nat
Cell Biol. 4:513–518. 2002.
|
|
20
|
Rutter M, Saunders B, Wilkinson K, et al:
Severity of inflammation is a risk factor for colorectal neoplasia
in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 126:451–459. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Franco M, Peters PJ, Boretto J, et al:
EFA6, a sec7 domain-containing exchange factor for ARF6,
coordinates membrane recycling and actin cytoskeleton organization.
EMBO J. 18:1480–1491. 1999.
|
|
22
|
Kurokawa K, Itoh RE, Yoshizaki H, Nakamura
YO and Matsuda M: Coactivation of Rac1 and Cdc42 at lamellipodia
and membrane ruffles induced by epidermal growth factor. Mol Biol
Cell. 15:1003–1010. 2004.
|
|
23
|
Boehm JE, Chaika OV and Lewis RE:
Rac-dependent anti-apoptotic signaling by the insulin receptor
cytoplasmic domain. J BiolChem. 274:28632–28636. 1999.
|
|
24
|
Joneson T and Bar-Sagi D: Suppression of
Ras-induced apoptosis by the RacGTPase. Mol Cell Biol.
19:5892–5901. 1999.
|
|
25
|
Nishida K, Kaziro Y and Satoh T:
Anti-apoptotic function of Rac in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene.
18:407–415. 1999.
|
|
26
|
Saez R, Chan AM, Miki T and Aaronson SA:
Oncogenic activation of human R-ras by point mutations analogous to
those of prototype H-ras oncogenes. Oncogene. 9:2977–2982.
1994.
|
|
27
|
Wang HG, Millan JA, Cox AD, et al: R-Ras
promotes apoptosis caused by growth factor deprivation via a Bcl-2
suppressible mechanism. J Cell Biol. 129:1103–1114. 1995.
|
|
28
|
Srinivasan S, Wang F, Glavas S, et al: Rac
and Cdc42 play distinct roles in regulating PI(3,4,5)P3 and
polarity during neutrophil chemotaxis. J Cell Biol. 160:375–385.
2003.
|
|
29
|
Lampinen M, Ronnblom A, Amin K, et al:
Eosinophil granulocytes are activated during the remission phase of
ulcerative colitis. Gut. 54:1714–1720. 2005.
|
|
30
|
Glogauer M, Marchal CC, Zhu F, et al: Rac1
deletion in mouse neutrophils has selective effects on neutrophil
functions. J Immunol. 170:5652–5657. 2003.
|
|
31
|
Roessner A, Kuester D, Malfertheiner P and
Schneider-Stock R: Oxidative stress in ulcerative
colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Pathol Res Pract. 204:511–524.
2008.
|