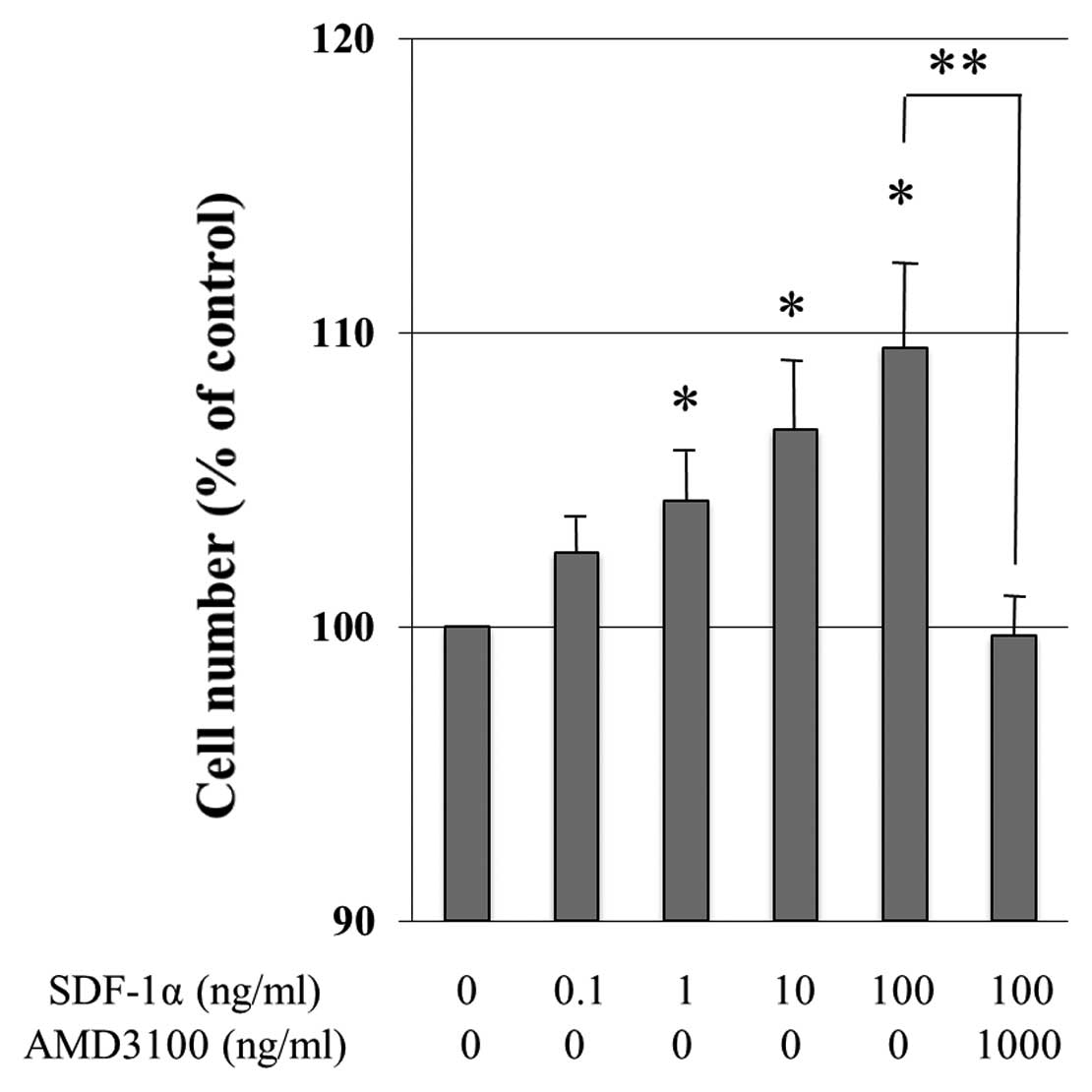
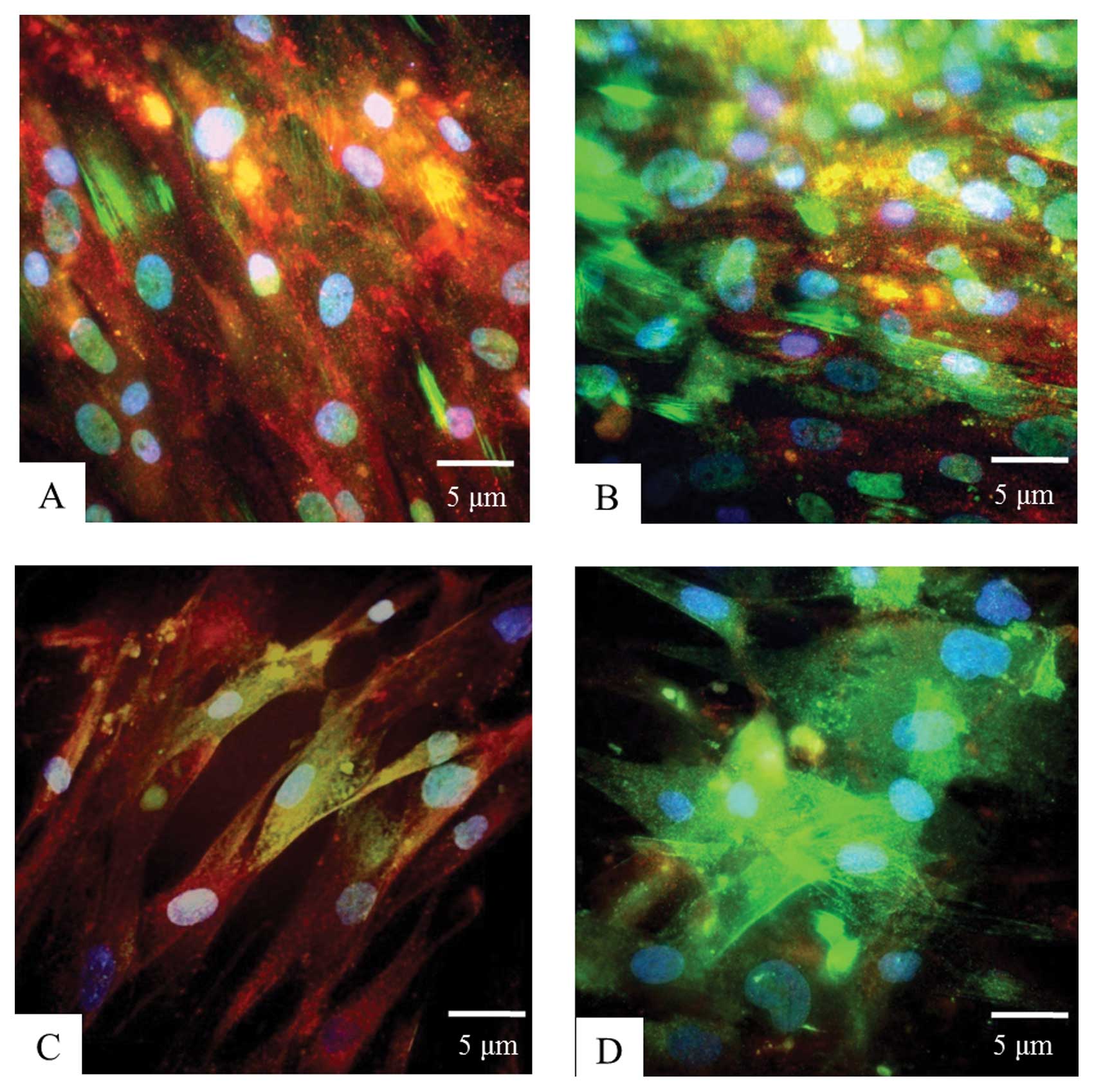
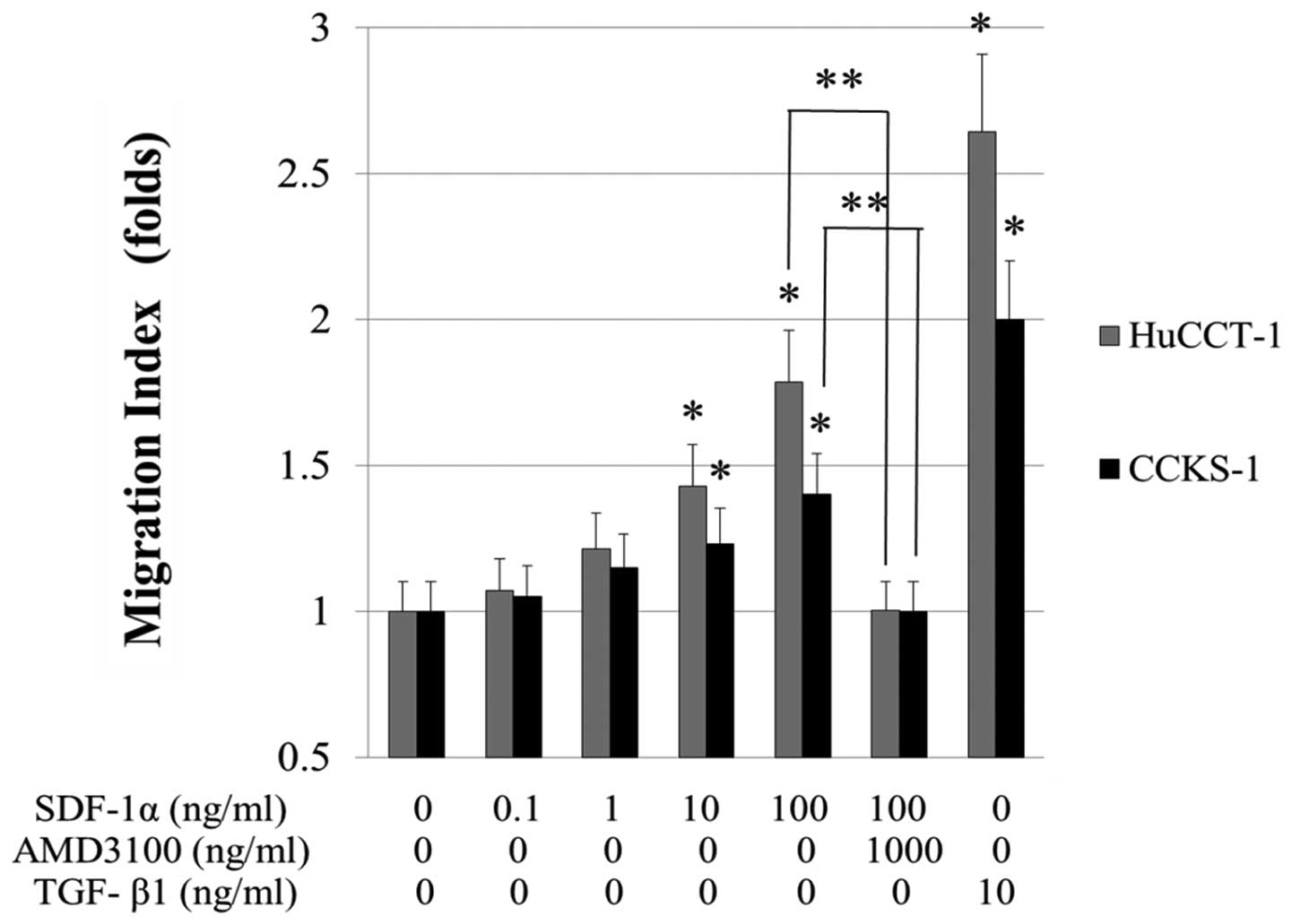
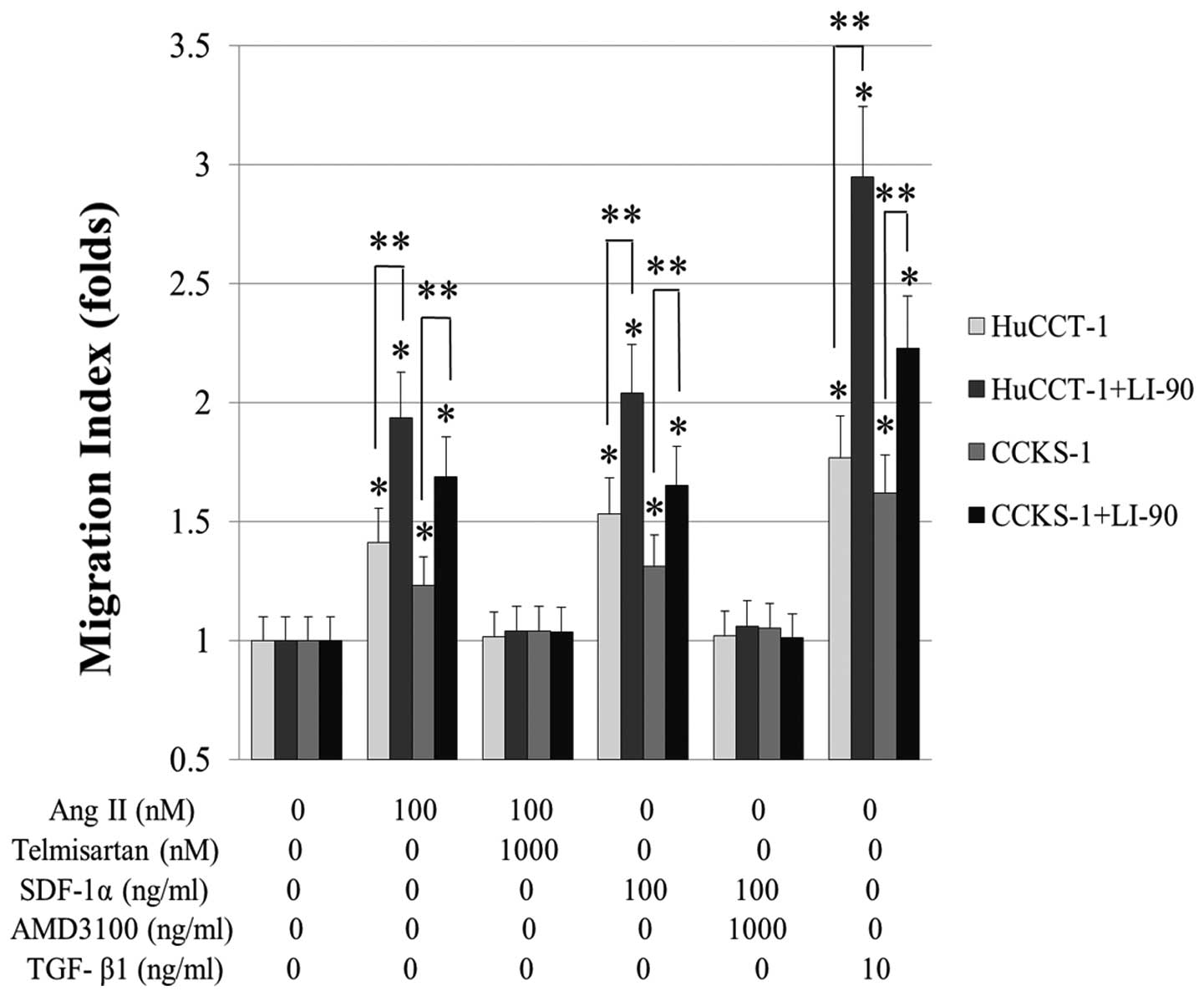
|
1
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC,
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL
and Weinberg RA: Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human
breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through
elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 121:335–348. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ohira S, Sasaki M, Harada K, Sato Y, Zen
Y, Isse K, Kozaka K, Ishikawa A, Oda K, Nimura Y and Nakanuma Y:
Possible regulation of migration of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
cells by interaction of CXCR4 expressed in carcinoma cells with
tumor necrosis factor-α and stromal-derived factor-1 released in
stroma. Am J Pathol. 168:1155–1168. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marchesi F, Monti P, Leone BE, Zerbi A,
Vecchi A, Piemonti L, Mantovani A and Allavena P: Increased
survival, proliferation, and migration in metastatic human
pancreatic tumor cells expressing functional CXCR4. Cancer Res.
64:8420–8427. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mishra PJ, Mishra PJ, Humeniuk R, Medina
DJ, Alexe G, Mesirov JP, Ganesan S, Glod JW and Banerjee D:
Carcinoma-associated fibroblast-like differentiation of human
mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer Res. 68:4331–4339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Okamoto K, Tajima H, Ohta T, Nakanuma S,
Hayashi H, Nakagawara H, Ohishi I, Takamura H, Ninomiya I, Kitagawa
H, Fushida S, Tani T, Fujimura T, Kayahara M, Harada S, Wakayama T
and Iseki S: Angiotensin II induces tumor progression and fibrosis
in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through an interaction with
hepatic stellate cells. Int J Oncol. 37:1251–1259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Anandanadesan R, Gong Q, Chipitsyna G,
Witkiewicz A, Yeo CJ and Arafat HA: Angiotensin II induces vascular
endothelial growth factor in pancreatic cancer cells through an
angiotensin II type 1 receptor and ERK1/2 signaling. J Gastrointest
Surg. 12:57–66. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amann T, Bataille F, Spruss T, Mühlbauer
M, Gäbele E, Schölmerich J, Kiefer P, Bosserhoff AK and Hellerbrand
C: Activated hepatic stellate cells promote tumorigenicity of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:646–653. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Buck E, Eyzaguirre A, Barr S, Thompson S,
Sennello R, Young D, Iwata KK, Gibson NW, Cagnoni P and Haley JD:
Loss of homotypic cell adhesion by epithelial-mesenchymal
transition or mutation limits sensitivity to epidermal growth
factor receptor inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:532–541. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Thompson EW, Newgreen DF and Tarin D:
Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: a role for
epithelial-mesenchymal transition? Cancer Res. 65:5991–5995. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valcourt U, Kowanetz M, Niimi H, Heldin CH
and Moustakas A: TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support
transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell
transition. Mol Biol Cell. 16:1987–2002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Elliott BE, Hung WL, Boag AH and Tuck AB:
The role of hepatocyte growth factor (scatter factor) in epithelial
mesenchymal transition and breast cancer. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
80:91–102. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang AD, Camp ER, Fan F, Shen L, Gray MJ,
Liu W, Somcio R, Bauer TW, Wu Y, Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1 activation mediates epithelial
to mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic carcinoma cells.
Cancer Res. 66:46–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rosanò L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Nicotra
MR, Dedhar S, De Herreros AG, Natali PG and Bagnato A: Endothelin-1
promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human ovarian
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:11649–11657. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Andl CD, Fargnoli BB, Okawa T, Bowser M,
Takaoka M, Nakagawa H, Klein-Szanto A, Hua X, Herlyn M and Rustgi
AK: Coordinated functions of E-cadherin and transforming growth
factor beta receptor II in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res.
66:9878–9885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen J, Chen JK and Harris RC: Angiotensin
II induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal epithelial
cells through ROS/Src/Caveolin-mediated activation of an EGFR-ERK
signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 32:981–991. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang J, Jiang Z, Zhang H, Zhu H, Zhou SF
and Yu X: NADPH oxidase-dependent formation of reactive oxygen
species contributes to angiotensin II-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in rat peritoneal mesothelial
cells. Int J Mol Med. 28:405–412. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Buckley ST, Medina C and Ehrhardt C:
Differential susceptibility to epithelial-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) of alveolar, bronchial and intestinal epithelial cells in
vitro and the effect of angiotensin II receptor inhibition. Cell
Tissue Res. 342:39–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan: The
general rules for the clinical and pathological study of primary
liver cancer. 5th edition. Kanehara, Tokyo: pp. 17–27. 2008
|
|
21
|
Morimoto T, Aoyama M, Gotoh E and
Shionoiri H: A method of radioimmunoassay of plasma angiotensin II
using Florisil. Folia Endocrinoa Jpn. 59:215–229. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyagiwa M, Ichida T, Tokiwa T, Sato J and
Sasaki H: A new human cholangiocellular carcinoma cell line
(HuCC-T1) producing carbohydrate antigen 19/9 in serum-free medium.
In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 25:503–510. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sugawara H, Yasoshima M, Katayanagi K,
Kono N, Watanabe Y, Harada K and Nakanuma Y: Relationship between
interleukin-6 and proliferation and differentiation in
cholangiocarcinoma. Histopathology. 33:145–153. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murakami K, Abe T, Miyazawa M, Yamaguchi
M, Masuda T, Matsuura T, Nagamori S, Takeuchi K, Abe K and Kyogoku
M: Establishment of a new human cell line, LI90, exhibiting
characteristics of hepatic Ito (fat-storing) cells. Lab Invest.
72:731–739. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Salguero Palacios R, Roderfeld M, Hemmann
S, Rath T, Atanasova S, Tschuschner A, Gressner OA, Weiskirchen R,
Graf J and Roeb E: Activation of hepatic stellate cells is
associated with cytokine expression in thioacetamide-induced
hepatic fibrosis in mice. Lab Invest. 88:1192–1203. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gressner AM and Weiskirchen R: Modern
pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and
TGF-β as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med.
10:76–99. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tien YW, Wu YM, Lin WC, Lee HS and Lee PH:
Pancreatic carcinoma cells stimulate proliferation and matrix
synthesis of hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol. 51:307–314. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Okabe H, Beppu T, Hayashi H, Horino K,
Masuda T, Komori H, Ishikawa S, Watanabe M, Takamori H, Iyama K and
Baba H: Hepatic stellate cells may relate to progression of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:2555–2564.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leelawat K, Leelawat S, Narong S and
Hongeng S: Roles of the MEK1/2 and AKT pathways in CXCL12/CXCR4
induced cholangiocarcinoma cell invasion. World J Gastroenterol.
13:1561–1568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gilles C and Thompson EW: The epithelial
to mesenchymal transition and metastatic progression in carcinoma.
Breast J. 2:83–96. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ellenrieder V, Hendler SF, Boeck W,
Seufferlein T, Menke A, Ruhland C, Adler G and Gress TM:
Transforming growth factor beta1 treatment leads to an
epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation of pancreatic cancer
cells requiring extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 activation.
Cancer Res. 61:4222–4228. 2001.
|
|
32
|
Peinado H, Portillo F and Cano A:
Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and
carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 48:365–375. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tomita K, van Bokhoven A, van Leenders GJ,
Ruijter ET, Jansen CF, Bussemakers MJ and Schalken JA: Cadherin
switching in human prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res.
60:3650–3654. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rodrigues-Díez R, Carvajal-González G,
Sánchez-López E, Rodríguez-Vita J, Rodrigues Díez R, Selgas R,
Ortiz A, Egido J, Mezzano S and Ruiz-Ortega M: Pharmacological
modulation of epithelial mesenchymal transition caused by
angiotensin II. Role of ROCK and MAPK pathways Pharm Res.
25:2447–2461. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rupérez M, Esteban V,
Rodríguez-Vita J, Sánchez-López E, Carvajal G and Egido J:
Angiotensin II: a key factor in the inflammatory and fibrotic
response in kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 21:16–20.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Carvajal G, Rodríguez-Vita J,
Rodrigues-Díez R, Sánchez-López E, Rupérez M, Cartier C, Esteban V,
Ortiz A, Egido J, Mezzano SA and Ruiz-Ortega M: Angiotensin II
activates the Smad pathway during epithelial mesenchymal
transdifferentiation. Kidney Int. 74:585–595. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wolf G: Renal injury due to
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation of the transforming
growth factor-beta pathway. Kidney Int. 70:1914–1919.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK and
Arteaga CL: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for
TGFbeta mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell
migration. J Cell Sci. 115:3193–3206. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rupérez M, Lorenzo O, Blanco-Colio LM,
Esteban V, Egido J and Ruiz-Ortega M: Connective tissue growth
factor is a mediator of angiotensin II-induced fibrosis.
Circulation. 108:1499–1505. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Non-Smad
TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci. 118:3573–3584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rodríguez-Vita J,
Sanchez-Lopez E, Carvajal G and Egido J: TGF-beta signaling in
vascular fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res. 74:196–206. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee BC, Lee TH, Avraham S and Avraham HK:
Involvement of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand stromal
cell-derived factor 1alpha in breast cancer cell migration through
human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res.
2:327–338. 2004.
|
|
43
|
Onoue T, Uchida D, Begum NM, Tomizuka Y,
Yoshida H and Sato M: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by
the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 system in oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 29:1133–1138. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ishii G, Sangai T, Ito T, Hasebe T, Endoh
Y, Sasaki H, Harigaya K and Ochiai A: In vivo and in vitro
characterization of human fibroblasts recruited selectively into
human cancer stroma. Int J Cancer. 117:212–220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kalluri R and Zeisberg M: Fibroblasts in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:392–401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|