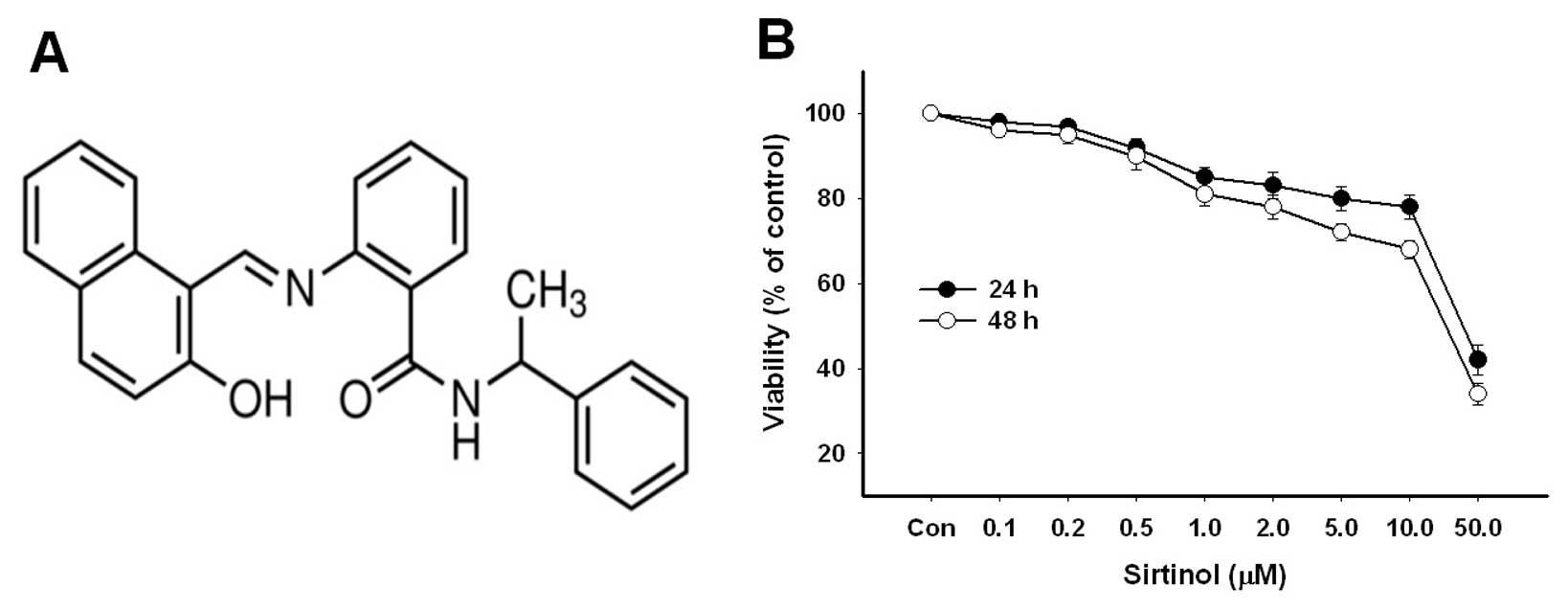
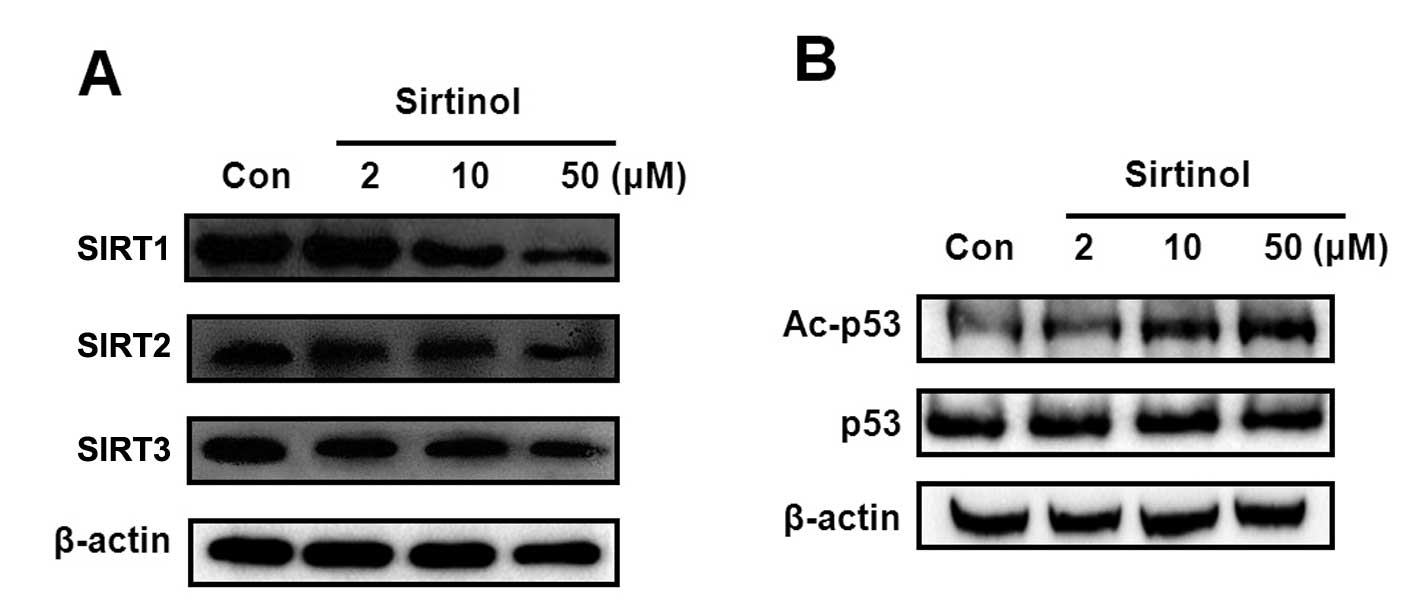
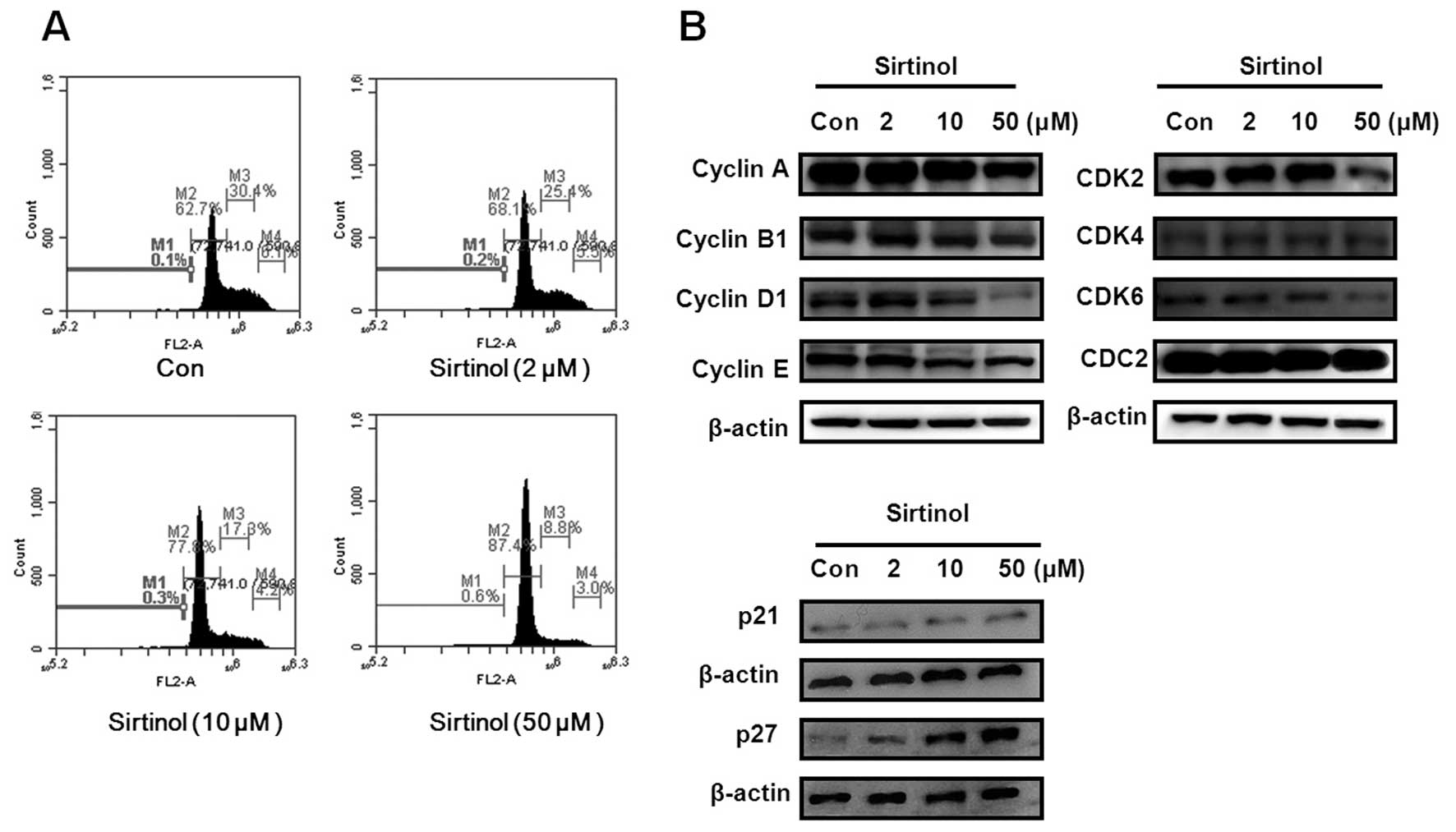
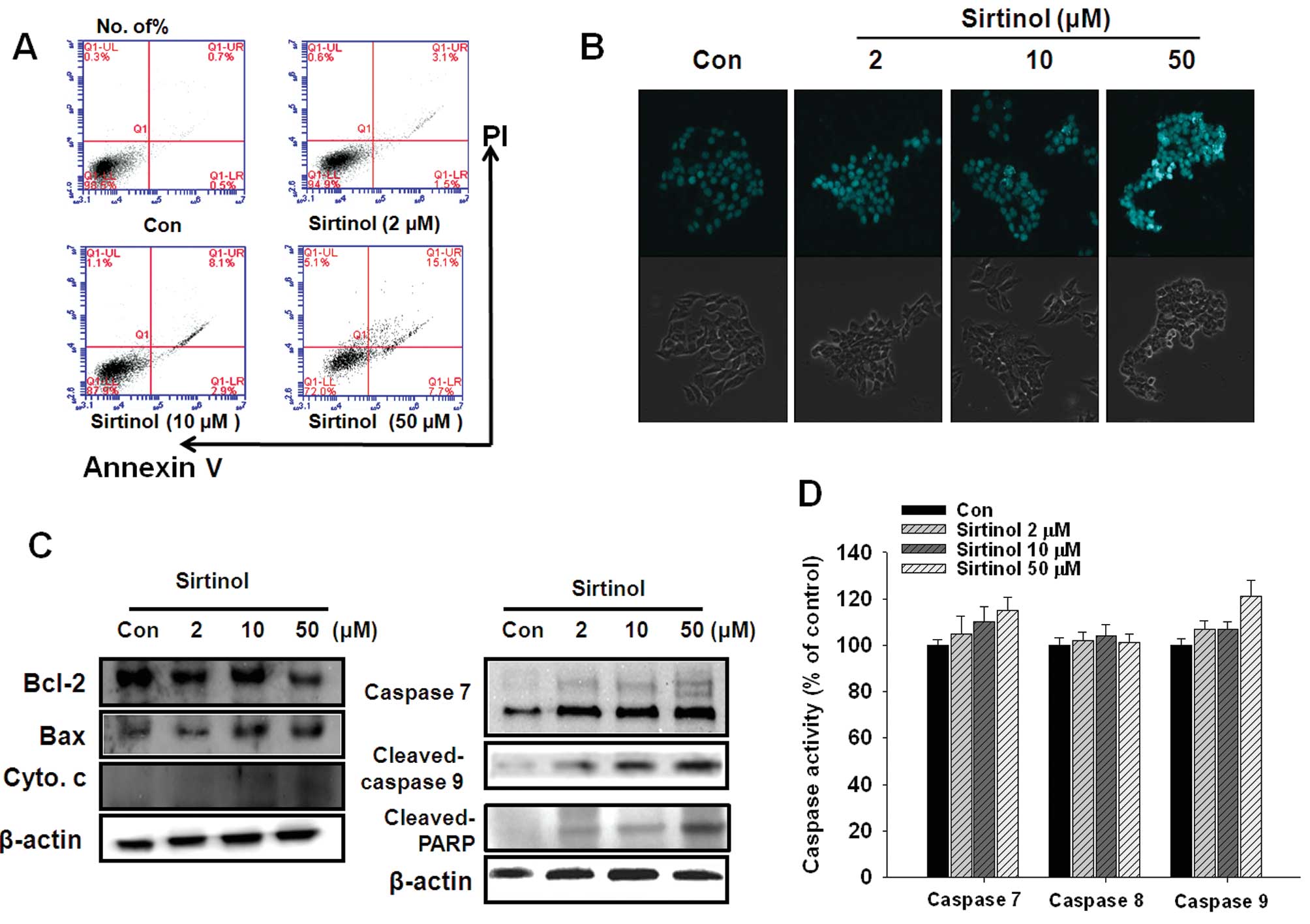
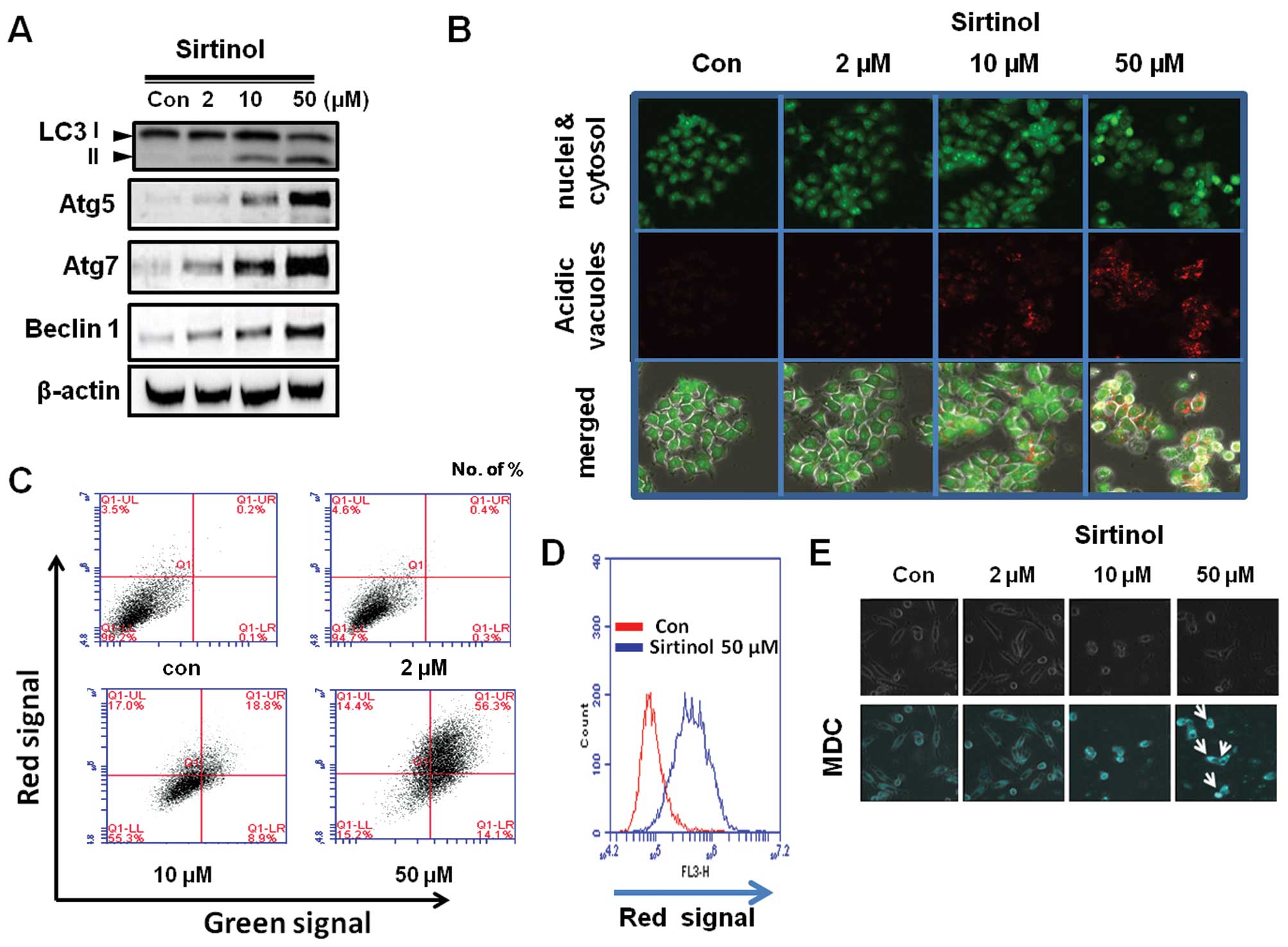
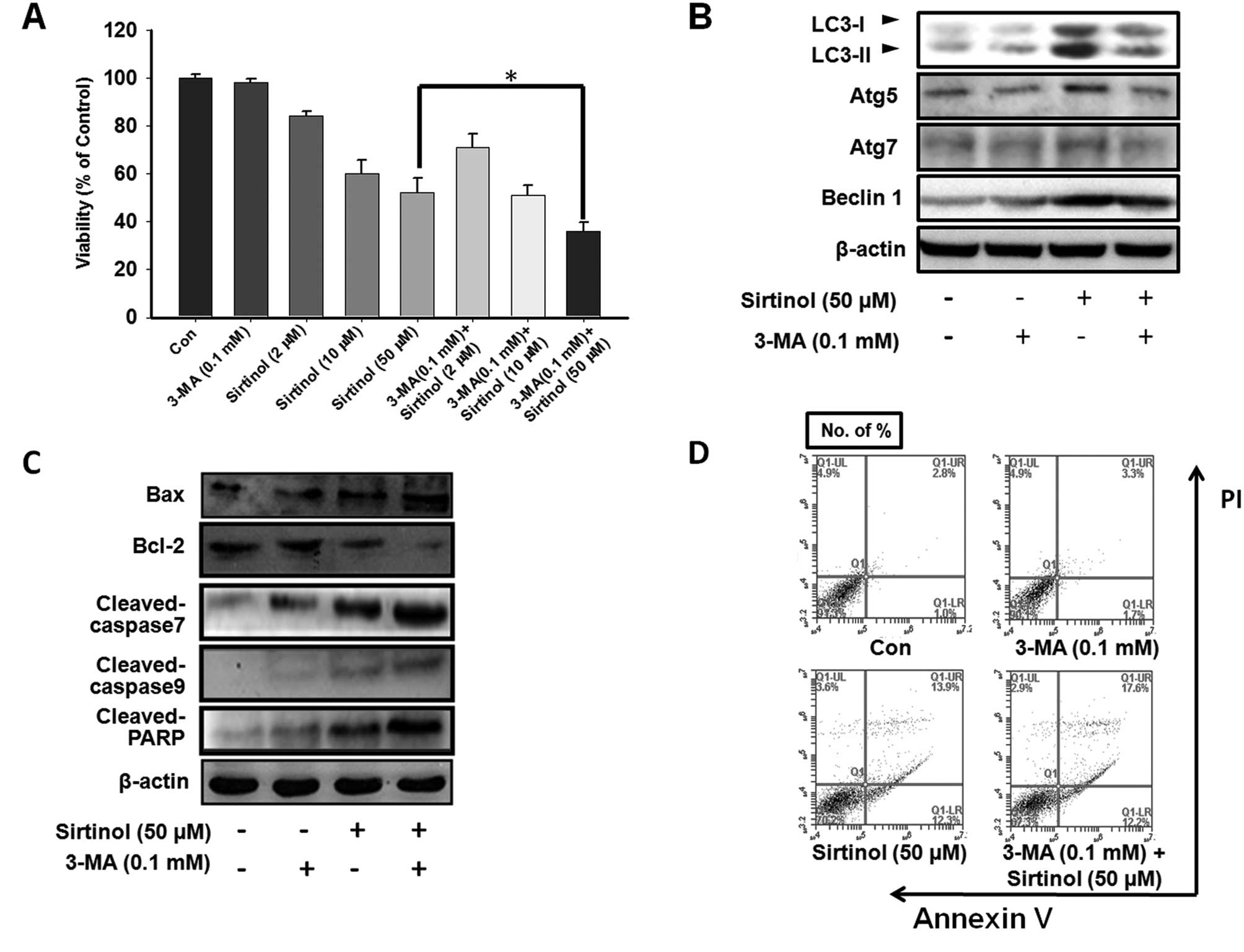
|
1.
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC): World Cancer Report. http://globocan.iarc.fr/factsheets/populations/factsheet.asp?uno=900,
2008.
|
|
2.
|
Yoo KY, Kang D, Park SK, et al:
Epidemiology of breast cancer in Korea: occurrence, high-risk
groups, and prevention. J Korean Med Sci. 17:1–6. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Esteve JM and Knecht E: Mechanisms of
autophagy and apoptosis: Recent developments in breast cancer
cells. World J Biol Chem. 26:232–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Cook KL, Shajahan AN and Clarke R:
Autophagy and endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 11:1283–1294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Aguilar H, Solé X, Bonifaci N, et al:
Biological reprogramming in acquired resistance to endocrine
therapy of breast cancer. Oncogene. 29:6071–6083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Yue W, Fan P, Wang J, Li Y and Santen RJ:
Mechanisms of acquired resistance to endocrine therapy in
hormone-dependent breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
106:102–110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Notte A, Leclere L and Michiels C:
Autophagy as a mediator of chemotherapy-induced cell death in
cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:427–434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Minucci S and Pelicci PG: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more)
treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:38–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB and Marks PA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene.
26:5541–5552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Blander G and Guarente L: The Sir2 family
of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:417–435. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Frye RA: Characterization of five human
cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene: Sir2-like proteins
(sirtuins) metabolize NAD and may have protein
ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
260:273–279. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Liszt G, Ford E, Kurtev M and Guarente L:
Mouse Sir2 homolog SIRT6 is a nuclear ADP-ribosyltransferase. J
Biol Chem. 280:21313–21320. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Liu T, Liu PY and Marshall GM: The
critical role of the class III histone deacetylase SIRT1 in cancer.
Cancer Res. 69:1702–1705. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Fraga MF and Esteller M: Epigenetics and
aging: the targets and the marks. Trends Gene. 23:413–418. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Lim CS: Human SIRT1: a protein biomarker
for tumorigenesis? Cell Bio Int. 31:636–637. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Vaquero A, Scher MB, Lee DH, et al: SirT2
is a histone deacetylase with preference for histone H4 Lys 16
during mitosis. Genes Dev. 20:1256–1261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Jeong J, Juhn K, Lee H, et al: SIRT1
promotes DNA repair activity and deacetylation of Ku70. Exp Mol
Med. 39:8–13. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, et al:
Modulation of NF-κB-dependent transcription and cell survival by
the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 23:2369–2380. 2004.
|
|
20.
|
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, et al:
Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the
SIRT1 deacetylase. Science. 303:2011–2015. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Motta MC, Divecha N, Lemieux M, et al:
Mammalian SIRT represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell.
116:551–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Bouras T, Fu M, Sauve AA, et al: SIRT1
deacetylation and repression of p300 involves lysine residues
1020/1024 within the cell cycle regulatory domain 1. J Bio Chem.
280:10264–10276. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, et al:
Hsir2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell.
107:149–159. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Bedalov A, Gatbonton T, Irvine WP,
Gottschling DE and Simon JA: Identification of a small molecule
inhibitor of Sir2p. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:15113–15118. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Grozinger CM, Chao ED, Blackwell HE,
Moazed D and Schreiber SL: Identification of a class of small
molecule inhibitors of the sirtuin family of NAD-dependent
deacetylases by phenotypic screening. J Biol Chem. 276:38837–38843.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Avalos JL, Bever KM and Wolberger C:
Mechanism of sirtuin inhibition by nicotinamide: altering the
NAD(+) cosubstrate specificity of a Sir2 enzyme. Mol Cell.
17:855–868. 2005.
|
|
27.
|
Bitterman KJ, Anderson RM, Cohen HY,
Latorre-Esteves M and Sinclair DA: Inhibition of silencing and
accelerated aging by nicotinamide, a putative negative regulator of
yeast sir2 and human SIRT1. J Biol Chem. 277:45099–45107. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ota H, Akishita M, Eto M, Iijima K, Kaneki
M and Ouchi Y: Sirt1 modulates premature senescence-like phenotype
in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Cardiol. 43:571–579. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Heltweg B, Gatbonton T, Schuler AD, et al:
Antitumor activity of a small-molecule inhibitors of human silent
information regulator 2 enzymes. Cancer Res. 66:4368–4377. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Olaharski AJ, Rine J, Marshall BL, et al:
The flavoring agent dihydrocoumarin reverses epigenetic silencing
and inhibits sirtuin deacetylases. PLoS Genet. 1:e772005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Napper AD, Hixon J, McDonagh T, et al:
Discovery of indoles as potent and selective inhibitors of the
deacetylase SIRT1. J Med Chem. 48:8045–8054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Saunders LR and Verdin E: Sirtuins:
critical regulators at the crossroads between cancer and aging.
Oncogene. 26:5489–5504. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Millot C, Millot JM, Morjani H, Desplaces
A and Manfait M: Characterization of acidic vesicles in
multidrug-resistant and sensitive cancer cells by acridine orange
staining and confocal micro-spectrofluorometry. J Histochem
Cytochem. 45:1255–1264. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
De Duve C, de Barsy T, Poole B, Trouet A,
Tulkens P and van Hoof F: Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents.
Biochem Pharmacol. 23:2495–2531. 1974.
|
|
35.
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, et al:
A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy
and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Petiot A, Ogier-Denis E, Blommaart EF,
Meijer AJ and Codogno P: Distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinases are involved in signaling pathways that control
macroautophagy in HT-29 cells. J Biol Chem. 275:992–998. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Fraga MF, Agrelo R and Esteller M:
Cross-talk between aging and cancer: the epigenetic language. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1100:60–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Mahlknecht U and Hoelzer D: Histone
acetylation modifiers in the pathogenesis of malignant disease. Mol
Med. 6:623–644. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Michishita E, Park JY, Burneskis JM,
Barrett JC and Horikawa I: Evolutionarily conserved and
nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT
proteins. Mol Biol Cell. 16:4623–4635. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Arico S, Petiot A, Bauvy C, et al: The
tumor suppressor PTEN positively regulates macroautophagy by
inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B
pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:35243–35246. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|