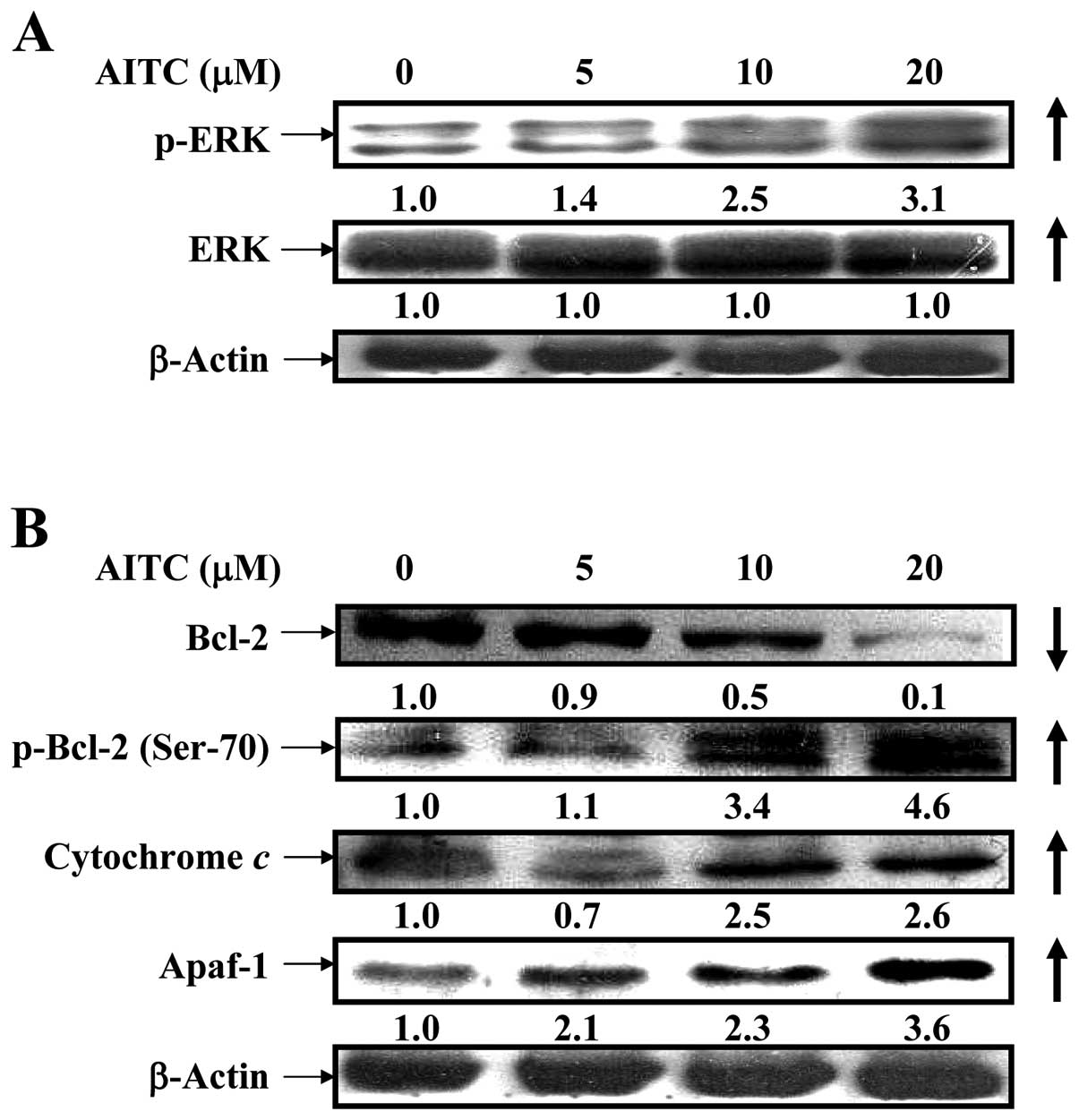
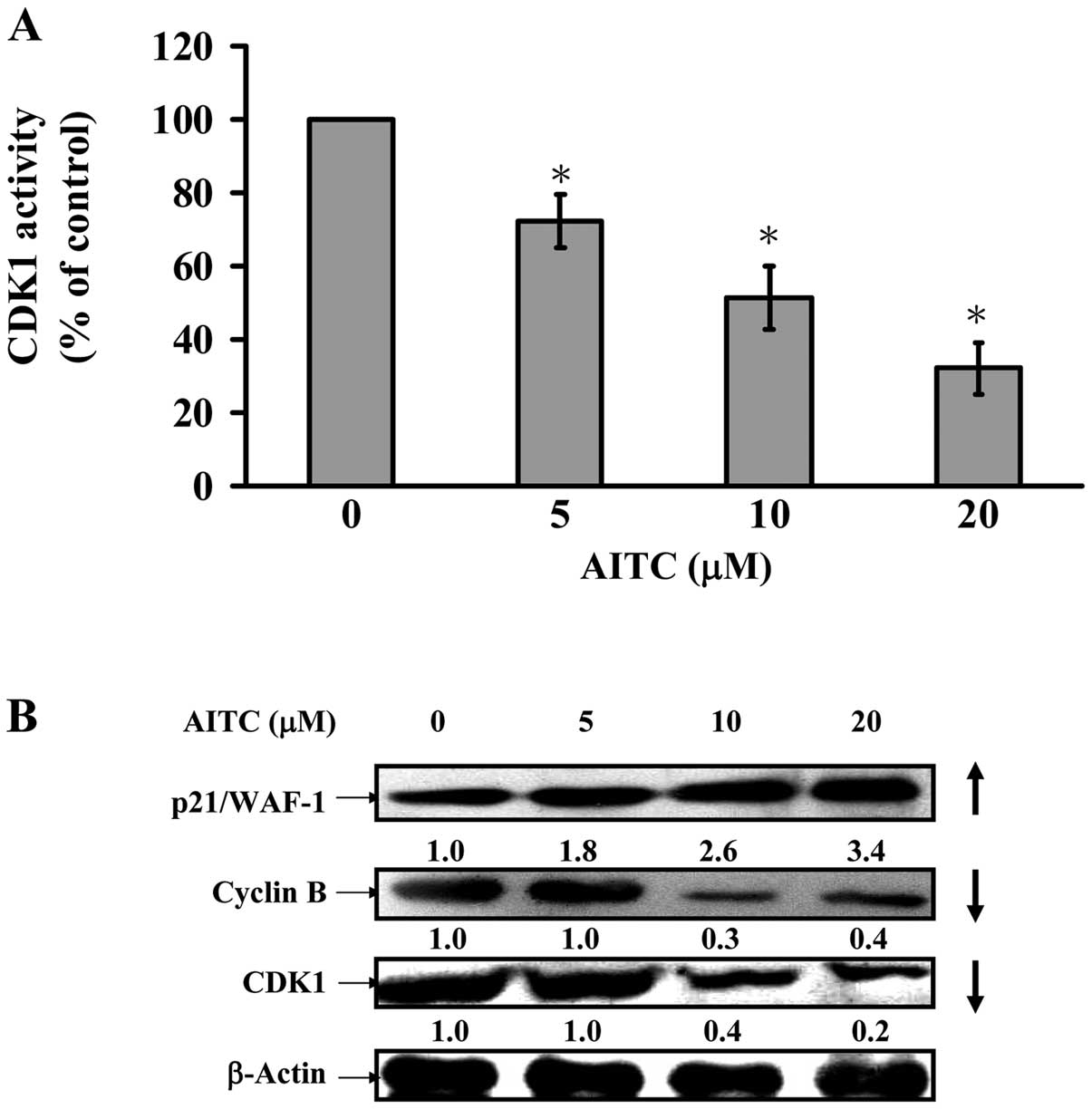
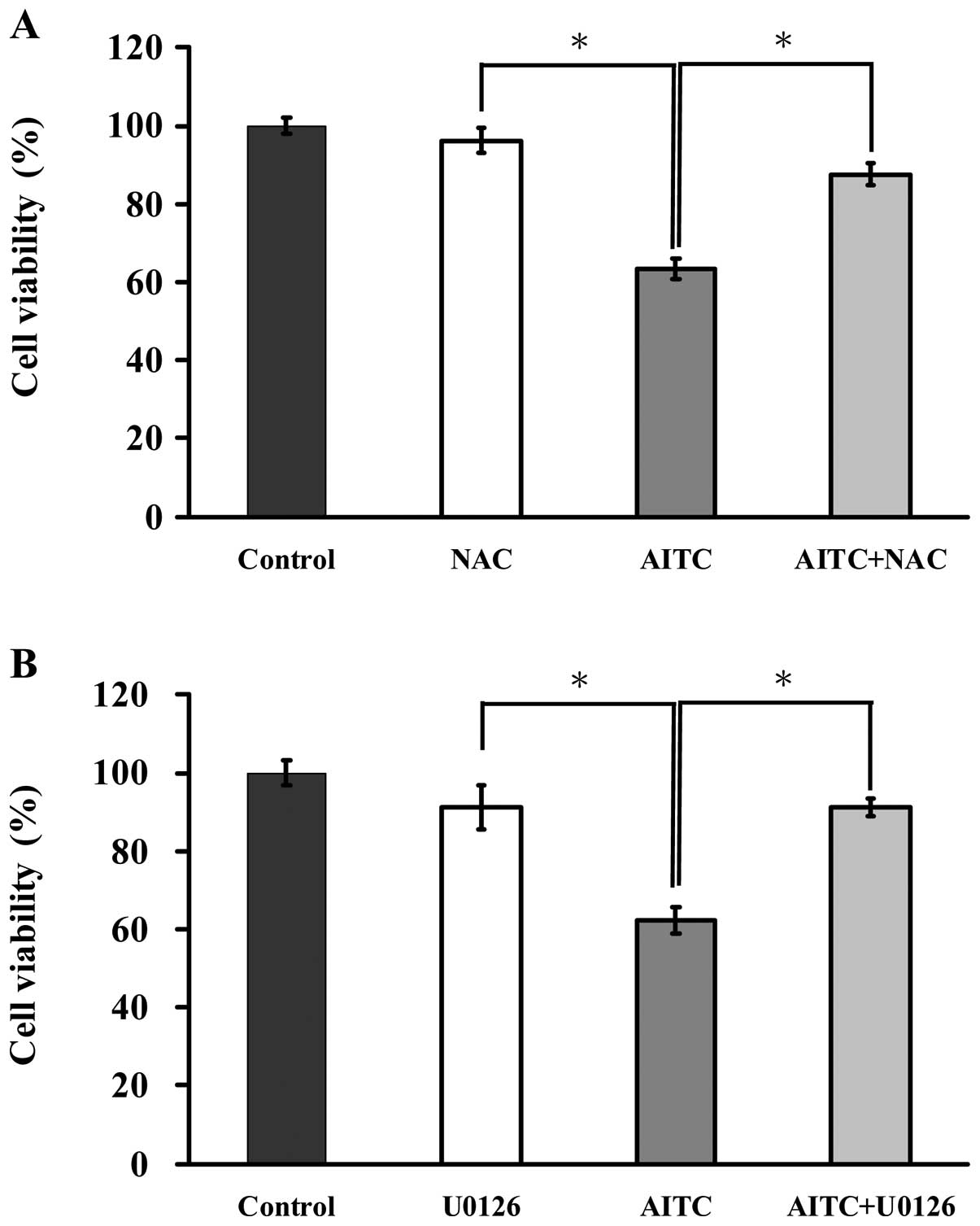
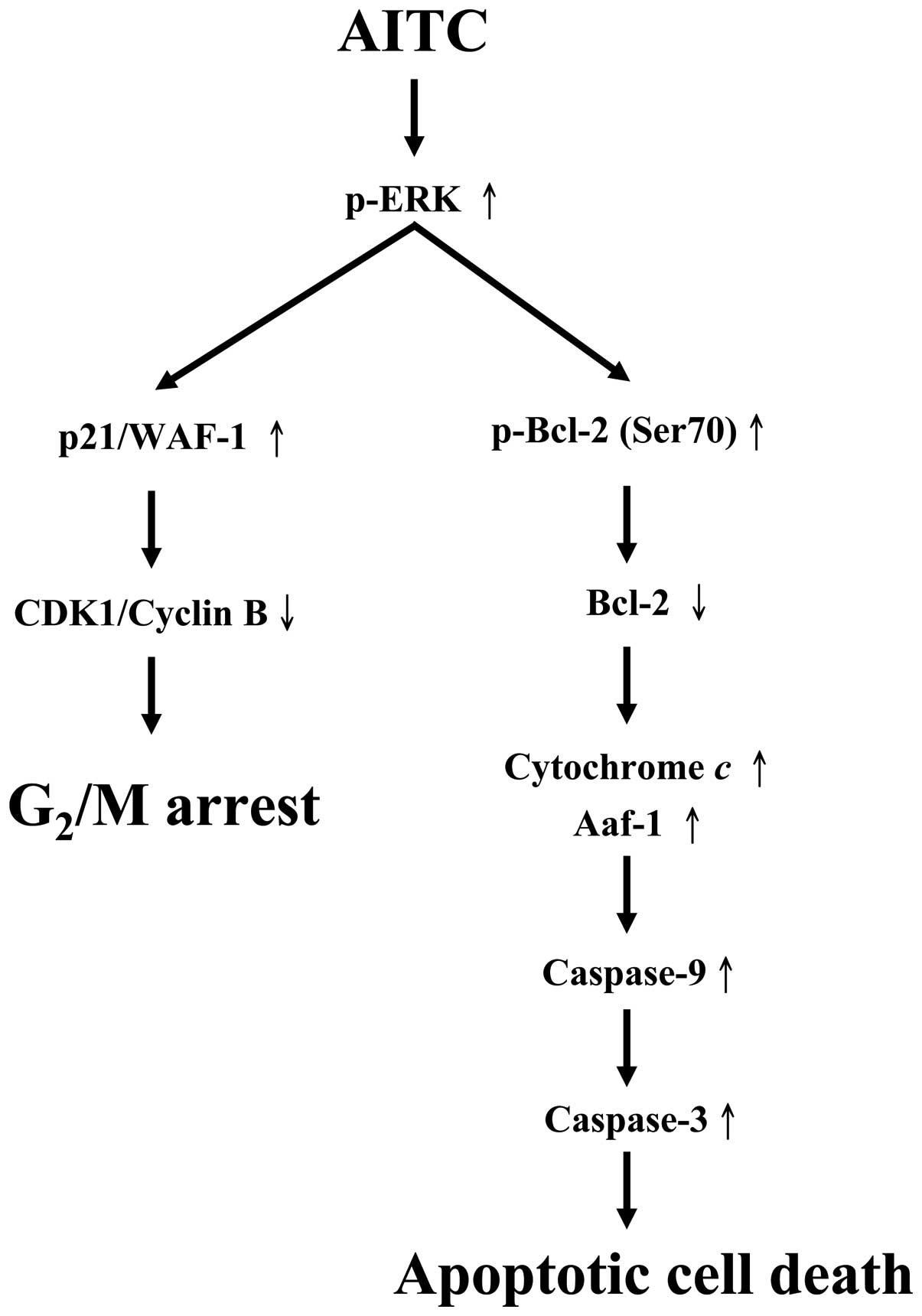
|
1.
|
Kushad MM, Brown AF, Kurilich AC, et al:
Variation of glucosinolates in vegetable crops of Brassica
oleracea. J Agric Food Chem. 47:1541–1548. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Rungapamestry V, Duncan AJ, Fuller Z and
Ratcliffe B: Changes in glucosinolate concentrations, myrosinase
activity, and production of metabolites of glucosinolates in
cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) cooked for
different durations. J Agric Food Chem. 54:7628–7634. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Uematsu Y, Hirata K, Suzuki K, Iida K,
Ueta T and Kamata K: Determination of isothiocyanates and related
compounds in mustard extract and horseradish extract used as
natural food additives. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 43:10–17.
2002.(In Japanese).
|
|
4.
|
Zhang Y: Allyl isothiocyanate as a cancer
chemopreventive phytochemical. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:127–135. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Negri R, Muntoni F and D’Amore R:
Antibiotic effect of the allyl isothiocyanate extracted from
various horticultural forms of the seeds of Raphanus Sativus
L. var. radicula pers towards various bacteria, including two
strains of tubercle bacillus avian type, Cow 18 and Cow 70. Note II
Rend Ist Sup Sanit. 14:186–193. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Wagner AE, Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Dose J,
Schultheiss G and Rimbach G: Anti-inflammatory potential of
allyl-isothiocyanate - role of Nrf2, NF-(kappa) B and microRNA-155.
J Cell Mol Med. 16:836–843. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Sellam A, Dongo A, Guillemette T, Hudhomme
P and Simoneau P: Transcriptional responses to exposure to the
brassicaceous defence metabolites camalexin and
allyl-isothiocyanate in the necrotrophic fungus Alternaria
brassicicola. Mol Plant Pathol. 8:195–208. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Srivastava SK, Xiao D, Lew KL, et al:
Allyl isothiocyanate, a constituent of cruciferous vegetables,
inhibits growth of PC-3 human prostate cancer xenografts in vivo.
Carcinogenesis. 24:1665–1670. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Smith TK, Lund EK, Parker ML, Clarke RG
and Johnson IT: Allyl-isothiocyanate causes mitotic block, loss of
cell adhesion and disrupted cytoskeletal structure in HT29 cells.
Carcinogenesis. 25:1409–1415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Smith T, Musk SR and Johnson IT: Allyl
isothiocyanate selectively kills undifferentiated HT29 cells in
vitro and suppresses aberrant crypt foci in the colonic mucosa of
rats. Biochem Soc Trans. 24:381S1996.
|
|
11.
|
Bhattacharya A, Li Y, Geng F, Munday R and
Zhang Y: The principal urinary metabolite of allyl isothiocyanate,
N-acetyl-S-(N-allylthiocarbamoyl)cysteine, inhibits the growth and
muscle invasion of bladder cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:394–398.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Bhattacharya A, Tang L, Li Y, et al:
Inhibition of bladder cancer development by allyl isothiocyanate.
Carcinogenesis. 31:281–286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Hasegawa T, Nishino H and Iwashima A:
Isothiocyanates inhibit cell cycle progression of HeLa cells at
G2/M phase. Anticancer Drugs. 4:273–279. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zhang Y, Tang L and Gonzalez V: Selected
isothiocyanates rapidly induce growth inhibition of cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 2:1045–1052. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Lau WS, Chen T and Wong YS: Allyl
isothiocyanate induces G2/M arrest in human colorectal
adenocarcinoma SW620 cells through downregulation of Cdc25B and
Cdc25C. Mol Med Rep. 3:1023–1030. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Chen NG, Chen KT, Lu CC, et al: Allyl
isothiocyanate triggers G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis
in human brain malignant glioma GBM 8401 cells through a
mitochondria-dependent pathway. Oncol Rep. 24:449–455.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Hwang ES and Lee HJ: Allyl isothiocyanate
and its N-acetylcysteine conjugate suppress metastasis via
inhibition of invasion, migration, and matrix
metalloproteinase-2/-9 activities in SK-Hep 1 human hepatoma cells.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 231:421–430. 2006.
|
|
18.
|
Rodrigues-Ferreira S, Abdelkarim M,
Dillenburg-Pilla P, et al: Angiotensin II facilitates breast cancer
cell migration and metastasis. PLoS One. 7:e356672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Ossovskaya V, Wang Y, Budoff A, et al:
Exploring molecular pathways of triple-negative breast cancer.
Genes Cancer. 2:870–879. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS and Ellis IO:
Basal-like breast cancer: a critical review. J Clin Oncol.
26:2568–2581. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Gucalp A and Traina TA: Triple-negative
breast cancer: adjuvant therapeutic options. Chemother Res Pract.
2011:6962082011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Gelmon K, Dent R, Mackey JR, Laing K,
McLeod D and Verma S: Targeting triple-negative breast cancer:
optimising therapeutic outcomes. Ann Oncol. Apr 19–2012, (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
24.
|
Li C, Zhao X, Toline EC, et al: Prevention
of carcinogenesis and inhibition of breast cancer tumor burden by
dietary stearate. Carcinogenesis. 32:1251–1258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ebert T, Kleine-Gunk B, Altwein JE, Miller
K and Mallmann P: Dietary prevention of carcinomas of the breast
and prostate: fundamental and practical aspects of the Nutritional
Cancer Prevention (NCP) program. Dtsch Med Wochenschr.
127:1392–1396. 2002.(In German).
|
|
26.
|
Chen KT, Hour MJ, Tsai SC, et al: The
novel synthesized
6-fluoro-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-(3-methoxyanilino)quinazoline (LJJ-10)
compound exhibits anti-metastatic effects in human osteosarcoma U-2
OS cells through targeting insulin-like growth factor-I receptor.
Int J Oncol. 39:611–619. 2011.
|
|
27.
|
Liao CL, Lai KC, Huang AC, et al: Gallic
acid inhibits migration and invasion in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS
cells through suppressing the matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9,
protein kinase B (PKB) and PKC signaling pathways. Food Chem
Toxicol. 50:1734–1740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Yu FS, Wu CC, Chen CT, et al: Diallyl
sulfide inhibits murine WEHI-3 leukemia cells in BALB/c mice in
vitro and in vivo. Hum Exp Toxicol. 28:785–790. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Tsou MF, Peng CT, Shih MC, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate inhibits murine WEHI-3 leukemia cells in vitro and
promotes phagocytosis in BALB/c mice in vivo. Leuk Res.
33:1505–1511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Huang AC, et al:
Chrysophanol induces necrosis through the production of ROS and
alteration of ATP levels in J5 human liver cancer cells. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 54:967–976. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, et al: Novel
quinazolinone MJ-29 triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress and
intrinsic apoptosis in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells and inhibits
leukemic mice. PLoS One. 7:e368312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Lin JP, Yang JS, Chang NW, et al: GADD153
mediates berberine-induced apoptosis in human cervical cancer Ca
ski cells. Anticancer Res. 27:3379–3386. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Lin YT, Yang JS, Lin HJ, et al: Baicalein
induces apoptosis in SCC-4 human tongue cancer cells via a
Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial pathway. In Vivo.
21:1053–1058. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Ying WZ and Sanders PW: Cytochrome c
mediates apoptosis in hypertensive nephrosclerosis in Dahl/Rapp
rats. Kidney Int. 59:662–672. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Yang JS, Hour MJ, Huang WW, Lin KL, Kuo SC
and Chung JG: MJ-29 inhibits tubulin polymerization, induces
mitotic arrest, and triggers apoptosis via cyclin-dependent kinase
1-mediated Bcl-2 phosphorylation in human leukemia U937 cells. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:477–488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Liu KC, Huang AC, Wu PP, et al: Gallic
acid suppresses the migration and invasion of PC-3 human prostate
cancer cells via inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9
signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 26:177–184. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Lan YH, Wu YC, Wu KW, et al: Death
receptor 5-mediated TNFR family signaling pathways modulate
γ-humulene-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer HT29 cells.
Oncol Rep. 25:419–424. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Wu SH, Hang LW, Yang JS, et al: Curcumin
induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H460
cells through ER stress and caspase cascade- and
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Anticancer Res. 30:2125–2133.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Lai WW, Yang JS, Lai KC, et al: Rhein
induced apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress,
caspase- and mitochondria-dependent pathways in SCC-4 human tongue
squamous cancer cells. In Vivo. 23:309–316. 2009.
|
|
40.
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Ma CY, et al:
Danthron, an anthraquinone derivative, induces DNA damage and
caspase cascades-mediated apoptosis in SNU-1 human gastric cancer
cells through mitochondrial permeability transition pores and
Bax-triggered pathways. Chem Res Toxicol. 24:20–29. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Huang WW, Chiu YJ, Fan MJ, et al:
Kaempferol induced apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondria-dependent pathway in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:1585–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Huang WW, Ko SW, Tsai HY, et al:
Cantharidin induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in
human colorectal cancer colo 205 cells through inhibition of CDK1
activity and caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Int J Oncol.
38:1067–1073. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Chou LC, Yang JS, Huang LJ, et al: The
synthesized 2-(2-fluorophenyl)-6,7-methylenedioxyquinolin-4-one
(CHM-1) promoted G2/M arrest through inhibition of CDK1 and induced
apoptosis through the mitochondrial-dependent pathway in CT-26
murine colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. J Gastroenterol.
44:1055–1063. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44.
|
Deng X, Kornblau SM, Ruvolo PP and May WS
Jr: Regulation of Bcl2 phosphorylation and potential significance
for leukemic cell chemoresistance. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr.
30–37. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Mai H, May WS, Gao F, Jin Z and Deng X: A
functional role for nicotine in Bcl2 phosphorylation and
suppression of apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 278:1886–1891. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Lavrik IN, Golks A and Krammer PH:
Caspases: pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin
Invest. 115:2665–2672. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Choi JA, Kim JY, Lee JY, et al: Induction
of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by
quercetin. Int J Oncol. 19:837–844. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Tang L and Zhang Y: Dietary
isothiocyanates inhibit the growth of human bladder carcinoma
cells. J Nutr. 134:2004–2010. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Xiao D, Srivastava SK, Lew KL, et al:
Allyl isothiocyanate, a constituent of cruciferous vegetables,
inhibits proliferation of human prostate cancer cells by causing
G2/M arrest and inducing apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 24:891–897.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Watanabe N, Okochi E, Mochizuki M,
Sugimura T and Ushijima T: The presence of single nucleotide
instability in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res.
61:7739–7742. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Salem SD, Abou-Tarboush FM, Saeed NM, et
al: Involvement of p53 in gemcitabine mediated cytotoxicity and
radiosensitivity in breast cancer cell lines. Gene. 498:300–307.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Lobrich M and Jeggo PA: The impact of a
negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer
induction. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:861–869. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Maeda T, Nagaoka Y, Kawai Y, et al:
Inhibitory effects of cancer cell proliferation by novel histone
deacetylase inhibitors involve p21/WAF1 induction and G2/M arrest.
Biol Pharm Bull. 28:849–853. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Wu L and Levine AJ: Differential
regulation of the p21/WAF-1 and mdm2 genes after high-dose UV
irradiation: p53-dependent and p53-independent regulation of the
mdm2 gene. Mol Med. 3:441–451. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Ciccarelli C, Marampon F, Scoglio A, et
al: p21WAF1 expression induced by MEK/ERK pathway activation or
inhibition correlates with growth arrest, myogenic differentiation
and onco-phenotype reversal in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Mol Cancer.
4:412005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56.
|
Lee B and Moon SK: Ras/ERK signaling
pathway mediates activation of the p21WAF1 gene promoter in
vascular smooth muscle cells by platelet-derived growth factor.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 443:113–119. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Lai E, Teodoro T and Volchuk A:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: signaling the unfolded protein
response. Physiology (Bethesda). 22:193–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Park HH: Structural features of
caspase-activating complexes. Int J Mol Sci. 13:4807–4818. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Geng F, Tang L, Li Y, et al: Allyl
isothiocyanate arrests cancer cells in mitosis, and mitotic arrest
in turn leads to apoptosis via Bcl-2 protein phosphorylation. J
Biol Chem. 286:32259–32267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Xu C, Shen G, Yuan X, et al: ERK and JNK
signaling pathways are involved in the regulation of activator
protein 1 and cell death elicited by three isothiocyanates in human
prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Carcinogenesis. 27:437–445. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|