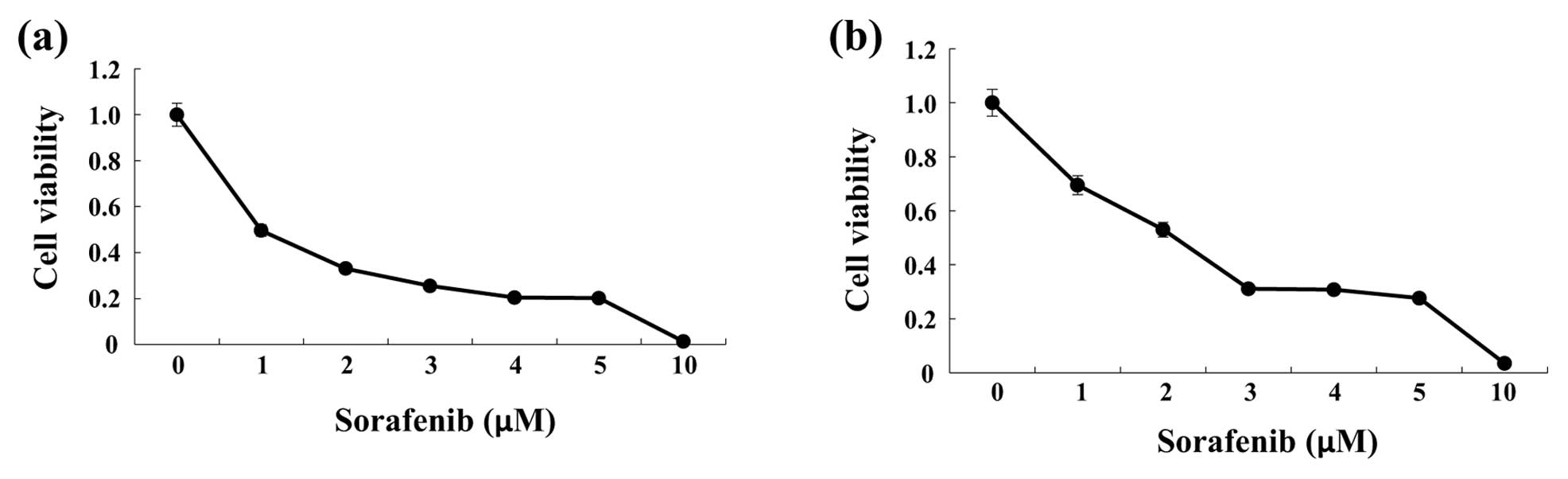
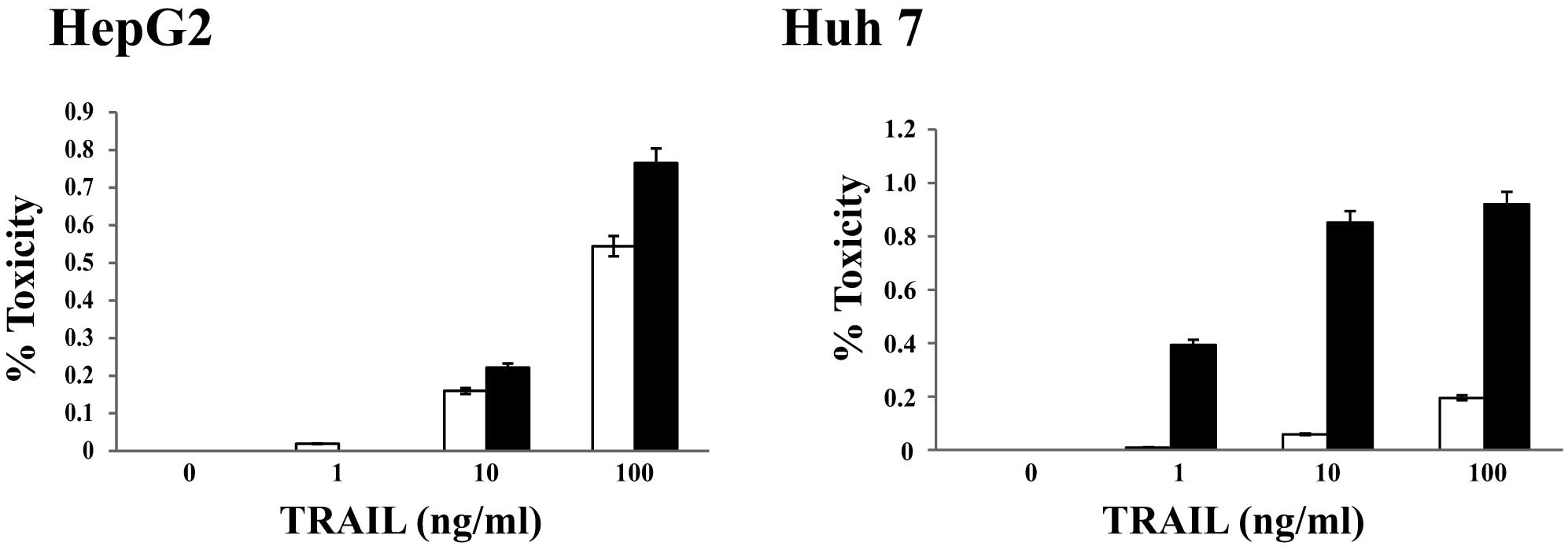
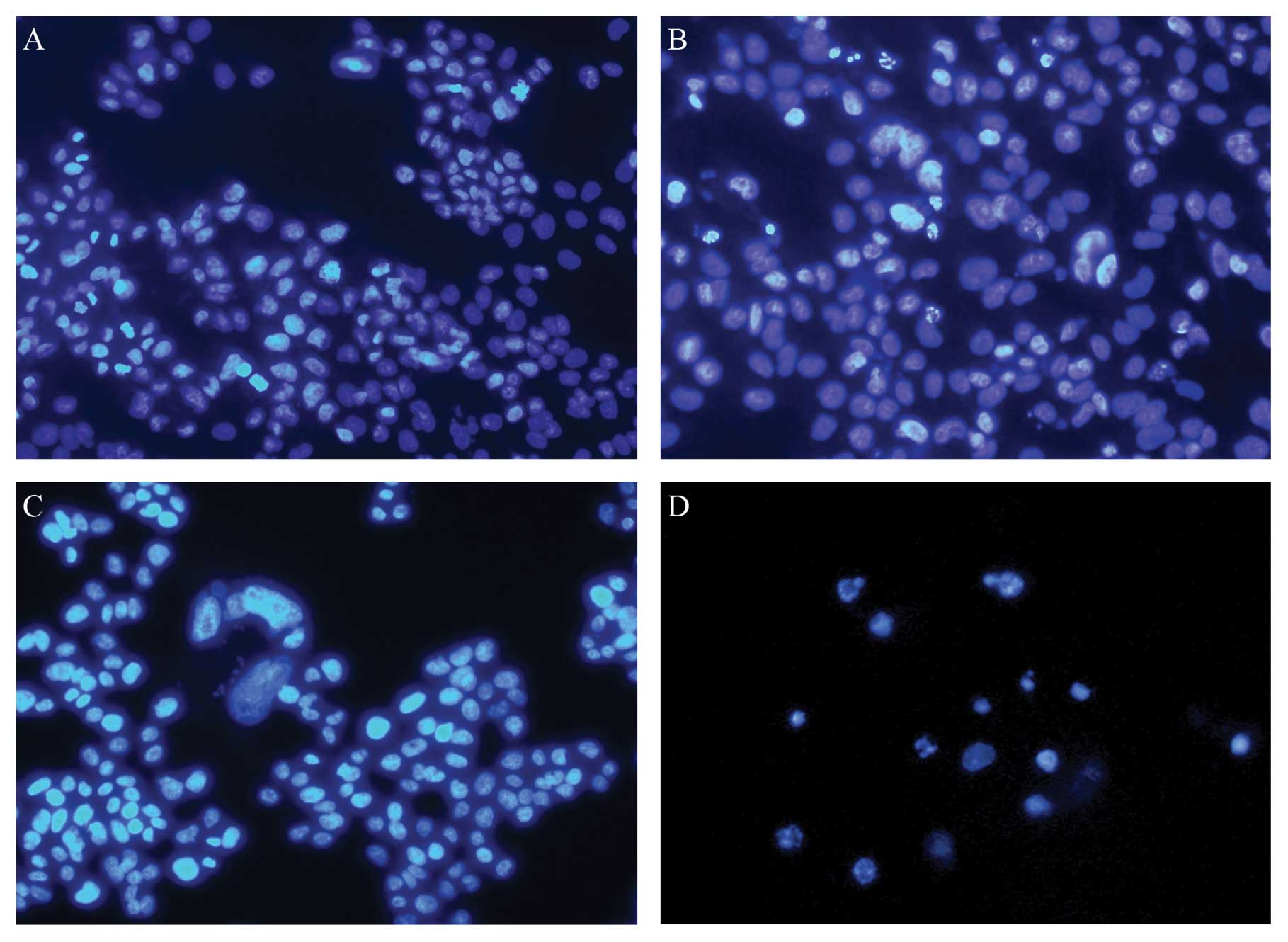
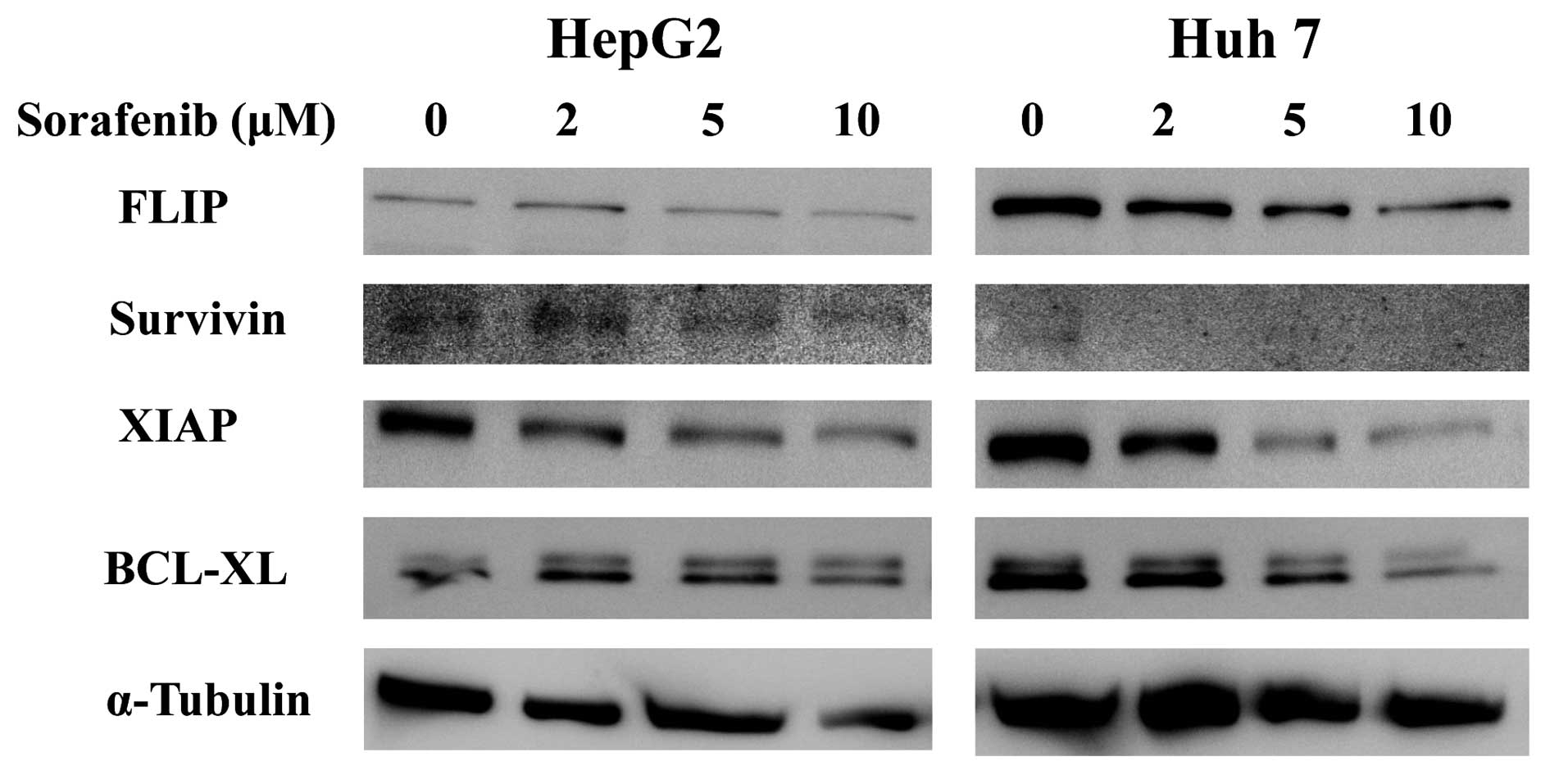
|
1.
|
Lo CM, Ngan H, Tso WK, et al: Randomized
controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 35:1164–1171.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Systematic review
of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma:
chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 37:429–442. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL and Wong J:
Intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular
carcinoma: long-term results of treatment and prognostic factors.
Ann Surg. 229:216–222. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Minagawa M, Makuuchi M, Takayama T and
Kokudo N: Selection criteria for repeat hepatectomy in patients
with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 238:703–710.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Takada Y and Uemoto S: Liver
transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: the Kyoto experience.
J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 17:527–532. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Thomas MB, Jaffe D, Choti MM, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: consensus recommendations of the National
Cancer Institute Clinical Trials Planning Meeting. J Clin Oncol.
28:3994–4005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al:
Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, et al: Efficacy
and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al: BAY
43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets
the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in
tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Chang YS, Adnane J, Trail PA, et al:
Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) inhibits tumor growth and vascularization
and induces tumor apoptosis and hypoxia in RCC xenograft models.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 59:561–574. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Hoffmann K, Glimm H, Radeleff B, et al:
Prospective, randomized, double-blind, multi-center, phase III
clinical study on transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined
with Sorafenib versus TACE plus placebo in patients with
hepatocellular cancer before liver transplantation - HeiLivCa
[ISRCTN24081794]. BMC Cancer. 8:3492008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Johnson P, Knox JJ, et al:
Doxorubicin plus sorafenib vs doxorubicin alone in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized trial. JAMA.
304:2154–2160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Hsu CH, Shen YC, Lin ZZ, et al: Phase II
study of combining sorafenib with metronomic tegafur/uracil for
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 53:126–131. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Pawlik TM, Reyes DK, Cosgrove D, Kamel IR,
Bhagat N and Geschwind JF: Phase II trial of sorafenib combined
with concurrent transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting
beads for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 29:3960–3967.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Cabrera R, Pannu DS, Caridi J, et al: The
combination of sorafenib with transarterial chemoembolisation for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 34:205–213. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Petrini I, Lencioni M, Ricasoli M, et al:
Phase II trial of sorafenib in combination with 5-fluorouracil
infusion in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 69:773–780. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yamanaka T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, et al:
Chemotherapeutic agents augment TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Hepatology. 32:482–490. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Shin EC, Seong YR, Kim CH, et al: Human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells resist to TRAIL-induced apoptosis,
and the resistance is abolished by cisplatin. Exp Mol Med.
34:114–122. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ricci MS, Kim SH, Ogi K, et al: Reduction
of TRAIL-induced Mcl-1 and cIAP2 by c-Myc or sorafenib sensitizes
resistant human cancer cells to TRAIL-induced death. Cancer Cell.
12:66–80. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Koehler BC, Urbanik T, Vick B, et al:
TRAIL-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells is
augmented by targeted therapies. World J Gastroenterol.
15:5924–5935. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Chen KF, Tai WT, Liu TH, et al: Sorafenib
overcomes TRAIL resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through the inhibition of STAT3. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5189–5199.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Ito T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, et al:
Survivin promotes cell proliferation in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 31:1080–1085. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Okano H, Shiraki K, Inoue H, et al:
Cellular FLICE/caspase-8-inhibitory protein as a principal
regulator of cell death and survival in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Lab Invest. 83:1033–1043. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Yamanaka Y, et al:
Overexpression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 12:705–708.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Yamaguchi Y, Shiraki K, Fuke H, et al:
Targeting of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein or survivin by
short interfering RNAs sensitize hepatoma cells to TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand- and chemotherapeutic agent-induced cell
death. Oncol Rep. 14:1311–1316. 2005.
|
|
26.
|
Kim JW, Lee JO, Han SW, et al: Clinical
outcomes of sorafenib treatment in patients with metastatic
hepatocellular carcinoma who had been previously treated with
fluoropyrimidine plus platinum-based chemotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol.
34:125–129. 2010.
|
|
27.
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Molecular targeted
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 48:1312–1327.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Koschny R, Walczak H and Ganten TM: The
promise of TRAIL - potential and risks of a novel anticancer
therapy. J Mol Med (Berl). 85:923–935. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ and Smyth MJ: The
TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 8:782–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Huang S and Sinicrope FA: Sorafenib
inhibits STAT3 activation to enhance TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in
human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:742–750. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Llobet D, Eritja N, Yeramian A, et al: The
multikinase inhibitor Sorafenib induces apoptosis and sensitises
endometrial cancer cells to TRAIL by different mechanisms. Eur J
Cancer. 46:836–850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33.
|
Heim M, Scharifi M, Zisowsky J, et al: The
Raf kinase inhibitor BAY 43-9006 reduces cellular uptake of
platinum compounds and cytotoxicity in human colorectal carcinoma
cell lines. Anticancer Drugs. 16:129–136. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Willert K and Jones KA: Wnt signaling: is
the party in the nucleus? Genes Dev. 20:1394–1404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Kaidi A, Williams AC and Paraskeva C:
Interaction between beta-catenin and HIF-1 promotes cellular
adaptation to hypoxia. Nat Cell Biol. 9:210–217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Lim JH, Chun YS and Park JW:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha obstructs a Wnt signaling pathway
by inhibiting the hARD1-mediated activation of beta-catenin. Cancer
Res. 68:5177–5184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Mazumdar J, O’Brien WT, Johnson RS, et al:
O2 regulates stem cells through Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nat
Cell Biol. 12:1007–1013. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Lehwald N, Tao GZ, Jang KY, Sorkin M,
Knoefel WT and Sylvester KG: Wnt-beta-catenin signaling protects
against hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice.
Gastroenterology. 141:707–718. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|