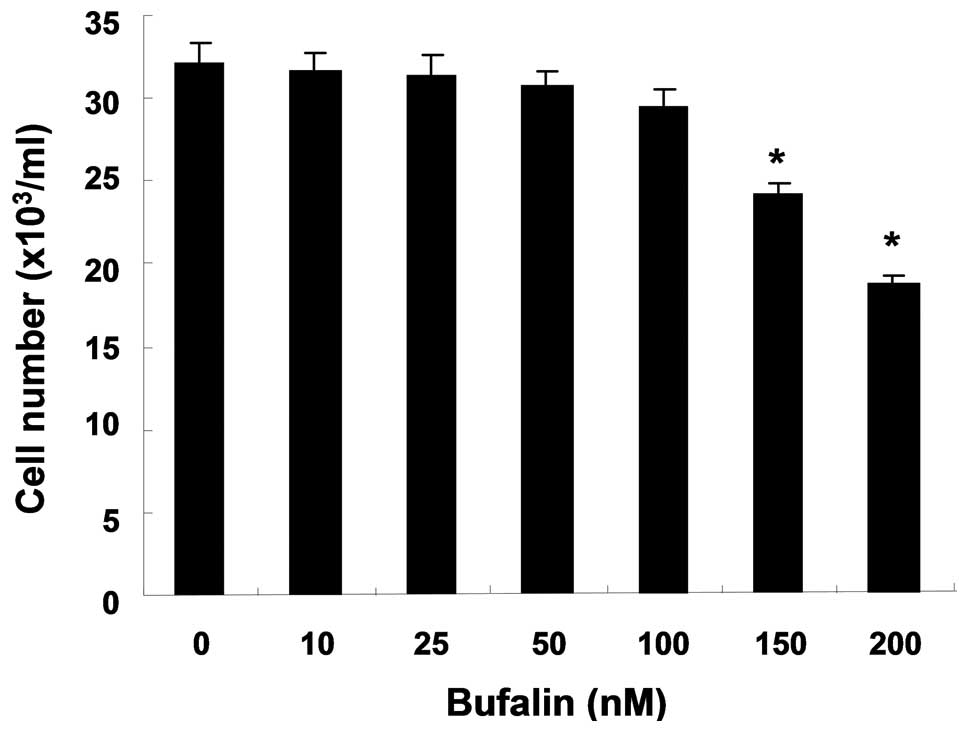
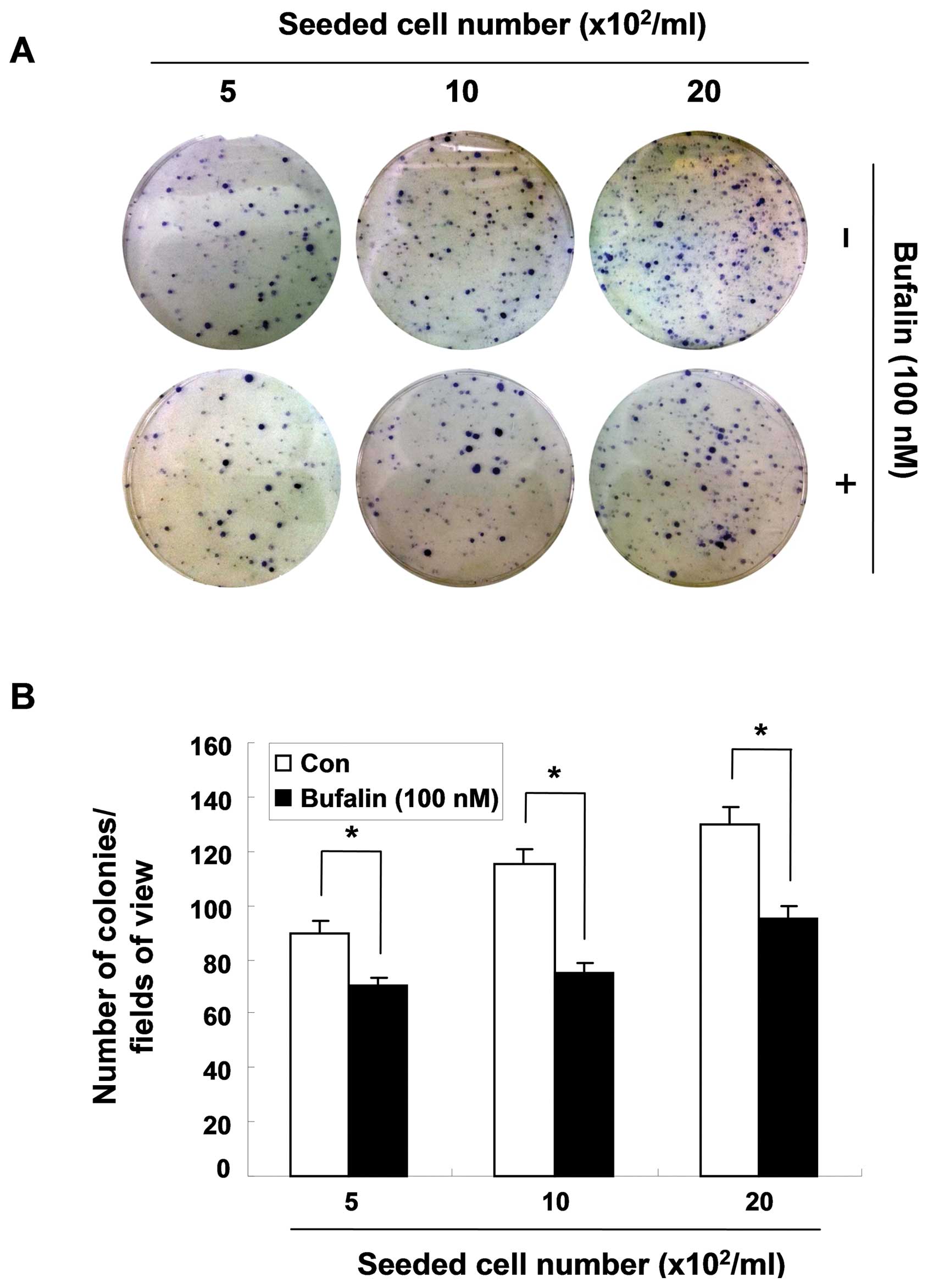
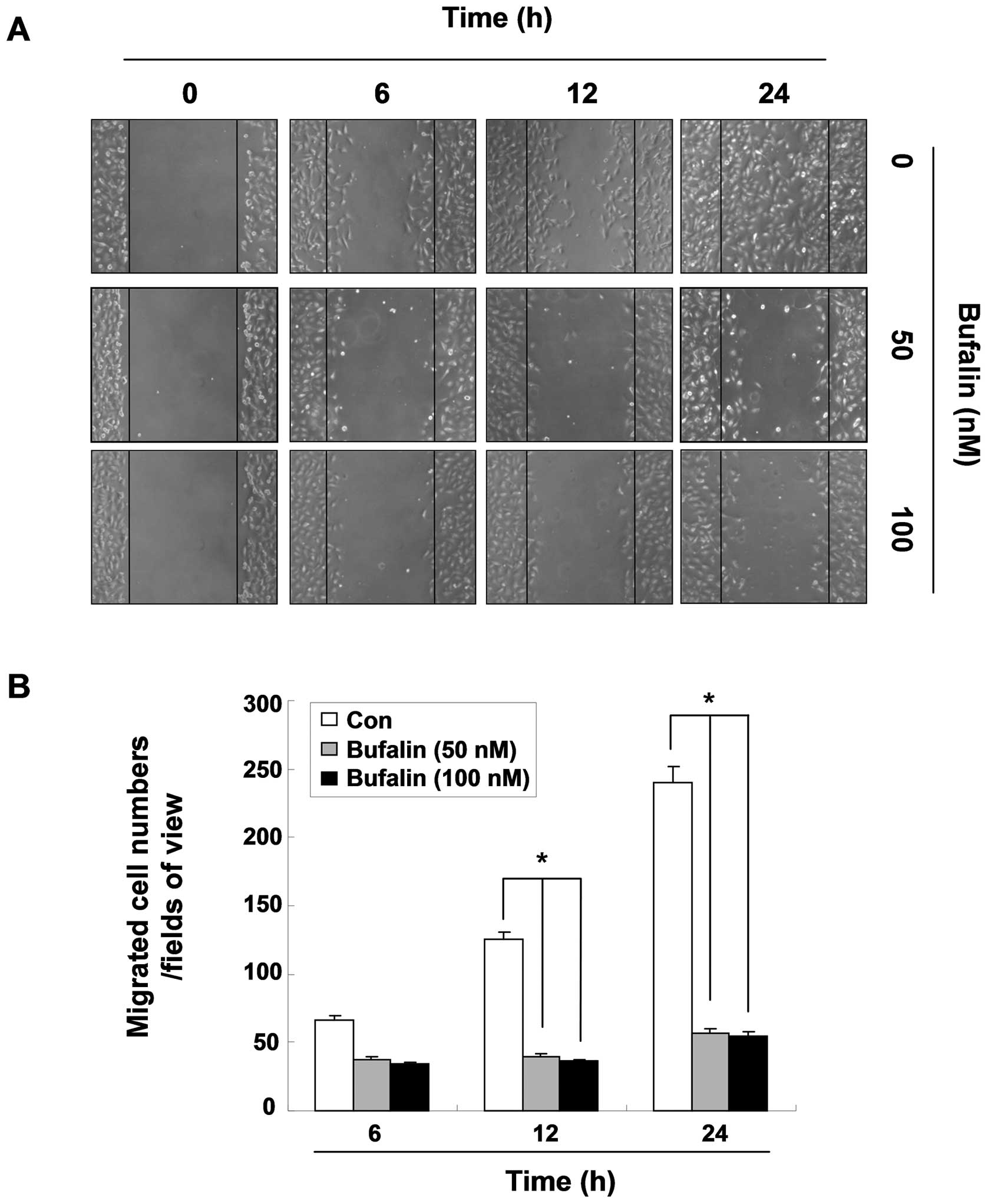
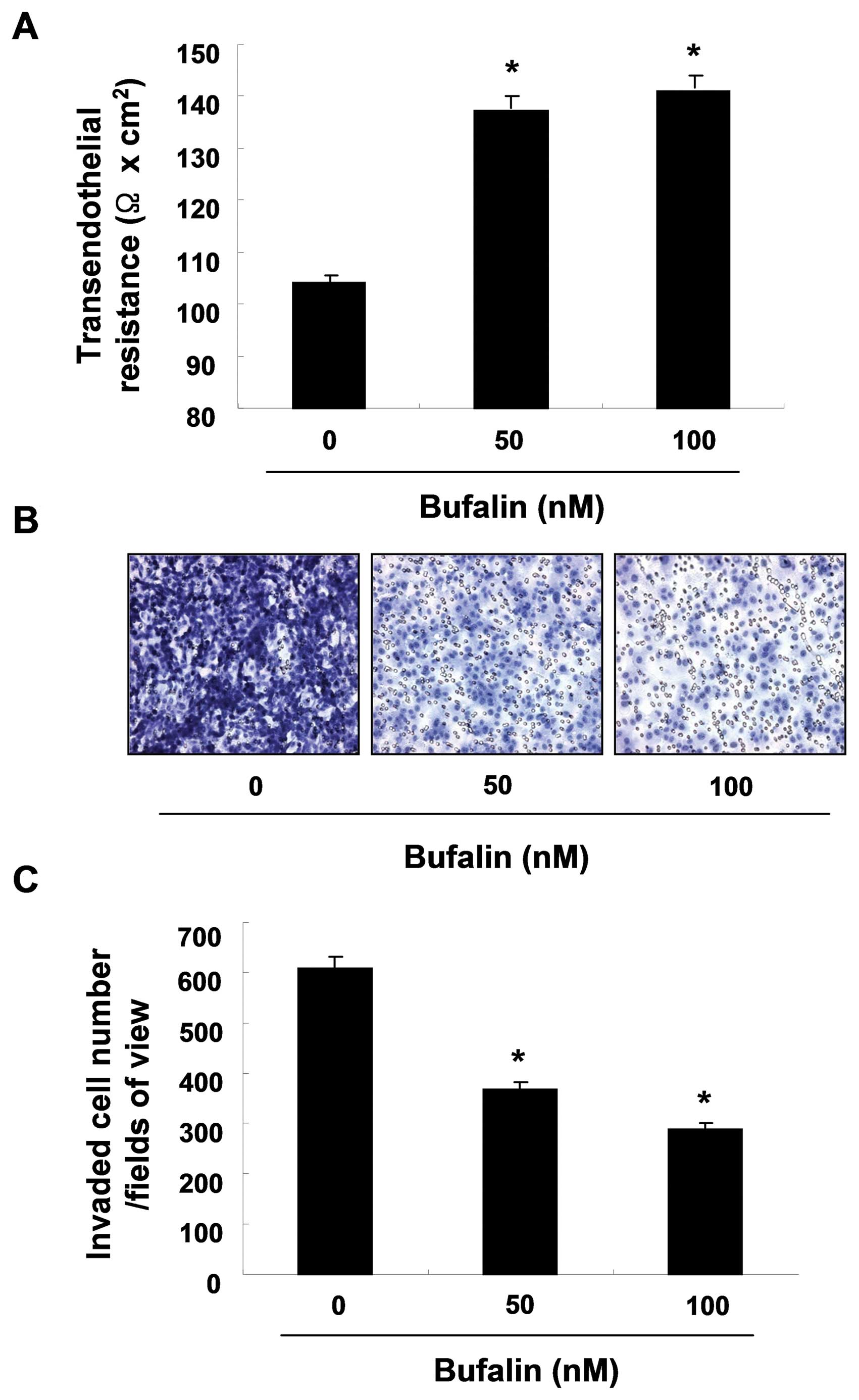
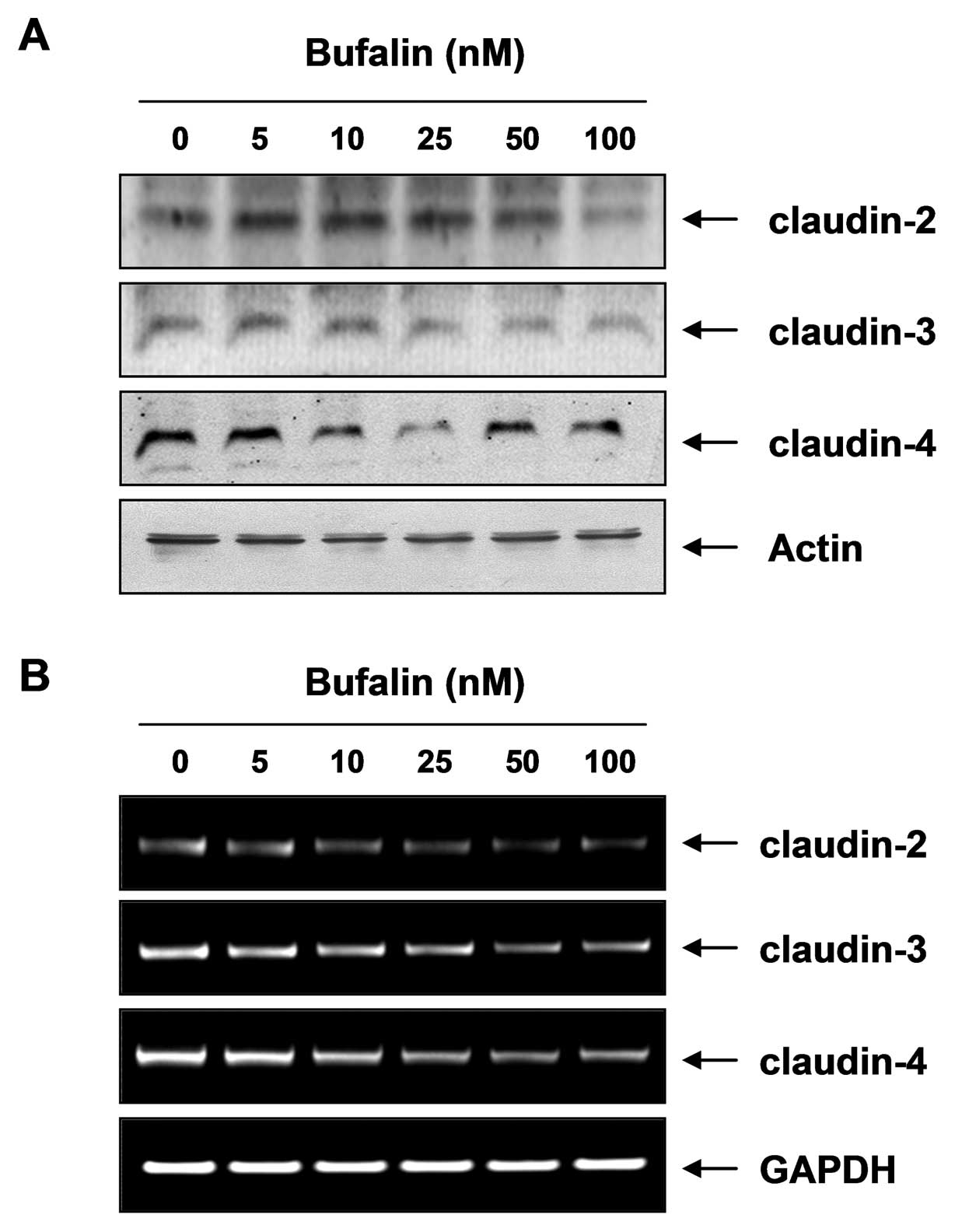
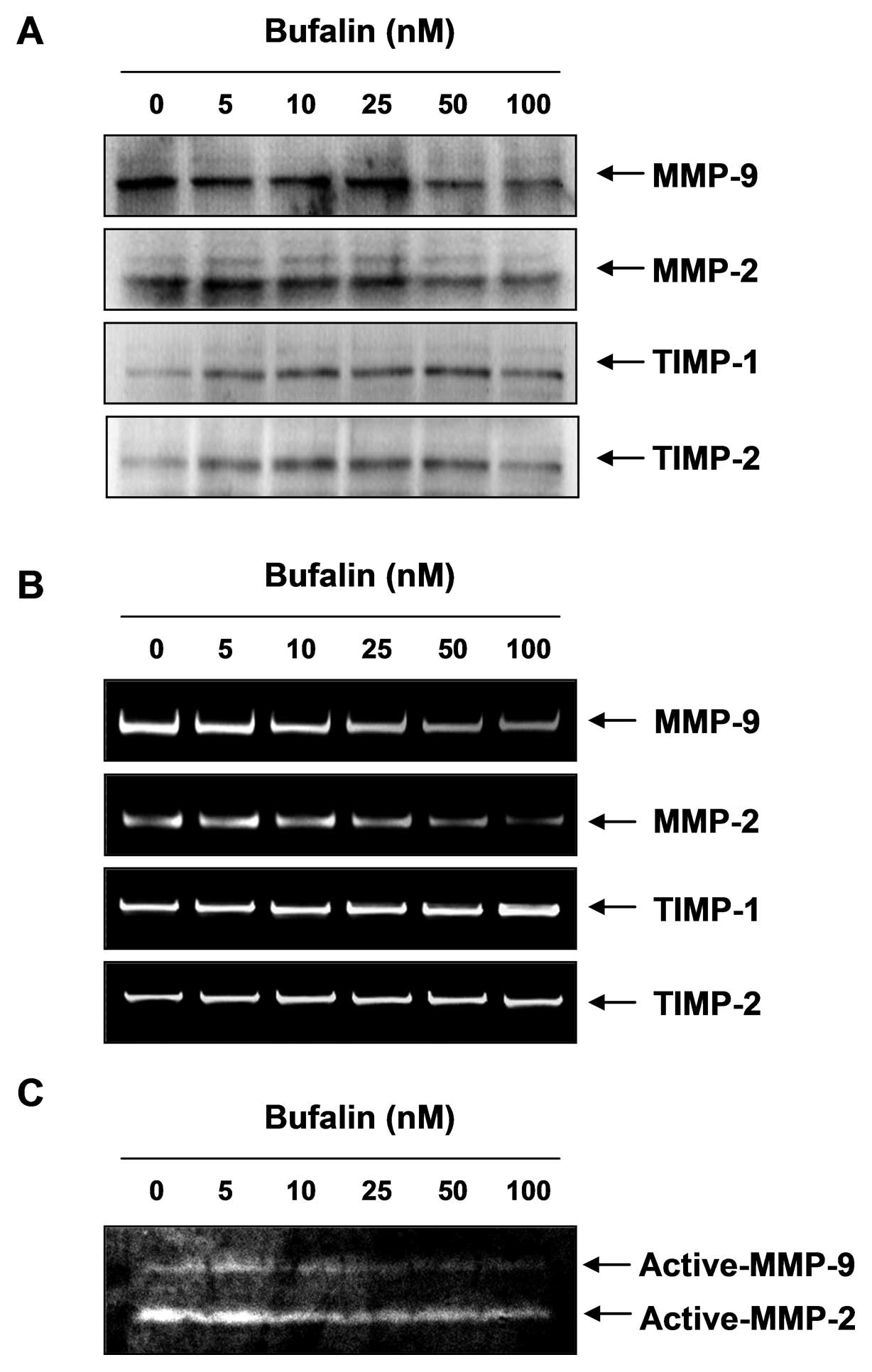
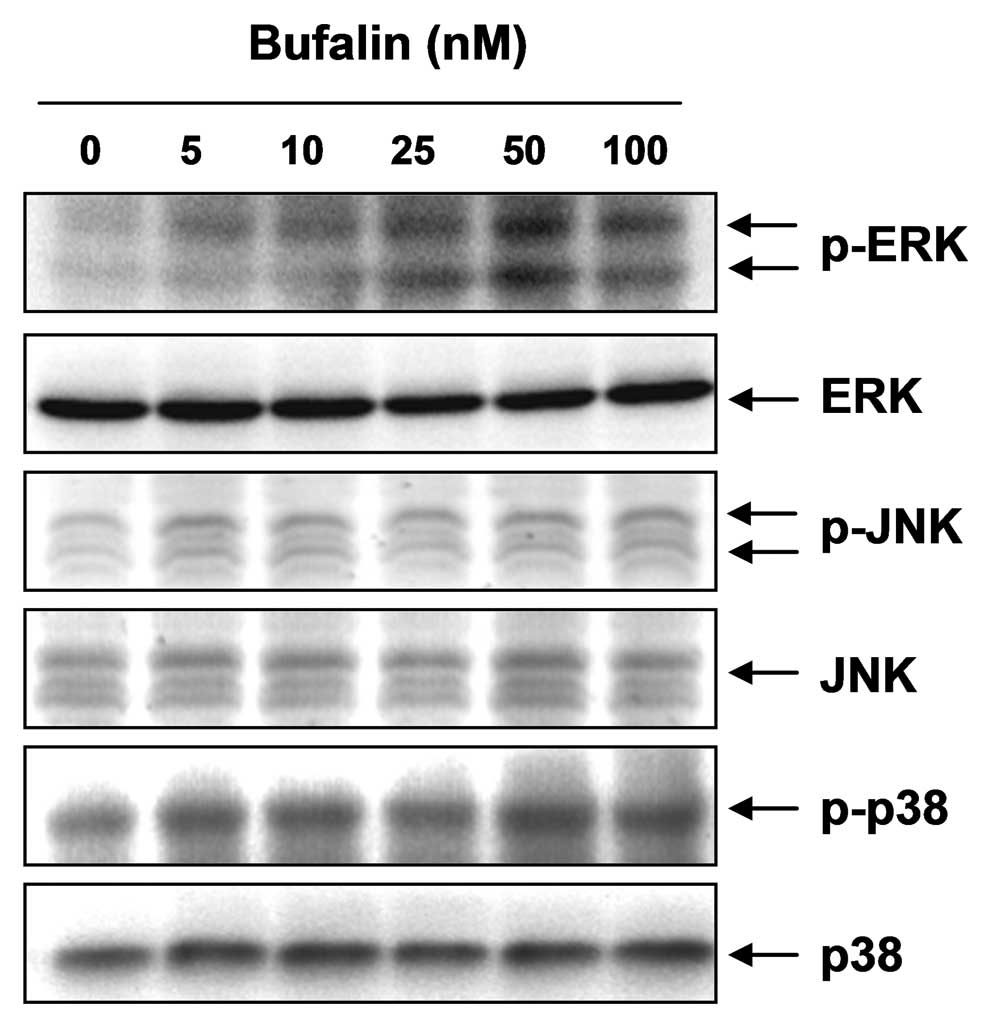
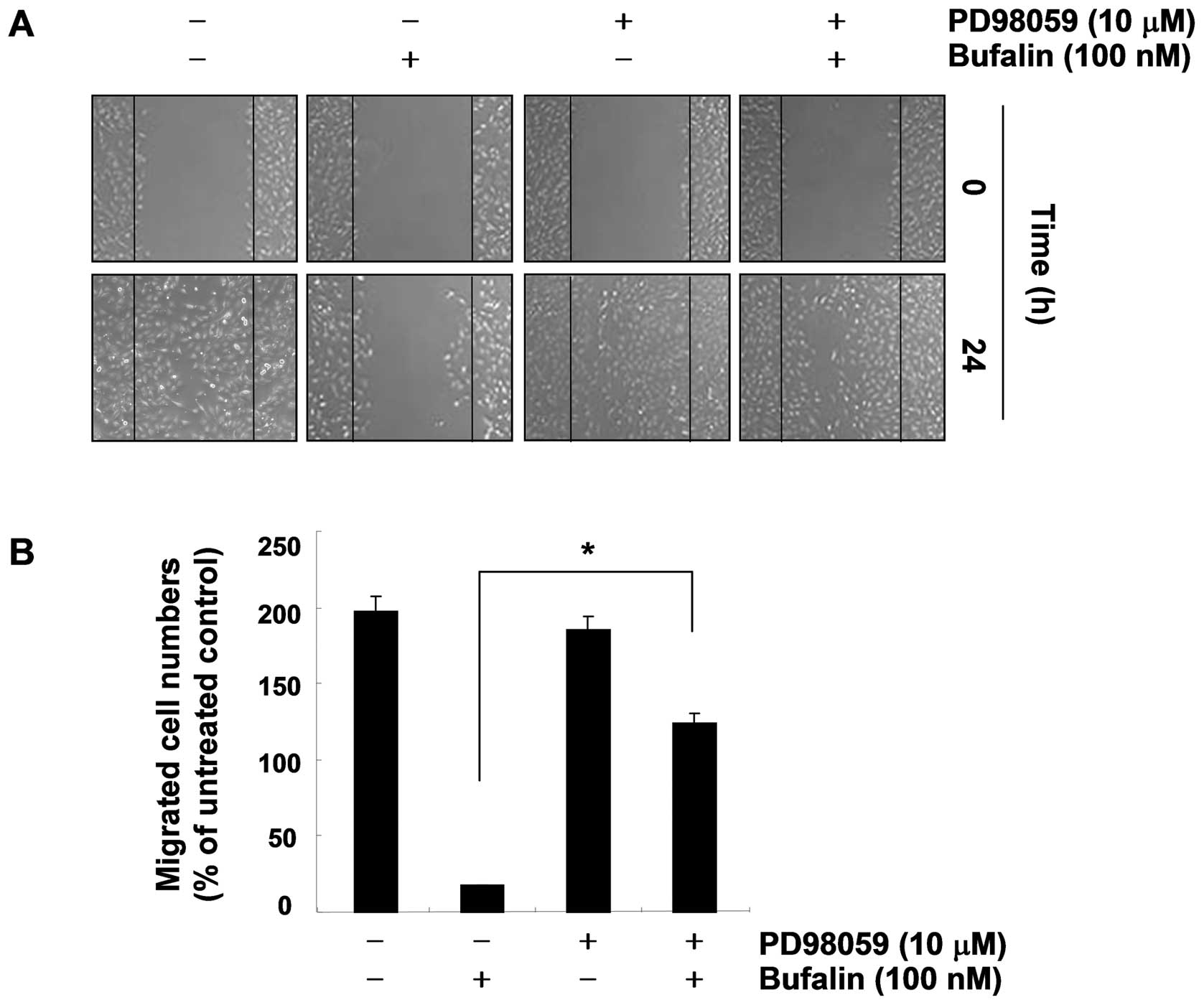
|
1.
|
Gunawardane RN, Sgroi DC, Wrobel CN, Koh
E, Daley GQ and Brugge JS: Novel role for PDEF in epithelial cell
migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 65:11572–11580. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Timpson P, Serrels A, Canel M, Frame MC,
Brunton VG and Anderson KI: Quantitative real-time imaging of
molecular dynamics during cancer cell invasion and metastasis in
vivo. Cell Adh Migr. 3:351–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Choi YH, Choi WY, Hong SH, Kim SO, Kim GY,
Lee WH and Yoo YH: Anti-invasive activity of sanguinarine through
modulation of tight junctions and matrix metalloproteinase
activities in MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells. Chem Biol
Interact. 179:185–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Boireau S, Buchert M, Samuel MS, Pannequin
J, Ryan JL, Choquet A, Chapuis H, Rebillard X, Avancès C, Ernst M,
Joubert D, Mottet N and Hollande F: DNA-methylation-dependent
alterations of claudin-4 expression in human bladder carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 28:246–258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Angelow S and Yu AS: Claudins and
paracellular transport: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens.
16:459–464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Morin PJ: Claudin proteins in human
cancer: promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer
Res. 65:9603–9606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Utech M, Brüwer M and Nusrat A: Tight
junctions and cell-cell interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
341:185–195. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Agarwal R, D’Souza T and Morin PJ:
Claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression in ovarian epithelial cells
enhances invasion and is associated with increased matrix
metalloproteinase-2 activity. Cancer Res. 65:7378–7385. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hewitt KJ, Agarwal R and Morin PJ: The
claudin gene family: expression in normal and neoplastic tissues.
BMC Cancer. 6:1862006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Morin PJ: Claudin proteins in ovarian
cancer. Dis Markers. 23:453–457. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Neesse A, Griesmann H, Gress TM and Michl
P: Claudin-4 as therapeutic target in cancer. Arch Biochem Biophys.
524:64–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Nakanishi K, Ogata S, Hiroi S, Tominaga S,
Aida S and Kawai T: Expression of occludin and claudins 1, 3, 4 and
7 in urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Am J Clin
Pathol. 130:43–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Törzsök P, Riesz P, Kenessey I, Székely E,
Somorácz A, Nyirády P, Romics I, Schaff Z, Lotz G and Kiss A:
Claudins and ki-67: potential markers to differentiate low- and
high-grade transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder. J
Histochem Cytochem. 59:1022–1030. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ouban A and Ahmed AA: Claudins in human
cancer: a review. Histol Histopathol. 25:83–90. 2010.
|
|
16.
|
Takahashi A, Kondoh M, Suzuki H and Yagi
K: Claudin as a target for drug development. Curr Med Chem.
18:1861–1865. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Martin MD and Matrisian LM: The other side
of MMPs: protective roles in tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 26:717–724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Pytliak M, Vargová V and Mechírová V:
Matrix metalloproteinases and their role in oncogenesis: a review.
Onkologie. 35:49–53. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Zhong WD, Han ZD, He HC, Bi XC, Dai QS,
Zhu G, Ye YK, Liang YX, Qin WJ, Zhang Z, Zeng GH and Chen ZN:
CD147, MMP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 protein expression as significant
prognostic factors in human prostate cancer. Oncology. 75:230–236.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Amălinei C, Căruntu ID, Giuşcă SE and
Bălan RA: Matrix metalloproteinases involvement in pathologic
conditions. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 51:215–228. 2010.
|
|
22.
|
Zhang L, Shi J, Feng J, Klocker H, Lee C
and Zhang J: Type IV collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-2 and
-9) in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 7:327–332.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Black PC and Dinney CP: Bladder cancer
angiogenesis and metastasis-translation from murine model to
clinical trial. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:623–634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Szarvas T, vom Dorp F, Ergün S and Rübben
H: Matrix metalloproteinases and their clinical relevance in
urinary bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 8:241–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Wojtowicz-Praga SM, Dickson RB and Hawkins
MJ: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Invest New Drugs.
15:61–75. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Yang LH, Zhang HZ, Zhang B, Chen F, Lai
ZH, Xu LF and Jin XQ: Studies on the chemical constituents from the
skin of Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor. Yao Xue Xue Bao.
27:679–683. 1992.(In Chinese).
|
|
27.
|
Zhang LS, Nakaya K, Yoshida T and Kuroiwa
Y: Bufalin as a potent inducer of differentiation of human myeloid
leukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 178:686–693. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Jing Y, Nakaya K and Han R:
Differentiation of promyelocytic leukemia cells HL-60 induced by
daidzein in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Res. 13:1049–1054.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Szabo E, Francis J and Birrer MJ:
Alterations in differentiation and apoptosis induced by bufalin in
cJun overexpressing U-937 cells. Int J Oncol. 12:403–409.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Takai N, Ueda T, Nishida M, Nasu K and
Narahara H: Bufalin induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Int J
Mol Med. 21:637–643. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Luan J, Duan H, Zhang F,
Yagasaki K and Zhang G: Effects of bufalin on the proliferation of
human lung cancer cells and its molecular mechanisms of action.
Cytotechnology. 62:573–583. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Takai N, Kira N, Ishii T, Yoshida T,
Nishida M, Nishida Y, Nasu K and Narahara H: Bufalin, a traditional
oriental medicine, induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:399–402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Hong SH and Choi YH: Bufalin induces
apoptosis through activation of both the intrinsic and extrinsic
pathways in human bladder cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:114–120.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Chueh FS, Chen YY, Huang AC, Ho HC, Liao
CL, Yang JS, Kuo CL and Chung JG: Bufalin-inhibited migration and
invasion in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells is carried out by
suppression of the matrix metalloproteinase-2, ERK, and JNK
signaling pathways. Environ Toxicol. Sep 16–2011.(E-pub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35.
|
Kim TH, Ku SK, Lee IC and Bae JS:
Anti-inflammatory functions of purpurogallin in LPS-activated human
endothelial cells. BMB Rep. 45:200–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Wang YG, Kim SJ, Baek JH, Lee HW, Jeong SY
and Chun KH: Galectin-3 increases the motility of mouse melanoma
cells by regulating matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression. Exp Mol
Med. 44:387–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Mori T, Wang X, Aoki T and Lo EH:
Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and attenuation of
edema via inhibition of ERK mitogen activated protein kinase in
traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 19:1411–1419. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Shin DY, Lu JN, Kim GY, Jung JM, Kang HS,
Lee WS and Choi YH: Anti-invasive activities of anthocyanins
through modulation of tight junctions and suppression of matrix
metalloproteinase activities in HCT-116 human colon carcinoma
cells. 25:567–572. 2011.
|
|
39.
|
Chen F, Hori T, Ohashi N, Baine AM, Eckman
CB and Nguyen JH: Occludin is regulated by epidermal growth factor
receptor activation in brain endothelial cells and brains of mice
with acute liver failure. Hepatology. 53:1294–1305. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Yin JQ, Shen JN, Su WW, Wang J, Huang G,
Jin S, Guo QC, Zou CY, Li HM and Li FB: Bufalin induces apoptosis
in human osteosarcoma U-2OS and U-2OS methotrexate300-resistant
cell lines. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:712–720. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Dong Y, Yin S, Li J, Jiang C, Ye M and Hu
H: Bufadienolide compounds sensitize human breast cancer cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis via inhibition of STAT3/Mcl-1 pathway.
Apoptosis. 16:394–403. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Qi F, Li A, Inagaki Y, Kokudo N, Tamura S,
Nakata M and Tang W: Antitumor activity of extracts and compounds
from the skin of the toad Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:342–349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Myal Y, Leygue E and Blanchard AA: Claudin
1 in breast tumorigenesis: revelation of a possible novel ‘claudin
high’ subset of breast cancers. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:9568972010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Newby AC: Matrix metalloproteinases
regulate migration, proliferation, and death of vascular smooth
muscle cells by degrading matrix and non-matrix substrates.
Cardiovasc Res. 69:614–624. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45.
|
Visse R and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases:
structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 92:827–839. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|