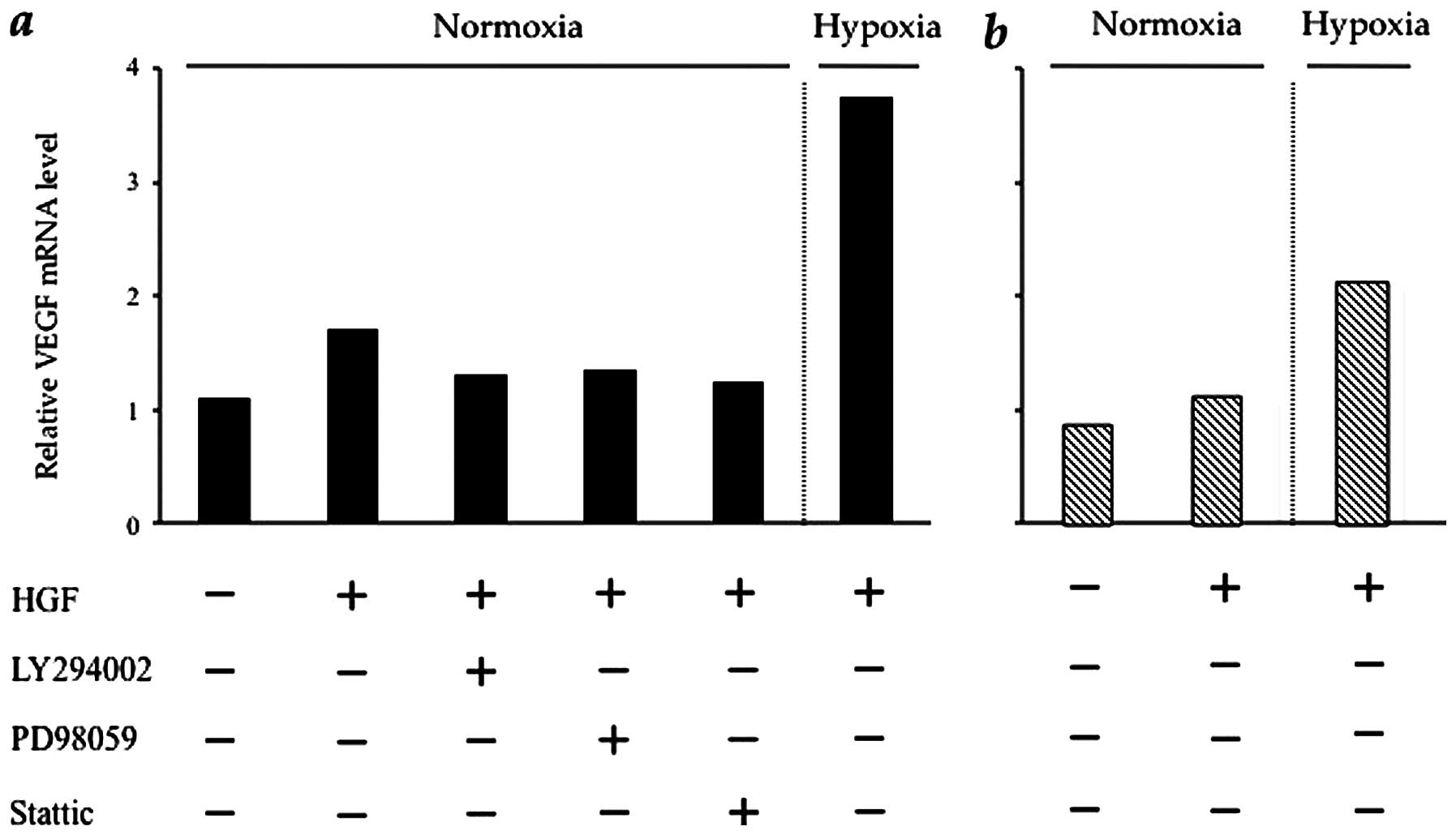
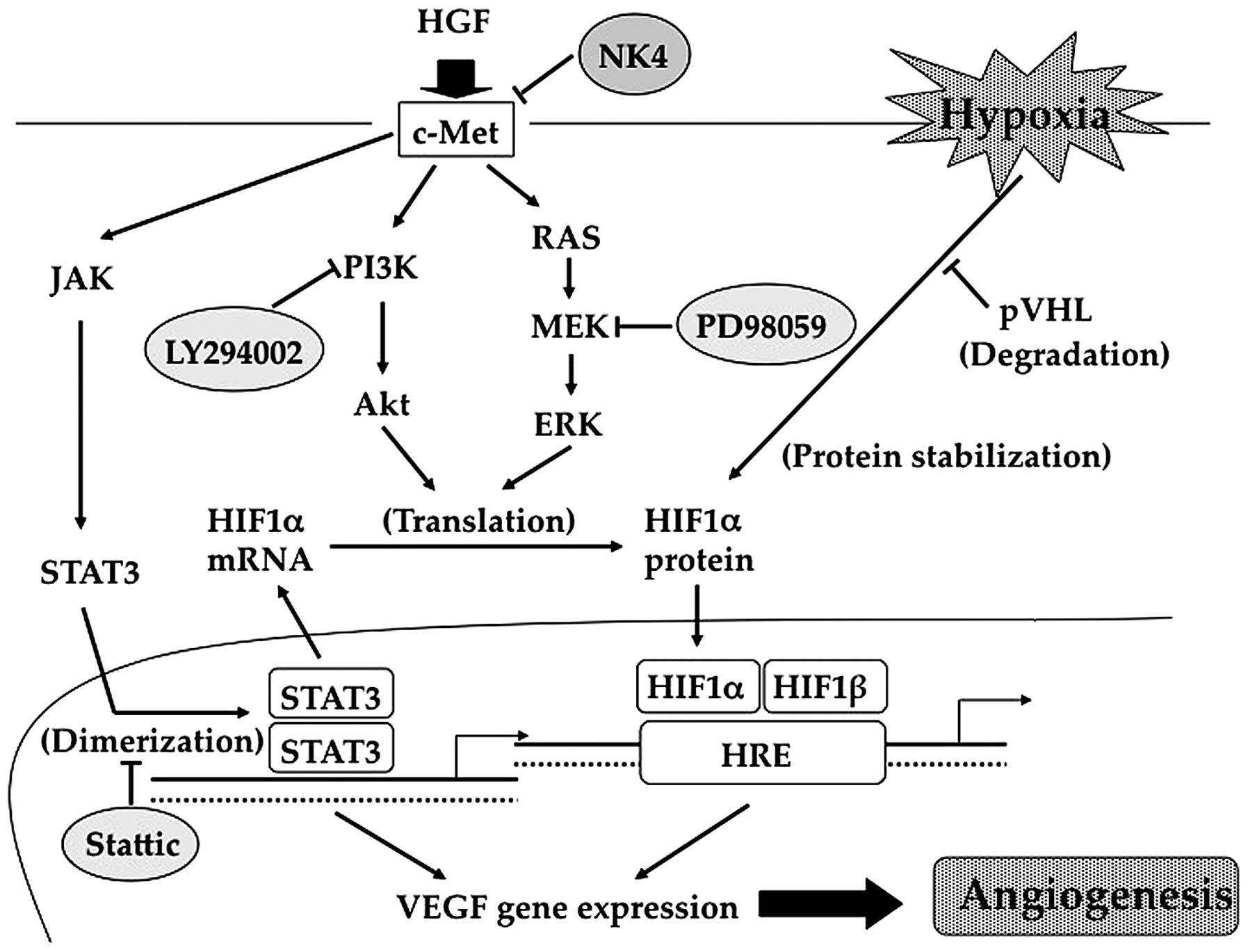
|
1.
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D and Keshet E:
Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate
hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 359:843–845. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Liao D and Johnson RS: Hypoxia: a key
regulator of angiogenesis in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:281–290. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Trusolino L and Comoglio PM:
Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: cell signalling for
invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:289–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M, et al:
Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor.
Nature. 342:440–443. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Jiang WG and Hiscox S: Hepatocyte growth
factor/scatter factor, a cytokine playing multiple and converse
roles. Histol Histopathol. 12:537–555. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Matsumoto K and Nakamura T: Emerging
multipotent aspects of hepatocyte growth factor. J Biochem.
119:591–600. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Bussolino F, Di Renzo MF, Ziche M, et al:
Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which
stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol.
119:629–641. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, et al:
Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the
c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 251:802–804. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E and
Vande Woude GF: Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:915–925. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Comoglio PM, Giordano S and Trusolino L:
Drug development of MET inhibitors: targeting oncogene addiction
and expedience. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:504–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Maulik G, Shrikhande A, Kijima T, Ma PC,
Morrison PT and Salgia R: Role of the hepatocyte growth factor
receptor, c-Met, in oncogenesis and potential for therapeutic
inhibition. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:41–59. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Di Renzo MF, Olivero M, Giacomini A, et
al: Overexpression and amplification of the met/HGF receptor gene
during the progression of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
1:147–154. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Ghoussoub RA, Dillon DA, D’Aquila T, Rimm
EB, Fearon ER and Rimm DL: Expression of c-met is a strong
independent prognostic factor in breast carcinoma. Cancer.
82:1513–1520. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Miller CT, Lin L, Casper AM, et al:
Genomic amplification of MET with boundaries within fragile site
FRA7G and upregulation of MET pathways in esophageal
adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 25:409–418. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ponzetto C, Bardelli A, Maina F, et al: A
novel recognition motif for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding
mediates its association with the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter
factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 13:4600–4608. 1993.
|
|
17.
|
Xiao GH, Jeffers M, Bellacosa A, et al:
Anti-apoptotic signaling by hepatocyte growth factor/Met via the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:247–252. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Boccaccio C, Andò M, Tamagnone L, et al:
Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor HGF depends on the
STAT pathway. Nature. 391:285–288. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Gerritsen ME, Tomlinson JE, Zlot C, Ziman
M and Hwang S: Using gene expression profiling to identify the
molecular basis of the synergistic actions of hepatocyte growth
factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in human endothelial
cells. Br J Pharmacol. 140:595–610. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Dong G, Chen Z, Li ZY, Yeh NT, Bancroft CC
and Van Waes C: Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced
activation of MEK and PI3K signal pathways contributes to
expression of proangiogenic cytokines interleukin-8 and vascular
endothelial growth factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 61:5911–5918. 2001.
|
|
21.
|
Rosen EM, Goldberg ID, Kacinski BM,
Buckholz T and Vinter DW: Smooth muscle releases an epithelial cell
scatter factor which binds to heparin. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol.
25:163–173. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Stoker M, Gherardi E, Perryman M and Gray
J: Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial
cell mobility. Nature. 327:239–242. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
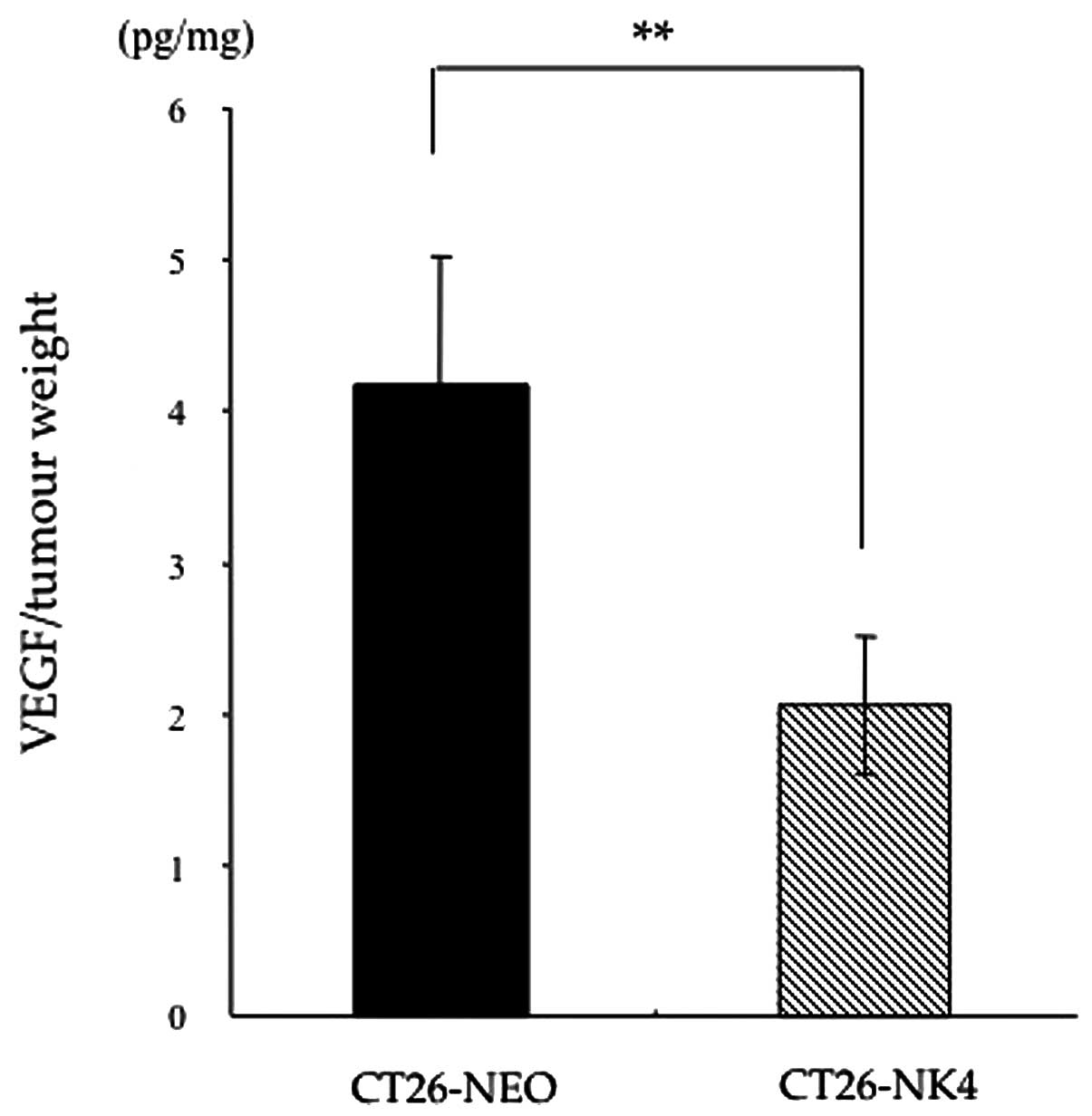
Kubota T, Fujiwara H, Amaike H, et al:
Reduced HGF expression in subcutaneous CT26 tumor genetically
modified to secrete NK4 and its possible relation with antitumor
effects. Cancer Sci. 95:321–327. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Kuba K, Matsumoto K, Date K, Shimura H,
Tanaka M and Nakamura T: HGF/NK4, a four-kringle antagonist of
hepatocyte growth factor, is an angiogenesis inhibitor that
suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Cancer Res.
60:6737–6743. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Date K, Matsumoto K, Shimura H, Tanaka M
and Nakamura T: HGF/NK4 is a specific antagonist for pleiotrophic
actions of hepatocyte growth factor. FEBS Lett. 420:1–6. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Workman P, Aboagye EO, Balkwill F, et al:
Committee of the National Cancer Research Institute: Guidelines for
the welfare and use of animals in cancer research. Br J Cancer.
102:1555–1577. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Furge KA, Zhang YW and Vande Woude GF: Met
receptor tyrosine kinase: enhanced signaling through adapter
proteins. Oncogene. 19:5582–5589. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kubota T, Taiyoh H, Matsumura A, et al:
NK4, an HGF antagonist, prevents hematogenous pulmonary metastasis
by inhibiting adhesion of CT26 cells to endothelial cells. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 26:447–456. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Brown LF, Berse B, Jackman RW, et al:
Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial
growth factor) and its receptors in adenocarcinomas of the
gastrointestinal tract. Cancer Res. 53:4727–4735. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Tomioka D, Maehara N, Kuba K, et al:
Inhibition of growth, invasion, and metastasis of human pancreatic
carcinoma cells by NK4 in an orthotopic mouse model. Cancer Res.
61:7518–7524. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Saimura M, Nagai E, Mizumoto K, et al:
Tumor suppression through angiogenesis inhibition by SUIT-2
pancreatic cancer cells genetically engineered to secrete NK4. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:3243–3249. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Van Belle E, Witzenbichler B, Chen D, et
al: Potentiated angiogenic effect of scatter factor/hepatocyte
growth factor via induction of vascular endothelial growth factor:
the case for paracrine amplification of angiogenesis. Circulation.
97:381–390. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Xin X, Yang S, Ingle G, et al: Hepatocyte
growth factor enhances vascular endothelial growth factor-induced
angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Am J Pathol. 158:1111–1120.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Sulpice E, Ding S, Muscatelli-Groux B, et
al: Cross-talk between the VEGF-A and HGF signalling pathways in
endothelial cells. Biol Cell. 101:525–539. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Vaupel P: The role of hypoxia-induced
factors in tumor progression. Oncologist. 9(Suppl 5): 10–17. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Fukuda R, Hirota K, Fan F, Jung YD, Ellis
LM and Semenza GL: Insulin-like growth factor 1 induces
hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated vascular endothelial growth
factor expression, which is dependent on MAP kinase and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in colon cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 277:38205–38211. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37.
|
Burroughs KD, Oh J, Barrett JC and
DiAugustine RP: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mek1/2 are
necessary for insulin-like growth factor-I-induced vascular
endothelial growth factor synthesis in prostate epithelial cells: a
role for hypoxia-inducible factor-1? Mol Cancer Res. 1:312–322.
2003.
|
|
38.
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, et al:
Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 21:2000–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, et al:
Interleukin-6 promotes cervical tumor growth by VEGF-dependent
angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. Oncogene. 22:1517–1527. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Niu G, Briggs J, Deng J, et al: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha RNA expression in both tumor cells
and tumor-associated myeloid cells. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1099–1105.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Jung JE, Kim HS, Lee CS, et al: STAT3
inhibits the degradation of HIF-1alpha by pVHL-mediated
ubiquitination. Exp Mol Med. 40:479–485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Xu Q, Briggs J, Park S, et al: Targeting
Stat3 blocks both HIF-1 and VEGF expression induced by multiple
oncogenic growth signaling pathways. Oncogene. 24:5552–5560. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|