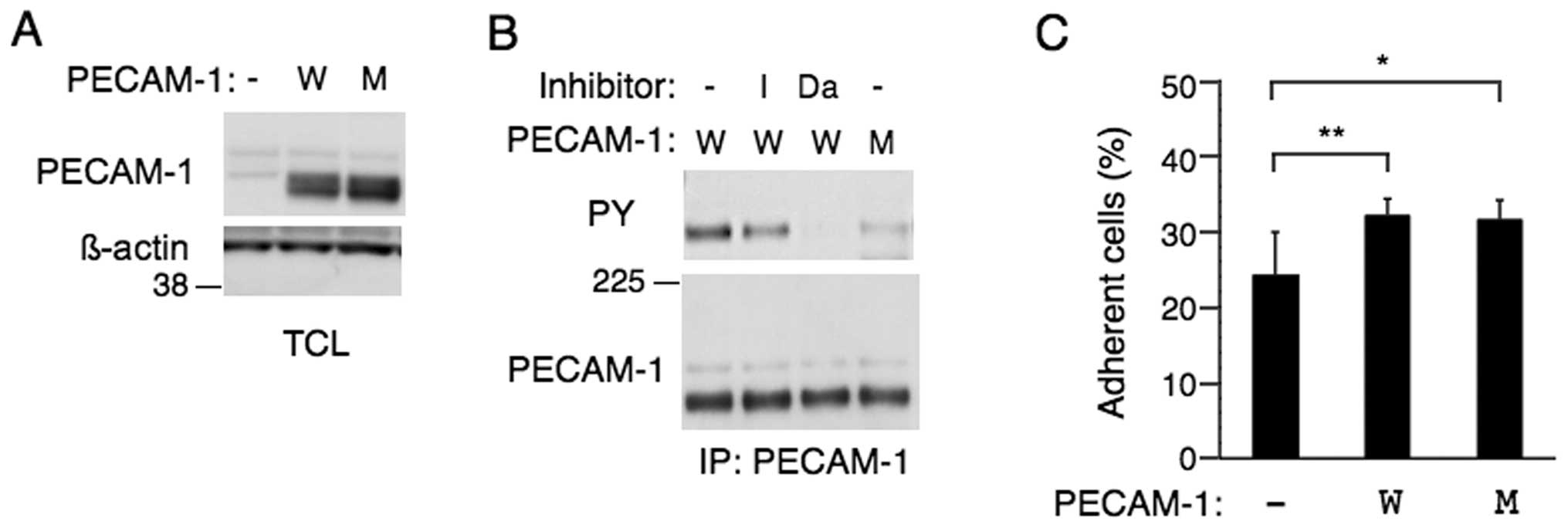
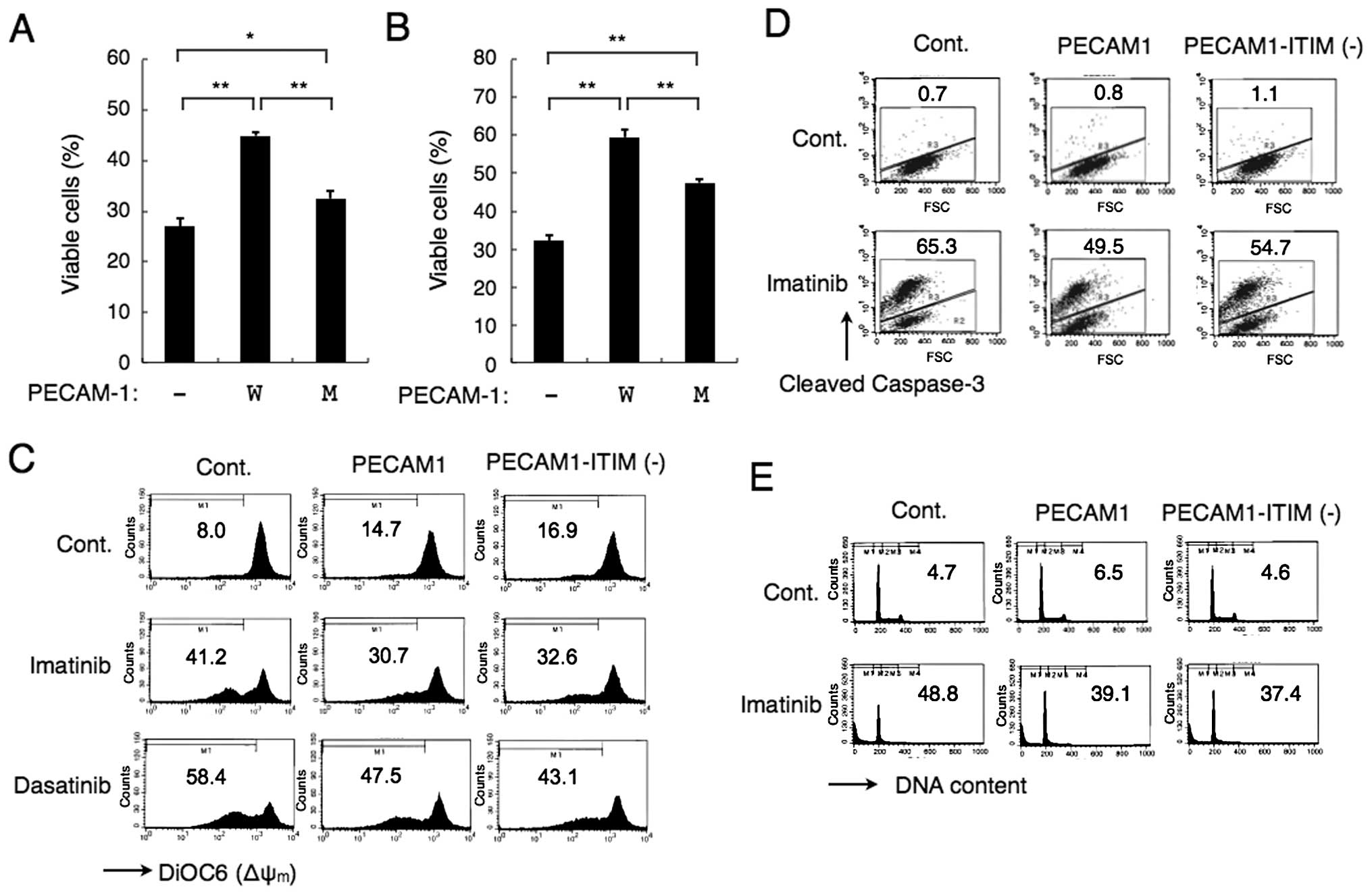
|
1.
|
Newman PJ: The biology of PECAM-1. J Clin
Invest. 99:3–8. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Privratsky JR, Newman DK and Newman PJ:
PECAM-1: conflicts of interest in inflammation. Life Sci. 87:69–82.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Ilan N and Madri JA: PECAM-1: old friend,
new partners. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:515–524. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Jackson DE: The unfolding tale of PECAM-1.
FEBS Lett. 540:7–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Dhanjal TS, Pendaries C, Ross EA, et al: A
novel role for PECAM-1 in megakaryocytokinesis and recovery of
platelet counts in thrombocytopenic mice. Blood. 109:4237–4244.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ross EA, Freeman S, Zhao Y, et al: A novel
role for PECAM-1 (CD31) in regulating haematopoietic progenitor
cell compartmentalization between the peripheral blood and bone
marrow. PLoS One. 3:e23382008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wheadon H, Edmead C and Welham MJ:
Regulation of interleukin-3-induced substrate phosphorylation and
cell survival by SHP-2 (Src-homology protein tyrosine phosphatase
2). Biochem J. 376:147–157. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Gallay N, Anani L, Lopez A, et al: The
role of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (CD31) and
CD38 antigens in marrow microenvironmental retention of acute
myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 67:8624–8632. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Akers SM, O’Leary HA, Minnear FL, et al:
VE-cadherin and PECAM-1 enhance ALL migration across brain
microvascular endothelial cell monolayers. Exp Hematol. 38:733–743.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ibrahim S, Jilani I, O’Brien S, et al:
Clinical relevance of the expression of the CD31 ligand for CD38 in
patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer.
97:1914–1919. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Tonino SH, Spijker R, Luijks DM, van Oers
MH and Kater AP: No convincing evidence for a role of CD31-38
interactions in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Blood. 112:840–843. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Goldman JM and Melo JV: Chronic myeloid
leukemia - advances in biology and new approaches to treatment. N
Engl J Med. 349:1451–1464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Wong S and Witte ON: The BCR-ABL story:
bench to bedside and back. Annu Rev Immunol. 22:247–306. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Gruber F, Mustjoki S and Porkka K: Impact
of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on patient outcomes in Philadelphia
chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol.
145:581–597. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Yamamoto M, Kurosu T, Kakihana K, Mizuchi
D and Miura O: The two major imatinib resistance mutations E255K
and T315I enhance the activity of BCR/ABL fusion kinase. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 319:1272–1275. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Kurosu T, Tsuji K, Kida A, Koyama T,
Yamamoto M and Miura O: Rottlerin synergistically enhances
imatinib-induced apoptosis of BCR/ABL-expressing cells through its
mitochondrial uncoupling effect independent of protein kinase
C-delta. Oncogene. 26:2975–2987. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Kurosu T, Ohki M, Wu N, Kagechika H and
Miura O: Sorafenib induces apoptosis specifically in cells
expressing BCR/ABL by inhibiting its kinase activity to activate
the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Res. 69:3927–3936.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Griswold IJ, MacPartlin M, Bumm T, et al:
Kinase domain mutants of Bcr-Abl exhibit altered transformation
potency, kinase activity, and substrate utilization, irrespective
of sensitivity to imatinib. Mol Cell Biol. 26:6082–6093. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Skaggs BJ, Gorre ME, Ryvkin A, et al:
Phosphorylation of the ATP-binding loop directs oncogenicity of
drug-resistant BCR-ABL mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:19466–19471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Danhauser-Riedl S, Warmuth M, Druker BJ,
Emmerich B and Hallek M: Activation of Src kinases p53/56lyn and
p59hck by p210bcr/abl in myeloid cells. Cancer Res. 56:3589–3596.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Wu J, Meng F, Kong LY, et al: Association
between imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutation-negative leukemia and
persistent activation of LYN kinase. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:926–939. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Quintas-Cardama A, Kantarjian H and Cortes
J: Flying under the radar: the new wave of BCR-ABL inhibitors. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 6:834–848. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Klucher KM, Lopez DV and Daley GQ:
Secondary mutation maintains the transformed state in BaF3 cells
with inducible BCR/ABL expression. Blood. 91:3927–3934.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Tohda S, Sakashita C, Fukuda T, Murakami N
and Nara N: Establishment of a double Philadelphia
chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia-derived cell line,
TMD5: effects of cytokines and differentiation inducers on growth
of the cells. Leuk Res. 23:255–261. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Morita S, Kojima T and Kitamura T: Plat-E:
an efficient and stable system for transient packaging of
retroviruses. Gene Ther. 7:1063–1066. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
DuBridge RB, Tang P, Hsia HC, Leong PM,
Miller JH and Calos MP: Analysis of mutation in human cells by
using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol.
7:379–387. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Mizuchi D, Kurosu T, Kida A, et al:
BCR/ABL activates Rap1 and B-Raf to stimulate the MEK/Erk signaling
pathway in hematopoietic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
326:645–651. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Chin H, Arai A, Wakao H, Kamiyama R,
Miyasaka N and Miura O: Lyn physically associates with the
erythropoietin receptor and may play a role in activation of the
Stat5 pathway. Blood. 91:3734–3745. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Kitamura T, Koshino Y, Shibata F, et al:
Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression cloning: powerful
tools in functional genomics. Exp Hematol. 31:1007–1014. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Jackson DE, Kupcho KR and Newman PJ:
Characterization of phosphotyrosine binding motifs in the
cytoplasmic domain of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
(PECAM-1) that are required for the cellular association and
activation of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase, SHP-2. J Biol Chem.
272:24868–24875. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Newman DK, Hamilton C and Newman PJ:
Inhibition of antigen-receptor signaling by platelet endothelial
cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) requires functional ITIMs, SHP-2,
and p56(lck). Blood. 97:2351–2357. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Kolli S, Zito CI, Mossink MH, Wiemer EA
and Bennett AM: The major vault protein is a novel substrate for
the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 and scaffold protein in epidermal
growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 279:29374–29385. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Oshikawa G, Nagao T, Wu N, Kurosu T and
Miura O: c-Cbl and Cbl-b ligases mediate
17-allylaminodemethoxygeldanamycin-induced degradation of
autophosphorylated Flt3 kinase with internal tandem duplication
through the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem.
286:30263–30273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Miura O, Cleveland JL and Ihle JN:
Inactivation of erythropoietin receptor function by point mutations
in a region having homology with other cytokine receptors. Mol Cell
Biol. 13:1788–1795. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Arai A, Nosaka Y, Kanda E, Yamamoto K,
Miyasaka N and Miura O: Rap1 is activated by erythropoietin or
interleukin-3 and is involved in regulation of beta1
integrin-mediated hematopoietic cell adhesion. J Biol Chem.
276:10453–10462. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Jin A, Kurosu T, Tsuji K, et al: BCR/ABL
and IL-3 activate Rap1 to stimulate the B-Raf/MEK/Erk and Akt
signaling pathways and to regulate proliferation, apoptosis, and
adhesion. Oncogene. 25:4332–4340. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Newman PJ and Newman DK: Signal
transduction pathways mediated by PECAM-1: new roles for an old
molecule in platelet and vascular cell biology. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 23:953–964. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Flint AJ, Tiganis T, Barford D and Tonks
NK: Development of ‘substrate-trapping’ mutants to identify
physiological substrates of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:1680–1685. 1997.
|
|
39.
|
Albelda SM, Muller WA, Buck CA and Newman
PJ: Molecular and cellular properties of PECAM-1 (endoCAM/CD31): a
novel vascular cell-cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol.
114:1059–1068. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Bergom C, Goel R, Paddock C, et al: The
cell-adhesion and signaling molecule PECAM-1 is a molecular
mediator of resistance to genotoxic chemotherapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
5:1699–1707. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Bird IN, Taylor V, Newton JP, et al:
Homophilic PECAM-1(CD31) interactions prevent endothelial cell
apoptosis but do not support cell spreading or migration. J Cell
Sci. 112:1989–1997. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Ferrero E, Belloni D, Contini P, et al:
Transendothelial migration leads to protection from
starvation-induced apoptosis in CD34+CD14+
circulating precursors: evidence for PECAM-1 involvement through
Akt/PKB activation. Blood. 101:186–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Gao C, Sun W, Christofidou-Solomidou M, et
al: PECAM-1 functions as a specific and potent inhibitor of
mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Blood. 102:169–179. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Limaye V, Li X, Hahn C, et al: Sphingosine
kinase-1 enhances endothelial cell survival through a
PECAM-1-dependent activation of PI-3K/Akt and regulation of Bcl-2
family members. Blood. 105:3169–3177. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Chan G, Kalaitzidis D and Neel BG: The
tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 (PTPN11) in cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 27:179–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Scherr M, Chaturvedi A, Battmer K, et al:
Enhanced sensitivity to inhibition of SHP2, STAT5, and Gab2
expression in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Blood. 107:3279–3287.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Chen J, Yu WM, Daino H, Broxmeyer HE,
Druker BJ and Qu CK: SHP-2 phosphatase is required for
hematopoietic cell transformation by Bcr-Abl. Blood. 109:778–785.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Biswas P, Canosa S, Schoenfeld D, et al:
PECAM-1 affects GSK-3beta-mediated beta-catenin phosphorylation and
degradation. Am J Pathol. 169:314–324. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Coluccia AM, Vacca A, Dunach M, et al:
Bcr-Abl stabilizes beta-catenin in chronic myeloid leukemia through
its tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 26:1456–1466. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Hu Y, Chen Y, Douglas L and Li S:
beta-Catenin is essential for survival of leukemic stem cells
insensitive to kinase inhibition in mice with BCR-ABL-induced
chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 23:109–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Shang YC, Zhang C, Wang SH, et al:
Activated beta-catenin induces myogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis
in BM-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 9:667–681.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Meads MB, Hazlehurst LA and Dalton WS: The
bone marrow microenvironment as a tumor sanctuary and contributor
to drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2519–2526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|