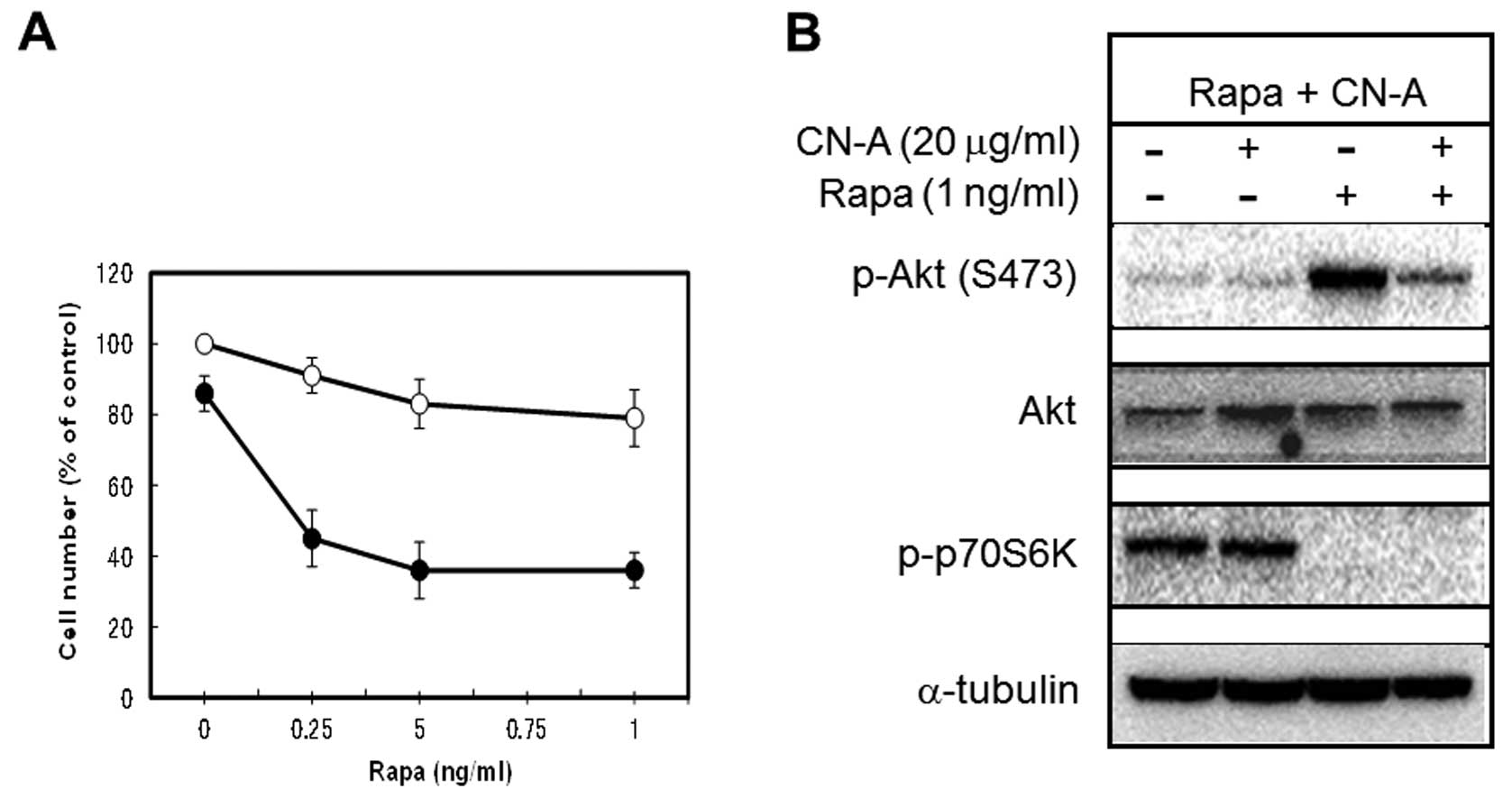
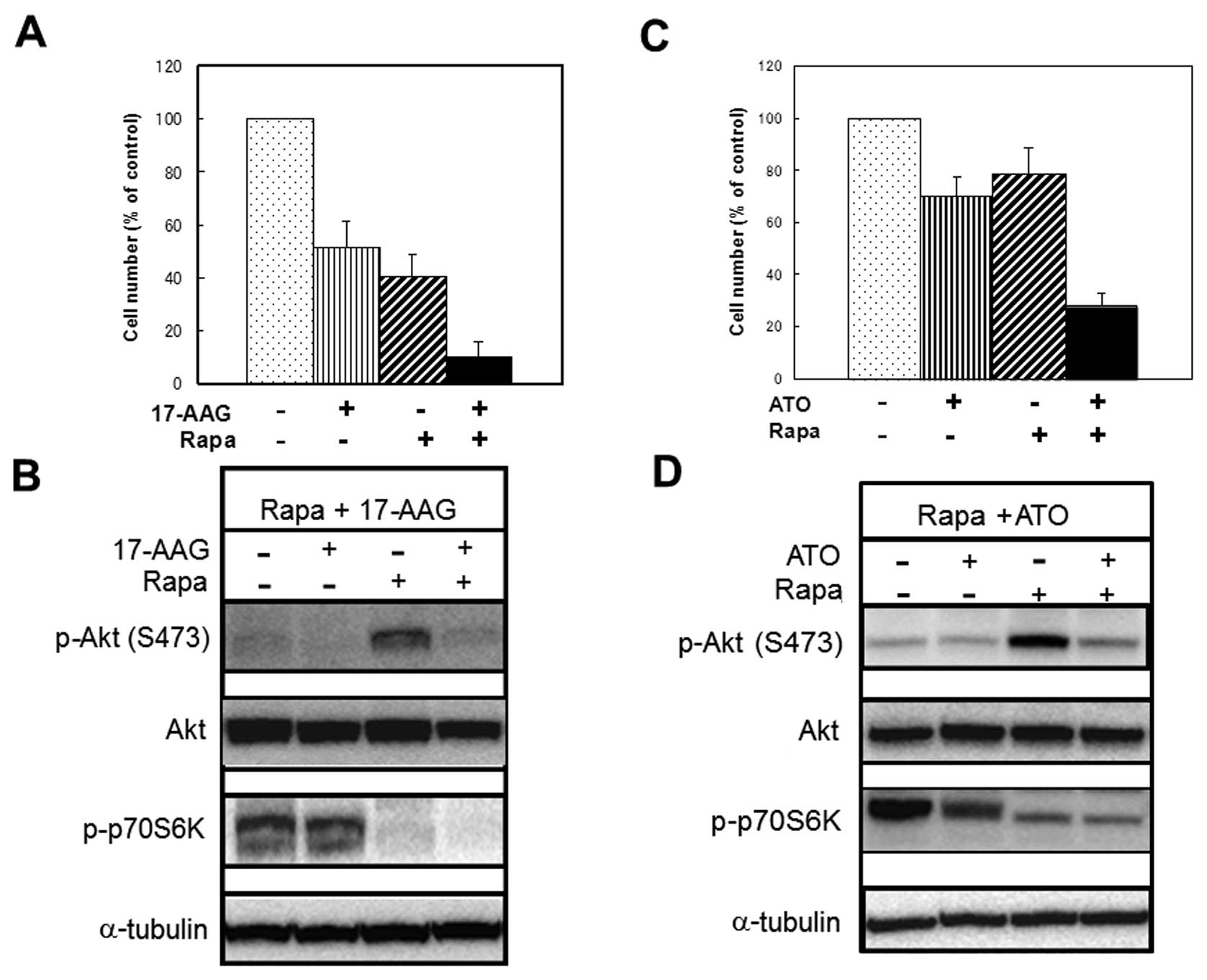
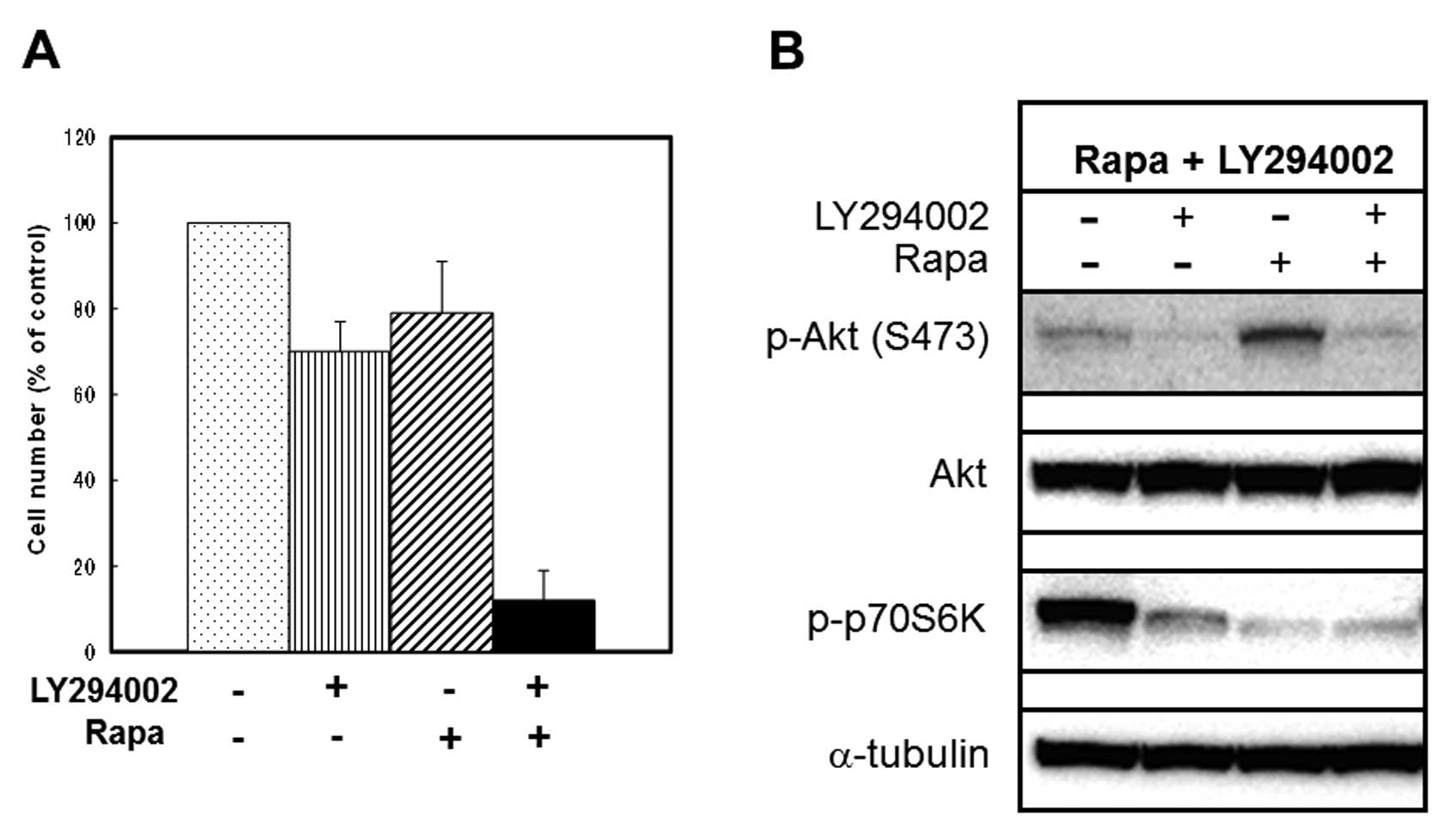
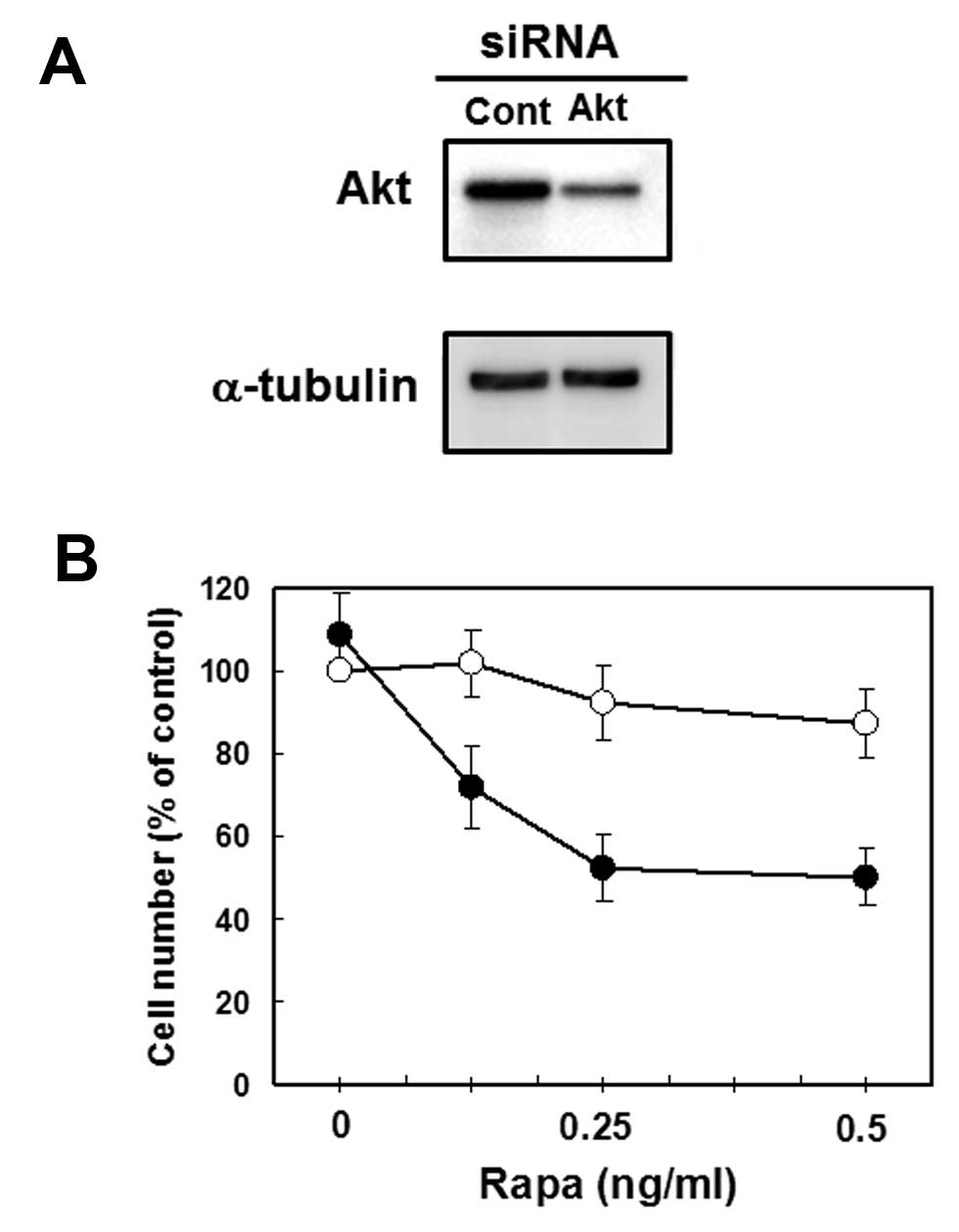
|
1
|
Jemar A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hurvitz SA, Hu Y, O’Brien N and Finn RS:
Current approaches and future directions in the treatment of
HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. May 31–2012, (Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Meric-Bernstam FM and Gonzalez-Angulo M:
Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J Clin
Oncol. 27:2278–2287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signaling in
cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wong KK, Engelman JA and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K signaling pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 20:87–90. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ma XM and Blenis J: Molecular mechanisms
of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:307–318. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang S, Xiao X, Meng X and Leslie K: A
mechanism for synergy with mTOR and PI3 kinase inhibitors. PLoS
One. 6:e263432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang X and Sun SY: Enhancing mTOR-targeted
cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 13:1193–1203. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsieh AC, Costa M, Zollo O, et al: Genetic
dissection of the oncogenic mTOR pathway reveals druggable
addiction to translational control via 4EBP-eIF4E. Cancer Cell.
17:249–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Janes MR, Limon JJ, Chen J, et al:
Effective and selective targeting of leukemia cells using a TOR1/2
kinase inhibitor. Nat Med. 16:205–213. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sassa T, Tojyo T and Munakata K: Isolation
of a new plant growth substance with cytokinin-like activity.
Nature. 227:3791970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Asahi K, Honma Y and Hazeki K: Cotylenin
A, a plant-growth regulator, induces the differentiation in murine
and human myeloid leukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
238:758–763. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y, Yamada K, Ishii Y,
Asahi KI, Tomoyasu S and Honma Y: Induction of the monocytic
differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells by cotylenin A, a plant
growth regulator. Br J Haematol. 112:697–705. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamada K, Honma Y, Asahi KI, Sassa T, Hino
KI and Tomoyasu S: Differentiation of human acute myeloid leukemia
cells in primary culture in response to cotylenin A, a plant growth
regulator. Br J Haematol. 114:814–821. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Honma Y: Cotylenin A - a plant growth
regulator as a differentiation-inducing agent against myeloid
leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 43:1169–1178. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y, Okabe-Kado J,
Kasukabe T and Honma Y: Induction of differentiation of human
myeloid leukemia cells by immunosuppressant macrolides (rapamycin
and FK506) and calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Exp
Hematol. 29:582–588. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J, Kato N, Sassa T
and Honma Y: Effects of combined treatment with rapamycin and
cotylenin A, a novel differentiation-inducing agent, on human
breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells and xenografts. Breast Cancer Res.
7:R1097–R1110. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kawakami K, Hattori M, Inoue T, et al: A
novel fusicoccin derivative preferentially targets hypoxic tumor
cells and inhibits tumor growth in xenografts. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 12:791–800. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kasukabe T, Okabe-Kado J and Honma Y:
Cotylenin A, a new differentiation inducer, and rapamycin
cooperatively inhibit growth of cancer cells through induction of
cyclin G2. Cancer Sci. 99:1693–1698. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun SH, Rosenberg LM, Wang X, et al:
Activation of AKT and eIF4E survival pathways by rapamycin-mediated
mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition. Cancer Res. 65:7052–7058.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Harkavy N, Shen N, Grohar P and
Helman LJ: Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling
through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 26:1932–1940.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gazitt T, Kolaparthi V, Moncada K, Thomas
C and Freeman J: Targeted therapy of human osteosarcoma with 17AAG
or rapamycin: characterization of induced apoptosis and inhibition
of mTOR and Akt/MAPK/Wnt pathways. Int J Oncol. 34:551–561.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vaseva AV, Yallowitz AR, Marchenko ND, Xu
S and Moll UM: Blockade of Hsp90 by 17AAG antagonizes MDMX and
synergizes with Nutlin to induce p53-mediated apoptosis in solid
tumors. Cell Death Disease. 2:e1562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiao Y, Ou W, Meng F, Zhou H and Wang A:
Targeting HSP90 in ovarian cancers with multiple receptor tyrosine
kinase coactivation. Mol Cancer. 10:1252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mann KK, Colombo M and Miller WH Jr:
Arsenic trioxide decreases AKT protein in a caspase-dependent
manner. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1680–1687. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yuan Z, Wang F, Zhao Z, et al:
BIM-mediated AKT phosphorylation is a key modulator of arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis is cisplatin-sensitive and - resistant
ovarian cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e205862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chiu HW, Chen YA, Ho SY and Wang YJ:
Arsenic trioxide enhances the radiation sensitivity of
androgen-dependent and -independent human prostate cancer cells.
PLoS One. 7:e315792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ray S, Fry MJ and Darbre PD: Enhanced
sensitivity to rapamycin following long-term oestrogen deprivation
in MCF-7, T-47-D and ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cells. J
Endocrinol. 208:21–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Elfiky A, Aziz SA, Conrad PJ, et al:
Characterization and targeting of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
(PI3K) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in renal cell
cancer. J Trans Med. 9:1332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Honma Y, Kasukabe T, Yamori T, Kato N and
Sassa T: Antitumor effect of cotylenin A plus interferon-alpha:
possible therapeutic agents against ovary carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol.
99:680–688. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen Y, Shen ZX, Chen YJ, et al: Studies
on the clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics of low-dose arsenic
trioxide in the treatment of relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia:
a comparison with conventional dosage. Leukemia. 15:735–741. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Douer D and Tallman MS: Arsenic trioxide:
new clinical experience with an old medication in hematologic
malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 23:2395–2410. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim KB, Bedikian AY, Camacho LH,
Papadopoulos NE and McCullough C: A phase II trial of arsenic
trioxide in patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer.
104:1687–1692. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Loehberg CR, Strissel PL, Dittrich R, et
al: Akt and p53 are potential mediators of reduced mammary tumor
growth by Chloroquine and the mTOR inhibitor RAD001. Biochem
Pharmacol. 83:480–488. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Horne MC, Goolsby GL, Donaldson KL, Tran
D, Neubauer M and Wahl AF: Cyclin G1 and cyclin G2 comprise a new
family of cyclins with contrasting tissue-specific and cell
cycle-regulated expressions. J Biol Chem. 271:6050–6061. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Horne MC, Donaldson KL, Goolsby GL, et al:
Cyclin G2 is up-regulated during growth inhibition and B cell
antigen receptor-mediated cell cycle arrest. J Biol Chem.
272:12650–12661. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bates S, Rowan S and Vousden KH:
Characterization of human cyclin G1 and G2: DNA damage inducible
genes. Oncogene. 13:1103–1109. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fei M, Zhao Y, Wang Y, et al: Low
expression of Foxo3a is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian
cancer patients. Cancer Invest. 27:52–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weidinger C, Krause K, Klagge A, Karger S
and Fuhrer D: Forkhead box-O transcription factor: critical
conductors of cancer’s fate. Endocr Relat Cancer. 15:917–929.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Katayama K, Nakamura A, Sugimoto Y, Tsuruo
T and Fujita N: FOXO transcription factor-dependent p15(INK4b) and
p19(INK4d) expression. Oncogene. 27:1677–1686. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fu G and Peng C: Nodal enhances the
activity of FoxO3a and its synergistic interaction with Smad to
regulate cyclin G2 transcription in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene.
30:3953–3966. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meric-Bernstam F, Akcakanat A and Chen H:
PI3CA/PTEN mutations and Akt activation as markers of sensitivity
to allosteric mTOR inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1777–1789. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Montero JC, Chen X, Ocana A and Pandiella
A: Predominance of mTORC1 over mTORC2 in the regulation of
proliferation of ovarian cancer cells: therapeutic implications.
Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1342–1352. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu CX, Li Y, Yue P, et al: The combination
of RAD001 and NVP-BEZ235 exerts synergistic anticancer activity
against non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
6:e2208992011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Honma Y, Ishii Y, Yamamoto-Yamaguchi Y,
Sassa T and Asahi K: Cotylenin A, a differentiation-inducing agent,
and IFN-alpha cooperatively induce apoptosis and have an antitumor
effect on human non-small lung carcinoma cells in nude mice. Cancer
Res. 63:3659–3666. 2003.
|