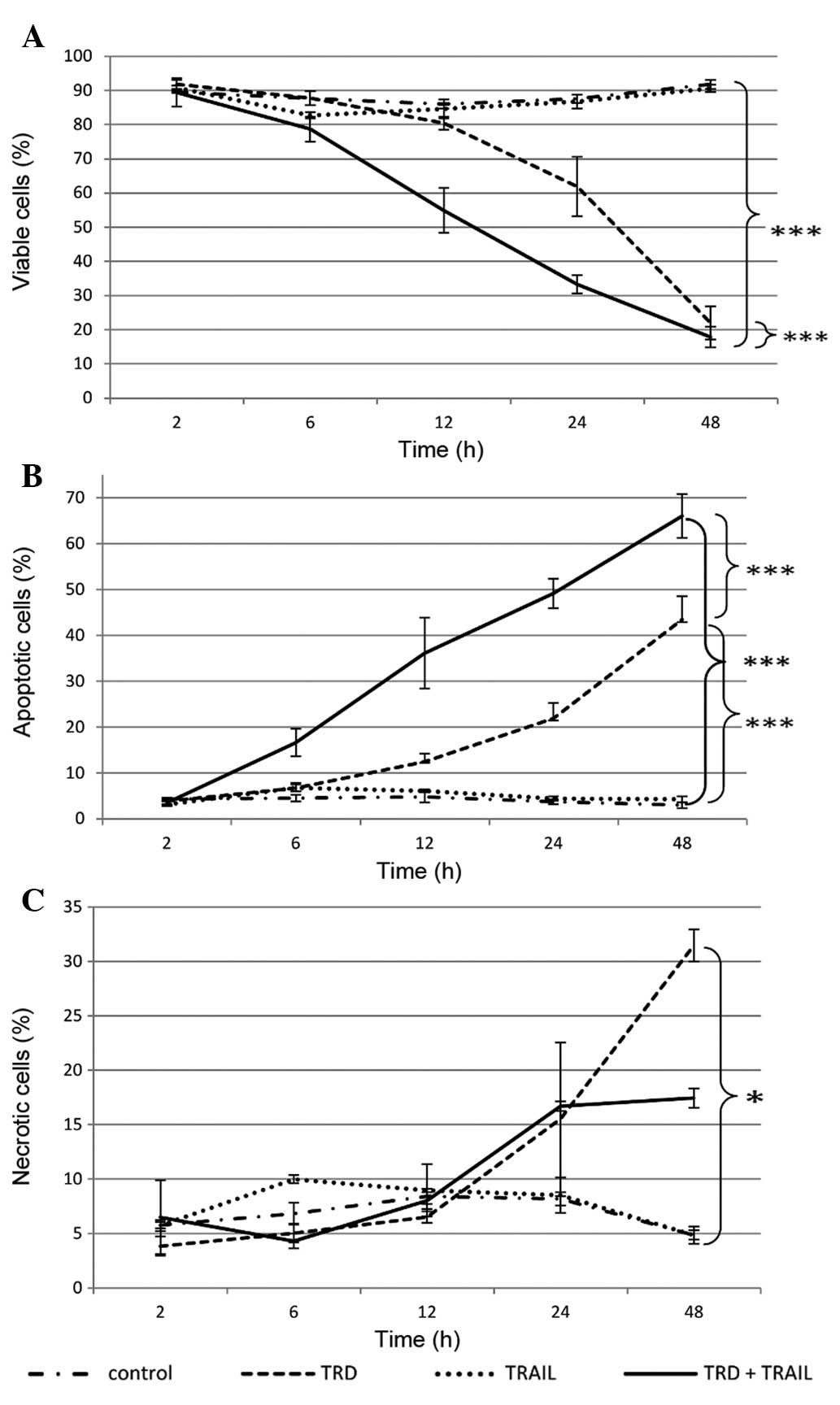
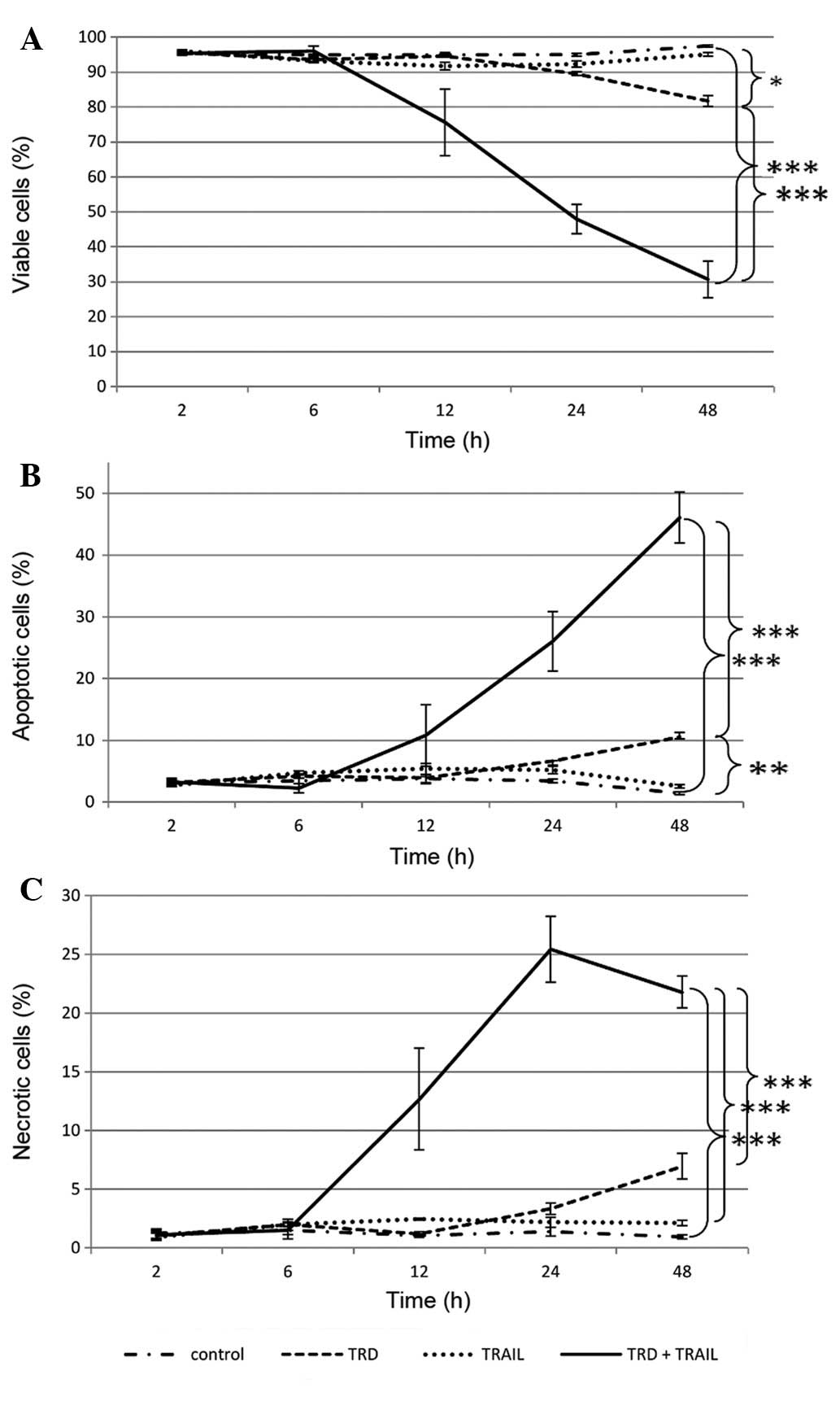
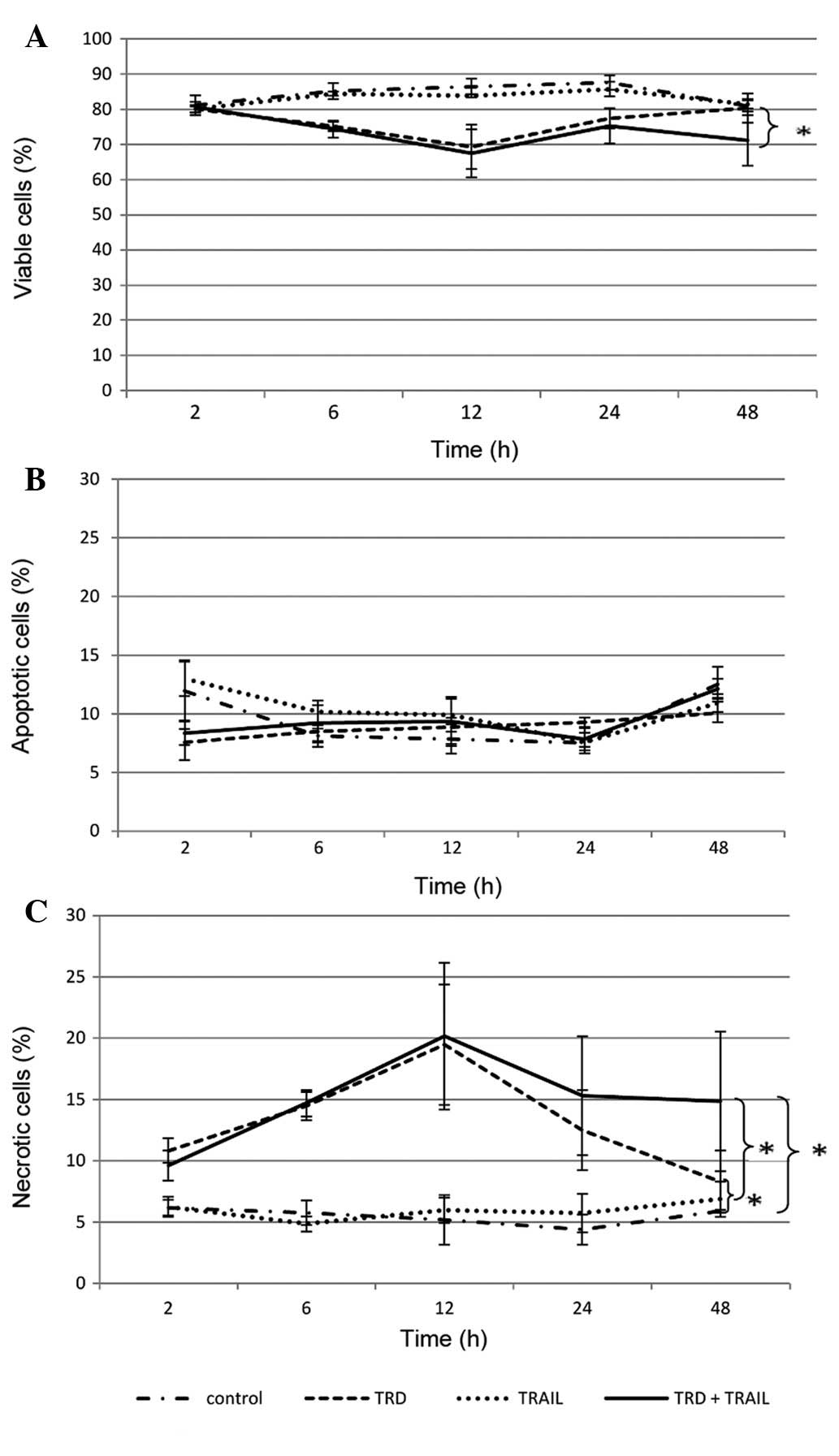
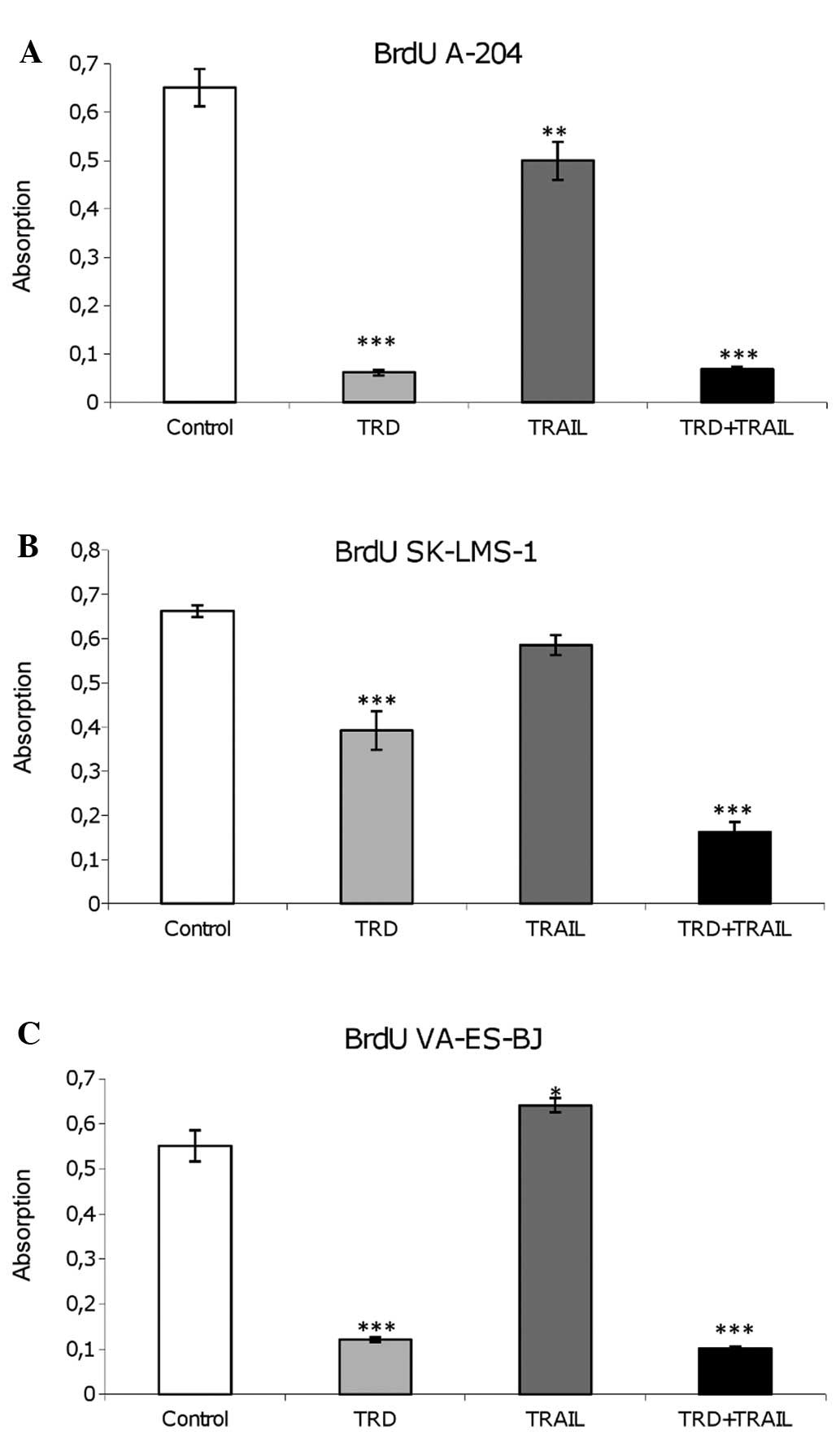
|
1
|
Hoos A, Lewis JJ and Brennan MF: Soft
tissue sarcoma: prognostic factors and multimodal treatment.
Chirurg. 71:787–794. 2000.(In German).
|
|
2
|
Patrikidou A, Domont J, Cioffi A and Le
Cesne A: Treating soft tissue sarcomas with adjuvant chemotherapy.
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 12:21–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kaushal A and Citrin D: The role of
radiation therapy in the management of sarcomas. Surg Clin North
Am. 88:629–646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O’Brien GC, Cahill RA, Bouchier-Hayes DJ
and Redmond HP: Co-immunotherapy with interleukin-2 and taurolidine
for progressive metastatic melanoma. Ir J Med Sci. 175:10–14.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Solomon LR, Cheesbrough JS, Bhargava R, et
al: Observational study of need for thrombolytic therapy and
incidence of bacteremia using taurolidine-citrate-heparin,
taurolidine-citrate and heparin catheter locks in patients treated
with hemodialysis. Semin Dial. 25:233–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Karavasilis V, Seddon BM, Ashley S,
Al-Muderis O, Fisher C and Judson I: Significant clinical benefit
of first-line palliative chemotherapy in advanced soft-tissue
sarcoma: retrospective analysis and identification of prognostic
factors in 488 patients. Cancer. 112:1585–1591. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Billingsley KG, Lewis JJ, Leung DH, Casper
ES, Woodruff JM and Brennan MF: Multifactorial analysis of the
survival of patients with distant metastasis arising from primary
extremity sarcoma. Cancer. 85:389–395. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pezzi CM, Pollock RE, Evans HL, et al:
Preoperative chemo-therapy for soft-tissue sarcomas of the
extremities. Ann Surg. 211:476–481. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Donato Di Paola E and Nielsen OS: The
EORTC soft tissue and bone sarcoma group. European Organisation for
Research and Treatment of Cancer. Eur J Cancer. 38(Suppl 4):
S138–S141. 2002.
|
|
10
|
Nedea EA and DeLaney TF: Sarcoma and skin
radiation oncology. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 20:401–429. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brodowicz T, Schwameis E, Widder J, et al:
Intensified adjuvant IFADIC chemotherapy for adult soft tissue
sarcoma: a prospective randomized feasibility trial. Sarcoma.
4:151–160. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frustaci S, Gherlinzoni F, De Paoli A, et
al: Adjuvant chemotherapy for adult soft tissue sarcomas of the
extremities and girdles: results of the Italian randomized
cooperative trial. J Clin Oncol. 19:1238–1247. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bramwell V, Rouesse J, Steward W, et al:
Adjuvant CYVADIC chemotherapy for adult soft tissue sarcoma -
reduced local recurrence but no improvement in survival: a study of
the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Soft
Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol. 12:1137–1149.
1994.
|
|
14
|
Sarcoma Meta-analysis Collaboration:
Adjuvant chemotherapy for localised resectable soft-tissue sarcoma
of adults: meta-analysis of individual data. Lancet. 350:1647–1654.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hirata T, Yonemori K, Ando M, et al:
Efficacy of taxane regimens in patients with metastatic
angiosarcoma. Eur J Dermatol. 21:539–545. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Penel N, Van Glabbeke M, Marreaud S, Ouali
M, Blay JY and Hohenberger P: Testing new regimens in patients with
advanced soft tissue sarcoma: analysis of publications from the
last 10 years. Ann Oncol. 22:1266–1272. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mentzel T: Epithelioid sarcoma:
morphologic variants and differential diagnosis. Pathologe.
31:135–141. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chromik AM, Daigeler A, Bulut D, et al:
Comparative analysis of cell death induction by Taurolidine in
different malignant human cancer cell lines. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
29:212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chromik AM, Daigeler A, Hilgert C, et al:
Synergistic effects in apoptosis induction by taurolidine and TRAIL
in HCT-15 colon carcinoma cells. J Invest Surg. 20:339–348. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Daigeler A, Chromik AM, Geisler A, et al:
Synergistic apoptotic effects of taurolidine and TRAIL on squamous
carcinoma cells of the esophagus. Int J Oncol. 32:1205–1220. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Daigeler A, Chromik AM, Haendschke K, et
al: Synergistic effects of sonoporation and taurolidin/TRAIL on
apoptosis in human fibrosarcoma. Ultrasound Med Biol. 36:1893–1906.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yagita H, Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Smyth MJ
and Okumura K: TRAIL and its receptors as targets for cancer
therapy. Cancer Sci. 95:777–783. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bouralexis S, Findlay DM and Evdokiou A:
Death to the bad guys: targeting cancer via Apo2L/TRAIL. Apoptosis.
10:35–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rowinsky EK: Targeted induction of
apoptosis in cancer management: the emerging role of tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor activating
agents. J Clin Oncol. 23:9394–9407. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, et al: Safety
and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin
Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ganten D, Ruckpaul K and Daniel P:
Molekulare Grundlagen der Apoptose. Grundlagen der Molekularen
Medizin. Springer Berlin; Heidelberg: pp. 159–203. 2008
|
|
27
|
Newsom-Davis T, Prieske S and Walczak H:
Is TRAIL the holy grail of cancer therapy? Apoptosis. 14:607–623.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
LeBlanc HN and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL
and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ. 10:66–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Beere HM: Death versus survival:
functional interaction between the apoptotic and stress-inducible
heat shock protein pathways. J Clin Invest. 115:2633–2639. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jacobi CA, Menenakos C and Braumann C:
Taurolidine - a new drug with anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic
effects. Anticancer Drugs. 16:917–921. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McCourt M, Wang JH, Sookhai S and Redmond
HP: Taurolidine inhibits tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
Ann Surg Oncol. 7:685–691. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Petrovic L, Schlegel KA, Ries J, et al: In
vitro effect of taurolidine on squamous cell carcinoma in the oral
cavity. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 7:102–107. 2003.(In German).
|
|
33
|
Gallagher KA, Liu ZJ, Xiao M, et al:
Diabetic impairments in NO-mediated endothelial progenitor cell
mobilization and homing are reversed by hyperoxia and SDF-1 alpha.
J Clin Invest. 117:1249–1259. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Calabresi P, Goulette FA and Darnowski JW:
Taurolidine: cytotoxic and mechanistic evaluation of a novel
antineoplastic agent. Cancer Res. 61:6816–6821. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Braumann C, Henke W, Jacobi CA and Dubiel
W: The tumor-suppressive reagent taurolidine is an inhibitor of
protein biosynthesis. Int J Cancer. 112:225–230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Neary PM, Hallihan P, Wang JH, Pfirrmann
RW, Bouchier-Hayes DJ and Redmond HP: The evolving role of
taurolidine in cancer therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1135–1143. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Darnowski JW, Goulette FA, Cousens LP,
Chatterjee D and Calabresi P: Mechanistic and antineoplastic
evaluation of taurolidine in the DU145 model of human prostate
cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 54:249–258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stendel R, Biefer HR, Dekany GM, et al:
The antibacterial substance taurolidine exhibits anti-neoplastic
action based on a mixed type of programmed cell death. Autophagy.
5:194–210. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stendel R, Scheurer L,
Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Brock M and Mohler H: Enhancement of
Fas-ligand-mediated programmed cell death by taurolidine.
Anticancer Res. 23:2309–2314. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Daigeler A, Brenzel C, Bulut D, et al:
TRAIL and Taurolidine induce apoptosis and decrease proliferation
in human fibrosarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 27:822008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han Z, Ribbizi I, Pantazis P, Wyche J,
Darnowski J and Calabresi P: The antibacterial drug taurolidine
induces apoptosis by a mitochondrial cytochrome c-dependent
mechanism. Anticancer Res. 22:1959–1964. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Braumann C, Winkler G, Rogalla P,
Menenakos C and Jacobi CA: Prevention of disease progression in a
patient with a gastric cancer-re-recurrence. Outcome after
intravenous treatment with the novel antineoplastic agent
taurolidine Report of a case. World J Surg Oncol. 4:342006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Imhof L, Goldinger SM, Baumann K, et al:
The antibacterial substance, taurolidine in the second/third-line
treatment of very advanced stage IV melanoma including brain
metastases: results of a phase 2, open-label study. Melanoma Res.
Nov 3–2010.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
44
|
Stendel R, Picht T, Schilling A, et al:
Treatment of glioblastoma with intravenous taurolidine. First
clinical experience. Anticancer Res. 24:1143–1147. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Backes C, Keller A, Kuentzer J, et al:
GeneTrail - advanced gene set enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 35:W186–W192. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue
CJ, Moore A and Ashkenazi A: Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2
ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family.
J Biol Chem. 271:12687–12690. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, et al:
Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF
family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 3:673–682. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tomek S, Koestler W, Horak P, et al:
Trail-induced apoptosis and interaction with cytotoxic agents in
soft tissue sarcoma cell lines. Eur J Cancer. 39:1318–1329. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Clayer M, Bouralexis S, Evdokiou A, Hay S,
Atkins GJ and Findlay DM: Enhanced apoptosis of soft tissue sarcoma
cells with chemotherapy: A potential new approach using TRAIL. J
Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 9:19–22. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kondo K, Yamasaki S, Inoue N, et al:
Prospective antitumor effects of the combination of tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and cisplatin
against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surg Today. 36:966–974.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Walters DK, Muff R, Langsam B, Gruber P,
Born W and Fuchs B: Taurolidine: a novel anti-neoplastic agent
induces apoptosis of osteosarcoma cell lines. Invest New Drugs.
25:305–312. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kluttermann K, Banning U, Kachel M, Krause
C, Korholz D and Mauz-Korholz C: TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity in a
melphalan-resistant rhabdomyosarcoma cell line via activation of
caspase-2. Anticancer Res. 26:351–356. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Komdeur R, Meijer C, Van Zweeden M, et al:
Doxorubicin potentiates TRAIL cytotoxicity and apoptosis and can
overcome TRAIL-resistance in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Int J Oncol.
25:677–684. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Heikaus S, Matuszek KS, Suschek CV, et al:
Paclitaxel (Taxol)-induced apoptosis in human epithelioid sarcoma
cell lines is enhanced by upregulation of CD95 ligand
(FasL/Apo-1L). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:689–695. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gheorghescu B, Gherman I, Jovin GH, et al:
Absorption studies in patients with parasitic infestation of the
small intestine, before and after treatment. Med Interne. 14:31–38.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nedeau AE, Gallagher KA, Liu ZJ and
Velazquez OC: Elevation of hemopexin-like fragment of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 tissue levels inhibits ischemic wound healing
and angiogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 54:1430–1438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nedea ME, Vasilescu F, Gheorghescu B,
Pavelescu E and Runcan V: Determination with thin layer
chromatography of the distribution of lipids in the feces and study
of the incorporation of certain C 14 -labeled 1-fatty acids into
the different lipid fractions. Fiziol Norm Patol. 19:67–73.
1973.(In Romanian).
|
|
58
|
Hollander MC, Poola-Kella S and Fornace
AJ: Gadd34 functional domains involved in growth suppression and
apoptosis. Oncogene. 22:3827–3832. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hollander MC, Zhan Q, Bae I and Fornace AJ
Jr: Mammalian GADD34, an apoptosis- and DNA damage-inducible gene.
J Biol Chem. 272:13731–13737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Adler HT, Chinery R, Wu DY, et al:
Leukemic HRX fusion proteins inhibit GADD34–induced apoptosis and
associate with the GADD34 and hSNF5/INI1 proteins. Mol Cell Biol.
19:7050–7060. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Grishin AV, Azhipa O, Semenov I and Corey
SJ: Interaction between growth arrest-DNA damage protein 34 and Src
kinase Lyn negatively regulates genotoxic apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 98:10172–10177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chromik AM, Hahn SA, Daigeler A, et al:
Gene expression analysis of cell death induction by taurolidine in
different malignant cell lines. BMC Cancer. 10:5952010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Rohde M, Daugaard M, Jensen MH, Helin K,
Nylandsted J and Jaattela M: Members of the heat-shock protein 70
family promote cancer cell growth by distinct mechanisms. Genes
Dev. 19:570–582. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Daugaard M, Rohde M and Jaattela M: The
heat shock protein 70 family: highly homologous proteins with
overlapping and distinct functions. FEBS Lett. 581:3702–3710. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Noguchi T, Takeno S, Shibata T, Uchida Y,
Yokoyama S and Muller W: Expression of heat shock protein 70 in
grossly resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Thorac
Surg. 74:222–226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Huang WJ, Xia LM, Zhu F, et al:
Transcriptional upregulation of HSP70-2 by HIF-1 in cancer cells in
response to hypoxia. Int J Cancer. 124:298–305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Scieglinska D, Piglowski W, Mazurek A, et
al: The HspA2 protein localizes in nucleoli and centrosomes of heat
shocked cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 104:2193–2206. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Garg M, Kanojia D, Seth A, et al:
Heat-shock protein 70-2 (HSP70-2) expression in bladder urothelial
carcinoma is associated with tumour progression and promotes
migration and invasion. Eur J Cancer. 46:207–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Grivicich I, Regner A, Zanoni C, et al:
Hsp70 response to 5-fluorouracil treatment in human colon cancer
cell lines. Int J Colorectal Dis. 22:1201–1208. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Park SR, Lee KD, Kim UK, et al:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A reduces chemoresistance of oral
squamous carcinoma cell via inhibition of heat shock proteins 70
(HSP70). Yonsei Med J. 51:708–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Beere HM: ‘The stress of dying’: the role
of heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis. J Cell Sci.
117:2641–2651. 2004.
|
|
72
|
Valoti G, Nicoletti MI, Pellegrino A, et
al: Ecteinascidin-743, a new marine natural product with potent
antitumor activity on human ovarian carcinoma xenografts. Clin
Cancer Res. 4:1977–1983. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang L and Fang B: Mechanisms of
resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
12:228–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kuang AA, Diehl GE, Zhang J and Winoto A:
FADD is required for DR4- and DR5-mediated apoptosis: lack of
trail-induced apoptosis in FADD-deficient mouse embryonic
fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 275:25065–25068. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bodmer JL, Holler N, Reynard S, et al:
TRAIL receptor-2 signals apoptosis through FADD and caspase-8. Nat
Cell Biol. 2:241–243. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Petak I, Vernes R, Szucs KS, et al: A
caspase-8-independent component in TRAIL/Apo-2L-induced cell death
in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Cell Death Differ. 10:729–739.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Piras V, Hayashi K, Tomita M and
Selvarajoo K: Enhancing apoptosis in TRAIL-resistant cancer cells
using fundamental response rules. Sci Rep. 1:1442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Duckett CS: Apoptosis and NF-kappa B: the
FADD connection. J Clin Invest. 109:579–580. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Park JM, Kim A, Oh JH and Chung AS:
Methylseleninic acid inhibits PMA-stimulated pro-MMP-2 activation
mediated by MT1-MMP expression and further tumor invasion through
suppression of NF-kappaB activation. Carcinogenesis. 28:837–847.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, et al: Wip1, a
novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to
ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:6048–6053. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Lambros MB, Natrajan R, Geyer FC, et al:
PPM1D gene amplification and overexpression in breast cancer: a
qRT-PCR and chromogenic in situ hybridization study. Mod Pathol.
23:1334–1345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Natrajan R, Lambros MB, Rodriguez-Pinilla
SM, et al: Tiling path genomic profiling of grade 3 invasive ductal
breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2711–2722. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tan DS, Lambros MB, Rayter S, et al: PPM1D
is a potential therapeutic target in ovarian clear cell carcinomas.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:2269–2280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Xia Y, Ongusaha P, Lee SW and Liou Y-C:
Loss of Wip1 sensitizes cells to stress- and DNA damage-induced
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 284:17428–17437. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Saito-Ohara F, Imoto I, Inoue J, et al:
PPM1D is a potential target for 17q gain in neuroblastoma. Cancer
Res. 63:1876–1883. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Loukopoulos P, Shibata T, Katoh H, et al:
Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis
of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: identification of genetic indicators
that predict patient outcome. Cancer Sci. 98:392–400. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Fuku T, Semba S, Yutori H and Yokozaki H:
Increased wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (Wip1 or PPM1D)
expression correlated with downregulation of checkpoint kinase 2 in
human gastric carcinoma. Pathol Int. 57:566–571. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Castellino RC, De Bortoli M, Lu X, et al:
Medulloblastomas overexpress the p53-inactivating oncogene
WIP1/PPM1D. J Neurooncol. 86:245–256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Lu X, Nguyen TA, Moon SH, Darlington Y,
Sommer M and Donehower LA: The type 2C phosphatase Wip1: an
oncogenic regulator of tumor suppressor and DNA damage response
pathways. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:123–135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Rayter S, Elliott R, Travers J, et al: A
chemical inhibitor of PPM1D that selectively kills cells
overexpressing PPM1D. Oncogene. 27:1036–1044. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sorensen CS and Syljuasen RG: Safeguarding
genome integrity: the checkpoint kinases ATR, CHK1 and WEE1
restrain CDK activity during normal DNA replication. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40:477–486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Mir SE, De Witt Hamer PC, Krawczyk PM, et
al: In silico analysis of kinase expression identifies WEE1 as a
gatekeeper against mitotic catastrophe in glioblastoma. Cancer
Cell. 18:244–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Iorns E, Lord CJ, Grigoriadis A, et al:
Integrated functional, gene expression and genomic analysis for the
identification of cancer targets. PloS One. 4:e51202009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Posthuma DeBoer J, Wurdinger T, Graat HC,
et al: WEE1 inhibition sensitizes osteosarcoma to radiotherapy. BMC
Cancer. 11:1562011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Magnussen GI, Holm R, Emilsen E, Rosnes
AK, Slipicevic A and Florenes VA: High expression of wee1 is
associated with poor disease-free survival in malignant melanoma:
potential for targeted therapy. PloS One. 7:e382542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hirai H, Iwasawa Y, Okada M, et al:
Small-molecule inhibition of Wee1 kinase by MK-1775 selectively
sensitizes p53-deficient tumor cells to DNA-damaging agents. Mol
Cancer Ther. 8:2992–3000. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Rajeshkumar NV, De Oliveira E, Ottenhof N,
et al: MK-1775, a potent Wee1 inhibitor, synergizes with
gemcitabine to achieve tumor regressions, selectively in
p53-deficient pancreatic cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res.
17:2799–2806. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Bridges KA, Hirai H, Buser CA, et al:
MK-1775, a novel Wee1 kinase inhibitor, radiosensitizes
p53-defective human tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res. 17:5638–5648.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Hirai H, Arai T, Okada M, et al: MK-1775,
a small molecule Wee1 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor efficacy of
various DNA-damaging agents, including 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol
Ther. 9:514–522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Kreahling JM, Gemmer JY, Reed D, Letson D,
Bui M and Altiok S: MK1775, a selective Wee1 inhibitor, shows
single-agent antitumor activity against sarcoma cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 11:174–182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Saito YD, Jensen AR, Salgia R and Posadas
EM: Fyn: a novel molecular target in cancer. Cancer. 116:1629–1637.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Chen Z-Y, Cai L, Bie P, et al: Roles of
Fyn in pancreatic cancer metastasis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
25:293–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Koike K, Kogawa K, Takayama T, et al:
Enhanced expression of type IV collagen-binding protein (p29) in
Fyn-transfected murine fibrosarcoma cells. Jpn J Cancer Res.
93:1090–1099. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|