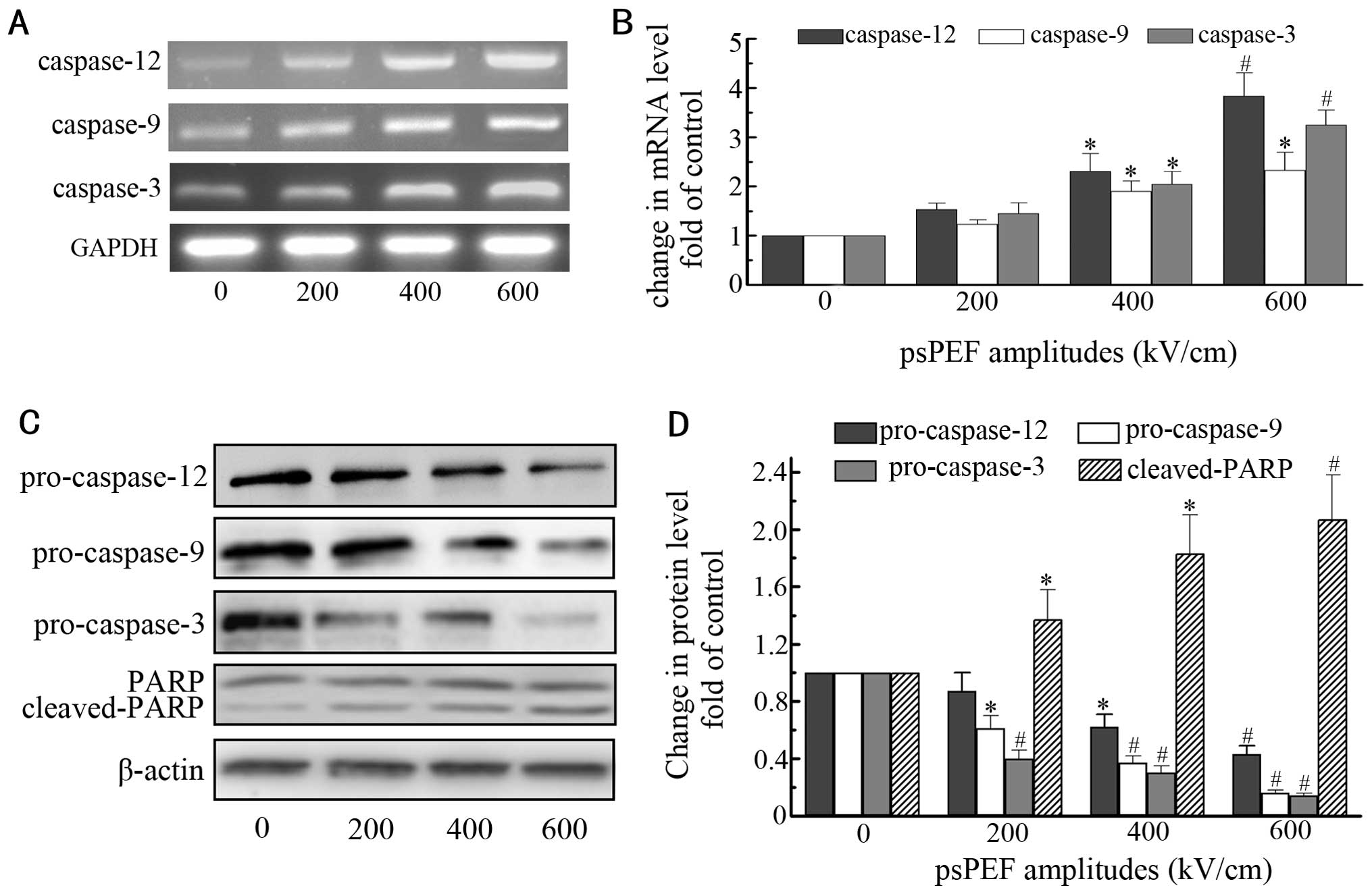
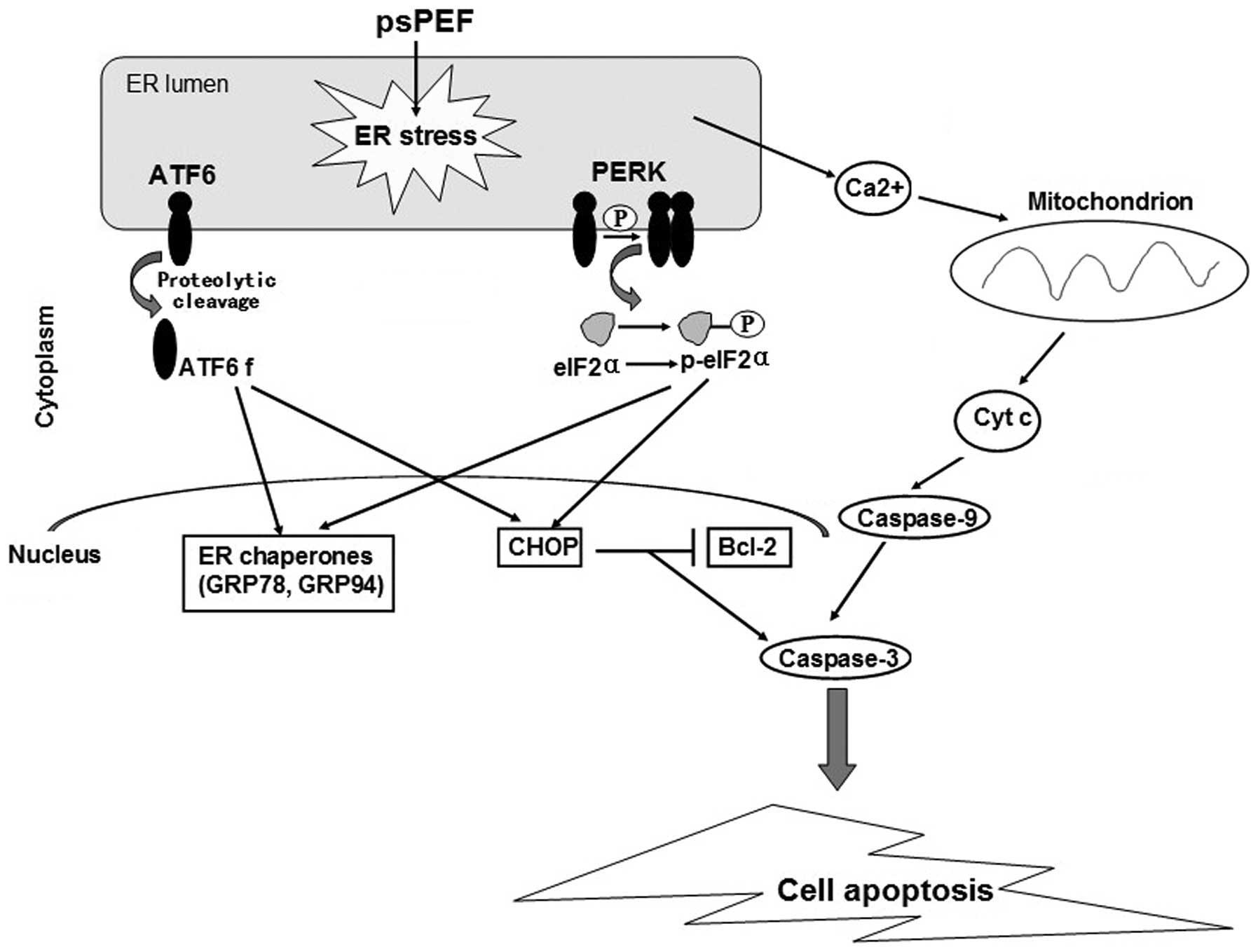
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Karimi Zarchi M, Mousavi A, Malekzadeh M,
Dehghani A, Behnamfar Z and Godarzi A: Conservative treatment in
young patients with cervical cancer: a review. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 11:589–594. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Okino M, Tomie H, Kanesada H, et al:
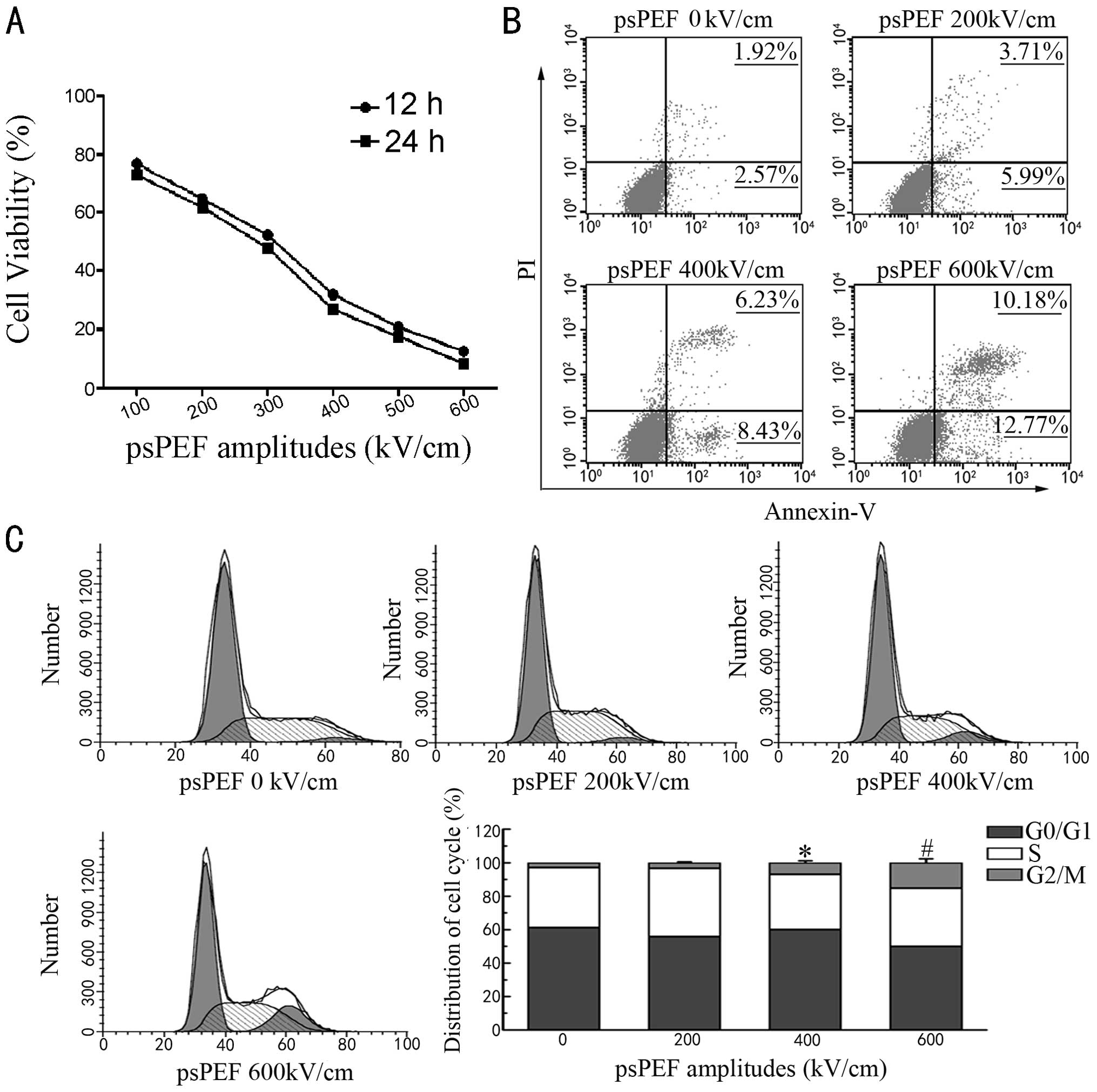
Optimal electric conditions in electrical impulse chemotherapy. Jpn
J Cancer Res. 83:1095–1101. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weaver JC: Electroporation: a general
phenomenon for manipulating cells and tissues. J Cell Biochem.
51:426–435. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hofmann GA, Dev SB, Dimmer S, et al:
Electroporation therapy: a new approach for the treatment of head
and neck cancer. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 46:752–759. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dev SB, Rabussay DP, Widera G, et al:
Medical applications of electroporation. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci.
28:206–223. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Stacey M, Stickley J, Fox P, Statler V,
Schoenbach K, Beebe SJ and Buescher S: Differential effects in
cells exposed to ultra-short, high intensity electric fields: cell
survival, DNA damage and cell cycle analysis. Mutat Res. 542:65–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Craviso GL, Chatterjee P, Maalouf G, et
al: Nanosecond electric pulse-induced increase in intracellular
calcium in adrenal chromaffin cells triggers calcium-dependent
catecholamine release. IEEE Trans Dielect El In. 16:1294–1301.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Stacey M, Fox P, Buescher S and Kolb J:
Nanosecond pulsed electric field induced cytoskeleton, nuclear
membrane and telomere damage adversely impact cell survival.
Bioelectrochemistry. 82:131–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis
and treatment of disease. Science. 267:1456–1462. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thorburn A: Death receptor-induced cell
killing. Cell Signal. 16:139–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li UX, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R and
Wang X: Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts:
requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 86:147–157. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yokouchi M, Hiramatsu N, Hayakawa K, Kasai
A, Takano Y, Yao J and Kitamura M: Atypical, bidirectional
regulation of cadmiuminduced apoptosis via distinct signaling of
unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ. 14:1467–1474. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boyce M and Yuan J: Cellular response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death
Differ. 13:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
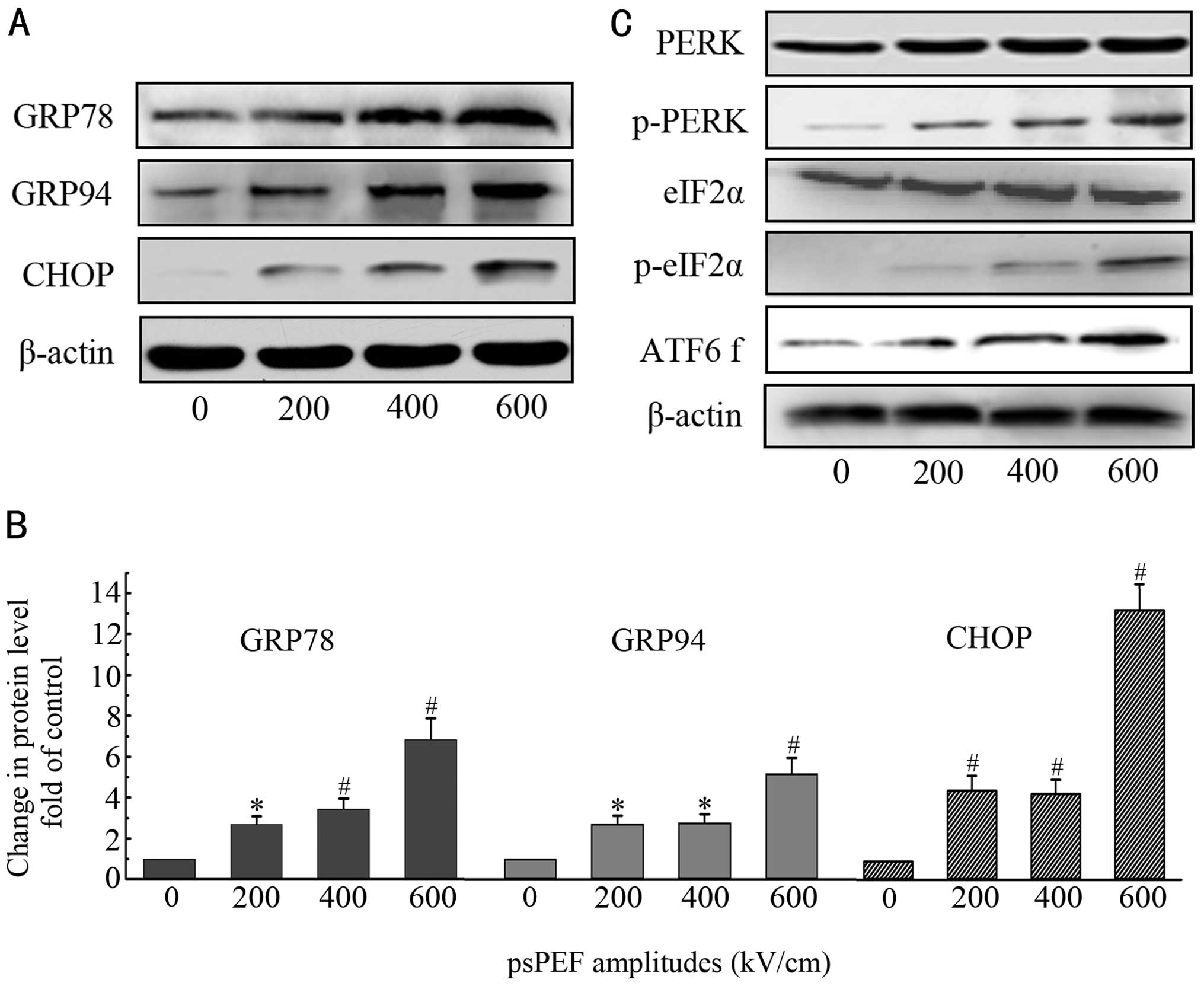
Yamaguchi H and Wang HG: CHOP is involved
in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5
expression in human carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 279:45495–45502.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moenner M, Pluquet O, Bouchecareilh M and
Chevet E: Integrated endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in
cancer. Cancer Res. 67:10631–10634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schroder M and Kaufman RJ: ER stress and
the unfolded protein response. Mutat Res. 569:29–63. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao CG, Guo F, Wang J, Li CX, Wen YQ and
Tang JY: Study of tumor cell mitochondrial apoptosis signaling
pathway induced by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Chin J Biomed
Eng. 29:724–730. 2010.
|
|
20
|
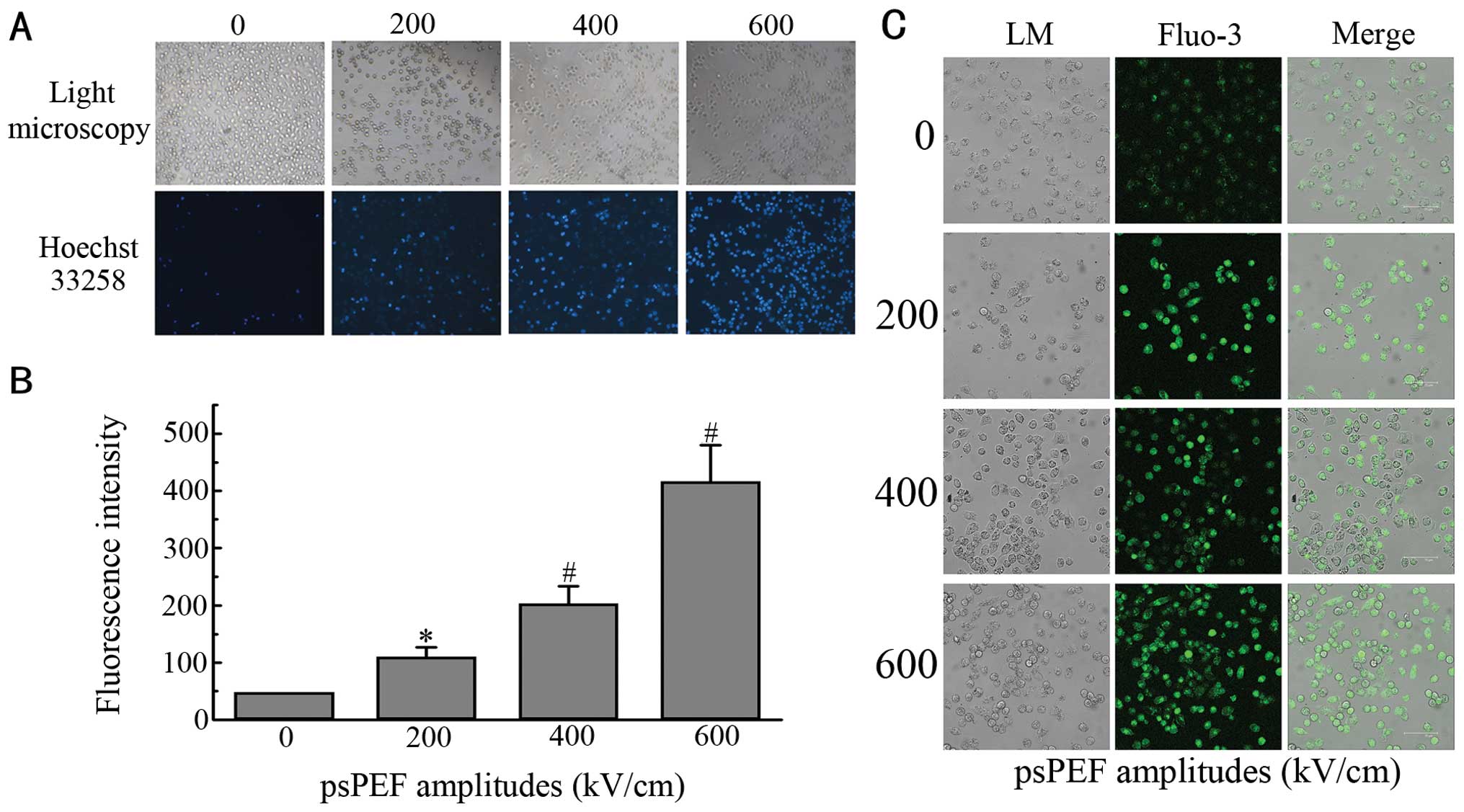
Liu LJ, Zhao DY, Wang J, Yao CG, Sun CX
and Tang JY: Ca2+ is an important mediator of nanosecond
steep pulse-induced apoptosis in human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells.
J Southern Med Univ. 31:772–776. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Tang JY, Wu XJ, Yao CG, et al: The effects
of nanosecond steep pulse on apoptosis and the concentration of
intracellular calcium of human ovarian carcinoma cell Line SKOV3.
Prog Obstet Gynecol. 16:827–831. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Hua YY, Wang XS, Zhang Y, Yao CG, Zhang XM
and Xiong ZA: Intense picosecond pulsed electric fields induce
apoptosis through a mitochondrial-mediated pathway in HeLa cells.
Mol Med Rep. 5:981–987. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hamanaka RB, Bennett BS, Cullinan SB and
Diehl JA: PERK and GCN2 contribute to eIF2alpha phosphorylation and
cell cycle arrest after activation of the unfolded protein response
pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 16:5493–5501. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Davenport EL, Moore HE, Dunlop AS, Sharp
SY, Workman P, Morgan GJ and Davies FE: Heat shock protein
inhibition is associated with activation of the unfolded protein
response pathway in myeloma plasma cells. Blood. 110:2641–2649.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
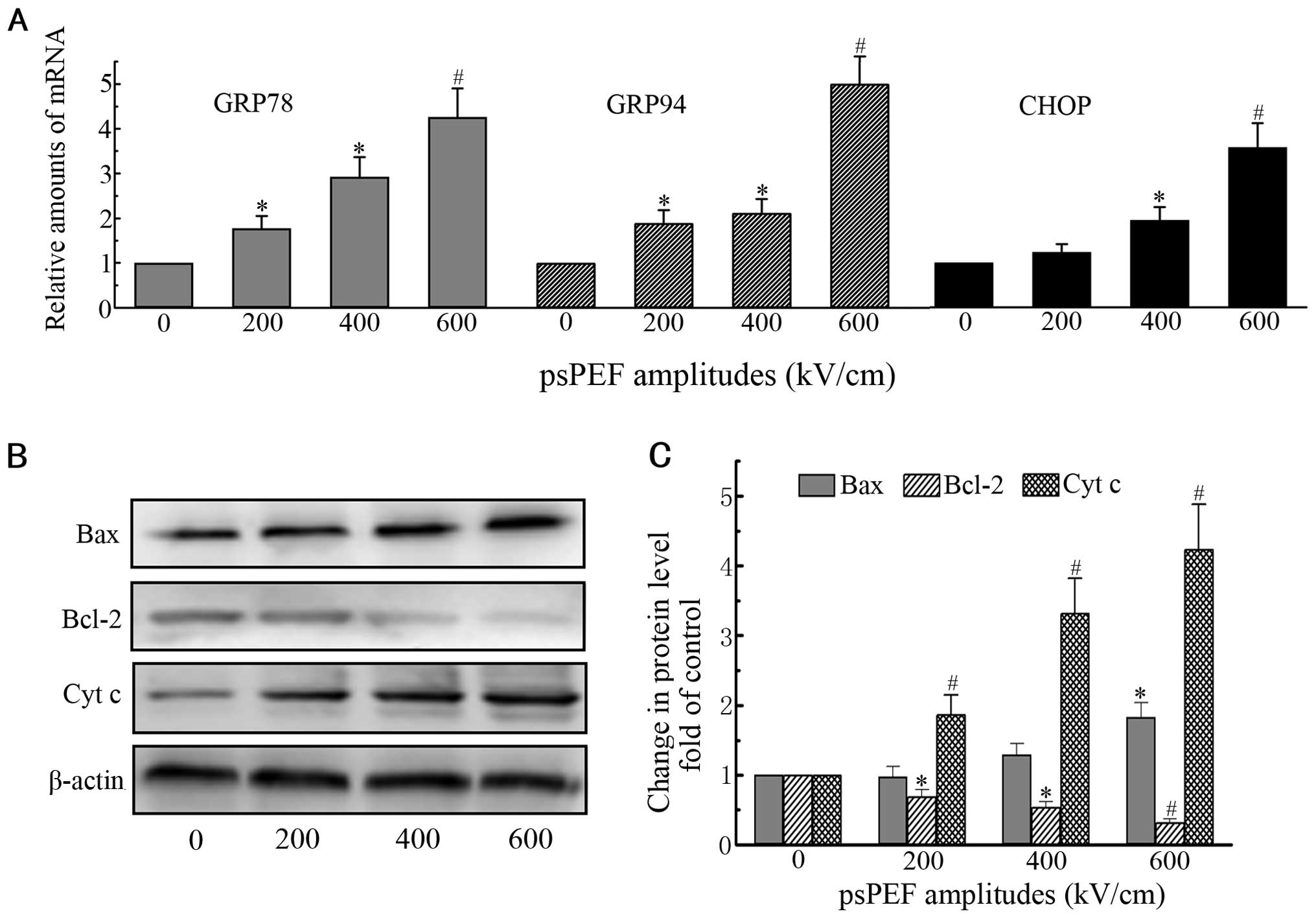
Zhang D and Armstrong JS: Bax and the
mitochondrial permeability transition cooperate in the release of
cytochrome c during endoplasmic reticulum-stress-induced apoptosis.
Cell Death Differ. 14:703–715. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Crow MT, Mani K, Nam YJ and Kitsis RN: The
mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ
Res. 95:957–970. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Degli Esposti M and Dive C: Mitochondrial
membrane permeabilisation by Bax/Bak. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
304:455–461. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou J, Zhang S, Ong CN and Shen HM:
Critical role of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members in
andrographolide-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 72:132–144. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schlegel J, Peters I, Orrenius S, et al:
CPP32/apopain is a key interleukin 1 beta converting enzyme-like
protease involved in Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
271:1841–1844. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Baum CE, Stone AP and Tyo JS:
Ultra-Wideband, Short-Pulse Electromagnetics 8. Springer Press; New
York, NY: 2007
|
|
31
|
Bajracharya C, Shu X, Baum CE and
Schoenbach KH: Target detection with impulse radiating antenna.
IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag Lett. 10:496–499. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Beebe SJ, Fox PM, Rec LJ, Willis EL and
Schoenbach KH: Nanosecond, high-intensity pulsed electric fields
induce apoptosis in human cells. FASEB J. 17:1493–1495.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rao RV, Ellerby HM and Bredesen DE:
Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program.
Cell Death Differ. 11:372–380. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decision. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ni M and Lee AS: ER chaperones in
mammalian development and human diseases. FEBS Lett. 581:3641–3651.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw
TY and Holbrook NJ: Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic
reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl-2 and perturbing the
cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1249–1259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang JC and Cortopassi GA: Induction of
the mitochondrial permeability transition causes release of the
apoptogenic factor cytochrome c. Free Radic Biol Med. 24:624–631.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nakagawa T and Yuan J: Cross-talk between
two cysteine protease families. Activation of caspase-12 by calpain
in apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 150:887–894. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boitier E, Rea R and Duchen MR:
Mitochondria exert a negative feedback on the propagation of
intracellular Ca2+ waves in rat cortical astrocytes. J
Cell Biol. 145:795–808. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA: Apoptosis.
Life and death decisions. Science. 299:214–215. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|