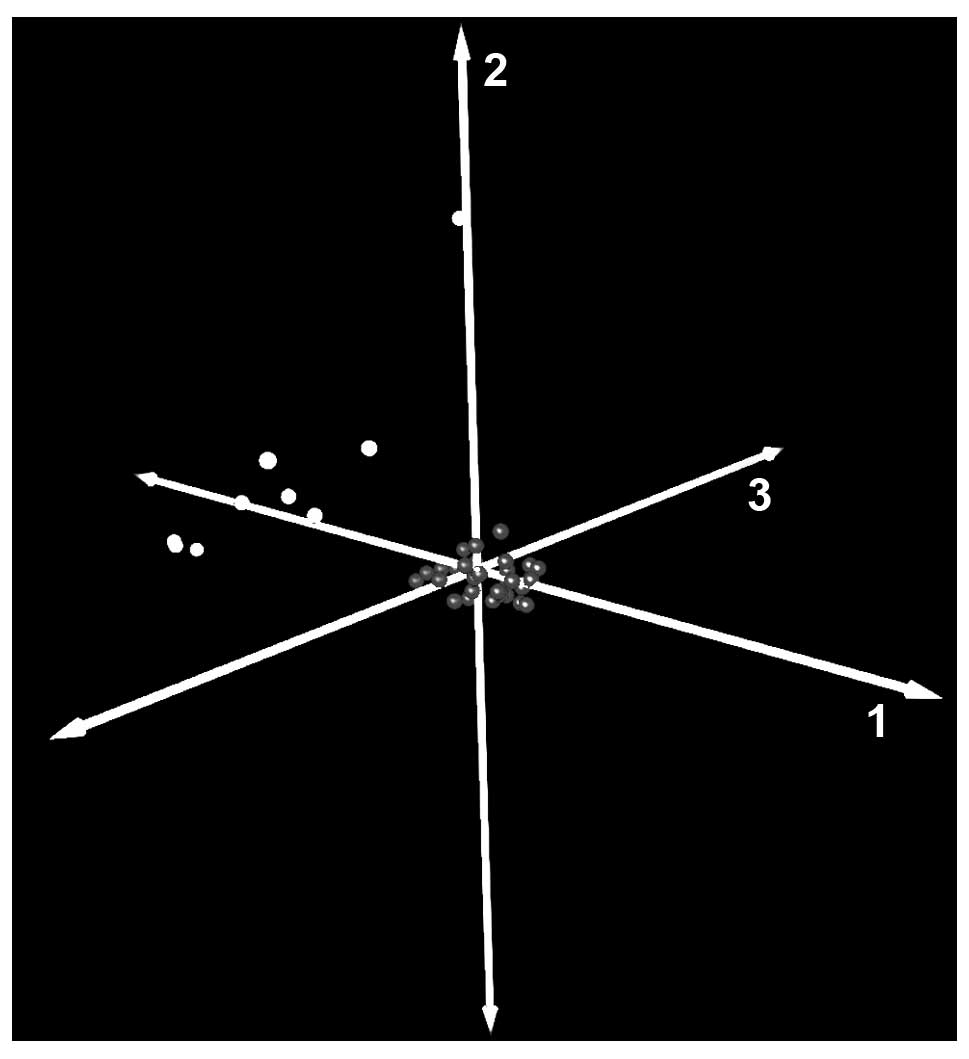
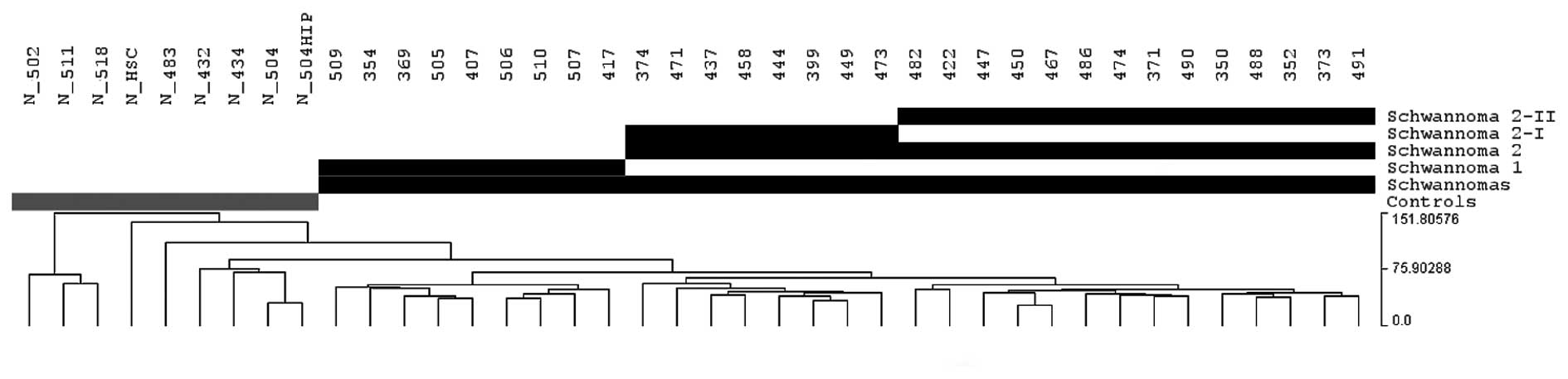
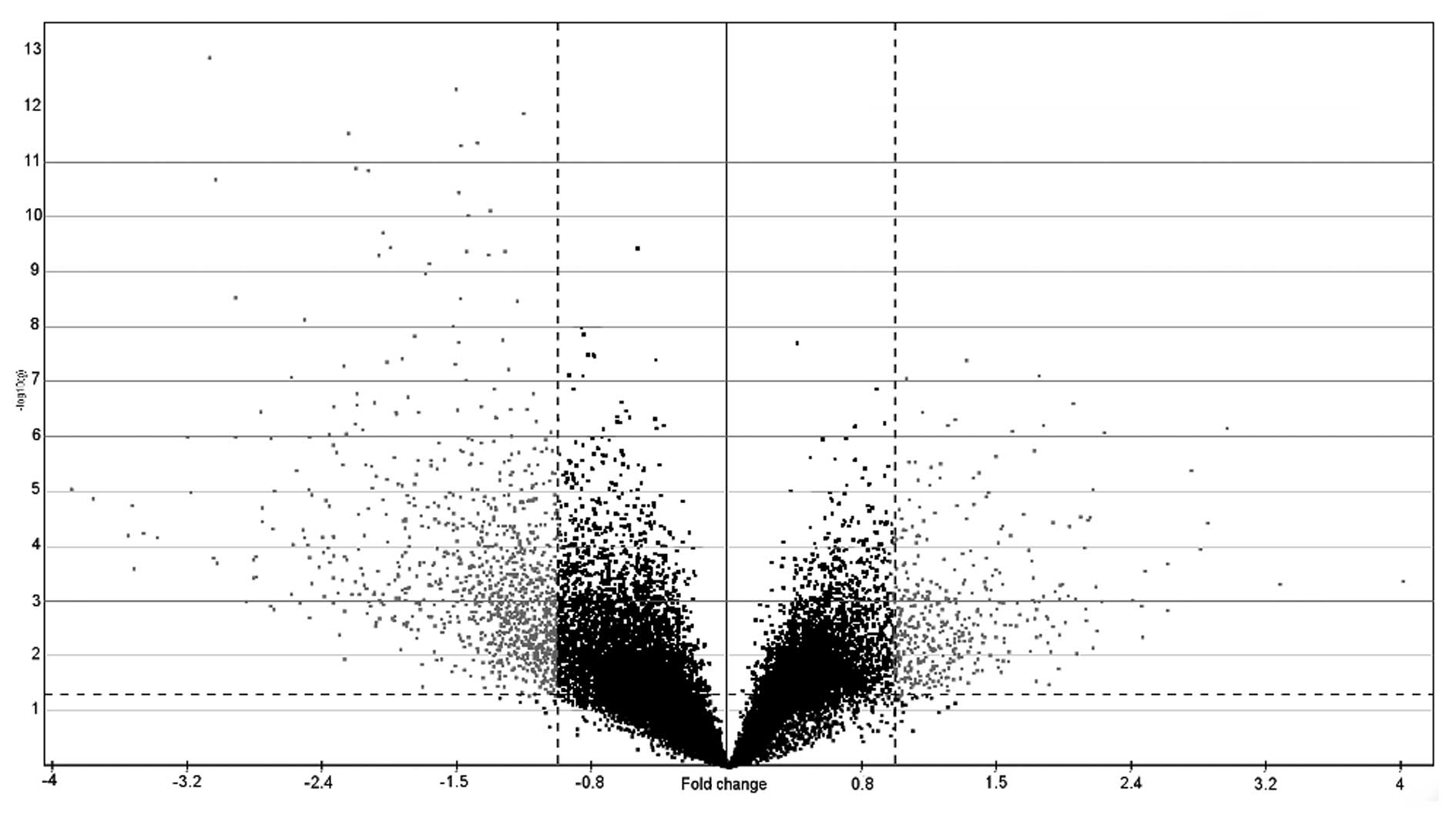
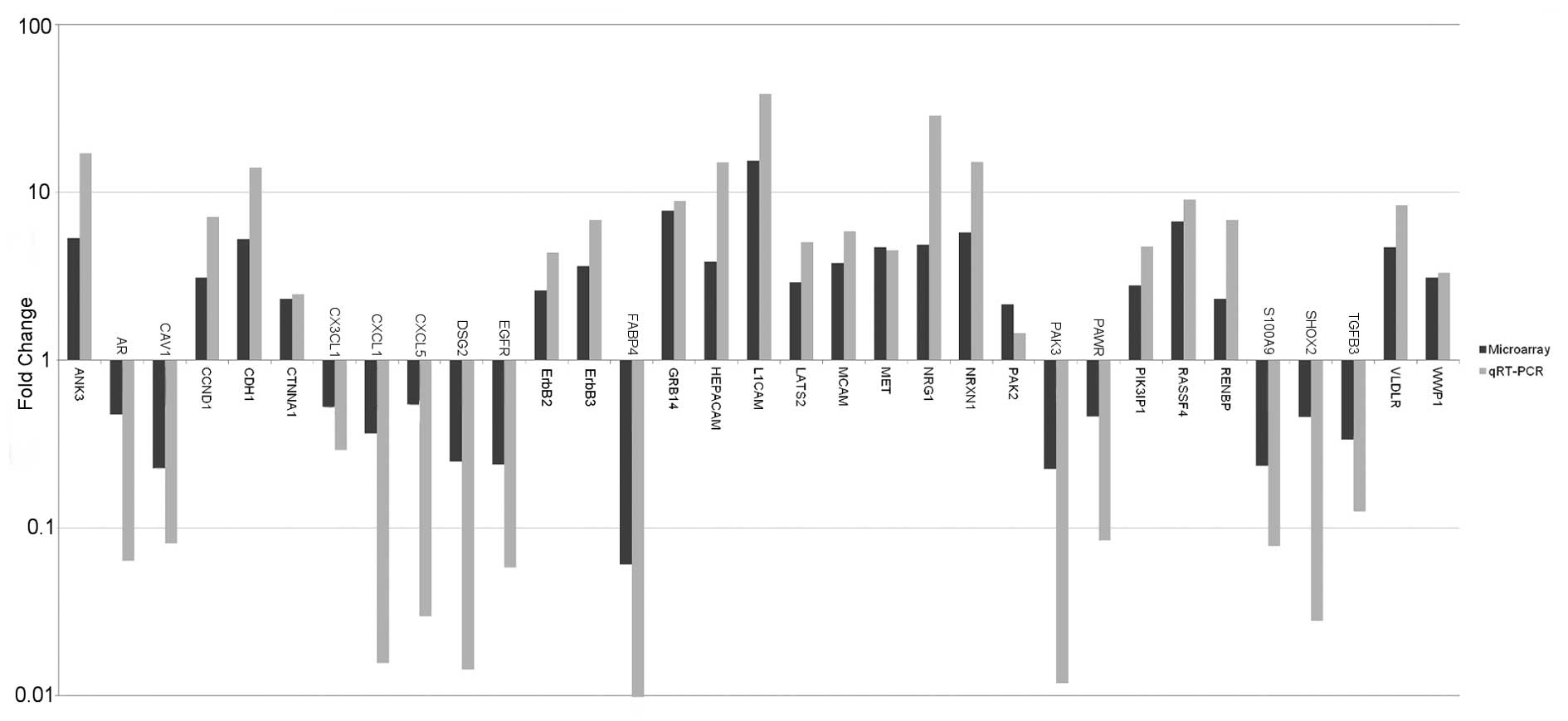
|
1
|
Roosli C, Linthicum FH Jr, Cureoglu S and
Merchant SN: What is the site of origin of cochleovestibular
schwannomas? Audiol Neurootol. 17:121–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Evans DG, Sainio M and Baser ME:
Neurofibromatosis type 2. J Med Genet. 37:897–904. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rouleau GA, Merel P, Lutchman M, et al:
Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing
protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2. Nature. 363:515–521.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hadfield KD, Smith MJ, Urquhart JE, et al:
Rates of loss of heterozygosity and mitotic recombination in NF2
schwannomas, sporadic vestibular schwannomas and schwannomatosis
schwannomas. Oncogene. 29:6216–6221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Xu L,
Gonzalez-Agosti C, et al: Universal absence of merlin, but not
other ERM family members, in schwannomas. Am J Pathol.
151:1649–1654. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yi C, Troutman S, Fera D,
Stemmer-Rachamimov A, et al: A tight junction-associated
Merlin-angiomotin complex mediates Merlin’s regulation of mitogenic
signaling and tumor suppressive functions. Cancer Cell. 19:527–540.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
James MF, Han S, Polizzano C, et al:
NF2/merlin is a novel negative regulator of mTOR complex 1, and
activation of mTORC1 is associated with meningioma and schwannoma
growth. Mol Cell Biol. 29:4250–4261. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamaratoglu F, Willecke M, Kango-Singh M,
et al: The tumour-suppressor genes NF2/Merlin and Expanded act
through Hippo signalling to regulate cell proliferation and
apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 8:27–36. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okada T, Lopez-Lago M and Giancotti FG:
Merlin/NF-2 mediates contact inhibition of growth by suppressing
recruitment of Rac to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol.
171:361–371. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lallemand D, Manent J, Couvelard A, et al:
Merlin regulates transmembrane receptor accumulation and signaling
at the plasma membrane in primary mouse Schwann cells and in human
schwannomas. Oncogene. 28:854–865. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Curto M, Cole BK, Lallemand D, Liu CH and
McClatchey AI: Contact-dependent inhibition of EGFR signaling by
Nf2/Merlin. J Cell Biol. 177:893–903. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li W, You L, Cooper J, et al: Merlin/NF2
suppresses tumorigenesis by inhibiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase
CRL4(DCAF1) in the nucleus. Cell. 140:477–490. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li W, Cooper J, Karajannis MA and
Giancotti FG: Merlin: a tumour suppressor with functions at the
cell cortex and in the nucleus. EMBO Rep. Feb 21–2012.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Morrow KA, Das S, Metge BJ, et al: Loss of
tumor suppressor Merlin in advanced breast cancer is due to
post-translational regulation. J Biol Chem. 286:40376–40385. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leone PE, Bello MJ, Mendiola M, et al:
Allelic status of 1p, 14q, and 22q and NF2 gene mutations in
sporadic schwannomas. Int J Mol Med. 1:889–892. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Warren C, James LA, Ramsden RT, Wallace A,
Baser ME, Varley JM and Evans DG: Identification of recurrent
regions of chromosome loss and gain in vestibular schwannomas using
comparative genomic hybridisation. J Med Genet. 40:802–806. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kino T, Takeshima H, Nakao M, et al:
Identification of the cis-acting region in the NF2 gene promoter as
a potential target for mutation and methylation-dependent silencing
in schwannoma. Genes Cells. 6:441–454. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gonzalez-Gomez P, Bello MJ, Alonso ME, et
al: CpG island methylation in sporadic and neurofibromatis type
2-associated schwannomas. Clin Cancer Res. 9:5601–5606.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kullar PJ, Pearson DM, Malley DS, Collins
VP and Ichimura K: CpG island hypermethylation of the
neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) gene is rare in sporadic vestibular
schwannomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 36:505–514. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koutsimpelas D, Ruerup G, Mann WJ and
Brieger J: Lack of neurofibromatosis type 2 gene promoter
methylation in sporadic vestibular schwannomas. ORL J
Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 74:33–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JD, Kwon TJ, Kim UK and Lee WS:
Genetic and epigenetic alterations of the NF2 gene in sporadic
vestibular schwannomas. PLoS One. 7:e304182012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bello MJ, Martinez-Glez V,
Franco-Hernandez C, et al: DNA methylation pattern in 16
tumor-related genes in schwannomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet.
172:84–86. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Welling DB, Lasak JM, Akhmametyeva E,
Ghaheri B and Chang LS: cDNA microarray analysis of vestibular
schwannomas. Otol Neurotol. 23:736–748. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cayé-Thomasen P, Borup R, Stangerup SE,
Thomsen J and Nielsen FC: Deregulated genes in sporadic vestibular
schwannomas. Otol Neurotol. 31:256–266. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Aarhus M, Bruland O, Sætran HA, Mork SJ,
Lund-Johansen M and Knappskog PM: Global gene expression profiling
and tissue microarray reveal novel candidate genes and
down-regulation of the tumor suppressor gene CAV1 in sporadic
vestibular schwannomas. Neurosurgery. 67:998–1019. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lassaletta L, Patrón M, Del Río L, Alfonso
C, Roda JM, Rey JA and Gavilan J: Cyclin D1 expression and
histopathologic features in vestibular schwannomas. Otol Neurotol.
28:939–941. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gonzalez-Roca E, Garcia-Albéniz X,
Rodriguez-Mulero S, Gomis RR, Kornacker K and Auer H: Accurate
expression profiling of very small cell populations. PLoS One.
5:e144182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope
LM, Hobbs B and Speed TP: Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe
level data. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:e152003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Johnson WE, Li C and Rabinovic A:
Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using
empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 8:118–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen C, Grennan K, Badner J, Zhang D,
Gershon E, Jin L and Liu C: Removing batch effects in analysis of
expression microarray data: an evaluation of six batch adjustment
methods. PLoS One. 6:e172382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
MAQC Consortium; Shi L, Reid LH, Jones WD,
et al: The MicroArray Quality Control (MAQC) project shows inter-
and intraplatform reproducibility of gene expression measurements.
Nat Biotechnol. 24:1151–1161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang X, De la Cruz O, Pinto JM, Nicolae
D, Firestein S and Gilad Y: Characterizing the expression of the
human olfactory receptor gene family using a novel DNA microarray.
Genome Biol. 8:R862007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, et al: TM4: a
free, open-source system for microarray data management and
analysis. Biotechniques. 34:374–378. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Saeed AI, Bhagabati NK, Braisted JC, et
al: TM4 microarray software suite. Meth Enzymol. 411:134–193. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Duncan D, Prodduturi N and Zhang B:
WebGestalt2: an updated and expanded version of the Web-based Gene
Set Analysis Toolkit. BMC Bioinformatics. 11:P102010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
39
|
Canzian F, Salovaara R, Hemminki A, Kristo
P, Chadwick RB, Aaltonen LA and de la Chapelle A: Semiautomated
assessment of loss of heterozygosity and replication error in
tumors. Cancer Res. 56:3331–3337. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Abruzzo LV, Lee KY, Fuller A, Silverman A,
Keating MJ, Medeiros LJ and Coombes KR: Validation of
oligonucleotide microarray data using microfluidic low-density
arrays: a new statistical method to normalize real-time RT-PCR
data. Biotechniques. 38:785–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Frohnert PW, Stonecypher MS and Carroll
SL: Constitutive activation of the neuregulin-1/ErbB receptor
signaling pathway is essential for the proliferation of a
neoplastic Schwann cell line. Glia. 43:104–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stonecypher MS, Chaudhury AR, Byer SJ and
Carroll SL: Neuregulin growth factors and their ErbB receptors form
a potential signaling network for schwannoma tumorigenesis. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 65:162–175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hansen MR, Roehm PC, Chatterjee P and
Green SH: Constitutive neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling contributes to
human vestibular schwannoma proliferation. Glia. 53:593–600. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Newbern J and Birchmeier C: Nrg1/ErbB
signaling networks in Schwann cell development and myelination.
Semin Cell Dev Biol. 21:922–928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Houshmandi SS, Emnett RJ, Giovannini M and
Gutmann DH: The neurofibromatosis 2 protein, merlin, regulates
glial cell growth in an ErbB2- and Src-dependent manner. Mol Cell
Biol. 29:1472–1486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tao Y, Dai P, Liu Y, Marchetto S, Xiong
WC, Borg JP and Mei L: Erbin regulates NRG1 signaling and
myelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:9477–9482. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wilkes MC, Repellin CE, Hong M, Bracamonte
M, Penheiter SG, Borg JP and Leof EB: Erbin and the NF2 tumor
suppressor Merlin cooperatively regulate cell-type-specific
activation of PAK2 by TGF-beta. Dev Cell. 16:433–444. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Löttrich M, Mawrin C, Chamaon K, Kirches
E, Dietzmann K and Freigang B: Expression of transforming growth
factor-beta receptor type 1 and type 2 in human sporadic vestibular
Schwannoma. Pathol Res Pract. 203:245–249. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cole BK, Curto M, Chan AW and McClatchey
AI: Localization to the cortical cytoskeleton is necessary for
Nf2/merlin-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor silencing.
Mol Cell Biol. 28:1274–1284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ammoun S, Flaiz C, Ristic N, Schuldt J and
Hanemann CO: Dissecting and targeting the growth factor-dependent
and growth factor-independent extracellular signal-regulated kinase
pathway in human schwannoma. Cancer Res. 68:5236–5245. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bartolami S, Augé C, Travo C, Ventéo S,
Knipper M and Sans A: Vestibular Schwann cells are a distinct
subpopulation of peripheral glia with specific sensitivity to
growth factors and extracellular matrix components. J Neurobiol.
57:270–290. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Prayson RA, Yoder BJ and Barnett GH:
Epidermal growth factor receptor is not amplified in schwannomas.
Ann Diagn Pathol. 11:326–329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wickremesekera A, Hovens CM and Kaye AH:
Expression of ErbB-1 and 2 in vestibular schwannomas. J Clin
Neurosci. 14:1199–1206. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Doherty JK, Ongkeko W, Crawley B, Andalibi
A and Ryan AF: ErbB and Nrg: potential molecular targets for
vestibular schwannoma pharmacotherapy. Otol Neurotol. 29:50–57.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhu H, Yue J, Pan Z, et al: Involvement of
Caveolin-1 in repair of DNA damage through both homologous
recombination and non-homologous end joining. PLoS One.
5:e120552010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cerezo A, Guadamillas MC, Goetz JG,
Sánchez-Perales S, Klein E, Assoian RK and del Pozo MA: The absence
of caveolin-1 increases proliferation and anchorage-independent
growth by a Rac-dependent, Erk-independent mechanism. Mol Cell
Biol. 29:5046–5059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Brennan D, Peltonen S, Dowling A, et al: A
role for caveolin-1 in desmoglein binding and desmosome dynamics.
Oncogene. 31:1636–1648. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ciocca DR, Cuello-Carrión FD, Natoli AL,
Restall C and Anderson RL: Absence of caveolin-1 alters heat shock
protein expression in spontaneous mammary tumors driven by
Her-2/neu expression. Histochem Cell Biol. 137:187–194. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chung Moh M, Hoon Lee L and Shen S:
Cloning and characterization of hepaCAM, a novel Ig-like cell
adhesion molecule suppressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Hepatol. 42:833–841. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Moh MC, Tian Q, Zhang T, Lee LH and Shen
S: The immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule hepaCAM modulates
cell adhesion and motility through direct interaction with the
actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Physiol. 219:382–391. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Moh MC, Lee LH, Zhang T and Shen S:
Interaction of the immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule
hepaCAM with caveolin-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 378:755–760.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hung G, Colton J, Fisher L, Oppenheimer M,
Faudoa R, Slattery W and Linthicum F: Immunohistochemistry study of
human vestibular nerve schwannoma differentiation. Glia.
38:363–370. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hortsch M: The L1 family of neural cell
adhesion molecules: old proteins performing new tricks. Neuron.
17:587–593. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Fogel M, Gutwein P, Mechtersheimer S, et
al: L1 expression as a predictor of progression and survival in
patients with uterine and ovarian carcinomas. Lancet. 362:869–875.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tilley WD, Buchanan G, Hickey TE and
Bentel JM: Mutations in the androgen receptor gene are associated
with progression of human prostate cancer to androgen independence.
Clin Cancer Res. 2:277–285. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lu ML, Schneider MC, Zheng Y, Zhang X and
Richie JP: Caveolin-1 interacts with androgen receptor. A positive
modulator of androgen receptor mediated transactivation. J Biol
Chem. 276:13442–13451. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bryant KG, Camacho J, Jasmin JF, et al:
Caveolin-1 overexpression enhances androgen-dependent growth and
proliferation in the mouse prostate. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
43:1318–1329. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gao S, Wang H, Lee P, et al: Androgen
receptor and prostate apoptosis response factor-4 target the c-FLIP
gene to determine survival and apoptosis in the prostate gland. J
Mol Endocrinol. 36:463–483. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Vetterkind S, Lee E, Sundberg E, Poythress
RH, Tao TC, Preuss U and Morgan KG: Par-4: a new activator of
myosin phosphatase. Mol Biol Cell. 21:1214–1224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cook J, Krishnan S, Ananth S, et al:
Decreased expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Par-4 in renal
cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 18:1205–1208. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kögel D, Reimertz C, Mech P, et al:
Dlk/ZIP kinase-induced apoptosis in human medulloblastoma cells:
requirement of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Br J Cancer.
85:1801–1808. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
García-Cao I, Duran A, Collado M, et al:
Tumour-suppression activity of the proapoptotic regulator Par4.
EMBO Rep. 6:577–583. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Goswami A, Burikhanov R, de Thonel A, et
al: Binding and phosphorylation of par-4 by akt is essential for
cancer cell survival. Mol Cell. 20:33–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Jacob A, Lee TX, Neff BA, Miller S,
Welling B and Chang LS: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway
activation in human vestibular schwannoma. Otol Neurotol. 29:58–68.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Krasilnikov MA: Phosphatidylinositol-3
kinase dependent pathways: the role in control of cell growth,
survival, and malignant transformation. Biochemistry (Mosc).
65:59–67. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhu Z, He X, Johnson C, et al: PI3K is
negatively regulated by PIK3IP1, a novel p110 interacting protein.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 358:66–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Organ SL and Tsao MS: An overview of the
c-MET signaling pathway. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 3(Suppl 1): S7–S19.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Moriyama T, Kataoka H, Kawano H, et al:
Comparative analysis of expression of hepatocyte growth factor and
its receptor, c-met, in gliomas, meningiomas and schwannomas in
humans. Cancer Lett. 124:149–155. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cantiani L, Manara MC, Zucchini C, et al:
Caveolin-1 reduces osteosarcoma metastases by inhibiting c-Src
activity and met signaling. Cancer Res. 67:7675–7685. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Artigiani S, Conrotto P, Fazzari P, et al:
Plexin-B3 is a functional receptor for semaphorin 5A. EMBO Rep.
5:710–714. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Mirsky R, Woodhoo A, Parkinson DB,
Arthur-Farraj P, Bhaskaran A and Jessen KR: Novel signals
controlling embryonic Schwann cell development, myelination and
dedifferentiation. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 13:122–135. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Takahashi M and Osumi N: Identification of
a novel type II classical cadherin: rat cadherin19 is expressed in
the cranial ganglia and Schwann cell precursors during development.
Dev Dyn. 232:200–208. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Martinez-Glez V, Franco-Hernandez C,
Alvarez L, et al: Meningiomas and schwannomas: molecular subgroup
classification found by expression arrays. Int J Oncol. 34:493–504.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Bottos A, Destro E, Rissone A, et al: The
synaptic proteins neurexins and neuroligins are widely expressed in
the vascular system and contribute to its functions. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:20782–20787. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|