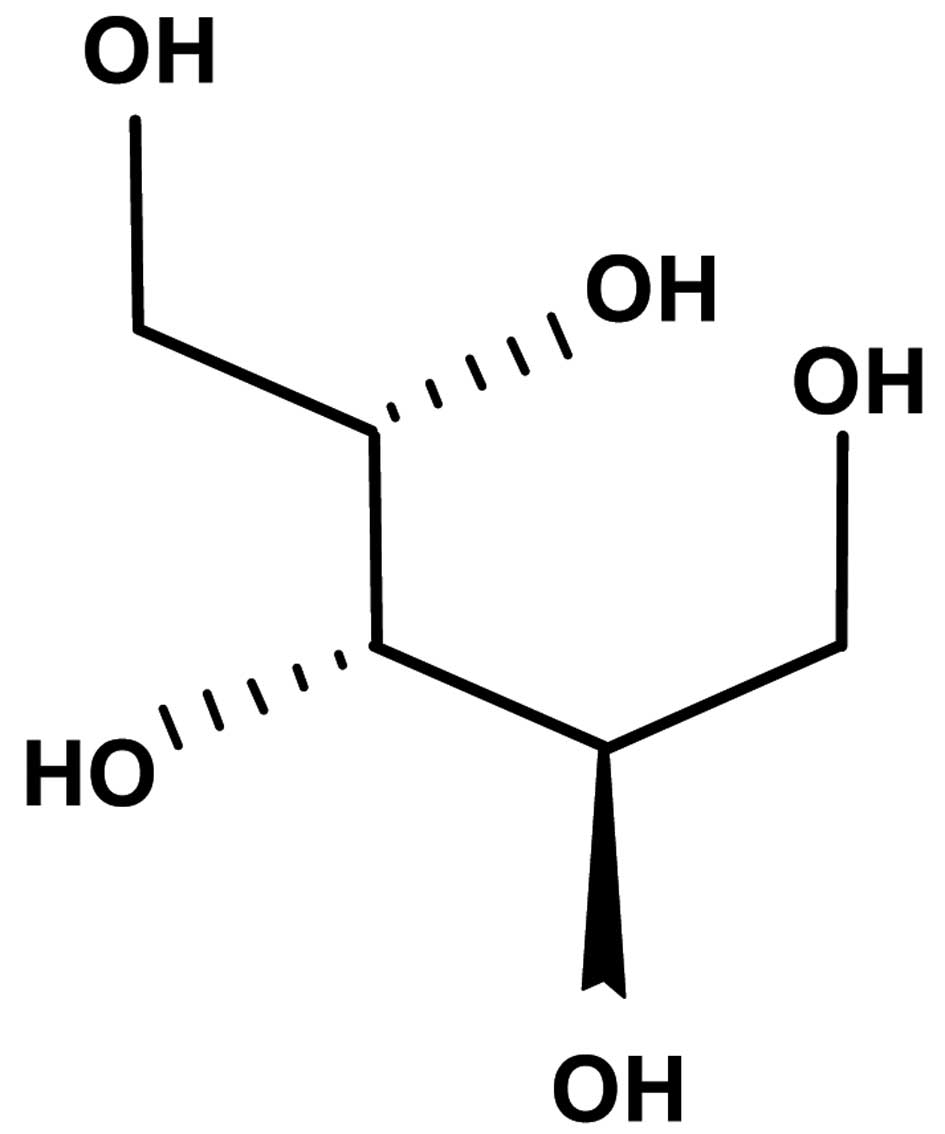
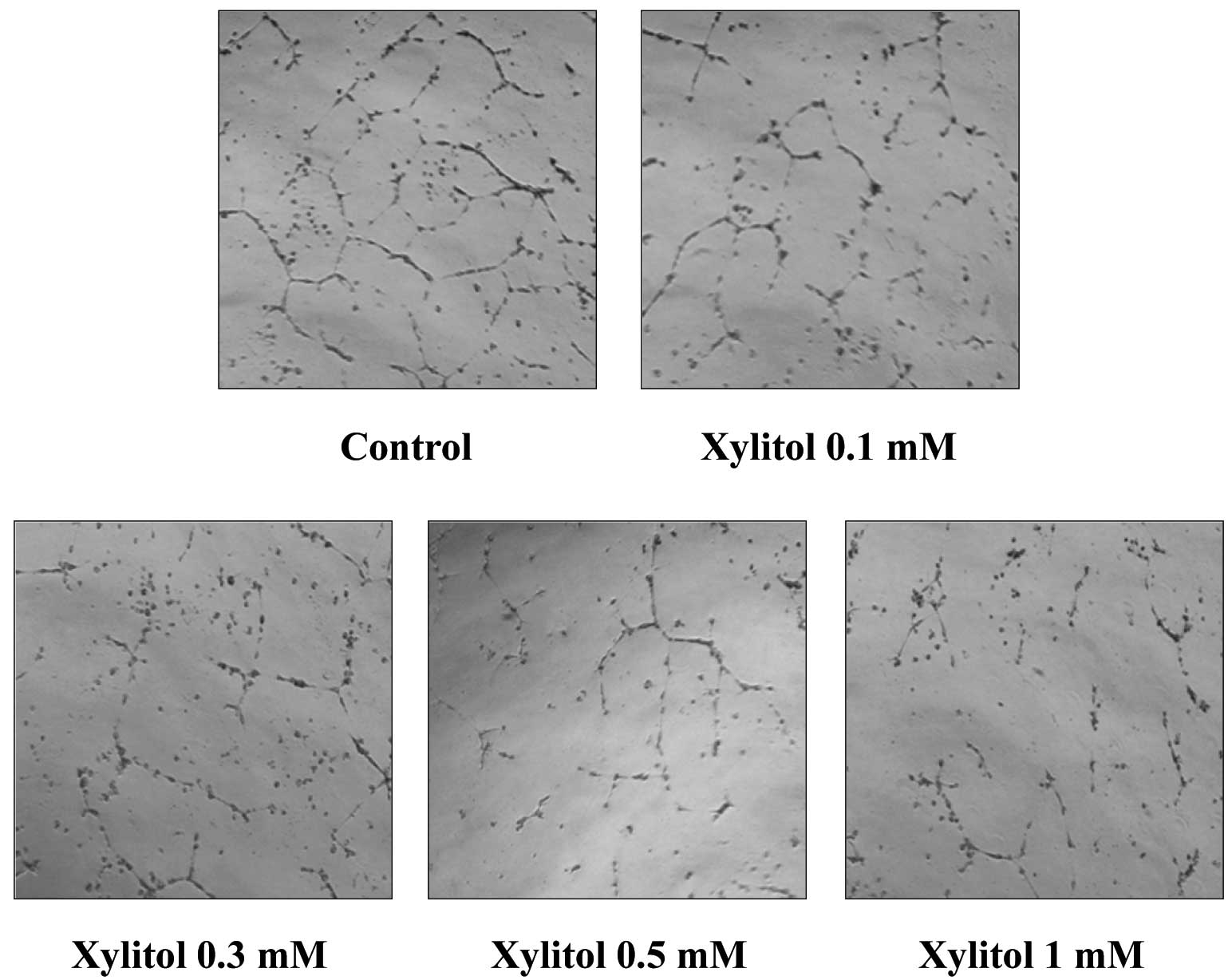
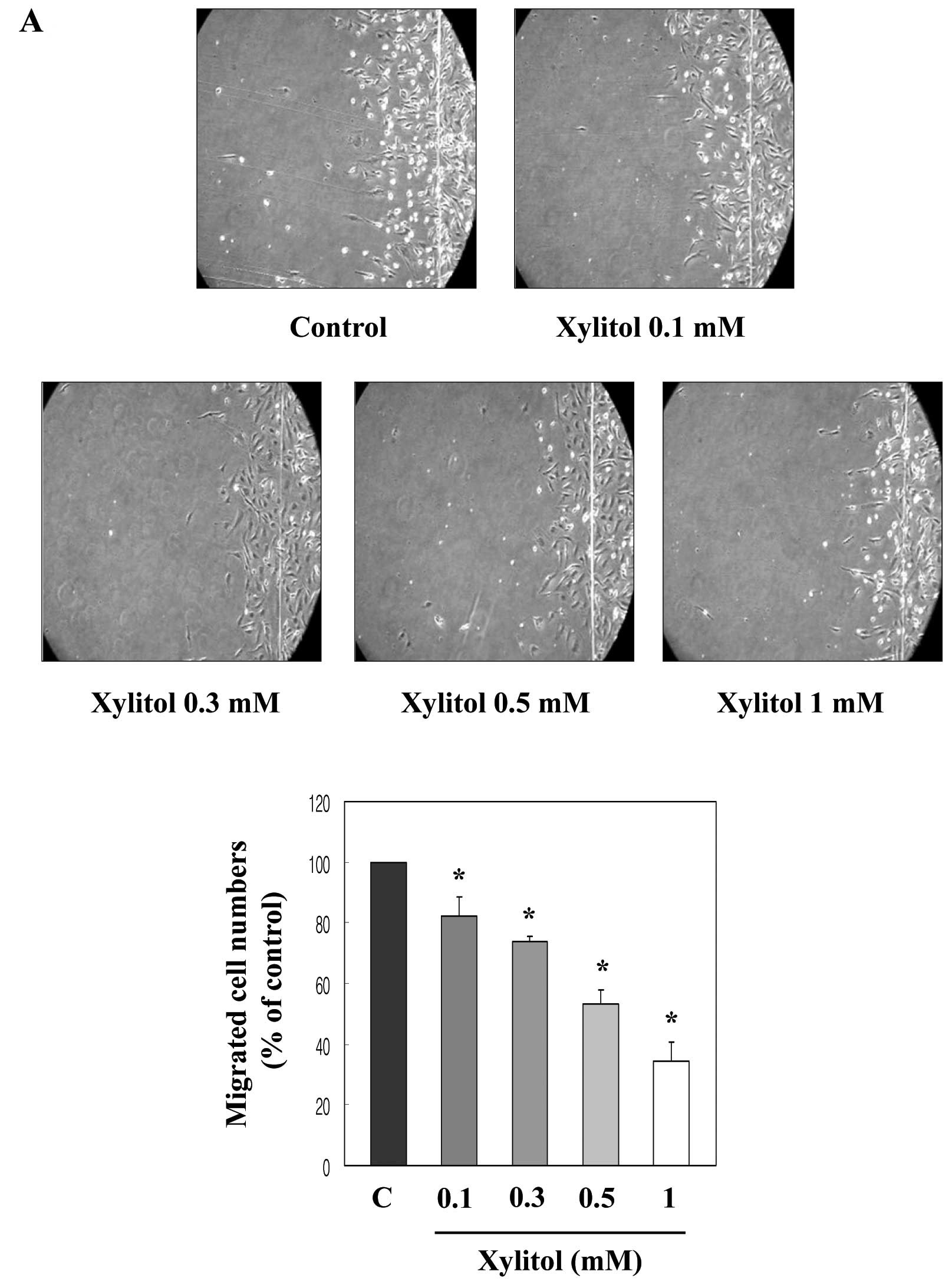
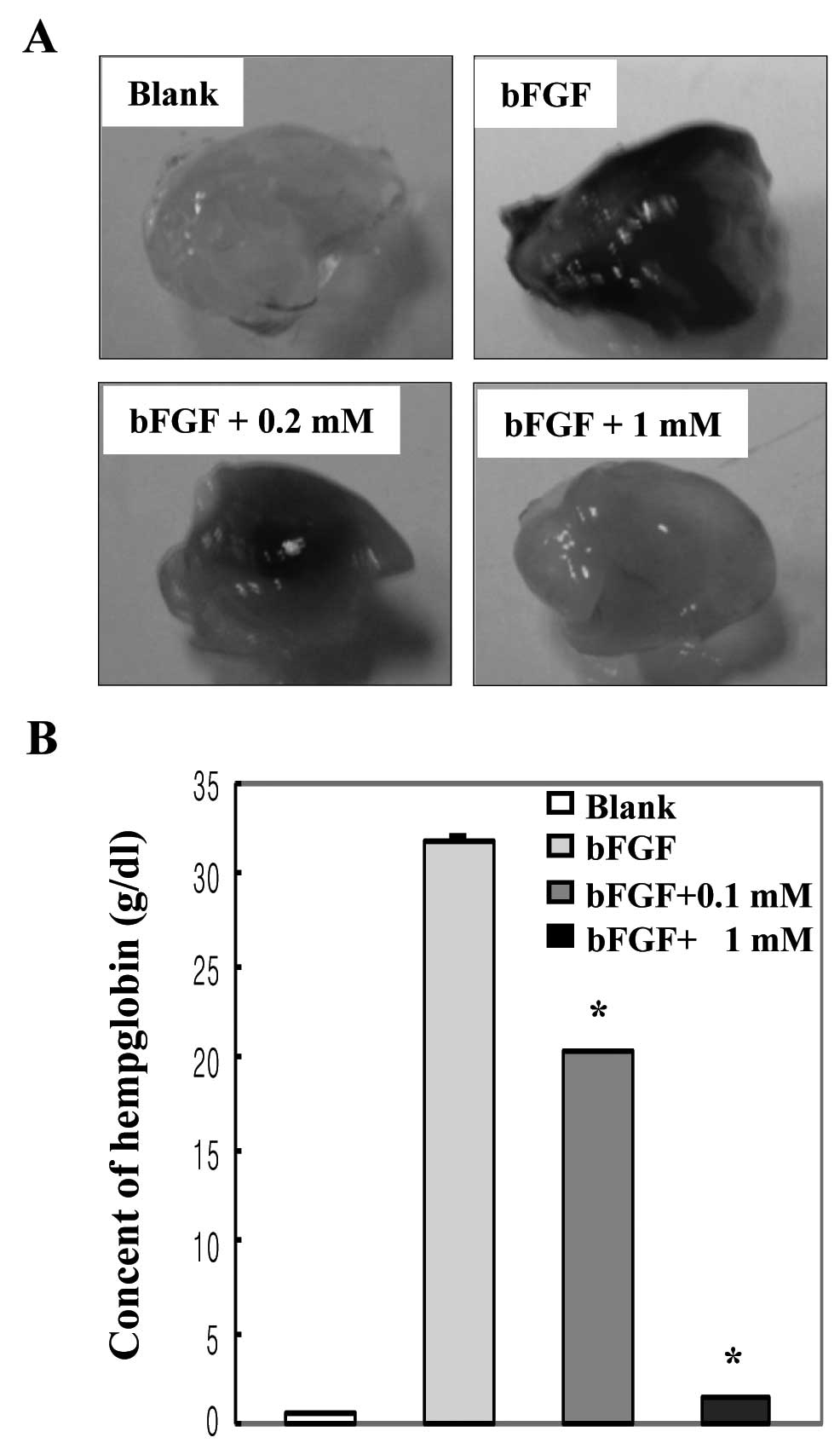
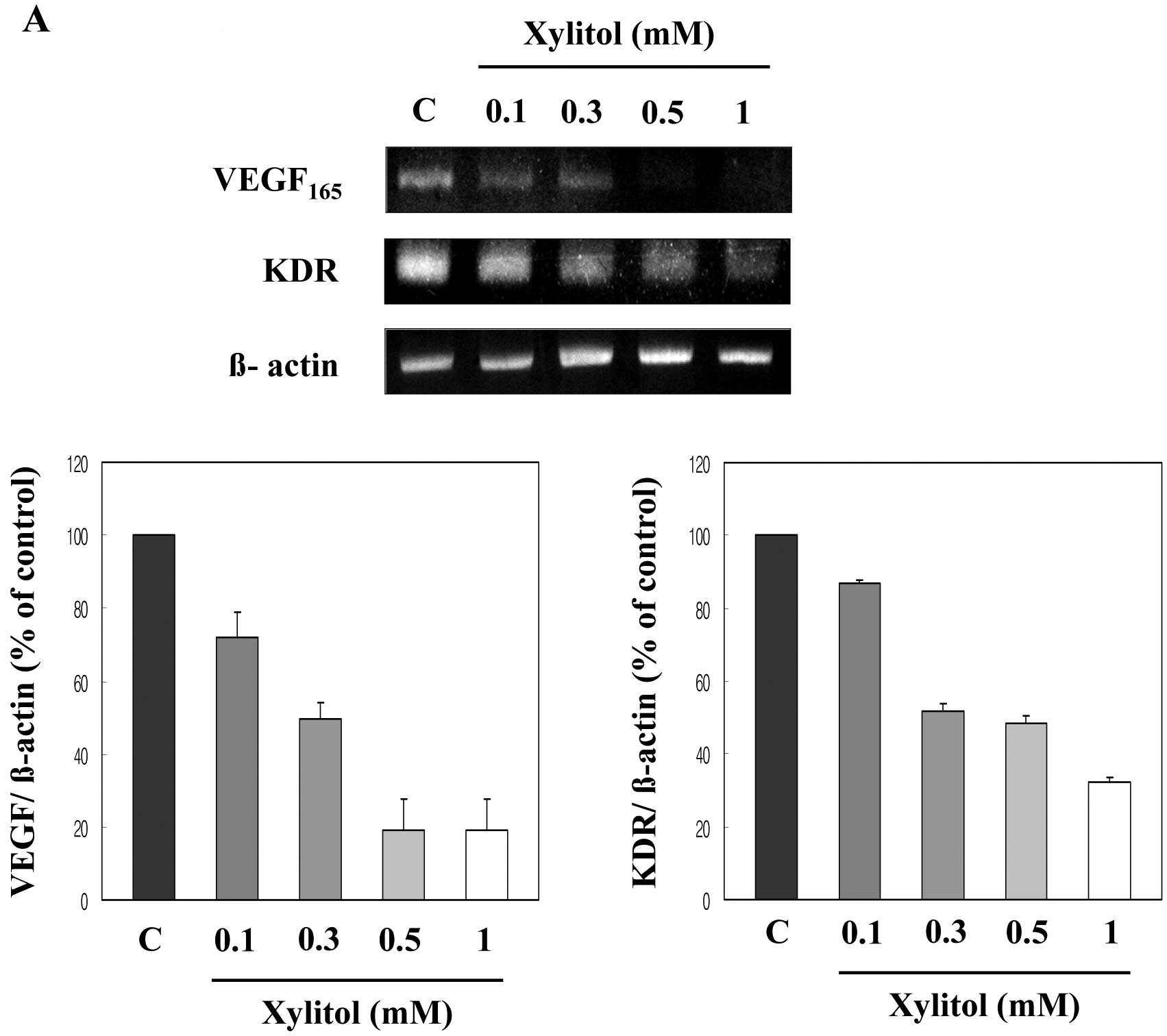
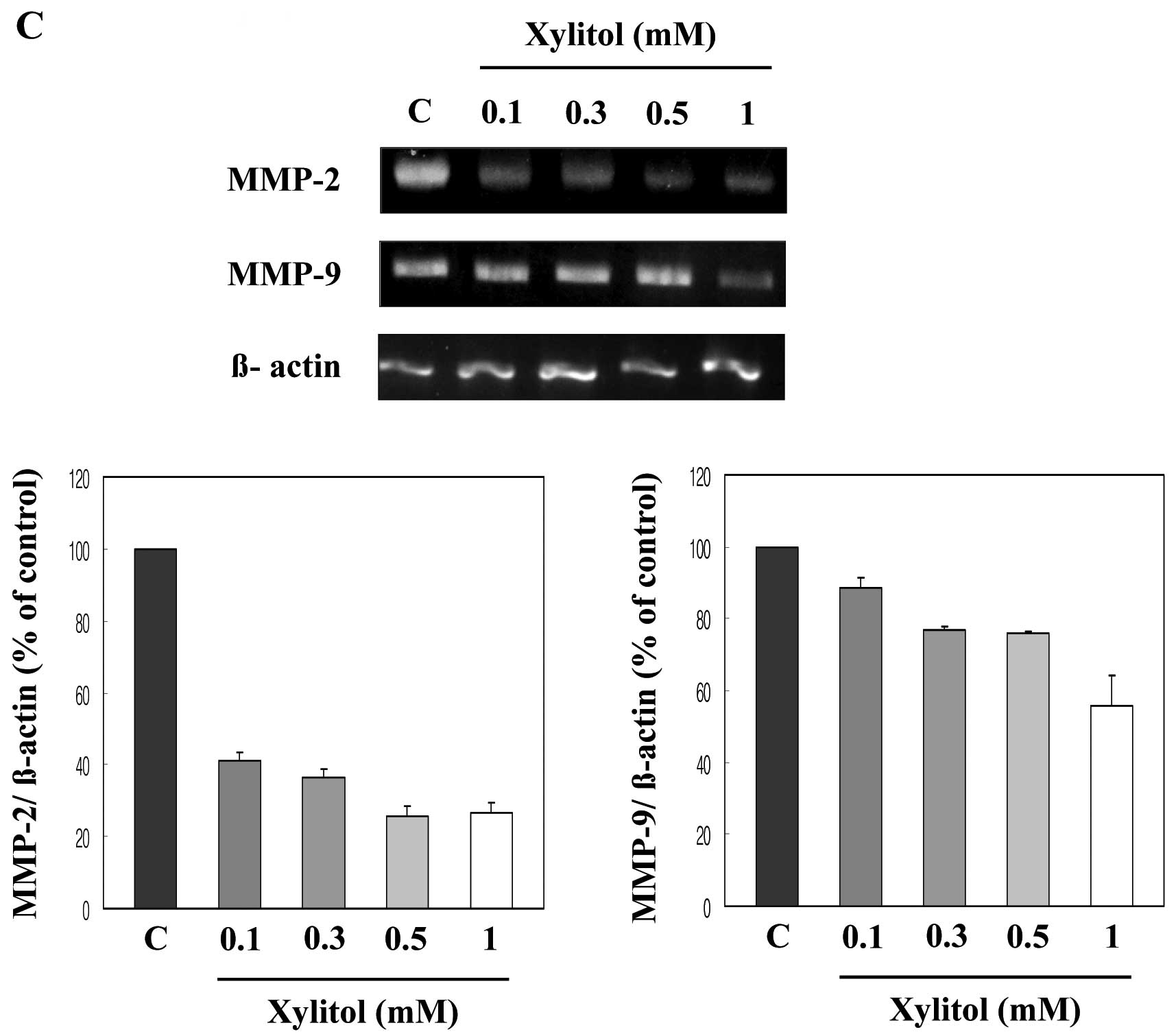
|
1.
|
Folkman J and Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J
Biol Chem. 267:10931–10934. 1992.
|
|
2.
|
Siddiqui FA, Desai H, Siddiqui TF and
Francis JL: Hemoglobin induces the expression and secretion of
vascular endothelial growth factor from human malignant cells.
Hematol J. 3:264–270. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Ferrara N and Kerbel RS: Angiogenesis as
therapeutic target. Nature. 438:967–974. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Isner JM and Asahara T: Angiogenesis and
vasculogenesis as therapeutics strategies for postnatal
neovascularization. J Clin Invest. 103:1231–1236. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis; therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Szekanecz Z and Koch AE: Endothelial cells
in inflammation and angiogenesis. Curr Drug Targets Inflam Allergy.
4:319–323. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Ono M: Molecular links between tumor
angiogenesis and inflammation: inflammatory stimuli of macrophages
and cancer cells as targets for therapeutic strategy. Cancer Sci.
99:1501–1506. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Karin M and Greteo FR: NF-κB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005.
|
|
10.
|
Albini A, Tosetti F, Benelli R and Noonan
DM: Tumor inflammatory angiogenesis and its chemoprevention. Cancer
Res. 65:10639–10641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Tanzer JM: Xylitol chewing gum and dental
caries. Int Dent J. 45:65–76. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Bradshaw DJ and Marsh PD: Effect of sugar
alcohols on the composition and metabolism of a mixed culture of
oral bacteria grown in a chemostat. Caries Res. 28:251–256. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Makinen KK and Soderling E: A quantitative
study of mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol, and xylose in wild berries
and commercial fruits. J Food Sci. 45:367–371. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Makinen KK, Bennett CA, Hujoel PP, et al:
Xylitol chewing gums and caries rates: a 40-month cohort study. J
Dent Res. 74:1904–1913. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Söderling E, Mäkinen KK, Chen CY, et al:
Effect of sorbitol, xylitol, and xylitol/sorbitol chewing gums on
dental plaque. Caries Res. 23:378–384. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Han SJ, Jeong SY, Nam YJ, et al: Xylitol
inhibits inflammatory cytokine expression induced by
lipopolysaccharide from Porphyromonas gingivalis. Clin Diagn
Lab Immunol. 12:1285–1291. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Bisacchi D, Benelli R, Venzetto C, et al:
Anti-angiognesis and angioprevention: mechanisms, problems and
perspectives. Cancer Detect Prev. 27:229–238. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Yoshimura A: Signal transduction of
inflammatory cytokines and tumor development. Cancer Sci.
97:439–447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Pang R and Poon RT: Angiogenesis and
antiangiogenic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
242:151–167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Femke H and Arjan WG: Tumor
vascularization: sprouting angiogenesis and beyond. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 26:489–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, et al:
Matrix matalloproteinases-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during
angiogenesis. Nature Cell Biol. 2:737–744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Francesco P and Antonio L: NF-κB solid
tumors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1142–1152. 2006.
|
|
23.
|
Lin YG, Kunnumarkkara AB, Nair A, et al:
Curcumin inhibits growth and angiogenesis in ovarian carcinoma by
targeting the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3423–3430. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-κB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006.
|
|
25.
|
Pawel D, Kathryn H, Susan JB and Hong C:
Antiangiogenic and antitumor efficacy of EphA2 receptor antagonist.
Cancer Res. 64:910–919. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Sporn MB and Suh N: Chemoprevention of
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 21:525–530. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Jones KM, Wang H, Peskar BM, et al:
Inhibition of angiogenesis by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
insight into mechanism and implications for cancer growth ulcer
healing. Nat Med. 5:1418–1423. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Renko M, Valkonen P, Tapiainen T, et al:
Xylitol-supplemented nutrition enhances bacterial killing and
prolongs survival of rats in experimental pneumococcal sepsis. BMC
Microbiol. 8:1–7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Georgieff M, Moldawer LL, Bistrian BR, et
al: Xylitol, an energy source for intravenous nutrition after
trauma. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 9:199–209. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Panagiotou G, Christakopoulos P, Grotkjaer
T, et al: Engineering of the redox imbalance of Fusarium
oxysporum enables anaerobic growth on xylose. Metab Eng.
8:474–482. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Loesche WJ, Grossman NS, Earnest R, et al:
The effect of chewing xylitol gum on the plaque and saliva levels
of Streptococcus mutans. J Am Dent Assoc. 108:587–592. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Miyasawa H, Iwami Y, Mayanagi H, et al:
Xylitol inhibition of anaerobic acid production by Streptococcus
mutans at various pH levels. Oral Microbiol Immunol.
18:215–219. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Meadows KN, Bryant P and Pumiglia K:
Vascular endothelial growth factor induction of the angiogenic
phenotype requires ras activation. J Bio Chem. 276:49289–49298.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic
mitogen. Science. 246:1306–1309. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Asahara T, Bauters C, Zheng LP, et al:
Synergistic effect of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic
fibroblast growth factor on angiogenesis in vivo. Circulation.
92:11365–11371. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Gilmore TD: The Rel/NF-κB/IκB signal
transduction pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 115:241–265.
2003.
|