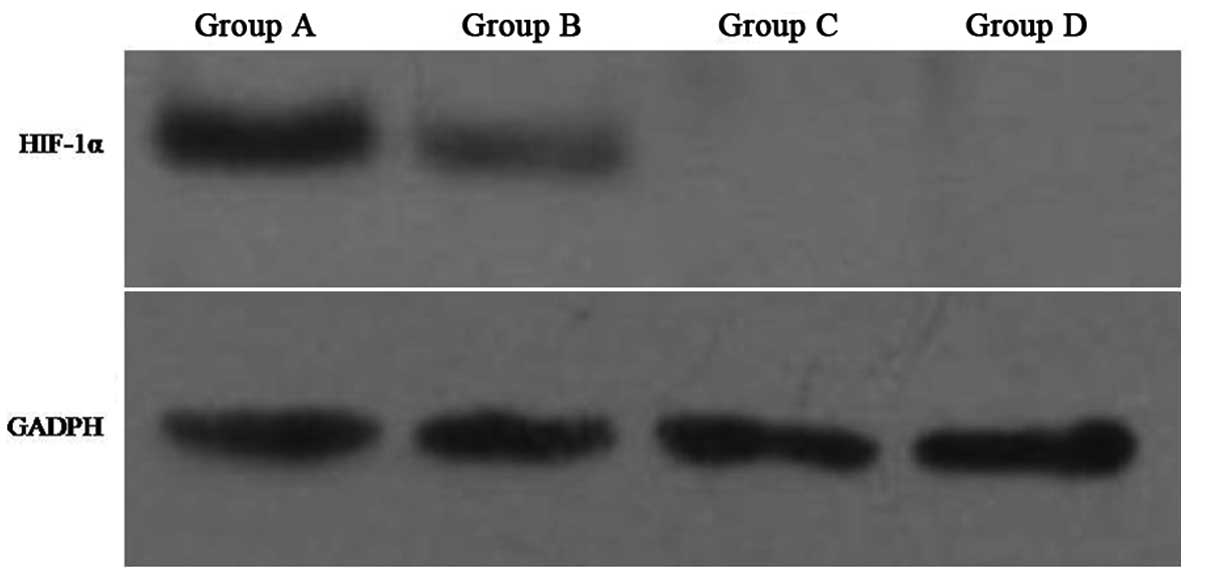
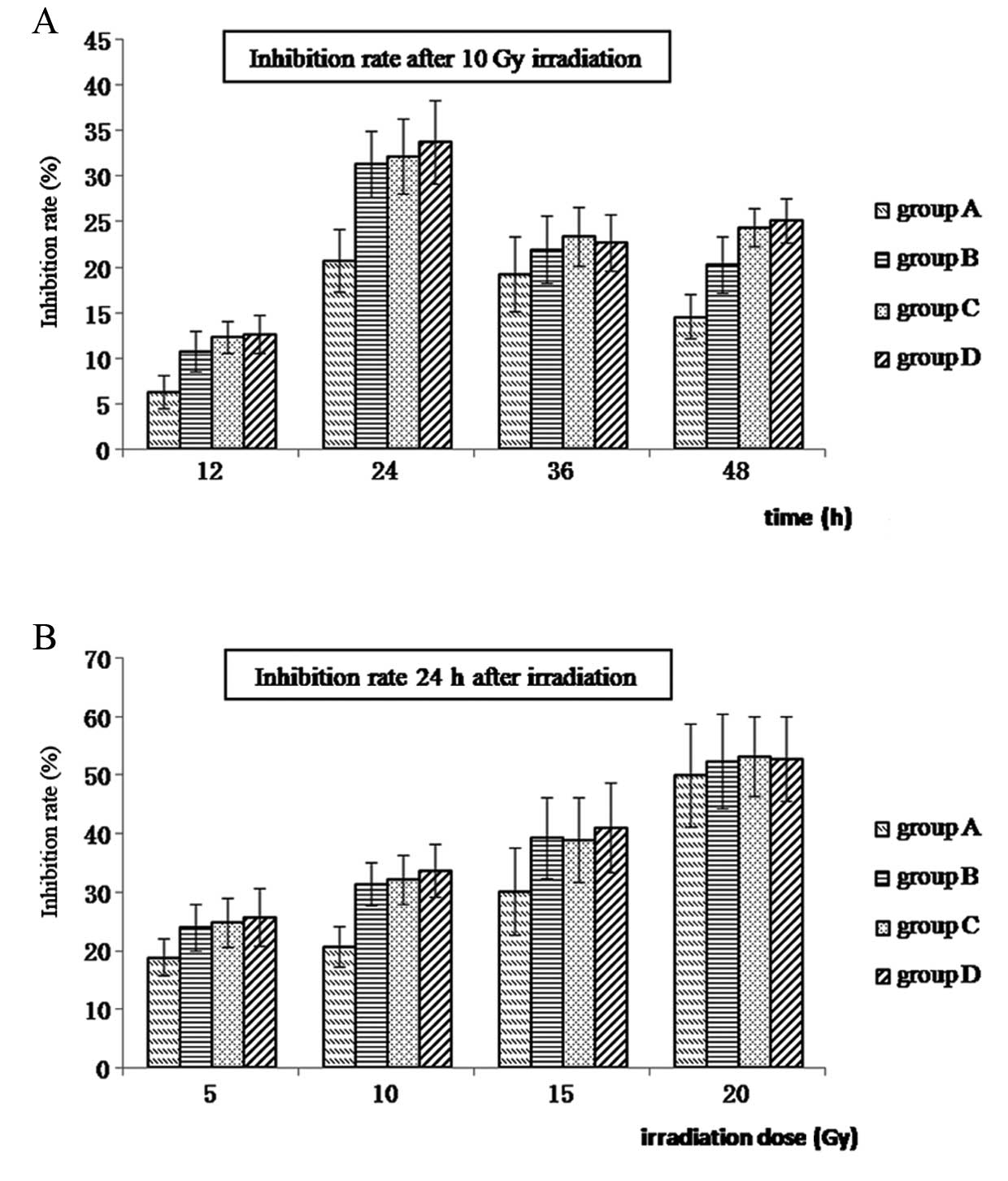
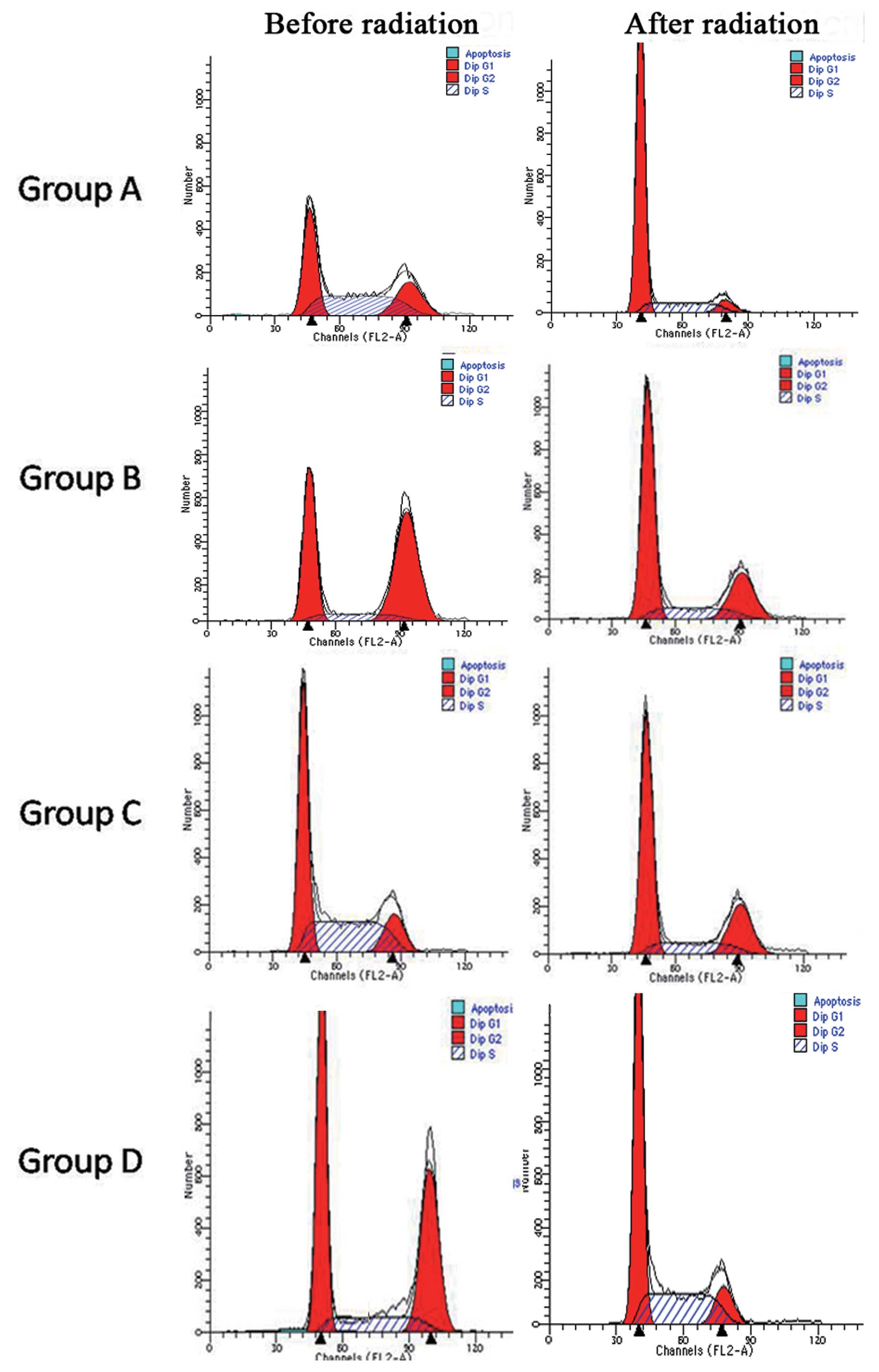
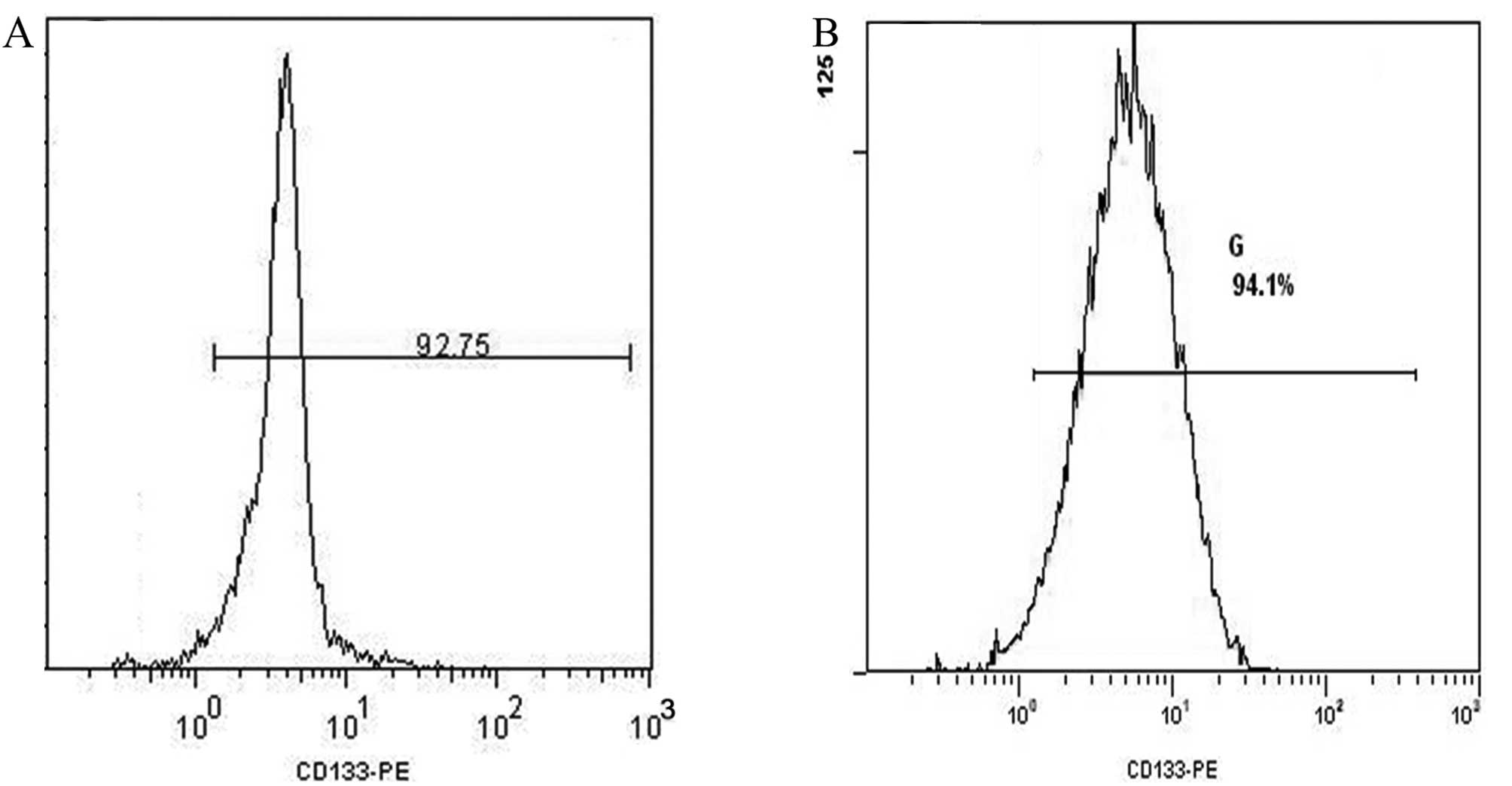
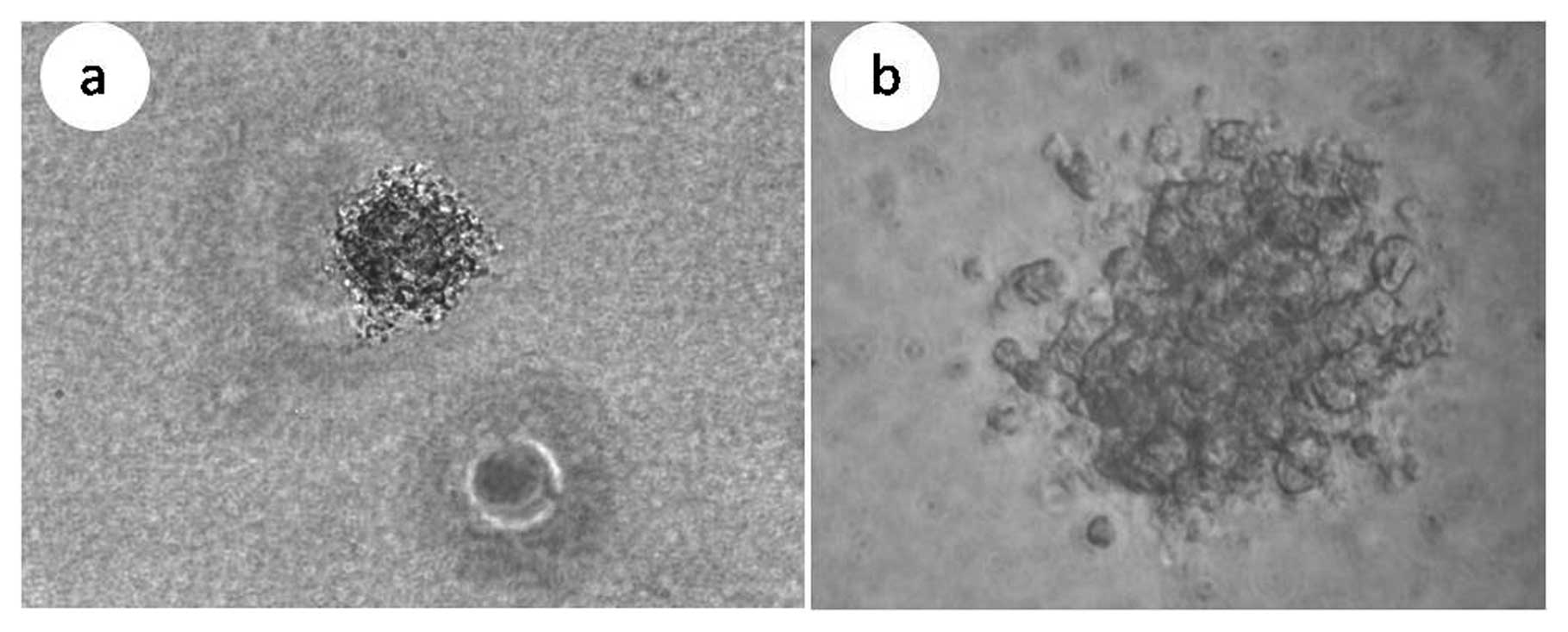
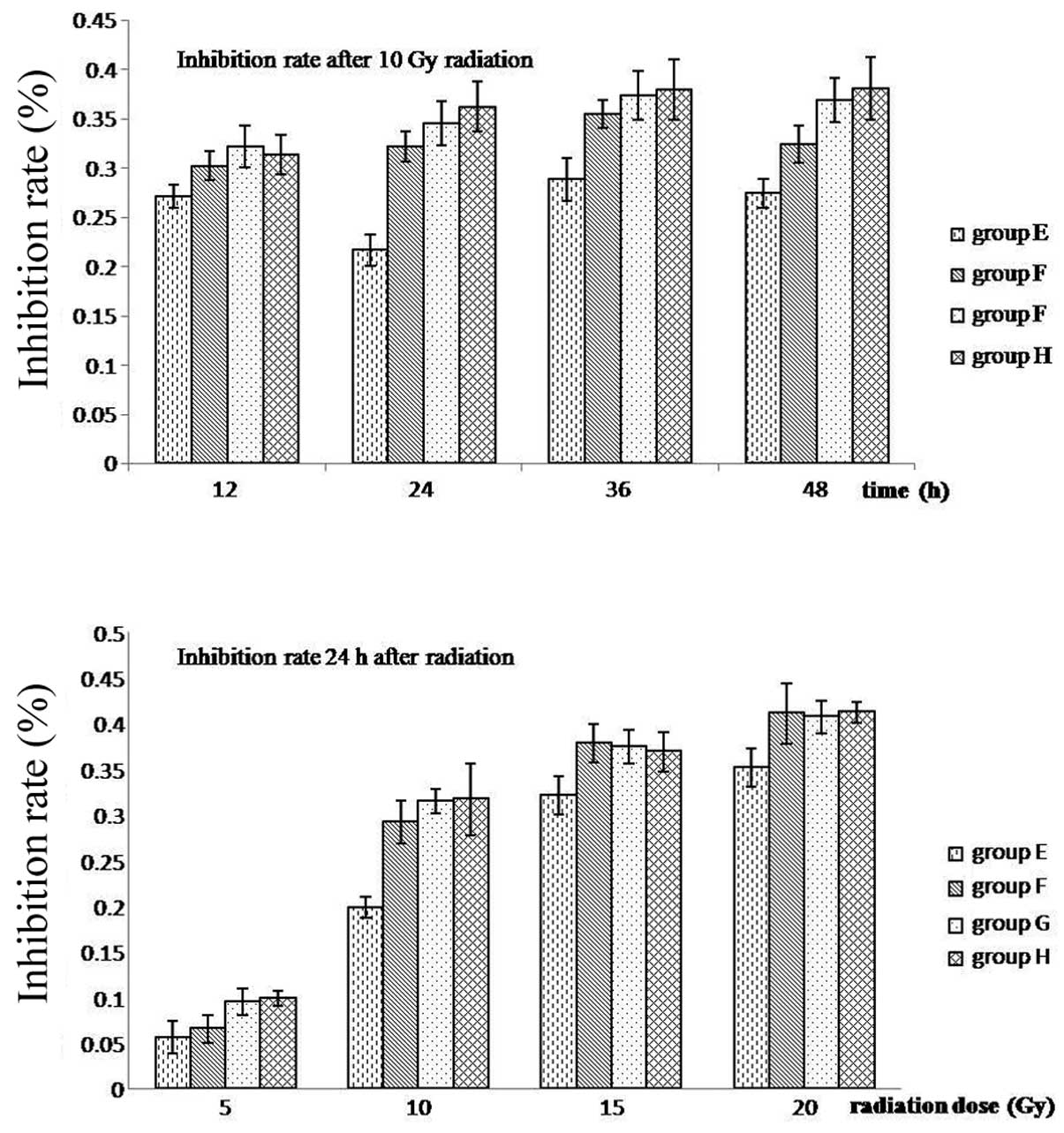
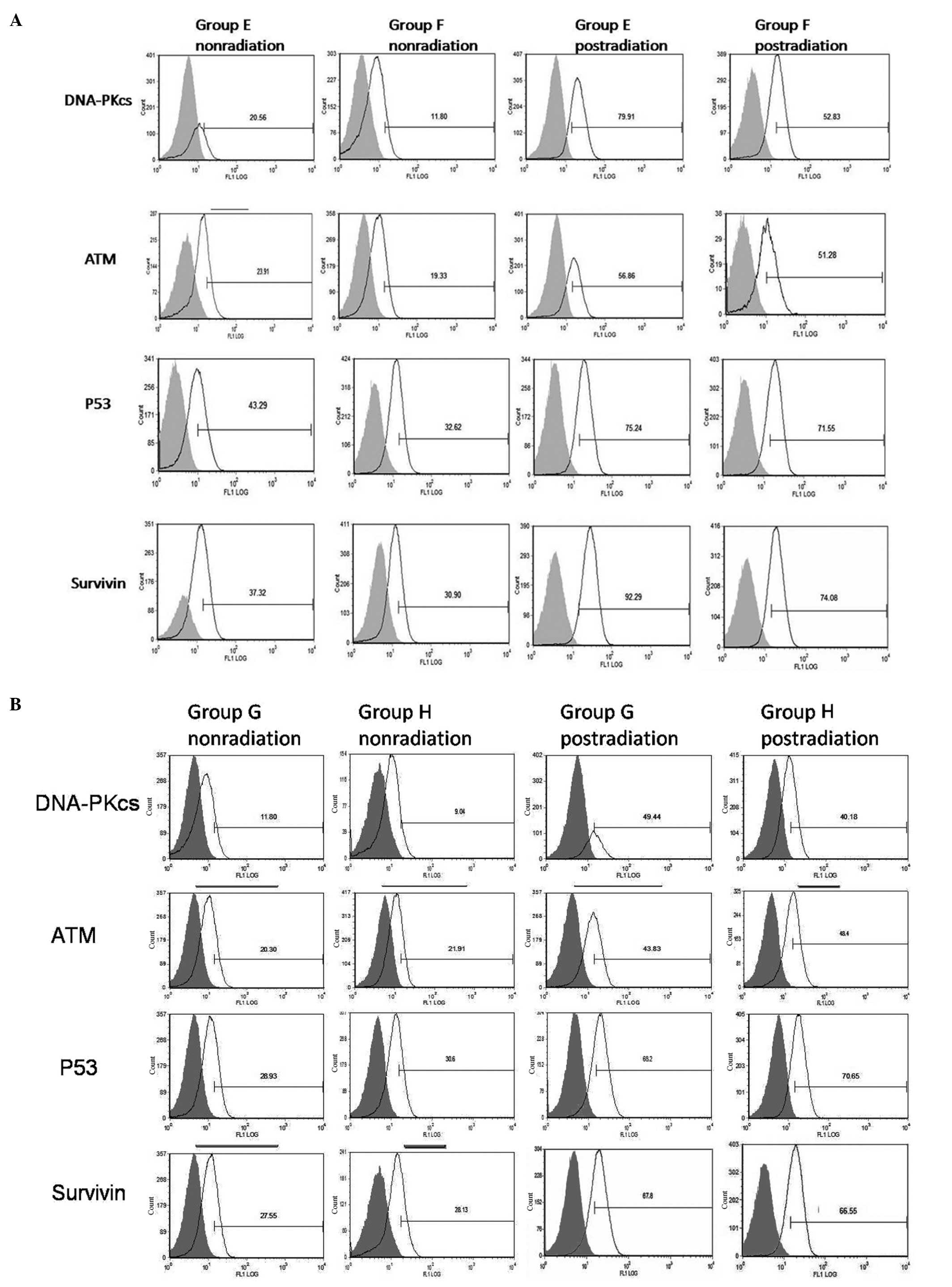
|
1.
|
Nix P, Greenman J, Cawkwell L and Stafford
N: Radioresistant laryngeal cancer: beyond the TNM stage. Clin
Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 29:105–114. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Velasco-Velázquez M, Homsi N, De L and
Pestell R: Breast cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:573–577. 2012.
|
|
3.
|
Vaiopoulos A, Kostakis I, Koutsilieris M
and Papavassiliou A: Colorectal cancer stem cells. Stem Cells.
30:363–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Guerrero-Cazares H, Attenello FJ and
Quinones-Hinojosa A: Stem cells in gliomas. Handb Clin Neurol.
104:63–73. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Mannelli G and Gallo O: Cancer stem cells
hypothesis and stem cells in head and neck cancers. Cancer Treat
Rev. 38:515–539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Tu S and Lin S: Prostate cancer stem
cells. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 10:69–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Singh S, Hawkins C, Clarke I, et al:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Chen Y, Hsu H, Chen Y, et al: Oct-4
expression maintained cancer stem-like properties in lung
cancer-derived CD133-positive cells. PLoS One. 3:e26372008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hermann P, Huber S, Herrler T, et al:
Distinct populations of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth
and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell.
1:313–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ma S, Chan K, Lee T, et al: Aldehyde
dehydrogenase discriminates the CD133 liver cancer stem cell
populations. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1146–1153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Miki J, Furusato B, Li H, et al:
Identification of putative stem cell markers, CD133 and CXCR4, in
hTERT-immortalized primary nonmalignant and malignant tumor-derived
human prostate epithelial cell lines and in prostate cancer
specimens. Cancer Res. 67:3153–3161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Zhang Q, Shi S, Yen Y, Brown J, Ta J and
Le A: A subpopulation of CD133 (+) cancer stem-like cells
characterized in human oral squamous cell carcinoma confer
resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 289:151–160. 2009.
|
|
13.
|
Matsumoto K, Arao T, Tanaka K, et al: mTOR
signal and hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha regulate CD133
expression in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:7160–7164. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Wei X, Zhou L, Cheng L and Tian J:
Experimental investigation of CD133 as a putative marker of
tumor-initiating cell in laryngeal carcinoma. Chin J
Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 41:940–944. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ailles L and Weissman I: Cancer stem cells
in solid tumors. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 18:460–466. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon R, et al: Glioma
stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of
the DNA damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, et al: Analysis of
gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer
stem cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. 5:672006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Nie D: Cancer stem cell and niche. Front
Biosci (Schol Ed). 2:184–193. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Iwasaki H and Suda T: Cancer stem cells
and their niche. Cancer Sci. 100:1166–1172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Julie B, Sneddon and Zena W: Location,
location, location: the cancer stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell.
1:607–611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
McCord A, Jamal M, Shankavaram U, Lang F,
Camphausen K and Tofilon P: Physiologic oxygen concentration
enhances the stem-like properties of CD133+ human
glioblastoma cells in vitro. Mol Cancer Res. 7:489–497. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Mazumdar J, Dondeti V and Simon M:
Hypoxia-inducible factors in stem cells and cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
13:11–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Kessler J, Hahnel A, Wichmann H, et al:
HIF-1alpha inhibition by siRNA or chetomin in human malignant
glioma cells: effects on hypoxic radioresistance and monitoring via
CA9 expression. BMC Cancer. 10:6052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Wei X, Zhou L, Cheng L, Tian J, Jiang J
and Maccallum J: In vivo investigation of CD133 as a putative
marker of cancer stem cells in Hep-2 cell line. Head Neck.
31:94–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun T,
Schneider-Broussard R, Zhou J, Claypool K and Tang D: Side
population is enriched in tumorigenic, stemlike cancer cells,
whereas ABCG2+ and ABCG2-cancer cells are similarly
tumorigenic. Cancer Res. 65:6207–6219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kondo T, Setoguchi T and Taga T:
Persistence of a small subpopulation of cancer stem-like cells in
the C6 glioma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:781–786. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Soeda A, Park M, Lee D, et al: Hypoxia
promotes expansion of the CD133-positive glioma stem cells through
activation of HIF-1alpha. Oncogene. 28:3949–3959. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Hashimoto O, Shimizu K, Semba S, et al:
Hypoxia induces tumor aggressiveness and the expansion of
CD133-positive cells in a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-dependent
manner in pancreatic cancer cells. Pathobiology. 78:181–192.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Wicha M: Hedgehog signaling and Bmi-1
regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant human mammary stem
cells. Cancer Res. 66:6063–6071. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Diamandis P, Wildenhain J, Clarke I, et
al: Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of
neural stem cells. Nat Chem Biol. 3:268–273. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, et al:
CD133 (+) and CD133 (−) glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cells show
differential growth characteristics and molecular profiles. Cancer
Res. 67:4010–4015. 2007.
|
|
32.
|
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, et al:
Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res.
65:5506–5511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, et al: let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Dobbs T, Tainer J and Lees-Miller S: A
structural model for regulation of NHEJ by DNA-PKcs
autophosphorylation. DNA Repair. 9:1307–1314. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Tomita M: Involvement of DNA-PK and ATM in
radiation- and heat-induced DNA damage recognition and apoptotic
cell death. J Radiat Res. 51:493–501. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Asumen M, Ifeacho T, Cockerham L, Pfandl C
and Wall N: Dynamic changes to survivin subcellular localization
are initiated by DNA damage. Onco Targets Ther. 3:129–137.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Wang S, Wang W, Chang Y, et al: p53
controls cancer cell invasion by inducing the MDM2-mediated
degradation of Slug. Nat Cell Biol. 11:694–705. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Qu Y, Li X, Xu O, Wang M and Lu X: Impacts
of hypoxia on the features and chemoresistance of cancer stem cells
in Hep-2 cells and underlying mechanism. Chin J Otorhinolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 47:228–233. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|