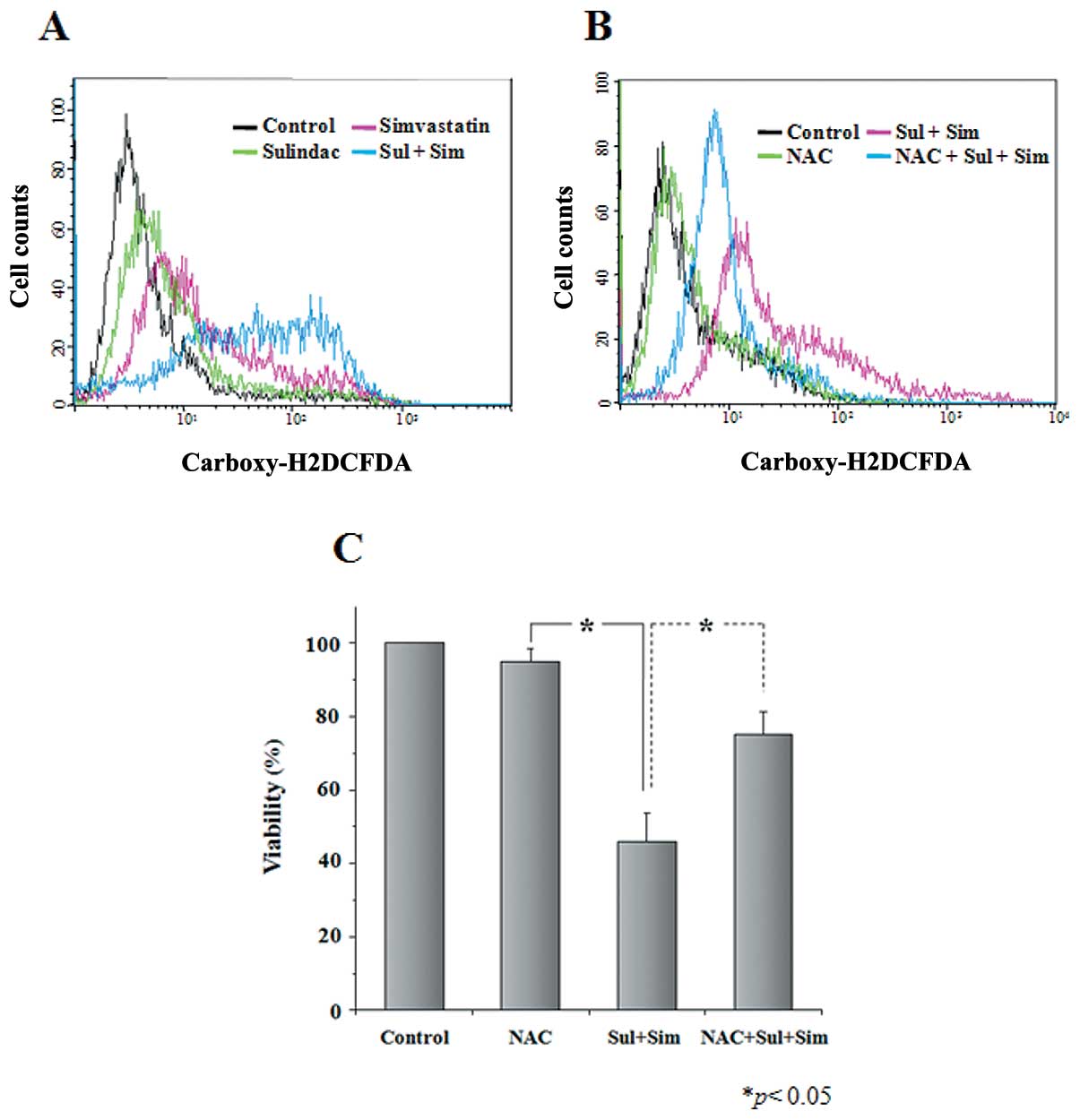
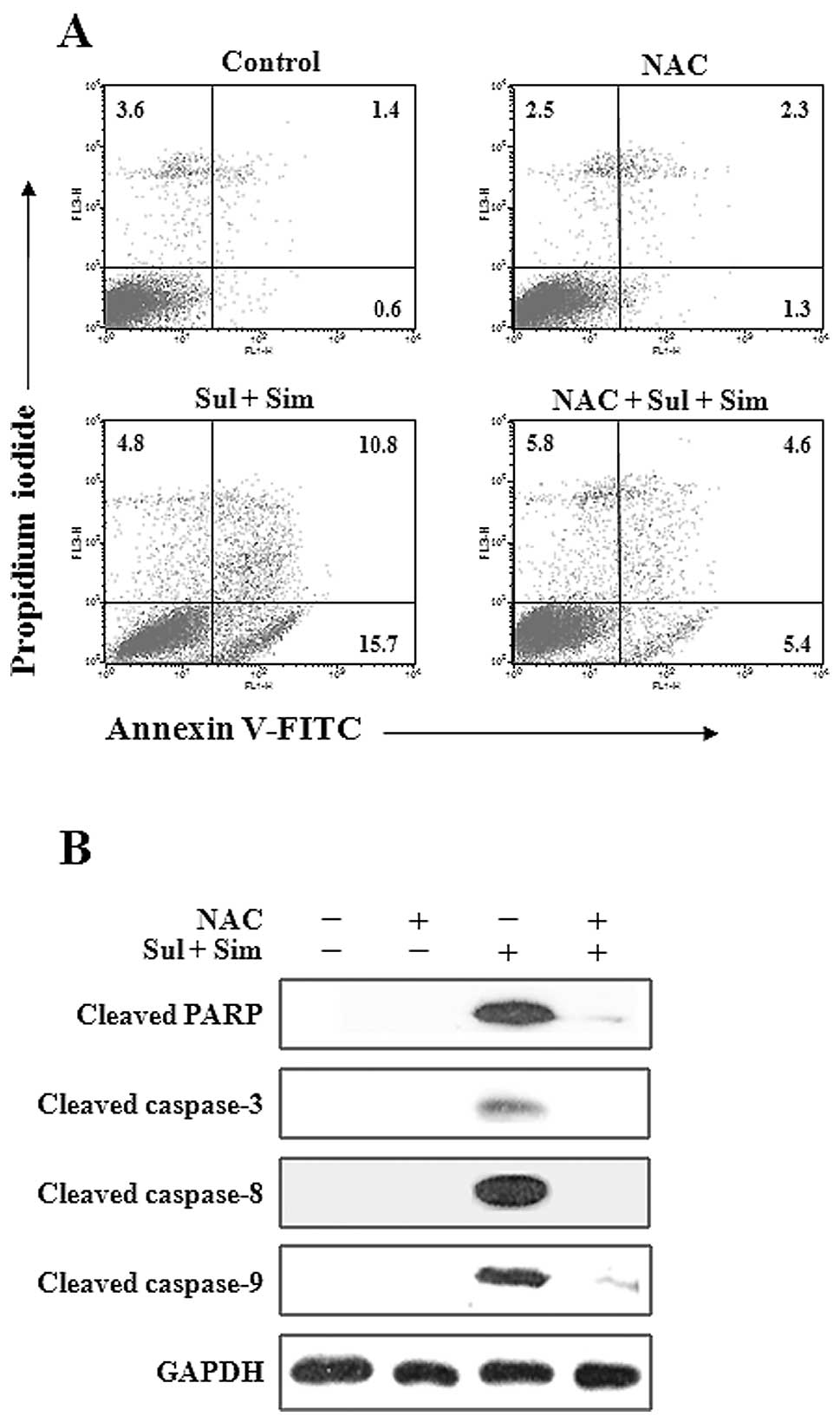
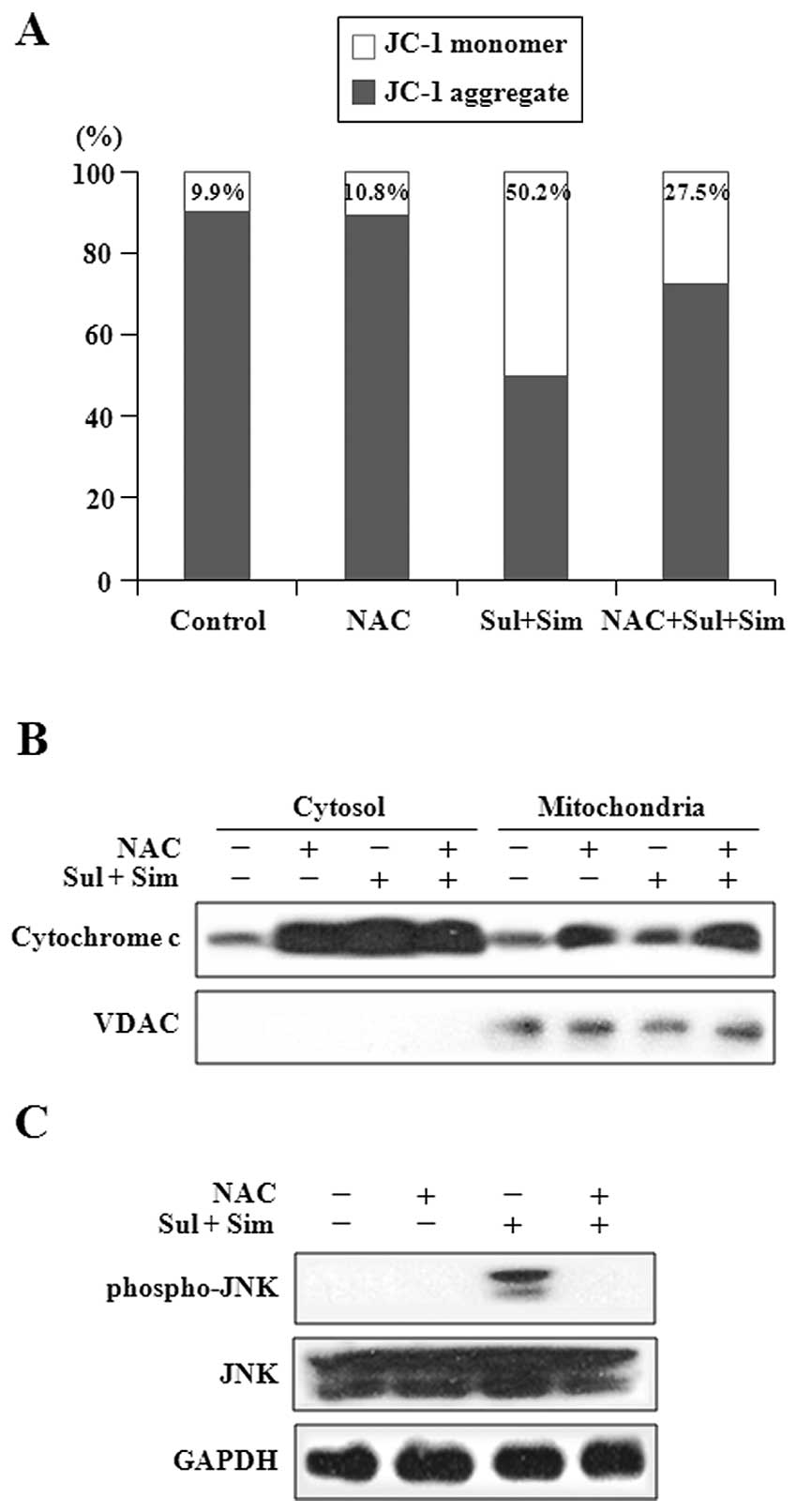
|
1.
|
Tanaka K, Iwamoto S, Gon G, Nohara T,
Iwamoto M and Tanigawa N: Expression of survivin and its
relationship to loss of apoptosis in breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer
Res. 6:127–134. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Velmurugan B, Mani A and Nagini S:
Combination of S-allylcysteine and lycopene induces apoptosis by
modulating Bcl-2, Bax, Bim and caspases during experimental gastric
carcinosenesis. Eur J Cancer Prev. 14:387–393. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Lin J, Hsiao PW, Chiu TH and Chao JI:
Combination of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and oxaliplatin
increases the growth inhibition and death in human colon cancer
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:658–667. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Banerjee S, Zhang Y, Ali S, Bhuiyan M,
Wang Z, Chiao PJ, Philip PA, Abbruzzese J and Sarkar FH: Molecular
evidence for increased antitumor activity of gemcitabine by
genistein in vitro and in vivo using an orthotopic model of
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 65:9064–9072. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Khor TO, Keum YS, Lin W, Kim JH, Hu R,
Shen G, Xu C, Gopalakrishnan A, Reddy B, Zheng X, Conney AH and
Kong AN: Combined inhibitory effects of curcumin and phenethyl
isothiocyanate on the growth of human PC-3 prostate xenografts in
immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res. 66:613–621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Giardiello FM, Spannhake EW, DuBois RN,
Hylind LM, Robinson CR, Hubbard WC, Hamilton SR and Yang VW:
Prostaglandin levels in human colorectal mucosa: effects sulindac
in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dig Dis Sci.
43:311–316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Shiff SJ, Qiao L, Tsai LL and Rigas B:
Sulindac sulfide, an aspirin-like compound, inhibits proliferation,
causes cell cycle quiescence, and induces apoptosis in HT-29 colon
adenocarcinoma cells. J Clin Invest. 96:491–503. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Chan TA, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and
Kinzler KW: Mechanism underlying nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
drug-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:681–686. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Williams CS, Mann M and DuBios RN: The
role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer, and development.
Oncogene. 18:7908–7916. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Thompson HJ, Jiang C, Lu J, Mehta RG,
Piazza GA, Paranka NS, Pamukcu R and Ahnen DJ: Sulfone metabolite
of sulindac inhibits mammary carcinogenesis. Cancer Res.
57:267–271. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Piazza GA, Rahm AL, Krutzsch M, Sperl G,
Paranka NS, Gross PH, Brendel K, Burt RW, Alberts DS and Pamukcu R:
Antineoplastic drugs sulindac sulfide and sulfone inhibit cell
growth by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Res. 55:3110–3116.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Tegeder I, Pfeilschifter J and Geisslinger
G: Cyclooxygenase-independent actions of cyclooxygenase inhibitors.
FASEB J. 15:2057–2072. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Seo SK, Lee HC, Woo SH, Jin HO, Yoo DH,
Lee SJ, An S, Choe TB, Park MJ, Hong SI, Park IC and Rhee CH:
Sulindac-derived reactive oxygen species induce apoptosis of human
multiple myeloma cells via p38 mitogen activated protein
kinase-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Apoptosis. 12:195–209.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Goldstein JL and Brown MS: Regulation of
the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 343:425–430. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Chan KK, Oza AM and Siu LL: The statins as
anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res. 9:10–19. 2003.
|
|
16.
|
Demierre MF, Higgins PD, Gruber SB, Hawk E
and Lippman SM: Statins and cancer prevention. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:930–942. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Mantha AJ, Hanson JE, Goss G, Lagarde AE,
Lorimer IA and Dimitroulakos J: Targeting the mevalonate pathway
inhibits the function of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:2398–2407. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Wong WW, Dimitroulakos J, Minden MD and
Penn LZ: HMB-CoA reductase inhibitors and the malignant cell: the
statin family of drugs as triggers of tumor-specific apoptosis.
Leukemia. 16:508–519. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Holstein SA and Hohl RJ: Synergistic
interaction of lovastatin and paclitaxel in human cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 1:141–149. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Feleszko W, Mlynarczuk I, Olszewska D,
Jalili A, Grzela T, Lasek W, Hoser G, Korczak-Kowalska G and
Jakobisiak M: Lovastatin potentiates antitumor activity of
doxorubicin in murine melanoma via an apoptosis-dependent
mechanism. Int J Cancer. 100:111–118. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Khanzada UK, Pardo OE, Meier C, Downward
J, Seckl MJ and Arcaro A: Potent inhibition of small-cell lung
cancer cell growth by simvastatin reveals selective functions of
Ras isoforms in growth factor signaling. Oncogene. 25:877–887.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kozar K, Kaminski R, Legat M, Kopec M,
Nowis D, Skierski JS, Koronkiewicz M, Jakobisiak M and Golab J:
Cerivastatin demonstrates enhanced antitumor activity against human
breast cancer cell lines when used in combination with doxorubicin
or cisplatin. Int J Oncol. 24:1149–1157. 2004.
|
|
23.
|
Wallace JL: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs and gastroenteropathy: the second hundred years.
Gastroenterology. 112:1000–1016. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA,
Wittes J, Fowler R, Finn R, Anderson WF, Zauber A, Hawk E and
Bertagnolli M: Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a
clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Eng J Med.
352:1071–1080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Psaty BM and Potter JD: Risks and benefits
of celecoxib to prevent recurrent adenomas. N Engl J Med.
355:950–952. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Jalving M, Koorntra JJ, De Jong S, De
Vries EG and Kleibeuker JH: Review article: the potential of
combinational regimen with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in
the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
21:321–339. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Xiao H and Yang CS: Combination regimen
with statins and NSAIDs: a promising strategy for cancer
chemoprevention. Int J Cancer. 123:983–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Suh N, Reddy BS, DeCastro A, Paul S, Lee
HJ, Smolarek AK, So JY, Simi B, Wang CX, Janakiram NB, Steele V and
Rao CV: Combination of atorvastatin with sulindac or naproxen
profoundly inhibits colonic adenocarcinomas by suppressing the
p65/β-catenin/cyclin D1 signaling pathway in rats. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 4:1895–1902. 2011.
|
|
29.
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Wolf CM and Eastman A: The temporal
relationship between protein phosphatase, mitochondrial cytochrome
c release. Exp Cell Res. 247:505–513. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Smiley ST, Reers M, Mottola-Hartshorn C,
Lin M, Chen A, Smith TW, Steele GD Jr and Chen LB: Intracellular
heterogeneity in mitochondrial membrane potentials revealed by a
J-aggregate-forming lipophilic cation JC-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
88:3671–3675. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Park JH, Kim EJ, Jang HY, Shim H, Lee KK,
Jo HJ, Kim HJ, Yang SH, Jeong ET and Kim HR: Combination treatment
with arsenic trioxide and sulindac enhances apoptotic cell death in
lung cancer cells via activation of oxidative stress and
mitogen-activated protein kinases. Oncol Rep. 20:379–384. 2008.
|
|
33.
|
Ralph SJ, Rondriguez-Enriquez S, Neuzil J,
Saavedra E and Moreno-Sanchez R: The causes of cancer revisited:
‘mitochondrial malignancy’ and ROS-induced oncogenic transformation
- why mitochondria are targets for cancer therapy. Mol Aspects Med.
31:145–170. 2010.
|
|
34.
|
Copeland WC, Wachsman JT, Johnson FM and
Penta JS: Mitochondrial DNA alterations in cancer. Cancer Invest.
20:557–569. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Seo SK, Lee HC, Woo SH, Jin HO, Yoo DH,
Lee SJ, An S, Choe TB, Park MJ, Hong SI, Park IC and Rhee CH:
Sulindac-derived reactive oxygen species induce apoptosis of human
multiple myeloma cells via p38 mitogen activated protein
kinase-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Apoptosis. 12:195–209.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Frank S, Gaume B, Bergmann-Leitner ES,
Leitner WW, Robert EG, Catez F, Smith CL and Youle RJ: The role of
dynamic-related protein 1, a mediator of mitochondrial fission, in
apoptosis. Dev Cell. 1:515–525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Karbowski M, Lee YJ, Gaume B, Jeong SY,
Frank S, Nechushtan A, Santel A, Fuller M, Smith CL and Youle RJ:
Spatial and temporal association of Bax with mitochondrial fission
sites, Drp1, and Mfn2 during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 159:931–938.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Li LY, Luo X and Wang X: Endonuclease G is
an apoptotic DNase when released from mitochondria. Nature.
412:95–99. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Tournier C, Hess P, Yang DD, Xu J, Turner
TK, Nimnual A, Bar-Sagi D, Jones SN, Flavell RA and Davis RJ:
Requrement of JNK for stress-induced activation of the cytochrome
c-mediated death pathway. Science. 288:870–874. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Burdon RH: Control of cell proliferation
by reactive oxygen species. Biochem Soc Trans. 24:1028–1032.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Minami T, Adachi M, Kawamura R, Zhang Y,
Shinomura Y and Imai K: Sulindac enhances the proteasome inhibitor
bortezomib-mediated oxidative stress and anticancer activity. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:5248–5256. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Fiers W, Beyaert R, Declercq W and Van den
Abeele P: More than one way to die: apoptosis, necrosis and
reactive oxygen damage. Oncogene. 18:7719–7730. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|